Protein-Protein Interactions Prediction Based on Graph Energy and Protein Sequence Information
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation Metrics
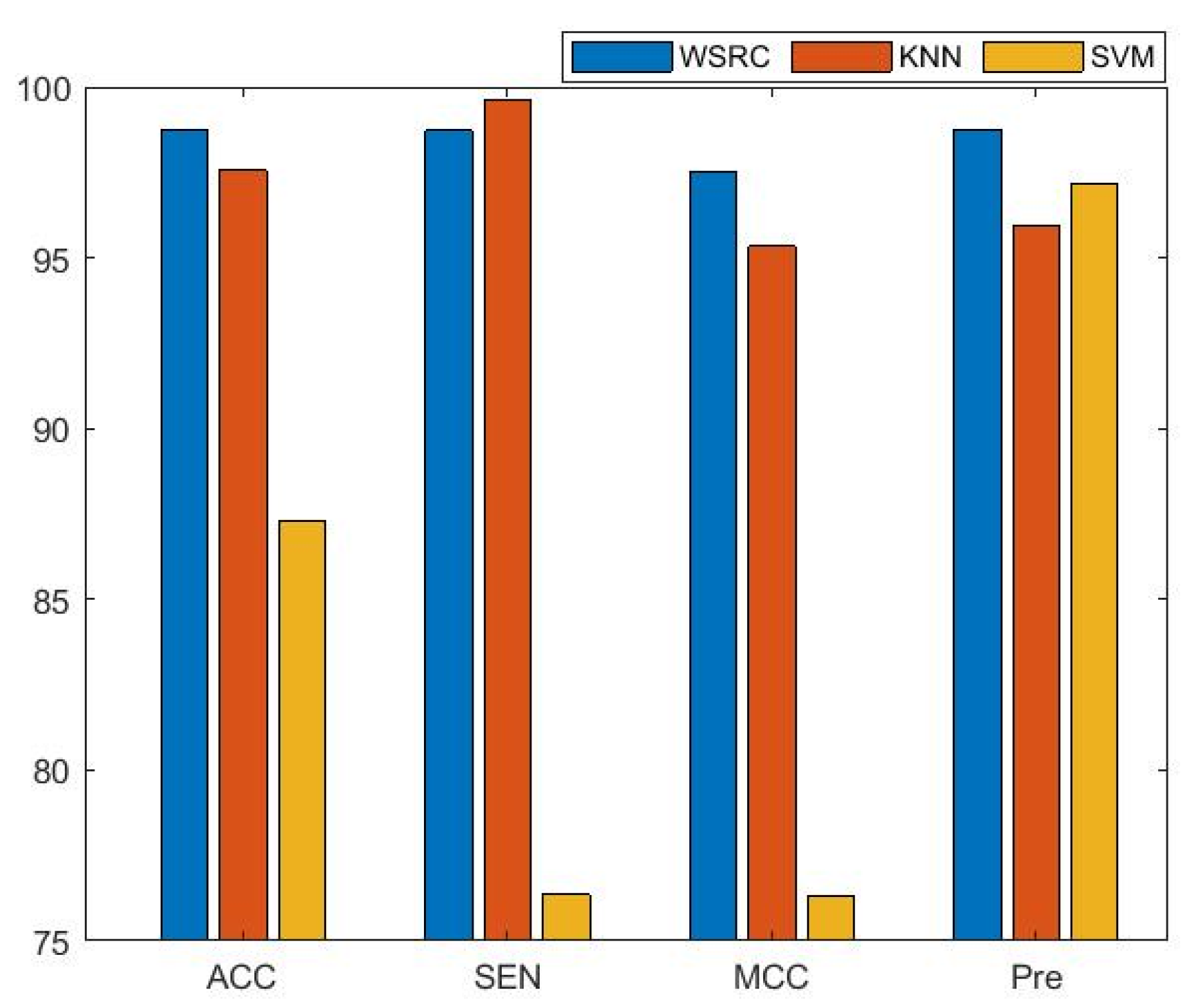
2.2. The Performance Comparisons of Different Classifiers
2.3. Prediction Performances of the Proposed Method
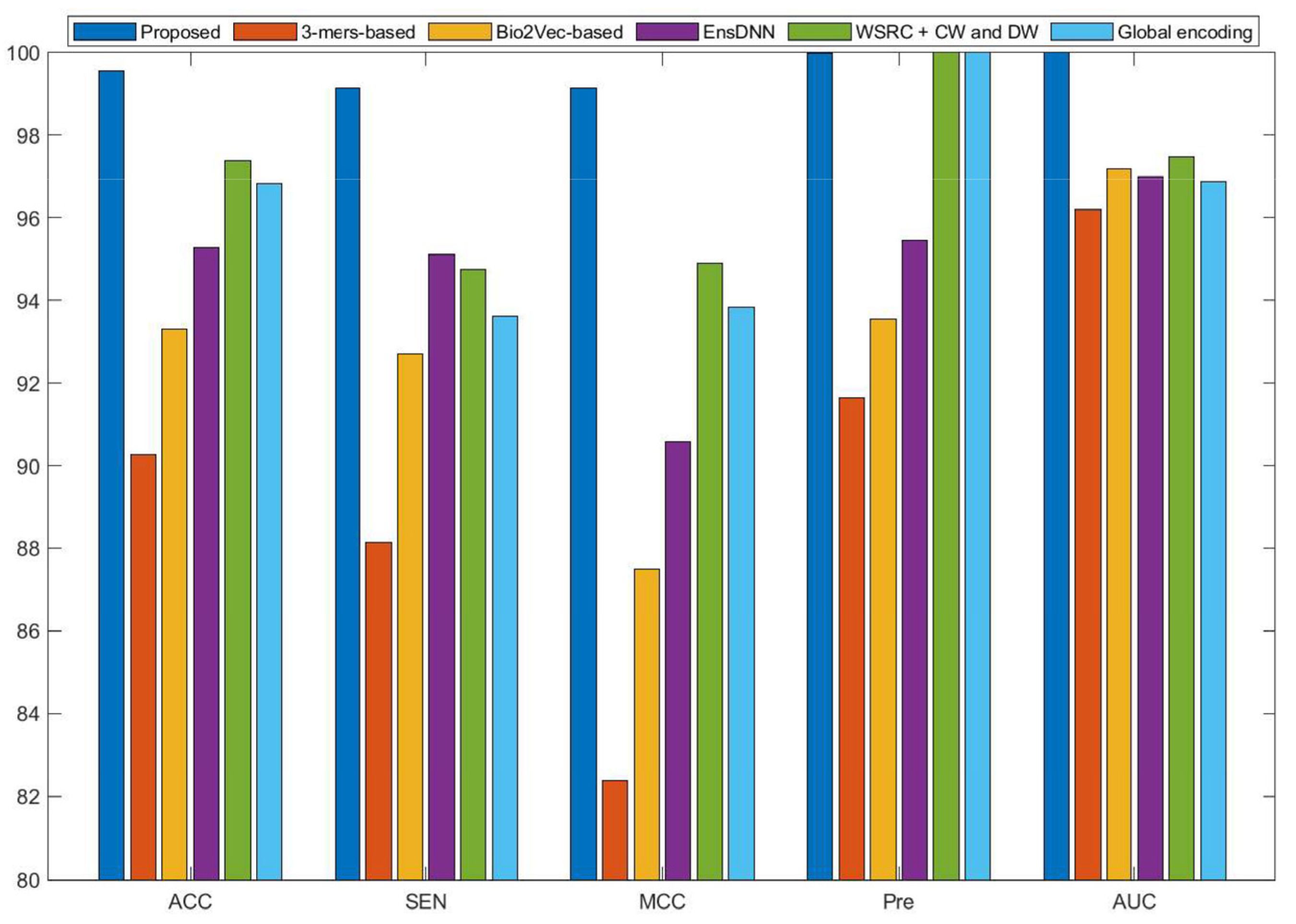
2.4. Comparison with Other Methods
2.5. Performance on PPI Networks
2.6. Performance on Independent Data Sets
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Datasets
3.2. Feature Extraction
3.2.1. Physicochemical Graph Energy
3.2.2. Contact Graph Energy
3.2.3. N-peptide Composition Representation
3.3. Principal Component Analysis
3.4. Weighted Sparse Representation Based Classification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, M.; Ju, C.J.T.; Zhou, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, T.; Chang, K.W.; Zaniolo, C.; Wang, W. Multifaceted protein-protein interaction prediction based on Siamese residual RCNN. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, i305–i314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, J.Y.; Meng, F.R.; You, Z.H.; Chen, X.; Yan, G.Y.; Hu, J.P. Improving protein–protein interactions prediction accuracy using protein evolutionary information and relevance vector machine model. Protein Sci. 2016, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le, D.H.; Kwon, Y.K. Neighbor-favoring weight reinforcement to improve random walk-based disease gene prioritization. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2013, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rual, J.F.; Venkatesan, K.; Hao, T.; Hirozane-Kishikawa, T.; Dricot, A.; Li, N.; Berriz, G.F.; Gibbons, F.D.; Dreze, M.; Ayivi-Guedehoussou, N.; et al. Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Nature 2005, 437, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Johnson, K.S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene 1988, 67, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Snyder, M. Protein chip technology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Chiba, T.; Ozawa, R.; Yoshida, M.; Hattori, M.; Sakaki, Y. A comprehensive two-hybrid analysis to explore the yeast protein interactome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4569–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigaut, G.; Shevchenko, A.; Rutz, B.; Wilm, M.; Mann, M.; Seraphin, B. A generic protein purification method for protein complex characterization and proteome exploration. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 1030–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemifar, S.; Neyshabur, B.; Khan, A.A.; Xu, J. Predicting protein-protein interactions through sequence-based deep learning. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i802–i810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, Z.H.; Chan, K.C.C.; Hu, P. Predicting protein-protein interactions from primary protein sequences using a novel multi-scale local feature representation scheme and the random forest. