Simultaneous Determination of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Triterpenoids in Psidium guajava Using HPLC–DAD–ELSD and Pressurized Liquid Extraction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Conditions
2.2. Optimization of Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE) Procedure
2.3. Method Validation
2.4. Quantitation of Triterpenoids in Fruit and Leaf of P. guajava
2.5. Inhibition Activity of α-Glucosidase.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Preparation of Standard Solutions
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. HPLC Analysis
3.5. Method Validation
3.6. Inhibition Assay of α-Glucosidase Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutirrez, R.M.P.; Mitchell, S.; Solis, R.V. Psidium guajava: A review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Wang, Y.; Jian, Y.Q.; Huang, X.J.; Zhang, D.M.; Tang, Q.F.; Jiang, R.W.; Sun, X.G.; Lv, Z.P.; Zhang, X.Q.; et al. Guadial A and psiguadials C and D, three unusual meroterpenoids from Psidium guajava. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5262–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, W.K.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, M.S.; Bae, E.Y.; Sohn, C.B.; Oh, H.; Kim, B.Y.; Ahn, J.S. Antidiabetic effects of extracts from Psidium guajava. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bontempo, P.; Doto, A.; Miceli, M.; Mita, L.; Benedetti, R.; Nebbioso, A.; Veglione, M.; Rigano, D.; Cioffi, M.; Sica, V.; et al. Psidium guajava L. anti-neoplastic effects: Induction of apoptosis and cell differentiation. Cell Proliferat. 2011, 45, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, N.H.; Park, K.R.; Kim, S.M.; Yun, H.M.; Nam, D.; Lee, S.G.; Jang, H.J.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, S.H.; Shim, B.S.; et al. A hexane fraction of guava Leaves (Psidium guajava L.) induces anticancer activity by suppressing AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin/ribosomal p70 S6 kinase in human prostate cancer cells. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birdi, T.; Daswani, P.; Brijesh, S.; Tetali, P.; Natu, A.; Antia, N. Newer insights into the mechanism of action of Psidium guajava L. leaves in infectious diarrhoea. BMC Complem. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, H.; Nihorimbere, V. Antioxidant power of phytochemicals from Psidium guajava leaf. J. Zhejiang Univ-SC. 2004, 5, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Livingston Raja, N.R.; Sundar, K. Psidium guajava Linn confers gastro protective effects on rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. 2012, 16, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- Sambo, N.; Garba, S.H.; Timothy, H. Effect of the aqueous extract of Psidium guajava on erythromycin-induced liver damage in rats. Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 2009, 24, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutta, S.; Das, S. A study of the anti-inflammatory effect of the leaves of Psidium guajava Linn. on experimental animal models. Pharmacogn. Res. 2010, 2, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Lee, J.S. Natural ingredients for diabetes which are approved by Korean FDA. Biomed. Res. 2013, 24, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.K.; Ye, K.H.; Lv, Y.Q.; Wei, S.C.; Li, X.C.; Ma, J.J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Ye, C.L. Ameliorative effect and underlying mechanisms of total triterpenoids from Psidium guajava Linn (Myrtaceae) leaf on high-fat streptozotocin-induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats. Trop. J. Pharma Res. 2016, 15, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.C.; Ma, J.J.; Zhao, J.J.; Ye, K.H.; Lv, Y.Q.; Wang, X.K.; Wei, S.C.; Zhang, X.Q.; Ye, C.L. Total triterpenoids from Psidium guajava leaf improves insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 2016, 32, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Park, M.; Lee, H.C.; Kang, Y.H.; Kang, E.S.; Kim, S.K. Antidiabetic agents from medicinal plants. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 1203–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soman, S.; Rajamanickam, C.; Rauf, A.A.; Indira, M. Beneficial effects of Psidium guajava leaf extract on diabetic myocardium. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 65, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngbolua, J. A review on the Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Psidium guajava L.(Myrtaceae) and Future direction. Discov. Phytomed. 2018, 5, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Hassan, S.I.; Siddiqui, B.S.; Shaheen, F.; Ghayur, M.N.; Gilani, A.H. Triterpenoids from the leaves of Psidium guajava. Phytochemistry 2002, 61, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Hassan, S.I.; Siddiqui, B.S. Two new triterpenoids from the fresh leaves of Psidium guajava. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garo, E.; Eldridge, G.R.; Goering, M.G.; DeLancey Pulcini, E.; Hamilton, M.A.; Costerton, J.W.; James, G.A. Asiatic acid and corosolic acid enhance the susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms to tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1813–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yap, W.H.; Khoo, K.S.; Lim, S.H.; Yeo, C.C.; Lim, Y.M. Proteomic analysis of the molecular response of Raji cells to maslinic acid treatment. Phytomedicine 2011, 19, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Guan, T.; Tang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, H. Maslinic acid, a natural triterpenoid compound from Olea europaea, protects cortical neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stohs, S.J.; Miller, H.; Kaats, G.R. A review of the efficacy and safety of banaba (Lagerstroemia speciosa L.) and corosolic acid. Phytother. Res. 2011, 26, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanay, S.; Grare, M.; Mayer, J.; Finance, C.; Duval, R.E. Ursolic, oleanolic and betulinic acids: Antibacterial spectra and selectivity indexes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 120, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J. Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid: Research perspectives. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.J.; Fan, C.L.; Zhang, Q.W.; Zhang, X.Q.; Ye, W.C. Four new triterpenoids from the leaves of Psidium guajava. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 14, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.W.; Li, S.L.; Yi, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, W.C. Psidium guajava, a potential resource rich in corosolic acid revealed by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Med. Plants Res. 2011, 5, 4261–4266. [Google Scholar]
- El Sohafy, S.M.; Metwalli, A.M.; Harraz, F.M.; Omar, A.A. Quantification of flavonoids of Psidium guajava L. preparations by Planar Chromatography (HPTLC). Pharmacogn. Mag. 2009, 5, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.R.; Qian, H.; Yao, W.R. Identification of flavonoids and their glycosides by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and with diode array ultraviolet detection. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 11, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, W.N.L.; da Silva Sauthier, M.C.; dos Santos, A.M.P.; de Andrade Santana, D.; Azevedo, R.S.A.; da Cruz Caldas, J. Simultaneous determination of 13 phenolic bioactive compounds in guava (Psidium guajava L.) by HPLC–PAD with evaluation using PCA and Neural Network Analysis (NNA). Microchem. J. 2017, 133, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liao, Y.; Fang, C.; Tsunoda, M.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Deng, S. Simultaneous analysis of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid in guava leaves using QuEChERS-based extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2017, 2017, 2984562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.T.; Qi, L.W.; Li, P.; Yi, L.; Zhao, J.; Bi, Z.M. Determination of seventeen main flavonoids and saponins in the medicinal plant Huang-qi (Radix Astragali) by HPLC-DAD-ELSD. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.W.; Yu, Q.T.; Li, P.; Li, S.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Sheng, L.H.; Yi, L. Quality evaluation of Radix Astragali through a simultaneous determination of six major active isoflavonoids and four main saponins by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array and evaporative light scattering detectors. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1134, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.L.; Yao, W.F.; Zhu, D.N.; Hu, Y.Z. Chemical Fingerprinting by HPLC-DAD-ELSD and Principal Component Analysis of Polygala japonica from Different Locations in China. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2010, 8, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutschlechner, B.; Schwaiger, S.; Tran, T.V.A.; Stuppner, H. Development of a selective HPLC-DAD/ELSD method for the qualitative and quantitative assessment of commercially available Eurycoma longifolia products and plant extracts. Fitoterapia 2018, 124, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Roig, P.; Picó, Y. Pressurized liquid extraction of organic contaminants in environmental and food samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 71, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Lin, L.G.; Ye, W.C. Techniques for extraction and isolation of natural products: A comprehensive review. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shu, J.; Chou, G.; Wang, Z. Triterpenoid constituents in fruits of Psidum guajava. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2009, 34, 3047–3050. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D.; Meng, F.C.; Liu, H.; Xiao, T.; Lu, J.J.; Lin, L.G.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, Q.W. Novel biflavonoids from Cephalotaxus oliveri Mast. Phytochem Lett. 2018, 24, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.J.; Hu, H.; He, M.X.; Zhang, Q.W.; Li, P.; Wan, J.B.; He, C.W. α-Glucosidase inhibitory activity and structural characterization of polysaccharide fraction from Rhynchosia minima root. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 28, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G.; Li, P.; Yan, R.; Zhang, X.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.T.; Ye, W.C.; Zhang, Q.W. α-Glucosidase inhibitory effect and simultaneous quantification of three major flavonoid glycosides in Microctis folium. Molecules 2013, 18, 4221–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.C.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, X.Q.; Ye, W.C.; Zhang, Q.W. Flavonoids with α-glucosidase inhibitory activities and their contents in the leaves of Morus atropurpurea. Chin. Med. 2013, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the nine triterpenoids are available from the authors. |
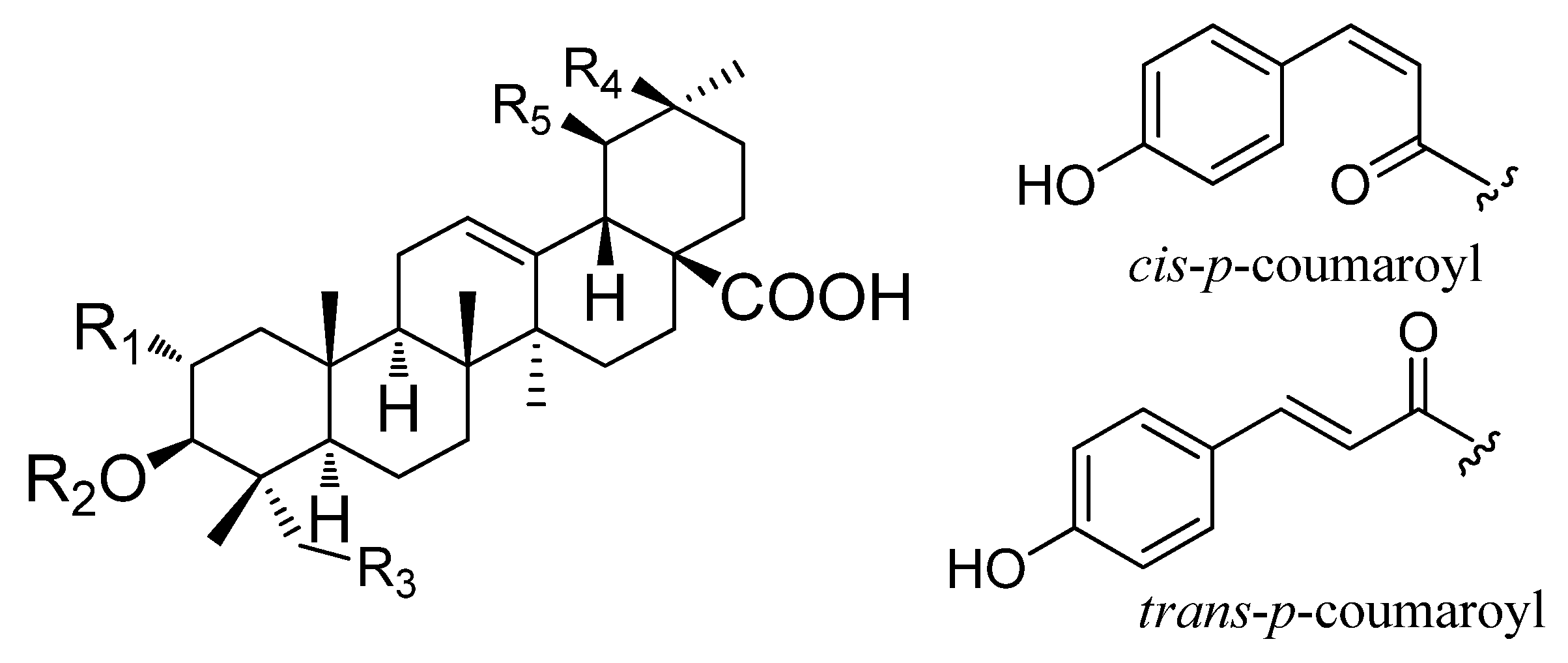


| No | Chemical Name | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | asiatic acid | OH | H | OH | H | CH3 |
| 2 | maslinic acid | OH | H | H | CH3 | H |
| 3 | corosolic acid | OH | H | H | H | CH3 |
| 4 | 3β-O-cis-p-coumaroyl-2α-hydroxy-olean-12-en-28-oic acid | OH | cis-p-coumaroyl | H | CH3 | H |
| 5 | 3β-O-cis-p-coumaroyl-2α-hydroxy-urs-12-en-28-oic acid | OH | cis-p-coumaroyl | H | H | CH3 |
| 6 | 3β-O-trans-p-coumaroyl-2α-hydroxy-olean-12-en-28-oic acid | OH | trans-p-coumaroyl | H | CH3 | H |
| 7 | 3β-O-trans-p-coumaroyl-2α-hydroxy-urs-12-en-28-oic acid | OH | trans-p-coumaroyl | H | H | CH3 |
| 8 | oleanolic acid | H | H | H | CH3 | H |
| 9 | ursolic acid | H | H | H | H | CH3 |
| Analytes | Retention Time (min) | Calibration Curve a | Test Range (ug/mL) | R2 | LOD b (μg/mL) | LOQ c (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21.95 | y = 1.39x + 4.46 | 3.03–48.40 | 0.9993 | 3.34 | 11.12 |
| 2 | 34.47 | y = 1.52x + 4.76 | 3.43–54.80 | 0.9992 | 2.99 | 9.96 |
