Natural Compounds Rosmarinic Acid and Carvacrol Counteract Aluminium-Induced Oxidative Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cl− Controls
2.2. Effects of AlCl3, Rosmarinic Acid, and Carvacrol Treatment on the Amount of Al in Mice Blood and Brain and Liver Tissues
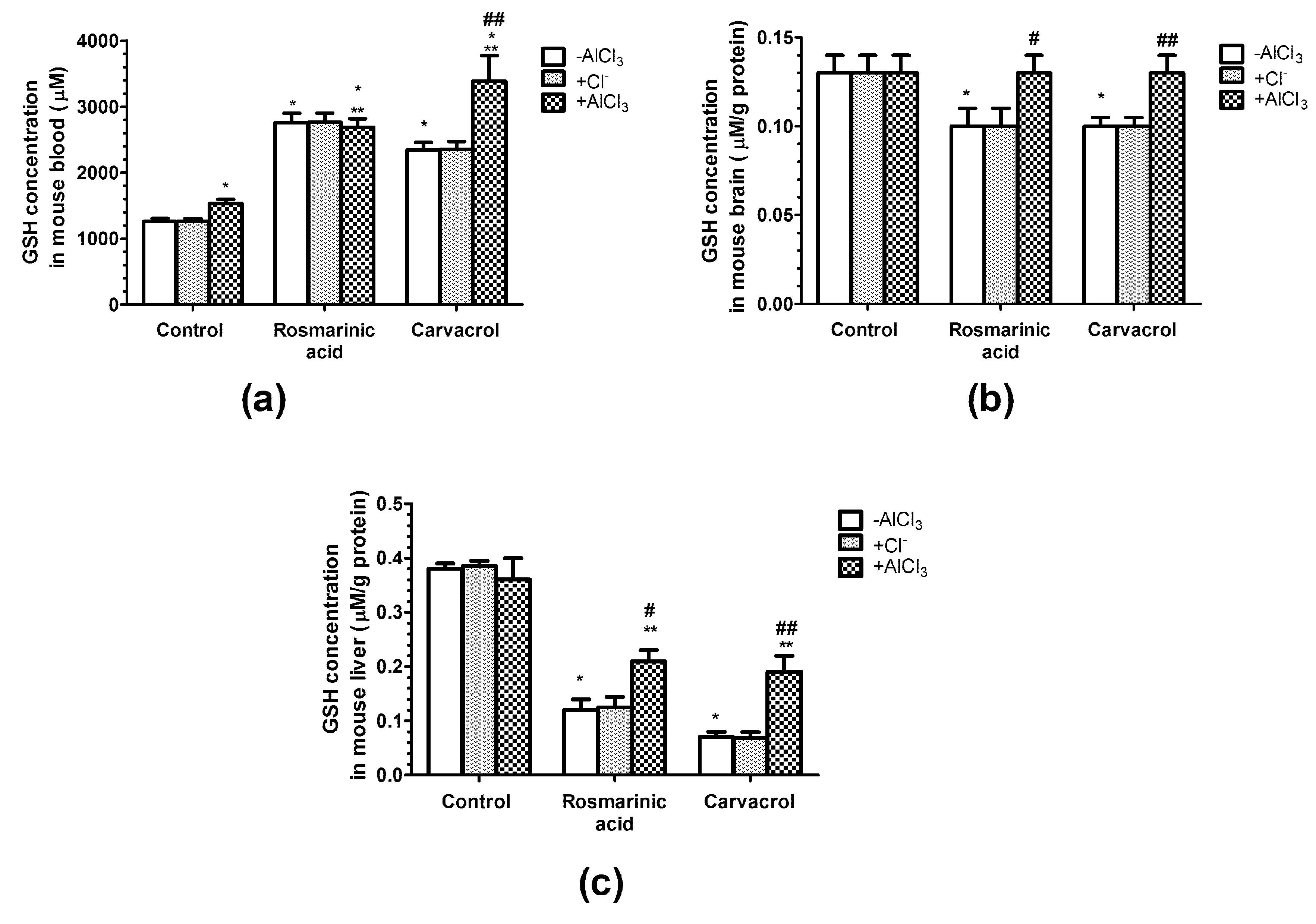
2.3. Effects of AlCl3, Rosmarinic Acid, and Carvacrol Treatment on the Concentration of Gsh in Mice Erythrocytes and Brain and Liver Homogenates
2.4. Effects of AlCl3, Rosmarinic Acid, and Carvacrol Treatment on the Concentration of MDA in Mice Erythrocytes and Brain and Liver Homogenates
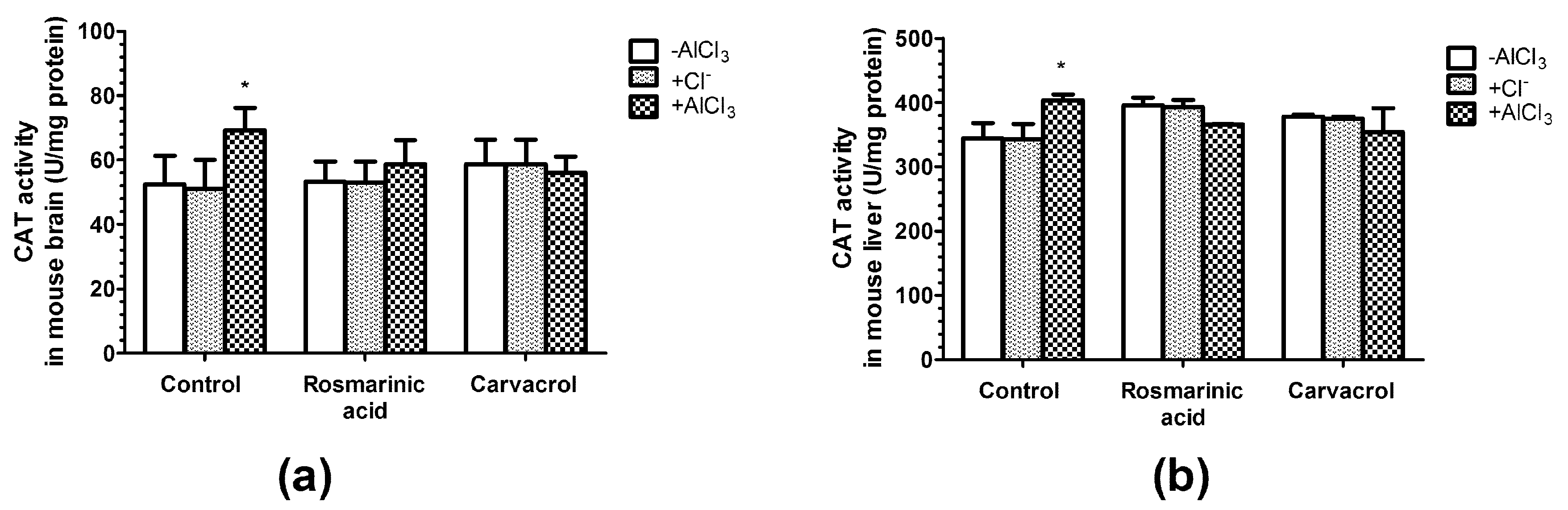
2.5. Effects of AlCl3, Rosmarinic Acid, and Carvacrol Treatment on the Activities of CAT and SOD in Mice Brain and Liver Homogenates
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animal Model
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. Determination of Al Amount in Blood and Target Tissues
4.5. Determination of Glutathione Level
4.6. Determination of Malondialdehyde Level
4.7. Catalase Activity Assay
4.8. Superoxide Dismutase Activity Assay
4.9. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willhite, C.C.; Karyakina, N.A.; Yokel, R.A.; Yenugadhati, N.; Wisniewski, T.M.; Arnold, I.M.; Momoli, F.; Krewski, D. Systematic review of potential health risks posed by pharmaceutical, occupational and consumer exposures to metallic and nanoscale aluminum, aluminum oxides, aluminum hydroxide and its soluble salts. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 1–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabsolghar, R.; Saberzadeh, J.; Khodaei, F.; Borojeni, R.A.; Khorsand, M.; Rashedinia, M. The protective effect of sodium benzoate on aluminum toxicity in PC12 cell line. Res. Pharm Sci. 2017, 12, 391–400. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, C.G.; Oteiza, P.I.; Golub, M.S.; Gershwin, M.E.; Keen, C.L. Effects of aluminum on brain lipid peroxidation. Toxicol. Lett. 1990, 51, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutteridge, J.M.; Quinlan, G.J.; Clark, I.; Halliwell, B. Aluminium salts accelerate peroxidation of membrane lipids stimulated by iron salts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 835, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savory, J.; Rao, J.K.; Huang, Y.; Letada, P.R.; Herman, M.M. Age-related hippocampal changes in Bcl-2: Bax ratio, oxidative stress, redox-active iron and apoptosis associated with aluminum-induced neurodegeneration: Increased susceptibility with aging. Neurotoxicology 1999, 20, 805–817. [Google Scholar]
- Tomljenovic, L. Aluminum and Alzheimer′s disease: After a century of controversy, is there a plausible link? J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 23, 567–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatta, P.; Lain, E.; Cagnolini, C. Effects of aluminum on activity of krebs cycle enzymes and glutamate dehydrogenase in rat brain homogenate. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 3049–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, R.; Kim, N.S.; Parsons, P.; Lee, B.K.; Jaar, B.; Fadrowski, J.; Agnew, J.; Matanoski, G.M.; Schwartz, B.S.; Steuerwald, A.; et al. Associations of multiple metals with kidney outcomes in lead workers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 69, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrosa, M.; Llanes, F.; Gayoso, M.J. Histopathological changes in gerbil liver and kidney after aluminum subchronic intoxication. Histol. Histopathol. 2011, 26, 883–892. [Google Scholar]
