Doxorubicin Loaded Poloxamer Thermosensitive Hydrogels: Chemical, Pharmacological and Biological Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
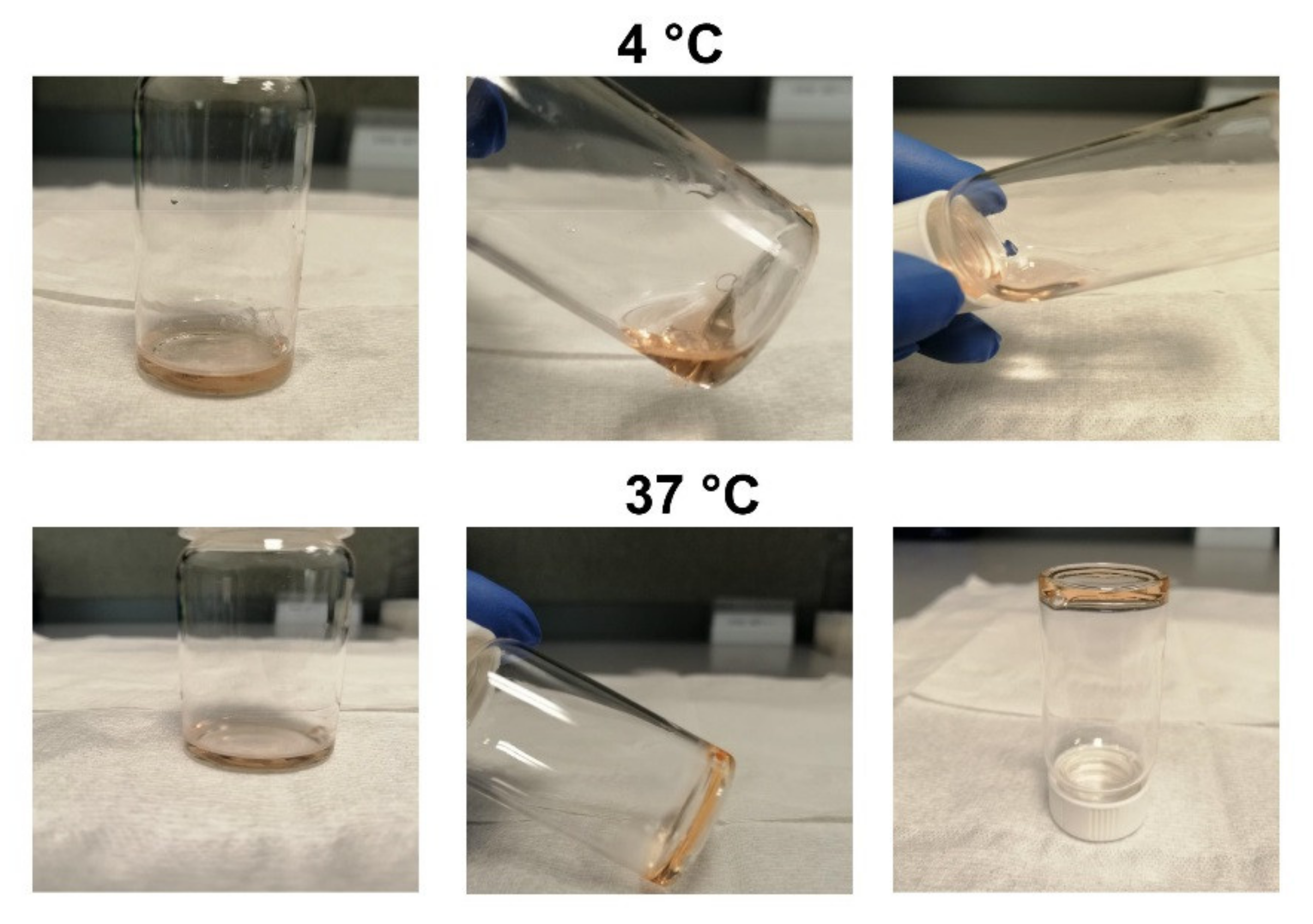
2.1. P407 Hydrogel Time-to-Gelation Assay
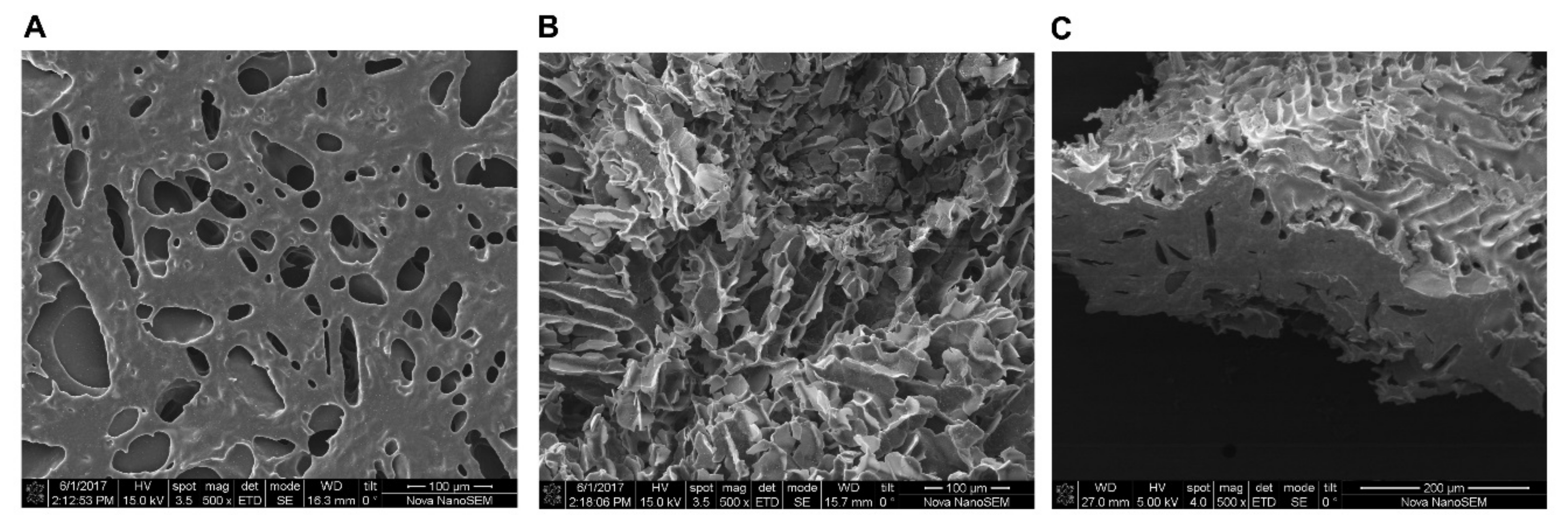
2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Reveals Porous and Tunnel like Morphology of Lyophilized P407 Hydrogel
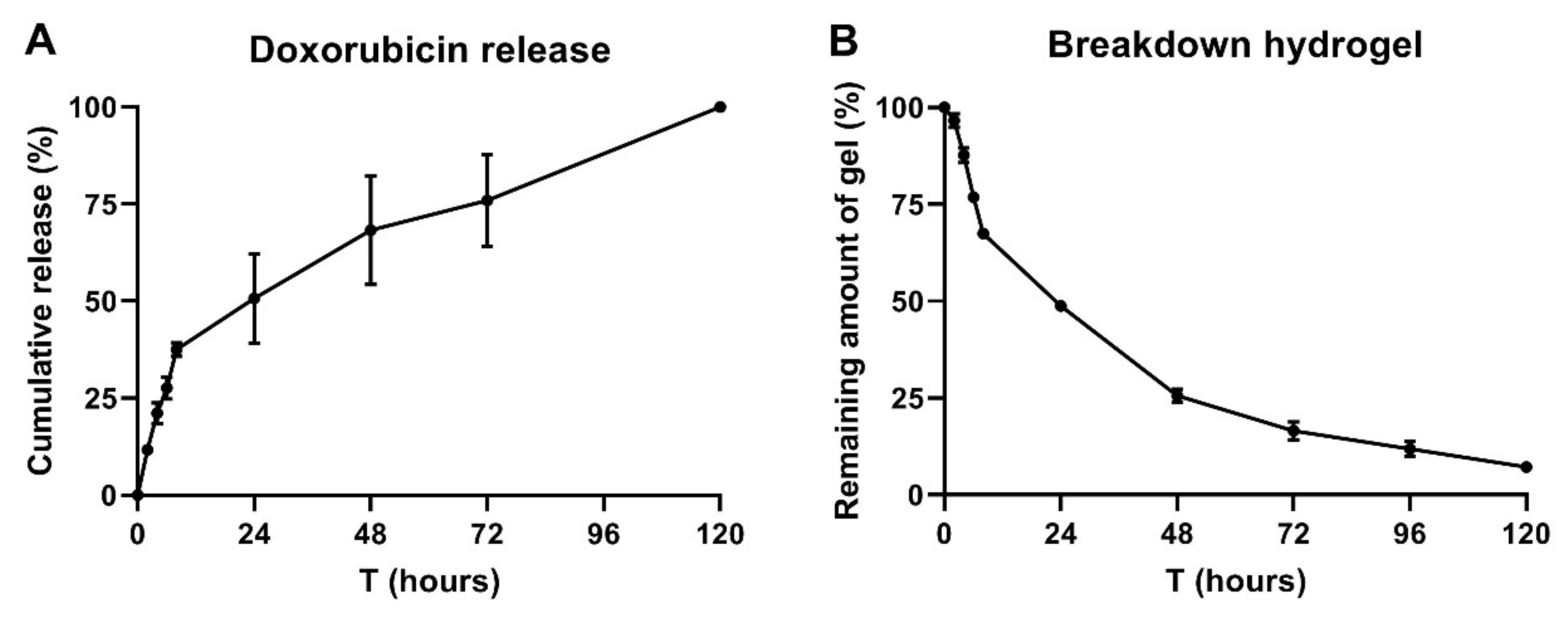
2.3. 25% P407 Hydrogel Facilitates Doxorubicin Release Over 120 h
2.4. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Measurements on Different Concentrations P407
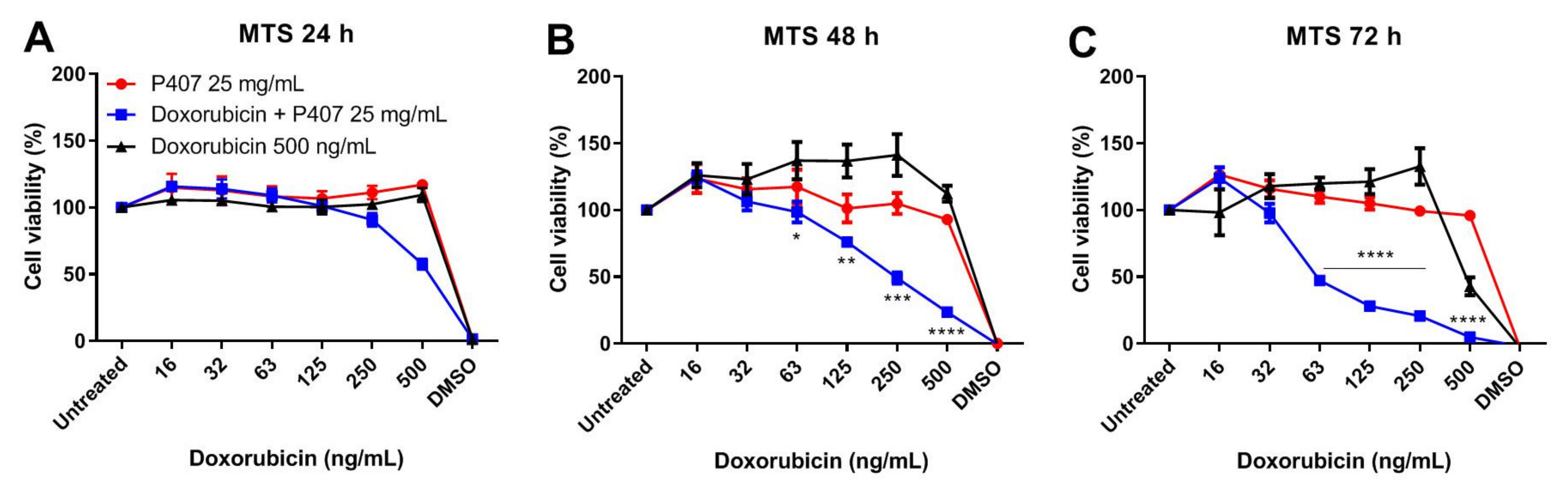
2.5. P407 Synergize with Doxorubicin in Killing Tumor Cells
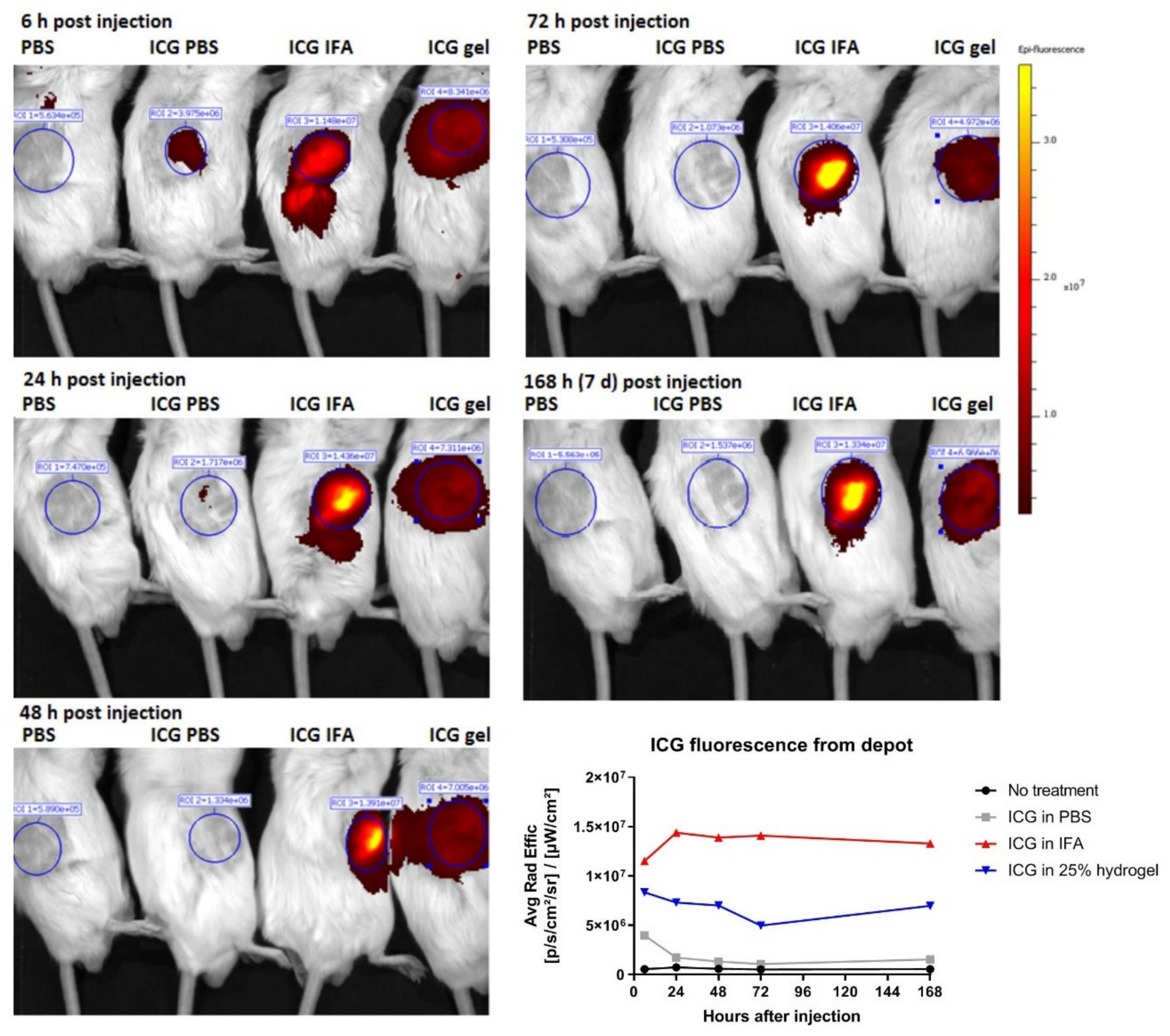
2.6. Hydrogel Breakdown and ICG Release Visualized by Non-Invasive Molecular Imaging
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. P407 Hydrogel Preparation
4.2. Time-to-Gelation Assay
4.3. Morphology of P407 Hydrogel by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4. P407 Hydrogel Degradation and Doxorubicin Release
4.5. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Measurements
4.6. Cytotoxicity (MTS) Assays
4.7. In Vivo P407 Hydrogel Fluorescence Follow-Up
4.8. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
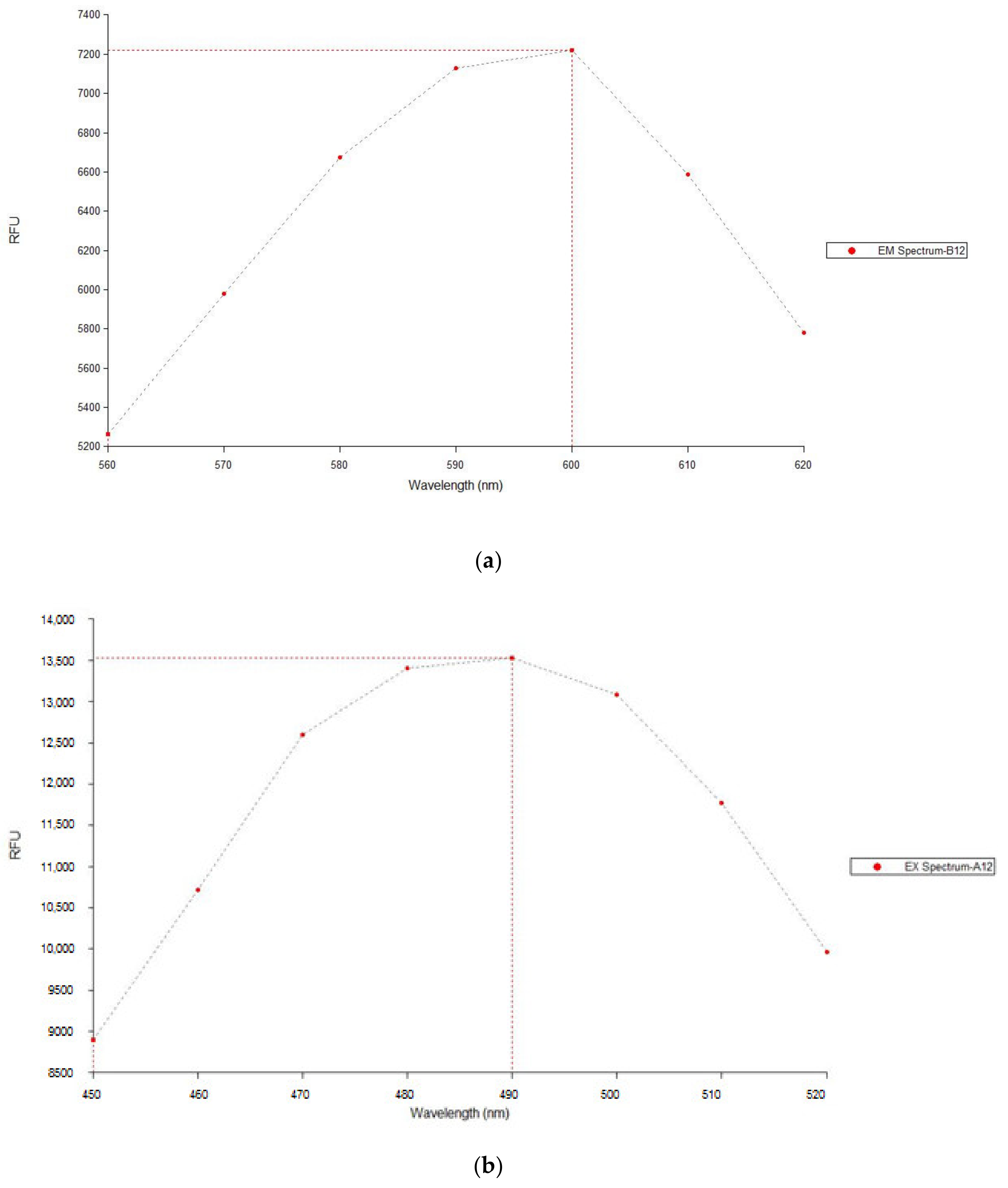
| Condition | Measurement 1 (RFU) | Measurement 2 (RFU) | Average RFU (±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Doxorubicin 10 µg/mL in P407 | 8926 | 8390 | 8658 ± 268 |
| Doxorubicin 10 µg/mL in PBS | 1178 | 1209 | 1194 ± 16 |
References
- Thorn, C.F.; Oshiro, C.; Marsh, S.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; McLeod, H.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Doxorubicin pathways: Pharmacodynamics and adverse effects. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2011, 21, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minotti, G.; Menna, P.; Salvatorelli, E.; Cairo, G.; Gianni, L. Anthracyclines: Molecular advances and pharmacologic developments in antitumor activity and cardiotoxicity. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 185–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivankar, S. An overview of doxorubicin formulations in cancer therapy. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2014, 10, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappetta, D.; Rossi, F.; Piegari, E.; Quaini, F.; Berrino, L.; Urbanek, K.; De Angelis, A. Doxorubicin targets multiple players: A new view of an old problem. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 127, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Kang, Y.M.; Kim, E.S.; Hwang, S.J.; Lee, H.B.; Min, B.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.S. In vivo efficacy of paclitaxel-loaded injectable in situ-forming gel against subcutaneous tumor growth. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 392, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagel, M.; Grotz, E.; Bernabeu, E.; Moretton, M.A.; Chiappetta, D.A. Doxorubicin: Nanotechnological overviews from bench to bedside. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Couce, J.; Almirall, A.; Fuentes, G.; Kaijzel, E.; Chan, A.; Cruz, L.J. Targeting Polymeric Nanobiomaterials as a Platform for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 1915–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, M.T.; Jhan, H.J.; Su, C.Y.; Chen, L.C.; Chang, C.E.; Liu, D.Z.; Ho, H.O. Codelivery of doxorubicin-containing thermosensitive hydrogels incorporated with docetaxel-loaded mixed micelles enhances local cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z. Thermo-sensitive hydrogels for delivering biotherapeutic molecules: A review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumortier, G.; Grossiord, J.L.; Agnely, F.; Chaumeil, J.C. A review of poloxamer 407 pharmaceutical and pharmacological characteristics. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 2709–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, M.S.; Rehman, K. Recent progress in biomedical applications of Pluronic (PF127): Pharmaceutical perspectives. J. Control. Release 2015, 209, 120–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abd, A.M.; Hong, K.Y.; Song, S.C.; Kuh, H.J. Pharmacokinetics