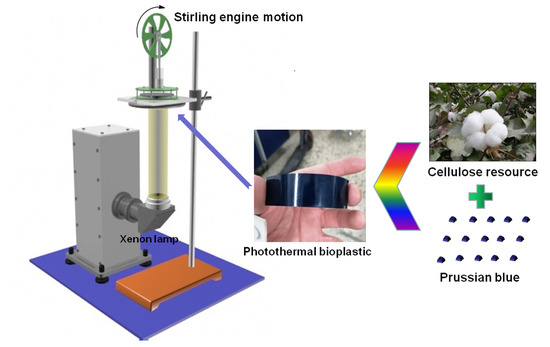
Mechanically Strong, Liquid-Resistant Photothermal Bioplastic Constructed from Cellulose and Metal-Organic Framework for Light-Driven Mechanical Motion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Formation of Prussian Blue@Cellulose Bioplastic (PCBP)
2.2. The Properties Analysis of PCBP
2.3. Photothermal Conversion Behavior of PCBP and Applications
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Prussian Blue Powder
3.3. Fabrication of Cellulose Hydrogel
3.4. Fabrication of Prussian Blue@Cellulose Bioplastics
3.5. Characterization
3.6. Light Drive Stirling Engine Motion Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Derkowska-Zielinska, B.; Gondek, E.; Pokladko-Kowar, M.; Kaczmarek-Kedziera, A.; Kysil, A.; Lakshminarayana, G.; Krupka, O. Photovoltaic cells with various azo dyes as components of the active layer. Solar Energy 2020, 203, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trefon-Radziejewska, D.; Hamaoui, G.; Chirtoc, M.; Horny, N.; Smokal, V.; Biitseva, A.; Krupka, O.; Derkowska-Zielinska, B. Thermophysical properties of methacrylic polymer films with guest-host and side-chain azobenzene. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 223, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, W.; Tang, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. Graphene oxide-based efficient and scalable solar desalination under one sun with a confined 2D water path. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13953–13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, P. Self-floating carbon nanotube membrane on macroporous silica substrate for highly efficient solar-driven interfacial water evaporation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Hitz, E.; Jia, C.; Gong, A.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J.Y.; et al. Highly flexible and efficient solar steam generation device. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, K.; Kang, G.; Cho, S.K.; Park, W.; Kim, K.; Padilla, W.J. Flexible thin-film black gold membranes with ultrabroad band plasmonic nanofocusing for efficient solar vapour generation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Gu, J.; Su, Y.; Su, H.; Guo, C.; Zhang, D. Ag/diatomite for highly efficient solar vapor generation under one-sun irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17817–17821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Cheng, G.; Zhu, J. Solar steam generation through bio-inspired interface heating of broadband-absorbing plasmonic membranes. Appl. Energy 2017, 195, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, M.; Raza, G.; Xin, Y.; Pervaiz, S.; Xu, J.; Du, X.; Wen, D. Volumetric solar heating and steam generation via gold nanofluids. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, M.; Jia, J.; Wu, Z.; Qian, C.; Chen, R.; O’Brien, P.; Sun, W.; Dong, Y.; Ozin, G. Synthesis of black TiOx nanoparticles by Mg reduction of TiO2 nanocrystals and their application for solar water evaporation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1601811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Shi, L.; Wang, P. MXene Ti3C2: An effective 2D light-to-heat conversion material. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3752–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Yan, C.; Xue, Z.; Yu, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, T. Shape-controlled synthesis of high-quality Cu7S4 nanocrystals for efficient light-induced water evaporation. Small 2016, 12, 5320–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, B.; Wu, J.; Li, R.; Wang, P. Hydrophobic light-to-heat conversion membranes with self-healing ability for interfacial solar heating. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4889–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Cai, X.; Xiao, J.; Ding, Z.; Yang, J. Macroporous double-network hydrogel for high-efficiency solar steam generation under 1 sun illumination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 10998–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Fu, L.; Zou, M.; Li, Z.; Cao, A.; Yuan, Q. An ultrathin flexible 2d membrane based on single-walled nanotube–MoS2 hybrid film for high-performance solar steam generation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Ci, S.; Luo, S.; Shao, P.; Hou, Y.; Wen, Z. Scalable and low-cost synthesis of black amorphous Al-Ti-O nanostructure for high-efficient photothermal desalination. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Wei, N.; Weng, Y.; Dong, S.; Qi, D.; Qiu, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, T. High-performance photothermal conversion of narrow-bandgap Ti2O3 nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Han, K.; Hong, J.; Yoon, D.-Y.; Park, C.; Kim, Y. Photothermal cellulose-patch with gold-spiked silica microrods based on Escherichia coli. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5244–5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Mu, L.; Chen, M.