| 3 | 35.82 | y = 1.50x + 4.60 | 7.75–124 | 0.9993 | 2.95 | 9.84 |
| 4 | 39.18 | y = 8,165.82x -0.51 | 0.28–2.25 | 1.0000 | 0.30 | 1.01 |
| 5 | 41.48 | y = 10,232.97x − 5.44 | 0.52–8.25 | 0.9998 | 0.25 | 0.85 |
| 6 | 45.75 | y = 13,596.12x − 3.55 | 0.47–7.50 | 0.9998 | 0.18 | 0.61 |
| 7 | 48.30 | y = 14,543.73x – 11.33 | 0.54–8.63 | 0.9999 | 0.23 | 0.77 |
| 8 | 52.49 | y = 1.57x + 4.24 | 7.38–1.18 | 0.9993 | 10.85 | 36.15 |
| 9 | 54.27 | y = 1.59x + 4.44 | 4.75–76.0 | 0.9992 | 9.76 | 32.53 |
| Analytes | Intra-Day (n = 6) | Inter-Day (n = 3) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | RSD (%) a | Content | RSD (%) | |
| 1 | 4.30 ± 0.06 | 1.35 | 4.48 ± 0.20 | 4.50 |
| 2 | 3.6 ± 0.10 | 2.84 | 3.64 ± 0.01 | 0.39 |
| 3 | 19.27 ± 0.14 | 0.70 | 19.4 ± 0.86 | 4.44 |
| 4 | 0.7 ± 0.03 | 4.97 | 0.70 ± 0.01 | 1.81 |
| 5 | 1.25 ± 0.04 | 2.94 | 1.22 ± 0.03 | 2.18 |
| 6 | 0.77 ± 0.03 | 4.20 | 0.77 ± 0.02 | 2.70 |
| 7 | 1.63 ± 0.05 | 3.25 | 1.60 ± 0.03 | 1.90 |
| 8 | ND b | NA b | ND | NA |
| 9 | 4.26 ± 0.05 | 1.21 | 4.35 ± 0.17 | 3.96 |
| Analyte | Original (mg) | Spike (mg) a | Found (mg) a | Recovery (%) (n = 3) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.54 | 1.23 | 2.76 | 99.19 | 1.42 |
| 1.60 | 3.25 | 106.87 | 1.02 | ||
| 1.89 | 3.54 | 105.82 | 1.57 | ||
| 2 | 1.33 | 1.01 | 2.32 | 98.02 | 1.64 |
| 1.38 | 2.74 | 102.17 | 3.37 | ||
| 1.60 | 2.90 | 98.12 | 2.60 | ||
| 3 | 6.81 | 5.50 | 12.45 | 102.55 | 1.67 |
| 6.80 | 13.70 | 101.32 | 1.24 | ||
| 8.16 | 14.85 | 98.50 | 3.57 | ||
| 4 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.55 | 104.54 | 1.04 |
| 0.33 | 0.66 | 103.03 | 1.97 | ||
| 0.40 | 0.73 | 102.50 | 4.42 | ||
| 5 | 0.67 | 0.52 | 1.16 | 94.23 | 0.22 |
| 0.62 | 1.27 | 96.77 | 4.33 | ||
| 0.81 | 1.46 | 97.53 | 2.49 | ||
| 6 | 0.51 | 0.35 | 0.85 | 97.14 | 3.80 |
| 0.52 | 1.05 | 103.84 | 2.74 | ||
| 0.62 | 1.16 | 104.84 | 8.50 | ||
| 7 | 1.18 | 0.80 | 1.94 | 95.00 | 0.70 |
| 1.18 | 2.39 | 102.50 | 1.15 | ||
| 1.42 | 2.62 | 102.82 | 0.24 | ||
| 8 | - b | 4.27 | 4.48 | 104.92 | 3.20 |
| 4.98 | 5.32 | 106.83 | 1.87 | ||
| 5.55 | 5.85 | 105.41 | 3.51 | ||
| 9 | 1.77 | 1.50 | 3.30 | 102.00 | 0.73 |
| 1.79 | 3.58 | 101.69 | 1.32 | ||
| 2.10 | 3.77 | 95.24 | 0.76 |
| Samples No. | Location | Parts | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PGL-1 | Zhanjiang | Leaves | 2.50 ± 0.09 | 1.35 ± 0.07 | 7.05 ± 0.34 | 0.45 ± 0.1 | 1.01 ± 0.08 | 0.75 ± 0.03 | 1.78 ± 0.01 | - a | 2.55 ± 0.07 | 17.94 |
| PGL-2 | Qingping1 | Leaves | 4.60 ± 0.07 | 3.85 ± 0.06 | 19.4 ± 0.07 | 0.74 ± 0.04 | 1.29 ± 0.04 | 0.83 ± 0.05 | 1.70 ± 0.05 | - | 5.30 ± 0.07 | 38.66 |
| PGL-3 | Conghua | Leaves | 2.75 ± 0.07 | 2.15 ± 0.07 | 11.91 ± 0.13 | 0.46 ± 0.03 | 0.91 ± 0.02 | 0.62 ± 0.03 | 1.41 ± 0.08 | - | 3.28 ± 0.14 | 24.20 |
| PGL-4 | Qingping2 | Leaves | 3.34 ± 0.06 | 2.68 ± 0.09 | 14.17 ± 0.18 | 0.4 ± 0.01 | 0.81 ± 0.04 | 0.52 ± 0.01 | 1.11 ± 0.03 | - | 4.00 ± 0.08 | 27.83 |
| PGL-5 | Shunde | Leaves | 3.26 ± 0.15 | 11.65 ± 0.24 | 5.95 ± 0.07 | 0.41 ± 0.02 | 0.77 ± 0.03 | 0.50 ± 0.03 | 1.21 ± 0.07 | - | 2.73 ± 0.16 | 16.74 |