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Pei, Z.; Qin, S.; Zhao, X. Prediction of protein-protein interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae based on protein secondary structure. Int. Conf. Biomed. Eng. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.B.; Morcos, F.; Kanaan, S.P.; Wuchty, S.; Chen, D.Z.; Izaguirre, J.A. Predicting protein-protein interactions from protein domains using a set cover approach. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinforma. 2007, 4, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, R.; Yu, H.; Greenbaum, D.; Kluger, Y.; Krogan, N.J.; Chung, S.; Emili, A.; Snyder, M.; Greenblatt, J.F.; Gerstein, M. A Bayesian Networks Approach for Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions from Genomic Data. Science 2003, 302, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pazos, F.; Valencia, A. Similarity of phylogenetic trees as indicator of protein-protein interaction. Protein Eng. 2001, 14, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; You, Z.H.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, J. PCVMZM: Using the probabilistic classification vector machines model combined with a Zernike moments descriptor to predict protein-protein interactions from protein sequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- You, Z.H.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, C.H.; Yu, H.J.; Deng, S.P.; Ji, Z. Prediction of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences using a novel multi-scale continuous and discontinuous feature set. BMC Bioinf. 2014, 15, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; You, Z.H.; Xia, S.X.; Chen, X.; Yan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, F. An improved efficient rotation forest algorithm to predict the interactions among proteins. Soft Comput. 2018, 22, 3373–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Z.; Yu, L.; Wen, Z.; Li, M. Using support vector machine combined with auto covariance to predict protein-protein interactions from protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3025–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, J.Y.; You, Z.H.; Meng, F.R.; Xu, S.J.; Wang, Y. RVMAB: Using the relevance vector machine model combined with average blocks to predict the interactions of proteins from protein sequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.A.; You, Z.H.; Gao, X.; Wong, L.; Wang, L. Using Weighted Sparse Representation Model Combined with Discrete Cosine Transformation to Predict Protein-Protein Interactions from Protein Sequence. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Göktepe, Y.E.; Kodaz, H. Prediction of Protein-Protein Interactions Using an Effective Sequence Based Combined Method. Neurocomputing 2018, 303, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, G.; Xia, D.; Wang, J. Protein–protein interactions prediction based on ensemble deep neural networks. Neurocomputing 2019, 324, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutman, I. The energy of a graph. Ber. Math. Statist. Sekt. Forsch-Ungszentram Graz. 1978, 103, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gutman, I.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, J.B. Graph energy. In Analysis of Complex Networks. From Biology to Linguistics; Dehmer, M., Emmert-Streib, F., Eds.; Wiley–VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2009; pp. 145–174. [Google Scholar]
- Gutman, I.; Shao, J.Y. The energy change of weighted graphs. Linear Algebra Appl. 2011, 435, 2425–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutman, I.; Wagner, S. The matching energy of a graph. Discret. Appl. Math. 2012, 160, 2177–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gutman, I.; Shi, Y.; Dehmer, M. Protein Sequence Comparison Based on Physicochemical Properties and the Position-Feature Energy Matrix. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, D.D.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y. A novel method of 2D graphical representation for proteins and its application. Match 2016, 75, 431–446. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Q.; Yu, B. LightGBM-PPI: Predicting protein-protein interactions through LightGBM with multi-information fusion. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2019, 191, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Tang, J.; Guo, F. Identification of protein-protein interactions via a novel matrix-based sequence representation model with amino acid contact information. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; You, Z.-H.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Jiang, T.-H.; Zhou, X. A High Efficient Biological Language Model for Predicting Protein–Protein Interactions. Cells 2019, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.A.; You, Z.H.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, P.; Li, S.; Luo, X. Construction of reliable protein–protein interaction networks using weighted sparse representation based classifier with pseudo substitution matrix representation features. Neurocomputing 2016, 218, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.A.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, X. Prediction of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences based on continuous and discrete wavelet transform features. Molecules 2018, 23, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.A.; You, Z.H.; Chen, X.; Chan, K.; Luo, X. Sequence-based prediction of proteinprotein interactions using weighted sparse representation model combined with global encoding. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Zhu, W.; Yu, K.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H. Predicting protein-protein interactions based only on sequences information. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4337–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, C.; Yu, H.; Ding, Y.; Guo, F.; Gong, X.J. Multi-scale encoding of amino acid sequences for predicting protein interactions using gradient boosting decision tree. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.Q.; Sun, S.W.; Hu, C.L.; Yao, Y.; Yan, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.P. DeepPPI: Boosting Prediction of Protein-Protein Interactions with Deep Neural Networks. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.; Roe, D.; Faulon, J.L. Predicting protein-protein interactions using signature products. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzl, U.; Worm, U.; Lalowski, M.; Haenig, C.; Brembeck, F.H.; Goehler, H.; Stroedicke, M.; Zenkner, M.; Schoenherr, A.; Koeppen, S.; et al. A human protein-protein interaction network: A resource for annotating the proteome. Cell 2005, 122, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, R.J. Transcriptional regulation by MAP kinases. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1995, 42, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.H.; Dai, Q.; Li, C.; He, P.A.; Nan, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z. Analysis of similarity/dissimilarity of protein sequences. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 2008, 73, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randić, M. 2-D graphical representation of proteins based on physico-chemical properties of amino acids. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2007, 444, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, S.C.; Wang, L. P-binder: A system for the protein-protein binding sites identification. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2012, 7292, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.K.; Gillil, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Q.Y.; You, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Prediction of protein–protein interactions with clustered amino acids and weighted sparse representation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 10855–10869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khosravian, M.; Kazemi Faramarzi, F.; Mohammad Beigi, M.; Behbahani, M.; Mohabatkar, H. Predicting Antibacterial Peptides by the Concept of Chou’s Pseudo-amino Acid Composition and Machine Learning Methods. Protein Pept. Lett. 2013, 20, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.H.; Lei, Y.K.; Zhu, L.; Xia, J.; Wang, B. Prediction of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences with ensemble extreme learning machines and principal component analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.Y.; Min, H.; Gui, J.; Zhu, L.; Lei, Y.K. Face recognition via Weighted Sparse Representation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2013, 24, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors. |






