Sucupira Oil-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): Lipid Screening, Factorial Design, Release Profile, and Cytotoxicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Lipids
2.1.2. Surfactants
2.1.3. Other Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Lipid Screening
2.2.2. Surfactant Screening
2.2.3. Preparation of Sucupira Oil-Loaded NLC
2.2.4. Physicochemical Characterization: Size, Polydispersity Index, and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.2.5. Encapsulation Efficiency (EE) and Loading Capacity (LC)
2.2.6. Experimental Factorial Design
2.2.7. In Vitro Release Profile
2.2.8. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies
2.2.9. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ragonese, C.; Sciarrone, D.; Tranchida, P.Q.; Dugo, P.; Dugo, G.; Mondello, L. Evaluation of a Medium-Polarity Ionic Liquid Stationary Phase in the Analysis of Flavor and Fragrance Compounds. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7947–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranchida, P.Q.; Zoccali, M.; Bonaccorsi, I.L.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L.; Dugo, G. The off-line combination of high performance liquid chromatography and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography–mass spectrometry: A powerful approach for highly detailed essential oil analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1305, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turek, C.; Stintzing, F.C. Stability of Essential Oils: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.S.; Ponte, B.M.; Boonme, P.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Nanoencapsulation of polyphenols for protective effect against colon-rectal cancer. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Izzo, A.A.; Milić, N.; Cicala, C.; Santini, A.; Capasso, R. Milk thistle (Silybum marianum): A concise overview on its chemistry, pharmacological, and nutraceutical uses in liver diseases. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2202–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesano, D.; Blasi, F.; Simonetti, M.S.; Santini, A.; Cossignani, L. Chemical and Nutritional Characterization of Seed Oil from Cucurbita maxima L. (var. Berrettina) Pumpkin. Foods 2018, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbone, C.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Caddeo, C.; Silva, A.; Musumeci, T.; Pignatello, R.; Puglisi, G.; Souto, E. Mediterranean essential oils as precious matrix components and active ingredients of lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, I.; Zielińska, A.; Ferreira, N.R.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Optimization of linalool-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles using experimental factorial design and long-term stability studies with a new centrifugal sedimentation method. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Andreani, T.; Chaud, M.; Benites, C.; Pinho, S.; Souto, E. Essential Oils as Active Ingredients of Lipid Nanocarriers for Chemotherapeutic Use. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, A.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Ferreira, N.R.; Silva, A.M.; Nowak, I.; Souto, E.B. Anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activity of citral: Optimization of citral-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) using experimental factorial design and LUMiSizer®. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 553, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Venditti, A.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Kręgiel, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B.; Novellino, E.; et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Apigenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benameur, Q.; Gervasi, T.; Pellizzeri, V.; Pľuchtová, M.; Tali-Maama, H.; Assaous, F.; Guettou, B.; Rahal, K.; Gruľová, D.; Dugo, G.; et al. Antibacterial activity of Thymus vulgaris essential oil alone and in combination with cefotaxime against blaESBL producing multidrug resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolates. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daliu, P.; Santini, A.; Novellino, E. From pharmaceuticals to nutraceuticals: Bridging disease prevention and management. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, A.; Tenore, G.C.; Novellino, E. Nutraceuticals: A paradigm of proactive medicine. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Novellino, E.; Souto, E.B.; Daliu, P.; Santini, A. Abelmoschus esculentus (L.): Bioactive Components’ Beneficial Properties—Focused on Antidiabetic Role—For Sustainable Health Applications. Molecules 2018, 24, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Asbahani, A.; Miladi, K.; Badri, W.; Sala, M.; Addi, E.A.; Casabianca, H.; El Mousadik, A.; Hartmann, D.; Jilale, A.; Renaud, F.; et al. Essential oils: From extraction to encapsulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 483, 220–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoscheid, J.; Cardoso, M.L.C. Sucupira as a Potential Plant for Arthritis Treatment and Other Diseases. Arthritis 2015, 2015, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zielińska, A.; Ferreira, N.R.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Cicero, N.; El Mamouni, S.; Silva, A.M.; Nowak, I.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B. Development and Optimization of Alpha-Pinene-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) Using Experimental Factorial Design and Dispersion Analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souto, S.B.; Souto, E.B.; Braga, D.C.; Medina, J.L. Prevention and current onset delay approaches of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, R.; Souto, S.B.; Sánchez-López, E.; López Machado, A.; Severino, P.; Jose, S.; Santini, A.; Fortuna, A.; García, M.L.; Silva, A.M.; et al. Sugar-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome—Review of Classical and New Compounds: Part-I. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, R.; Souto, S.B.; Sánchez-López, E.; López Machado, A.; Severino, P.; Jose, S.; Santini, A.; Silva, A.M.; Fortuna, A.; García, M.L.; et al. Sugar-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome—Strategies for In Vivo Administration: Part-II. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharabi, K.; Tavares, C.D.J.; Rines, A.K.; Puigserver, P. Molecular pathophysiology of hepatic glucose production. Mol. Asp. Med. 2015, 46, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Souto, E.B.; Souto, S.B.; Campos, J.R.; Severino, P.; Pashirova, T.N.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Silva, A.M.