Structural and Binding Effects of Chemical Modifications on Thrombin Binding Aptamer (TBA)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Chemicals
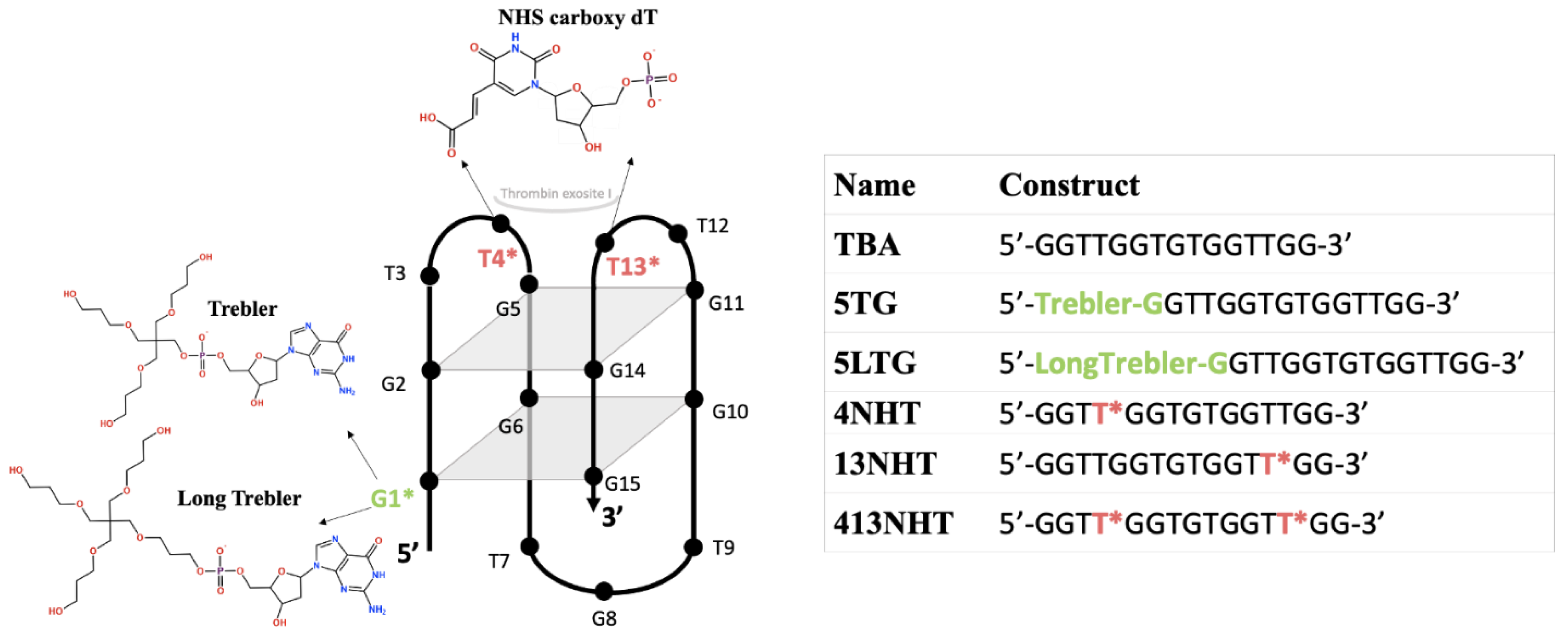
2.2. Oligonucleotide Synthesis
2.3. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
2.4. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Binding Study
2.5. Molecular Modelling and Simulation Methods
3. Results
3.1. Modified TBA Constructs Maintain Native TBA Folding
3.2. Binding Affinities of Modified TBA Constructs Are Comparable to Native TBA
3.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of TBA and Its Modified Constructs Agree with CD Data
3.4. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Thrombin Bound TBA and Its Modified Constructs Agree with SPR Experiments
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krishnaswamy, S. The transition of prothrombin to thrombin. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davie, E.W.; Fujikawa, K.; Kisiel, W. The coagulation cascade: Initiation, maintenance, and regulation. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 10363–10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmon, C.T. Basic mechanisms and pathogenesis of venous thrombosis. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alias, S.; Lang, I.M. Coagulation and the Vessel Wall in Pulmonary Embolism. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarich, T.C.; Peters, G.; Berkowitz, S.; Misselwitz, F.; Nessel, C.C.; Burton, P.; Cook-Bruns, N.; Lensing, A.W.; Haskell, L.; Perzborn, E.; et al. Rivaroxaban: A novel oral anticoagulant for the prevention and treatment of several thrombosis-mediated conditions. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1291, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alquwaizani, M.; Buckley, L.; Adams, C.; Fanikos, J. Anticoagulants: A Review of the Pharmacology, Dosing, and Complications. Curr. Emerg. Hosp. Med. Rep. 2013, 1, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Josyln, J.A.; Khattak, F.H.; Geraci, S.A. A Case of a Reversible Neurologic Adverse Reaction to Apixaban Confirmed by Re-Challenge. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2018, 10, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakagia, D.D.; Papanas, N.; Karadimas, E.; Polychronidis, A. Warfarin-Induced Skin Necrosis. Ann. Dermatol. 2014, 26, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watras, M.M.; Patel, J.P.; Arya, R. Traditional Anticoagulants and Hair Loss: A Role for Direct Oral Anticoagulants? A Review of the Literature. Drugs Real World Outcomes 2016, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keefe, A.D.; Pai, S.; Ellington, A. Aptamers as therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaya, R.; Schultze, P.; Smith, F.W.; Roe, J.A.; Feigon, J. Thrombin-binding DNA aptamer forms a unimolecular quadruplex structure in solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3745–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsvetkov, V.; Varizhuk, A.; Pozmogova, G.E.; Smirnov, I.P.; Kolganova, N.A.; Timofeev, E.N. A Universal Base in a Specific Role: Tuning up a Thrombin Aptamer with 5-Nitroindole. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, K.; Tulinsky, A. An Ambiguous Structure of a DNA 15-mer Thrombin Complex. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1996, 52, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nallagatla, S.R.; Heuberger, B.; Haque, A.; Switzer, C. Combinatorial Synthesis of Thrombin-Binding Aptamers Containing iso-Guanine. J. Comb. Chem. 2009, 11, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padmanabhan, K.P.; Ferrara, J.; Sadler, J.; Tulinsky, A. The structure of alpha-thrombin inhibited by a 15-mer single-stranded dna aptamer. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 17651–17654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study of NU172 as Anticoagulation in Patients Undergoing Off-pump CABG Surgery—Full Text View—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00808964?term=NU+172&rank=1 (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Virgilio, A.; Petraccone, L.; Vellecco, V.; Bucci, M.; Varra, M.; Irace, C.; Santamaria, R.; Pepe, A.; Mayol, L.; Esposito, V.; et al. Site-specific replacement of the thymine methyl group by fluorine in thrombin binding aptamer significantly improves structural stability and anticoagulant activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 10602–10611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotkowiak, W.; Lisowiec-Wachnicka, J.; Grynda, J.; Kierzek, R.; Wengel, J.; Pasternak, A. Thermodynamic, Anticoagulant, and Antiproliferative Properties of Thrombin Binding Aptamer Containing Novel UNA Derivative. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 10, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasternak, A.; Hernandez, F.J.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Vester, B.; Wengel, J. Improved thrombin binding aptamer by incorporation of a single unlocked nucleic acid monomer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Li, D. Structural transformation induced by locked nucleic acid or 2′–O-methyl nucleic acid site-specific modifications on thrombin binding aptamer. Chem. Central J. 2014, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaitseva, M.; Kaluzhny, D.; Shchyolkina, A.; Borisova, O.; Smirnov, I.; Pozmogova, G. Conformation and thermostability of oligonucleotide d(GGTTGGTGTGGTTGG) containing thiophosphoryl internucleotide bonds at different positions. Biophys. Chem. 2010, 146, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varizhuk, A.M.; Tsvetkov, V.; Tatarinova, O.N.; Kaluzhny, D.N.; Florentiev, V.L.; Timofeev, E.N.; Shchyolkina, A.K.; Borisova, O.F.; Smirnov, I.P.; Grokhovsky, S.L.; et al. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro activity of thrombin-binding DNA aptamers with triazole internucleotide linkages. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 67, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koniev, O.; Wagner, A. Developments and recent advancements in the field of endogenous amino acid selective bond forming reactions for bioconjugation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 5495–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornell, W.D.; Cieplak, P.; Bayly, C.I.; Gould, I.R.; Merz, K.M.; Ferguson, D.M.; Spellmeyer, D.C.; Fox, T.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A. A Second Generation Force Field for the Simulation of Proteins, Nucleic Acids, and Organic Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 5179–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornell, W.D.; Cieplak, P.; Bayly, C.I.; Kollman, P.A. Application of RESP charges to calculate conformational energies, hydrogen bond energies, and free energies of solvation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 9620–9631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupradeau, F.-Y.; Pigache, A.; Zaffran, T.; Savineau, C.; Lelong, R.; Grivel, N.; Lelong, D.; Rosanski, W.; Cieplak, P. The REd. Tools: Advances in RESP and ESP charge derivation and force field library building. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 7821–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivani, I.; Dans, P.D.; Noy, A.; Perez, A.; Faustino, I.; Hospital, A.; Walther, J.; Andrio, P.; Goñi, R.; Balaceanu, A.; et al. Parmbsc1: A refined force field for DNA simulations. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE) Chemical. Computing Group ULC: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021. Available online: https://www.chemcomp.com/Products.htm (accessed on 29 July 2021).
