Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Reversal of Thymol and Carvacrol against Staphylococcus aureus and Their Toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
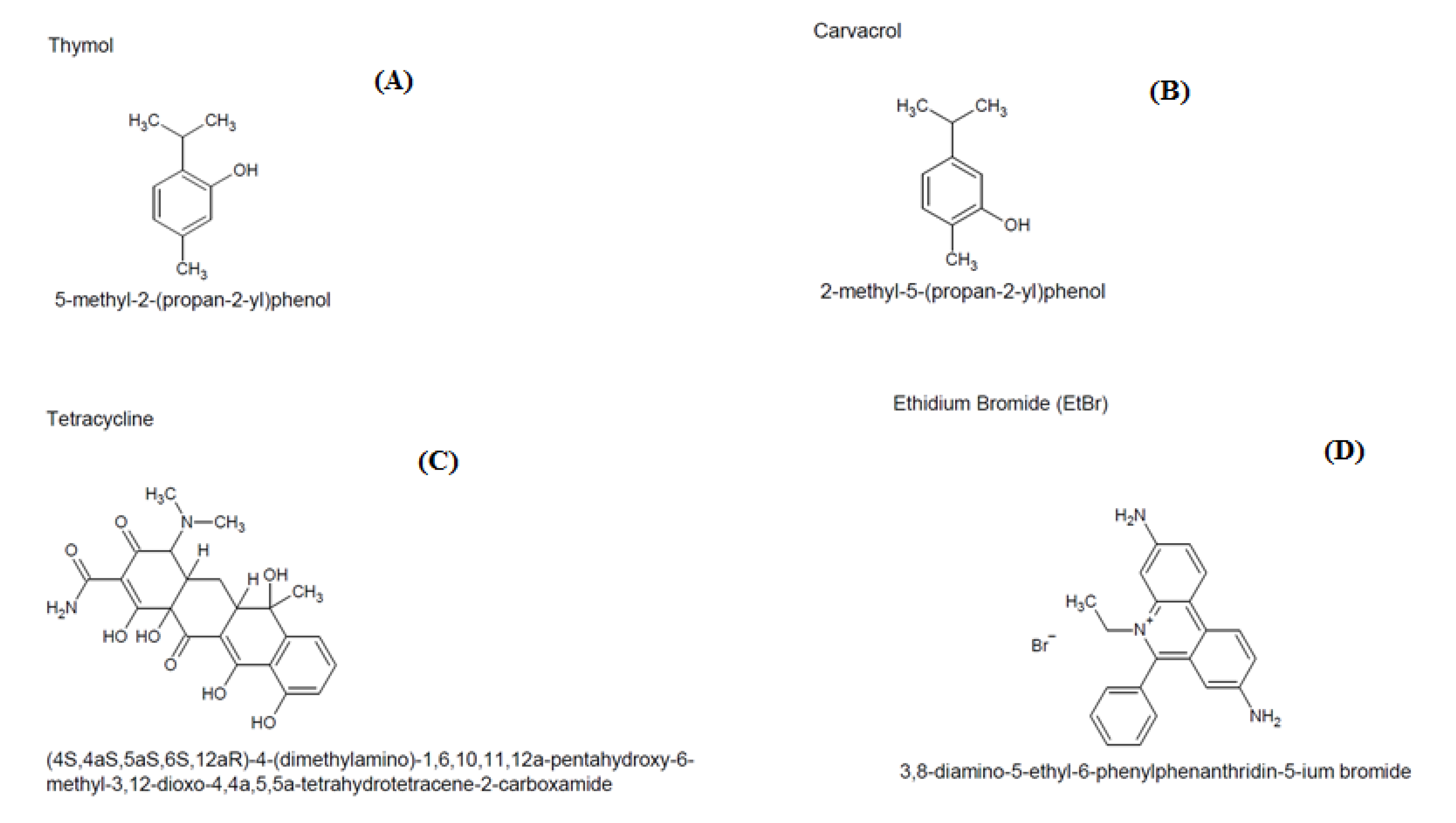
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
2.2. Modulatory Effect over Antibiotic Activity and Ethidium Bromide
2.3. Drosophila Melanogaster Toxicity Assay and Negative Geotaxis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strain and Culture Media
4.2. Substances
4.3. Determining the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
4.4. Evaluation of Efflux Pump Inhibition
4.5. Drosophila melanogaster Toxicity Assays
4.6. Negative Geotaxis Assays
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Porse, A.; Schou, T.S.; Munck, C.; Ellabaan, M.M.H.; Sommer, A.O. Biochemical mechanisms determine the functional compatibility of heterologous genes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J. Antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Current status and future prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Deng, Z.; Yan, A. Bacterial multidrug efflux pumps: Mechanisms, physiology and pharmacological exploitations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 453, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yilmaz, E.Ş.; Aslantaş, Ö. Antimicrobial resistance and underlying mechanisms in Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 10, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S. Multidrug efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus and their clinical implications. J. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.K.; Mohanty, P. Bacterial efflux pumps involved in multidrug resistance and their inhibitors: Rejuvinating the antimicrobial chemotherapy. Recent Pat. Anti-Infect. Drug Discovery 2012, 7, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.Y.; Jamshidi, S.; Sutton, M.J.; Rahman, K.M. Current advances in developing inhibitors of bacterial multidrug efflux pumps. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 1062–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, A.C.; Mcbain, A.J.; Simoes, M. Plants as sources of new antimicrobials and resistance-modifying agents. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, J.M.; Amaral, L. Mechanisms of drug efflux and strategies to combat them: Challenging the efflux pump of Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (Baa)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzym. 2009, 1794, 826–833. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalcze, M.; Jakubowska, M. Multivariate approach in voltammetric identification and simultaneous determination of eugenol, carvacrol, and thymol on boron-doped diamond electrode. Mon. Chem. Chem. Mon. 2019, 150, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braga, P.C.; Alfieri, M.; Culici, M.; Dal Sasso, M. Inhibitory activity of thymol against the formation and viability of Candida albicans hyphae. Mycoses 2007, 50, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadil, M.; Fikri-Benbrahim, K.; Rachiq, S.; Ihssane, B.; Lebrazi, S.; Chraibi, M.; Farah, A. Combined treatment of Thymus vulgaris L., Rosmarinus officinalis L. and Myrtus communis L. essential oils against Salmonella typhimurium: Optimization of antibacterial activity by mixture design methodology. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 126, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenzi, M.; Stammati, A.; Vincenzi, A.; Silano, M. Constituents of aromatic plants: Carvacrol. Fitoterapia 2004, 75, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limaverde, P.W.; Campina, F.F.; Cunha, F.A.; CRISPIM, F.D.; Figueredo, F.G.; Lima, L.F.; Tintino, S.R. Inhibition of the TetK efflux-pump by the essential oil of Chenopodium ambrosioides L. and α-terpinene against Staphylococcus aureus IS-58. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, M.D.; Montgomery, S.L.; Prince, L.; Vorojeikina, D. Developmental toxicity assays using the Drosophila model. Curr. Protoc. Toxicol. 2014, 59, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miladi, H.; Zmantar, T.; Chaabouni, Y.; Fedhila, K.; Bakhrouf, A.; Mahdouani, K.; Chaieb, K. Antibacterial and efflux pump inhibitors of thymol and carvacrol against food-borne pathogens. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 99, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.J.W.; Skandamis, P.N.; Coote, P.J.; Nychas, G.J. A study of the minimum inhibitory concentration and mode of action of oregano essential oil, thymol and carvacrol. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 1, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trombetta, D.; Castelli, F.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Venuti, V.; Cristani, M.; Daniele, C.; Bisignano, G. Mechanisms of antibacterial action of three monoterpenes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2474–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obaidat, R.M.; Bader, A.; Al-Rajab, W.; Sheikha, G.A.; Obaidat, A.A. Preparation of mucoadhesive oral patches containing tetracycline hydrochloride and carvacrol for treatment of local mouth bacterial infections and candidiasis. Sci. Pharm. 2011, 79, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorman, H.J.D.; Deans, S.G. Antimicrobial agents from plants: Antibacterial activity of plant volatile oils. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 88, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.; Wright, G.D. Bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Trends Microbiol. 1997, 5, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirino, I.C.S.; Menezes-Silva, S.M.P.; Silva, H.T.D.; Souza, E.L.; Siqueira-Júnior, J.P. The essential oil from Origanum vulgare L. and its individual constituents carvacrol and thymol enhance the effect of tetracycline against Staphylococcus aureus. Chemotherapy 2014, 60, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Novick, R.P. Complete nucleotide sequence of pT181, a tetracycline-resistance plasmid from Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid 1983, 10, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.M.S.; Oliveira, A.B.M.; Leal, A.L.A.B.; Alcântara, F.A.O.; Portela, A.L.; Lima Neto, J.D.S.; Barreto, H.M. Antimicrobial activity and inhibition of the NorA efflux pump of Staphylococcus aureus by extract and isolated compounds from Arrabidaea brachypoda. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 40, 103935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafis, A.; Kasrati, A.; Jamali, C.A.; Custódio, L.; Vitalini, S.; Iriti, M.; Hassani, L. A Comparative Study of the in Vitro Antimicrobial and Synergistic Effect of Essential Oils from Laurus nobilis L. and Prunus armeniaca L. from Morocco with Antimicrobial Drugs: New Approach for Health Promoting Products. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Niu, H.; Zhang, W.; Mu, H.; Sun, C.; Duan, J. Synergy among thymol, eugenol, berberine, cinnamaldehyde and streptomycin against planktonic and biofilm-associated food-borne pathogens. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 60, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaatz, G.W.; Moudgal, V.V.; Seo, S.M.; Kristiansen, J.E. Fenotiazinas e tioxantenos inibem a atividade da bomba de efluxo de múltiplas drogas no Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. E Quim. 2003, 47, 719–726. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y. Fumigant toxicity of monoterpenes against fruitfly, Drosophila melanogaster. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 81, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodenizer, D.; Martin, I.; Bhandari, P.; Pletcher, S.D.; Grotewiel, M. Genetic and environmental factors impact age-related impairment of negative geotaxis in Drosophila by altering age-dependent climbing speed. Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karpouhtsis, I.; Pardali, E.; Feggou, E.; KokkinI, S.; Scouras, Z.G.; Mavragani-Tsipidou, P. Insecticidal and genotoxic activities of oregano essential oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, H.E.D.M.; Abdelgaleil, A.S. Insecticidal and developmental inhibitory properties of monoterpenes on Culex pipiens L. (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2011, 14, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.E. Monoterpenes from thyme (Thymus vulgaris) as potential mosquito repellents. J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 2005, 21, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, X.; Abdala-Roberts, L.; Nell, C.S.; Vázquez-González, C.; Pratt, J.D.; Keefover-Ring, K.; Mooney, K.A. Sexual and genotypic variation in terpene quantitative and qualitative profiles in the dioecious shrub Baccharis salicifolia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisi, A.; Lionetto, M.G.; Schettino, T. Biomarker response in the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris exposed to chemical pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4456–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Fu, W.; Yang, X.; Mu, Y.; Gu, W.; Zhang, M. Effects of cadmium on fecundity and defence ability of Drosophila melanogaster. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, A.; Sorbo, S.; Lentini, M.; Conte, B.; Esposito, S. Water pollution causes ultrastructural and functional damages in Pellia neesiana (Gottsche) Limpr. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2017, 43, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadpour, M.M.; Juban, M.M.; Lo, W.C.J.; Bishop, S.M.; Alberty, J.B.; Cowell, S.M.; Mclaughlin, M.L. De novo antimicrobial peptides with low mammalian cell toxicity. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 3107–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Twentythird Informational Supplement; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, H.D.M.; Costa, J.G.; Lima, E.O.; Falcão-Silva, V.S.; Siqueira-Júnior, J.P. Enhancement of the antibiotic activity against a multiresistant Escherichia coli by Mentha arvensis L. and chlorpromazine. Chemotherapy 2008, 54, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, F.A.B.; Wallau, G.L.; Pinho, A.I.; Nunes, M.E.M.; Leite, N.F.; Tintino, R.S.; Franco, J.L. Eugenia uniflora leaves essential oil induces toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster: Involvement of oxidative stress mechanisms. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 4, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulom, H.; Birman, S. Chronic exposure to rotenone models sporadic Parkinson’s disease in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 10993–10998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Sample Availability: Samples of the all compounds assayed are available from the authors. |




| Strain | MIC (µg/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus IS-58 | Thymol | Carvacrol | Tetracycline |
| 72 | 256 | 128 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sousa Silveira, Z.d.; Macêdo, N.S.; Sampaio dos Santos, J.F.; Sampaio de Freitas, T.; Rodrigues dos Santos Barbosa, C.; Júnior, D.L.d.S.; Muniz, D.F.; Castro de Oliveira, L.C.; Júnior, J.P.S.; Cunha, F.A.B.d.; et al. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Reversal of Thymol and Carvacrol against Staphylococcus aureus and Their Toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Molecules 2020, 25, 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092103
Sousa Silveira Zd, Macêdo NS, Sampaio dos Santos JF, Sampaio de Freitas T, Rodrigues dos Santos Barbosa C, Júnior DLdS, Muniz DF, Castro de Oliveira LC, Júnior JPS, Cunha FABd, et al. Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Reversal of Thymol and Carvacrol against Staphylococcus aureus and Their Toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Molecules. 2020; 25(9):2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092103
Chicago/Turabian StyleSousa Silveira, Zildene de, Nair Silva Macêdo, Joycy Francely Sampaio dos Santos, Thiago Sampaio de Freitas, Cristina Rodrigues dos Santos Barbosa, Dárcio Luiz de Sousa Júnior, Débora Feitosa Muniz, Lígia Claudia Castro de Oliveira, José Pinto Siqueira Júnior, Francisco Assis Bezerra da Cunha, and et al. 2020. "Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Reversal of Thymol and Carvacrol against Staphylococcus aureus and Their Toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster" Molecules 25, no. 9: 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092103
APA StyleSousa Silveira, Z. d., Macêdo, N. S., Sampaio dos Santos, J. F., Sampaio de Freitas, T., Rodrigues dos Santos Barbosa, C., Júnior, D. L. d. S., Muniz, D. F., Castro de Oliveira, L. C., Júnior, J. P. S., Cunha, F. A. B. d., Melo Coutinho, H. D., Balbino, V. Q., & Martins, N. (2020). Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity and Efflux Pump Reversal of Thymol and Carvacrol against Staphylococcus aureus and Their Toxicity in Drosophila melanogaster. Molecules, 25(9), 2103. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092103