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Izzo, A.A.; et al. Nanoparticle Delivery Systems in the Treatment of Diabetes Complications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, C.Y.; Al-Salami, H.; Dass, C.R. Potential of insulin nanoparticle formulations for oral delivery and diabetes treatment. J. Control. Release 2017, 264, 247–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.Y.; Martinez, J.; Dass, C.R. Oral delivery of insulin for treatment of diabetes: Status quo, challenges and opportunities. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menditto, E.; Cahir, C.; Aza-Pascual-Salcedo, M.; Bruzzese, D.; Poblador-Plou, B.; Malo, S.; Costa, E.; Rubio, F.G.; Gimeno-Miguel, A.; Orlando, V.; et al. Adherence to chronic medication in older populations: Application of a common protocol among three European cohorts. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2018, 12, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menditto, E.; Guerriero, F.; Orlando, V.; Crola, C.; Di Somma, C.; Illario, M.; Morisky, N.E.; Colao, A. Self-Assessment of Adherence to Medication: A Case Study in Campania Region Community-Dwelling Population. J. Aging Res. 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindola, H.M.; Grando, R.; Figueiredo, M.C.; Basting, R.; Queiroz, N.; De Fátima, Â.; De Carvalho, J.E.; Wang, Z.J.; Foglio, M. Derivatives of furanditerpenes from Pterodon genus: Pharmacological studies disclose their potential as chronic pain relief in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 804, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.; Martín, M.J.; Ruiz, M.A.; Clares, B. Current encapsulation strategies for bioactive oils: From alimentary to pharmaceutical perspectives. Food Res. Int. 2016, 83, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, C.; Teixeira, M.D.C.; Sousa, M.D.C.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.M.B.; Musumeci, T. Clotrimazole-Loaded Mediterranean Essential Oils NLC: A Synergic Treatment of Candida Skin Infections. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pashirova, T.N.; Zueva, I.V.; Petrov, K.A.; Babaev, V.M.; Lukashenko, S.S.; Rizvanov, I.K.; Souto, E.B.; Nikolsky, E.E.; Zakharova, L.Y.; Masson, P.; et al. Nanoparticle-Delivered 2-PAM for Rat Brain Protection against Paraoxon Central Toxicity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16922–16932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavendish, M.; Nalone, L.; Barbosa, T.; Barbosa, R.; Costa, S.; Nunes, R.; Da Silva, C.F.; Chaud, M.V.; Souto, E.B.; Hollanda, L.; et al. Study of pre-formulation and development of solid lipid nanoparticles containing perillyl alcohol. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Andreani, T.; Macedo, A.S.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Santana, M.H.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Current State-of-Art and New Trends on Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN and NLC) for Oral Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012, 750–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Muller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles: Effect on bioavailability and pharmacokinetic changes. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2010, 197, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Wissing, S.A.; Barbosa, C.M.; Müller, R.H. Comparative study between the viscoelastic behaviors of different lipid nanoparticle formulations. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2004, 55, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doktorovová, S.; Kovačević, A.B.; Garcia, M.L.; Souto, E.B. Preclinical safety of solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers: Current evidence from in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 108, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Shegokar, R.; Rakovsky, E.; González-Mira, E.; Lopes, C.; Silva, A.; Martins-Lopes, P.; Müller, R.; Souto, E.B. Cationic solid lipid nanoparticles (cSLN): Structure, stability and DNA binding capacity correlation studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 420, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Silva, A.M.; Gaivao, I.; Souto, E.B.; Teixeira, J.P.; Martins-Lopes, P. Comet assay reveals no genotoxicity risk of cationic solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2014, 34, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. Nanotoxicology applied to solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers—A systematic review of in vitro data. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Santana, M.H.A.; Souto, E.B. Optimizing SLN and NLC by 22 full factorial design: Effect of homogenization technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Mehnert, W.; Muller, R.H. Polymorphic behaviour of Compritol®888 ATO as bulk lipid and as SLN and NLC. J. Microencapsul. 2006, 23, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, E.B.; Muller, R.H. Investigation of the factors influencing the incorporation of clotrimazole in SLN and NLC prepared by hot high-pressure homogenization. J. Microencapsul. 2006, 23, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, E.B.; Müller, R.H. The use of SLN and NLC as topical particulate carriers for imidazole antifungal agents. Die Pharm. 2006, 61, 431–437. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, M.; Carbone, C.; Souto, E.B. Beyond liposomes: Recent advances on lipid based nanostructures for poorly soluble/poorly permeable drug delivery. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Kovačević, A.B. Theoretical prediction versus experimental screening for determination of the solubility capacity of solid lipids for poorly soluble drugs. In Proceedings of the 11th Central European Symposium on Pharmaceutical Technology, Belgrade, Serbia, 22–24 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Souto, E.B.; Anselmi, C.; Centini, M.; Müller, R. Preparation and characterization of n-dodecyl-ferulate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN®). Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 295, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mors, W.B.; Fo, M.F.D.S.; Monteiro, H.J.; Gilbert, B.; Pellegrino, J. Chemoprophylactic Agent in Schistosomiasis: 14,15-Epoxygeranylgeraniol. Science 1967, 157, 950–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Jang, M. Light absorption coefficient measurement of SOA using a UV–Visible spectrometer connected with an integrating sphere. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4263–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigon, R.B.; Gonçalez, M.L.; Severino, P.; Alves, D.A.; Santana, M.H.; Souto, E.B.; Chorilli, M. Solid lipid nanoparticles optimized by 22 factorial design for skin administration: Cytotoxicity in NIH3T3 fibroblasts. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jose, S.; Fangueiro, J.; Smitha, J.; Cinu, T.; Chacko, A.; Premaletha, K.; Souto, E.B. Predictive modeling of insulin release profile from cross-linked chitosan microspheres. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 60, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Andreani, T.; Jäger, A.; Chaud, M.V.; Santana, M.H.A.