Probing the Nature of Chemical Bonds by Atomic Force Microscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
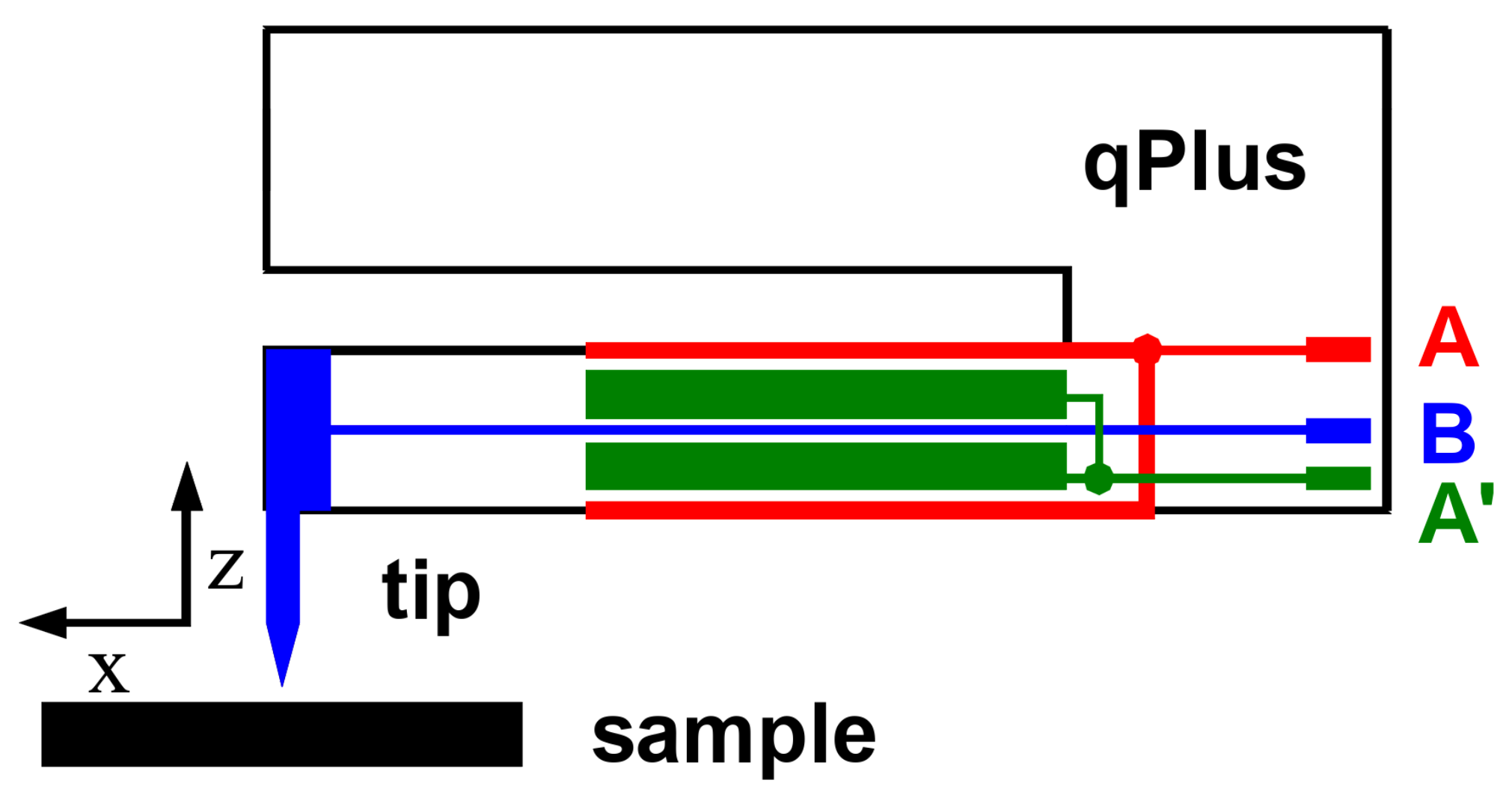
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
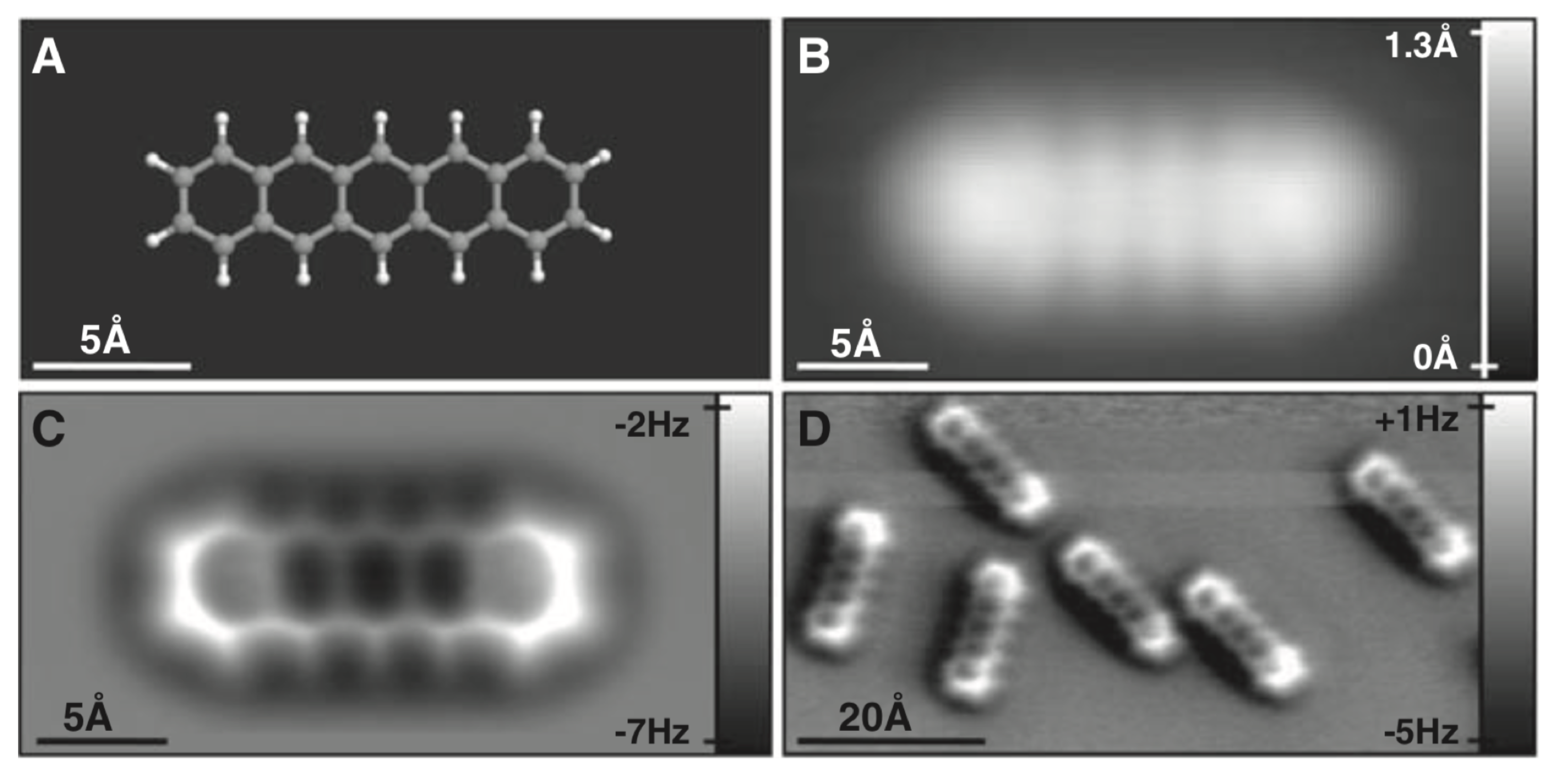
3.1. Covalent Bonds
3.2. Van-der-Waals Bonds
3.3. Metallic Bonds
3.4. Ionic Bonds
3.5. Antibonds Due to Pauli Repulsion and Their Role in Imaging Organic Molecules
3.6. Hydrogen Bonds
3.7. Transition from Physisorption to Chemisorption
3.8. Measuring the Very Weak Bond to an Artificial Atom with a Very Low Electron Density
3.9. Resolving the Directionality of Covalent Bonds by AFM—Subatomic Spatial Resolution
4. Discussion
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| COFI | Carbon monOxide Front atom Identification |
| DFT | Density Functional Theory |
| DFT D3 | DFT dispersion correction (van-der-Waals) |
| FM | Frequency Modulation |
| STM | Scanning Tunneling Microscopy |
| UHV | UltraHigh Vacuum |
References
- Pauling, L. The Nature of the Chemical Bond and the Structure of Molecules and Crystals, 3rd ed.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Binnig, G.; Quate, C.F.; Gerber, C. Atomic Force Microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 56, 930–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnig, G.; Rohrer, H.; Gerber, C.; Weibel, E. Surface Studies by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnig, G.; Rohrer, H.; Gerber, C.; Weibel, E. 7 × 7 Reconstruction on Si (111) Resolved in Real Space. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983, 50, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. Atomic Resolution of the Silicon (111)–(7×7) Surface by Atomic Force Microscopy. Science 1995, 267, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R. Interaction of orbitals through space and through bonds. Account. Chem. Res. 1971, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; Pérez, R. Dynamic atomic force microscopy methods. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2002, 47, 197–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. Advances in atomic force microscopy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 949–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. AFM’s path to atomic resolution. Mater. Today 2005, 8, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custance, O.; Perez, R.; Morita, S. Atomic force microscopy as a tool for atom manipulation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.; Wiesendanger, R.; Meyer, E. (Eds.) Noncontact Atomic Force Microscopy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, E.; Hug, H.J.; Bennewitz, R. (Eds.) Scanning Probe Microscopy. The Lab on a Tip; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, S.; Giessibl, F.J.; Wiesendanger, R.; Meyer, E. (Eds.) Noncontact Atomic Force Microscopy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Morita, S.; Giessibl, F.J.; Meyer, E.; Wiesendanger, R. (Eds.) Noncontact Atomic Force Microscopy; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Y. Atomic and subnanometer resolution in ambient conditions by atomic force microscopy. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2009, 64, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufrene, Y.F.; Andio, T.; Garcia, R.; Alsteens, D.; Martinez-Martin, D.; Engel, A.; Gerber, C.; Müller, D.J. Imaging modes of atomic force microscopy for application in molecular and cell biology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J.; Hembacher, S.; Bielefeldt, H.; Mannhart, J. Subatomic Features on the Silicon (111)–(7×7) Surface Observed by Atomic Force Microscopy. Science 2000, 289, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, H.J.; Lantz, M.A.; Abdurixit, A.P.; van Schendel, J.A.; Hoffmann, R.; Kappenberger, P.; Baratoff, A.; Giessibl, F.J.; Hembacher, S.; Bielefeldt, H.; et al. Subatomic Features in Atomic Force Microscopy Images. Technical Comment. Science 2001, 291, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, T.R.; Grutter, P.; Horne, D.; Rugar, D. Frequency modulation detection using high-Q cantilevers for enhanced force microscope sensitivity. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürig, U.; Züger, O.; Stalder, A. Interaction force detection in scanning probe microscopy: Methods and applications. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 72, 1778–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. Forces and frequency shifts in atomic-resolution dynamic-force microscopy. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 56, 16010–16015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. A direct method to calculate tip–sample forces from frequency shifts in frequency-modulation atomic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J. Introduction to Scanning Tunneling Microscopy, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Stroscio, J.A.; Kaiser, W.J. (Eds.) Scanning Tunneling Microscopy, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Israelachvili, J. Intermolecular and Surface Forces, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Giessibl, F.J.; Bielefeldt, H.; Hembacher, S.; Mannhart, J. Calculation of the optimal imaging parameters for frequency modulation atomic force microscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1999, 140, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. High-speed force sensor for force microscopy and profilometry utilizing a quartz tuning fork. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 3956–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. Atomic resolution on Si (111)–(7×7) by noncontact atomic force microscopy with a force sensor based on a quartz tuning fork. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 76, 1470–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J. The qPlus sensor, a powerful core for the atomic force microscope. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2019, 99, 011101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, F.; Giessibl, F.J. Low noise current preamplifier for qPlus sensor deflection signal detection in atomic force microscopy at room and low temperatures. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 073702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sader, J.E.; Jarvis, S. Accurate formulas for interaction force and energy in frequency modulation force spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 1801–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sader, J.E.; Hughes, B.D.; Huber, F.; Giessibl, F.J. Interatomic force laws that evade dynamic measurement. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1088–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Giessibl, F.J. Experimental use of the inflection point test for force deconvolution in frequency-modulation atomic force microscopy to turn an ill-posed situation into a well-posed one by proper choice of amplitude. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 184301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sader, J.E. The automation of robust interatomic-force measurements. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 103702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, R.; Payne, M.C.; Stich, I.; Terakura, K. Role of covalent tip-surface interactions in noncontact atomic force microscopy on reactive surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, R.; Štich, I.; Payne, M.C.; Terakura, K. Surface-tip interactions in noncontact atomic-force microscopy on reactive surfaces: Si(111). Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 10835–10849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelikowsky, J.R.; Cohen, M.L. Nonlocal pseudopotential calculations for the electronic structure of eleven diamond and zinc-blende semiconductors. Phys. Rev. B 1976, 14, 556–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz, M.A.; Hug, H.J.; Hoffmann, R.; van Schendel, J.A.; Kappenberger, P.; Martin, S.; Baratoff, A.; Guentherodt, H.J. Quantitative Measurement of Short-Range Chemical Bonding Forces. Science 2001, 291, 2580–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, Y.; Pou, P.; Abe, M.; Jelinek, P.; Perez, R.; Morita, S.; Custance, O. Chemical identification of individual surface atoms by atomic force microscopy. Nature 2007, 446, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, S.; Foster, A.; Björkman, T.; Nowakowska, S.; Björk, J.; Federici Canova, F.; Gade, L.H.; Jung, T.A.; Meyer, E. Van der Waals interactions and the limits of isolated atom models at interfaces. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigler, D.M.; Schweizer, E.K. Positioning single atoms with a scanning tunneling microscope. Nature 1990, 344, 524–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crommie, M.F.; Lutz, C.P.; Eigler, D.M. Confinement of Electrons to Quantum Corrals on a Metal Surface. Science 1993, 262, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ternes, M.; Lutz, C.P.; Hirjibehedin, C.F.; Giessibl, F.J.; Heinrich, A. The Force Needed to Move an Atom on a Surface. Science 2008, 319, 1066–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K. Scientists Measure What it Takes to Push a Single Atom. The New York Times, 22 February 2008. Available online: www.nytimes.com/2008/02/22/science/22atom.html(accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Repp, J.; Meyer, G.; Paavilainen, S.; Olsson, F.E.; Persson, M. Imaging Bond Formation Between Gold and Pentacene on an Insulating Surface. Science 2006, 312, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, M.; Gonzalez, C.; Lutz, C.P.; Hapala, P.; Giessibl, F.J.; Jelinek, P.; Heinrich, A.J. Interplay of Conductance, Force, and Structural Change in Metallic Point Contacts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 016802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, A.; Barth, C.; Shlugher, A.L.; Reichling, M. Unambiguous Interpretation of Atomically Resolved Force Microscopy Images of an Insulator. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 2373–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennard-Jones, J.E.; Dent, B.M. Cohesion at a crystal surface. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1928, 24, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, A.; Peronio, A.; Meuer, D.; Weymouth, A.J.; Giessibl, F.J. High-precision atomic force microscopy with atomically-characterized tips. New J. Phys. 2020, 22, 063040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, P.W. The stability of ionic crystal surfaces. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1979, 12, 4977–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welker, J.; Giessibl, F.J. Revealing the Angular Symmetry of Chemical Bonds by Atomic Force Microscopy. Science 2012, 336, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gretz, O.; Weymouth, A.J.; Giessibl, F.J. Identifying the atomic configuration of the tip apex using STM and frequency-modulation AFM with CO on Pt(111). Phys. Rev. Res. 2020, 2, 033094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, L.; Meyer, G.; Rieder, K.