- Krauss, I.R.; Merlino, A.; Mazzarella, L.; Sica, F. X-ray structure of the complex between human alpha thrombin and thrombin binding aptamer in the presence of potassium ions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 268, 17651–17654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bussi, G.; Donadio, D.; Parrinello, M. Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 126, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berendsen, H.J.C.; Postma, J.P.M.; Van Gunsteren, W.F.; DiNola, A.; Haak, J.R. Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parrinello, M.; Rahman, A. Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 7182–7190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A linear constraint solver for molecular simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD-Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatoishi, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Tsumoto, K. Circular dichroism spectra demonstrate formation of the thrombin-binding DNA aptamer G-quadruplex under stabilizing-cation-deficient conditions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 352, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolot, R.; Lam, C.H.; Sierant, M.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, F.-W.; Nawrot, B.; Egli, M.; Yang, X. Crystal structures of thrombin in complex with chemically modified thrombin DNA aptamers reveal the origins of enhanced affinity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 4819–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virno, A.; Randazzo, A.; Giancola, C.; Bucci, M.; Cirino, G.; Mayol, L. A novel thrombin binding aptamer containing a G-LNA residue. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 5710–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonifacio, L.; Church, F.C.; Jarstfer, M.B. Effect of Locked-Nucleic Acid on a Biologically Active G-Quadruplex. A Structure-Activity Relationship of the Thrombin Aptamer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Name of the Construct | Dissociation Constant KD (Average Values Calculated from Our SPR Experiments) (nM) | Reported KD (from Literature [19] for Unmodified/Modified TBA at Same Locations) (nM) |
|---|---|---|
| TBA | 99.8 (±8.96) | 102.6 ± 5.1 |
| 5TG | 102 (±2.22) | - |
| 5LTG | 99.6 (±1.2) | - |
| 4NHT | 102 (±2.21) | 172.3 ± 8.1 a |
| 13NHT | 99.7 (±1.34) | - |
| 413NHT | 102 (±2.22) | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valsangkar, V.; Vangaveti, S.; Lee, G.W.; Fahssi, W.M.; Awan, W.S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, A.A.; Sheng, J. Structural and Binding Effects of Chemical Modifications on Thrombin Binding Aptamer (TBA). Molecules 2021, 26, 4620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154620
Valsangkar V, Vangaveti S, Lee GW, Fahssi WM, Awan WS, Huang Y, Chen AA, Sheng J. Structural and Binding Effects of Chemical Modifications on Thrombin Binding Aptamer (TBA). Molecules. 2021; 26(15):4620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154620
Chicago/Turabian StyleValsangkar, Vibhav, Sweta Vangaveti, Goh Woon Lee, Walid M. Fahssi, Waqas S. Awan, Yicheng Huang, Alan A. Chen, and Jia Sheng. 2021. "Structural and Binding Effects of Chemical Modifications on Thrombin Binding Aptamer (TBA)" Molecules 26, no. 15: 4620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154620
APA StyleValsangkar, V., Vangaveti, S., Lee, G. W., Fahssi, W. M., Awan, W. S., Huang, Y., Chen, A. A., & Sheng, J. (2021). Structural and Binding Effects of Chemical Modifications on Thrombin Binding Aptamer (TBA). Molecules, 26(15), 4620. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154620






