Ellagitannin Digestion in Moth Larvae and a New Dimeric Ellagitannin from the Leaves of Platycarya strobilacea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Constituents of Insect Tea
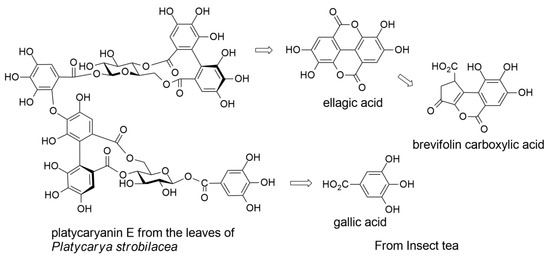
2.2. Ellagitannins of Platycarya strobilacea
2.3. Polymeric Polyphenols
2.4. Decomposition of Ellagitannins in the Digestive Tract of Moth Larvae
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Materials
3.3. HPLC Analysis
3.4. Extraction and Separation
3.4.1. Insect Tea
3.4.2. Platycarya strobilacea
3.5. Spectroscopic Data
Platycaryanin E (13)
3.6. Thiol Degradation of Polymeric Polyphenols
3.7. Acid Hydrolysis of Polymeric Polyphenols
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Haslam, E.; Cai, Y. Plant polyphenols (vegetable tannins): Gallic acid metabolism. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1994, 11, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeriglio, A.; Barreca, D.; Bellocco, E.; Trombetta, D. Proanthocyanidins and hydrolysable tannins: Occurrence, dietary intake and pharmacological effects. Br. J. Pharm. 2017, 174, 1244–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T. Hydrolyzable tannins and related polyphenols. In Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products; Herz, W., Kirby, G.W., Moore, R.E., Steglich, W., Tamm, C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 66, pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Ito, H.; Okuda, T. Structural diversity and antimicrobial activities of ellagitannins. In Chemistry and Biology of Ellagitannins, An Underestimated Class of Bioactive Plant Polyphenols; Quideau, S., Ed.; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2009; pp. 55–93. [Google Scholar]
- Quideau, S.; Feldman, K.S. Ellagitannin chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 475–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlton, A.J.; Baxter, N.J.; Khan, M.L.; Moir, A.J.G.; Haslam, E.; Davies, A.P.; Williamson, M.P. Polyphenol/peptide binding and precipitation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehansho, H.; Butler, L.G.; Carlson, D.M. Dietary tannins and salivary proline-rich proteins: Interactions, induction, and defense mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1987, 7, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstett, D.N.; Cheval, I.; D’Souza, C.; Salminen, J.; Johnson, M.T.J. Ellagitannins from the Onagraceae decrease the performance of generalist and specialist herbivores. J. Chem. Ecol. 2019, 45, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constabel, C.P.; Yoshida, K.; Walker, V. Diverse ecological roles of plant tannins: Plant defense and beyond. In Recent Advances in Polyphenol Research; Romani, A., Lattanzio, V., Quideau, S., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2014; Volume 4, pp. 115–142. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, K.J.; Wallis, I.R.; Kulheim, C.; Clark, R.; Nicolle, D.; Foley, W.J.; Salminen, J.-P. New approaches to tannin analysis of leaves can be used to explain in vitro biological activities associated with herbivore defence. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Gil, A.; del Alamo-Sanza, M.; Sanchez-Gomez, R.; Nevares, I. Alternative woods in enology: Characterization of tannin and low molecular weight phenol compounds with respect to traditional oak woods. Molecules 2020, 25, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.-Y.; Duan, C.-Q. Astringency, bitterness and color changes in dry red wines before and during oak barrel aging: An updated phenolic perspective review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 1840–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Gonzalez-Sarrias, A.; Garcia-Villalba, R.; Nunez-Sanchez, M.A.; Selma, M.V.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T.; Espin, J.C. Urolithins, the rescue of "old" metabolites to understand a “new” concept: Metabotypes as a nexus among phenolic metabolism, microbiota dysbiosis, and host health status. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1500901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, D.; Andreux, P.A.; Valdés, P.; Singh, A.; Rinsch, C.; Auwerx, J. Impact of the natural compound urolithin a on health, disease, and aging. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X.; Cao, Y.; Shi, J.; Ye, X.; Chen, S. Rethinking the mechanism of the health benefits of proanthocyanidins: Absorption, metabolism, and interaction with gut microbiota. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 971–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Barrio, R.; Truchado, P.; Ito, H.; Espin, J.C.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. UV and MS identification of urolithins and nasutins, the bioavailable metabolites of ellagitannins and ellagic acid in different mammals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, G.S. Isolation of two benzocoumarins from clover stone, a type of renal calculus found in sheep. Biochem. J. 1964, 93, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbehenn, R.V.; Jones, C.P.; Hagerman, A.E.; Karonen, M.; Salminen, J. Ellagitannins have greater oxidative activities than condensed tannins and galloyl glucoses at high pH: Potential impact on caterpillars. J. Chem. Ecol. 2006, 32, 2253–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vihakas, M.; Gómez, I.; Karonen, M.; Tähtinen, P.; Sääksjärvi, I.; Salminen, J. Phenolic compounds and their fates in tropical lepidopteran larvae: Modifications in alkaline conditions. J. Chem. Ecol. 2015, 41, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Huimin Pan, H.; Lei, O.; Xiao, W.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, P. Insect tea, a wonderful work in the Chinese tea culture. Food Res. Int. 2013, 53, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. C.: Reaction of dehydrohexahydroxydiphenic acid esters with bases, and its application to the structure determination of pomegranate tannins, granatins A and B. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 2424–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Era, M.; Matsuo, Y.; Saito, Y.; Tanaka, T. Production of ellagitannin hexahydroxydiphenoyl ester by spontaneous reduction of dehydrohexahydroxydiphenoyl ester. Molecules 2020, 25, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawwar, M.A.M.; Hussein, S.A.M.; Merfort, I. NMR spectral analysis of polyphenols from Punica granatum. Phytochemistry 1994, 36, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglione, L.; Gambuti, A.; De Cicco, P.; Ercolano, G.; Ianaro, A.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Moio, L.; Forino, M. NMR-based phytochemical analysis of Vitis vinifera cv Falanghina leaves. Characterization of a previously undescribed biflavonoid with antiproliferative activity. Fitoterapia 2018, 125, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, K.R.; Ternai, B.; Stanley, R.; Geiger, H.; Mabry, T.J. Carbon-13 NMR studies of flavonoids—III: Naturally occurring flavonoid glycosides and their acylated derivatives. Tetrahedron 1978, 34, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, A.; Shoji, T.; Shibusawa, Y. Separation of proanthocyanidins by degree of polymerization by means of size-exclusion chromatography and related techniques. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2003, 56, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbehenn, R.; Dodick, T.; Poopat, U.; Spencer, B. Fenton-type reactions and iron concentrations in the midgut fluids of tree-feeding caterpillars, Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 60, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Palijarvi, M.; Karonen, M.; Salminen, J.-P. Distribution of enzymatic and alkaline oxidative activities of phenolic compounds in plants. Phytochemistry 2020, 179, 112501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Jiang, Z.; Kouno, I. Distribution of ellagic acid derivatives and a diarylheptanoid in wood of Platycarya strobolacea. Phytochemistry 1998, 47, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Kouno, I. Whisky lactone precursors from the wood of Platycarya strobilacea. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 997–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Kirihara, S.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. CXXIV. Five new ellagitannins, platycaryanins A, B, C, and D, and platycariin, and a new complex tannin, strobilanin, from the fruits and bark of Platycarya strobilacea Sieb. et Zucc., and biomimetic synthesis of C-glycosidic ellagitannins from glucopyranose-based ellagitannins. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 1708–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Tsujita, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Saito, Y.; Tanaka, T. Enzymatic oxidation of ellagitannin and a new ellagitannin metabolite from Camellia japonica leaves. Tetrahadron 2017, 73, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Ashida, M. Casuarictin and casuarinin, two new ellagitannins from Casuarina stricta. Heterocycles 1981, 16, 1681–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishimatsu, M.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. Part 78. Alnusnins A and B from the leaves of Alnus sieboldiana. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 3179–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mousallamy, A.M.D.; Barakat, H.H.; Soulememan, A.M.A.; Awadallah, S. Polyphenols of Acacia raddiana. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3767–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Al-Shafi, S.M.K.; Layden, K.; Haslam, E. The metabolism of gallic acid and hexahydroxydiphenic acid in plants. Part 2. Esters of (S)-hexahydroxydiphenic acid with D-glucopyranose (4C1). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1982, 1, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, T.; Kira, R.; Yasuhara, T.; Okuda, T. Structure of isorugosin B, and the orientation of valoneoyl group in the related monomeric, dimeric and trimeric hydrolyzable tannins. Heterocycles 1988, 27, 2081–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-H.; Ishimatsu, M.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. XCVI. Structures of macaranins and macarinins, new hydrolyzable tannins possessing macaranoyl and tergalloyl ester groups, from the leaves of Macaranga sinensis (Baill.) Muell.-Arg. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 1844–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Koga, T.; Toh, N.; Kuriyama, K. Circular dichroism of hydrolyzable tannins. I. Ellagitannins and gallotannins. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 3937–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, R.; Kouno, I.; Nonaka, G. Chemical evidence for the de-astringency (insolubilization of tannins) of persimmon fruit. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1994, 1, 3013–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takayoshi, J.; Huang, Y.-L.; Matsuo, Y.; Saito, Y.; Li, D.-P.; Tanaka, T. Ellagitannin Digestion in Moth Larvae and a New Dimeric Ellagitannin from the Leaves of Platycarya strobilacea. Molecules 2021, 26, 4134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144134
Takayoshi J, Huang Y-L, Matsuo Y, Saito Y, Li D-P, Tanaka T. Ellagitannin Digestion in Moth Larvae and a New Dimeric Ellagitannin from the Leaves of Platycarya strobilacea. Molecules. 2021; 26(14):4134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144134
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakayoshi, Juri, Yong-Lin Huang, Yosuke Matsuo, Yoshinori Saito, Dian-Peng Li, and Takashi Tanaka. 2021. "Ellagitannin Digestion in Moth Larvae and a New Dimeric Ellagitannin from the Leaves of Platycarya strobilacea" Molecules 26, no. 14: 4134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144134
APA StyleTakayoshi, J., Huang, Y.-L., Matsuo, Y., Saito, Y., Li, D.-P., & Tanaka, T. (2021). Ellagitannin Digestion in Moth Larvae and a New Dimeric Ellagitannin from the Leaves of Platycarya strobilacea. Molecules, 26(14), 4134. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144134