Abstract
A series of ruthenium(II) complexes with N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands of the general type (arene)(NHC)Ru(II)X2 (where X = halide) was prepared, characterized, and evaluated as antibacterial agents in comparison to the respective metal free benzimidazolium cations. The ruthenium(II) NHC complexes generally triggered stronger bacterial growth inhibition than the metal free benzimidazolium cations. The effects were much stronger against Gram-positive bacteria (Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus) than against Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa), and all complexes were inactive against the fungus Candida albicans. Moderate inhibition of bacterial thioredoxin reductase was confirmed for selected complexes, indicating that inhibition of this enzyme might be a contributing factor to the antibacterial effects.
1. Introduction
Metal complexes with N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands represent an important type of catalysts, however, in addition to their application in chemistry, the biomedical properties have been evaluated intensively. In particular, inorganic medicinal chemistry and bioorganometallic chemistry nowadays make intensive use of the relatively high stability of the metal-carbon bonds of these compounds and the convenient synthetic access to a broad variety of NHC ligands [1,2,3,4,5,6,7].
The design of drug candidates based on metal NHC complexes has been dominated by gold and silver as metals, however, more recently, an increasing number of metals has demonstrated very promising results, including, for example, rhodium [8,9,10,11,12] and iridium [12,13] species.
We and others have recently reported on ruthenium(II) NHC complexes of the general type (p-cymene)(NHC)Ru(II)X2 (where X = halide) and structurally related complexes as novel anticancer drug candidates [14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. For complexes with the general structure (p-cymene)(NHC)Ru(II)Cl2 with different substituents on the NHC nitrogen atoms, the antiproliferative activity was dependent on the lipophilicity of the nitrogen side chains and on cellular uptake. The compounds inhibited thiol or selenol containing enzymes (e.g., thioredoxin reductase, cathepsin B), were generally reactive towards biologically relevant thiols, and underwent ligand exchange reactions (e.g., the replacement of the NHC ligand upon reaction with N-acetylcysteine could be confirmed by NMR). Interestingly, the complexes were well tolerated regarding toxicity in zebrafish embryos and mouse models [14,17]. Hartinger et al. demonstrated by means of X-ray crystallography with the model protein hen egg white lysozyme that, upon binding, the p-cymene ligand of the complexes was replaced, while the NHC ligand remained coordinated in this case [21]. Interestingly, the same group also demonstrated that derivatives with a pyridine in one of the side chain showed enhanced stability towards cysteine [19].
Notably, the probably first report on biological activity of (arene)(NHC)Ru(II)X2 complexes describes their application as antibacterial agents [22]. However, the literature on such application of the complexes appears limited to very few reports [22,23,24,25].
In order to shed more light on the potential of ruthenium NHC complexes as antibacterial agents, we synthesized and evaluated their bacterial cell growth inhibition. Furthermore, the inhibition of bacterial thioredoxin reductase was studied as a possible mechanism of action. The target compounds are based on the (p-cymene)(NHC)Ru(II)Cl2 scaffold of our previous work [14] and contain substituents with different inductive and mesomeric effects on the NHC moiety. The substituents are thus expected to influence the donor capacity of the NHC ligand, and with this, the reactivity and biological activity of the organometallics.
2. Synthesis and Characterization
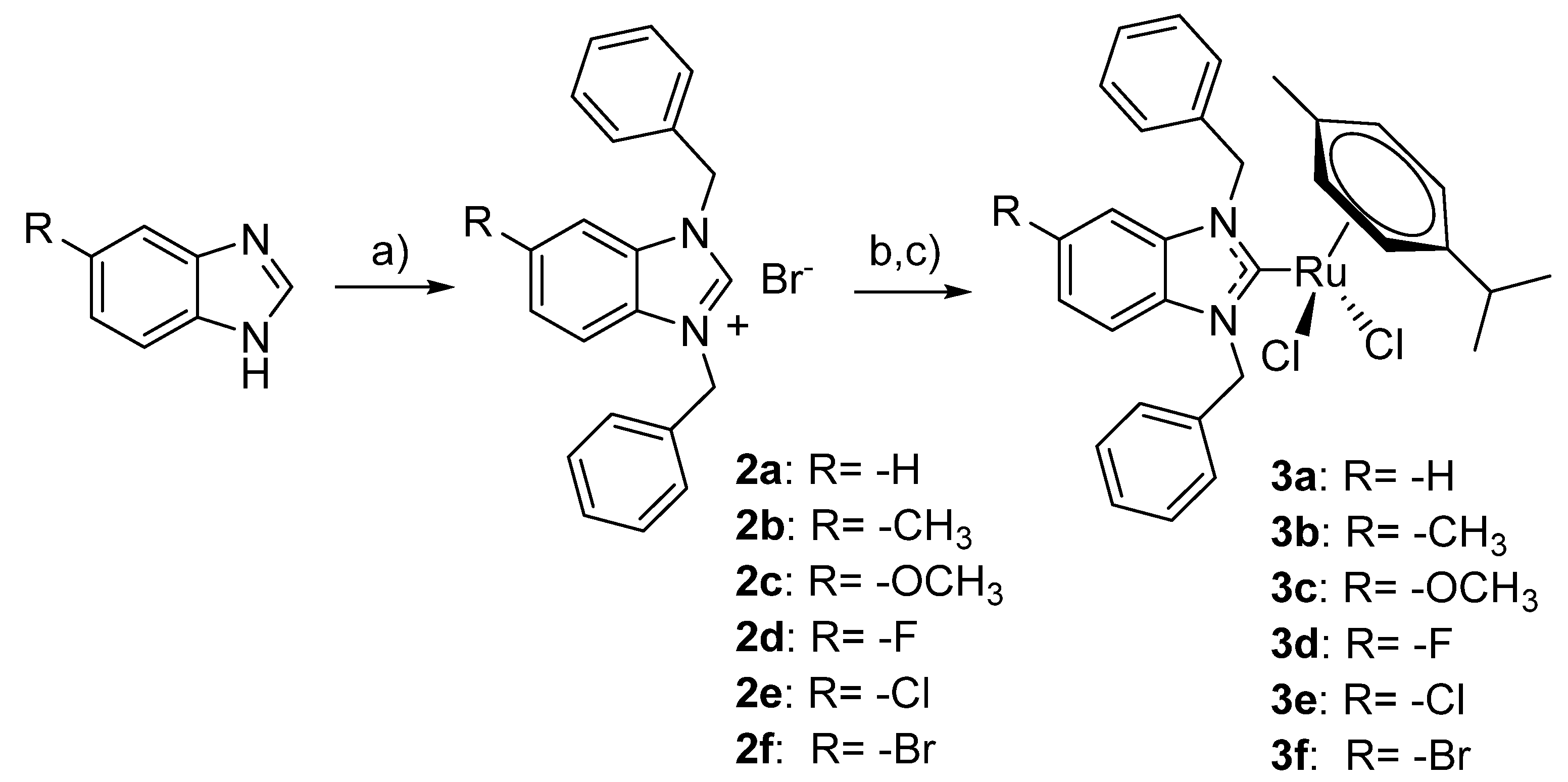
The (p-cymene)(NHC)Ru(II)Cl2 target compounds were obtained based on an established two-step procedure (Scheme 1). In the first step, the benzimidazoles 1a–1f were alkylated with benzyl bromide resulting in the benzimidazolium bromides 2a–2f. In the second step, the target compounds 3a–3f were obtained in a one-pot reaction by activating 2a–2f with silver oxide followed by transmetalation with [(p-Cym)RuCl2]2. The respective complexes required adjustments regarding the reaction period of the transmetalation reaction in step 2 and the isolation procedure. Thus, to obtain complexes 3d–3f with halide substituents, extended reaction periods of up to 7 days were required. Complex 3f was isolated by column chromatography over silica in contrast to the other complexes, which could be obtained in high purity by filtration over celite followed by crystallization.
