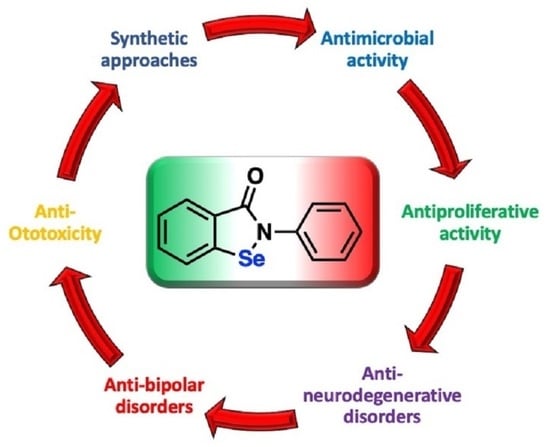
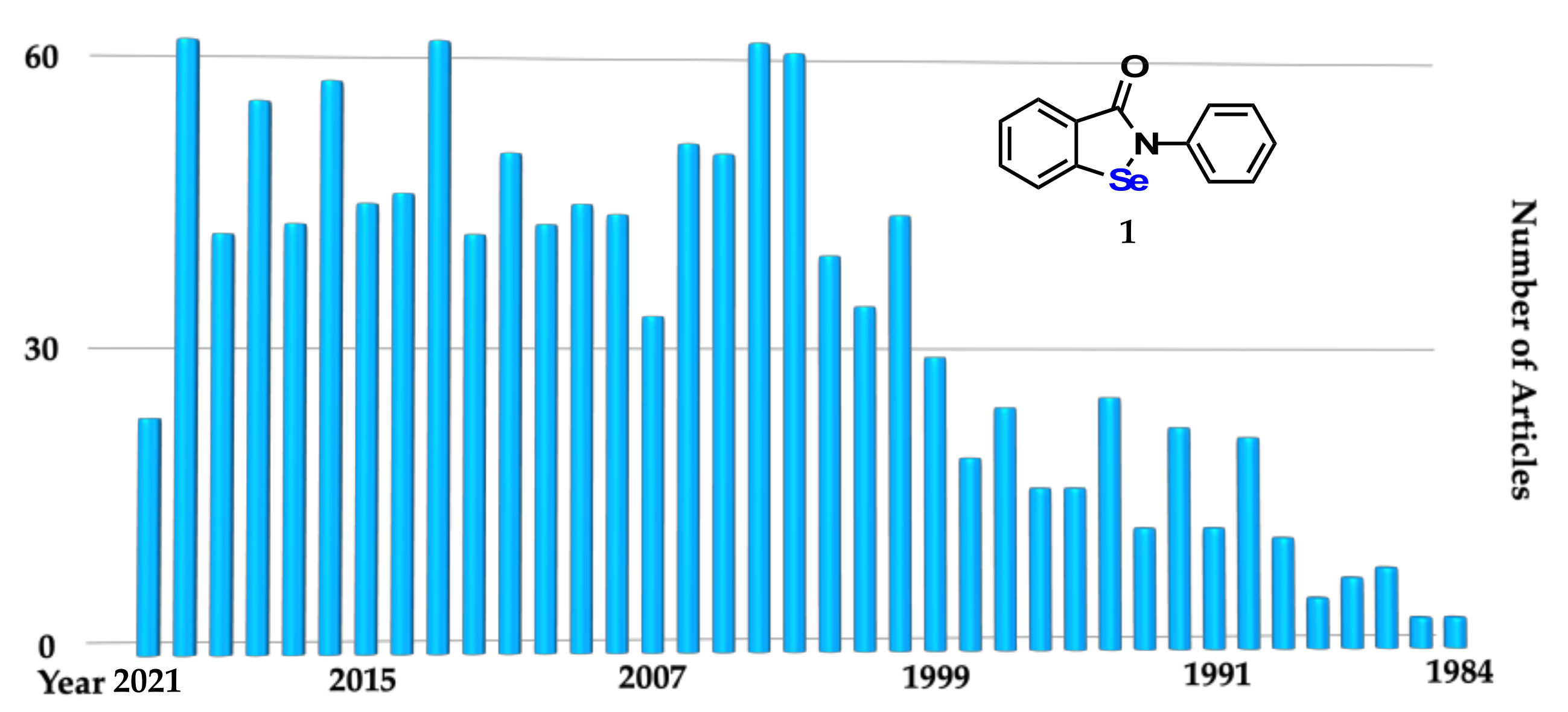
Ebselen and Analogues: Pharmacological Properties and Synthetic Strategies for Their Preparation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
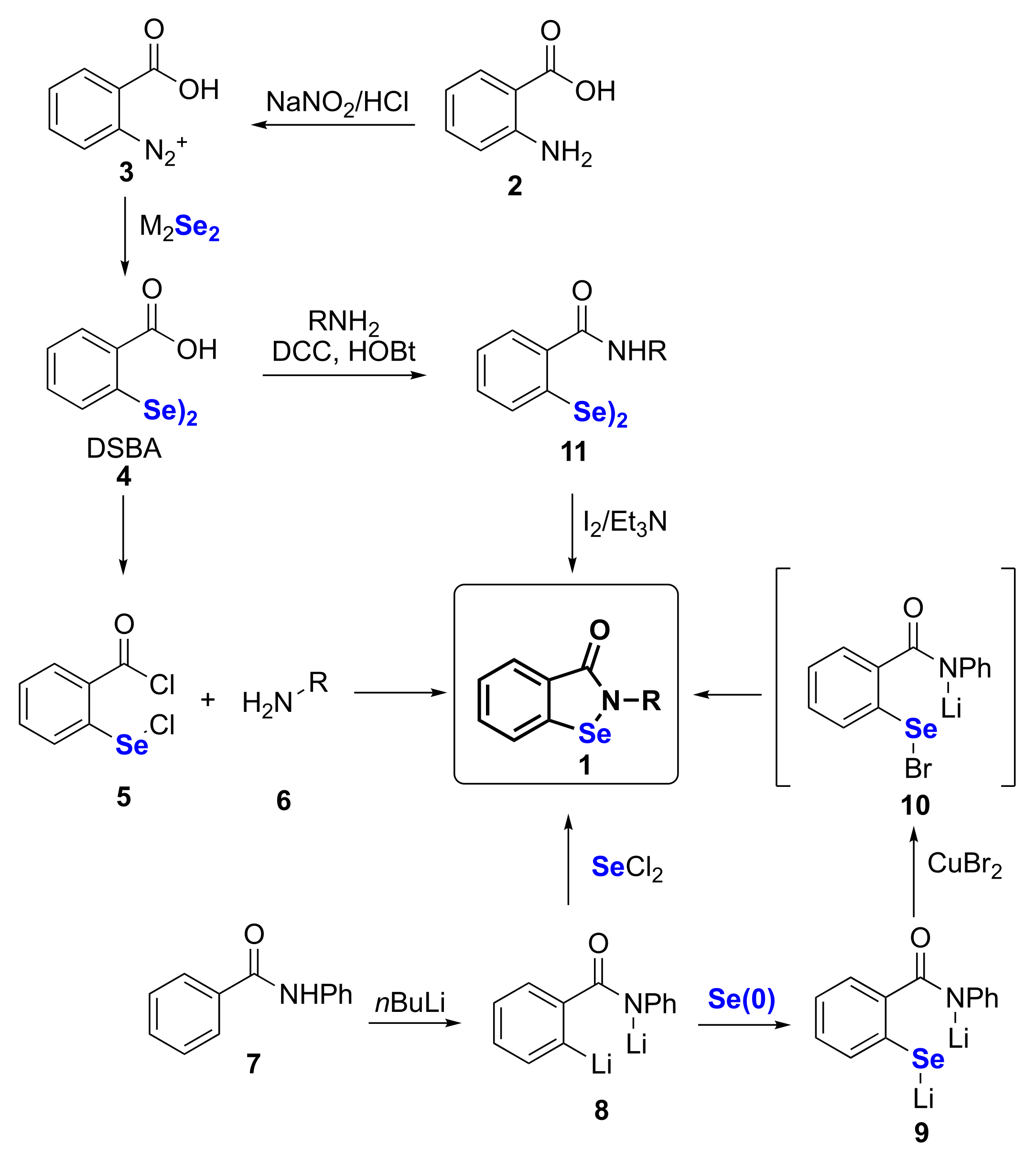
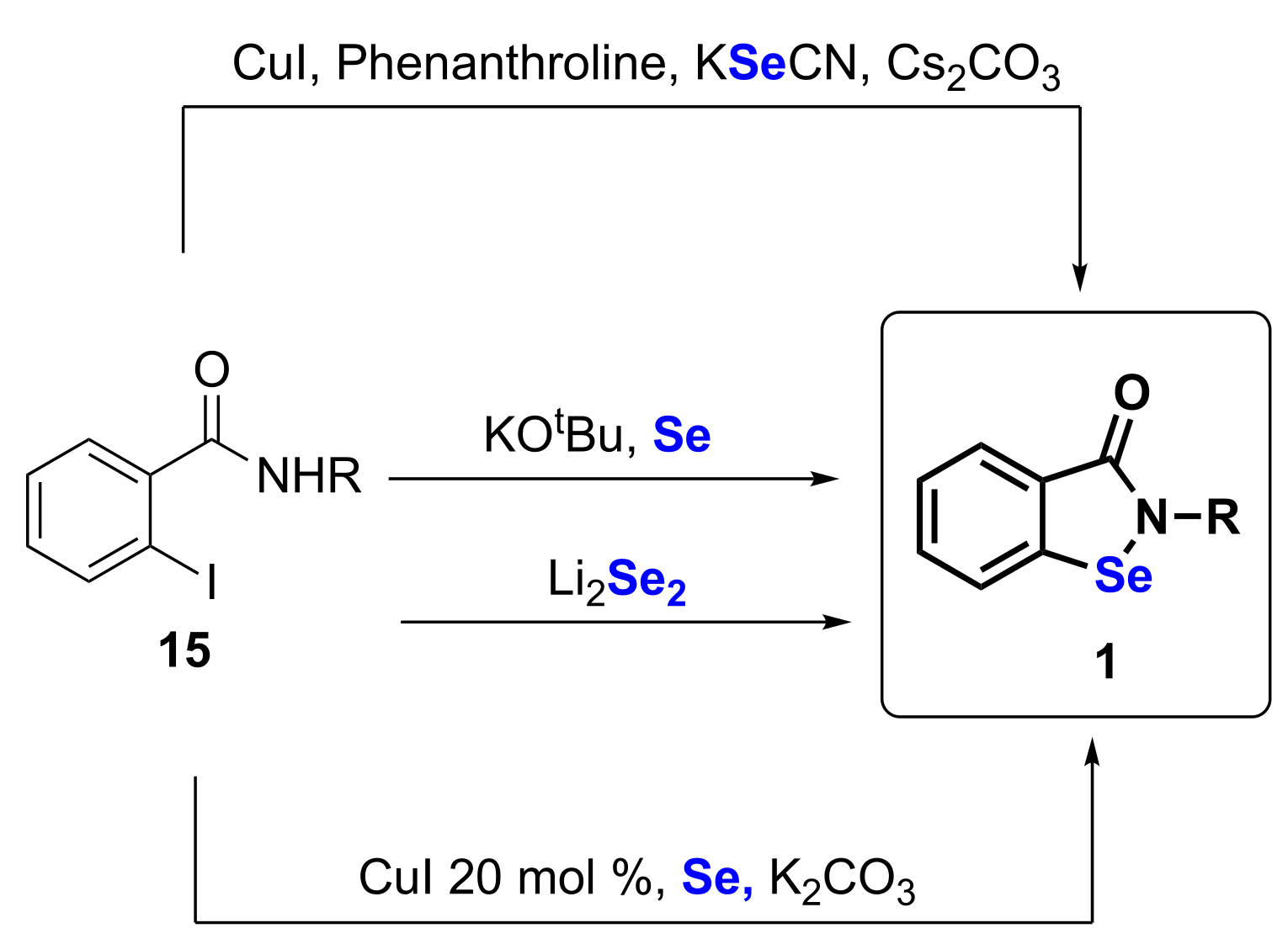
2. Synthetic Approaches to Ebselen and Benzisoselenazolones
| Method | Starting Compound | Number of Steps | Yield (%) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 16–67 | [18,19,20,21,22,23,24] |
| 2 | 7 | 3 | 63 | [25,26,27] |
| 3 | 7 | 2 | 40 | [28] |
| 4 | 2 | 4 | 60 | [15,16,32,33] |
| 5 | 13 | 1 | 85 | [34] |
| 6 | 12 | 2 | 53 | [35] |
| 7 | 15 | 1 | 47–96 | [36,37] |
| 8 | 15 | 1 | 35–88 | [38] |
| 9 | 15 | 1 | 44–91 | [39] |
| 10 | 15 | 1 | 59–98 | [40,41] |
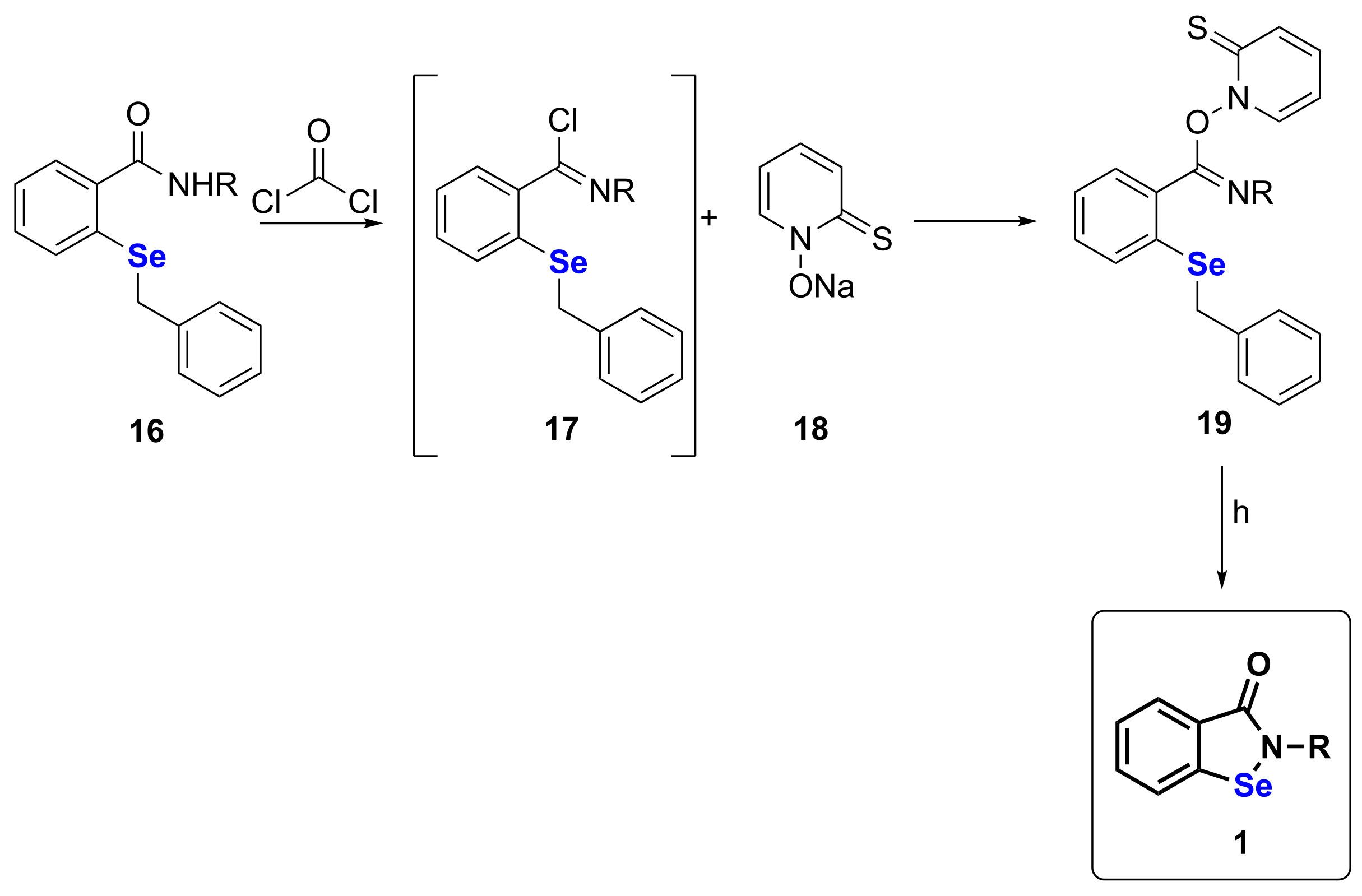
| 11 | 16 | 3 | 76 | [42] |
3. Antimicrobial Activities
3.1. Antiviral
3.1.1. Anti-Sars-CoV-2
3.1.2. Anti-HIV
3.1.3. Anti-Influenza, Zika and Other Viruses
3.2. Antibacterial
3.2.1. Against Pathogenetic Gram-Positive Bacteria
3.2.2. Against Pathogenetic Gram-Negative Bacteria
3.2.3. Against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
3.2.4. Against Pathogenetic Fungi
3.2.5. Against Other Pathogenetic Microorganisms
4. Antiproliferative Activities
5. Anti-Neurodegenerative Disorders
5.1. Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease
5.2. Anti-Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
6. Anti-Bipolar Disorders
7. Anti-Hearing Loss/Ototoxicity
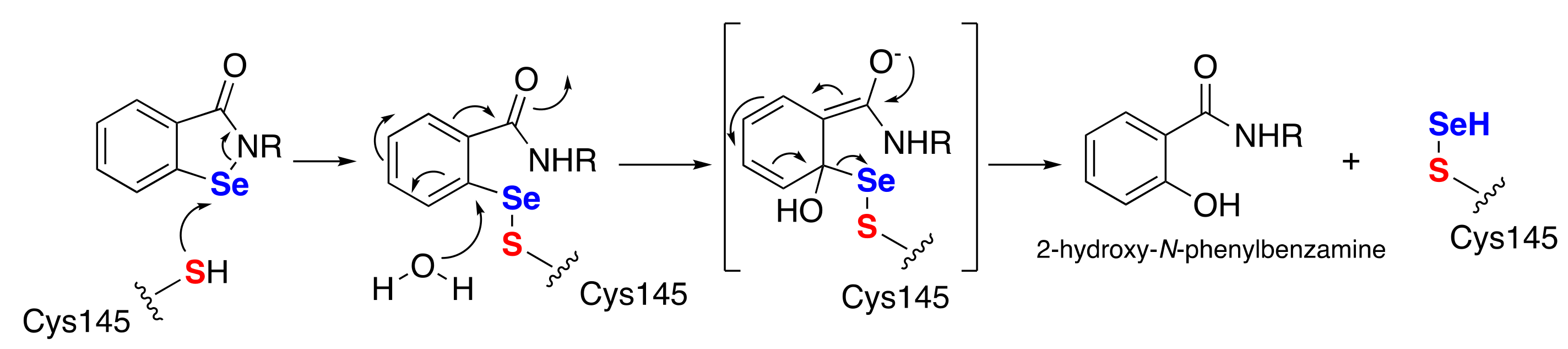
8. Miscellaneous Activities
8.1. In Vivo
8.2. In Vitro
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lesser, R.; Weiss, R. Über selenhaltige aromatische Verbindungen (VI). Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1924, 57, 1077–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Cadenas, E.; Graf, P.; Sies, H. A novel biologically active seleno-organic compound-1. Glutathione peroxidase-like activity in vitro and antioxidant capacity of PZ 51 (Ebselen). Biochem. Pharmacol. 1984, 33, 3235–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, K.N.; Back, T.G. Key steps and intermediates in the catalytic mechanism for the reduction of peroxides by the antioxidant ebselen. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 4959–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotruck, J.T.; Pope, A.L.; Ganther, H.E.; Swanson, A.B.; Hafeman, D.G.; Hoekstra, W.G. Selenium: Biochemical Role as a Component of Glutathione Peroxidase. Science 1973, 179, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohe, L.; Günzler, W.A.; Schock, H.H. Glutathione peroxidase: A selenoenzyme. FEBS Lett. 1973, 32, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenardão, E.J.; Santi, C.; Sancineto, L. Bioactive Organoselenium Compounds and Therapeutic Perspectives. In New Frontiers in Organoselenium Compounds; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 99–143. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, G.K.; Tomar, R.S. Ebselen, a promising antioxidant drug: Mechanisms of action and targets of biological pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4865–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacuła, A.J.; Mangiavacchi, F.; Sancineto, L.; Lenardão, E.J.; Ścianowski, J.; Santi, C. An Update on “Selenium Containing Compounds from Poison to Drug Candidates: A Review on the GPx-like Activity. Curr. Chem. Biol. 2016, 9, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zou, L.; Lu, J.; Holmgren, A. Selenocysteine in mammalian thioredoxin reductase and application of ebselen as a therapeutic. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 127, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benelli, J.L.; Poester, V.R.; Munhoz, L.S.; Melo, A.M.; Trápaga, M.R.; Stevens, D.A.; Xavier, M.O. Ebselen and diphenyl diselenide against fungal pathogens: A systematic review. Med. Mycol. 2021, 59, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Parnham, M.J. Potential therapeutic use of ebselen for COVID-19 and other respiratory viral infections. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 156, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, L.; Welter, A.; Wirtz, P. New benzisoselenazolones, process for producing the same and pharmaceutical preparations containing the same. EP0044453A2, 27 January 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Cantineau, R.; Tihange, G.; Plenevaux, A.; Christiaens, L.; Guillaume, M.; Welter, A.; Dereu, N. Synthesis of 75Se-2-phenyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one (PZ 51; ebselen. A novel biologically active organo-selenium compound. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1986, 23, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begini, F.; Krasowska, D.; Jasiak, A.; Drabowicz, J.; Santi, C.; Sancineto, L. Continuous flow synthesis of 2,2′-diselenobis(benzoic acid) and derivatives. React. Chem. Eng. 2020, 5, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowska, D.; Begini, F.; Santi, C.; Mangiavacchi, F.; Drabowicz, J.; Sancineto, L. Ultrasound-assisted synthesis of alkali metals diselenides (M2Se2) and their application for the gram-scale preparation of 2,2′-diselenobis(benzoic acid). Arkivoc 2019, 2019, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, D.; Commodi, J.; Piroddi, M.; Incipini, L.; Sancineto, L.; Santi, C.; Galli, F. Glutathione S-transferase pi expression regulates the Nrf2-dependent response to hormetic diselenides. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küppers, J.; Schulz-Fincke, A.; Palus, J.; Giurg, M.; Skarżewski, J.; Gütschow, M. Convergent Synthesis of Two Fluorescent Ebselen-Coumarin Heterodimers. