Assessment of Growth Factors, Cytokines, and Cellular Markers in Saliva of Patients with Trigeminal Neuralgia
Abstract
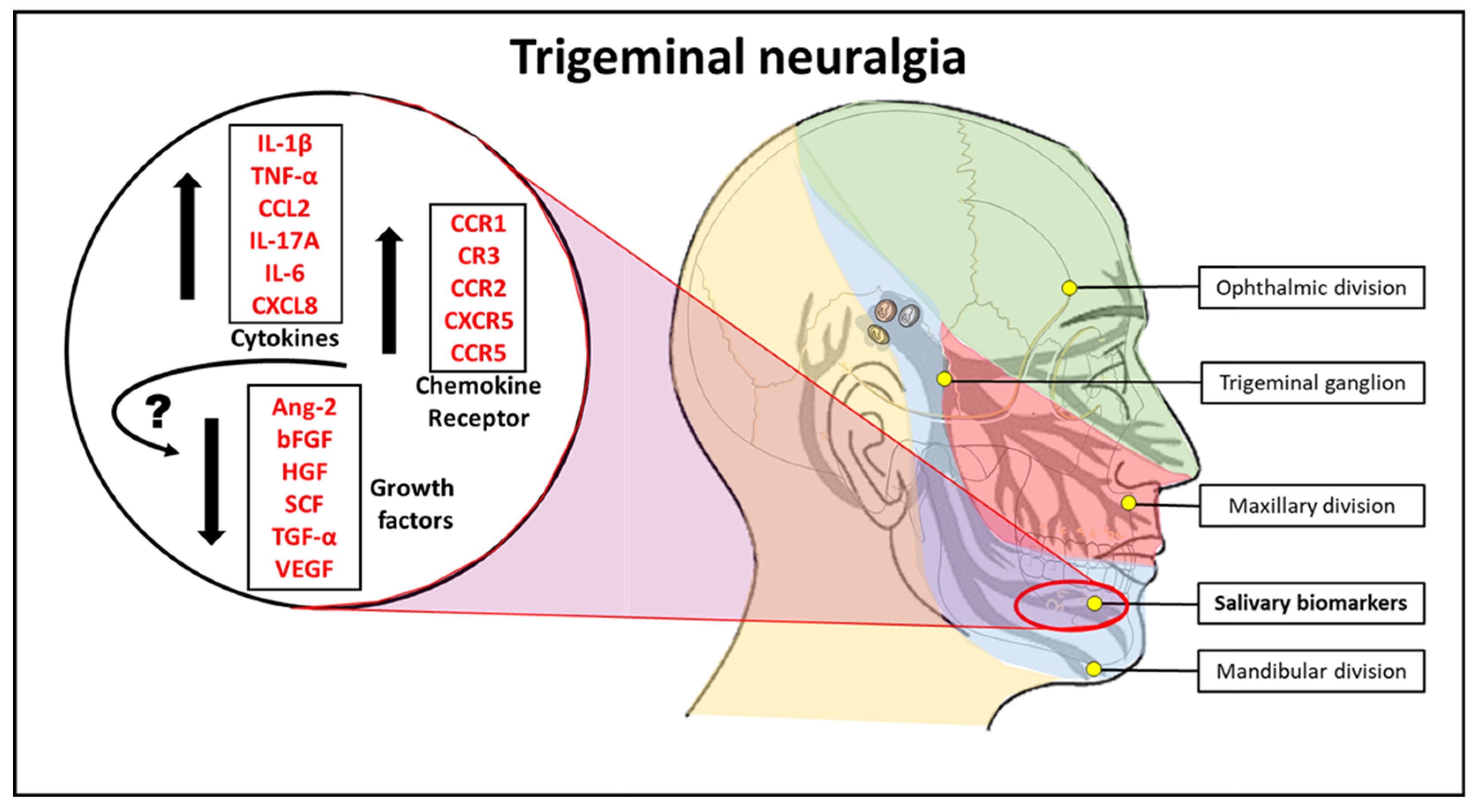
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Saliva from TN Subjects Show Lower Growth Factor Levels of Angiopoietin-2, bFGF, HGF, SCF, TGF-α, and VEGF than Saliva from Normal Subjects
2.2. Saliva from TN Subjects Show Higher Cytokine Levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, CCL2, IL-17A, IL-6, and CXCL8 than Saliva from Normal Subjects
2.3. Cell Isolated from the Saliva of TN Subjects Exhibit Higher Marker Expression for Chemokine Receptors CD191, CD11b, CD192, CD185, and CD196 than the cells from the Saliva of Normal Subjects
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Ethical Permissions
4.2. Isolation of Cells from Saliva and Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.3. Cytometric Bead Array for the Detection of Cytokines and Growth Factors
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Di Stefano, G.; Maarbjerg, S.; Nurmikko, T.; Truini, A.; Cruccu, G. Triggering trigeminal neuralgia. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.H.; Girgis, F. Trigeminal Neuralgia: Medical Management and Surgical Options. J. Pain Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2019, 33, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eboli, P.; Stone, J.L.; Aydin, S.; Slavin, K.V. Historical characterization of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 2009, 64, 1183–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, S. Trigeminal neuralgia: Pathology and pathogenesis. Brain 2001, 124, 2347–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maarbjerg, S.; Di Stefano, G.; Bendtsen, L.; Cruccu, G. Trigeminal neuralgia—Diagnosis and treatment. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Rodríguez, B.; Simonet, C.; Cerdán, D.M.; Morollón, N.; Guerrero, P.; Tabernero, C.; Duarte, J. Neuralgia del trigémino clásica familiar. Neurología 2019, 34, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermann, M. Recent advances in understanding/managing trigeminal neuralgia. F1000Research 2019, 8, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puskar, K.R.; Droppa, M. Trigeminal Neuralgia: Pain, Pricks, and Anxiety. J. Gerontol. Nurs. 2015, 41, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bick, S.K.B.; Eskandar, E.N. Surgical Treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 28, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, T.D. Antiepileptic Drugs in the Management of Cluster Headache and Trigeminal Neuralgia. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2001, 41, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.A.; Frederickson, A.M.; Branstetter, B.F.; Zhu, X.; Sekula, R.F. MRI of the Trigeminal Nerve in Patients With Trigeminal Neuralgia Secondary to Vascular Compression. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 206, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batbold, D.; Shinoda, M.; Honda, K.; Furukawa, A.; Koizumi, M.; Akasaka, R.; Yamaguchi, S.; Iwata, K. Macrophages in trigeminal ganglion contribute to ectopic mechanical hypersensitivity following inferior alveolar nerve injury in rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, G.W.; Son, J.Y.; Lee, A.R.; Ju, J.S.; Bae, Y.C.; Ahn, D.K. Central VEGF-A pathway plays a key role in the development of trigeminal neuropathic pain in rats. Mol. Pain 