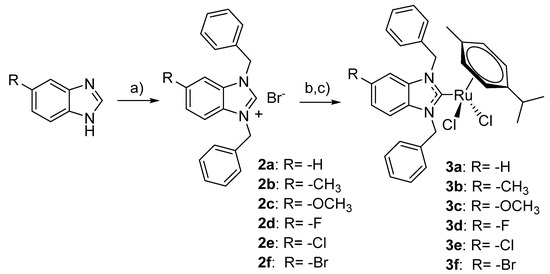
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of the (NHC)(p-Cym)Ru(II)Cl2 complexes; (a) K2CO3, benzyl bromide, (b) Ag2O, (c) [(p-Cym)RuCl2]2..
The obtained target compounds were characterized by 1H- and 13C-NMR and mass spectroscopy. The high purities were confirmed by elemental analyses.
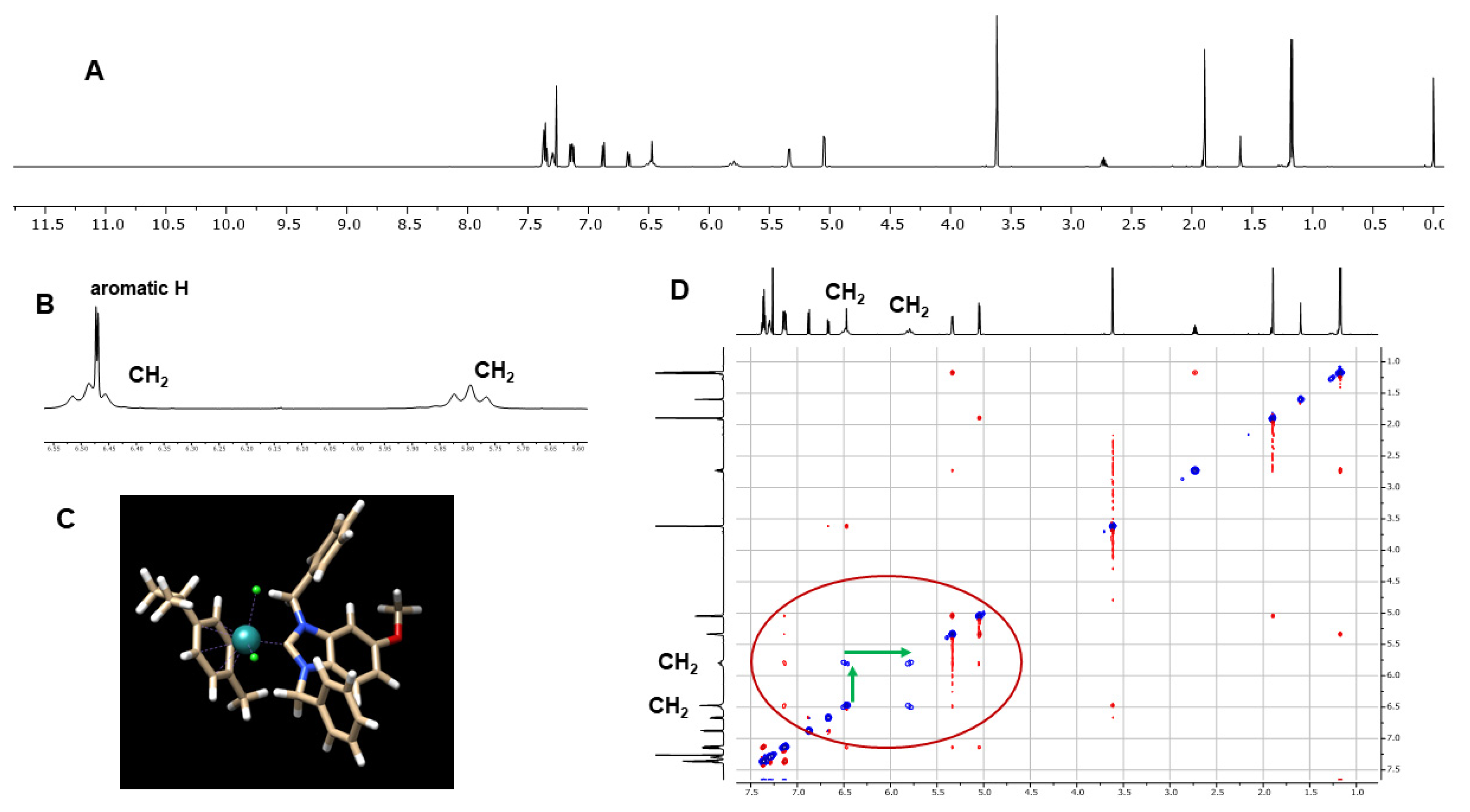
Several diagnostic features confirming complex formation can be observed in the NMR spectra. The hydrogen signal of the benzimidazole C2 carbon in the 1H-NMR spectra, which appears in the range of 11.6–12.1 ppm in the spectra of the benzimidazolium bromides 2a–2f, is missing in the spectra of the metal complexes 3a–3f. In the 13C-NMR spectra, the signal of the C2 carbon is shifted downfield from 142–144 ppm in the spectra of 2a–2f to 192–194 ppm in the spectra of 3a–3f. The CH2 groups of the benzyl side chains in the benzimidazolium cations 2a–2f form the expected singlets in the 1H-NMR spectra. The respective CH2 groups in the complexes 3a–3f, however, are non-equivalent, with diastereotopic protons and each individual hydrogen appears as a separate broadened signal (Figure 1A,B).
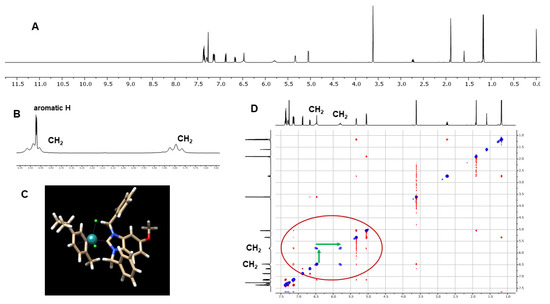
Figure 1.
(A) 1H-NMR spectrum (600 MHz, CDCl3) of 3c; (B) magnification of the section between 5.6 and 6.5 ppm; (C) DFT calculated geometry of 3c; (D) NOESY spectrum (600 MHz, CDCl3) of 3c, the EXSY correlation peaks between the CH2 hydrogens are marked with green arrows.
Figure 1 shows exemplarily the 1H-NMR spectrum of 3c (Figure 1A) with the broadened CH2 signals (Figure 1B), which appear as pseudo-triplets due to the overlapping of two doublets. The calculated geometries of 3c (Figure 1C) show that, for each CH2 group, only one individual hydrogen is directed towards a chlorido ligand, causing a different chemical environment for the individual protons of each CH2 group that results in a signal shift of approximately 0.7 ppm. Further confirmation was obtained by a NOESY/EXSY spectrum, which shows EXSY correlation signals as a consequence of the slow dynamic exchange process between the two individual hydrogens of each CH2 group (Figure 1D).
