Application of Green Algal Planktochlorella nurekis Biomasses to Modulate Growth of Selected Microbial Species
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
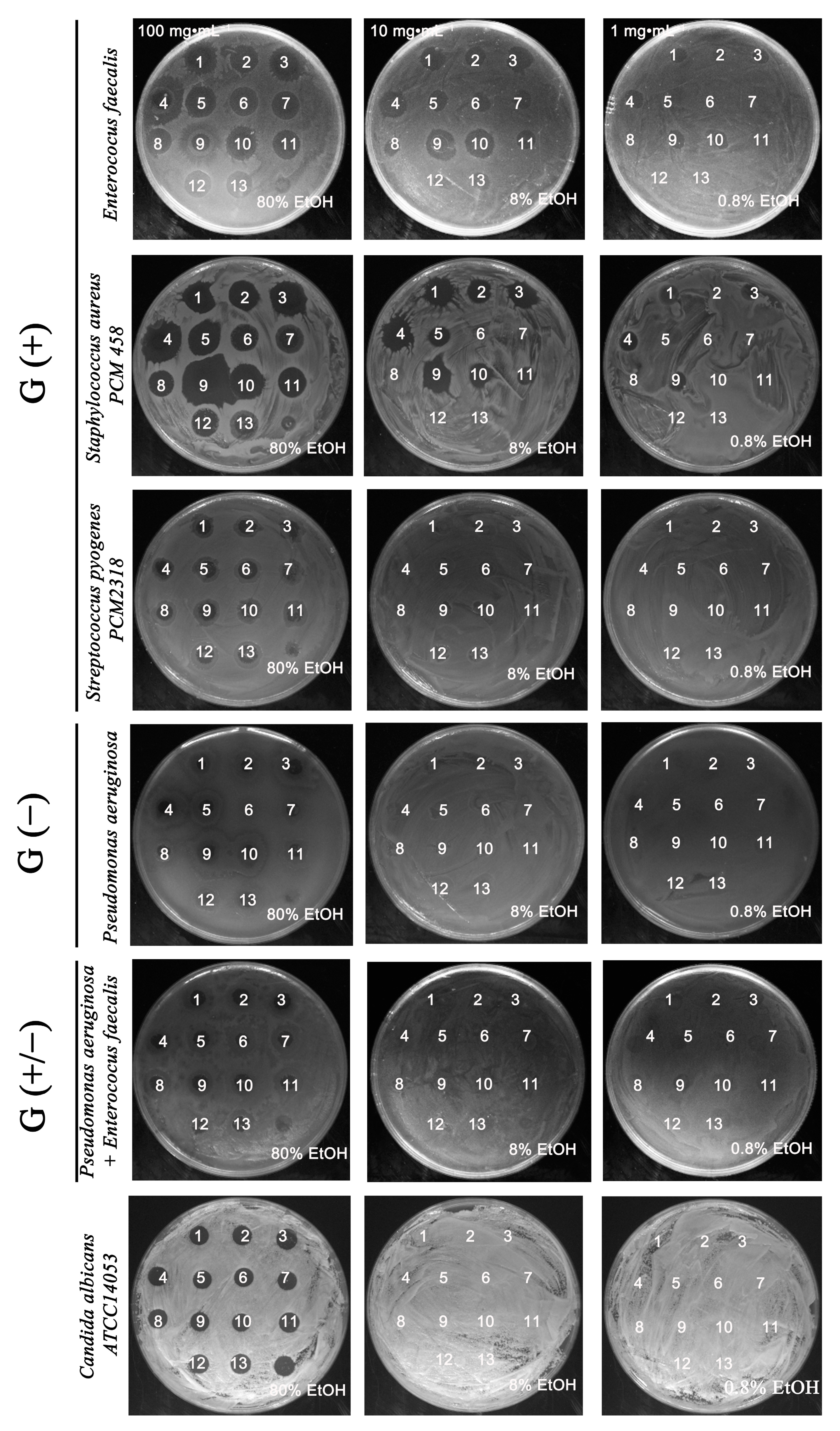
2.1. Antimicrobially Active Ethanolic Extracts of the Microalga Planktochlorella nurekis
2.2. Different Effects (Stimulatory and Inhibitory) of Water and Ethanolic Extracts (WE, EE) on Metabolic Activity of the Studied Microorganisms
2.3. Probiotic Efficiency of Planktochlorella Nurekis Extracts—Stimulating Growth of Lactic Acid Bacteria Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC 53103
2.4. Absence of Synergism and Antagonism between Selected Groups of Bacteria in the Presence of Algal Extracts
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Microalgal Extracts Preparation
3.2. Bacterial Strains and Antimicrobial Potential of Algal Extracts against Selected Microorganisms
3.3. Fatty Acids Composition Analysis
3.4. Growth Inhibition Assay—Effect of Water and Ethanolic Extracts of Microalgae (WE, EE) on Metabolic Activity of Tested Microorganisms in Liquid Cultures
3.5. Prebiotic Effect of Water and Ethanolic Algal Extracts (WE, EE) on the Growth of the Probiotic Species Lactobacillus rhamnosus ATCC 53103
3.6. Determination of the Effect of Algal Extracts on the Synergistic Growth of a 2 Species Culture of Gram (+/+), Gram (−/−), Gram (+/−) Bacteria Using a Resazurin Assay
- Gram-negative (−) with Gram-positive (+) (Escherichia coli PCM 2209 + Enterococcus faecalis)
- Gram-positive (+) with Gram-positive (+) (Staphylococcus aureus PCM 458 + Streptococcus pyogenes PCM 2318)
- Gram-negative (−) with Gram-negative (−) (Escherichia coli PCM 2209 + Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
3.7. Effect of Water (WE) and Ethanolic (EE) Algal Extracts P. nurekis on a Microbial Antagonism
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Prestinaci, F.; Pezzotti, P.; Pantosti, A. Antimicrobial resistance: A global multifaceted phenomenon. Pathog. Glob. Health 2015, 109, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spera, A.M.; Esposito, S.; Pagliano, P. Emerging antibiotic resistance: Carbapenemase-producing enterobacteria. Bad new bugs, still no new drugs. Infez. Med. 2019, 27, 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Falaise, C.; François, C.; Travers, M.A.; Morga, B.; Haure, J.; Tremblay, R.; Turcotte, F.; Pasetto, P.; Gastineau, R.; Hardivillier, Y.; et al. Antimicrobial Compounds from Eukaryotic Microalgae against Human Pathogens and Diseases in Aquaculture. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Čermák, L.; Pražáková, Š.; Marounek, M.; Skrivan, M.; Skřivanová, E. Effect of green alga Planktochlorella nurekis on selected bacteria revealed antibacterial activity in vitro. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 60, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtolera, M.S.P.; Semesi, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Extracts from Six Green Algae from Tanzania. Curr. Trends Mar. Bot. Res. East Afr. Reg. 1996, 211–217. [Google Scholar]
- Somarathna, T.; Fernando, W.; Ranaweera, K.; Premakumara, G.; Abeysinghe, T.; Weerakkody, N. Antimicrobial activity and phytochemical screening of Alpinia malaccensis (Ran-kiriya) against food-borne bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 125, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashjoor, S.; Yousefzadi, M.; Esmaeili, M.A.; Rafiee, R. Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial activity of marine macro algae (Dictyotaceae and Ulvaceae) from the Persian Gulf. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pratt, R.; Daniels, T.C.; Eiler, J.J.; Gunnison, J.B.; Kumler, W.D.; Oneto, J.F.; Strait, L.A.; Spoehr, H.A.; Hardin, G.J.; Milner, H.W.; et al. Chlorellin, an Antibacterial Substance from Chlorella. Science 1944, 99, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, G.; Ameneh, M.; Abdolali, M.; Shadman, S.; Mohammad Hossein, M. Antifungal and Antibacterial Activity of the Microalgae Collected from Paddy Fields of Iran: Characterization of Antimicrobial Activity of Chroococcus dispersus. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 7, 904–910. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, N.; Gupta, S.; Singh, D.P. Antimicrobial and antioxidant property of commonly found microalgae Spirulina platensis, Nostoc muscorum and Chlorella pyrenoidosa against some pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 4866. [Google Scholar]
