Unveiling the Molecular Basis of Mascarpone Cheese Aroma: VOCs analysis by SPME-GC/MS and PTR-ToF-MS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
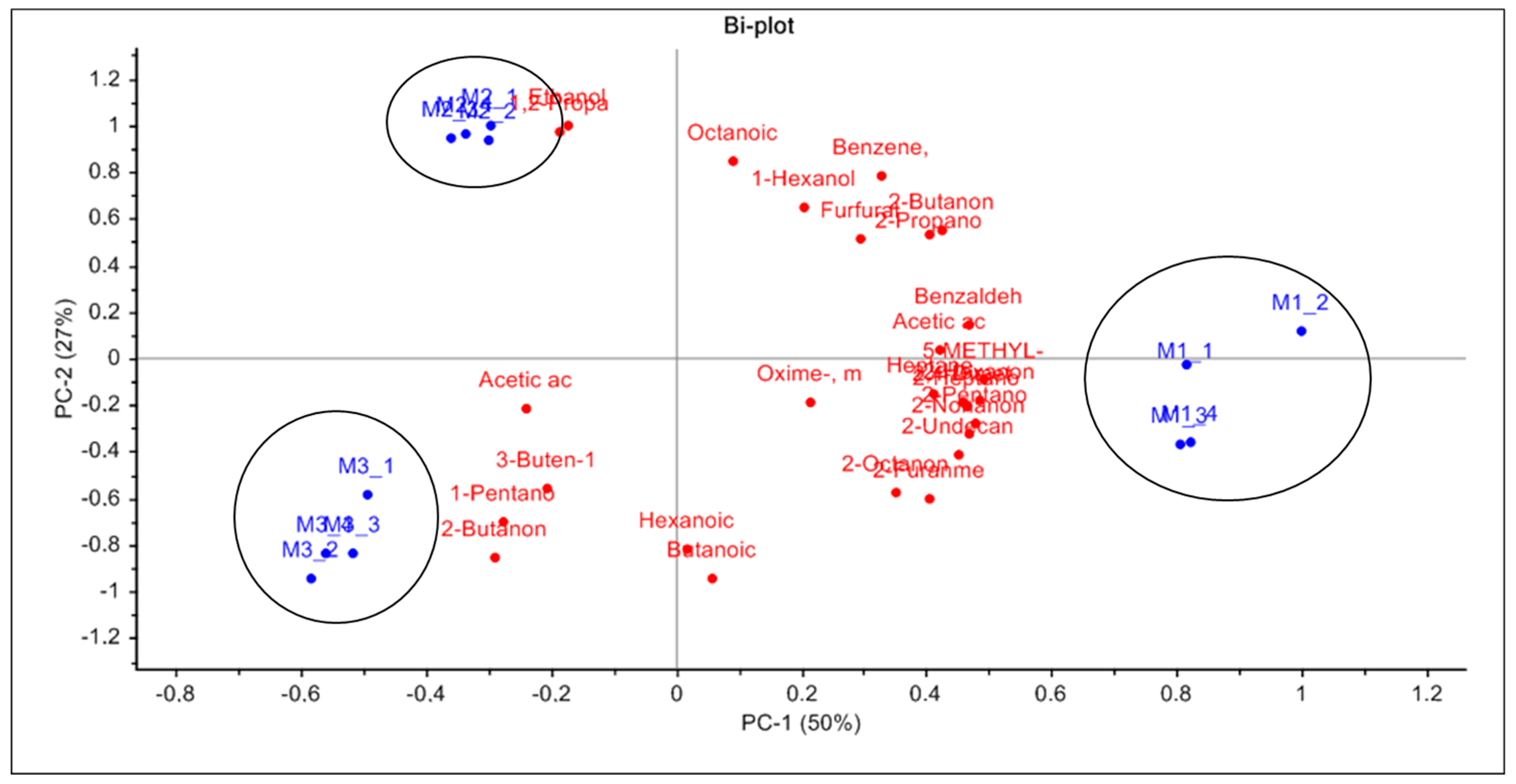
2.1. HS-SPME GC-MS Results
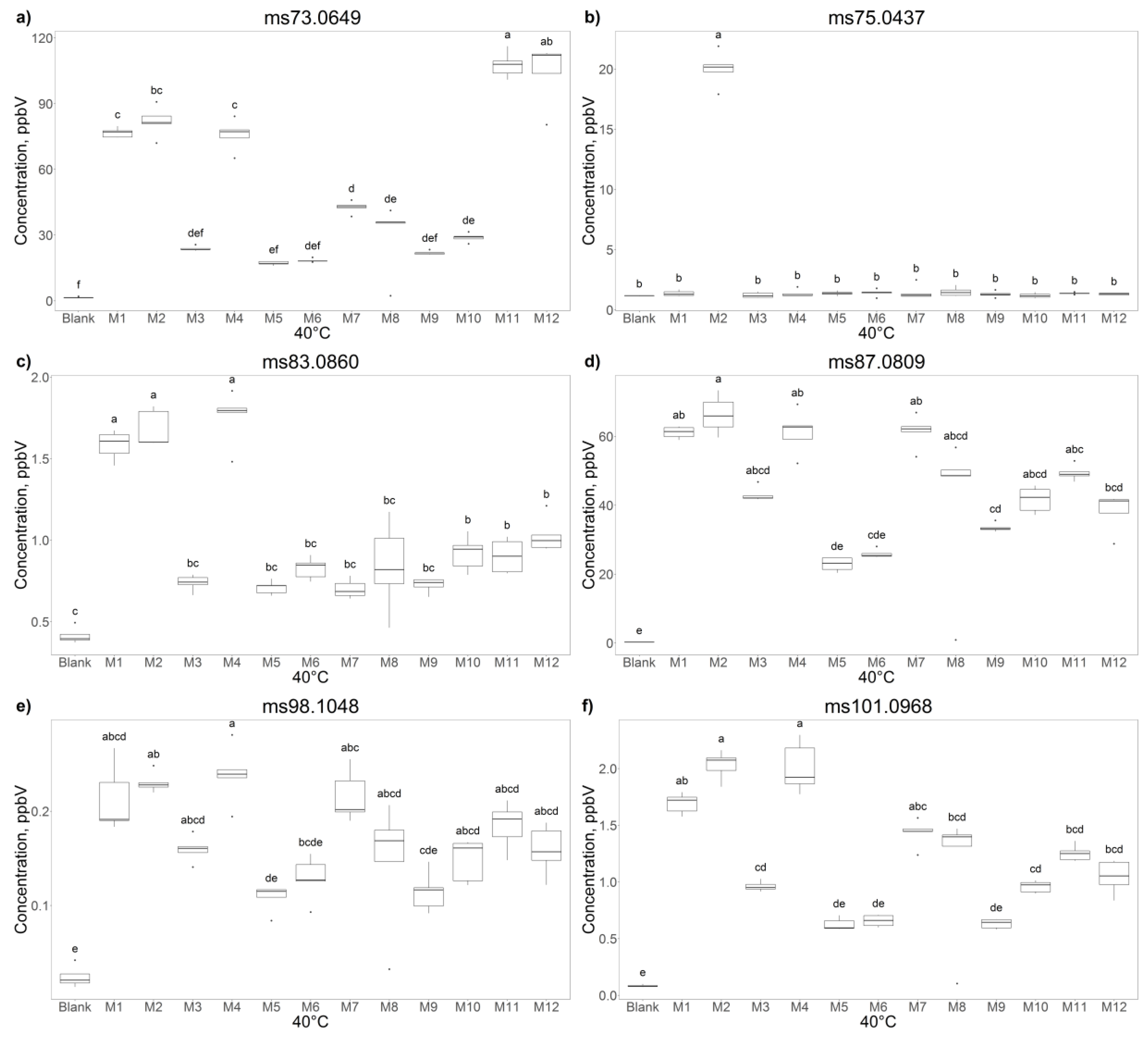
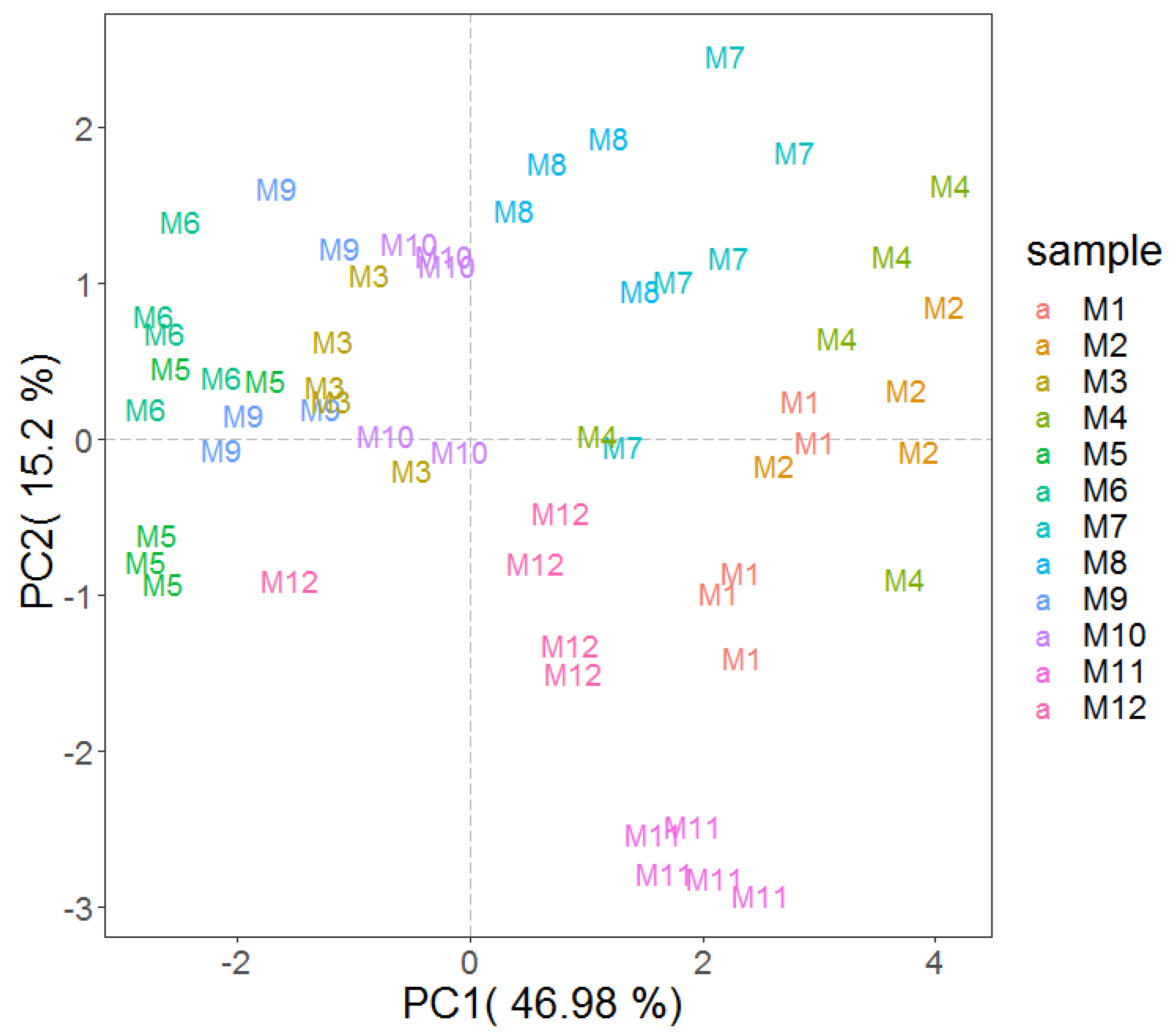
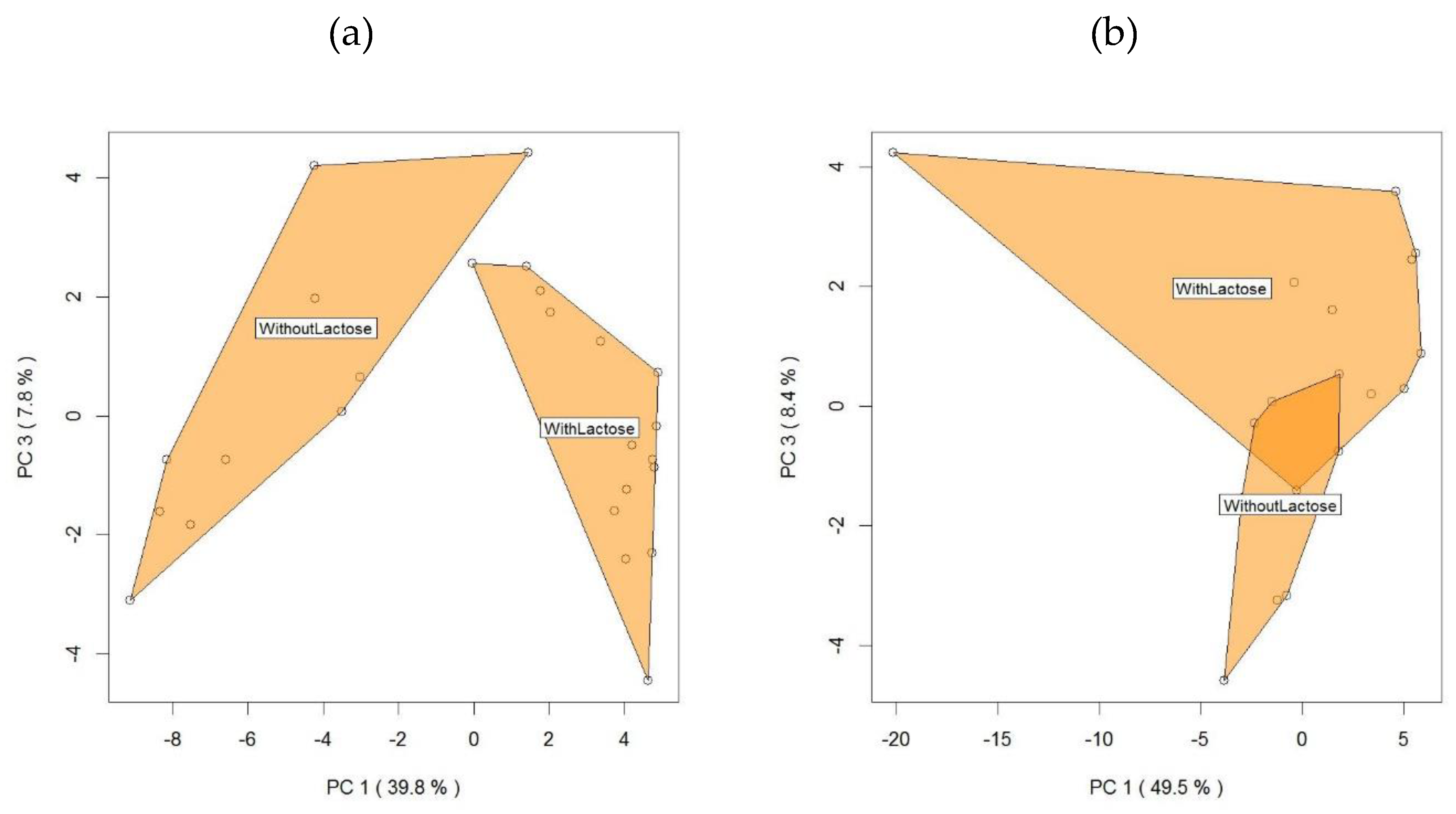
2.2. PTR-ToF-MS Results and Comparison with HS-SPME GC-MS Findings
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Selection and Preparation
3.2. HS-SPME GC-MS Measurements
3.3. PTR-ToF-MS Measurements
3.4. Statistical Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carminati, D.; Perrone, A.; Neviani, E. Inhibition of Clostridium sporogenes growth in mascarpone cheese by co-inoculation with Streptococcus thermophilus under conditions of temperature abuse. Food Microbiol. 2001, 18, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Franciosa, G.; Pourshaban, M.; Gianfranceschi, M.; Gattuso, A.; Fenicia, L.; Ferrini, A.M.; Mannoni, V.; De Luca, G.; Aureli, P. Clostridium botulinum spores and toxin in mascarpone cheese and other milk products. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hinrichs, J. Mediterranean milk and milk products. Eur. J. Nutr. 2004, 43, i12–i17. [Google Scholar]
- Del Prato, O.S. Trattato di Tecnologia Casearia; Edagricole: Bologna, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Donelly, C. The Oxford Companion to Cheese; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-0-19-933088-1. [Google Scholar]
- Majchrzak, T.; Wojnowski, W.; Lubinska-Szczygeł, M.; Różańska, A.; Namieśnik, J.; Dymerski, T. PTR-MS and GC-MS as complementary techniques for analysis of volatiles: A tutorial review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1035, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dewulf, J.; Van Langenhove, H.; Wittmann, G. Analysis of volatile organic compounds using gas chromatography. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2002, 21, 637–646. [Google Scholar]