- Bhadauria, M. Combined treatment of HEDTA and propolis prevents aluminum induced toxicity in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2487–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, S.; Bor-Kucukatay, M.; Emmungil, G.; Atsak, P.; Turgut, G. The effects of low dose aluminum on hemorheological and hematological parameters in rats. Arch. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viezeliene, D.; Jansen, E.; Rodovicius, H.; Kasauskas, A.; Ivanov, L. Protective effect of selenium on aluminium-induced oxidative stress in mouse liver in vivo. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 31, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, W.A.; Niehoff, M.L.; Drago, D.; Zatta, P. Aluminum complexing enhances amyloid beta protein penetration of blood–brain barrier. Brain Res. 2006, 1116, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Bal, A.; Gill, K.D. Impairment of mitochondrial energy metabolism in different regions of rat brain following chronic exposure to aluminium. Brain Res. 2008, 1232, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschuler, E. Aluminum-containing antacids as a cause of idiopathic Parkinson′s disease. Med. Hypotheses 1999, 53, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, J.R. Cognitive deterioration and associated pathology induced by chronic low-level aluminum ingestion in a translational rat model provides an explanation of Alzheimer′s disease, tests for susceptibility and avenues for treatment. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 2012, 914–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokel, R.A. The toxicology of aluminum in the brain: A review. Neurotoxicology 2000, 21, 813–828. [Google Scholar]
- Bigford, G.E.; Del Rossi, G. Supplemental substances derived from foods as adjunctive therapeutic agents for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and disorders. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Cole, G.; Head, E.; Ingram, D. Nutrition, brain aging, and neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 12795–12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Hossain, S. Neuroprotective and ameliorative actions of polyunsaturated fatty acids against neuronal diseases: Beneficial effect of docosahexaenoic acid on cognitive decline in Alzheimer′s disease. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 116, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.L.; McDonald, D.A.; Borum, P.R. Acylcarnitines: Role in brain. Prog. Lipid Res. 2010, 49, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguarnera, M. Carnitine derivatives: Clinical usefulness. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 28, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.; Simmonds, M.S. Rosmarinic acid. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Fu, B.; Xu, B.; Mi, X.; Li, G.; Ma, C.; Xie, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. Rosmarinic Acid Alleviates the Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by Hydrogen Peroxide in Rat Aortic Rings via Activation of AMPK. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 7091904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Cho, H.S.; Park, E.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, S.J.; Chun, H.S. Rosmarinic acid protects human dopaminergic neuronal cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis. Toxicology 2008, 250, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.R.; Choi, J.S.; Han, Y.N.; Bae, S.J.; Chung, H.Y. Peroxynitrite scavenging activity of herb extracts. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Li, W.; Tsubouchi, R.; Haneda, M.; Murakami, K.; Takeuchi, F.; Nisimoto, Y.; Yoshino, M. Rosmarinic acid inhibits the formation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in RAW264.7 macrophages. Free Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Kan, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lv, C.; Jiang, W. Rosmarinic acid protects against experimental diabetes with cerebral ischemia: Relation to inflammation response. J. Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Chemistry and multibeneficial bioactivities of carvacrol (4-isopropyl-2-methylphenol), a component of essential oils produced by aromatic plants and spices. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7652–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soobrattee, M.A.; Neergheen, V.S.; Luximon-Ramma, A.; Aruoma, O.I.; Bahorun, T. Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: Mechanism and actions. Mutat. Res. 2005, 579, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baser, K.H. Biological and pharmacological activities of carvacrol and carvacrol bearing essential oils. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3106–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nostro, A.; Papalia, T. Antimicrobial activity of carvacrol: Current progress and future prospectives. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suntres, Z.E.; Coccimiglio, J.; Alipour, M. The bioactivity and toxicological actions of carvacrol. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya, S.; Prakash, T.; Madhu, K.D.; Goli, D. Multifaceted effects of aluminium in neurodegenerative diseases: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, H.; Irino, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Miyakawa, T. Behavioral effects of long-term oral administration of aluminum ammonium sulfate in male and female C57BL/6J mice. Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep. 2018, 38, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, C.S.; Vera, G.; Ocio, J.A.U.; Pecanha, F.M.; Vassallo, D.V.; Miguel, M.; Wiggers, G.A. Aluminum exposure for 60days at an equivalent human dietary level promotes peripheral dysfunction in rats. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2018, 181, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birben, E.; Sahiner, U.M.; Sackesen, C.; Erzurum, S.; Kalayci, O. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense. World Allergy Organ. J. 2012, 5, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Diez, C.; Miguel, V.; Mennerich, D.; Kietzmann, T.; Sanchez-Perez, P.; Cadenas, S.; Lamas, S. Antioxidant responses and cellular adjustments to oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, D.A.; Forman, H.J. Glutathione in defense and signaling: Lessons from a small thiol. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2002, 973, 488–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, G.M.; Draper, H.H. Metabolism of malonaldehyde in vivo and in vitro. Lipids 1982, 17, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotti, A.W. Mechanisms of lipid peroxidation. J. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1985, 1, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Rio, D.; Stewart, A.J.; Pellegrini, N. A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2005, 15, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Salam, O.M.E.; Hamdy, S.M.; Seadawy, S.A.M.; Galal, A.F.; Abouelfadl, D.M.; Atrees, S.S. Effect of piracetam, vincamine, vinpocetine, and donepezil on oxidative stress and neurodegeneration induced by aluminum chloride in rats. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 25, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amin, M.M.; Reza, H.M.; Saadi, H.M.; Mahmud, W.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Alam, M.M.; Kabir, N.; Saifullah, A.R.; Tropa, S.T.; Quddus, A.H. Astaxanthin ameliorates aluminum chloride-induced spatial memory impairment and neuronal oxidative stress in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 777, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Slikker, W., Jr.; Ali, S.F. Age-related changes in antioxidant enzymes, superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase and glutathione in different regions of mouse brain. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 1995, 13, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiao, Y.; Jin, T.; Sun, H.; Li, S.; Jin, C.; Hu, S.; Ji, J.; Xiang, L. Phenolic alkaloid oleracein E attenuates oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in AlCl3-treated mice. Life Sci. 2017, 191, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Vallinas, M.; Reglero, G.; Ramirez de Molina, A. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extract as a Potential Complementary Agent in Anticancer Therapy. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duthie, S.J.; Collins, A.R. The influence of cell growth, detoxifying enzymes and DNA repair on hydrogen peroxide-mediated DNA damage (measured using the comet assay) in human cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 22, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, G.; Sabzevari, O.; Wilson, J.X.; O′Brien, P.J. Prooxidant activity and cellular effects of the phenoxyl radicals of dietary flavonoids and other polyphenolics. Toxicology 2002, 177, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, L.R. Role of plant polyphenols in genomic stability. Mutat. Res. 2001, 475, 89–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Gill, K.D. Aluminium neurotoxicity: Neurobehavioral and oxidative aspects. Arch. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krewski, D.; Yokel, R.A.; Nieboer, E.; Borchelt, D.; Cohen, J.; Harry, J.; Kacew, S.; Lindsay, J.; Mahfouz, A.M.; Rondeau, V. Human health risk assessment for aluminium, aluminium oxide, and aluminium hydroxide. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2007, 10, 1–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Lei, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, X.; Yang, J.; He, Q. Metal Ion Imbalance-Related Oxidative Stress Is Involved in the Mechanisms of Liver Injury in a Rat Model of Chronic Aluminum Exposure. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 173, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisponi, G.; Fanni, D.; Gerosa, C.; Nemolato, S.; Nurchi, V.M.; Crespo-Alonso, M.; Lachowicz, J.I.; Faa, G. The meaning of aluminium exposure on human health and aluminium-related diseases. Biomol. Concepts 2013, 4, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyikoglu, F.; Turkez, H.; Bakir, T.O.; Cicek, M. The genotoxic, hepatotoxic, nephrotoxic, haematotoxic and histopathological effects in rats after aluminium chronic intoxication. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2013, 29, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanein, P.; Sharifi, M. Effects of rosmarinic acid on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in male Wistar rats. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.; Hwang, B.R.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, E.J. Perilla frutescens var. japonica and rosmarinic acid improve amyloid-beta25-35 induced impairment of cognition and memory function. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2016, 10, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Zu, Y.; Lu, Q. Effects of rosmarinic acid on liver and kidney antioxidant enzymes, lipid peroxidation and tissue ultrastructure in aging mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbach, R.; Loliger, J.; Scott, B.C.; Murcia, A.; Butler, J.; Halliwell, B.; Aruoma, O.I. Antioxidant actions of thymol, carvacrol, 6-gingerol, zingerone and hydroxytyrosol. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1994, 32, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teissedre, P.L.; Waterhouse, A.L. Inhibition of oxidation of human low-density lipoproteins by phenolic substances in different essential oils varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3801–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, S. Carvacrol protects against acute myocardial infarction of rats via anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic pathways. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ba, L.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Pan, H.; Mingyao, E.; Shi, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Qi, H.; et al. Role of carvacrol in cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through activation of MAPK/ERK and Akt/eNOS signaling pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 796, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Goel, R.K. Neuroprotective effect of Allium cepa L. in aluminium chloride induced neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 2015, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangra, A.; Kasbe, P.; Pandey, S.N.; Dwivedi, S.; Gurjar, S.S.; Kwatra, M.; Mishra, M.; Venu, A.K.; Sulakhiya, K.; Gogoi, R.; et al. Hesperidin and Silibinin Ameliorate Aluminum-Induced Neurotoxicity: Modulation of Antioxidants and Inflammatory Cytokines Level in Mice Hippocampus. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2015, 168, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacanli, M.; Aydin, S.; Taner, G.; Goktas, H.G.; Sahin, T.; Basaran, A.A.; Basaran, N. Does rosmarinic acid treatment have protective role against sepsis-induced oxidative damage in Wistar Albino rats? Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlak, J.; Lindsay, R.H. Estimation of total, protein-bound, and nonprotein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellman′s reagent. Anal. Biochem. 1968, 25, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moron, M.S.; Depierre, J.W.; Mannervik, B. Levels of glutathione, glutathione reductase and glutathione S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1979, 582, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliutina, C.N.; Seliutin, A.; Pal, A.I. Modification of estimation the concentrations of serum TBA-active product. Klin. Lab. Diagn. 2000, 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mihara, M.; Uchiyama, M. Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Vermelho, A.B.; Couri, S. Methods to Determine Enzymatic Activity; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, U.A.E., 2013; p. 334. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Not available. |



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baranauskaite, J.; Sadauskiene, I.; Liekis, A.; Kasauskas, A.; Lazauskas, R.; Zlabiene, U.; Masteikova, R.; Kopustinskiene, D.M.; Bernatoniene, J. Natural Compounds Rosmarinic Acid and Carvacrol Counteract Aluminium-Induced Oxidative Stress. Molecules 2020, 25, 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081807
Baranauskaite J, Sadauskiene I, Liekis A, Kasauskas A, Lazauskas R, Zlabiene U, Masteikova R, Kopustinskiene DM, Bernatoniene J. Natural Compounds Rosmarinic Acid and Carvacrol Counteract Aluminium-Induced Oxidative Stress. Molecules. 2020; 25(8):1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081807
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaranauskaite, Juste, Ilona Sadauskiene, Arunas Liekis, Arturas Kasauskas, Robertas Lazauskas, Ugne Zlabiene, Ruta Masteikova, Dalia M. Kopustinskiene, and Jurga Bernatoniene. 2020. "Natural Compounds Rosmarinic Acid and Carvacrol Counteract Aluminium-Induced Oxidative Stress" Molecules 25, no. 8: 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081807
APA StyleBaranauskaite, J., Sadauskiene, I., Liekis, A., Kasauskas, A., Lazauskas, R., Zlabiene, U., Masteikova, R., Kopustinskiene, D. M., & Bernatoniene, J. (2020). Natural Compounds Rosmarinic Acid and Carvacrol Counteract Aluminium-Induced Oxidative Stress. Molecules, 25(8), 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081807