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; She, G.; Shi, W. Bifunctional gold nanobipyramids for photothermal therapy and temperature monitoring. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2668–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Li, T.; Chen, Z.; Lin, H.; Wang, P.; Liu, F. Full biomass-derived solar stills for robust and stable evaporation to collect clean water from various water-bearing media. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10672–10679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chala, T.; Wu, C.-M.; Chou, M.-H.; Guo, Z.-L. Melt electrospun reduced tungsten oxide/polylactic acid fiber membranes as a photothermal material for light-driven interfacial water evaporation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 28955–28962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Ma, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Niu, N.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Li, S. Biomass-derived solar-to-thermal materials: Promising energy absorbers to convert light to mechanical motion. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 4002–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.-L.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Chen, F.-F.; Qin, D.-D.; Xiong, Z.-C. Superhydrophobic photothermal paper based on ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires for controllable light-driven self-propelled motion. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13226–13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inonu, Z.; Keskin, S.; Erkey, C. An emerging damily of hybrid nanomaterials: Metal–organic framework/aerogelcomposites. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 5959–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betard, A.; Fischer, R. Metal–organic framework thin films: From fundamentals to applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1055–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Mo, J.; Lu, Y.; Cai, C.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, S.; Nie, S. Improved capture and removal efficiency of gaseous acetaldehyde by a self-powered photocatalytic system with an external electric field. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 10577–10586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.; Kim, S.-H.; Rethinasabapathy, M.; Haldorai, Y.; Lee, G.-W.; Choe, S.R.; Jang, S.-C.; Kang, S.-M.; Han, Y.-K.; Roh, C. Porous 3D Prussian blue/cellulose aerogel as a decorporation agent for removal of ingested cesium from the gastrointestinal tract. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Q.; Li, G.; Lin, H.; Liu, F. Solar-driven organic solvent purification enabled by the robust cubic Prussian blue. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 8960–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; He, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Yu, M. Highly efficient photothermal sterilization of water mediated by prussian blue nanocages. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liang, X.; Feng, S.; Dai, Z. Magnetic Prussian blue nanoparticles for targeted photothermal therapy under magnetic resonance imaging guidance. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Selomulya, C.; Zheng, G.; Zhao, D. New faces of porous Prussian blue: Interfacial assembly of integrated hetero-structures for sensing applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 7997–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, X.; Feng, W.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, J.; Li, F. Optimization of Prussian blue coated NaDyF4: x% lu nanocomposites for multifunctional imaging-guided photothermal therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 5120–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zeng, K.; Liu, H.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Deng, L.; Liu, Y.N. Cell membrane camouflaged hollow Prussian blue nanoparticles for synergistic photothermal-/chemotherapy of cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, L.; Mathlouthi, E.; Kajdan, M.; Daurat, M.; Long, J.; Sidi-Boulenouar, R.; Cardoso, M.; Goze-Bac, C.; Amdouni, N.; Guari, Y. Multifunctional manganese-doped Prussian blue nanoparticles for two-photon photothermal therapy and magnetic resonance imaging. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2018, 22, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kam, N.W.S.; O’Connell, M.; Wisdom, J.A.; Dai, H. Carbon nanotubes as multifunctional biological transporters and near-infrared agents for selective cancer cell destruction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11600–11605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, J.T.; Tabakman, S.M.