Environment-Sensitive Fluorescence of 7-Nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl (NBD)-Labeled Ligands for Serotonin Receptors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
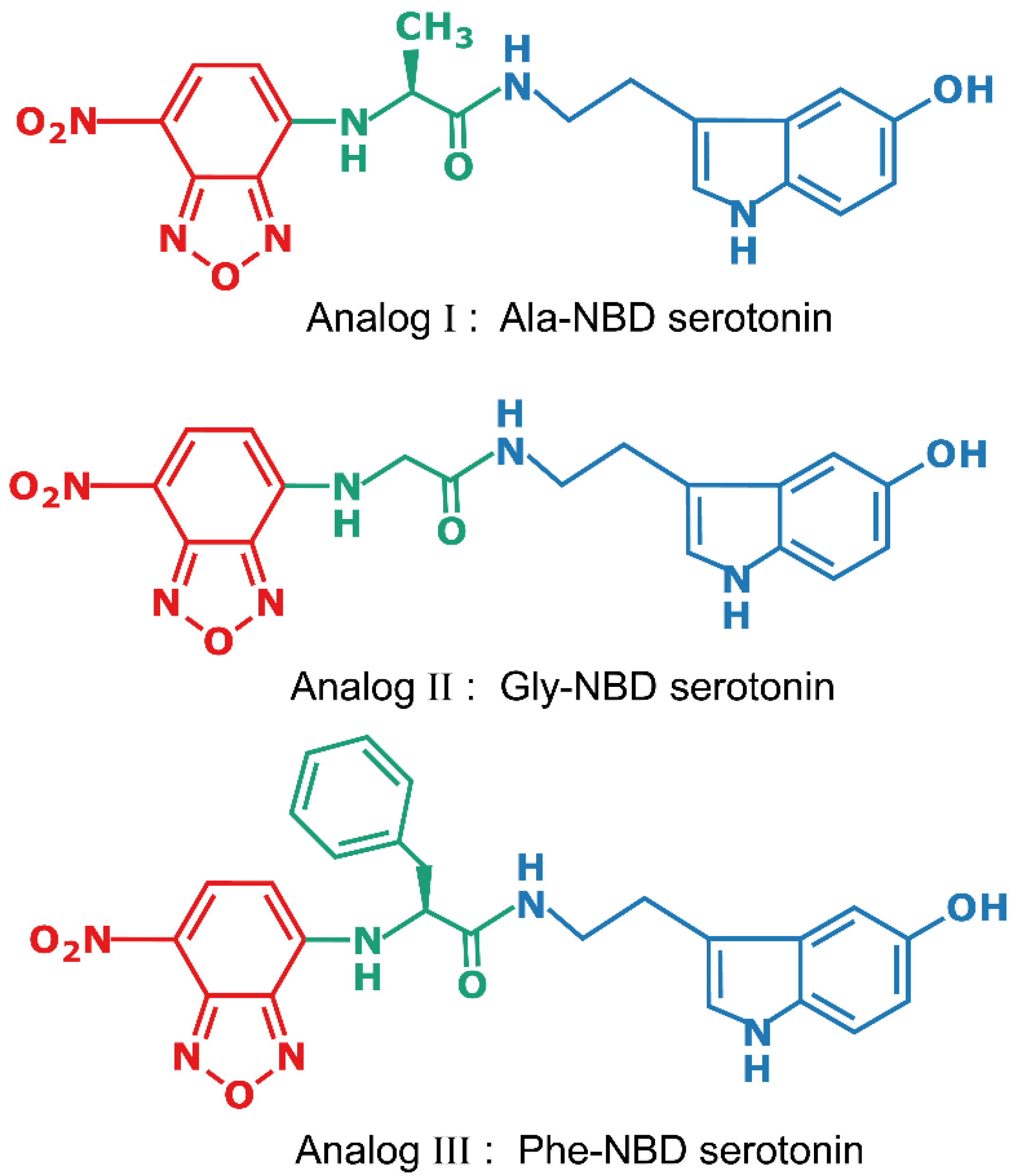
2.1. Design of the Fluorescent Analogs of Serotonin
2.2. Competition Binding of the Fluorescent Ligands to Serotonin1A Receptors
2.3. Fluorescence Characteristics of the Analogs
2.4. Specific Fluorescent Labeling of Serotonin1A Receptors with NBD-Labeled Serotonin Analog
2.5. NBD Group Senses Slow Solvent Relaxation around the Ligand Binding Pocket in the Serotonin1A Receptor
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of NBD-Labeled Serotonin Analogs
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. Cell Membrane Preparation
4.5. Radioligand Binding Assay
4.6. Saturation Binding Assay
4.7. Competition Binding Assay
4.8. Checking the Purity of Organic Solvents Using the ET(30) Dye
4.9. Steady State Fluorescence Measurements
4.10. Absorption Measurements
4.11. Fluorescent Labeling of CHO-K1 Cells Stably Expressing Serotonin1A Receptors
4.12. Fluorescence Microscopy and Imaging
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Whitaker-Azmitia, P.M. The discovery of serotonin and its role in neuroscience. Neuropsychopharmacology 1999, 21, 2S–8S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, B.L.; Azmitia, E.C. Structure and function of the brain serotonin system. Physiol. Rev. 1992, 72, 165–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hen, R. Of mice and flies: Commonalities among 5-HT receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1992, 13, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, D.E.; Nichols, C.D. Serotonin receptors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 1614–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-H.; Lee, L.-T.; Yang, Y.K. Serotonin and mental disorders: A concise review on molecular neuroimaging evidence. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2014, 12, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cowen, P.J.; Browning, M. What has serotonin to do with depression? World Psychiatry 2015, 14, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stiedl, O.; Pappa, E.; Konradsson-Geuken, Å.; Ögren, S.O. The role of the serotonin receptor subtypes 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 and its interaction in emotional learning and memory. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yohn, C.N.; Gergues, M.M.; Samuels, B.A. The role of 5-HT receptors in depression. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carhart-Harris, R.L.; Nutt, D.J. Serotonin and brain function: A tale of two receptors. J. Psychopharm. 2017, 31, 1091–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Underwood, M.D.; Kassir, S.A.; Bakalian, M.J.; Galfalvy, H.; Dwork, A.J.; Mann, J.J.; Arango, V. Serotonin receptors and suicide, major depression, alcohol use disorder and reported early life adversity. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heisler, L.K.; Chu, H.-M.; Brennan, T.J.; Danao, J.A.; Bajwa, P.; Parsons, L.H.; Tecott, L.H. Elevated anxiety and antidepressant-like responses in serotonin 5-HT1A receptor mutant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15049–15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berger, M.; Gray, J.A.; Roth, B.L. The expanded biology of serotonin. Ann. Rev. Med. 2009, 60, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCorvy, J.D.; Roth, B.L. Structure and function of serotonin G protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 150, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peroutka, S.J. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors. J. Neurochem. 1993, 60, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, P.; Kumar, G.A.; Pal, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Biophysics of Serotonin and the Serotonin1a Receptor: Fluorescence and Dynamics. In Serotonin: The Mediator that Spans Evolution; Pilowsky, P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, P.; Mozumder, S.; Bej, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Sengupta, J.; Chattopadhyay, A. Structure, dynamics and lipid interactions of serotonin receptors: Excitements and challenges. Biophys. Rev. 2021, 13, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, N.M.; Ahern, G.P.; Becamel, C.; Bockaert, J.; Camilleri, M.; Chaumont-Dubel, S.; Claeysen, S.; Cunningham, K.A.; Fone, K.C.; Gershon, M. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CX. Classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine; pharmacology and function. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021, 73, 310–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westkaemper, R.B.; Roth, B.L. Structure and Function Reveal Insights in the Pharmacology of 5ht Receptor Subtype. In The Serotonin Receptors; Roth, B.L., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 39–58. [Google Scholar]
- Pucadyil, T.J.; Kalipatnapu, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. The serotonin1A receptor: A representative member of the serotonin receptor family. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2005, 25, 553–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Berardi, F.; Perrone, R. 5-HT1A receptor, an old target for new therapeutic agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiorino, F.; Severino, B.; Magli, E.; Ciano, A.; Caliendo, G.; Santagada, V.; Frecentese, F.; Perissutti, E. 5-HT1A receptor: An old target as a new attractive tool in drug discovery from CNS to cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4407–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Rukmini, R.; Mukherjee, S. Photophysics of a neurotransmitter: Ionization and spectroscopic properties of serotonin. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 1952–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunn, K.; Maxfield, F.R. Ratio imaging instrumentation. Methods Cell Biol. 2003, 56, 217–236. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, A. Chemistry and biology of N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)-labeled lipids: Fluorescent probes of biological and model membranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1990, 53, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Application of NBD-Labeled Lipids in Membrane and Cell Biology. In Springer Series on Fluorescence; Mély, Y., Duportail, G., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 13, pp. 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T.; Pagano, R.E. ATP-dependent fusion of liposomes with the Golgi apparatus of perforated cells. Cell 1988, 55, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, K.S.; Reinhart, G.D.; Johnson, A.E. The signal sequence moves through a ribosomal tunnel into a noncytoplasmic aqueous environment at the ER membrane early in translocation. Cell 1993, 73, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazeres, S.; Schram, V.; Tocanne, J.-F.; Lopez, A. 7-Nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-4-yl-labeled phospholipids in lipid membranes: Differences in fluorescence behavior. Biophys. J. 1996, 71, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, S.; Lin, J.; Do, H.; Johnson, A.E. Both lumenal and cytosolic gating of the aqueous ER translocon pore are regulated from inside the ribosome during membrane protein integration. Cell 1997, 90, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Mukherjee, S. Red edge excitation shift of a deeply embedded membrane probe: Implications in water penetration in the bilayer. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 8180–8185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucadyil, T.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Organization and dynamics of NBD-labeled lipids in membranes analyzed by fluorescence recovery after photobleaching. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 1975–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajevardipour, A.; Chon, J.W.M.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Clayton, A.H.A. Imaging cellular dynamics with spectral relaxation imaging microscopy: Distinct spectral dynamics in Golgi membranes of living cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; London, E. Spectroscopic and ionization properties of N-(7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl)-labeled lipids in model membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 938, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajarathnam, K.; Hochman, J.; Schindler, M.; Ferguson-Miller, S. Synthesis, location, and lateral mobility of fluorescently labeled ubiquinone 10 in mitochondrial and artificial membranes. Biochemistry 1989, 28, 3168–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Struve, W.S. Time-resolved fluorescence of nitrobenzoxadiazole-aminohexanoic acid: Effect of intermolecular hydrogen-bonding on non-radiative decay. Photochem. Photobiol. 