- Panseri, S.; Soncin, S.; Chiesa, L.M.; Biondi, P.A. A headspace solid-phase microextraction gas-chromatographic mass-spectrometric method (HS-SPME–GC/MS) to quantify hexanal in butter during storage as marker of lipid oxidation. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 886–889. [Google Scholar]
- Biasioli, F.; Gasperi, F.; Yeretzian, C.; Märk, T.D. PTR-MS monitoring of VOCs and BVOCs in food science and technology. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 968–977. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, A.; Haidacher, S.; Hanel, G.; Hartungen, E.; Märk, L.; Seehauser, H.; Schottkowsky, R.; Sulzer, P.; Märk, T.D. A high resolution and high sensitivity proton-transfer-reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometer (PTR-TOF-MS). Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 286, 122–128. [Google Scholar]
- Capozzi, V.; Yener, S.; Khomenko, I.; Farneti, B.; Cappellin, L.; Gasperi, F.; Scampicchio, M.; Biasioli, F. PTR-ToF-MS Coupled with an Automated Sampling System and Tailored Data Analysis for Food Studies: Bioprocess Monitoring, Screening and Nose-space Analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 123, e54075. [Google Scholar]
- Marsili, R. Flavors and off-flavors in dairy foods. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Fuquay, J.W., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2011; pp. 533–551. ISBN 978-0-12-374407-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mutarutwa, D.; Navarini, L.; Lonzarich, V.; Compagnone, D.; Pittia, P. GC-MS aroma characterization of vegetable matrices: Focus on 3-alkyl-2-methoxypyrazines. J. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 53, 871–881. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, F.J.; González-Crespo, J.; Cava, R.; Ramírez, R. Formation of the aroma of a raw goat milk cheese during maturation analysed by SPME–GC–MS. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Curioni, P.M.G.; Bosset, J.O. Key odorants in various cheese types as determined by gas chromatography-olfactometry. Int. Dairy J. 2002, 12, 959–984. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.J.; Ganesan, P.; Lee, S.J.; Kwak, H.S. Comparative study of flavor in cholesterol-removed Gouda cheese and Gouda cheese during ripening. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 1972–1983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mallia, S.; Escher, F.; Rehberger, B.; Schlichtherle-Cerny, H. Aroma-active secondary oxidation products of butter. In Proceedings of the 3rd QLIF Congress: Improving Sustainability in Organic and Low Input Food Production Systems, Stuttgart, Germany, 20–23 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, D.G.; Reineccius, G.A. Characterization of the volatile compounds that constitute fresh sweet cream butter aroma. Flavour Fragr. J. 2003, 18, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Production of Volatile Compounds in Reconstituted Milk Reduced-Fat Cheese and the Physicochemical Properties as Affected by Exopolysaccharide-Producing Strain. Molecules 2012, 17, 14393–14408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Povolo, M.; Contarini, G. Comparison of solid-phase microextraction and purge-and-trap methods for the analysis of the volatile fraction of butter. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 985, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, M.; Reineccius, G. Identification of aroma compounds in Parmigiano-Reggiano cheese by gas chromatography/olfactometry. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar]
- Gasperi, F.; Gallerani, G.; Boschetti, A.; Biasioli, F.; Monetti, A.; Boscaini, E.; Jordan, A.; Lindinger, W.; Iannotta, S. The mozzarella cheese flavour profile: A comparison between judge panel analysis and proton transfer reaction mass spectrometry. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Boscaini, E.; van Ruth, S.; Biasioli, F.; Gasperi, F.; Märk, T.D. Gas Chromatography−Olfactometry (GC-O) and Proton Transfer Reaction−Mass Spectrometry (PTR-MS) Analysis of the Flavor Profile of Grana Padano, Parmigiano Reggiano, and Grana Trentino Cheeses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo-Escamilla, F.J.; Kelly, A.L.; Delahunty, C.M. Influence of Starter Culture on Flavor and Headspace Volatile Profiles of Fermented Whey and Whey Produced from Fermented Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3745–3753. [Google Scholar]