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Sanchez Casalongue, H.; Vinh, D.; Dai, H. Ultrasmall reduced graphene oxide with high near-infrared absorbance for photothermal therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6825–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, M.; Kanaizuka, K.; Abe, M.; Hoshi, Y.; Sakamoto, M.; Kawamoto, T.; Tanaka, H.; Kurihara, M. Preparation of electrochromic Prussian blue nanoparticles dispersible into various solvents for realisation of printed electronics. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Fu, Q.; Lin, X.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S. Enhanced performance of a cellulose nanofibrils-based triboelectric nanogenerator by tuning the surface polarizability and hydrophobicity. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 404, 126512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Meng, J.; Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Ni, Y. Synthesis of novel cellulose-based antibacterial composites of Ag nanoparticles@metal-organic frameworks@carboxymethylated fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, Z.; Mao, X.; Che, X.L.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Multifunctional textiles/metal−organic frameworks composites for efficient eltraviolet radiation blocking and noise reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 55316–55323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Cui, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Su, C.Y. Applications of metal–organic frameworks in heterogeneous supramolecular catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6011–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nabipour, H.; Nie, S.B.; Wang, X.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Highly flame retardant zeolitic imidazole framework-8@cellulose composite aerogels as absorption materials for organic pollutants. Cellulose 2020, 27, 2237–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhameed, R.M.; Ananias, D.; Silva, A.M.S.; Rocha, J. Building light-emitting metal-organic frameworks by post-synthetic modification. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Gao, J.; Ren, W.; Xie, Y.; Abdalkarim, S.Y.H.; Wang, S.; Ni, Q.; Yao, J. Fabrication of metal-organic frameworks@cellulose aerogels composite materials for removal of heavy metal ions in water. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 205, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Kong, X.; Zheng, B.; Huo, F.; Xu, C. Cellulose nanofiber@conductive metalorganic frameworks for high performance flexible supercapacitors. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 9578–9586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Q.; Gong, S.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, T.; Wang, C.-Y.; Gu, N. Prussian blue modified iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles and their high peroxidase-like activity. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5110–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hou, X.; Song, N.; Shi, L.; Ding, P. Cellulose/graphene bioplastic for thermal management: Enhanced isotropic thermally conductive property by three-dimensional interconnected graphene aerogel. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 107, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipin, A.K.; Fugetsu, B.; Sakata, I.; Isogai, A.; Endo, M.; Li, M.; Dresselhaus, M.S. Cellulose nanofiber backboned Prussian blue nanoparticles as powerful adsorbents for the selective elimination of radioactive cesium. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Rykov, A.I.; Wang, J. Hydrazine drastically promoted Fenton oxidation of bisphenol A catalysed by a Fe III–Co Prussian blue analogue. Catal. Commun. 2016, 77, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, A.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Biosensor based on Prussian blue nanocubes/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4674–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Li, L.; An, X.; Qian, X. Mechanically Strong, Liquid-Resistant Photothermal Bioplastic Constructed from Cellulose and Metal-Organic Framework for Light-Driven Mechanical Motion. Molecules 2021, 26, 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154449
Sun L, Li L, An X, Qian X. Mechanically Strong, Liquid-Resistant Photothermal Bioplastic Constructed from Cellulose and Metal-Organic Framework for Light-Driven Mechanical Motion. Molecules. 2021; 26(15):4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154449
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Lijian, Limei Li, Xianhui An, and Xueren Qian. 2021. "Mechanically Strong, Liquid-Resistant Photothermal Bioplastic Constructed from Cellulose and Metal-Organic Framework for Light-Driven Mechanical Motion" Molecules 26, no. 15: 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154449
APA StyleSun, L., Li, L., An, X., & Qian, X. (2021). Mechanically Strong, Liquid-Resistant Photothermal Bioplastic Constructed from Cellulose and Metal-Organic Framework for Light-Driven Mechanical Motion. Molecules, 26(15), 4449. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154449