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. Solid lipid nanoparticles for hydrophilic biotech drugs: Optimization and cell viability studies (Caco-2 & HEPG-2 cell lines). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 81, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Andreani, T.; Kiill, C.P.; De Souza, A.L.R.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Fernandes, L.S.G.; Doktorovova, S.; Santos, D.L.; Garcia, M.L.; Gremião, M.P.D.; Souto, E.B.; et al. Surface engineering of silica nanoparticles for oral insulin delivery: Characterization and cell toxicity studies. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fangueiro, J.F.; Andreani, T.; Egea, M.A.; Garcia, M.L.; Souto, S.B.; Souto, E.B. Experimental factorial design applied to mucoadhesive lipid nanoparticles via multiple emulsion process. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 100, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojo, A.A.M.; Fernandes, A.R.V.; Ferreira, N.R.E.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Santana, M.H.A.; Souto, E.B. Evaluation of the Influence of Process Parameters on the Properties of Resveratrol-Loaded NLC Using 22 Full Factorial Design. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. Hansen solubility parameters (HSP) for prescreening formulation of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN): In vitro testing of curcumin-loaded SLN in MCF-7 and BT-474 cell lines. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, E.B.; Doktorovova, S.; Zielinska, A.; Silva, A.M. Key production parameters for the development of solid lipid nanoparticles by high shear homogenization. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Muller, R.H.; Gohla, S. A novel approach based on lipid nanoparticles (SLN®) for topical delivery of α-lipoic acid. J. Microencapsul. 2005, 22, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjidi, F.; Shahedi, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Nasirpour, A. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC): A potential delivery system for bioactive food molecules. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Luo, J.; Tan, S.-W.; Otieno, B.O.; Zhang, Z. The applications of Vitamin E TPGS in drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tan, S.-W.; Feng, S.-S. Vitamin E TPGS as a molecular biomaterial for drug delivery. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 4889–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, P.; Pinho, S.C.; Souto, E.B.; Santana, M.H. Polymorphism, crystallinity and hydrophilic–lipophilic balance of stearic acid and stearic acid–capric/caprylic triglyceride matrices for production of stable nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 86, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.R.; Fernandes, A.R.; Sousa, R.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Boonme, P.; Garcia, M.L.; Silva, A.M.; Naveros, B.C.; Souto, E.B. Optimization of nimesulide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) by factorial design, release profile and cytotoxicity in human Colon adenocarcinoma cell line. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mira, E.; Egea, M.; García, M.; Souto, E.B. Design and ocular tolerance of flurbiprofen loaded ultrasound-engineered NLC. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Egea, M.A.; Souto, E.B.; Calpena, A.C.; Garcia, M.L. Optimizing flurbiprofen-loaded NLC by central composite factorial design for ocular delivery. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 45–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Nikolić, S.; Calpena, A.C.; Egea, M.A.; Souto, E.B.; Garcia, M.L. Improved and Safe Transcorneal Delivery of Flurbiprofen by NLC and NLC-Based Hydrogels. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, S.; Tho, I.; Souto, E.B.; Ferreira, D.; Brandl, M. Multivariate design for the evaluation of lipid and surfactant composition effect for optimisation of lipid nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Cinu, T.A.; Sebastian, R.; Shoja, M.H.; Aleykutty, N.A.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B. Transferrin-Conjugated Docetaxel–PLGA Nanoparticles for Tumor Targeting: Influence on MCF-7 Cell Cycle. Polymers 2019, 11, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.M.; Alvarado, H.L.; Abrego, G.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Garduno-Ramirez, M.L.; Garcia, M.L.; Calpena, A.C.; Souto, E.B. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Oleanolic/Ursolic Acids-Loaded in PLGA Nanoparticles in Different Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.M.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Coutinho, T.E.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Pashirova, T.N.; Andreani, T.; Souto, E.B. Soft Cationic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Production and Cytotoxicity of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.M.; Martins-Gomes, C.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Andreani, T.; Souto, E.B. Comparison of antiproliferative effect of epigallocatechin gallate when loaded into cationic solid lipid nanoparticles against different cell lines. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Wu, T.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Z. Recent Advances in the Application of Vitamin E TPGS for Drug Delivery. Theranostics 2018, 8, 464–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Severino, P.; Andreani, T.; Boonme, P.; Santini, A.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, E.B. d-alpha-tocopherol nanoemulsions: Size properties, rheological behavior, surface tension, osmolarity and cytotoxicity. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of Sucupira oil are available from the authors. |



| Samples (VT = 1 mL) | TPGS % (m/V) | Tween 80% (m/V) | Poloxamer® 188 % (m/V) | Lecithin % (m/V) | Sucupira % (m/V) | Kollivax® GMS II % (m/V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.5 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | - | - |
| 2 | 4.5 | 1 | 1 | - | - | - |
| 3 | 4.5 | 2 | - | 0.5 | - | - |
| 4 | 4.5 | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| 5 | 4.5 | - | 2 | 0.5 | - | - |
| 6 | 4.5 | - | 2 | - | - | - |
| 7 | - | 0.5 | - | - | 0.5 | 4.5 |
| 8 | - | 1 | - | - | 0.5 | 4.5 |
| 9 | - | 1.5 | - | - | 0.5 | 4.5 |
| 10 | 4.5 | 1 | 1 | - | 0.5 | - |
| 11 | - | 1.5 | - | - | 0.5 | - |
| 12 | - | 1.5 | - | 0.5 | 0.5 | - |
| Samples (VT = 1 mL) | Sucupira Oil % (m/V) | Imwitor® 900K % (m/V) | Kollivax® GMS II % (m/V) | TPGS % (m/V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.5 | 4.5 | - | 0.475 |
| 2 | 0.5 | 4.5 | - | 0.950 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 4.5 | - | 1.425 |
| 4 | 0.5 | - | 4.5 | 0.475 |
| 5 | 0.5 | - | 4.5 | 0.950 |
| 6 | 0.5 | - | 4.5 | 1.425 |
| 7 | 0.75 | 4.25 | - | 0.475 |
| 8 | 0.75 | 4.25 | - | 0.950 |
| 9 | 0.75 | 4.25 | - | 1.425 |