3. Antibacterial Activity and Inhibition of Bacterial TrxR
The antibacterial activity of compounds 2a/3a–2f/3f was assessed in three Gram-negative (Escherichia coli, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) and in three Gram-positive strains (Bacillus subtilis, two different strains of Staphylococcus aureus) as minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC). The fungus Candida albicans was used as a non-bacterial reference organism. The broad-spectrum antibiotic Ciprofloxacin was used as a reference drug. The results are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
MIC values (µM) against Gram-negative bacteria (E. coli DSM 30083, A. baumannii, P. aeruginosa), Gram-positive bacteria (B. subtilis 168, S. aureus DSM 20231, S. aureus ATCC 43300), and C. albicans DSM 1386.
The benzimidazolium cations 2a–2f were inactive (MIC values > 1000 µM) against the Gram-negative bacteria as well as against C. albicans; however, low to moderate activity was recorded against the Gram-positive bacteria. Among them, compound 2c was the most active with a MIC value of 19.5 µM against both S. aureus strains.
The ruthenium NHC complexes 3a–3f caused very low activity against the Gram-negative bacteria (all MIC values above 200 µM) and were inactive against C. albicans (MIC values > 700 µM). Good activity was noted against all Gram-positive bacteria, with MIC values in the range of 11 to 53 µM. The most active complex was 3f, for which an MIC value of 11.7 µM was recorded against B. subtilis and the methicillin and oxacillin resistant S. aureus ATCC 43300 strain. Comparing the metal free compounds 2a–2f with the respective ruthenium(II) NHC complexes 3a–3f confirms the activity-enhancing effect of the metal coordination. With the exception of the couple 2c/3c all ruthenium complexes were substantially more active than the respective benzimidazolium derivatives.
The inhibition of TrxR has been considered as a novel mode of action for antibiotics and in our previous report, the relevance for gold NHC complexes had been shown [26]. In order to evaluate TrxR inhibition of ruthenium NHC complexes, complexes 3a, 3b, and 3f were selected and the inhibition of purified E. coli TrxR was determined by the 5,5-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) reduction assay. The respective metal free benzimidazolium derivatives 2a, 2b, and 2f were used as references and as expected were inactive (IC50 values > 100 µM). For the ruthenium NHC complexes 3a and 3b IC50 values of 24.8 (±5.4) µM (3a) and 14.0 (±1.6) µM (3b) were recorded, while 3f was inactive (IC50 value > 100 µM). On the one hand, this confirms a moderate activity as bacterial TrxR inhibitors for ruthenium NHC complexes, but on the other hand, the missing efficacy as TrxR inhibitor of the strongest antibacterial complex 3f shows that there is no direct correlation between bacterial TrxR inhibition and antibacterial activity.
4. Conclusions
A series of benzimidazolium cations and the corresponding organometallics of the type (p-cymene)(NHC)Ru(II)Cl2 were synthesized, characterized, and evaluated as antibacterial agents. The ruthenium(II) complexes were overall more active inhibitors of bacterial growth than the respective metal free benzimidazolium derivatives, confirming an activity enhancing effect of the metal coordination. Complex 3f was the most active compound and exhibited a considerable selectivity for Gram-positive bacteria in comparison to Gram-negative bacteria or C. albicans. Such preference for Gram-positive bacteria is common due to the different characteristics of the bacterial cell wall of Gram-positive versus Gram-negative bacteria. In addition to that, many Gram-positive bacteria lack sufficient levels of glutathione and are highly dependent on an operating Trx/TrxR-system, making them very sensitive to strong TrxR inhibitors, such as gold compounds [26,27,28]. Accordingly, the ruthenium(II) NHC complexes were studied as inhibitors of bacterial TrxR. Moderate inhibition was noted for some complexes, however, there was no correlation to the antibacterial effects. Inhibition of TrxR is therefore unlikely a major mechanism of the antibacterial activity of the ruthenium NHC complexes, but might contribute to their biological profile in the sense of the complexes “hitting” multiple targets or disease pathways.
Further optimization of the efficacy of ruthenium(II) NHC complexes as antibacterial agents and studies on their mechanism of action are the subject of ongoing projects.
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. General
The reagents were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), Thermo Fisher (Kandel, Germany), or TCI (Eschborn, Germany), and used without additional purification steps. All reactions were performed without precautions to exclude air or moisture. 1H and 13C NMR were recorded on a Bruker Biospin (Germany) DRX-400 AS (Germany), AVIIIHD 500, or AVII 600. A Finnigan MAT 95 was used to record the ESI mass spectra. The elemental analyses were performed using a Flash EA 1112 (Thermo Quest CE Instruments, Egelsbach, Germany). Absorption measurements for TrxR inhibition, and antiproliferative activity were performed on a Perkin-Elmer 2030 Multilabel Reader VICTORTM X4 (Rodgau, Germany). The synthesis of 2a [29], 2c [30], and 3a [14] was reported. For computational chemistry, Gaussian 98 W (5.4 Rev A.9) was used with the B3LYP functional and LANL2DZ basis set [31].
5.2. Synthesis of the Benzimidazolium Bromides
The respective benzimidazole was dissolved in acetonitrile, treated with 2.5 equivalents K2CO3, and stirred at room temperature for 30 min. Two equivalents of benzyl bromide were added and stirring was continued until the reaction was complete as monitored by thin layer chromatography (periods are indicated below). The solvent was removed by reduced pressure; the residue was resuspended in dichloromethane and filtered. After evaporation under reduced pressure, the remaining oil was treated with diethyl ether to precipitate the product.
1,3-Dibenzyl-5-methyl-1H-benzimidazolium bromide (2b) prepared starting from 5-methyl-1H-benzimidazol (300.5 mg, 2.27 mmol), reaction period: 3 days; yield: 624.6 mg (1.59 mmol, 69.8%), white-yellowish powder; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 11.83 (s, BeIm-H2, 1H), 7.52–7.48 (m, Bn1+Bn2-H2+H6, 4H), 7.44 (dd, 3JH,H = 8.5 Hz, 5JH,H = 0.7 Hz, BeIm-H7, 1H), 7.36 (m, Bn1+Bn2-H3-H5, 6H), 7.34 (m, BeIm-H4, 1H), 7.30 (dd, 3JH,H = 8.6 Hz, 4JH,H = 2.1 Hz, BeIm-H6, 1H), 5.85 (s, Bn1-CH2, 2H), 5.83 (s, Bn2-CH2, 2H), 2.45 (s, 4JH,H = 0.7 Hz, BeIm-CH3, 3H); 13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 142.55 (BeIm-C2), 138.09 (BeIm-C5quart.), 132.60 (Bn2-C1quart.), 132.56 (Bn1/Bn2-C1quart.), 131.61 (BeIm-C7aquart.), 129.39 (BeIm-C3aquart.), 129.36 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 129.33 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 129.19 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 129.18 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 128.79 (BeIm-C6), 128.24 (Bn1/Bn2-C2+C6), 128.17 (Bn1/Bn2-C2+C6), 113.27 (BeIm-C7), 113.08 (BeIm-C4), 51.46 (Bn1-CH2), 51.24 (Bn2-CH2), 21.76 (BeIm-CH3); elemental analysis for C22H21BrN2 (theoreticalfound [%]): C (67.18/67.08), H (5.38/5.55), N (7.12/7.10); MS (ESI): m/z 313.17 [M − Br]+, 493.26 [M + 2H2O + 2MeOH]+, 707.26 [M + M – Br + 2H+]+.
