Herb–Drug Interaction of Red Ginseng Extract and Ginsenoside Rc with Valsartan in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
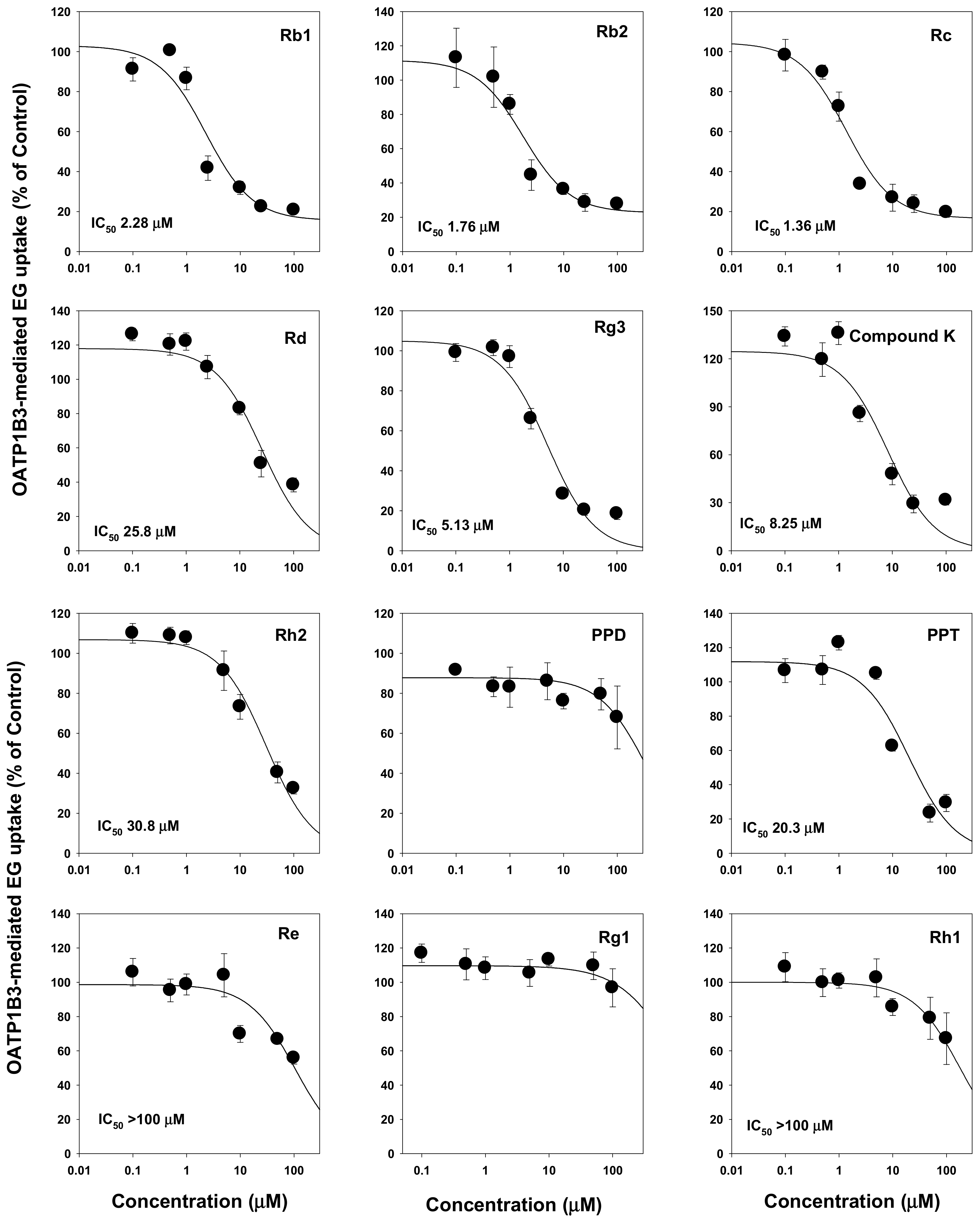
2.1. Inhibitory Effect of Ginsenosides on Drug Transporters
2.2. Valsartan as a Substrate for Oatp Transporter
2.3. Effect of RGE on the Pharmacokinetics of Valsartan in Rats
2.4. Effect of Ginsenoside Rc on the Pharmacokinetics of Valsartan in Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Inhibitory Effects of Ginsenosides on Drug Transporters
4.3. Animals and Ethical Approval
4.4. Pharmacokinetic Study
4.5. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Valsartan
4.6. LC-MS/MS analysis of Ginsenosides
4.7. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ru, W.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y.; He, X.; Sun, Y.E.; Qian, L.; Zhou, X.; Qin, Y. Chemical constituents and bioactivities of Panax ginseng (C. A. Mey.). Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, J.H. A review on the medicinal potentials of ginseng and ginsenosides on cardiovascular diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.T. Botanical characteristics, pharmacological effects and medicinal components of Korean Panax ginseng C A Meyer. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yun, T.K.; Choi, S.Y.; Yun, H.Y. Epidemiological study on cancer prevention by ginseng: Are all kinds of cancers preventable by ginseng? J. Korean Med. Sci. 2001, 16, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gui, Q.F.; Xu, Z.R.; Xu, K.Y.; Yang, Y.M. The efficacy of ginseng-related therapies in type 2 diabetes mellitus: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.Y.; Hong, M.; Sung, H.; Kim, S.; Suk, K.T. Effect of Korean Red Ginseng in chronic liver disease. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kwon, M.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Effects of red ginseng extract on the pharmacokinetics and elimination of methotrexate via Mrp2 regulation. Molecules 2018, 23, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Ginseng compounds: An update on their molecular mechanisms and medical applications. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 7, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Ye, Y.; Lin, G. Transporter modulation by Chinese herbal medicines and its mediated pharmacokinetic herb-drug interactions. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1026, 236–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, D.H.; Ji, H.Y.; Park, E.J.; Kim, M.S.; Liu, K.H.; Lee, H.S. Evaluation of metabolism-mediated herb-drug interactions. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 1829–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.J.; Lee, S. Investigation of herb-drug interactions between Korean red ginseng extract and five Cyp substrates by LC-MS/MS. Mass Spectrom. Lett. 2017, 8, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Nam, W.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, H.R.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, T.W.; Lee, S. Modulatory effects of Korean red ginseng extract (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) on cytochrome P450 after oral administration to mice for 14 days. J. Life Sci. 2012, 22, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seong, S.J.; Kang, W.Y.; Heo, J.K.; Jo, J.; Choi, W.G.; Liu, K.H.; Lee, S.; Choi, M.K.; Han, Y.H.; Lee, H.S.; et al. A comprehensive in vivo and in vitro assessment of the drug interaction potential of red ginseng. Clin. Ther. 2018, 40, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Kim, Y.; Jeon, J.Y.; Kim, M.G. Effect of Red Ginseng on cytochrome P450 and P-glycoprotein activities in healthy volunteers. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malati, C.Y.; Robertson, S.M.; Hunt, J.D.; Chairez, C.; Alfaro, R.M.; Kovacs, J.A.; Penzak, S.R. Influence of Panax ginseng on cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) activity in healthy participants. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 52, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.J.; Choi, S.; Kim, M.; Park, C.; Kim, G.L.; Lee, S.O.; Kang, W.; Rhee, D.K. Effect of Korean Red Ginseng extracts on drug-drug interactions. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jie, J.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, W. Long-term effects of Panax ginseng on disposition of fexofenadine in rats in vivo. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2009, 37, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Lee, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Enhanced intestinal permeability and plasma concentration of metformin in rats by the repeated administration of red ginseng extract. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Interactions of ginseng with therapeutic drugs. Arch. Pharm Res. 2019, 42, 862–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Heo, J.-K.; Lee, G.-H.; Park, S.-Y.; Jang, S.N.; Kim, H.-J.; Kwon, M.J.; Song, I.-S.; Liu, K.-H. Ginsenoside Rc is a new selective UGT1A9 inhibitor in human liver microsomes and recombinant human UGT isoforms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2019, 47, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Zheng, Y.F.; Min, J.S.; Park, J.B.; Bae, S.H.; Yoon, K.D.; Chin, Y.W.; Oh, E.; Bae, S.K. In vitro stereoselective inhibition of ginsenosides toward UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) isoforms. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 259, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Dong, J.; Li, X.; Du, F.; Jia, W.; Xu, F.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Niu, W.; Li, C. Molecular mechanisms governing different pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides and potential for ginsenoside-perpetrated herb-drug interactions on OATP1B3. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.-K.; Reichold, M.; Edemir, B.; Ciarimboli, G.; Warth, R.; Koepsell, H.; Thévenod, F. Organic cation transporters OCT1, 2, and 3 mediate high-affinity transport of the mutagenic vital dye ethidium in the kidney proximal tubule. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2009, 296, F1504–F1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.K.; Jin, Q.R.; Jin, H.E.; Shim, C.K.; Cho, D.Y.; Shin, J.G.; Song, I.S. Effects of tetraalkylammonium compounds with different affinities for organic cation transporters on the pharmacokinetics of metformin. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2007, 28, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, W.-G.; Kwon, M.; Lee, S.; Cho, Y.-Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, H.C.; Song, I.