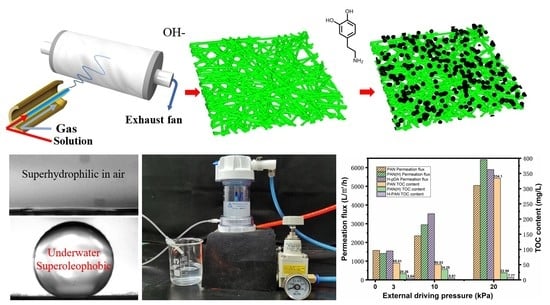
Polydopamine Nanocluster Embedded Nanofibrous Membrane via Blow Spinning for Separation of Oil/Water Emulsions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
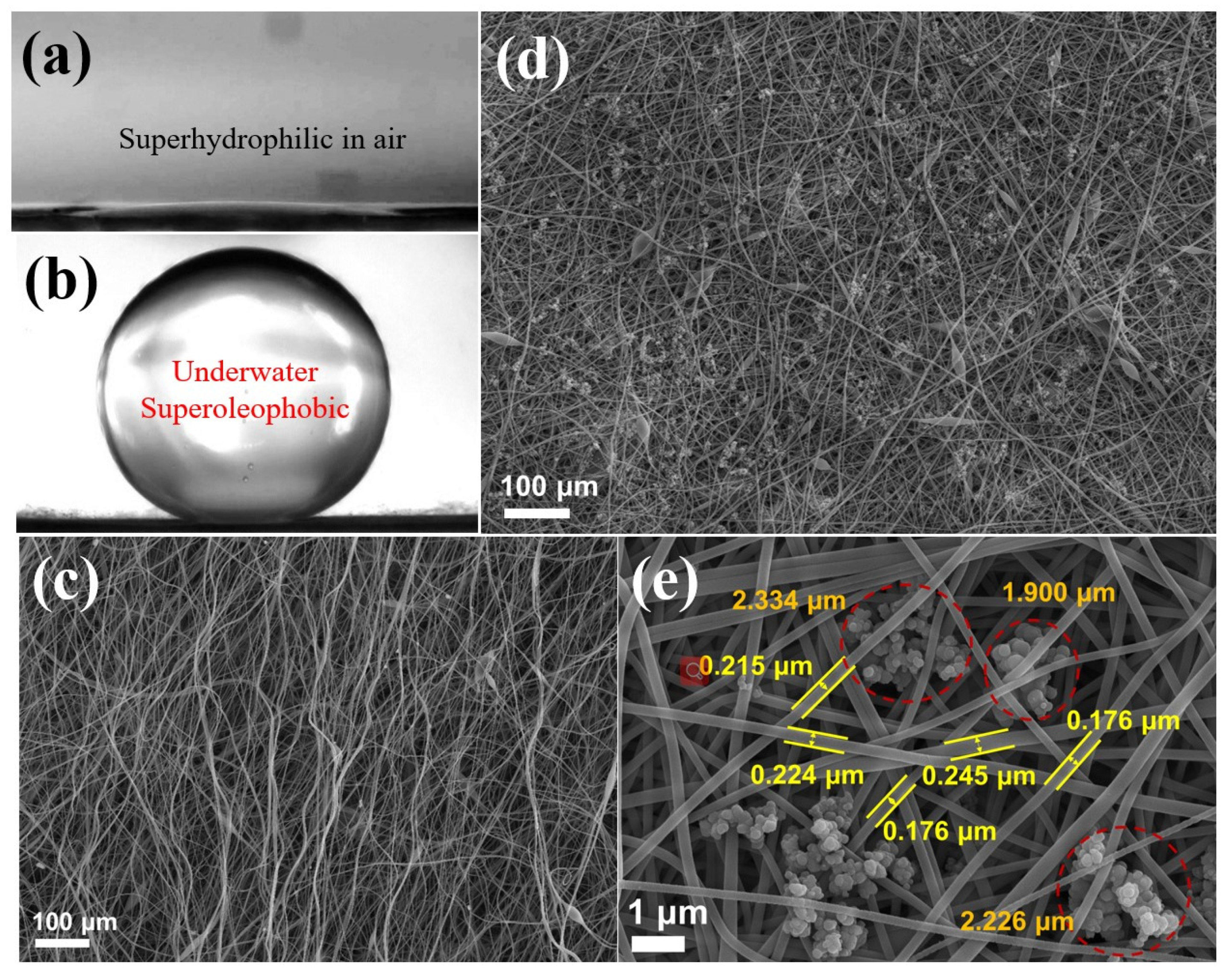
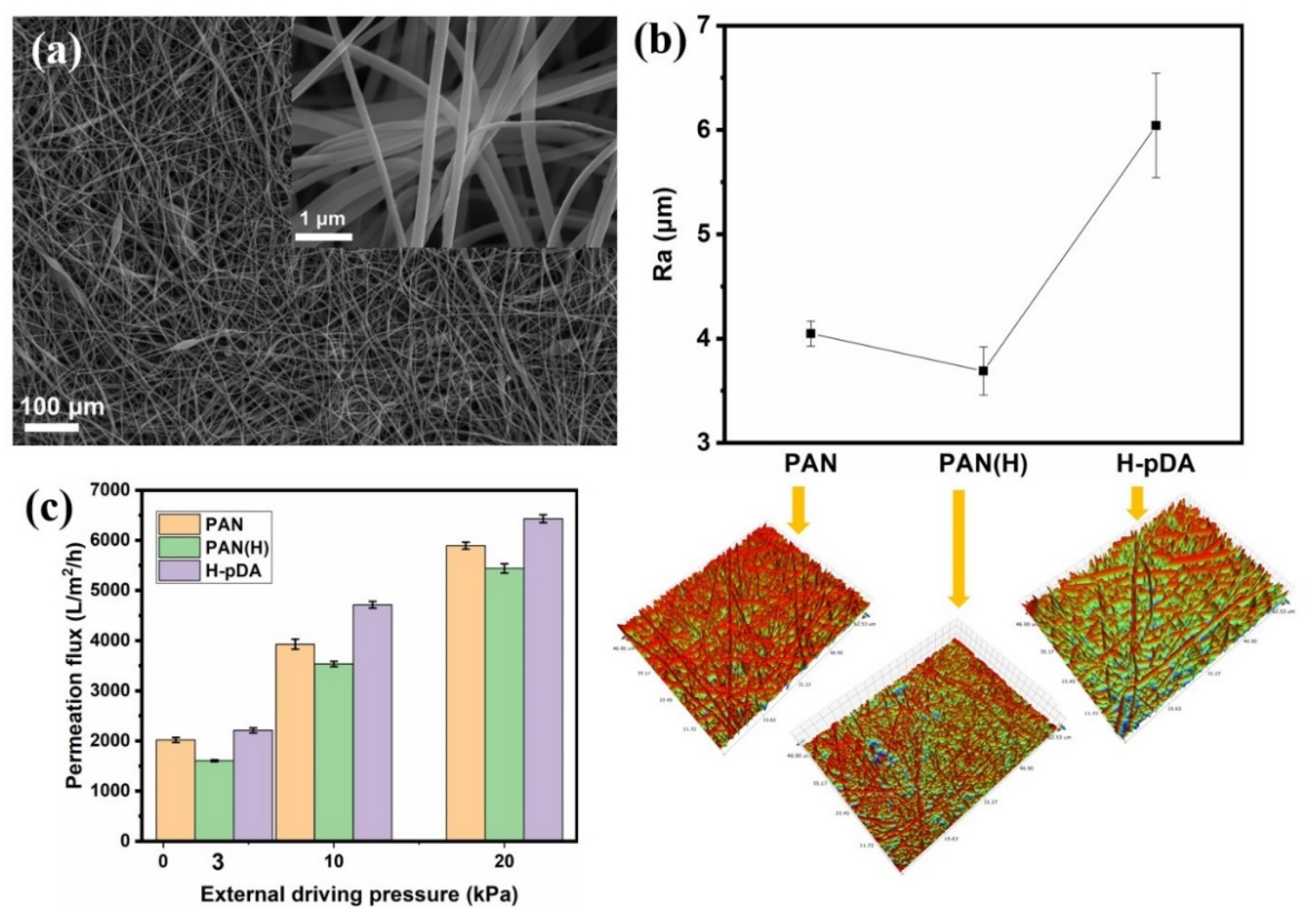
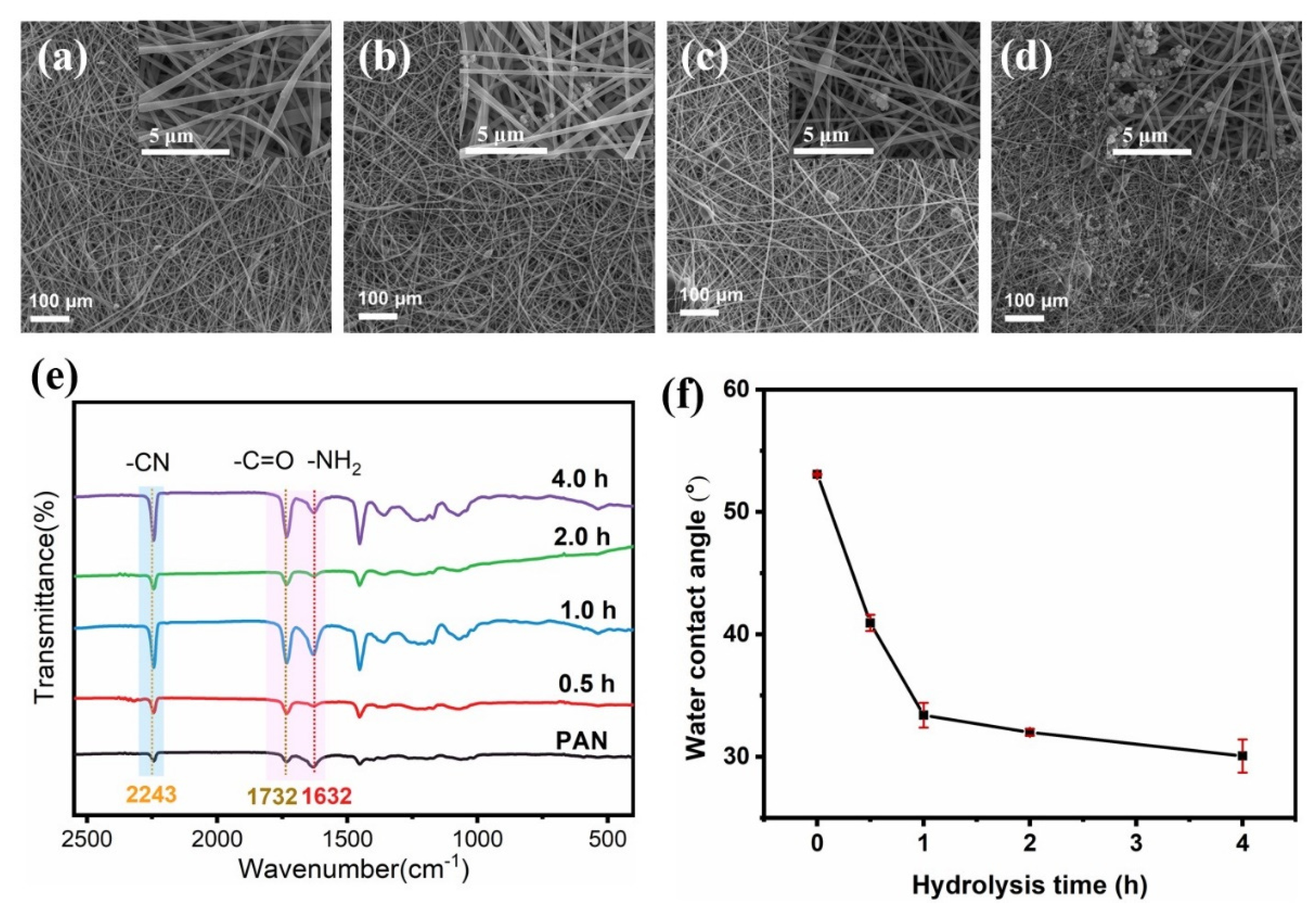
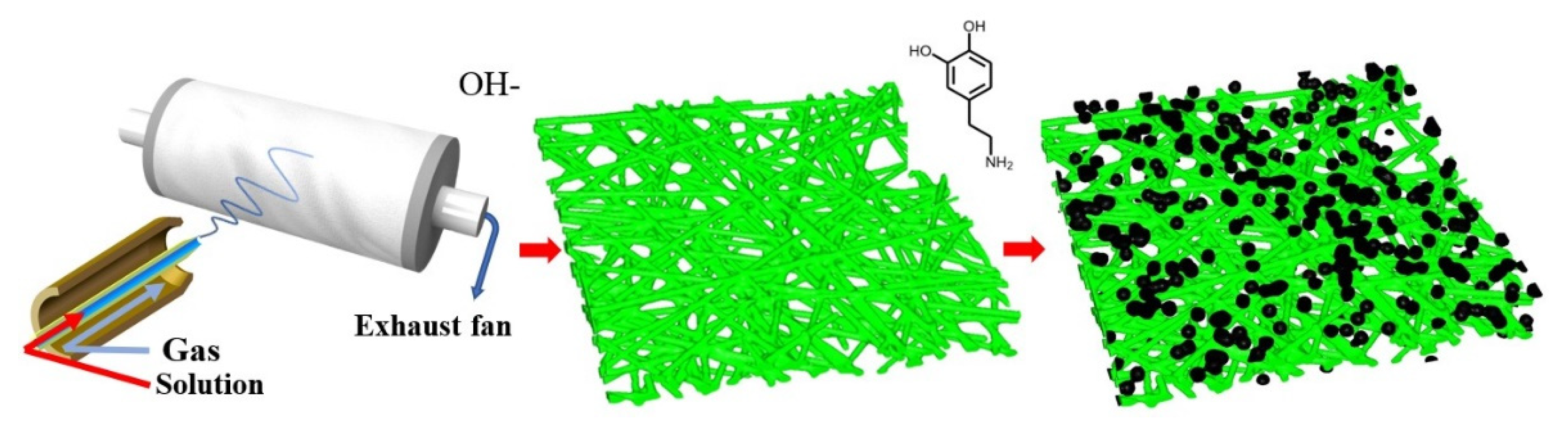
2.1. Preparation and Microstructural Characterization
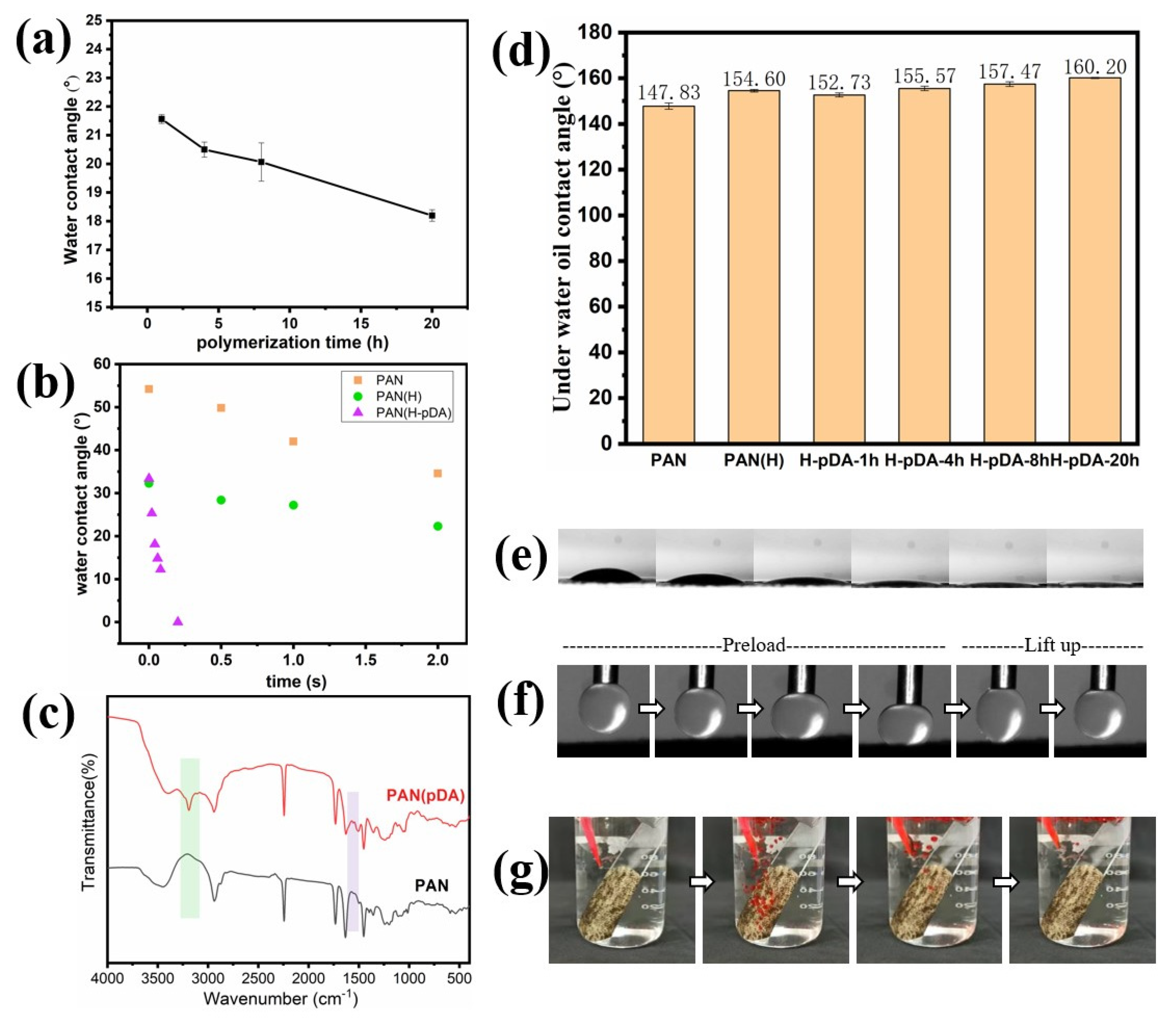
2.2. Optimization of Surface Wettability
2.3. Evaluation of the Oil–Water Emulsion Separation Performance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Fabrication of PAN-Nanofiber Membranes
3.3. Construction of Superhydrophilic Nanofiber Membranes
3.4. Preparation of Emulsions
3.5. Oil–Water Emulsion Separation Experiments
3.6. Characterizations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qu, X.; Brame, J.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J. Nanotechnology for a safe and sustainable water supply: Enabling integrated water treatment and reuse. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M. Energy, environment and sustainable development. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2008, 12, 2265–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.H.; Rice, S.D.; Short, J.W.; Esler, D.; Bodkin, J.L.; Ballachey, B.E.; Irons, D.B. Long-term ecosystem response to the Exxon Valdez oil spill. Science 2003, 302, 2082–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCay, D.F.; Rowe, J.J.; Whittier, N.