of doxorubicin after intratumoral injection using a thermosensitive hydrogel in tumor-bearing mice. J. Control. Release 2010, 142, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiji, M.M.; Lai, P.K.; Shenoy, D.B.; Rao, M. Intratumoral administration of paclitaxel in an in situ gelling poloxamer 407 formulation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2002, 7, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, J.J.; Yan, Y.D.; Oh, D.H.; Choi, Y.K.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.G. Development of thermo-sensitive injectable hydrogel with sustained release of doxorubicin: Rheological characterization and in vivo evaluation in rats. Drug Deliv. 2011, 18, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumdar, D.; Peng, X.H.; Shin, D.M. The medicinal chemistry of theragnostics, multimodality imaging and applications of nanotechnology in cancer. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 1211–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, K.H.; Chung, H.J.; Park, T.G. Nanomaterials for cancer therapy and imaging. Mol. Cells 2011, 31, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Z.J. Injectable Hydrogels for Localized Cancer Therapy. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salis, A.; Rassu, G.; Budai-Szucs, M.; Benzoni, I.; Csanyi, E.; Berko, S.; Maestri, M.; Dionigi, P.; Porcu, E.P.; Gavini, E.; et al. Development of thermosensitive chitosan/glicerophospate injectable in situ gelling solutions for potential application in intraoperative fluorescence imaging and local therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: A preliminary study. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 1583–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Sun, J.; Zi, P.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C. Thermosensitive micelles-hydrogel hybrid system based on poloxamer 407 for localized delivery of paclitaxel. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 2707–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, N. Thermosensitive Hydrogel Co-loaded with Gold Nanoparticles and Doxorubicin for Effective Chemoradiotherapy. AAPS J. 2016, 18, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, T.; Li, C.; Guo, Y.; Liu, G.; Hao, L.; Shen, J.; Qi, L.; Liu, X.; et al. In vitro and in vivo study of Gal-OS self-assembled nanoparticles for liver-targeting delivery of doxorubicin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelmer, A.; Ward, T.H. Noninvasive fluorescence imaging of small animals. J. Microsc. 2013, 252, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, C.F. Multiple molecular mechanisms for multidrug resistance transporters. Nature 2007, 446, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollazadeh, S.; Sahebkar, A.; Hadizadeh, F.; Behravan, J.; Arabzadeh, S. Structural and functional aspects of P-glycoprotein and its inhibitors. Life Sci. 2018, 214, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Li, Z.; Gao, C.Y.; Cho, C.H. Mechanisms of drug resistance in colon cancer and its therapeutic strategies. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6876–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Hui, P.C.L.; Wat, E.; Ng, F.S.F.; Kan, C.W.; Lau, C.B.S.; Leung, P.C. Enhanced Transdermal Permeability via Constructing the Porous Structure of Poloxamer-Based Hydrogel. Polymers 2016, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Blanchard, J. Controlled-release delivery system for the α-MSH analog melanotan-I using poloxamer 407. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 915–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.C.; Jun, H.W. Release rates of ketoprofen from poloxamer gels in a membraneless diffusion cell. J. Pharm. Sci. 1991, 80, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Chandra, A.; Kaur, A.; Sabnis, N.; Lacko, A.; Gryczynski, Z.; Fudala, R.; Gryczynski, I. Fluorescence properties of doxorubicin in PBS buffer and PVA films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 170, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, P.; Alan Hatton, T. Poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide)-poly(ethylene oxide) block copolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: Thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1995, 96, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimian, S.; Fransen, M.F.; Kleinovink, J.W.; Amidi, M.; Ossendorp, F.; Hennink, W.E. Polymeric microparticles for sustained and local delivery of antiCD40 and antiCTLA-4 in immunotherapy of cancer. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.K.; Fransen, M.F.; van der Maaden, K.; Campos, Y.; Garcia-Couce, J.; Kralisch, D.; Chan, A.; Ossendorp, F.; Cruz, L.J. Thermosensitive hydrogels as sustained drug delivery system for CTLA-4 checkpoint blocking antibodies. J. Control. Release 2020, 323, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, E.; Park, M.; Jeong, S.; Kwon, T.; Kim, E.H.; Jung, K.; Kim, A. Poloxamer-Based Thermoreversible Gel for Topical Delivery of Emodin: Influence of P407 and P188 on Solubility of Emodin and Its Application in Cellular Activity Screening. Molecules 2017, 22, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenite, A.; Chaput, C.; Wang, D.; Combes, C.; Buschmann, M.D.; Hoemann, C.D.; Leroux, J.C.; Atkinson, B.L.; Binette, F.; Selmani, A. Novel injectable neutral solutions of chitosan form biodegradable gels in situ. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksiriworapong, J.; Rungvimolsin, T.; A-gomol, A.; Junyaprasert, V.B.; Chantasart, D. Development and characterization of lyophilized diazepam-loaded polymeric micelles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ye, J.; Sha, X.; Fang, X. Multifunctional Pluronic P123/F127 mixed polymeric micelles loaded with paclitaxel for the treatment of multidrug resistant tumors. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2894–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Lv, X.; Xu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, R. Pluronic micelles with suppressing doxorubicin efflux and detoxification for efficiently reversing breast cancer resistance. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 146, 105275–105288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Pellosi, D.S.; Pagliara, V.; Milone, M.R.; Pucci, B.; Caetano, W.; Hioka, N.; Budillon, A.; Ungaro, F.; Russo, G.; et al. Biotin-targeted Pluronic((R)) P123/F127 mixed micelles delivering niclosamide: A repositioning strategy to treat drug-resistant lung cancer cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sha, X.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Ren, Q.; Fang, X. Pluronic P105/F127 mixed micelles for the delivery of docetaxel against Taxol-resistant non-small cell lung cancer: Optimization and in vitro, in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Sha, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, W.; Fan, Z.; Ren, Q.; Chen, L.; Fang, X. Pluronic mixed micelles overcoming methotrexate multidrug resistance: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Gu, J.; Ren, Q.; Fan, Z.; Zhong, W.; Fang, X.; Sha, X. Enhanced antitumor efficacy by methotrexate conjugated Pluronic mixed micelles against KBv multidrug resistant cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 452, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Y.; Gao, F.; Sha, X.; Fang, X. Pluronic-based functional polymeric mixed micelles for co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel to multidrug resistant tumor. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 488, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, S. Thermosensitive Hydrogel System With Paclitaxel Liposomes Used in Localized Drug Delivery System for In Situ Treatment of Tumor: Better Antitumor Efficacy and Lower Toxicity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S.; Hsiao, W.L.; Pan, W.; Yang, Z. Thermoreversible Pluronic F127-based hydrogel containing liposomes for the controlled delivery of paclitaxel: In vitro drug release, cell cytotoxicity, and uptake studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 151–166. [Google Scholar]