-H. Controlled vertical manipulation of single CO molecules with the scanning tunneling microscope: A route to chemical contrast. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 71, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, L.; Mohn, F.; Moll, N.; Liljeroth, P.; Meyer, G. The Chemical Structure of a Molecule Resolved by Atomic Force Microscopy. Science 2009, 325, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohn, F.; Schuler, B.; Gross, L.; Meyer, G. Different tips for high-resolution atomic force microscopy and scanning tunneling microscopy of single molecules. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 073109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moenig, H.; Hermoso, D.R.; Arado, O.D.; Todorovic, M.; Timmer, A.; Schüer, S.; Langewisch, G.; Perez, R.; Fuchs, H. Submolecular Imaging by Noncontact Atomic Force Microscopy with an Oxygen Atom Rigidly Connected to a Metallic Probe. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moenig, H.; Amirjalayer, S.; Timmer, A.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Arado, O.D.; Cnudde, M.; Strassert, A.A.; Ji, W.; Rohlfing, M.; et al. Quantitative assessment of intermolecular interactions by atomic force microscopy imaging using copper oxide tips. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebig, A.; Giessibl, F.J. In-situ characterization of O-terminated Cu tips for high-resolution atomic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 143103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weymouth, A.J.; Hofmann, T.; Giessibl, F.J. Quantifying Molecular Stiffness and Interaction with Lateral Force Microscopy. Science 2013, 343, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, L.; Schuler, B.; Pavlicek, N.; Fatayer, S.; Majzik, Z.; Moll, N.; Pena, D.; Meyer, G. Atomic Force Microscopy for Molecular Structure Elucidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3888–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmrich, M.; Huber, F.; Pielmeier, F.; Welker, J.; Hofmann, T.; Schneiderbauer, M.; Meuer, D.; Polesya, S.; Mankovsky, S.; Ködderitzsch, D.; et al. Subatomic resolution force microscopy reveals internal structure and adsorption sites of small iron clusters. Science 2015, 348, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berwanger, J.; Huber, F.; Stilp, F.; Giessibl, F.J. Lateral manipulation with combined atomic force and scanning tunneling microscopy using CO-terminated tips. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 195409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berwanger, J.; Polesya, S.; Mankovsky, S.; Ebert, H.; Giessibl, F.J. Atomically Resolved Chemical Reactivity of Small Fe Clusters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 096001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moll, N.; Gross, L.; Mohn, F.; Curioni, A.; Meyer, G. The mechanisms underlying the enhanced resolution of atomic force microscopy with functionalized tips. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 125020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavliček, N.; Fleury, B.; Neu, M.; Niedenführ, J.; Herranz-Lancho, C.; Ruben, M.; Repp, J. Atomic Force Microscopy Reveals Bistable Configurations of Dibenzo[a,h]thianthrene and their Interconversion Pathway. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 086101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiotari, A.; Sugimoto, Y. Ultrahigh-resolution imaging of water networks by atomic force microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Guo, J.; Hapala, P.; Cao, D.; Ma, R.; Xu, L.; Ondracek, M.; Jelinek, P.; Wang, E.; Jiang, Y. Weakly perturbative imaging of interfacial water with submolecular resolution by atomic force microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Cao, D.; He, Z.; Guo, J.; Hapala, P.; Ma, R.; Cheng, B.; Chen, J.; Xi, J.W.; Li, X.Z.; et al. The effect of hydration number on the interfacial transport of sodium ions. Nature 2018, 557, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Xenon Conundrum. Available online: http://scarc.library.oregonstate.edu/coll/pauling/bond/narrative/page38.html (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Bartlett, N. Xenon Hexafluoroplatinate(V) Xe+[PtF6]-. Proc. Chem. Soc. 1962, 6, 197–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, F.; Berwanger, J.; Polesya, S.; Mankovsky, S.; Ebert, H.; Giessibl, F.J. Chemical bond formation showing a transition from physisorption to chemisorption. Science 2019, 366, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneiderbauer, M.; Emmrich, M.; Weymouth, A.J.; Giessibl, F.J. CO Tip Functionalization Inverts Atomic Force Microscopy Contrast via Short-Range Electrostatic Forces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 166102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellner, M.; Pavlicek, N.; Pou, P.; Schuler, B.; Moll, N.; Meyer, G.; Gross, L. The Electric Field of CO Tips and Its Relevance for Atomic Force Microscopy. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1974–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebig, A.; Hapala, P.; Weymouth, A.J.; Giessibl, F.J. Quantifying the evolution of atomic interaction of a complex surface with a functionalized atomic force microscopy tip. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, P.; Yuan, B.; Ji, W.; Cheng, Z.; Qiu, X. Real-Space Identification of Intermolecular Bonding with Atomic Force Microscopy. Science 2013, 342, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämäläinen, S.K.; van der Heijden, N.; van der Lit, J.; den Hartog, S.; Liljeroth, P.; Swarz, I. Intermolecular Contrast in Atomic Force Microscopy Images without Intermolecular Bonds. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 186102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapala, P.; Kichin, G.; Wagner, C.; Tautz, F.S.; Temirov, R.; Jelinek, P. Mechanism of high-resolution STM/AFM imaging with functionalized tips. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 085421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellner, M.; Pou, P.; Perez, R. Molecular Identification, Bond Order Discrimination, and Apparent Intermolecular Features in Atomic Force Microscopy Studied with a Charge Density Based Method. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, S.; Nishiuchi, T.; Kodama, T.; Spijker, P.; Pawlak, R.; Meier, T.; Tracey, J.; Kubo, T.; Meyer, E.; Foster, A.S. Direct quantitative measurement of the C-O...H-C bond by atomic force microscopy. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1603258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Meyer, B.; Setvin, M.; Schmid, M.; Diebold, U. Direct assessment of the aciditiy of individual surface hydroxyls. Nature 2021, 592, 722–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Extance, A. How atomic imaging is being pushed to its limit. Nature 2018, 555, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennard-Jones, J.E. Processes of adsorption and diffusion on solid surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1932, 28, 333–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastner, M. Artificial Atoms. Phys. Today 1993, 46, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilp, F.; Bereczuk, A.; Berwanger, J.; Mundigl, N.; Richter, K.; Giessibl, F.J. Very weak bonds to artificial atoms formed by quantum corrals. Science 2021, 372, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stillinger, F.H.; Weber, T.A. Computer simulation of local order in condensed phases of silicon. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 31, 5262–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Cuma, M.; Liu, F. Seeing the Atomic Orbital: First-Principles Study of the Effect of Tip Termination on Atomic Force Microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 256101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, A. Erster Blick in das Innere eines Atoms. Frankf. Allg. Ztg. 2000, 171, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, K.H. Nanotech, Blur and Tragedy in Recent Artworks by Gerhard Richter. Leonardo 2008, 41, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giessibl, F.J.; Bielefeldt, H.; Hembacher, S.; Mannhart, J. Imaging of atomic orbitals with the Atomic Force Microscope—experiments and simulations. Ann. Phys. 2001, 10, 887–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, M.; Giessibl, F.J.; Mannhart, J. Probing the shape of atoms in real space. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 045301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hembacher, S.; Giessibl, F.J.; Mannhart, J. Force microscopy with light-atom probes. Science 2004, 305, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.A.; Solares, S.D. On Mapping Subangstrom Electron Clouds with Force Microscopy. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuma, T. True atomic resolution in liquid by frequency-modulation atomic force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 034101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuma, T. Revealing molecular-level surface structure of amyloid fibrils in liquid by means of frequency modulation atomic force microscopy. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 384010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wastl, D.S.; Weymouth, A.J.; Giessibl, F.J. Optimizing atomic resolution of force microscopy in ambient conditions. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 245415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pürckhauer, K.; Weymouth, A.J.; Pfeffer, K.; Kullmann, L.; Mulvihill, E.; Krahn, M.P.; Müller, D.J.; Giessibl, F.J. Imaging in Biologically-Relevant Environments with AFM Using Stiff qPlus Sensors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 9, 9330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auer, A.; Andersen, M.; Wernig, E.M.; Hörmann, N.G.; Buller, N.; Reuter, K.; Kunze-Liebhäuser, J. Self-activation of copper electrodes during CO electro-oxidation in alkaline electrolyte. Nat. Catal. 2020, 3, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giessibl, F.J. Probing the Nature of Chemical Bonds by Atomic Force Microscopy. Molecules 2021, 26, 4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134068
Giessibl FJ. Probing the Nature of Chemical Bonds by Atomic Force Microscopy. Molecules. 2021; 26(13):4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134068
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiessibl, Franz J. 2021. "Probing the Nature of Chemical Bonds by Atomic Force Microscopy" Molecules 26, no. 13: 4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134068
APA StyleGiessibl, F. J. (2021). Probing the Nature of Chemical Bonds by Atomic Force Microscopy. Molecules, 26(13), 4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26134068