1,3-Dibenzyl-5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazolium bromide (2c) [30] prepared starting from 5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazole (250.0 mg, 1.69 mmol); reaction period: 3 days; yield: 131.7 mg (0.32 mmol, 19.1%), white-grey powder; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 11.62 (s, BeIm-H2, 1H), 7.53 (m, Bn1-H2+H6, 2H), 7.48 (m, Bn2-H2+H6, 2H), 7.43 (dd, 3JH,H = 9.1 Hz, 5JH,H = 0.6 Hz, BeIm-H7, 1H), 7.36 (m, Bn2-H3-H5, 3H), 7.33 (m, Bn1-H3-H5, 3H), 7.05 (dd, 3JH,H = 9.1 Hz, 4JH,H = 2.3 Hz, BeIm-H6, 1H), 7.02 (dd, 4JH,H = 2.3 Hz, 5JH,H = 0.6 Hz, BeIm-H4, 1H), 5.86 (s, Bn2-CH2, 2H), 5.81 (s, Bn1-CH2, 2H), 3.80 (s, BeIm-OCH3, 3H); 13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 159.3 (BeIm-C5quart.), 141.9 (BeIm-C2), 132.61 (Bn2-C1quart.), 132.55 (Bn1-C1quart.), 132.54 (BeIm-C7aquart.), 129.31 (Bn1+Bn2-C2-C4), 129.29 (Bn1+Bn2-C2-C4), 129.18 (Bn1+Bn2-C2-C4), 129.14 (Bn1+Bn2-C2-C4), 128.30 (Bn2-C1,C5), 128.19 (Bn1-C1,C5), 125.34 (BeIm-C3aquart.), 117.21 (BeIm-C6), 114.4 (BeIm-C7), 96.18 (BeIm-C4), 56.2 (BeIm-OCH3), 51.5 (Bn1-CH2), 51.2 (Bn2-CH2); elemental analysis for C22H21BrN2O (theoretical/found [%]): C (64.56/64.82), H (5.17/5.14), N (6.84/6.78); MS (ESI): m/z 329.2 [M − Br]+, 509.26 [M + 2H2O + 2MeOH]+, 737.25 [M + M − Br]+.
1,3-Dibenzyl-5-fluoro-1H-benzimidazolium bromide (2d) prepared starting from 5-fluoro-1H-benzimidazole (269.5, 1.98 mmol); reaction period: 10 days; yield: 432.0 mg (1.09 mmol, 54.9%), grey powder; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 11.98 (s, BeIm-H2, 1H), 7.55 (dd, 3JH,F = 4.4 Hz, 4JH,H = 1.7 Hz, BeIm-H6, 1H), 7.54–7.50 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H2-H6, 4H), 7.41–7.33 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H2-H6, 6H), 7.24–7.21 (m, BeIm-H7, 1H), 7.20 (d, 3JH,F = 2.0 Hz, BeIm-H4, 1H), 5.91 (s, Bn1/Bn2-CH2, 2H), 5.86 (s, Bn1/Bn2-CH2, 2H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 161.14 (d, 1JC,F = 249.7 Hz, BeIm-C5quart.), 144.39 (BeIm-C2), 132.21 (Bn1-C1quart.), 132.02 (Bn2-C1quart.), 131.93 (BeIm-C7aquart.), 129.52 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 129.46 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 129.40 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 128.34 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 128.33 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 127.82 (BeIm-C3aquart.), 116.17 (d, 3JC,F = 26.2 Hz, BeIm-C4), 115.39 (d, 4JC,F = 10.1 Hz, BeIm-C7), 100.77 (d, 3JC,F = 28.3 Hz, BeIm-C6), 51.93 (Bn1-CH2), 51.90 (Bn2-CH2); elemental analysis for C21H18BrFN2 (theroretical/found [%]): C (63.49/63.22), H (4.57/4.55), N (7.05/6.64); MS (ESI): m/z 317.14 [M − Br]+, 497.24 [M + 2H2O + 2MeOH]+, 713.21 [M + M − Br]+.
1,3-Dibenzyl-5-chloro-1H-benzimidazolium bromide (2e) prepared starting from 5-chloro-1H-benzimidazole (299.3 mg, 1.97 mmol); reaction period: 21 days; yield: 306.0 mg (0.74 mmol, 37.7%), white-yellowish powder; 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 12.00 (s, BeIm-H2, 1H), 7.53 (dd, 4JH,H = 2.0 Hz, 3JH,H = 1.0 Hz, BeIm-H6, 1H), 7.51 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H2-H6, 4H), 7.50 (dd, 3JH,H = 7.7, 5JH,H = 0.6 Hz, BeIm-H7, 1H), 7.43 (dd, 3JH,H = 8.9 Hz, 4JH,H = 1.8 Hz, BeIm-H4, 1H), 7.41–7.33 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H2-H6, 6H), 5.90 (s, Bn1-CH2, 2H), 5.85 (s, Bn2-CH2, 2H); 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 144.32 (BeIm-C2), 133.51 (BeIm-C7aquart.), 132.17 (Bn1-C1quart.), 132.03 (Bn2-C1quart.), 132.02 (BeIm-C3aquart.), 129.94 (BeIm-C5quart.), 129.54 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 129.49 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 129.47 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 129.42 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 128.34 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 128.30 (Bn1/Bn2-C2-C6), 127.99 (BeIm-C4), 114.96 (BeIm-C6), 113.68 (BeIm-C7), 51.94 (Bn1-CH2), 51.83 (Bn2-CH2); elemental analysis for C21H18BrClN2 (theoretical/found [%]): C (60.96/60.62), H (4.39/4.56), N (6.77/6.49); MS (ESI): m/z 333.12 [M − Br]+, 513.21 [M + 2H2O + 2MeOH]+, 747.15 [M + M − Br]+.
1,3-Dibenzyl-5-bromo-1H-benzimidazolium bromide (2f) prepared starting from 5-Bromo-1H-benzimidazol (298.4 mg, 1.51 mmol); reaction period: 21 days; yield: 182.1 mg (0.40 mmol, 26.2%), orange powder; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 11.98 (s, BeIm-H2, 1H), 7.68 (dd, 4JH,H = 1.7 Hz, 5JH,H = 0.6 Hz, BeIm-H4, 1H), 7.58 (dd, 3JH,H = 8.9 Hz, 4JH,H = 1.7 Hz, BeIm-H6, 1H), 7.52 (t, 4JH,H = 1.8 Hz, Bn2-H3+H5, 2H), 7.51 (dd, 4JH,H = 1.9 Hz, Bn1-H3+H5, 2H), 7.46 (dd, 3JH,H = 8.9 Hz, 5JH,H = 0.6 Hz, BeIm-H7, 1H), 7.42–7.38 (m, Bn2-H2+H4+H6, 3H), 7.38–7.34 (m, Bn2-H2+H4+H6, 3H), 5.89 (s, Bn1-CH2, 2H), 5.84 (s, Bn2-CH2 2H); 13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 144.06 (BeIm-C2), 132.38 (BeIm-C7aquart.), 132.16 (Bn1-C1quart.), 132.01 (Bn2-C1quart.), 130.66 (BeIm-C6), 130.33 (BeIm-C3aquart.), 129.56 (Bn1+Bn2-C2+C4+C6), 129.51 (Bn1+Bn2-C2+C4+C6), 129.47 (Bn+Bn2-C2+C4+C6), 129.43 (Bn1+Bn2-C2+C4+C6), 128.35 (Bn1+Bn2-C3+C5), 128.30 (Bn1+Bn2-C3+C5), 120.81 (BeIm-C5quart.), 116.63 (BeIm-C4), 115.22 (BeIm-C7), 51.90 (Bn1-CH2), 51.78 (Bn2-CH2); elemental analysis for C21H18Br2N2 (theoretical/found [%]): C (55.05/55.31), H (3.96/3.72), N (6.11/5.95); MS (ESI): m/z 377.10 [M − Br]+.