- van Ruth, S.M.; Koot, A.; Akkermans, W.; Araghipour, N.; Rozijn, M.; Baltussen, M.; Wisthaler, A.; Märk, T.D.; Frankhuizen, R. Butter and butter oil classification by PTR-MS. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 307–317. [Google Scholar]
- Makhoul, S.; Yener, S.; Khomenko, I.; Capozzi, V.; Cappellin, L.; Aprea, E.; Scampicchio, M.; Gasperi, F.; Biasioli, F. Rapid non-invasive quality control of semi-finished products for the food industry by direct injection mass spectrometry headspace analysis: The case of milk powder, whey powder and anhydrous milk fat. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 51, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benozzi, E.; Romano, A.; Capozzi, V.; Makhoul, S.; Cappellin, L.; Khomenko, I.; Aprea, E.; Scampicchio, M.; Spano, G.; Märk, T.D.; et al. Monitoring of lactic fermentation driven by different starter cultures via direct injection mass spectrometric analysis of flavour-related volatile compounds. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yépez, A.; Russo, P.; Spano, G.; Khomenko, I.; Biasioli, F.; Capozzi, V.; Aznar, R. In situ riboflavin fortification of different kefir-like cereal-based beverages using selected Andean LAB strains. Food Microbiol. 2019, 77, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romano, A.; Capozzi, V.; Spano, G.; Biasioli, F. Proton transfer reaction-mass spectrometry: Online and rapid determination of volatile organic compounds of microbial origin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3787–3795. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo-Escamilla, F.J.; Kelly, A.L.; Delahunty, C.M. Sensory Characteristics and Related Volatile Flavor Compound Profiles of Different Types of Whey. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar]