- Sosnik, A.; Seremeta, K.P. Polymeric Hydrogels as Technology Platform for Drug Delivery Applications. Gels 2017, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.J.; Tacken, P.J.; Zeelenberg, I.S.; Srinivas, M.; Bonetto, F.; Weigelin, B.; Eich, C.; de Vries, I.J.; Figdor, C.G. Tracking targeted bimodal nanovaccines: Immune responses and routing in cells, tissue, and whole organism. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 4299–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, S.; Herance, J.R.; Rojas, S.; Mena, J.F.; Gispert, J.D.; Acosta, G.A.; Albericio, F.; Kogan, M.J. Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of the biodistribution of a 18F-labeled conjugate gold-nanoparticle-peptide with potential biomedical application. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Ogawa, M.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H. Clinical implications of near-infrared fluorescence imaging in cancer. Future Oncol. 2009, 5, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.; Villa, C. Poloxamer Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Ozawa, S.; Miyamoto, C.; Maehata, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Maeda, T.; Baba, Y. Acidic extracellular microenvironment and cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiancich, C.; Bianco, J.; Vanvarenberg, K.; Ucakar, B.; Joudiou, N.; Gallez, B.; Bastiat, G.; Lagarce, F.; Preat, V.; Danhier, F. Injectable nanomedicine hydrogel for local chemotherapy of glioblastoma after surgical resection. J. Control. Release 2017, 264, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiancich, C.; Lemaire, L.; Bianco, J.; Franconi, F.; Danhier, F.; Preat, V.; Bastiat, G.; Lagarce, F. Evaluation of lauroyl-gemcitabine-loaded hydrogel efficacy in glioblastoma rat models. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1999–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiancich, C.; Vanvarenberg, K.; Ucakar, B.; Pitorre, M.; Bastiat, G.; Lagarce, F.; Preat, V.; Danhier, F. Lauroyl-gemcitabine-loaded lipid nanocapsule hydrogel for the treatment of glioblastoma. J. Control. Release 2016, 225, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauthoz, N.; Bastiat, G.; Moysan, E.; Cieslak, A.; Kondo, K.; Zandecki, M.; Moal, V.; Rousselet, M.C.; Hureaux, J.; Benoit, J.P. Safe lipid nanocapsule-based gel technology to target lymph nodes and combat mediastinal metastases from an orthotopic non-small-cell lung cancer model in SCID-CB17 mice. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 1237–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodratti, A.M.; Alexandridis, P. Formulation of Poloxamers for Drug Delivery. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds reported in this paper are available from the authors. |

| Formulation | Gelation Time (Seconds) at RT (20 °C) | Gelation Time (Seconds) at 37 °C |
|---|---|---|
| 16% P407 | - | - |
| 20% P407 | - | 47 ± 2.5 |
| 25% P407 1 | 275 ± 5 | 30 ± 1 |
| 25% P407 DOX | 264 ± 1.5 | 29 ± 1.5 |
| 30% P407 | 133 ± 7.5 | 18 ± 2.5 |
| Formulation | PDI |
|---|---|
| 2.5% P407 | 0.390 |
| 5.0% P407 | 0.321 |
| 7.5% P407 | 0.374 |
| 10.0% P407 | 0.597 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, C.K.; García-Couce, J.; Campos, Y.; Kralisch, D.; Bierau, K.; Chan, A.; Ossendorp, F.; Cruz, L.J. Doxorubicin Loaded Poloxamer Thermosensitive Hydrogels: Chemical, Pharmacological and Biological Evaluation. Molecules 2020, 25, 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092219
Chung CK, García-Couce J, Campos Y, Kralisch D, Bierau K, Chan A, Ossendorp F, Cruz LJ. Doxorubicin Loaded Poloxamer Thermosensitive Hydrogels: Chemical, Pharmacological and Biological Evaluation. Molecules. 2020; 25(9):2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092219
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Chih Kit, Jomarien García-Couce, Yaima Campos, Dana Kralisch, Katja Bierau, Alan Chan, Ferry Ossendorp, and Luis Javier Cruz. 2020. "Doxorubicin Loaded Poloxamer Thermosensitive Hydrogels: Chemical, Pharmacological and Biological Evaluation" Molecules 25, no. 9: 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092219
APA StyleChung, C. K., García-Couce, J., Campos, Y., Kralisch, D., Bierau, K., Chan, A., Ossendorp, F., & Cruz, L. J. (2020). Doxorubicin Loaded Poloxamer Thermosensitive Hydrogels: Chemical, Pharmacological and Biological Evaluation. Molecules, 25(9), 2219. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25092219