| Factors | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | +1 | |
| Kollivax® GMS II | 2.250 % (m/V) | 4.500 % (m/V) | 9.00 % (m/V) |
| TPGS | 0.7125 % (m/V) | 1.425 % (m/V) | 2.85 % (m/V) |
| Samples (VT = 1 mL) | Sucupira Oil % (m/V) | Solid Lipid % (m/V) | Visual Analysis of Melted Mixtures | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 1 h | 24 h | ||||
| 1 | 5 | Imwitor® 900 K 95 |  |  |  |  |
| 2 | 5 | Dynasan® 116 95 |  |  |  |  |
| 3 | 5 | Kollivax® GMS II 95 |  |  |  |  |
| 4 | 5 | Cetostearyl alcohol 95 |  |  |  |  |
| 5 | 10 | Imwitor® 900 K 90 |  |  |  |  |
| 6 | 10 | Dynasan® 116 90 |  |  |  |  |
| 7 | 10 | Kollivax® GMS II 90 |  |  |  |  |
| 8 | 15 | Imwitor® 900 K 85 |  |  |  |  |
| 9 | 15 | Kollivax® GMS II 85 |  |  |  |  |
| Formulations (VT = 1 mL) | Measurement Time (h) | Mean Particle Size (nm) ± SD | PI (arb. units) ± SD | ZP (mV) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 197.8 ± 6.3 | 0.327 ± 0.008 | −31.2 ± 1.7 |
| 24 | 173.3 ± 2.9 | 0.656 ± 0.036 | −28.7 ± 0.3 | |
| 2 | 0 | 337.5 ± 122.9 | 0.367 ± 0.089 | −7.0 ± 1.6 |
| 24 | 21.4 ± 2.1 | 0.242 ± 0.053 | −5.4 ± 1.4 | |
| 3 | 0 | 201.8 ± 18.2 | 0.385 ± 0.078 | −30.0 ± 0.7 |
| 24 | 239.0 ± 8.7 | 0.546 ± 0.176 | −28.6 ± 1.0 | |
| 4 | 0 | 213.6 ± 58.7 | 0.274 ± 0.037 | −13.8 ± 2.5 |
| 24 | 63.6 ± 63.9 | 0.192 ± 0.041 | −6.8 ± 2.1 | |
| 5 | 0 | 208.2 ± 7.6 | 0.354 ± 0.100 | −32.5 ± 1.2 |
| 24 | 298.8 ± 17.4 | 0.528 ± 0.071 | −32.6 ± 0.3 | |
| 6 | 0 | 213.9 ± 89.1 | 0.334 ± 0.117 | −0.32 ± 0.2 |
| 24 | 152.7 ± 94.7 | 0.304 ± 0.074 | −0.18 ± 0.3 | |
| 7 | 0 | 957.1 ± 488.5 | 0.782 ± 0.206 | −31.0 ± 1.1 |
| 24 | 831.7 ± 129.3 | 0.728 ± 0.105 | −26.4 ± 0.4 | |
| 8 | 0 | 342.9 ± 87.8 | 0.645 ± 0.126 | −30.1 ± 1.7 |
| 24 | 1101.0 ± 275.9 | 0.860 ± 0.043 | −23.8 ± 0.2 | |
| 9 | 0 | 538.5 ± 117.6 | 0.520 ± 0.091 | −28.0 ± 0.9 |
| 24 | 812.9 ± 166.7 | 0.655 ± 0.086 | −24.6 ± 0.6 | |
| 10 | 0 | 443.8 ± 132.9 | 0.502 ± 0.082 | −26.0 ± 1.4 |
| 24 | 1189.0 ± 218.1 | 0.764 ± 0.025 | −25.3 ± 0.5 | |
| 11 | 0 | 833.7 ± 174.9 | 0.762 ± 0.128 | −29.0 ± 0.4 |
| 24 | >1 µm | 0.908 ± 0.086 | −29.9 ± 0.2 | |
| 12 | 0 | 243.6 ± 94.0 | 0.351 ± 0.063 | −33.7 ± 0.4 |
| 24 | 969.4 ± 301.2 | 0.813 ± 0.104 | −27.7 ± 1.5 |
| Formulations (VT = 1 mL) | Measurement Time (h) | Mean Particle Size (nm) ± SD | PI (arb. units) ± SD | ZP (mV) ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 147.2 ± 0.4 | 0.291 ± 0.025 | - |
| 24 | 358.1 ± 2.2 | 0.660 ± 0.015 | +0.02 ± 0.18 | |
| 2 | 0 | 274.6 ± 10.6 | 0.645 ± 0.019 | - |
| 24 | 190.6 ± 4.1 | 0.363 ± 0.016 | −0.05 ± 0.07 | |
| 3 | 0 | 118.0 ± 1.7 | 0.278 ± 0.008 | - |
| 24 | 147.4 ± 2.3 | 0.337 ± 0.006 | +0.12 ± 0.11 | |
| 4 | 0 | 255.0 ± 8.4 | 0.526 ± 0.050 | +0.05 ± 0.24 |
| 24 | 318.8 ± 2.4 | 0.502 ± 0.001 | +0.05 ± 0.16 | |
| 5 | 0 | 164.8 ± 0.7 | 0.379 ± 0.020 | −0.14 ± 0.11 |
| 24 | 178.1 ± 1.0 | 0.298 ± 0.026 | −0.04 ± 0.14 | |
| 6 | 0 | 148.1 ± 1.0 | 0.274 ± 0.029 | −0.15±0.002 |
| 24 | 159.3 ± 9.5 | 0.305 ± 0.028 | +0.13 ± 0.16 | |
| 7 | 0 | 752.2 ± 752.5 | 0.602 ± 0.249 | −0.04 ± 0.06 |
| 24 | 244.5 ± 0.9 | 0.264 ± 0.007 | −0.07 ± 0.16 | |
| 8 | 0 | 136.2 ± 2.0 | 0.242 ± 0.009 | −0.04 ± 0.01 |
| 24 | 272.2 ± 1.4 | 0.498 ± 1.353 | +0.02 ± 0.1 | |
| 9 | 0 | 117.9 ± 0.7 | 0.267 ± 0.021 | +0.01 ± 0.07 |
| 24 | 202.1 ± 2.1 | 0.398 ± 0.023 | −0.09 ± 0.08 |
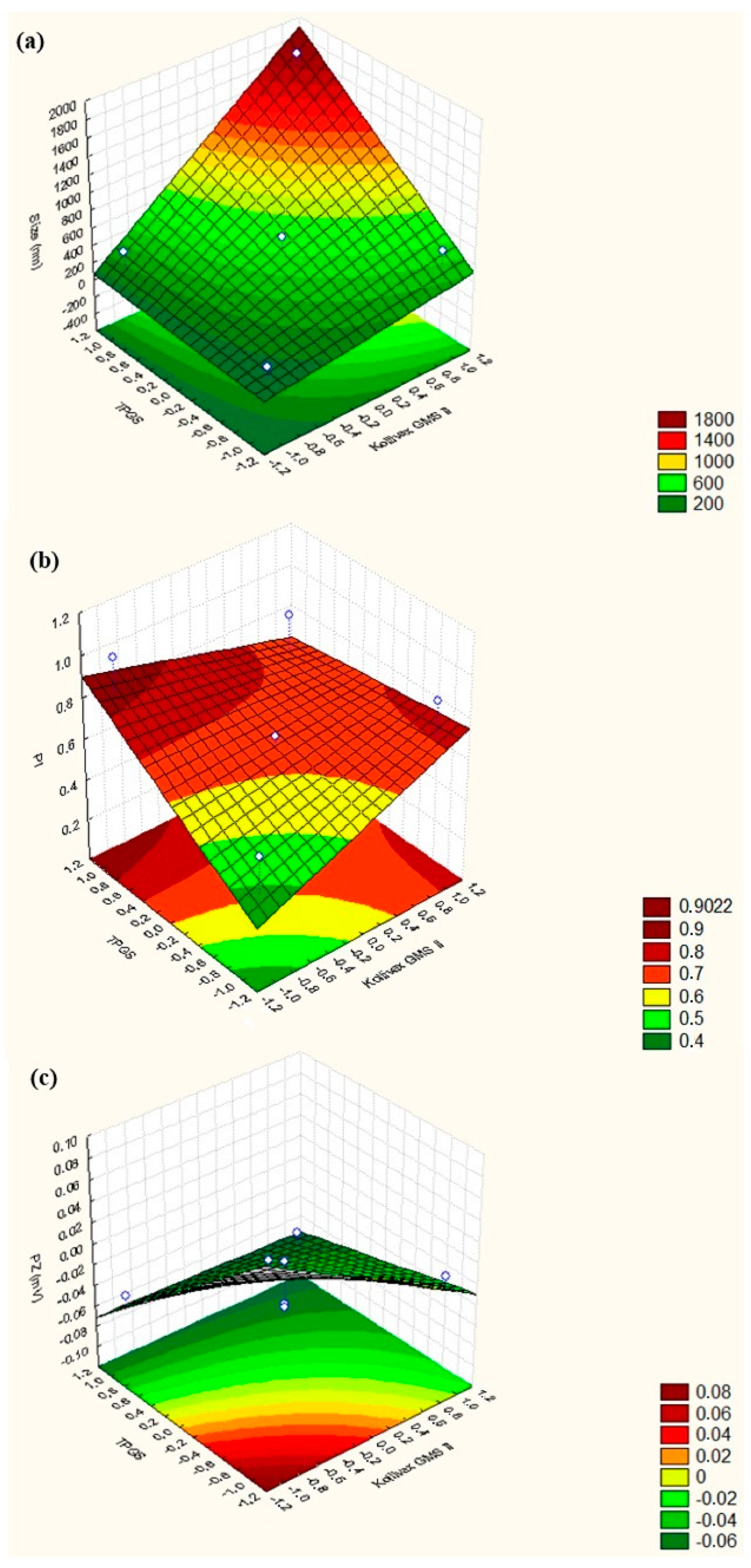