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Etkin, D.S. Estimation of potential impacts and natural resource damages of oil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 107, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, T.; Jin, D. Extent and frequency of vessel oil spills in US marine protected areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Garrett, C. The relationship between oil droplet size and upper ocean turbulence. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1998, 36, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheryan, M.; Rajagopalan, N. Membrane processing of oily streams. Wastewater treatment and waste reduction. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 151, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Z.; O’reilly, S.; Hao, X.; Zhao, D. A review of oil, dispersed oil and sediment interactions in the aquatic environment: Influence on the fate, transport and remediation of oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 79, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambiella, A.; Benito, J.; Pazos, C.; Coca, J. Centrifugal separation efficiency in the treatment of waste emulsified oils. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2006, 84, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putatunda, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sen, D.; Bhattacharjee, C. A review on the application of different treatment processes for emulsified oily wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.M.; Lee, H.S.; Miller, D.J.; Freeman, B.D.; McGrath, J.E.; Paul, D.R. Water purification by membranes: The role of polymer science. J. Polym. Sci. Part. B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 1685–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Phan, T.-D.; Luo, S.; Liu, Z.; Gamalski, A.D.; Tao, J.; Xu, W.; Stach, E.A.; Polyansky, D.E.; Senanayake, S.D.; Fujita, E. Striving toward noble-metal-free photocatalytic water splitting: The hydrogenated-graphene–TiO2 prototype. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 6282–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.R.; Huang, L.W.; McCutcheon, J.R. Thin Film Composite Membranes for Forward Osmosis Supported by Commercial Nanofiber Nonwovens. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Si, Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Yang, L.P.; Zhao, F.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.Y. Silica nanofibrous membranes with robust flexibility and thermal stability for high-efficiency fine particulate filtration. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 12216–12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, T. Hybrid membrane technology: A new nanofibre media platform. Filtr. Separat. 2007, 44, 28–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, J.; Long, Y.; Jia, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Large-scale blow spinning of heat-resistant nanofibrous air filters. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lin, S.; Yang, S.; Yang, X.; Song, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Fang, M.; et al. High-Temperature Particulate Matter Filtration with Resilient Yttria-Stabilized ZrO2 Nanofiber Sponge. Small 2018, 14, 1800258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pan, X.; Xue, Q.; He, D.; Zhu, L.; Guo, Q. Antifouling hydrolyzed polyacrylonitrile/graphene oxide membrane with spindle-knotted structure for highly effective separation of oil-water emulsion. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 532, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zong, D.; Jin, Q.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Biomimetic and Superwettable Nanofibrous Skins for Highly Efficient Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, L.A.; Yan, K.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q.J. Polydopamine nanocluster decorated electrospun nanofibrous membrane for separation of oil/water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 547, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Interfaces with Superwettability: From Materials to Chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1727–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, E.S.; Glenn, G.M.; Klamczynski, A.P.; Orts, W.J.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Solution Blow Spinning: A New Method to Produce Micro- and Nanofibers from Polymer Solutions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 113, 2322–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Z.; Fang, M.; Ou, G. Ultralight, scalable, and high-temperature–resilient ceramic nanofiber sponges. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1603170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daristotle, J.L.; Behrens, A.M.; Sandler, A.D.; Kofinas, P. A Review of the Fundamental Principles and Applications of Solution Blow Spinning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34951–34963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.E.; Moraes, E.A.; Costa, R.G.F.; Afonso, A.S.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Orts, W.J.; Medeiros, E.S. Nano and Submicrometric Fibers of Poly(D,L-Lactide) Obtained by Solution Blow Spinning: Process and Solution Variables. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 122, 3396–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutak, W.; Sarkar, S.; Lin-Gibson, S.; Farooque, T.M.; Jyotsnendu, G.; Wang, D.; Kohn, J.; Bolikal, D.; Simon, C.G., Jr. The support of bone marrow stromal cell differentiation by airbrushed nanofiber scaffolds. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2389–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, A.M.; Casey, B.J.; Sikorski, M.J.; Wu, K.L.; Tutak, W.; Sandler, A.D.; Kofinas, P. In Situ Deposition of PLGA Nanofibers via Solution Blow Spinning. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: Synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Jin, Q.; Zong, D.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Biomimetic Multilayer Nanofibrous Membranes with Elaborated Superwettability for Effective Purification of Emulsified Oily Wastewater. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16183–16192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil–water separation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, D.; Jiang, L.; Jin, J. Recent progress in developing advanced membranes for emulsified oil/water separation. NPG Asia Mater. 2014, 6, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, N.; Mao, X.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M.; Ding, B. Sandwich-structured PVdF/PMIA/PVdF nanofibrous separators with robust mechanical strength and thermal stability for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 14511–14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xue, Q.; Pan, X.; Jin, Y.; Lu, W.; Ding, D.; Guo, Q. Graphene oxide/polyacrylonitrile fiber hierarchical-structured membrane for ultra-fast microfiltration of oil-water emulsion. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ji, S.; He, F.; Cao, M.; Peng, S.; Li, Y. One-step transformation of highly hydrophobic membranes into superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic ones for high-efficiency separation of oil-in-water emulsions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3391–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, W. Effective Cd2+ chelating fiber based on polyacrylonitrile. React. Funct. Polym. 2009, 69, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhang, F.; Jin, J. Photoinduced superwetting single-walled carbon nanotube/TiO2 ultrathin network films for ultrafast separation of oil-in-water emulsions. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6344–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yin, K.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Chu, D.; He, J.; Duan, J.-A. Ultrafast nano-structuring of superwetting Ti foam with robust antifouling and stability towards efficient oil-in-water emulsion separation. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17607–17614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Song, A.Y.; Wu, P.; Hsu, P.C.; Peng, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Catrysse, P.B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, A.; et al. Warming up human body by nanoporous metallized polyethylene textile. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
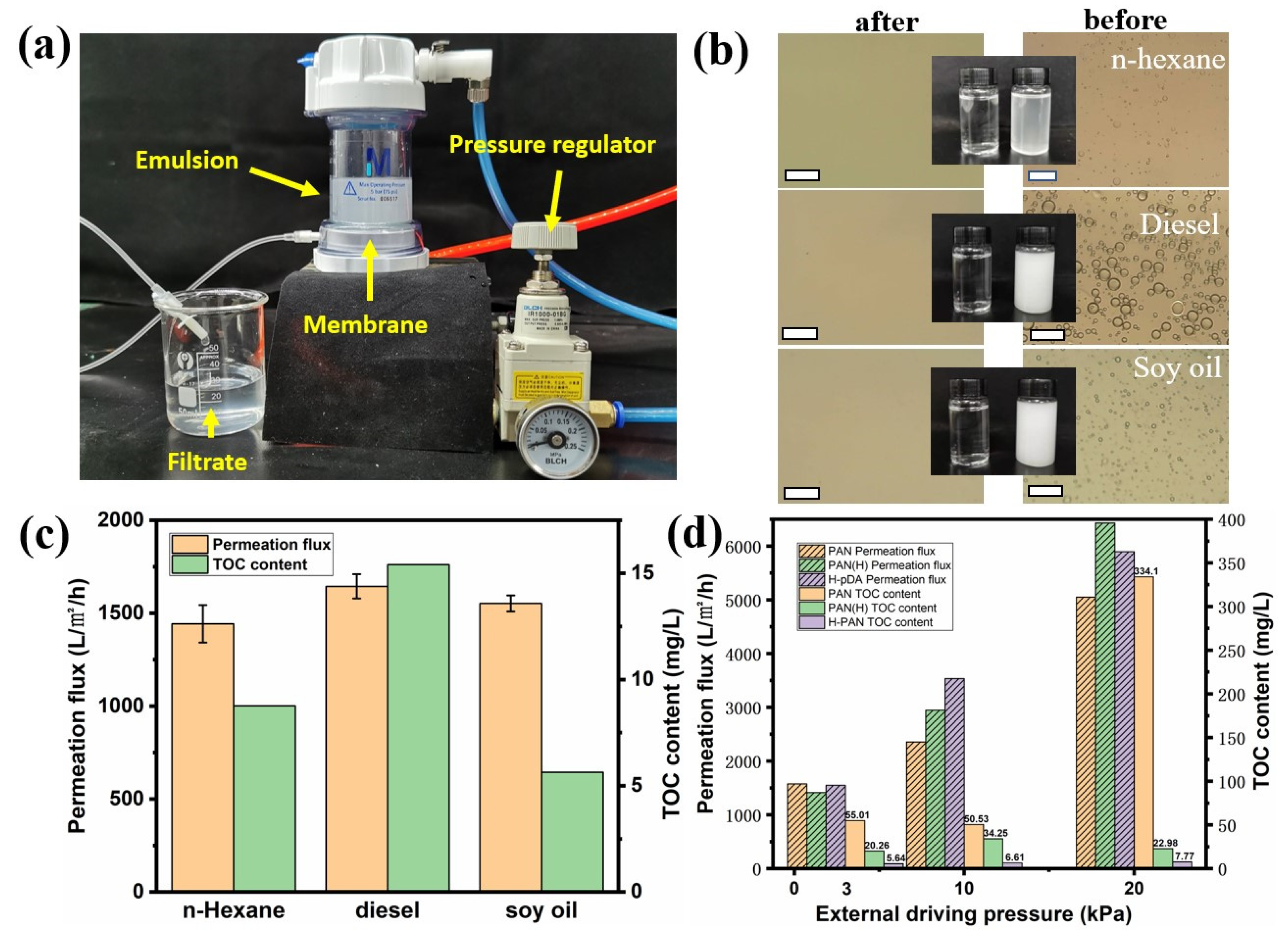
| Emulsion | TOC of before Filtration (mg/L) | TOC of after Filtration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|
| n-Hexane | 207.4 ± 24.9 | 8.77 ± 0.08 |
| diesel | 2288 ± 27.23 | 15.42 ± 0.31 |
| soy oil | 4132 ± 29.56 | 5.64 ± 0.46 |
| Membrane | TOC of before Filtration (mg/L) | TOC of after Filtration (mg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gravity | 10 kPa | 20 kPa | ||