5.3. Synthesis of Ru(II) NHC Complexes
The Ru(II) NHC complexes were prepared based on a reported procedure [14], which was optimized to achieve higher yields. The benzimidazolium bromides 2a–2f were dissolved in dichloromethane, 0.6 equivalents of silver oxide were added, and the mixture was stirred for 12 h at room temperature. The Ru(II)-dimer [(p-Cym)RuCl2]2 (0.5 equivalents) was added and stirring was continued for 2–7 days at room temperature (see the reaction periods below). The progress of the reaction was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (eluent: 5% methanol in dichloromethane). Precipitated silver halogenide was removed by filtration over celite, the volume of the filtrate was reduced under vacuum to approximately 1 mL, and the same volume of ethyl acetate was added. Within 2 days red, crystals were formed. Further purification steps (if any) are mentioned below.
(1,3-Dibenzyl-5-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-ylidene)-dichlorido-(η6-p-cymene)ruthenium(II) (3b) prepared starting from 1,3-dibenzyl-5-methyl-1H-benzimidazoliumbromide (132.9 mg, 0.34 mmol), reaction period with [(p-Cym)RuCl2]2: 48 h yield: 138.4 mg (0.22 mmol, 66%), red crystals; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 7.39–7.33 (m, Bn1+Bn2-H3+H5, 4H), 7.32–7.27 (m, Bn1+Bn2-H4, 2H), 7.14–7.10 (m, Bn1+Bn2-H2+H6, 4H), 6.89 (d, 4JH,H = 1.0 Hz, BeIm-H4+H7, 2H), 6.83 (m, BeIm-H6, 1H), 6.60 (d, 2JH,H = 17.2 Hz, Bn1-CH2, 1H), 6.51 (d, 2JH,H = 17.1 Hz, Bn2-CH2, 1H), 5.81 (d, 2JH,H = 17,1 Hz, Bn2-CH2, 1H), 5.73 (d, 2JH,H = 17.2 Hz, Bn1-CH2, 1H), 5.33 (d, 3JH,H = 5.4 Hz, p-Cym-H3+H5, 2H), 5.04 (d, 3JH,H = 5.7 Hz, p-Cym-H2+H6, 2H), 2.70 (hept, 3JH,H = 6.9 Hz, p-Cym-CH, 1H), 2.30 (d, 4JH,H = 1 Hz, BeIm-CH3, 3H), 1.87 (s, p-Cym-CH3, 3H), 1.16 (d, 3JH,H = 7.0 Hz, p-Cym-CH-CH3, 6H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 190.59 (BeIm-C2quart.), 137.69 (Bn1-C1quart.), 137.57 (Bn2-C1quart.), 135.91(BeIm-C3aquart.), 133.76 (BeIm-C7aquart.), 133.30 (BeIm-C5quart.), 128.92 (Bn1/Bn2-C3/C5), 128.87 (Bn1/Bn2-C3/C5), 127.41 (Bn1/Bn2-C2), 127.39 (Bn1/Bn2-C2), 125.95 (Bn1/Bn2-C2/C6), 125.80 (Bn1/Bn2-C2/C6), 124.46 (BeIm-C4), 111.44 (BeIm-C6), 111.22 (BeIm-C7), 107.73 (p-Cym-C4quart.), 97.12 (p-Cym-C1quart.), 85.31 (p-Cym-C3+C5), 84.61 (p-Cym-C2+C6), 52.96 (Bn2-CH2), 52.56 (Bn1-CH2), 30.58 (p-Cym-CH), 22.54 (p-Cym-CH-CH3), 22.42 (p-Cym-CH-CH3), 21.41 (BeIm-CH3), 18.21 (p-Cym-CH3); elemental analysis C32H34Cl2N2Ru (theoretical/found [%]): C (62.13/62.29), H (5.54/5.58) N (4.53/4.50); MS (ESI): m/z 583.15 [M − Cl]+, 548.19 [M − 2Cl]+, 413.06 [M − 2Cl – Cym − H]+.
(1,3-Dibenzyl-5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazol-2-ylidene)-dichlorido-(η6-p-cymene)ruthenium(II) (3c) prepared starting from 1,3-dibenzyl-5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazoliumbromide (65.0 mg, 0.16 mmol), reaction period with [(p-Cym)RuCl2]2: 48 h, yield: 49.7 mg (0.08 mmol, 49.3%), orange-red crystals; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 7.36 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H2+H6, 4H), 7.32–7.27 (m, 2H, Bn1/Bn2-H4, 2H), 7.16–7.11 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H3+H5, 4H), 6.88 (d, 3JH,H = 8.9 Hz, BeIm-H7, 1H), 6.67 (dd, 3JH,H = 8.9 Hz, 4JH,H = 2.3 Hz, BeIm-H6, 1H), 6.47 (d, 4JH,H = 2.3 Hz, BeIm-H4, 1H), 6.57 (m, Bn2-CH2, 1H), 6.52 (m, Bn1-CH2, 1H), 5.83 (m, Bn1-CH2, 1H), 5.80 (m, Bn2-CH2, 1H), 5.34 (d, 3JH,H = 6.0 Hz, p-Cym-H3+H5, 2H), 5.05 (d, 3JH,H = 6.0 Hz, p-Cym-H2+H6, 2H), 3.62 (s, BeIm-OCH3, 3H), 2.73 (hept, 3JH,H = 7.0 Hz, p-Cym-CH, 1H), 1.90 (s, p-Cym-CH3, 3H), 1.17 (d, 3JH,H = 7.0 Hz, p-Cym-CH-CH3, 6H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 190.25 (BeIm-C2quart.), 156.46 (BeIm-C5quart.), 137.52 (Bn1-C1quart.), 137.36 (Bn2-C1quart.), 136.42 (BeIm-C7aquart.), 130.18 (BeIm-C3aquart.), 128.93 (Bn1/Bn2-C2+C6), 128.88 (Bn1/Bn2-C2+C6), 127.49 (Bn1/Bn2-C4), 127.46 (Bn1/Bn2-C4), 126.03 (Bn1/Bn2-C3+C5), 126.00 (Bn1/Bn2-C3+C5), 112.14 (BeIm-C6), 111.50 (BeIm-C7), 107.90 (p-Cym-C4quart.), 97.22 (p-Cym-C1quart.), 95.73 (BeIm-C4), 85.36 (p-Cym-C3+C5), 84.51 (p-Cym-C2+C6), 55.73 (BeIm-OCH3), 53.05 (Bn1-CH2), 52.86 (Bn2-CH2), 30.60 (p-Cym-CH), 22.48 (p-Cym-CH-CH3), 18.29 (p-Cym-CH3); elemental analysis C32H34Cl2N2ORu (theoretical/found [%]): C (60.57/60.95), H (5.40/5.40) N (4.41/4.41); MS (ESI): m/z 599.14 [M − Cl], 465.03 [M – Cl − Cym], 429.05 [M − 2Cl – Cym − H], 329.17 [M − 2Cl – Cym − Ru].