- Burdock, G.A. Fenaroli’s Handbook of Flavor Ingredients; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-00-069466-6. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, W.; Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Zhang, F.; Fan, C.; Chen, X.; Chang, J.; Chu, X. High-throughput foodomics strategy for screening flavor components in dairy products using multiple mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Puniya, A.K. Fermented Milk and Dairy Products; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4665-7800-5. [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo, T.M.P.; Summa, C.; Bertolo, G.; Giangiacomo, R. Spreadability of Mascarpone cheese: Sensory and objective measurements. Milchwissenschaft 2005, 60, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.-H.; He, H.-J.; Sun, D.-W. Non-Destructive and rapid evaluation of staple foods quality by using spectroscopic techniques: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg, F.; Lyndgaard, C.B.; Sørensen, K.M.; Engelsen, S.B. Process Analytical Technology in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 27–35. [Google Scholar]
- Capozzi, V.; Makhoul, S.; Aprea, E.; Romano, A.; Cappellin, L.; Sanchez Jimena, A.; Spano, G.; Gasperi, F.; Scampicchio, M.; Biasioli, F. PTR-MS Characterization of VOCs Associated with Commercial Aromatic Bakery Yeasts of Wine and Beer Origin. Molecules 2016, 21, 483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campbell-Sills, H.; Capozzi, V.; Romano, A.; Cappellin, L.; Spano, G.; Breniaux, M.; Lucas, P.; Biasioli, F. Advances in wine analysis by PTR-ToF-MS: Optimization of the method and discrimination of wines from different geographical origins and fermented with different malolactic starters. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 397–398, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Bottiroli, R.; Pedrotti, M.; Aprea, E.; Biasioli, F.; Fogliano, V.; Gasperi, F. Application of PTR-TOF-MS for the quality assessment of lactose-free milk: Effect of storage time and employment of different lactase preparations. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellin, L.; Biasioli, F.; Fabris, A.; Schuhfried, E.; Soukoulis, C.; Märk, T.D.; Gasperi, F. Improved mass accuracy in PTR-TOF-MS: Another step towards better compound identification in PTR-MS. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 290, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Cappellin, L.; Biasioli, F.; Granitto, P.M.; Schuhfried, E.; Soukoulis, C.; Costa, F.; Märk, T.D.; Gasperi, F. On data analysis in PTR-TOF-MS: From raw spectra to data mining. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Lindinger, W.; Hansel, A.; Jordan, A. On-line monitoring of volatile organic compounds at pptv levels by means of proton-transfer-reaction mass spectrometry (PTR-MS) medical applications, food control and environmental research. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Process. 1998, 173, 191–241. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
| Sample | Claimed Characteristics | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | Mascarpone | A |
| M2 | Mascarpone | B |
| M3 | Mascarpone | C |
| M4 | Mascarpone | B |
| M5 | Mascarpone | C |
| M6 | Mascarpone | C |
| M7 | Mascarpone | M |
| M8 | Mascarpone | M |
| M9 | Mascarpone without lactose | M |
| M10 | Mascarpone without lactose | M |
| M11 | Mascarpone without lactose | C |
| M12 | Mascarpone without lactose | C |
| Compound | Chemical Class | Protonated Ion | |
|---|---|---|---|
| m/z | Sum Formula | ||
| Ethanol | Alcohols | 47.049 | C2H7O+ |
| 2-Propanone | Ketones | 59.049 | C3H7O+ |
| Acetic acid | Organic acids | 61.028 | C2H5O2+ |
| 2-Butanone | Ketones | 73.065 | C4H9O+ |
| 1,2-Propanediol = Propylene glycol | Alcohols | 77.060 | C3H9O2+ |
| 2-Pentanone/3-Buten-1-ol, 3-methyl- | Ketones/Alcohols | 87.080 | C5H11O+ |
| 2-Butanone, 3-hydroxy- (B) / Butanoic acid/Acetic acid ethyl ester | Ketones/Organic acids/Esters | 89.060 | C4H9O2+ |
| Toluene | Hydrocarbons | 93.070 | C7H9+ |
| Furfural | Furans | 97.028 | C5H5O2+ |
| 2-Hexanone | Ketones | 101.096 | C6H13O+ |
| Benzaldehyde | Aldehyde | 107.049 | C7H7O+ |
| 5-Methyl-delta-valerolactone | Lactones | 115.075 | C6H11O2+ |