1991, 54, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Mukherjee, S. Fluorophore environments in membrane-bound probes: A red edge excitation shift study. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 3804–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fery-Forgues, S.; Fayet, J.-P.; Lopez, A. Drastic changes in the fluorescence properties of NBD probes with the polarity of the medium: Involvement of a TICT state? J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 1993, 70, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Samanta, A.; Soujanya, T. Dipole moment change of NBD group upon excitation studied using solvatochromic and quantum chemical approaches: Implications in membrane research. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 2809–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Structural transition in the micellar assembly: A fluorescence study. J. Fluoresc. 1999, 9, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Raghuraman, H. Reverse micellar organization and dynamics: A wavelength-selective fluorescence approach. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 13002–13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuraman, H.; Chattopadhyay, A. Orientation and dynamics of melittin in membranes of varying composition utilizing NBD fluorescence. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagano, R.E.; Sleight, R.G. Defining lipid transport pathways in animal cells. Science 1985, 229, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meer, G.; Stelzer, E.H.K.; Wijnaendts-van-Resandt, R.W.; Simons, K. Sorting of sphingolipids in epithelial (Madin-Darby canine kidney) cells. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 105, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koval, M.; Pagano, R.E. Sorting of an internalized plasma membrane lipid between recycling and degradative pathways in normal and Niemann-Pick, type A fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 1990, 111, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, R.G. Fluorescent glycerolipid probes. Synthesis and use for examining intracellular lipid trafficking. Methods Mol. Biol. 1994, 27, 143–160. [Google Scholar]
- Huijbregts, R.P.H.; Kroon, A.I.P.M.D.; Kruijff, B.D. Rapid transmembrane movement of C6-NBD-labeled phospholipids across the inner membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1280, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grant, A.M.; Hanson, P.K.; Malone, L.; Nichols, J.W. NBD-labeled phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine are internalized by transbilayer transport across the yeast plasma membrane. Traffic 2001, 2, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.M.C.; Ogilvie, W.W.; Johnston, L.J. NBD-cholesterol probes to track cholesterol distribution in model membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elvington, S.M.; Bu, F.; Nichols, J.W. Fluorescent, acyl chain-labeled phosphatidylcholine analogs reveal novel transport pathways across the plasma membrane of yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40957–40964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, B.Y.; Karschin, A.; Branchek, T.; Davidson, N.; Lester, H.A. The role of conserved aspartate and serine residues in ligand binding and in function of the 5-HT1A receptor: A site-directed mutation study. FEBS Lett. 1992, 312, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bremner, D.H.; Ringan, N.S.; Wishart, G. Modeling of the agonist binding site of serotonin human 5-HT1A, 5-T1Dα and 5-HT1Dβ receptors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 32, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paila, Y.D.; Tiwari, S.; Sengupta, D.; Chattopadhyay, A. Molecular modeling of the human serotonin1A receptor: Role of membrane cholesterol in ligand binding of the receptor. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylte, I.; Edvardsen, Ø.; Dahl, S.G. Molecular modelling of UH-301 and 5-HT1a receptor interactions. Protein Eng. 1996, 9, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuipers, W.; Link, R.; Standaar, P.J.; Stoit, A.R.; Van Wijngaarden, I.; Leurs, R.; Ijzerman, A.P. Study of the interaction between aryloxypropanolamines and Asn386 in helix VII of the human 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Mao, C.; Zhou, X.E.; Cheng, X.; Simon, I.A.; Shen, D.-D.; et al. Structural insights into the lipid and ligand regulation of serotonin receptors. Nature 2021, 592, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogendorf, A.S.; Hogendorf, A.; Popiołek-Barczyk, K.; Ciechanowska, A.; Mika, J.; Satała, G.; Walczak, M.; Latacz, G.; Handzlik, J.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; et al. Fluorinated indole-imidazole conjugates: Selective orally bioavailable 5-HT7 receptor low-basicity agonists, potential neuropathic painkillers. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 170, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podlewska, S.; Bugno, R.; Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Bojarski, A.J.; Handzlik, J. Low basicity as a characteristic for atypical ligands of serotonin receptor 5-HT2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozlan, H.; Mestikawy, S.E.; Pichat, L.; Glowinski, J.; Hamon, M. Identification of presynaptic serotonin autoreceptors using a new ligand: 3H-PAT. Nature 1983, 305, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.D.; Mestikawy, S.E.; Emerit, M.B.; Pichat, L.; Hamon, M.; Gozlan, H. [3H]8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin binding to pre- and postsynatptic 5-hydroxytryptamine sites in various regions of the rat brain. J. Neurochem. 1985, 44, 1685–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (IC50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar]
- Hulme, E.C. Receptor-Effector Coupling: A Practical Approach; IRL Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chanda, P.K.; Minchin, M.C.; Davis, A.R.; Greenberg, L.; Reilly, Y.; McGregor, W.H.; Bhat, R.; Lubeck, M.D.; Mizutani, S.; Hung, P.P. Identification of residues important for ligand binding to the human 5-hydroxytryptamine1A serotonin receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 43, 516–520. [Google Scholar]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kalipatnapu, S.; Pucadyil, T.J.; Harikumar, K.G.; Chattopadhyay, A. Ligand binding characteristics of the human serotonin1A receptor heterologously expressed in CHO cells. Biosci. Rep. 2004, 24, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, S.; Chaudhuri, A.; Chattopadhyay, A. Organization and dynamics of membrane probes and proteins utilizing the red edge excitation shift. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 5693–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Haldar, S. Dynamic insight into protein structure utilizing red edge excitation shift. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Wavelength-selective fluorescence as a novel tool to study organization and dynamics in complex biological systems. J. Fluoresc. 1995, 5, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demchenko, A.P. Site-selective red-edge effects. Methods Enzymol. 2008, 450, 59–78. [Google Scholar]
- Brahma, R.; Raghuraman, H. Novel insights in linking solvent relaxation dynamics and protein conformations utilizing red edge excitation shift approach. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2021, 5, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leopoldo, M.; Lacivita, E.; Berardi, F.; Perrone, R. Developments in fluorescent probes for receptor research. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddart, L.A.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Briddon, S.J.; Hill, S.J. Probing the pharmacology of G protein-coupled receptors with fluorescent ligands. Neuropharmacology 2015, 98, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGrath, J.C.; Arribas, S.; Daly, C.J. Fluorescent ligands for the study of receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1996, 17, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Masotti, A.C.; Contino, M.; Berardi, F.; Perrone, R.; Ganguly, S.; Jafurulla, M.; Chattopadhyay, A. Synthesis and characterization of environment-sensitive fluorescent ligands for human 5-HT1A receptors with 1-arylpiperazine structure. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 7892–7896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacivita, E.; Masotti, A.C.; Jafurulla, M.; Saxena, R.; Rangaraj, N.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Colabufo, N.A.; Berardi, F.; Perrone, R.; Leopoldo, M. Identification of a red-emitting fluorescent ligand suitable for in vitro visualization of human serotonin 5-HT1A receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6628–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, R.; Zuber, J.; Connelly, S.M.; Mathew, E.; Dumont, M.E. Fluorescent approaches for understanding interactions of ligands with G protein coupled receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soave, M.; Briddon, S.J.; Hill, S.J.; Stoddart, L.A. Fluorescent ligands: Bringing light to emerging GPCR paradigms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rocheville, M.; Lange, D.C.; Kumar, U.; Patel, S.C.; Patel, R.C.; Patel, Y.C. Receptors for dopamine and somatostatin: Formation of hetero-oligomers with enhanced functional activity. Science 2000, 288, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roettger, B.F.; Pinon, D.I.; Burghardt, T.P.; Miller, L.J. Regulation of lateral mobility and cellular trafficking of the CCK receptor by a partial agonist. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, C539–C547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pucadyil, T.J.; Kalipatnapu, S.; Harikumar, K.G.; Rangaraj, N.; Karnik, S.S.; Chattopadhyay, A. G-protein-dependent cell surface dynamics of the human serotonin1A receptor tagged to yellow fluorescent protein. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 15852–15862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucadyil, T.J.; Chattopadhyay, A. Cholesterol depletion induces dynamic confinement of the G-protein coupled serotonin1A receptor in the plasma membrane of living cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1768, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Jafurulla, M. Novel insights in membrane biology utilizing fluorescence recovery after photobleaching. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 842, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, P.; Chattopadhyay, A. Exploring Membrane Lipid and Protein Diffusion by FRAP. In Analysis of Membrane Lipids; Prasad, R., Singh, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 119–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sako, Y.; Minoghchi, S.; Yanagida, T. Single-molecule imaging of EGFR signalling on the surface of living cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, S.; Chattopadhyay, A. Cholesterol depletion mimics the effect of cytoskeletal destabilization on membrane dynamics of the serotonin1A receptor: A zFCS study. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auer, M.; Moore, K.J.; Meyer-Almes, F.J.; Guenther, R.; Pope, A.J.; Stoeckli, K.A. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy: Lead discovery by miniaturized HTS. Drug Discov. Today 1998, 3, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wacker, D.; Wang, C.; Katritch, V.; Han, G.W.; Huang, X.-P.; Vardy, E.; McCorvy, J.D.; Jiang, Y.; Chu, M.; Siu, F.Y.; et al. Structural features for functional selectivity at serotonin receptors. Science 2013, 340, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, H.; Wacker, D.; Katritch, V.; Han, G.W.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.-P.; Vardy, E.; et al. Structural basis for molecular recognition at serotonin receptors. Science 2013, 340, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; McCorvy, J.D.; Harpsøe, K.; Lansu, K.; Yuan, S.; Popov, P.; Qu, L.; Pu, M.; Che, T.; Nikolajsen, L.F.; et al. 5-HT2C receptor structures reveal the structural basis of GPCR polypharmacology. Cell 2018, 172, 719–730.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Che, T.; Panova, O.; DiBerto, J.F.; Lyu, J.; Krumm, B.E.; Wacker, D.; Robertson, M.J.; Seven, A.B.; Nichols, D.E.; et al. Structure of a hallucinogen-activated Gq-coupled 5-HT2A serotonin receptor. Cell 2020, 182, 1574–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surgand, J.