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pietka-Ottlik, M.; Potaczek, P.; Piasecki, E.; Mlochowski, J. Crucial Role of Selenium in the Virucidal Activity of Benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-ones and Related Diselenides. Molecules 2010, 15, 8214–8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piętka-Ottlik, M.; Wójtowicz-Młochowska, H.; Kołodziejczyk, K.; Piasecki, E.; Młochowski, J. New Organoselenium Compounds Active against Pathogenic Bacteria, Fungi and Viruses. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo). 2008, 56, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osajda, M.; Młochowski, J. The reactions of 2-(chloroseleno)benzoyl chloride with nucleophiles. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 7531–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloc, K.; Maliszewska, I.; Młochowski, J. Synthesis of 7-Azabenzisoselenazol-3(2H)-ones: A New Group of Selenium Containing Antimicrobials. Synth. Commun. 2003, 33, 3805–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Liang, L.; Sheng, J.; Pang, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a new series of ebselen derivatives as glutathione peroxidase (GPx) mimics and cholinesterase inhibitors against Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obieziurska, M.; Pacuła, A.J.; Długosz-Pokorska, A.; Krzemiński, M.; Janecka, A.; Ścianowski, J. Bioselectivity Induced by Chirality of New Terpenyl Organoselenium Compounds. Materials (Basel). 2019, 12, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engman, L.; Hallberg, A. Expedient synthesis of ebselen and related compounds. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 2964–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, J.; Silks, L.A. Synthesis of 2-phenyl-1,2-benziso [77Se]selenazol-3(2H)-one: “Ebselen”. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 1996, 38, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-C.; Huang, M.-L.; Hsu, W.-L.; Hwang, J.-M.; Hsu, L.-Y. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Ebselen and Its Acyclic Derivatives. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zade, S.S.; Panda, S.; Singh, H.B.; Wolmershäuser, G. Synthesis of diaryl selenides using the in situ reagent SeCl2. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancineto, L.; Mariotti, A.; Bagnoli, L.; Marini, F.; Desantis, J.; Iraci, N.; Santi, C.; Pannecouque, C.; Tabarrini, O. Design and Synthesis of DiselenoBisBenzamides (DISeBAs) as Nucleocapsid Protein 7 (NCp7) Inhibitors with anti-HIV Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9601–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iraci, N.; Tabarrini, O.; Santi, C.; Sancineto, L. NCp7: Targeting a multitask protein for next-generation anti-HIV drug development part 2. Noncovalent inhibitors and nucleic acid binders. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancineto, L.; Iraci, N.; Tabarrini, O.; Santi, C. NCp7: Targeting a multitasking protein for next-generation anti-HIV drug development part 1: Covalent inhibitors. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, V.; Cordeiro, P.S.; Arca, M.; Marini, F.; Sancineto, L.; Braga, A.L.; Lippolis, V.; Iwaoka, M.; Santi, C. Fast and easy conversion of ortho amidoaryldiselenides into the corresponding ebselen-like derivatives driven by theoretical investigations. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 9444–9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, C.; Hilbert, M.; Christiaens, L.; Dereu, N. Ortholithiation As a Tool for the Synthesis of Ebselen Analogues. Synth. Commun. 1991, 21, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zade, S.S.; Panda, S.; Tripathi, S.K.; Singh, H.B.; Wolmershäuser, G. Convenient Synthesis, Characterization and GPx-Like Catalytic Activity of Novel Ebselen Derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 2004, 3857–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Poon, J.; Yan, J.; Lu, X.; Ott, M.K.; Butcher, R.J.; Gates, P.J.; Engman, L. Nitro-, Azo-, and Amino Derivatives of Ebselen: Synthesis, Structure, and Cytoprotective Effects. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balkrishna, S.J.; Bhakuni, B.S.; Chopra, D.; Kumar, S. Cu-Catalyzed Efficient Synthetic Methodology for Ebselen and Related Se−N Heterocycles. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 5394–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balkrishna, S.J.; Bhakuni, B.S.; Kumar, S. Copper catalyzed/mediated synthetic methodology for ebselen and related isoselenazolones. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 9565–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkrishna, S.J.; Kumar, S.; Azad, G.K.; Bhakuni, B.S.; Panini, P.; Ahalawat, N.; Tomar, R.S.; Detty, M.R.; Kumar, S. An ebselen like catalyst with enhanced GPx activity via a selenol intermediate. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanna, S.; Goins, C.M.; Knudson, S.E.; Slayden, R.A.; Ronning, D.R.; Sucheck, S.J. Thermal and Photoinduced Copper-Promoted C–Se Bond Formation: Synthesis of 2-Alkyl-1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-ones and Evaluation against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 3844–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacuła, A.J.; Ścianowski, J.; Aleksandrzak, K.B. Highly efficient synthesis and antioxidant capacity of N-substituted benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-ones. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 48959–48962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obieziurska, M.; Pacuła, A.; Juhas, U.; Antosiewicz, J.; Ścianowski, J. The Influence of O/S Exchange on the Biocatalytical Activity of Benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-ones. Catalysts 2018, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fong, M.C.; Schiesser, C.H. Intramolecular Homolytic Substitution with Amidyl Radicals: A Free-Radical Synthesis of Ebselen and Related Analogues. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 3103–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Leo, I.; Messina, F.; Nascimento, V.; Nacca, F.G.; Pietrella, D.; Lenardão, E.J.; Perin, G.; Sancineto, L. Synthetic approaches to organoselenium derivatives with antimicrobial and anti-biofilm activity. Mini. Rev. Org. Chem. 2019, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daolio, A.; Scilabra, P.; Di Pietro, M.E.; Resnati, C.; Rissanen, K.; Resnati, G. Binding motif of ebselen in solution: Chalcogen and hydrogen bonds team up. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 20697–20703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Du, X.; Xu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Peng, C.; et al. Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature 2020, 582, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haritha, C.V.; Sharun, K.; Jose, B. Ebselen, a new candidate therapeutic against SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 84, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Hu, Y.; Townsend, J.A.; Lagarias, P.I.; Marty, M.T.; Kolocouris, A.; Wang, J. Ebselen, Disulfiram, Carmofur, PX-12, Tideglusib, and Shikonin Are Nonspecific Promiscuous SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menéndez, C.A.; Byléhn, F.; Perez-Lemus, G.R.; Alvarado, W.; de Pablo, J.J. Molecular characterization of Ebselen binding activity to SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Sci. Adv. 2020, eabd3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogara, P.A.; Omage, F.B.; Bolzan, G.R.; Delgado, C.P.; Aschner, M.; Orian, L.; Teixeira Rocha, J.B. In silico Studies on the Interaction Between Mpro and PLpro From SARS-CoV-2 and Ebselen, its Metabolites and Derivatives. Mol. Inform. 2021, 40, 2100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Fei, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-P.; Sargsyan, K.; Chang, C.-P.; Yuan, H.S.; Lim, C. Synergistic Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Replication Using Disulfiram/Ebselen and Remdesivir. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 898–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weglarz-Tomczak, E.; Tomczak, J.M.; Talma, M.; Burda-Grabowska, M.; Giurg, M.; Brul, S. Identification of ebselen and its analogues as potent covalent inhibitors of papain-like protease from SARS-CoV-2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-Y.; Chen, C.; Su, J.; Li, J.-Q.; Jiang, Z.; Gao, H.; Chigan, J.-Z.; Ding, H.-H.; Zhai, L.; Yang, K.-W. Ebsulfur and Ebselen as highly potent scaffolds for the development of potential SARS-CoV-2 antivirals. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 112, 104889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amporndanai, K.; Meng, X.; Shang, W.; Jin, Z.; Rogers, M.; Zhao, Y.; Rao, Z.; Liu, Z.-J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. Inhibition mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 main protease by ebselen and its derivatives. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, A.D.; Wilbourn, B.; Magnus, M.; Greenberg, A.E. SARS-CoV-2 and HIV: Epidemiology, Treatment, and Lessons Learned from HIV. Aids Rev. 2020, 22, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thenin-Houssier, S.; de Vera, I.M.S.; Pedro-Rosa, L.; Brady, A.; Richard, A.; Konnick, B.; Opp, S.; Buffone, C.; Fuhrmann, J.; Kota, S.; et al. Ebselen, a Small-Molecule Capsid Inhibitor of HIV-1 Replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2195–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Yan, H.-L.; Xu, X.-S.; Xu, L.; Yin, Z.-H.; Chang, S.; Luo, H. The selenium-containing drug ebselen potently disrupts LEDGF/p75-HIV-1 integrase interaction by targeting LEDGF/p75. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 906–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gualano, R.C.; Hansen, M.J.; Vlahos, R.; Jones, J.E.; Park-Jones, R.A.; Deliyannis, G.; Turner, S.J.; Duca, K.A.; Anderson, G.P. Cigarette smoke worsens lung inflammation and impairs resolution of influenza infection in mice. Respir. Res. 2008, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belvisi, M.G.; Haddad, E.-B.; Battram, C.; Birrell, M.; Foster, M.; Webber, S. Anti-inflammatory properties of ebselen in a model of sephadex-induced lung inflammation. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 15, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, E.-B.; McCluskie, K.; Birrell, M.A.; Dabrowski, D.; Pecoraro, M.; Underwood, S.; Chen, B.; De Sanctis, G.T.; Webber, S.E.; Foster, M.L.; et al. Differential Effects of Ebselen on Neutrophil Recruitment, Chemokine, and Inflammatory Mediator Expression in a Rat Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oostwoud, L.C.; Gunasinghe, P.; Seow, H.J.; Ye, J.M.; Selemidis, S.; Bozinovski, S.; Vlahos, R. Apocynin and ebselen reduce influenza A virus-induced lung inflammation in cigarette smoke-exposed mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brassington, K.; Chan, S.M.H.; Seow, H.J.; Dobric, A.; Bozinovski, S.; Selemidis, S.; Vlahos, R. Ebselen reduces cigarette smoke-induced endothelial dysfunction in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 1805–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.R.; Jamieson, D.J.; Powers, A.M.; Honein, M.A. Zika Virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 1552–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plourde, A.R.; Bloch, E.M. A Literature Review of Zika Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Govero, J.; Esakky, P.; Scheaffer, S.M.; Fernandez, E.; Drury, A.; Platt, D.J.; Gorman, M.J.; Richner, J.M.; Caine, E.A.; Salazar, V.; et al. Zika virus infection damages the testes in mice. Nature 2016, 540, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simanjuntak, Y.; Liang, J.-J.; Chen, S.-Y.; Li, J.-K.; Lee, Y.-L.; Wu, H.-C.; Lin, Y.-L. Ebselen alleviates testicular pathology in mice with Zika virus infection and prevents its sexual transmission. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giurg, M.; Gołąb, A.; Suchodolski, J.; Kaleta, R.; Krasowska, A.; Piasecki, E.; Piętka-Ottlik, M. Reaction of bis[(2-chlorocarbonyl)phenyl] Diselenide with Phenols, Aminophenols, and Other Amines towards Diphenyl Diselenides with Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties. Molecules 2017, 22, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