(1,3-Dibenzyl-5-fluoro-1H-benzimidazol-2-ylidene)-dichlorido-(η6-p-cymene)ruthenium(II) (3d) prepared starting from 1,3-dibenzyl-5-fluoro-1H-benzimidazolium bromide (130.5 mg, 0.33 mmol), reaction period with [(p-Cym)RuCl2]2: 4 days; yield: 100.2 mg (0.18 mmol, 49%), orange powder; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 7.41–7.34 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H2+H6, 4H), 7.31 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H3-H5, 2H), 7.15–7.09 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H3-H5, 4H), 6.93 (dd, 3JH,H = 8.9 Hz, 4JH,F = 4.3 Hz, BeIm-H7, 1H), 6.81 (td, 3JH,H = 8.9 Hz, 3JH,F = 5.8 Hz, 4JH,H = 2.3 Hz, BeIm-H6, 1H), 6.71 (dd, 3JH,F = 8.3 Hz, 4JH,H = 2.3 Hz, BeIm-H4, 1H), 6.53 (s, Bn1/Bn2-CH2, 1H), 6.50 (s, Bn1/Bn2-CH2, 1H), 5.84 (d, 2JH,H = 18.4 Hz, Bn1/Bn2-CH2, 1H), 5.78 (d, 2JH,H = 17.7 Hz, Bn1/Bn2-CH2, 1H), 5.36 (d, 3JH,H = 5.9 Hz, p-Cym-H3+H5, 2H), 5.08 (d, 3JH,H = 5.9 Hz, p-Cym-H2+H6, 2H), 2.73 (hept, 3JH,H = 6.9 Hz, p-Cym-CH, 1H), 1.91 (s, p-Cym-CH3, 3H), 1.18 (d, 3JH,H = 6.9 Hz, p-Cym-CH-CH3, 6H); 13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 193.72 (BeIm-C2), 159.24 (d, J = 243.2 Hz, BeIm-C5), 137.11 (Bn1/Bn2-C1quart.), 136.81 (Bn1/Bn2-C1quart.), 135.92 (d, J = 12.2 Hz, BeIm-C7aquart.), 132.03 (BeIm-C3aquart.), 129.07 (Bn1/Bn2-C2+C6), 129.01 (Bn1/Bn2-C2+C6), 127.73 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 127.65 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 125.92 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 125.90 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 112.35 (d, J = 9.8 Hz, BeIm-C7), 111.21 (d, J = 25.5 Hz, BeIm-C6), 108.18 (p-Cym-C4quart.), 98.84 (d, J = 27.7 Hz, BeIm-C4), 97.30 (p-Cym-C1quart.), 85.45 (p-Cym-C3+C5), 84.79 (p-Cym-C2+C6), 53.27 (Bn1/Bn2-CH2), 53.18 (Bn1/Bn2-CH2), 30.64 (p-Cym-CH), 22.45 (p-Cym-CH-CH3), 18.31 (p-Cym-CH3); elemental analysis for C31H31Cl2FN2Ru (theoretical/found [%]): C (59.81/59.31), H (5.02/5.08) N (4.50/4.45); MS (ESI): m/z 587.12 [M − Cl], 552.16 [M − 2Cl], 417.03 [M − 2Cl − p − Cym − H].
(1,3-Dibenzyl-5-chloro-1H-benzimidazol-2-ylidene)-dichlorido-(η6-p-cymene)ruthenium(II) (3e) prepared starting from 1,3-dibenzyl-5-chloro-1H-benzimidazolium bromide (90.5 mg, 0.22 mmol), reaction period with [(p-Cym)RuCl2]2: 7 days, yield: 71.6 mg (0.11 mmol, 51%), orange-brown crystals; 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 7.41–7.36 (m, Bn1/Bn2,H3-H5, 3H), 7.35–7.28 (m, Bn1/Bn2,H3-H5, 3H), 7.12–7.08 (m, Bn1/Bn2,H2+H6, 4H), 7.05 (dd, 3JH,H = 8.7 Hz, 4JH,H = 1.9 Hz, BeIm-H6, 1H), 7.00 (dd, 4JH,H = 1.9 Hz, 5JH,H = 0.5 Hz, BeIm-H4, 1H), 6.92 (dd, 3JH,H = 8.7 Hz, 5JH,H = 0.5 Hz, BeIm-H7, 1H), 6.54 (m, Bn1-CH2, 1H), 6.51 (m, Bn2-CH2, 1H) 5.84 (d, 2JH,H = 17.2 Hz, Bn2-CH2, 1H), 5.75 (d, 2JH,H = 17.2 Hz, Bn1-CH2, 1H), 5.38–5.32 (m, p-Cym-H3+H5, 2H), 5.07 (d, J = 6.1 Hz, p-Cym-H3+H5, 2H), 2.71 (hept, J = 7.0 Hz, p-Cym-CH, 1H), 1.89 (s, p-Cym-CH3, 3H), 1.17 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, p-Cym-CH-CH3, 6H); 13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 194.18 (BeIm-C2, 1C), 137.02 (Bn2-C1quart.), 136.88 (Bn1-C1quart.), 136.16 (BeIm-C7aquart.), 134.14 (BeIm-C5), 129.35 (BeIm-C3aquart.), 129.12 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 129.03 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 127.75 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 127.68 (Bn1/Bn2-C3-C5), 125.88 (Bn1/Bn2-C2+C6), 125.78 (Bn1/Bn2-C2+C6), 123.70 (BeIm-C6), 112.45 (BeIm-C7), 111.56 (BeIm-C4), 108.19 (p-Cym-C4quart.), 97.36 (p-Cym-C1quart.), 85.49 (p-Cym-C3+C5), 84.86 (p-Cym-C2+C6), 53.23 (Bn2-CH2), 52.99 (Bn1-CH2), 30.63 (p-Cym-CH), 22.45 (p-Cym-CH-CH3), 18.27 (p-Cym-CH3); elemental analysis for C31H31Cl3N2Ru (theoretical/found [%]): C (58.27/58.33), H (4.89/4.84) N (4.38/4.26); MS (ESI): m/z 603.09 [M − Cl], 1243.15 [M + M − Cl + 2H], 433.00 [M − 2Cl − p − Cym − H], 333.12 [M − 2Cl − p − Cym − Ru].