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, A.M.W.; Ribeiro-da-Silva, A. GDNF levels in the lower lip skin in a rat model of trigeminal neuropathic pain: Implications for nonpeptidergic fiber reinnervation and parasympathetic sprouting. Pain 2011, 152, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, S.; Shinoda, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Saito, H.; Asano, S.; Kubo, A.; Shibuta, I.; Furukawa, A.; Toyofuku, A.; Iwata, K. Increase in IGF-1 Expression in the Injured Infraorbital Nerve and Possible Implications for Orofacial Neuropathic Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- dos Reis, R.C.; Kopruszinski, C.M.; Nones, C.F.M.; Chichorro, J.G. Nerve growth factor induces facial heat hyperalgesia and plays a role in trigeminal neuropathic pain in rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, Z.; Warsi, I.; Moin, S.F.; Slowey, P.D.; Latif, M.; Zohaib, S.; Zafar, M.S. Biochemical analysis of oral fluids for disease detection. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2021, 205–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahibzada, H.A.; Khurshid, Z.; Khan, R.S.; Naseem, M.; Siddique, K.M.; Mali, M.; Zafar, M.S. Salivary IL-8, IL-6 and TNF-α as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Oral Cancer. Diagnostics 2017, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khurshid, Z.; Zafar, M.S.; Khan, R.S.; Najeeb, S.; Slowey, P.D.; Rehman, I.U. Role of Salivary Biomarkers in Oral Cancer Detection. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2018, 80, 23–70. [Google Scholar]
- Cruccu, G.; Finnerup, N.B.; Jensen, T.S.; Scholz, J.; Sindou, M.; Svensson, P.; Treede, R.-D.; Zakrzewska, J.M.; Nurmikko, T. Trigeminal neuralgia. Neurology 2016, 87, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, J.; von Baehr, V. Peripheral Neuropathic Facial/Trigeminal Pain and RANTES/CCL5 in Jawbone Cavitation. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, Y.; Guo, R.; Shao, Y.; Ge, M.; Miao, C.; Cao, L.; Yang, Y.; Hu, L. Pretreatment with resveratrol ameliorate trigeminal neuralgia by suppressing matrix metalloproteinase-9/2 in trigeminal ganglion. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 72, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, G.; Benemei, S.; Materazzi, S.; De Logu, F.; De Siena, G.; Fusi, C.; Fortes Rossato, M.; Coppi, E.; Marone, I.M.; Ferreira, J.; et al. TRPA1 mediates trigeminal neuropathic pain in mice downstream of monocytes/macrophages and oxidative stress. Brain 2016, 139, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olesen, J. Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Long, M.; Wang, M.; Peng, S.; Chen, G.; Zhou, J.; Ou, C. Trigeminal neuralgia causes neurodegeneration in rats associated with upregulation of the CD95/CD95L pathway. Mol. Pain 2020, 16, 174480692090809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fagiani, E.; Christofori, G. Angiopoietins in angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2013, 328, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blottner, D.; Baumgarten, H.G. Basic fibroblast growth factor prevents neuronal death and atrophy of retrogradely labeled preganglionic neurons in vivo. Exp. Neurol. 1992, 118, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, S.; Tanaka, M.; Ishii, T.; Ohtaka, K.; Takahashi, T.; Tazawa, Y. Neuroprotective Effect of Hepatocyte Growth Factor against Photoreceptor Degeneration in Rats. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandapani, K.M.; Wade, F.M.; Wakade, C.; Mahesh, V.B.; Brann, D.W. Neuroprotection by stem cell factor in rat cortical neurons involves AKT and NFκB. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, P.; Johnson, J.; Son, D.-S.; Aschner, M.; Lee, E. Transcriptional Regulation of Human Transforming Growth Factor-α in Astrocytes. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, L.; Cahill, C.M. TNF-α and neuropathic pain—A review. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwasa, T.; Afroz, S.; Inoue, M.; Arakaki, R.; Oshima, M.; Raju, R.; Waskitho, A.; Inoue, M.; Baba, O.; Matsuka, Y. IL-10 and CXCL2 in trigeminal ganglia in neuropathic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 703, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauvergne, C.; Molet, J.; Reaux-Le Goazigo, A.; Mauborgne, A.; Mélik-Parsadaniantz, S.; Boucher, Y.; Pohl, M. Implication of the chemokine CCL2 in trigeminal nociception and traumatic neuropathic orofacial pain. Eur. J. Pain 2014, 18, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, H. CD11b-activated Src signal attenuates neuroinflammatory pain by orchestrating inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in microglia. Mol. Pain 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.-B.; Jing, P.-B.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Cao, D.-L.; Gao, M.-H.; Jiang, B.-C.; Gao, Y.-J. Chemokine receptor CCR2 contributes to neuropathic pain and the associated depression via increasing NR2B-mediated currents in both D1 and D2 dopamine receptor-containing medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens shell. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 2320–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lewis, N.D.; Muthukumarana, A.; Fogal, S.E.; Corradini, L.; Stefanopoulos, D.E.; Adusumalli, P.; Pelletier, J.; Panzenbeck, M.; Berg, K.; Canfield, M.; et al. CCR1 Plays a Critical Role in Modulating Pain through Hematopoietic and Non-Hematopoietic Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cao, D.-L.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Jiang, B.-C.; Gao, Y.-J. Chemokine CXCL13 mediates orofacial neuropathic pain via CXCR5/ERK pathway in the trigeminal ganglion of mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.K.; Choi, D.-Y.; Jung, Y.-Y.; Yun, Y.W.; Lee, B.J.; Han, S.B.; Hong, J.T. Decreased pain responses of C–C chemokine receptor 5 knockout mice to chemical or inflammatory stimuli. Neuropharmacology 2013, 67, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patil, S.; Testarelli, L. Assessment of Growth Factors, Cytokines, and Cellular Markers in Saliva of Patients with Trigeminal Neuralgia. Molecules 2021, 26, 2964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102964
Patil S, Testarelli L. Assessment of Growth Factors, Cytokines, and Cellular Markers in Saliva of Patients with Trigeminal Neuralgia. Molecules. 2021; 26(10):2964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102964
Chicago/Turabian StylePatil, Shankargouda, and Luca Testarelli. 2021. "Assessment of Growth Factors, Cytokines, and Cellular Markers in Saliva of Patients with Trigeminal Neuralgia" Molecules 26, no. 10: 2964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102964
APA StylePatil, S., & Testarelli, L. (2021). Assessment of Growth Factors, Cytokines, and Cellular Markers in Saliva of Patients with Trigeminal Neuralgia. Molecules, 26(10), 2964. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26102964