- Cakmak, Y.S.; Kaya, M.; Asan-Ozusaglam, M. Biochemical composition and bioactivity screening of various extracts from Dunaliella salina, a green microalga. EXCLI J. 2014, 13, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marrez, D.A.; Naguib, M.M.; Sultan, Y.Y.; Higazy, A.M. Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of Scenedesmus obliquus metabolites. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd El Baky, H.H.; El-Baroty, G.S. Healthy Benefit of Microalgal Bioactive Substances. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 1, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, Y.Y.; Ali, M.A.; Darwesh, O.M.; Embaby, M.A.; Marrez, D.A. Influence of nitrogen source in culture media on antimicrobial activity of Microcoleus lacustris and Oscillatoria rubescens. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Szpyrka, E.; Broda, D.; Oklejewicz, B.; Podbielska, M.; Slowik-Borowiec, M.; Jagusztyn, B.; Chrzanowski, G.; Kus-Liskiewicz, M.; Duda, M.; Zuczek, J.; et al. A Non-Vector Approach to Increase Lipid Levels in the Microalga Planktochlorella nurekis. Molecules 2020, 25, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, G. Infections caused by staphylococci. The human as a source of infection for S. aureus and coagulase negative staphylococci. Fortschr. Med. 1991, 109, 437–440. [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland, E.L.; Nathwani, N.; Dore, C.J.; Lewis, J.D. Bacterial colonisation of leg ulcers and its effect on the success rate of skin grafting. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 1988, 70, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, T.; Ullah, S.R.; Mehmood, K.; Andleeb, S. Vancomycin resistant Enterococci: A brief review. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2018, 68, 768–772. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, K.; Ahmadi, K.; Hashemian, A.M.; Bolvardi, E.; Hosseini, P.K. Vancomycin-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeroginosa in the Cases of Trauma. Med. Arch. 2016, 70, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wirsching, S.; Michel, S.; Köhler, G.; Morschhäuser, J. Activation of the multiple drug resistance gene MDR1 in fluconazole-resistant, clinical Candida albicans strains is caused by mutations in a trans-regulatory factor. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poirel, L.; Madec, J.Y.; Lupo, A.; Schink, A.K.; Kieffer, N.; Nordmann, P.; Schwarz, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli. In Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Livestock and Companion Animals; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dolganyuk, V.; Belova, D.; Babich, O.; Prosekov, A.; Ivanova, S.; Katserov, D.; Patyukov, N.; Sukhikh, S. Microalgae: A Promising Source of Valuable Bioproducts. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beveridge, T.J. Structures of gram-negative cell walls and their derived membrane vesicles. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 4725–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosanic, M.; Ranković, B.; Stanojković, T. Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer activity of 3 Umbilicaria species. J. Food Sci. 2011, 77, T20–T25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rang, H.P.; Dale, M.M.; Ritter, J.M.; Moore, P.K. Pharmacology, 5th ed.; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Albouchi, F.; Hassen, I.; Casabianca, H.; Hosni, K. Phytochemicals, antioxidant, antimicrobial and phytotoxic activities of Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) Swingle leaves. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2013, 87, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latgé, J.-P. The cell wall: A carbohydrate armour for the fungal cell. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, M.J.; Falqué, E.; Domínguez, H. Antimicrobial Action of Compounds from Marine Seaweed. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Shweta, K.; Jayanthi, G.; Prabhu, K.; Thirumaran, G. Antimicrobial and antioxidant potential of selected seaweeds from Kodinar, Southern Coast of Saurashtra, Gujarat, India. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Najdenski, H.M.; Gigova, L.G.; Iliev, I.I.; Pilarski, P.S.; Lukavský, J.; Tsvetkova, I.V.; Ninova, M.S.; Kussovski, V. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of selected microalgae and cyanobacteria. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pina-Pérez, M.; Rivas, A.; Martínez, A.; Rodrigo, D. Antimicrobial potential of macro and microalgae against pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms in food. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik-Skowrońska, B. Resistance, accumulation and allocation of zinc in two ecotypes of the green alga Stigeoclonium tenue Kütz. coming from habitats of different heavy metal concentrations. Aquat. Bot. 2003, 75, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosanić, M.; Ranković, B.; Stanojković, T. Biological activities of two macroalgae from Adriatic coast of Montenegro. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desbois, A.P.; Smith, V.J. Antibacterial free fatty acids: Activities, mechanisms of action and biotechnological potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero, M.; Ibáñez, E.; Cifuentes, A.; Reglero, G.; Santoyo, S. Dunaliella salina microalga pressurized liquid extracts as potential antimicrobials. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suresh, A.; Praveenkumar, R.; Thangaraj, R.; Oscar, F.L.; Baldev, E.; Dhanasekaran, D.; Thajuddin, N. Microalgal fatty acid methyl ester a new source of bioactive compounds with antimicrobial activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2014, 4, S979–S984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maadane, A.; Merghoub, N.; El Mernissi, N.; Ainane, T.; Amzazi, S. Antimicrobial activity of marine microalgae isolated from Moroccan coastlines. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2017, 6, 1257–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoramnia, A.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Ghanbari, R.; Ajdari, Z.; Lai, O.M. Improvement of medium chain fatty acid content and antimicrobial activity of coconut oil via solid-state fermentation using a Malaysian Geotrichum candidum. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 954542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El Shoubaky, G.A.; Salem, E.A. Active ingredients fatty acids as antibacterial agent from the brown algae Padina pavonica and Hormophysa triquetra. J. Coast. Life Med. 2014, 2, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Ruffell, S.E.; Müller, K.M.; McConkey, B.J. Comparative assessment of microalgal fatty acids as topical antibiotics. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saif SS, A.L.; Abdel-Raouf, N.; El-Wazanani, H.A.; Aref, I.A. Antibacterial substances from marine algae isolated from Jeddah coast of Red sea, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wille, J.J.; Kydonieus, A. Palmitoleic acid isomer (C16:1delta6) in human skin sebum is effective against gram-positive bacteria. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2003, 16, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.J.; Yoo, J.-S.; Lee, T.-G.; Cho, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, W.-G. Fatty acid synthesis is a target for antibacterial activity of unsaturated fatty acids. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5157–5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dilika, F.; Bremner, P.D.; Meyer, J.J.M. Antibacterial activity of linoleic and oleic acids isolated from Helichrysum pedunculatum: A plant used during circumcision rites. Fitoterapia 2000, 71, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freese, E.; Sheu, C.W.; Galliers, E. Function of Lipophilic Acids as Antimicrobial Food Additives. Nature 1973, 241, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabara, J.J.; Swieczkowski, D.M.; Conley, A.J.; Truant, J.P. Fatty Acids and Derivatives as Antimicrobial Agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1972, 2, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheu, C.W.; Freese, E. Lipopolysaccharide Layer Protection of Gram-Negative Bacteria Against Inhibition by Long-Chain Fatty Acids. J. Bacteriol. 