| 2-Heptanone | Ketones | 115.112 | C7H15O+ |
| Hexanoic acid | Organic acids | 117.091 | C6H13O2+ |
| 2,4-Dimethyl-1-heptene | Hydrocarbons | 127.148 | C9H19+ |
| 2-Octanone | Ketones | 129.127 | C8H17O+ |
| 1-Hexanol, 2-ethyl- | Alcohols | 131.143 | C8H19O+ |
| 2-Nonanone | Ketones | 143.143 | C9H19O+ |
| Octanoic acid | Organic acids | 145.122 | C8H17O2+ |
| Oxime-, methoxy-phenyl- | Oxime | 152.071 | C8H10NO2+ |
| 2-Undecanone | Ketones | 171.174 | C11H23O+ |
| Heptane, 2,2,4,6,6-pentamethyl | Hydrocarbons | 171.211 | C12H27+ |
| MM | TM | SF | M1 (A) | M2 (B) | M3 (C) | M4 (B) | M5 (C) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 41.039 | 41.039 | C3H5+ | 21.2 ± 0.9 b | 27 ± 3 c | 11.4 ± 0.6 a | 21 ± 1 b | 10 ± 1 a | 1 × 10−13 |
| 43.018 | 43.018 | C2H3O+ | 30.0 ± 0.7 b | 44 ± 3 c | 24 ± 2 a | 33 ± 2 b | 24 ± 5 a | 3 × 10−9 |
| 43.054 | 43.054 | C3H7+ | 11.5 ± 0.6 c | 16 ± 1 d | 3.5 ± 0.5 a | 6.7 ± 0.4 b | 3.1 ± 0.4 a | 4 × 10−17 |
| 45.033 | 45.033 | C2H5O+ | 113 ± 6 b | 175 ± 12 c | 81 ± 3 a | 114 ± 10 b | 88 ± 23 a | 2 × 10−9 |
| 47.049 | 47.049 | C2H7O+ | 8 ± 3 a | 52 ± 39 c | 10 ± 8 a | 16 ± 1 ab | 44 ± 5 bc | 2 × 10−3 |
| 55.054 | 55.054 | C4H7+ | 13.3 ± 0.4 c | 14.9 ± 0.8 d | 8.1 ± 0.3 b | 15 ± 1 d | 6.0 ± 0.4 a | 7 × 10−16 |
| 57.070 | 57.070 | C4H9+ | 6.0 ± 0.1 c | 5.6 ± 0.6 c | 3.9 ± 0.2 b | 12 ± 1 d | 2.7 ± 0.1 a | 7 × 10−17 |
| 59.049 | 59.049 | C3H7O+ | 1062 ± 35 c | 976 ± 72 c | 563 ± 29 b | 1230 ± 116 d | 355 ± 26 a | 9 × 10−15 |
| 61.029 | 61.028 | C2H5O2+ | 10 ± 3 a | 26 ± 6 b | 18 ± 5 ab | 11 ± 2 a | 24 ± 10 b | 4 × 10−4 |
| 63.026 | 63.026 | C2H7S+ | 15.1 ± 0.3 c | 16 ± 1 c | 7.2 ± 0.4 b | 20 ± 2 d | 3.3 ± 0.5 a | 4 × 10−16 |
| 69.070 | 69.07 | C5H9+ | 6.4 ± 0.2 a | 8.3 ± 0.6 b | 6.0 ± 0.4 a | 9.0 ± 0.8 b | 6.2 ± 0.6 a | 2 × 10−8 |
| 71.086 | 71.086 | C5H11+ | 1.2 ± 0.1 ab | 1.7 ± 0.8 b | 0.7 ± 0.1 a | 1.3 ± 0.1 ab | 0.72 ± 0.05 a | 1 × 10−3 |
| 73.065 | 73.065 | C4H9O+ | 77 ± 2 b | 82 ± 7 b | 24 ± 1 a | 76 ± 7 b | 17.2 ± 0.9 a | 1 × 10−16 |
| 75.044 | 75.044 | C3H7O2+ | 1.4 ± 0.2 a | 20 ± 1 b | 1.2 ± 0.2 a | 1.4 ± 0.3 a | 1.4 ± 0.2 a | 1 × 10−21 |