-S.; Lee, H.S. In Vitro Inhibitory Effects of APINACA on Human Major Cytochrome P450, UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase Enzymes, and Drug Transporters. Molecules 2019, 24, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parvez, M.M.; Jung, J.A.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Shin, J.G. Characterization of 22 Antituberculosis Drugs for Inhibitory Interaction Potential on Organic Anionic Transporter Polypeptide (OATP)-Mediated Uptake. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3096–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalliokoski, A.; Niemi, M. Impact of OATP transporters on pharmacokinetics. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamashiro, W.; Maeda, K.; Hirouchi, M.; Adachi, Y.; Hu, Z.; Sugiyama, Y. Involvement of transporters in the hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of valsartan, a selective antagonist of the angiotensin II AT1-receptor, in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poirier, A.; Cascais, A.C.; Funk, C.; Lave, T. Prediction of pharmacokinetic profile of valsartan in human based on in vitro uptake transport data. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2009, 36, 585–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kang, W.Y.; Seong, S.J.; Yoon, Y.R.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Detection of 13 ginsenosides (Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, Re, Rf, Rg1, Rg3, Rh2, F1, Compound K, 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol, and 20(S)-Protopanaxatriol) in human plasma and application of the analytical method to human pharmacokinetic studies following two week-repeated administration of red ginseng extract. Molecules 2019, 24, 2618. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.W.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, F.L.; Zhu, W.J.; Jiang, J.; Wu, S.; Yang, D.C.; Li, D.; Quan, L.H. Biotransformation of Panax ginseng extract by rat intestinal microflora: Identification and quantification of metabolites using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.K.; Jin, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kang, W.Y.; Seong, S.J.; Yoon, Y.R.; Han, Y.H.; Song, I.S. Tolerability and pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, and compound K after single or multiple administration of red ginseng extract in human beings. J. Ginseng Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, Y.; Maeda, K.; Ikejiri, K.; Yoshida, K.; Horie, T.; Sugiyama, Y. Clinical significance of organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATPs) in drug disposition: Their roles in hepatic clearance and intestinal absorption. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2013, 34, 45–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, W. Transporter-mediated natural product–drug interactions for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, S32–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nam, S.J.; Han, Y.J.; Lee, W.; Kang, B.; Choi, M.K.; Han, Y.H.; Song, I.S. Effect of red ginseng extract on the pharmacokinetics and efficacy of metformin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, B.N.; Ji, M.G.; Kang, T.H. The efficacy of red ginseng in type 1 and type 2 diabetes in animals. Evid Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2013, 2013, 593181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.D.