| Testing Set | ACC (%) | SEN (%) | MCC (%) | Pre (%) | AUC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99.33 | 98.76 | 98.66 | 99.87 | 99.99 |
| 2 | 99.63 | 99.34 | 99.26 | 99.87 | 100 |
| 3 | 99.57 | 99.22 | 99.14 | 99.87 | 100 |
| 4 | 99.39 | 99.24 | 98.77 | 99.49 | 99.98 |
| 5 | 99.51 | 99.49 | 99.02 | 99.49 | 99.99 |
| Average | 99.49 | 99.21 | 98.97 | 99.72 | 99.99 |
| Testing Set | ACC (%) | SEN (%) | MCC (%) | Pre (%) | AUC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 95.55 | 98.21 | 91.24 | 92.88 | 99.27 |
| 2 | 97.94 | 98.26 | 95.89 | 97.59 | 99.34 |
| 3 | 98.11 | 99.65 | 96.27 | 96.64 | 98.94 |
| 4 | 97.94 | 97.69 | 95.88 | 98.34 | 99.41 |
| 5 | 96.23 | 97.32 | 92.46 | 95.41 | 99.01 |
| Average | 97.15 | 98.23 | 94.35 | 96.17 | 99.19 |
| Testing Set | ACC (%) | SEN (%) | MCC (%) | Pre (%) | AUC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 99.60 | 99.18 | 99.20 | 100 | 100 |
| 2 | 99.46 | 98.95 | 98.93 | 100 | 100 |
| 3 | 99.55 | 99.20 | 99.11 | 99.91 | 100 |
| 4 | 99.51 | 99.00 | 99.02 | 100 | 100 |
| 5 | 99.69 | 99.38 | 99.38 | 100 | 100 |
| Average | 99.56 | 99.14 | 99.13 | 99.98 | 100 |
| Wnt-Related Network | Proportion | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Proposed method | 92/96 | 95.83 |
| Ding’s work [30] | 89/96 | 92.71 |
| Shen’s work [35] | 73/96 | 76.04 |
| Zhou’s work [36] | 87/96 | 90.63 |
| Chen’s work [29] | 89/96 | 92.71 |
| Data Set | Testing Pairs | Proposed Method | Huang’s Work [34] | Du’s Work [37] | Ding’s Work [30] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. pylori | 1420 | 93.80 | 85.77 | 93.66 | 92.03 |
| H. sapien | 1412 | 99.93 | 88.81 | 93.77 | 94.58 |
| C. elegans | 4013 | 86.24 | 72.79 | 94.84 | 90.28 |
| M. musculus | 313 | 94.57 | 83.39 | 91.37 | 92.25 |
| D. mela | 21975 | 99.87 | 89.35 | N/A | N/A |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, D.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Gao, R. Protein-Protein Interactions Prediction Based on Graph Energy and Protein Sequence Information. Molecules 2020, 25, 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081841
Xu D, Xu H, Zhang Y, Chen W, Gao R. Protein-Protein Interactions Prediction Based on Graph Energy and Protein Sequence Information. Molecules. 2020; 25(8):1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081841
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Da, Hanxiao Xu, Yusen Zhang, Wei Chen, and Rui Gao. 2020. "Protein-Protein Interactions Prediction Based on Graph Energy and Protein Sequence Information" Molecules 25, no. 8: 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081841
APA StyleXu, D., Xu, H., Zhang, Y., Chen, W., & Gao, R. (2020). Protein-Protein Interactions Prediction Based on Graph Energy and Protein Sequence Information. Molecules, 25(8), 1841. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081841