(1,3-Dibenzyl-5-bromo-1H-benzimidazol-2-ylidene)-dichlorido-(η6-p-cymene)ruthenium(II) (3f) prepared starting from 1,3-dibenzyl-5-bromo-1H-benzimidazolium bromide (84.0 mg, 0.18 mmol), reaction period with [(p-Cym)RuCl2]2: 7 days; additional purification: column chromatography over silica (eluent: 5% methanol in dichloromethane), evaporation, and recrystallization (dichloromethane/n-hexane); yield: 20.5 mg (0.03 mmol, 16%), orange-red powder; 1H-NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 7.41–7.38 (m, Bn2-H2+H6, 2H), 7.38–7.35 (m, Bn1-H2+H6, 2H), 7.34–7.28 (m, Bn1+Bn2-H4, 2H), 7.19 (dd, 3JH,H = 8.6 Hz, 4JH,H = 1.7 Hz, BeIm-H6, 1H), 7.15 (m, 4JH,H = 1.7 Hz, 5JH,H = 0.45 Hz, BeIm-H4, 1H), 7.12–7.10 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H3+H5, 2H), 7.09–7.08 (m, Bn1/Bn2-H3+H5, 2H), 6.87 (m, 3JH,H = 8.8 Hz, 5JH,H = 0.45 Hz, BeIm-H7, 1H), 6.58 (d, 2JH,H = 17.2 Hz, Bn2-CH2, 1H), 6.52 (d, 2JH,H = 17.1 Hz, Bn1-CH2, 1H), 5.85 (d, 2JH,H = 17.1 Hz, Bn1-CH2, 1H), 5.73 (d, 2JH,H = 17.2 Hz, Bn2-CH2, 1H), 5.35 (d, 3JH,H = 8.9 Hz, p-Cym-H3+H5, 2H), 5.06 (d, 3JH,H = 5.9 Hz, p-Cym-H2+H6, 2H), 2.75–2.66 (m, 3JH,H = 7.2 Hz, p-Cym-CH, 1H), 1.88 (s, p-Cym-CH3, 3H), 1.17 (d, 3JH,H = 7.2 Hz, p-Cym-CH-CH3, 6H); 13C-NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3-d1) δ = 194.09 (BeIm-C2), 137.01 (Bn1-C1quart.), 136.88 (Bn2-C1quart.), 136.48 (BeIm-C7aquart.), 134.49 (BeIm-C3aquart.), 129.12 (Bn2-C2+C6), 129.02 (Bn1-C2+C6), 127.74 (Bn1/Bn2-C4), 127.65 (Bn1/Bn2-C4), 126.40 (BeIm-C6), 125.85 (Bn1/Bn2-C3+C5), 125.74 (Bn1/Bn2-C3+C5), 116.69 (BeIm-C5), 114.36 (BeIm-C4), 112.86 (BeIm-C7), 108.16 (p-Cym-C4quart.), 97.34 (p-Cym-C1quart.), 85.47 (p-Cym-C3+C5), 84.86 (p-Cym-C2+C6), 53.18 (Bn1-CH2), 52.91 (Bn2-CH2), 30.61 (p-Cym-CH), 22.47 (p-Cym-CH-CH3), 18.25 (p-Cym-CH3); elemental analysis for C31H31BrCl2N2Ru (theoretical/found [%]): C (54.48/54.38), H (4.57/4.48) N (4.10/4.01); MS (ESI): m/z 1331.05 [M + M − 2Cl + 2H]+, 649.04 [M − Cl + 2H]+, 433.00 [M − 2Cl − p − Cym + H]+.
5.4. Inhibition of Bacterial TrxR (E. coli)
The TrxR (E. coli) inhibition assay was performed according to a previously published procedure [26]. It is partly based on the procedure developed by Lu et al. [32] and detects the formation of 5-TNB (5-thionitrobenzoic acid). Solutions of E. coli TrxR (35.4 U/mL) and of its substrate thioredoxin (Trx) E. coli (156 µg/mL) (both purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany) and diluted with distilled water) and fresh stock solutions of the test compounds (in DMF) were prepared. TE buffer (Tris-HCl 50 mM, EDTA 1 mM, pH 7.5) containing graded concentrations of the respective compounds (20 µL) or buffer without compounds (20 µL, as control) were mixed with TrxR solution (10 µL), Trx solution (10 µL), and a solution of NADPH (200 µM) in TE buffer (100 µL) in a well on a 96-well plate. As blank solution, 200 µM NADPH in TE buffer (100 µL) mixed with a DMF/buffer mixture (40 µL) was used (final concentrations of DMF: 0.5% v/v). The solutions on the 96-well plates were incubated for 75 min at 25 °C with moderate shaking. A volume of 100 µL of a reaction mixture (TE buffer containing 200 µM NADPH and 5 mM 5,5-dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) was added to each well to initiate the reaction. After thorough mixing, the formation of 5-TNB was monitored by a microplate reader at 405 nm in 35 s intervals (10 measurements). The values were corrected by subtraction of the blank solution’s values. The increase in concentration of 5-TNB followed a linear trend (r² ≥ 0.990) and the enzymatic activities were calculated as the slopes (increase in absorbance per second) thereof. Absence of interference with the assay components was confirmed by a negative control experiment for each test compound. The highest test compound concentration was used and the enzyme solution was replaced by TE buffer for this purpose. The IC50 values were calculated as the concentration of the compound decreasing the enzymatic activity of the positive control by 50%, and are presented as the means and standard deviations of three repeated experiments.
5.5. Antimicrobial Activity Assay
Compounds were tested in a microtiter plate assay according to CLSI guidelines against E. coli DSM 30083, A. baumannii DSM 30007, P. aeruginosa DSM 50071, B. subtilis DSM 402, S. aureus DSM 20231, S. aureus ATCC 43300 (MRSA), and C. albicans, as described previously [33]. E. coli, A. baumannii, S. aureus, and B. subtilis were grown in Mueller Hinton broth, P. aeruginosa in cation-adjusted Mueller Hinton II, and C. albicans DSM1386 in Sabouraud broth. Compounds were dissolved in DMSO at 10 mg/mL. Starting from a 10 mg/mL stock solution, serial dilutions in culture media were prepared with the Tecan Freedom Evo 75 liquid handling workstation (Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland), covering a range from 512 to 0.5 µg/mL. Assay volumes were 200 µL per well. After inoculating with 5 × 105 bacteria/mL from late exponential cultures grown in the same media, cultures were incubated for 16–18 h at 37 °C. The lowest compound concentration inhibiting visible bacterial growth was recorded as MIC.
Author Contributions
H.B.: performed experiments and analysed data; P.D.: performed experiments and analysed data; L.P.: computational chemistry; J.E.B.: supervision; I.O.: supervision, manuscript preparation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial supported by the Lower Saxony Ministry for Science and Culture for the doctoral program “Drug Discovery and Cheminformatics for New Anti-Infectives (iCA)” is gratefully acknowledged by I.O. J.E.B. gratefully acknowledges funding from the German Federal State of North Rhine-Westphalia and the European Union, European Regional Development Fund, Investing in Your Future for the Research Infrastructure Center for System-Based Antibiotic Research (CESAR).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Not applicable.