-S.; Rodrigo, J.; Kellenberger, E.; Rognan, D. A chemogenomic analysis of the transmembrane binding cavity of human G-protein-coupled receptors. Proteins 2006, 62, 509–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jürss, R.; Prinz, H.; Maelicke, A. NBD-5-acylcholine: Fluorescent analog of acetylcholine and agonist at the neuromuscular junction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 1064–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, K.A.; Ukena, D.; Padgett, W.; Kirk, K.L.; Daly, J.W. Molecular probes for extracellular adenosine receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1987, 36, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakthavachalam, V.; Baindur, N.; Madras, B.K.; Neumeyer, J.L. Fluorescent probes for dopamine receptors: Synthesis and characterization of fluorescein and 7-nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl conjugates of D-1 and D-2 receptor ligands. J. Med. Chem. 1991, 34, 3235–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, S.; Medzihradsky, F.; Seyed-Mozaffari, A.; Emmerson, P.J. Synthesis and characterization of 7-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole (NBD)-labeled fluorescent opioids. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992, 43, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozikowski, A.P.; Kotoula, M.; Ma, D.; Boujrad, N.; Tuckmantel, W.; Papadopoulos, V. Synthesis and biology of a 7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazol-4-yl derivative of 2-phenylindole-3-acetamide: A fluorescent probe for the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 2435–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitinger, H.-G.A.; Wieboldt, R.; Ramesh, D.; Carpenter, B.K.; Hess, G.P. Synthesis and characterization of photolabile derivatives of serotonin for chemical kinetic investigations of the serotonin 5-HT3 receptor. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 5500–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.T.; Mallia, A.K.; Gartner, F.H.; Provenzano, M.D.; Fujimoto, E.K.; Goeke, N.M.; Olson, B.J.; Klenk, D.C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| NBD-Labeled Analogs | IC50 (μM) | Ki (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| I | 1.74 ± 0.44 | 1.41 ± 0.36 |
| II | 3.43 ± 1.73 | 3.15 ± 1.41 |
| III | 13.70 ± 3.36 | 11.15 ± 2.73 |
| Solvents | Dielectric Constant b | Emission Maximum (nm) | Relative Intensity c | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analog | Analog | ||||||
| I | II | III | I | II | III | ||
| Tetrahydrofuran | 7.58 | 520 | 520 | 525 | 3.7 | 2.4 | 4.8 |
| Isopropanol | 18.30 | 520 | 524 | 525 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 1.8 |
| Acetone | 20.70 | 520 | 523 | 526 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 3.6 |
| Ethanol | 24.30 | 520 | 526 | 528 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 1.7 |
| Methanol | 32.63 | 526 | 530 | 532 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 1.3 |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide | 46.45 | 541 | 540 | 542 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarkar, P.; Harikumar, K.G.; Rawat, S.S.; Das, S.; Chakraborty, T.K.; Chattopadhyay, A. Environment-Sensitive Fluorescence of 7-Nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl (NBD)-Labeled Ligands for Serotonin Receptors. Molecules 2021, 26, 3848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133848
Sarkar P, Harikumar KG, Rawat SS, Das S, Chakraborty TK, Chattopadhyay A. Environment-Sensitive Fluorescence of 7-Nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl (NBD)-Labeled Ligands for Serotonin Receptors. Molecules. 2021; 26(13):3848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133848
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarkar, Parijat, Kaleeckal G. Harikumar, Satinder S. Rawat, Sanjib Das, Tushar K. Chakraborty, and Amitabha Chattopadhyay. 2021. "Environment-Sensitive Fluorescence of 7-Nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl (NBD)-Labeled Ligands for Serotonin Receptors" Molecules 26, no. 13: 3848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133848
APA StyleSarkar, P., Harikumar, K. G., Rawat, S. S., Das, S., Chakraborty, T. K., & Chattopadhyay, A. (2021). Environment-Sensitive Fluorescence of 7-Nitrobenz-2-oxa-1,3-diazol-4-yl (NBD)-Labeled Ligands for Serotonin Receptors. Molecules, 26(13), 3848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133848