| PAN | 4132 ± 29.56 | 55.01 ± 0.76 | 50.53 ± 0.97 | 334.1 ± 0.07 |
| PAN(H) | 20.26 ± 0.49 | 34.25 ± 0.11 | 22.98 ± 0.37 | |
| H-PAN | 5.64 ± 0.46 | 6.61 ± 0.27 | 7.77 ± 0.73 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, Q.; Fang, M.; Min, X.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X. Polydopamine Nanocluster Embedded Nanofibrous Membrane via Blow Spinning for Separation of Oil/Water Emulsions. Molecules 2021, 26, 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113258
Liu Z, Xu Z, Liu C, Zhao Y, Xia Q, Fang M, Min X, Huang Z, Liu Y, Wu X. Polydopamine Nanocluster Embedded Nanofibrous Membrane via Blow Spinning for Separation of Oil/Water Emulsions. Molecules. 2021; 26(11):3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113258
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhenglian, Ziling Xu, Chaoqi Liu, Yajing Zhao, Qingyin Xia, Minghao Fang, Xin Min, Zhaohui Huang, Yan’gai Liu, and Xiaowen Wu. 2021. "Polydopamine Nanocluster Embedded Nanofibrous Membrane via Blow Spinning for Separation of Oil/Water Emulsions" Molecules 26, no. 11: 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113258
APA StyleLiu, Z., Xu, Z., Liu, C., Zhao, Y., Xia, Q., Fang, M., Min, X., Huang, Z., Liu, Y., & Wu, X. (2021). Polydopamine Nanocluster Embedded Nanofibrous Membrane via Blow Spinning for Separation of Oil/Water Emulsions. Molecules, 26(11), 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113258