| 83.086 | 83.086 | C6H11+ | 1.6 ± 0.1 b | 1.7 ± 0.1 b | 0.7 ± 0.0 a | 1.8 ± 0.2 b | 0.71 ± 0.04 a | 4 × 10−14 |
| 87.044 | 87.044 | C4H7O2+ | 3.7 ± 0.5 bc | 3.8 ± 0.9 bc | 3.0 ± 0.4 ab | 4.3 ± 0.4 c | 2.0 ± 0.3 a | 2 × 10−5 |
| 87.081 | 87.08 | C5H11O+ | 61 ± 2 c | 66 ± 5 c | 43 ± 2 b | 61±6c | 23 ± 2 a | 6 × 10−13 |
| 89.060 | 89.06 | C4H9O2+ | 2.2 ± 0.6 a | 5.2 ± 0.6 c | 2.9 ± 0.3 ab | 2±1ab | 3.5 ± 0.3 b | 2 × 10−6 |
| 97.102 | 97.101 | C7H13+ | 2.3 ± 0.1 c | 2.7 ± 0.2 d | 1.8 ± 0.0 b | 2.6±0.1d | 1.1 ± 0.1 a | 4 × 10−14 |
| 101.097 | 101.096 | C7H7O+ | 1.7 ± 0.1 c | 2.0 ± 0.1 d | 1.0 ± 0.0 b | 2.0±0.2d | 0.6 ± 0.1 a | 5 × 10−14 |
| 115.113 | 115.112 | C7H15O+ | 28 ± 1 c | 30 ± 2 c | 20.5 ± 0.6 b | 30±2c | 12 ± 1 a | 7 × 10−14 |
| 143.145 | 143.143 | C9H19O+ | 2.1 ± 0.1 c | 2.5 ± 0.2 d | 1.7 ± 0.1 b | 2.4±0.2d | 1.1 ± 0.1 a | 2 × 10−12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Capozzi, V.; Lonzarich, V.; Khomenko, I.; Cappellin, L.; Navarini, L.; Biasioli, F. Unveiling the Molecular Basis of Mascarpone Cheese Aroma: VOCs analysis by SPME-GC/MS and PTR-ToF-MS. Molecules 2020, 25, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051242
Capozzi V, Lonzarich V, Khomenko I, Cappellin L, Navarini L, Biasioli F. Unveiling the Molecular Basis of Mascarpone Cheese Aroma: VOCs analysis by SPME-GC/MS and PTR-ToF-MS. Molecules. 2020; 25(5):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051242
Chicago/Turabian StyleCapozzi, Vittorio, Valentina Lonzarich, Iuliia Khomenko, Luca Cappellin, Luciano Navarini, and Franco Biasioli. 2020. "Unveiling the Molecular Basis of Mascarpone Cheese Aroma: VOCs analysis by SPME-GC/MS and PTR-ToF-MS" Molecules 25, no. 5: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051242
APA StyleCapozzi, V., Lonzarich, V., Khomenko, I., Cappellin, L., Navarini, L., & Biasioli, F. (2020). Unveiling the Molecular Basis of Mascarpone Cheese Aroma: VOCs analysis by SPME-GC/MS and PTR-ToF-MS. Molecules, 25(5), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25051242