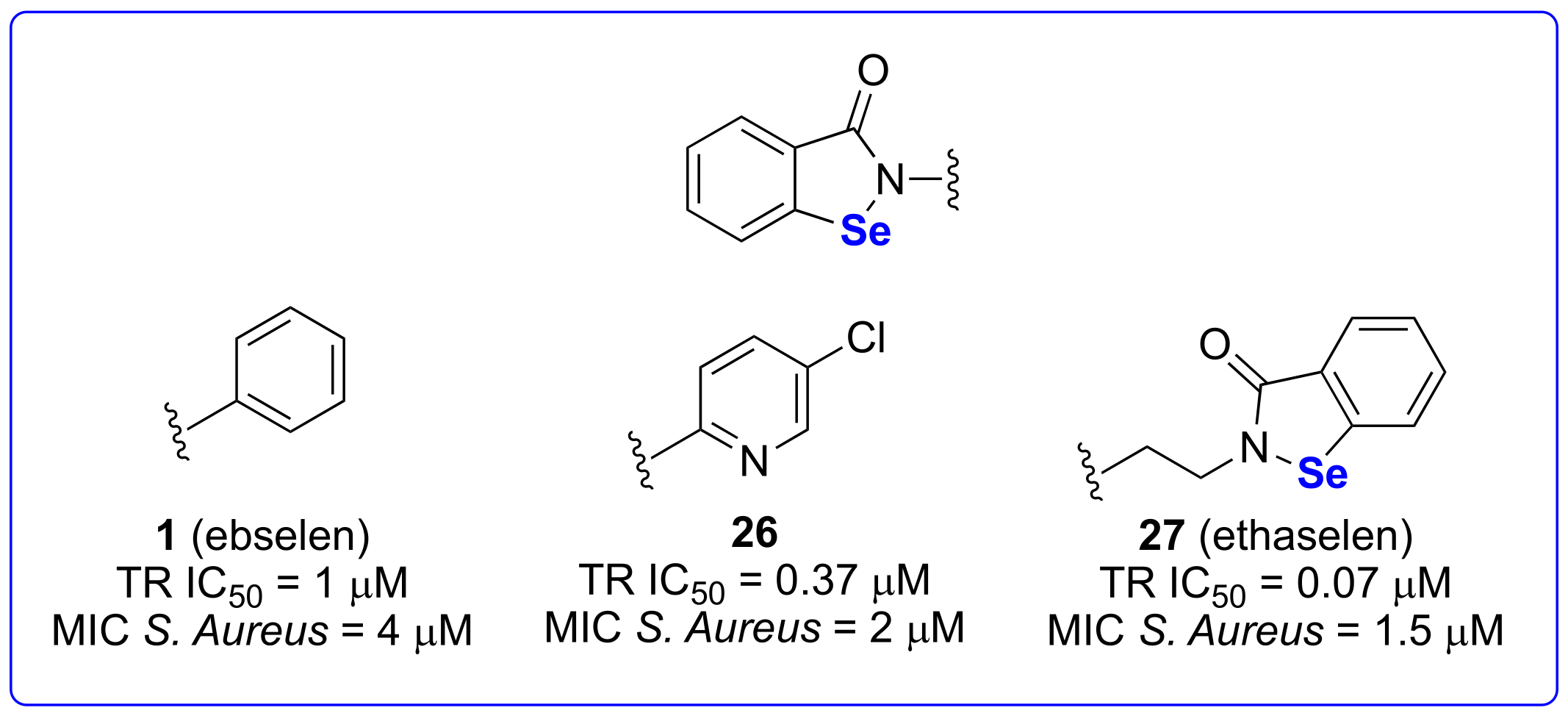
- Gustafsson, T.N.; Osman, H.; Werngren, J.; Hoffner, S.; Engman, L.; Holmgren, A. Ebselen and analogs as inhibitors of Bacillus anthracis thioredoxin reductase and bactericidal antibacterials targeting Bacillus species, Staphylococcus aureus and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, P.; Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Holmgren, A.; Zou, L. Topical Therapeutic Efficacy of Ebselen Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus LT-1 Targeting Thioredoxin Reductase. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- AbdelKhalek, A.; Abutaleb, N.S.; Mohammad, H.; Seleem, M.N. Repurposing ebselen for decolonization of vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammad, H.; Abutaleb, N.S.; Dieterly, A.M.; Lyle, L.T.; Seleem, M.N. Evaluation of ebselen in resolving a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection of pressure ulcers in obese and diabetic mice. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancineto, L.; Piccioni, M.; De Marco, S.; Pagiotti, R.; Nascimento, V.; Braga, A.L.; Santi, C.; Pietrella, D. Diphenyl diselenide derivatives inhibit microbial biofilm formation involved in wound infection. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leffler, D.A.; Lamont, J.T. Clostridium difficile Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1539–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schubert, A.M.; Rogers, M.A.M.; Ring, C.; Mogle, J.; Petrosino, J.P.; Young, V.B.; Aronoff, D.M.; Schloss, P.D. Microbiome Data Distinguish Patients with Clostridium difficile Infection and Non-C. difficile-Associated Diarrhea from Healthy Controls. MBio 2014, 5, e01021-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bender, K.O.; Garland, M.; Ferreyra, J.A.; Hryckowian, A.J.; Child, M.A.; Puri, A.W.; Solow-Cordero, D.E.; Higginbottom, S.K.; Segal, E.; Banaei, N.; et al. A small-molecule antivirulence agent for treating Clostridium difficile infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 306ra148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garland, M.; Hryckowian, A.J.; Tholen, M.; Oresic Bender, K.; Van Treuren, W.W.; Loscher, S.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Bogyo, M. The Clinical Drug Ebselen Attenuates Inflammation and Promotes Microbiome Recovery in Mice after Antibiotic Treatment for CDI. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.A.; Koehler, M.F.T.; Girgis, H.S.; Yan, D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Crawford, J.J.; Durk, M.R.; Higuchi, R.I.; Kang, J.; et al. Optimized arylomycins are a new class of Gram-negative antibiotics. Nature 2018, 561, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.F.; Hergenrother, P.J. The challenge of converting Gram-positive-only compounds into broad-spectrum antibiotics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1435, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
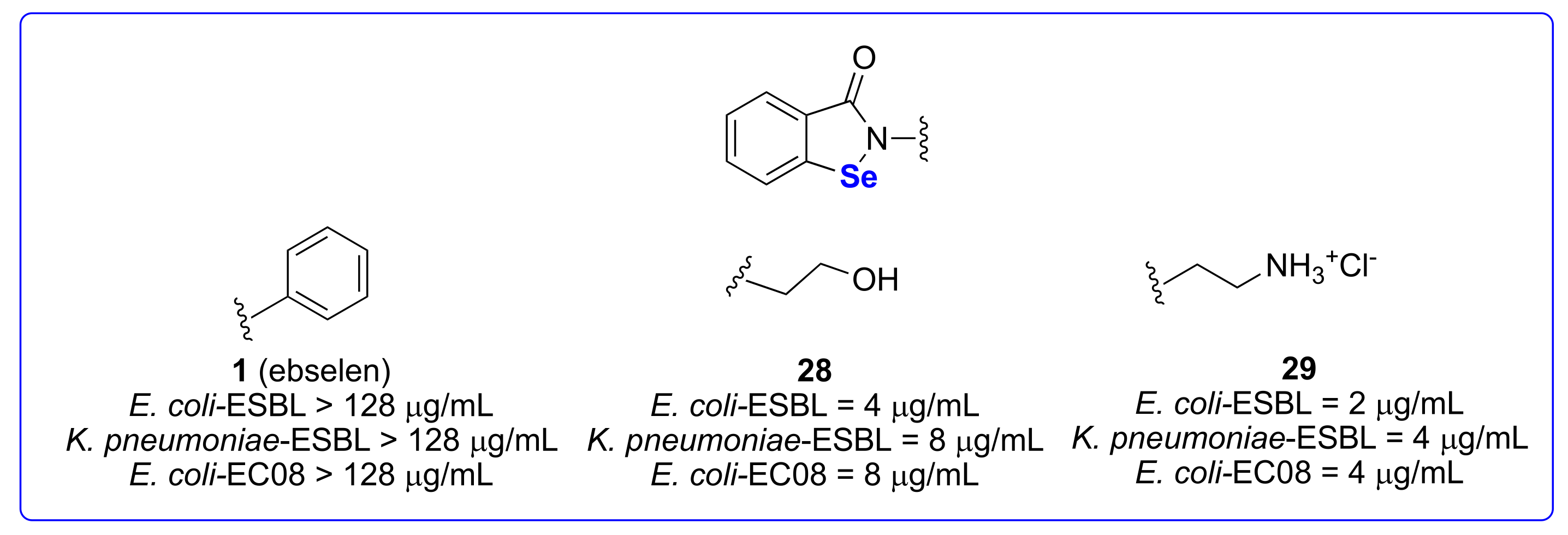
- Chen, C.; Yang, K. Ebselen bearing polar functionality: Identification of potent antibacterial agents against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.B.; Xu, C.; Cheung, Q.; Gao, W.; Zeng, P.; Liu, J.; Chan, E.W.C.; Leung, Y.-C.; Chan, T.H.; Wong, K.-Y.; et al. Bioisosteric investigation of ebselen: Synthesis and in vitro characterization of 1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one derivatives as potent New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 100, 103873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.B.; Xu, C.; Cheng, Q.; Qi, X.L.; Gao, W.; Zheng, Z.; Chan, E.W.C.; Leung, Y.-C.; Chan, T.H.; Wong, K.-Y.; et al. Investigation of synergistic antimicrobial effects of the drug combinations of meropenem and 1,2-benzisoselenazol-3(2H)-one derivatives on carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae producing NDM-1. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 155, 285–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, J.; Wan, S.; Chan, K.-F.; So, P.-K.; He, D.; Chan, E.W.; Chan, T.; Wong, K.; Tao, J.; Chen, S. Ebselen as a potent covalent inhibitor of New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM-1). Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9543–9546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y.; Rottenberg, M.E.; Holmgren, A. Synergistic antibacterial effect of silver and ebselen against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, C.; Zou, L. Depletion of multidrug-resistant uropathogenic Escherichia coli BC1 by ebselen and silver ion. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 13139–13150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klockgether, J.; Tümmler, B. Recent advances in understanding Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a pathogen. F1000Research 2017, 6, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, S.; Hayes, D.; Wozniak, D.J. Cystic Fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The Host-Microbe Interface. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.W.; Schurr, M.J.; Mudd, M.H.; Govan, J.R.; Holloway, B.W.; Deretic, V. Mechanism of conversion to mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa infecting cystic fibrosis patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8377–8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-K.; Ngo, H.X.; Dennis, E.K.; Thamban Chandrika, N.; DeShong, P.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S.; Lee, V.T. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Alginate Synthesis by Ebselen Oxide and Its Analogues. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loewenberg, S. India reports cases of totally drug-resistant tuberculosis. Lancet 2012, 379, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favrot, L.; Grzegorzewicz, A.E.; Lajiness, D.H.; Marvin, R.K.; Boucau, J.; Isailovic, D.; Jackson, M.; Ronning, D.R. Mechanism of inhibition of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigen 85 by ebselen. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goins, C.M.; Dajnowicz, S.; Thanna, S.; Sucheck, S.J.; Parks, J.M.; Ronning, D.R. Exploring Covalent Allosteric Inhibition of Antigen 85C from Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Ebselen Derivatives. ACS Infect. Dis. 2017, 3, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Munnik, M.; Lohans, C.T.; Lang, P.A.; Langley, G.W.; Malla, T.R.; Tumber, A.; Schofield, C.J.; Brem, J. Targeting the Mycobacterium tuberculosis transpeptidase Ldt Mt2 with cysteine-reactive inhibitors including ebselen. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 10214–10217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tirado-Sánchez, A.; González, G.M.; Bonifaz, A. Endemic mycoses: Epidemiology and diagnostic strategies. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galant, L.S.; Braga, M.M.; de Souza, D.; de Bem, A.F.; Sancineto, L.; Santi, C.; da Rocha, J.B.T. Induction of reactive oxygen species by diphenyl diselenide is preceded by changes in cell morphology and permeability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Free Radic. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangamani, S.; Eldesouky, H.E.; Mohammad, H.; Pascuzzi, P.E.; Avramova, L.; Hazbun, T.R.; Seleem, M.N. Ebselen exerts antifungal activity by regulating glutathione (GSH) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in fungal cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 3002–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orie, N.N.; Warren, A.R.; Basaric, J.; Lau-Cam, C.; Piętka-Ottlik, M.; Młochowski, J.; Billack, B. In vitro assessment of the growth and plasma membrane H + -ATPase inhibitory activity of ebselen and structurally related selenium- and sulfur-containing compounds in Candida albicans. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017, 31, e21892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vartak, R.; Menon, S.; Patki, M.; Billack, B.; Patel, K. Ebselen nanoemulgel for the treatment of topical fungal infection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 148, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, A.; Sharma, C.; Meis, J.F. Candida auris: A rapidly emerging cause of hospital-acquired multidrug-resistant fungal infections globally. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, G.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Wormley, F.L.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Patterson, H.P.; Patterson, T.F.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. Screening a Repurposing Library for Inhibitors of Multidrug-Resistant Candida auris Identifies Ebselen as a Repositionable Candidate for Antifungal Drug Development. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01084-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Büscher, P.; Cecchi, G.; Jamonneau, V.; Priotto, G. Human African trypanosomiasis. Lancet 2017, 390, 2397–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joice, A.C.; Harris, M.T.; Kahney, E.W.; Dodson, H.C.; Maselli, A.G.; Whitehead, D.C.; Morris, J.C. Exploring the mode of action of ebselen in Trypanosoma brucei hexokinase inhibition. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2013, 3, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordhan, H.M.; Patrick, S.L.; Swasy, M.I.; Hackler, A.L.; Anayee, M.; Golden, J.E.; Morris, J.C.; Whitehead, D.C. Evaluation of substituted ebselen derivatives as potential trypanocidal agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, L. Molecular Epidemiology of Cryptosporidiosis in China. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eltahan, R.; Guo, F.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, L.; Zhu, G. Discovery of ebselen as an inhibitor of Cryptosporidium parvum glucose-6-phosphate isomerase (CpGPI) by high-throughput screening of existing drugs. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2018, 8, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, A.; Nelson, A.T.; Silva-Olivares, A.; Shibayama, M.; Siegel, D.; McKerrow, J.H. In Vitro Efficacy of Ebselen and BAY 11-7082 Against Naegleria fowleri. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasowska, D.; Iraci, N.; Santi, C.; Drabowicz, J.; Cieslak, M.; Kaźmierczak-Barańska, J.; Palomba, M.; Królewska-Golińska, K.; Magiera, J.; Sancineto, L. Diselenides and Benzisoselenazolones as Antiproliferative Agents and Glutathione-S-Transferase Inhibitors. Molecules 2019, 24, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartolini, D.; Sancineto, L.; Fabro de Bem, A.; Tew, K.D.; Santi, C.; Radi, R.; Toquato, P.; Galli, F. Selenocompounds in Cancer Therapy: An Overview. Adv. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 259–302. [Google Scholar]