| PGL-6 | Gaoming | Leaves | 2.20 ± 0.09 | 0.91 ± 0.05 | 4.35 ± 0.04 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 0.56 ± 0.04 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 0.94 ± 0.02 | - | 2.41 ± 0.13 | 12.49 |
| PGL-7 | Macau1 | Leaves | 3.36 ± 0.05 | 2.31 ± 0.03 | 11.97 ± 0.17 | 0.77 ± 0.04 | 1.34 ± 0.05 | 0.80 ± 0.02 | 1.73 ± 0.06 | - | 4.83 ± 0.15 | 27.98 |
| PGL-8 | Guangzhou | Leaves | 3.88 ± 0.10 | 2.83 ± 0.09 | 15.25 ± 0.32 | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 1.26 ± 0.06 | 0.74 ± 0.04 | 1.56 ± 0.03 | - | 4.89 ± 0.03 | 32.04 |
| PGL-9 | Foshan | Leaves | 3.08 ± 0.19 | 2.67 ± 0.20 | 13.62 ± 0.30 | 0.63 ± 0.06 | 1.35 ± 0.05 | 1.03 ± 0.02 | 2.21 ± 0.03 | - | 3.54 ± 0.19 | 30.12 |
| PGF-1 | Macau1 | Fruits | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PGF-2 | Gaoming | Fruits | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PGF-3 | Macau2 | Fruits | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PGF-4 | Macau3 | Fruits | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PGF-5 | Guangzhou | Fruits | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PGF-6 | Zhuhai | Fruits | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| No. | IC50 (n = 3) against α-Glucosidase (µg/mL) * |
|---|---|
| 1 | NI |
| 2 | 3.82 ± 0.03 |
| 3 | 1.33 ± 0.11 |
| 4 | 2.25 ± 0.28 |
| 5 | 1.54 ± 0.15 |
| 6 | 1.93 ± 0.14 |
| 7 | 2.12 ± 0.15 |
| 8 | 3.40 ± 0.28 |
| 9 | 4.35 ± 0.30 |
| PGL | 0.13 ± 0.00 |
| PGF | NI |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao, I.-C.; Chen, Y.; Gao, M.-H.; Lin, L.-G.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Ye, W.-C.; Zhang, Q.-W. Simultaneous Determination of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Triterpenoids in Psidium guajava Using HPLC–DAD–ELSD and Pressurized Liquid Extraction. Molecules 2020, 25, 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061278
Chao I-C, Chen Y, Gao M-H, Lin L-G, Zhang X-Q, Ye W-C, Zhang Q-W. Simultaneous Determination of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Triterpenoids in Psidium guajava Using HPLC–DAD–ELSD and Pressurized Liquid Extraction. Molecules. 2020; 25(6):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061278
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao, In-Cheng, Ying Chen, Mei-Hua Gao, Li-Gen Lin, Xiao-Qi Zhang, Wen-Cai Ye, and Qing-Wen Zhang. 2020. "Simultaneous Determination of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Triterpenoids in Psidium guajava Using HPLC–DAD–ELSD and Pressurized Liquid Extraction" Molecules 25, no. 6: 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061278
APA StyleChao, I.-C., Chen, Y., Gao, M.-H., Lin, L.-G., Zhang, X.-Q., Ye, W.-C., & Zhang, Q.-W. (2020). Simultaneous Determination of α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Triterpenoids in Psidium guajava Using HPLC–DAD–ELSD and Pressurized Liquid Extraction. Molecules, 25(6), 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061278