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, S.H. Ginseng and diabetes: The evidences from in vitro, animal and human studies. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X.; Wu, X. Effects of Pluronic F68 and Labrasol on the intestinal absorption and pharmacokinetics of rifampicin in rats. Arch. Pharm Res. 2011, 34, 1939–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, H.; Nogami, R.; Shigeno, A.; Shimada, S.; Aoyama, T. Influence of Food on Rifampicin Pharmacokinetics in Rats. Biol Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mucalo, I.; Jovanovski, E.; Vuksan, V.; Bozikov, V.; Romic, Z.; Rahelic, D. American ginseng extract (Panax quinquefolius L.) Is safe in long-term use in type 2 diabetic patients. Evid Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2014, 2014, 969168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laube, R.; Liu, K. An unwanted complement: Rare case of potential liver injury induced by an interaction between ginseng and atorvastatin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 1612–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Zhang, H.C.; Li, S.M.; Wang, J.M.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.L.; Ma, X.H.; Zhou, S.P.; Zhu, Y.H.; et al. Determination of ginsenoside Rc in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2013, 919–920, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Hwang, J.T.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, S.; Kim, M.S.; Yang, H.J.; Kwon, D.Y. Ginsenoside Rc, an active component of Panax ginseng, stimulates glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes through an AMPK-dependent mechanism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.U.; Kang, H.E.; Choi, S.Z.; Son, M.; Song, I.S.; Lee, H.S. Evaluation of drug--drug interaction potential between DA-9801 and metformin. J. Pharm. Investig. 2014, 44, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.U.; Kwon, M.; Lee, Y.; Yoo, J.S.; Shin, D.H.; Song, I.S.; Lee, H.S. Organic anion transporter 3- and organic anion transporting polypeptides 1B1- and 1B3-mediated transport of catalposide. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 643–653. [Google Scholar]
- Schuhmacher, J.; Bühner, K.; Witt-Laido, A. Determination of the free fraction and relative free fraction of drugs strongly bound to plasma proteins. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 1008–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalvass, J.C.; Maurer, T.S. Influence of nonspecific brain and plasma binding on CNS exposure: implications for rational drug discovery. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2002, 23, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Not available. |








| Ginsenosides | IC50 (μM) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCT1 | OCT2 | OAT1 | OAT3 | OATP1B1 | OATP1B3 | ||
| PPD-type ginsenosides | Rb1 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 68.2 | 2.28 |
| Rb2 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 47.6 | 1.76 | |
| Rc | NI | NI | NI | NI | 18.3 | 1.36 | |
| Rd | NI | NI | NI | NI | 15.9 | 25.8 | |
| Rg3 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 7.99 | 5.13 | |
| Compound K | NI | NI | NI | NI | 22.5 | 8.25 | |
| Rh2 | NI | NI | NI | NI | 22.3 | 30.8 | |
| PPD | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | |
| PPT-type ginsenosides | PPT | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | 20.3 |
| Re | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | >100 | |
| Rg1 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | |
| Rh1 | NI | NI | NI | NI | NI | >100 | |
| Treatment | Valsartan + Rifampin | Valsartan + RGE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PK Parameters | Control | Rifampin | Control | RGE |
| T1/2 (h) | 4.48 ± 1.24 | 2.79 ± 0.32 * | 4.55 ± 0.98 | 4.59 ± 0.73 |
| C0 (ng/mL) | 1169.59 ± 118.78 | 1633.08 ± 1308.67 | 647.53 ± 50.49 | 781.47 ± 211.04 |
| AUC24h (ng·h/mL) | 667.56 ± 219.43 | 3318.65 ± 809.25 * | 859.36 ± 234.46 | 776.59 ± 228.82 |
| AUC∞ (ng·h/mL) | 681.03 ± 215.12 | 3325.83 ± 807.91 * | 881.62 ± 247.34 | 794.48 ± 226.13 |
| MRT (h) | 2.99 ± 0.47 | 3.37 ± 0.83 | 3.76 ± 1.16 | 3.81 ± 0.05 |
| CL (mL/min/kg) | 25.96 ± 6.30 | 15.55 ± 5.69 * | 20.03 ± 5.48 | 22.47 ± 7.12 |
| Vd (mL/kg) | 78.30 ± 25.66 | 55.03 ± 26.29 * | 72.16 ± 15.37 | 85.38 ± 25.82 |
| Ginsenosides | Pharmacokinetic Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (ng∙h/mL) | Cmax (ng/mL) | Tmax (h) | MRT (h) | T1/2 (h) | |
| Rb1 | 454.57 ± 111.33 | 17.84 ± 2.34 | 3.33 ± 1.15 | 17.13 ± 2.09 | 16.87 ± 5.81 |
| Rb2 | 282.80 ± 58.90 | 10.02 ± 1.04 | 3.33 ± 1.15 | 18.61 ± 1.43 | 30.19 ± 5.48 |
| Rc | 320.75 ± 97.23 | 11.67 ± 2.49 | 3.33 ± 1.15 | 18.35 ± 1.89 | 24.24 ± 7.51 |
| Rd | 163.83 ± 39.07 | 5.10 ± 0.74 | 2.17 ± 1.76 | 20.84 ± 1.68 | 43.49 ± 17.54 |
| PPD | 542.01 ± 141.09 | 20.56 ± 9.47 | 16.50 ± 12.48 | 21.56 ± 3.31 | 26.95 ± 18.33 |
| PPT | 429.91 ± 105.75 | 16.97 ± 8.99 | 16.50 ± 12.48 | 23.12 ± 2.26 | 46.38 ± 13.27 |
| Valsartan | Rc | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Control | Rc Treatment | Parameters | Rc Treatment |
| T1/2 (h) | 2.41 ± 1.30 | 3.30 ± 1.51 | T1/2 (h) | 27.51 ± 4.26 |
| C0 (ng/mL) | 400.66 ± 77.85 | 1451.25 ± 998.21 | C0 (μM) | 34.04 ± 5.22 |
| AUC24h (ng·h/mL) | 639.41 ± 80.71 | 808.86 ± 111.90 | AUC24h (μM·h) | 748.59 ± 184.79 |
| AUC∞ (ng·h/mL) | 657.34 ± 84.89 | 836.42 ± 112.34 | AUC∞ (μM·h) | 1064.50 ± 324.96 |
| MRT (h) | 2.27 ± 0.67 | 2.94 ± 1.52 | MRT (h) | 38.50 ± 5.11 |
| CL (mL/h/kg) | 25.66 ± 3.50 | 20.18 ± 2.86 | ||
| Vd (L/kg) | 57.14 ± 13.24 | 57.65 ± 27.32 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, J.-H.; Lee, S.; Lee, W.; Jin, S.; Kwon, M.; Shin, C.H.; Choi, M.-K.; Song, I.-S. Herb–Drug Interaction of Red Ginseng Extract and Ginsenoside Rc with Valsartan in Rats. Molecules 2020, 25, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030622
Jeon J-H, Lee S, Lee W, Jin S, Kwon M, Shin CH, Choi M-K, Song I-S. Herb–Drug Interaction of Red Ginseng Extract and Ginsenoside Rc with Valsartan in Rats. Molecules. 2020; 25(3):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030622
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Ji-Hyeon, Sowon Lee, Wonpyo Lee, Sojeong Jin, Mihwa Kwon, Chul Hwi Shin, Min-Koo Choi, and Im-Sook Song. 2020. "Herb–Drug Interaction of Red Ginseng Extract and Ginsenoside Rc with Valsartan in Rats" Molecules 25, no. 3: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030622
APA StyleJeon, J.-H., Lee, S., Lee, W., Jin, S., Kwon, M., Shin, C. H., Choi, M.-K., & Song, I.-S. (2020). Herb–Drug Interaction of Red Ginseng Extract and Ginsenoside Rc with Valsartan in Rats. Molecules, 25(3), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030622