- Plano, D.; Karelia, D.N.; Pandey, M.K.; Spallholz, J.E.; Amin, S.; Sharma, A.K. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Selenium (Se-NSAID) Molecules as Anticancer Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1946–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, B.; Plano, D.; Encío, I.; Palop, J.A.; Sanmartín, C. In vitro radical scavenging and cytotoxic activities of novel hybrid selenocarbamates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1716–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberte, A.C.; Sanmartin, C.; Aydillo, C.; Sharma, A.K.; Plano, D. Development and Therapeutic Potential of Selenazo Compounds. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1473–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radomska, D.; Czarnomysy, R.; Radomski, D.; Bielawski, K. Selenium Compounds as Novel Potential Anticancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.W.; Barbosa, N.V.; Rocha, J.B.T. Toxicology and pharmacology of synthetic organoselenium compounds: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 1179–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Z.; Fu, J.; Yin, H.; Xiong, K.; Tan, Q.; Jin, H.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Tang, W.; et al. Ethaselen: A potent mammalian thioredoxin reductase 1 inhibitor and novel organoselenium anticancer agent. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Vlamis-Gardikas, A.; Kandasamy, K.; Zhao, R.; Gustafsson, T.N.; Engstrand, L.; Hoffner, S.; Engman, L.; Holmgren, A. Inhibition of bacterial thioredoxin reductase: An antibiotic mechanism targeting bacteria lacking glutathione. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koh, W.X.; Coppo, L.; Ganguly, R.; Holmgren, A.; Leong, W.K. Metallocenyl derivatives of ebselen are selective and competitive inhibitors of thioredoxin reductase. J. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 943, 121822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santofimia-Castaño, P.; Izquierdo-Alvarez, A.; Plaza-Davila, M.; Martinez-Ruiz, A.; Fernandez-Bermejo, M.; Mateos-Rodriguez, J.M.; Salido, G.M.; Gonzalez, A. Ebselen impairs cellular oxidative state and induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and activation of crucial mitogen-activated protein kinases in pancreatic tumour AR42J cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Guan, B.; Zhang, S. Discovery of Ebselen as an Inhibitor of 6PGD for Suppressing Tumor Growth. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 6921–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, C.; Kumar, C.; Gnad, F.; Nielsen, M.L.; Rehman, M.; Walther, T.C.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. Lysine Acetylation Targets Protein Complexes and Co-Regulates Major Cellular Functions. Science 2009, 325, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wallach, J.; Duane, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Adejare, A.; Ma, H. Developing selective histone deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors through ebselen and analogs. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pacuła, A.J.; Kaczor, K.B.; Antosiewicz, J.; Janecka, A.; Długosz, A.; Janecki, T.; Wojtczak, A.; Ścianowski, J. New Chiral Ebselen Analogues with Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Potential. Molecules 2017, 22, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacuła, A.J.; Kaczor, K.B.; Wojtowicz, A.; Antosiewicz, J.; Janecka, A.; Długosz, A.; Janecki, T.; Ścianowski, J. New glutathione peroxidase mimetics—Insights into antioxidant and cytotoxic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczor-Keller, K.B.; Pawlik, A.; Scianowski, J.; Pacuła, A.; Obieziurska, M.; Marcheggiani, F.; Cirilli, I.; Tiano, L.; Antosiewicz, J. In Vitro Anti-Prostate Cancer Activity of Two Ebselen Analogues. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsherbini, M.; Hamama, W.S.; Zoorob, H.H. An Easy Synthetic Approach to Construct Some Ebselen Analogues and Benzo[b]selenophene Derivatives: Their Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Assessment. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2018, 55, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabet, N.M.; Moustafa, E.M. Synergistic effect of Ebselen and gamma radiation on breast cancer cells. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2020 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16, 391–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpini, E.; Schelterns, P.; Feldman, H. Treatment of Alzheimer’s disease; current status and new perspectives. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Du, X.; Liu, Q. Ebselen ameliorates β-amyloid pathology, tau pathology, and cognitive impairment in triple-transgenic Alzheimer’s disease mice. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 22, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, F.; Pesarico, A.P.; Brüning, C.A.; Zeni, G.; Nogueira, C.W. Ebselen inhibits the activity of acetylcholinesterase globular isoform G4 in vitro and attenuates scopolamine-induced amnesia in mice. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 5598–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, F.; Rosa, S.G.; Klann, I.P.; Fulco, B.C.W.; Carvalho, F.B.; Rahmeier, F.L.; Fernandes, M.C.; Nogueira, C.W. A multifunctional compound ebselen reverses memory impairment, apoptosis and oxidative stress in a mouse model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 109, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klann, I.P.; Martini, F.; Rosa, S.G.; Nogueira, C.W. Ebselen reversed peripheral oxidative stress induced by a mouse model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Sheng, J.; Sun, Y.; Lu, C.; Yan, J.; Liu, A.; Luo, H.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Synthesis and Evaluation of Multi-Target-Directed Ligands against Alzheimer’s Disease Based on the Fusion of Donepezil and Ebselen. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9089–9099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morphy, R.; Kay, C.; Rankovic, Z. From magic bullets to designed multiple ligands. Drug Discov. Today 2004, 9, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancineto, L.; Iraci, N.; Barreca, M.L.; Massari, S.; Manfroni, G.; Corazza, G.; Cecchetti, V.; Marcello, A.; Daelemans, D.; Pannecouque, C.; et al. Exploiting the anti-HIV 6-desfluoroquinolones to design multiple ligands. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4658–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, H.-L.; Chen, S.; Chew, E.-H.; Chui, W.