References
- Tacke, M. Benzyl-substituted carbene–metal complexes: Potential for novel antibiotics and anticancer drugs? J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 782, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, M.; Gimeno, M.C.; Visbal, R. Recent advances in gold-NHC complexes with biological properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahra, F.; Tzouras, N.V.; Collado, A.; Nolan, S.P. Synthesis of N-heterocyclic carbene gold(I) complexes. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 1476–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, I. Metal N-heterocyclic carbene complexes in medicinal chemistry. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 75, 121–148. [Google Scholar]
- Oehninger, L.; Rubbiani, R.; Ott, I. N-Heterocyclic carbene metal complexes in medicinal chemistry. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 3269–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarra, F.; Pratesi, A.; Gabbiani, C.; Biver, T. A focus on the biological targets for coinage metal-NHCs as potential anticancer complexes. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2021, 217, 111355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gust, R. Update on metal N-heterocyclic carbene complexes as potential anti-tumor metallodrugs. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 329, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehninger, L.; Küster, L.N.; Schmidt, C.; Muñoz-Castro, A.; Prokop, A.; Ott, I. A chemical-biological evaluation of rhodium(I) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes as prospective anticancer drugs. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 17871–17880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehninger, L.; Spreckelmeyer, S.; Holenya, P.; Meier, S.M.; Can, S.; Alborzinia, H.; Schur, J.; Keppler, B.K.; Wölfl, S.; Ott, I. Rhodium(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbene Bioorganometallics as in Vitro Antiproliferative Agents with Distinct Effects on Cellular Signaling. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9591–9600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, D.; Sullivan, M.P.; Tong, K.K.H.; Steel, T.R.; Prause, A.; Lovett, J.H.; Andersen, J.W.; Jamieson, S.M.F.; Harris, H.H.; Ott, I.; et al. Potent Inhibition of Thioredoxin Reductase by the Rh Derivatives of Anticancer M(arene/Cp*)(NHC)Cl2 Complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 3281–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daubit, I.M.; Sullivan, M.P.; John, M.; Goldstone, D.C.; Hartinger, C.G.; Metzler-Nolte, N. A Combined Spectroscopic and Protein Crystallography Study Reveals Protein Interactions of RhI(NHC) Complexes at the Molecular Level. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 17191–17199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubit, I.M.; Wortmann, S.; Siegmund, D.; Hahn, S.; Nuernberger, P.; Metzler-Nolte, N. Unveiling Luminescent IrI and RhI N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes: Structure, Photophysical Specifics, and Cellular Localization in the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 6783–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gothe, Y.; Marzo, T.; Messori, L.; Metzler-Nolte, N. Iridium(I) Compounds as Prospective Anticancer Agents: Solution Chemistry, Antiproliferative Profiles and Protein Interactions for a Series of Iridium(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 12487–12494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oehninger, L.; Stefanopoulou, M.; Alborzinia, H.; Schur, J.; Ludewig, S.; Namikawa, K.; Muñoz-Castro, A.; Köster, R.W.; Baumann, K.; Wölfl, S.; et al. Evaluation of arene ruthenium(II) N-heterocyclic carbene complexes as organometallics interacting with thiol and selenol containing biomolecules. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streciwilk, W.; Terenzi, A.; Cheng, X.; Hager, L.; Dabiri, Y.; Prochnow, P.; Bandow, J.E.; Wölfl, S.; Keppler, B.K.; Ott, I. Fluorescent organometallic rhodium(I) and ruthenium(II) metallodrugs with 4-ethylthio-1,8-naphthalimide ligands: Antiproliferative effects, cellular uptake and DNA-interaction. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 156, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabiri, Y.; Schmid, A.; Theobald, J.; Blagojevic, B.; Streciwilk, W.; Ott, I.; Wölfl, S.; Cheng, X. A Ruthenium(II) N-Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complex with Naphthalimide Ligand Triggers Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells via Activating the ROS-p38 MAPK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, N.Y.S.; Truong, D.; Burmeister, H.; Babak, M.V.; Holtkamp, H.U.; Movassaghi, S.; Ayine-Tora, D.M.; Zafar, A.; Kubanik, M.; Oehninger, L.; et al. From Catalysis to Cancer: Toward Structure-Activity Relationships for Benzimidazol-2-ylidene-Derived N-Heterocyclic-Carbene Complexes as Anticancer Agents. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 14427–14434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, F.; Müller-Bunz, H.; Smith, R.; Streciwilk, W.; Zhu, X.; Tacke, M. Novel Ruthenium(II) and Gold(I) NHC Complexes: Synthesis, Characterization, and Evaluation of Their Anticancer Properties. Organometallics 2013, 32, 5551–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movassaghi, S.; Singh, S.; Mansur, A.; Tong, K.K.H.; Hanif, M.; Holtkamp, H.U.; Söhnel, T.; Jamieson, S.M.F.; Hartinger, C.G. (Pyridin-2-yl)-NHC Organoruthenium Complexes: Antiproliferative Properties and Reactivity toward Biomolecules. Organometallics 2018, 37, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, L.; Tian, Z.; Liu, X.; Gong, Y.; Zheng, H.; Ge, X.; Liu, Z. Imine-N-Heterocyclic Carbenes as Versatile Ligands in Ruthenium(II) p-Cymene Anticancer Complexes: A Structure-Activity Relationship Study. Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 2923–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.P.; Nieuwoudt, M.K.; Bowmaker, G.A.; Lam, N.Y.S.; Truong, D.; Goldstone, D.C.; Hartinger, C.G. Unexpected arene ligand exchange results in the oxidation of an organoruthenium anticancer agent: The first X-ray structure of a protein-Ru(carbene) adduct. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 6120–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cetinkaya, B.; Cetinkaya, E.; Küçükbay, H.; Durmaz, R. Antimicrobial activity of carbene complexes of rhodium(I) and ruthenium(II). Arzneim. Forsch. Drug Res. 1996, 46, 821–823. [Google Scholar]
- Onar, G.; Gürses, C.; Karataş, M.O.; Balcıoğlu, S.; Akbay, N.; Özdemir, N.; Ateş, B.; Alıcı, B. Palladium(II) and ruthenium(II) complexes of benzotriazole functionalized N-heterocyclic carbenes: Cytotoxicity, antimicrobial, and DNA interaction studies. J. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 886, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, L.; Chakchouk-Mtibaa, A.; Al-Ayed, A.S.; Mansour, L.; Abutaha, N.; Harrath, A.H.; Mellouli, L.; Özdemir, I.; Yasar, S.; Hamdi, N. Ru(ii )–N-heterocyclic carbene complexes: Synthesis, characterization, transfer hydrogenation reactions and biological determination. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 34406–34420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slimani, I.; Chakchouk-Mtibaa, A.; Mansour, L.; Mellouli, L.; Özdemir, I.; Gürbüzd, N.; Hamdi, N. Synthesis, characterization, biological determination and catalytic evaluation of ruthenium(ii) complexes bearing benzimidazole-based NHC ligands in transfer hydrogenation catalysis. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 5309–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Karge, B.; Misgeld, R.; Prokop, A.; Franke, R.; Brönstrup, M.; Ott, I. Gold(I) NHC Complexes: Antiproliferative Activity, Cellular Uptake, Inhibition of Mammalian and Bacterial Thioredoxin Reductases, and Gram-Positive Directed Antibacterial Effects. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbut, M.B.; Vilchèze, C.; Luo, X.; Hensler, M.E.; Guo, H.; Yang, B.; Chatterjee, A.K.; Nizet, V.; Jacobs, W.R.; Schultz, P.G.; et al. Auranofin exerts broad-spectrum bactericidal activities by targeting thiol-redox homeostasis. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, C.; Karge, B.; Misgeld, R.; Prokop, A.; Brönstrup, M.; Ott, I. Biscarbene gold(i) complexes: Structure–activity-relationships regarding antibacterial effects, cytotoxicity, TrxR inhibition and cellular bioavailability. Med. Chem. Commun. 2017, 8, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbiani, R.; Kitanovic, I.; Alborzinia, H.; Can, S.; Kitanovic, A.; Onambele, L.A.; Stefanopoulou, M.; Geldmacher, Y.; Sheldrick, W.S.; Wolber, G.; et al. Benzimidazol-2-ylidene gold(I) complexes are thioredoxin reductase inhibitors with multiple antitumor properties. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8608–8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ollevier, T. Synthesis of Imidazolidinone, Imidazolone, and Benzimidazolone Derivatives through Oxidation Using Copper and Air. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 3572–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Zakrzewski, V.G.; Montgomery, J.A., Jr.; Stratmann, R.E.; Burant, J.C.; et al. Gaussian 98; Gaussian, Inc.: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Vlamis-Gardikas, A.; Kandasamy, K.; Zhao, R.; Gustafsson, T.N.; Engstrand, L.; Hoffner, S.; Engman, L.; Holmgren, A. Inhibition of bacterial thioredoxin reductase: An antibiotic mechanism targeting bacteria lacking glutathione. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albada, H.B.; Chiriac, A.-I.; Wenzel, M.; Penkova, M.; Bandow, J.E.; Sahl, H.-G.; Metzler-Nolte, N. Modulating the activity of short arginine-tryptophan containing antibacterial peptides with N-terminal metallocenoyl groups. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 1753–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).