| NLC Formulation (VT = 50 mL) | Independent Variables | Dependent Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kollivax® GMS II | TPGS | Particle Size (nm) ± SD | PI (arb units) ± SD | ZP (mV) ± SD | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 344.2 ± 39.43 | 0.0613 ± 0.066 | −0.0512 ± 0.0134 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 604.7 ± 83.64 | 0.666 ± 0.059 | −0.00793 ± 0.112 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 212.4 ± 9.158 | 0.567 ± 0.057 | −0.0483 ± 0.00758 |
| 4 | +1 | +1 | 1762 ± 225.8 | 0.832 ± 0.146 | −0.0604 ± 0.0290 |
| 5 | +1 | −1 | 537.5 ± 13.78 | 0.873 ± 0.094 | −0.0143 ± 0.0837 |
| 6 | −1 | −1 | 180.7 ± 11.82 | 0.553 ± 0.086 | +0.0757 ± 0.0425 |
| 7 | −1 | +1 | 337.6 ± 67.88 | 1.000 ± 0.000 | −0.0486 ± 0.0517 |
| Mean Particle Size | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors and Interactions | Sum of Squares (SS) | Degrees of Freedom (df) | Mean Square (MS) | F-Value | p-Value |
| (1) Kollivax® GMS II | 793,168 | 1 | 793,168.4 | 9.429096 | 0.054533 |
| (2) TPGS | 477,066 | 1 | 477,066.5 | 5.671312 | 0.097490 |
| 1 by 2 | 284,942 | 1 | 284,942.4 | 3.387363 | 0.162690 |
| Error | 252,358 | 3 | 84,119.2 | ||
| Total | 1,807,535 | 6 | |||
| Mean Polydispersity Index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors and Interactions | Sum of Squares (SS) | Degrees of Freedom (df) | Mean Square (MS) | F-Value | p-Value |
| (1) Kollivax® GMS II | 0.005776 | 1 | 0.005776 | 0.037510 | 0.858801 |
| (2) TPGS | 0.041209 | 1 | 0.041209 | 0.267618 | 0.640659 |
| 1 by 2 | 0.059536 | 1 | 0.059536 | 0.386637 | 0.578125 |
| Error | 0.461953 | 3 | 0.153984 | ||
| Total | 0.568474 | 6 | |||
| Mean Zeta Potential | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factors and Interactions | Sum of Squares (SS) | Degrees of Freedom (df) | Mean Square (MS) | F-Value | p-Value |
| (1) Kollivax® GMS II | 0.002591 | 1 | 0.002591 | 3.61478 | 0.153441 |
| (2) TPGS | 0.007259 | 1 | 0.007259 | 10.12803 | 0.050000 |
| 1 by 2 | 0.001529 | 1 | 0.001529 | 2.13304 | 0.240284 |
| Error | 0.002150 | 3 | 0.000717 | ||
| Total | 0.013529 | 6 | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vieira, R.; Severino, P.; Nalone, L.A.; Souto, S.B.; Silva, A.M.; Lucarini, M.; Durazzo, A.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B. Sucupira Oil-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): Lipid Screening, Factorial Design, Release Profile, and Cytotoxicity. Molecules 2020, 25, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030685
Vieira R, Severino P, Nalone LA, Souto SB, Silva AM, Lucarini M, Durazzo A, Santini A, Souto EB. Sucupira Oil-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): Lipid Screening, Factorial Design, Release Profile, and Cytotoxicity. Molecules. 2020; 25(3):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030685
Chicago/Turabian StyleVieira, Raquel, Patricia Severino, Luciana A. Nalone, Selma B. Souto, Amélia M. Silva, Massimo Lucarini, Alessandra Durazzo, Antonello Santini, and Eliana B. Souto. 2020. "Sucupira Oil-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): Lipid Screening, Factorial Design, Release Profile, and Cytotoxicity" Molecules 25, no. 3: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030685
APA StyleVieira, R., Severino, P., Nalone, L. A., Souto, S. B., Silva, A. M., Lucarini, M., Durazzo, A., Santini, A., & Souto, E. B. (2020). Sucupira Oil-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): Lipid Screening, Factorial Design, Release Profile, and Cytotoxicity. Molecules, 25(3), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030685