-K. Applying the designed multiple ligands approach to inhibit dihydrofolate reductase and thioredoxin reductase for anti-proliferative activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 115, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattrell, W.; Johnstone, C.; Patel, S.; Smith, C.S.; Scheel, A.; Schindler, M. Designed multiple ligands in metabolic disease research: From concept to platform. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Design, synthesis and evaluation of clioquinol–ebselen hybrids as multi-target-directed ligands against Alzheimer’s disease. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 7139–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landgraf, A.D.; Alsegiani, A.S.; Alaqel, S.; Thanna, S.; Shah, Z.A.; Sucheck, S.J. Neuroprotective and Anti-neuroinflammatory Properties of Ebselen Derivatives and Their Potential to Inhibit Neurodegeneration. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 3008–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, P.M. Metals and Motor Neuron Disease. In Biometals in Neurodegenerative Diseases; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 175–193. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, D.R.; Siddique, T.; Patterson, D.; Figlewicz, D.A.; Sapp, P.; Hentati, A.; Donaldson, D.; Goto, J.; O’Regan, J.P.; Deng, H.-X.; et al. Mutations in Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase gene are associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 1993, 362, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, M.J.; Wright, G.S.A.; Barbieri, L.; Luchinat, E.; Mercatelli, E.; McAlary, L.; Yerbury, J.J.; O’Neill, P.M.; Antonyuk, S.V.; Banci, L.; et al. The cysteine-reactive small molecule ebselen facilitates effective SOD1 maturation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantadul, V.; Wright, G.S.A.; Amporndanai, K.; Shahid, M.; Antonyuk, S.V.; Washbourn, G.; Rogers, M.; Roberts, N.; Pye, M.; O’Neill, P.M.; et al. Ebselen as template for stabilization of A4V mutant dimer for motor neuron disease therapy. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amporndanai, K.; Rogers, M.; Watanabe, S.; Yamanaka, K.; O’Neill, P.M.; Hasnain, S.S. Novel Selenium-based compounds with therapeutic potential for SOD1-linked amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. EBioMedicine 2020, 59, 102980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddes, J.R.; Goodwin, G.M.; Rendell, J.; Azorin, J.-M.; Cipriani, A.; Ostacher, M.J.; Morriss, R.; Alder, N.; Juszczak, E. Lithium plus valproate combination therapy versus monotherapy for relapse prevention in bipolar I disorder (BALANCE): A randomised open-label trial. Lancet 2010, 375, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, M.J.; Downes, C.P.; Hanley, M.R. Neural and developmental actions of lithium: A unifying hypothesis. Cell 1989, 59, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Halliday, A.C.; Thomas, J.M.; Kuznetsova, O.V.; Baldwin, R.; Woon, E.C.Y.; Aley, P.K.; Antoniadou, I.; Sharp, T.; Vasudevan, S.R.; et al. A safe lithium mimetic for bipolar disorder. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Sharpley, A.L.; Emir, U.E.; Masaki, C.; Herzallah, M.M.; Gluck, M.A.; Sharp, T.; Harmer, C.J.; Vasudevan, S.R.; Cowen, P.J.; et al. Effect of the Putative Lithium Mimetic Ebselen on Brain Myo-Inositol, Sleep, and Emotional Processing in Humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 1768–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaki, C.; Sharpley, A.L.; Godlewska, B.R.; Berrington, A.; Hashimoto, T.; Singh, N.; Vasudevan, S.R.; Emir, U.E.; Churchill, G.C.; Cowen, P.J. Effects of the potential lithium-mimetic, ebselen, on brain neurochemistry: A magnetic resonance spectroscopy study at 7 tesla. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2016, 233, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mota, F.; Sementa, T.; Taddei, C.; Moses, N.; Bordoloi, J.; Hader, S.; Eykyn, T.; Cash, D.; Turkheimer, F.; Veronese, M.; et al. Investigating the effects of ebselen, a potential new lithium mimetic, on glutamate transmission. Synapse 2020, 74, e22151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaki, C.; Sharpley, A.L.; Cooper, C.M.; Godlewska, B.R.; Singh, N.; Vasudevan, S.R.; Harmer, C.J.; Churchill, G.C.; Sharp, T.; Rogers, R.D.; et al. Effects of the potential lithium-mimetic, ebselen, on impulsivity and emotional processing. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 2655–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barkus, C.; Ferland, J.-M.N.; Adams, W.K.; Churchill, G.C.; Cowen, P.J.; Bannerman, D.M.; Rogers, R.D.; Winstanley, C.A.; Sharp, T. The putative lithium-mimetic ebselen reduces impulsivity in rodent models. J. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 32, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Serres, F.; Toker, L.; Sade, Y.; Blackburn, V.; Batra, A.S.; Saiardi, A.; Agam, G.; Belmaker, R.H.; Sharp, T.; et al. Effects of the putative lithium mimetic ebselen on pilocarpine-induced neural activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 883, 173377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenn, G.D.; Waller-Evans, H.; Atack, J.R.; Bax, B.D. Crystallization and structure of ebselen bound to Cys141 of human inositol monophosphatase. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2020, 76, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpley, A.L.; Williams, C.; Holder, A.A.; Godlewska, B.R.; Singh, N.; Shanyinde, M.; MacDonald, O.; Cowen, P.J. A phase 2a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, add-on clinical trial of ebselen (SPI-1005) as a novel treatment for mania or hypomania. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 3773–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadou, I.; Kouskou, M.; Arsiwala, T.; Singh, N.; Vasudevan, S.R.; Fowler, T.; Cadirci, E.; Churchill, G.C.; Sharp, T. Ebselen has lithium-like effects on central 5-HT 2A receptor function. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 2599–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuentes-López, E.; García-Huidobro Nuñez, F.; Acuña Caro, P.; Castro Becerra, N.; Jalil García, G.; Molina Marín, N.; Navea Stuardo, L.; Magallón, E.; Badía Venti, P. Auditory effects of recreational and occupational noise exposure among dental students: A cross-sectional study. Rev. CEFAC 2021, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlemiller, K.K.; McFadden, S.L.; Ding, D.-L.; Lear, P.M.; Ho, Y.-S. Targeted Mutation of the Gene for Cellular Glutathione Peroxidase (Gpx1) Increases Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Mice. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2000, 1, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kil, J.; Pierce, C.; Tran, H.; Gu, R.; Lynch, E.D. Ebselen treatment reduces noise induced hearing loss via the mimicry and induction of glutathione peroxidase. Hear. Res. 2007, 226, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourbakht, A.; Yamasoba, T. Ebselen attenuates cochlear damage caused by acoustic trauma. Hear. Res. 2003, 181, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, E.D.; Gu, R.; Pierce, C.; Kil, J. Ebselen-Mediated Protection From Single and Repeated Noise Exposure in Rat. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.Y.; Kabara, L.L.; Swiderski, D.L.; Raphael, Y.; Duncan, R.K.; Kim, Y.H. ROS Scavenger, Ebselen, Has No Preventive Effect in New Hearing Loss Model Using a Cholesterol-Chelating Agent. J. Audiol. Otol. 2019, 23, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kil, J.; Lobarinas, E.; Spankovich, C.; Griffiths, S.K.; Antonelli, P.J.; Lynch, E.D.; Le Prell, C.G. Safety and efficacy of ebselen for the prevention of noise-induced hearing loss: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 969–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.; Longenecker, R.J.; Homan, J.; Kil, J. Ebselen attenuates tobramycin-induced ototoxicity in mice. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leroux, F.; Bosc, D.; Beghyn, T.; Hermant, P.; Warenghem, S.; Landry, V.; Pottiez, V.; Guillaume, V.; Charton, J.; Herledan, A.; et al. Identification of ebselen as a potent inhibitor of insulin degrading enzyme by a drug repurposing screening. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 179, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kil, J.; Harruff, E.E.; Longenecker, R.J. Development of ebselen for the treatment of sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus. Hear. Res. 2021, 108209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, K.; Ohno, Y.; Kanematsu, T.; Sakurai-Yamashita, Y.; Niwa, M.; Hishikawa, Y.; Koji, T. Possible Protection of Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells by Endothelin B Receptor During Hepatic Warm Ischemia–Reperfusion. Surg. Today 2007, 37, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Zhong, J.; Wu, F.; Li, G.; Ruan, Q.; Luo, G.; Jiang, H. Ebselen protects rat hearts against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beckman, J.A.; Goldfine, A.B.; Leopold, J.A.; Creager, M.A. Ebselen does not improve oxidative stress and vascular function in patients with diabetes: A randomized, crossover trial. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 311, H1431–H1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, M.; Wang, F.; Cao, D.; Ruan, J.J.; Su, W.; Ruan, B.H. Mono-sulfonated tetrazolium salt based NAD(P)H detection reagents suitable for dehydrogenase and real-time cell viability assays. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 509, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ruan, H.; Zhao, H.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Ji, X.; Ruan, B.H. Ebselen: Mechanisms of Glutamate Dehydrogenase and Glutaminase Enzyme Inhibition. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 3003–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Li, D.; Lu, S.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Z.; Hou, W.; Ruan, B.H. Ebselen Reversibly Inhibits Human Glutamate Dehydrogenase at the Catalytic Site. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2018, 16, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Węglarz-Tomczak, E.; Burda-Grabowska, M.; Giurg, M.; Mucha, A. Identification of methionine aminopeptidase 2 as a molecular target of the organoselenium drug ebselen and its derivatives/analogues: Synthesis, inhibitory activity and molecular modeling study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5254–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, N.; Shi, Q.; Tong, L.; Kong, F.; Cheng, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Tang, B. Target discovery of ebselen with a biotinylated probe. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 9506–9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


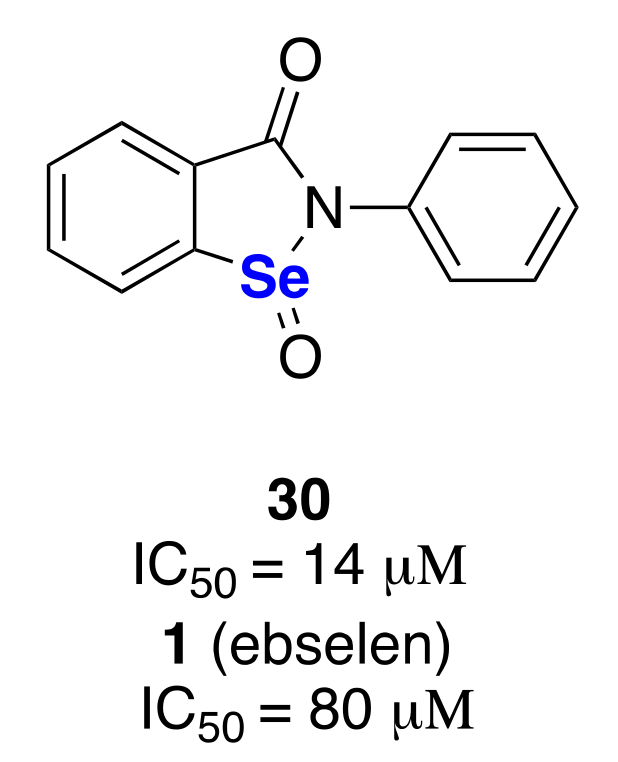

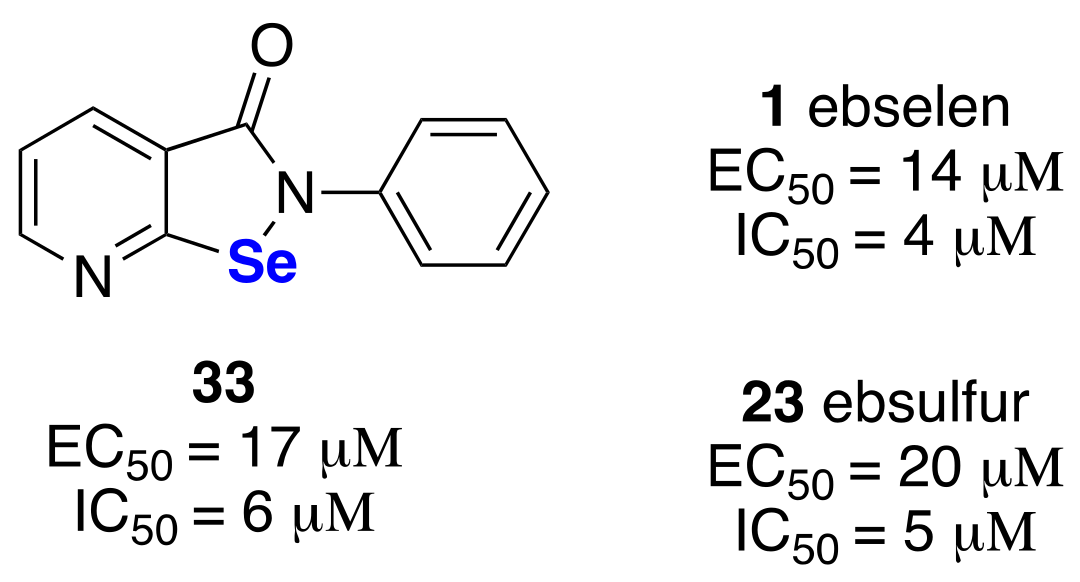

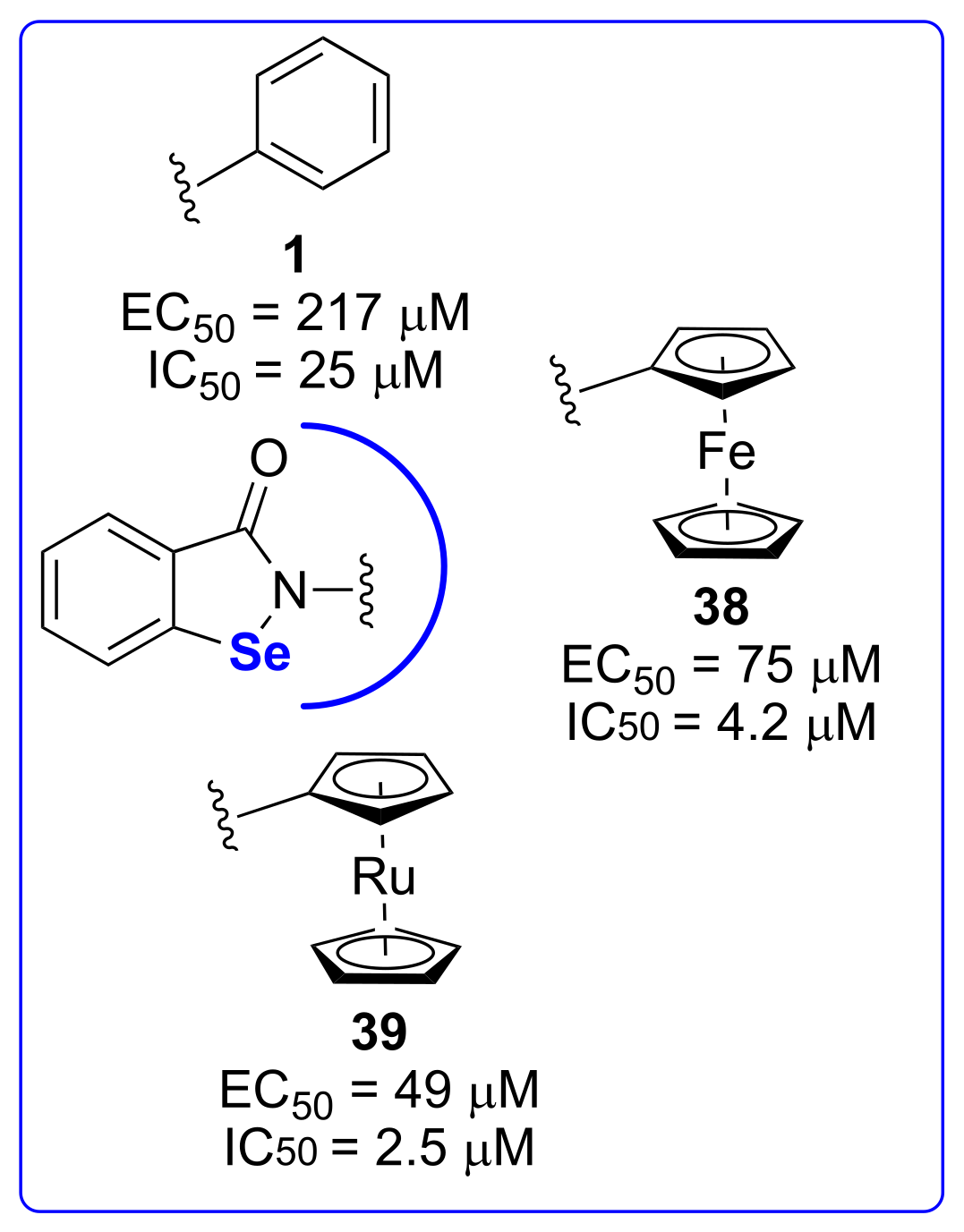

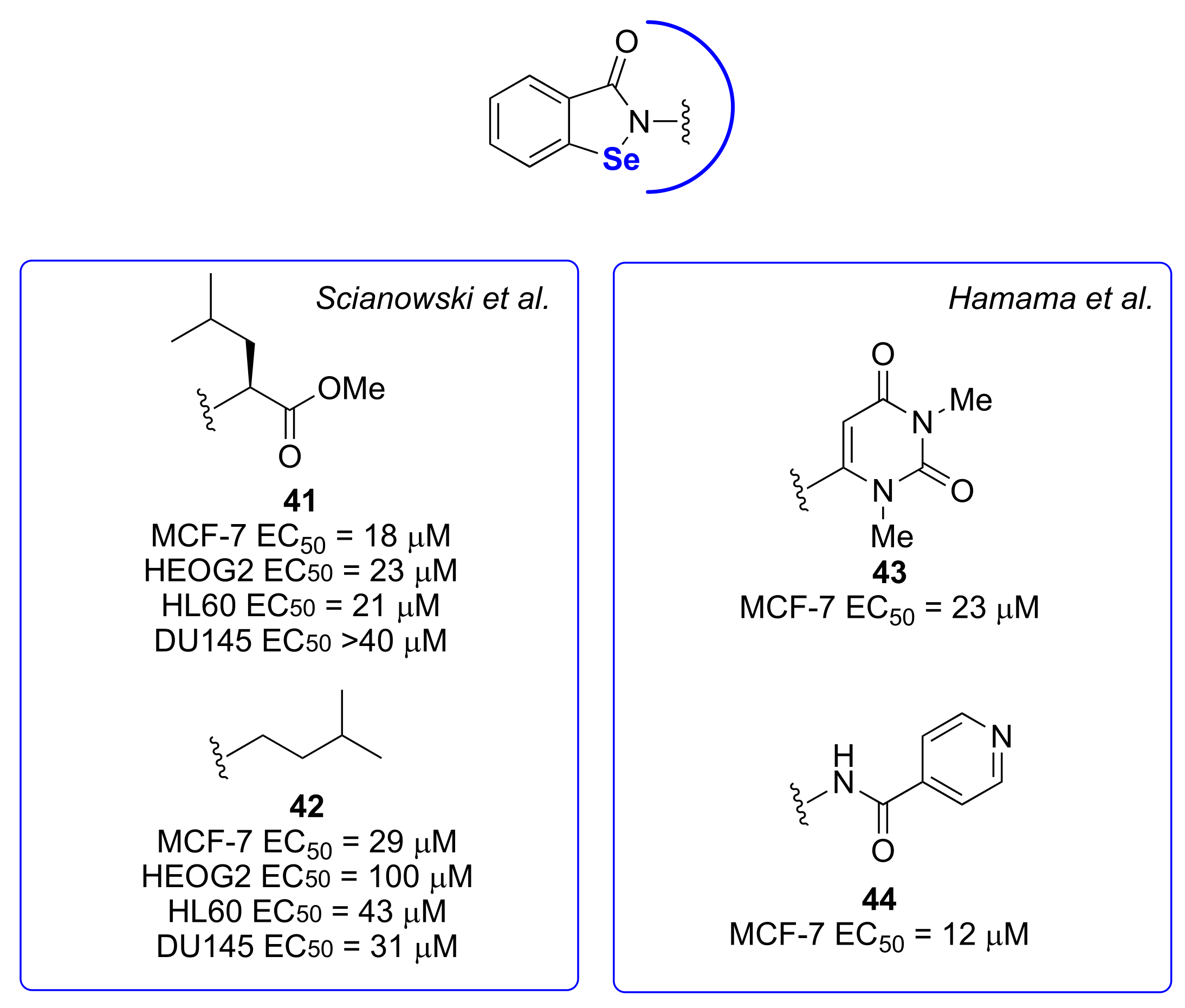

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santi, C.; Scimmi, C.; Sancineto, L. Ebselen and Analogues: Pharmacological Properties and Synthetic Strategies for Their Preparation. Molecules 2021, 26, 4230. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144230
Santi C, Scimmi C, Sancineto L. Ebselen and Analogues: Pharmacological Properties and Synthetic Strategies for Their Preparation. Molecules. 2021; 26(14):4230. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144230
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanti, Claudio, Cecilia Scimmi, and Luca Sancineto. 2021. "Ebselen and Analogues: Pharmacological Properties and Synthetic Strategies for Their Preparation" Molecules 26, no. 14: 4230. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144230
APA StyleSanti, C., Scimmi, C., & Sancineto, L. (2021). Ebselen and Analogues: Pharmacological Properties and Synthetic Strategies for Their Preparation. Molecules, 26(14), 4230. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144230