1973, 115, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, V.J.; Desbois, A.P.; Dyrynda, E.A. Conventional and unconventional antimicrobials from fish, marine invertebrates and micro-algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1213–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boutin, R.; Munnier, E.; Renaudeau, N.; Girardot, M.; Pinault, M.; Chevalier, S.; Chourpa, I.; Clément-Larosière, B.; Imbert, C.; Boudesocque-Delaye, L. Spirulina platensis sustainable lipid extracts in alginate-based nanocarriers: An algal approach against biofilms. Algal Res. 2019, 37, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.S.; Saber, A.A. Antifungal Potential of the Bioactive Constituents in Extracts of the Mostly Untapped Brown Seaweed Hormophysa cuneiformis from The Egyptian Coastal Waters. Egypt. J. Bot. 2019, 59, 695–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuwijitjaru, P.; Adachi, S.; Matsuno, R. Solubility of saturated fatty acids in water at elevated temperatures. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 1723–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanthoor-Koopmans, M.; Wijffels, R.H.; Barbosa, M.J.; Eppink, M.H. Biorefinery of microalgae for food and fuel. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppink, M.H.M.; Olivieri, G.; Reith, H.; Berg, C.V.D.; Barbosa, M.J.; Wijffels, R.H. From Current Algae Products to Future Biorefinery Practices: A Review. Biorefineries 2017, 166, 99–123. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.; Silva, S.A.; Carpena, M.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Gullón, P.; Barroso, M.F.; Prieto, M.; Simal-Gandara, J. Macroalgae as a Source of Valuable Antimicrobial Compounds: Extraction and Applications. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsenani, F.; Tupally, K.R.; Chua, E.T.; Eltanahy, E.; Alsufyani, H.; Parekh, H.S.; Schenk, P.M. Evaluation of microalgae and cyanobacteria as potential sources of antimicrobial compounds. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jesus Raposo, M.F.; de Morais, A.M.M.B.; de Morais, R.M.S.C. Emergent Sources of Prebiotics: Seaweeds and Microalgae. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmik, D.; Dubey, J.; Mehra, S. Probiotic Efficiency of Spirulina platensis-Stimulating Growth of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2009, 6, 546–549. [Google Scholar]
- Adamczyk-Grochala, J.; Wnuk, M.; Duda, M.; Zuczek, J.; Lewinska, A. Treatment with Modified Extracts of the Microalga Planktochlorella nurekis Attenuates the Development of Stress-Induced Senescence in Human Skin Cells. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneemann, I.; Nagel, K.; Kajahn, I.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Comprehensive investigation of marine Actinobacteria associated with the sponge Halichondria panicea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3702–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Potocki, L.; Oklejewicz, B.; Kuna, E.; Szpyrka, E.; Duda, M.; Zuczek, J. Application of Green Algal Planktochlorella nurekis Biomasses to Modulate Growth of Selected Microbial Species. Molecules 2021, 26, 4038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134038
Potocki L, Oklejewicz B, Kuna E, Szpyrka E, Duda M, Zuczek J. Application of Green Algal Planktochlorella nurekis Biomasses to Modulate Growth of Selected Microbial Species. Molecules. 2021; 26(13):4038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134038
Chicago/Turabian StylePotocki, Leszek, Bernadetta Oklejewicz, Ewelina Kuna, Ewa Szpyrka, Magdalena Duda, and Janusz Zuczek. 2021. "Application of Green Algal Planktochlorella nurekis Biomasses to Modulate Growth of Selected Microbial Species" Molecules 26, no. 13: 4038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134038
APA StylePotocki, L., Oklejewicz, B., Kuna, E., Szpyrka, E., Duda, M., & Zuczek, J. (2021). Application of Green Algal Planktochlorella nurekis Biomasses to Modulate Growth of Selected Microbial Species. Molecules, 26(13), 4038. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134038






