ROCK2-Specific Inhibitor KD025 Suppresses Adipocyte Differentiation by Inhibiting Casein Kinase 2
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Novel Targets of KD025
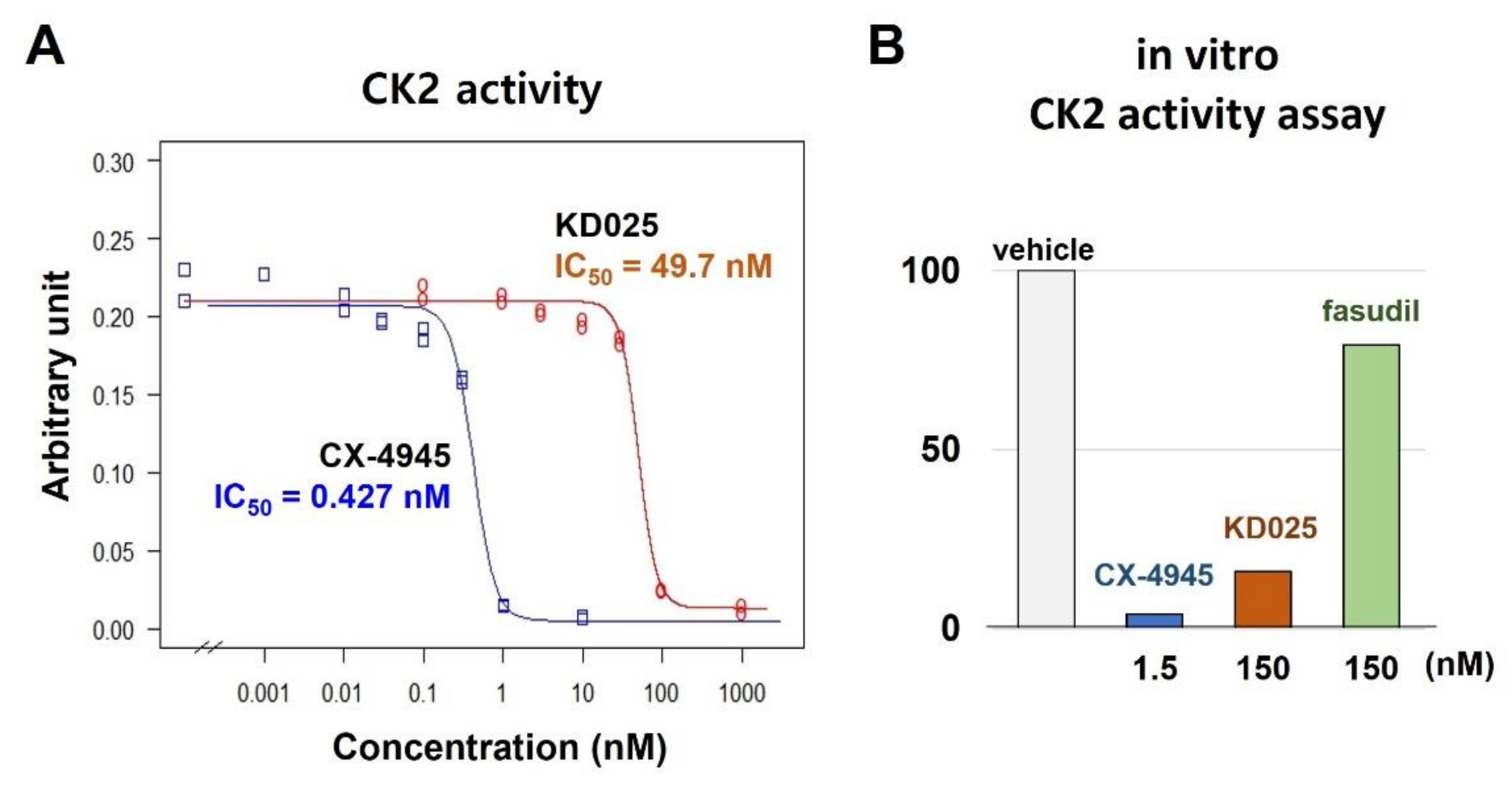
2.2. Binding and Inhibitory Activities of KD025 on CK2α
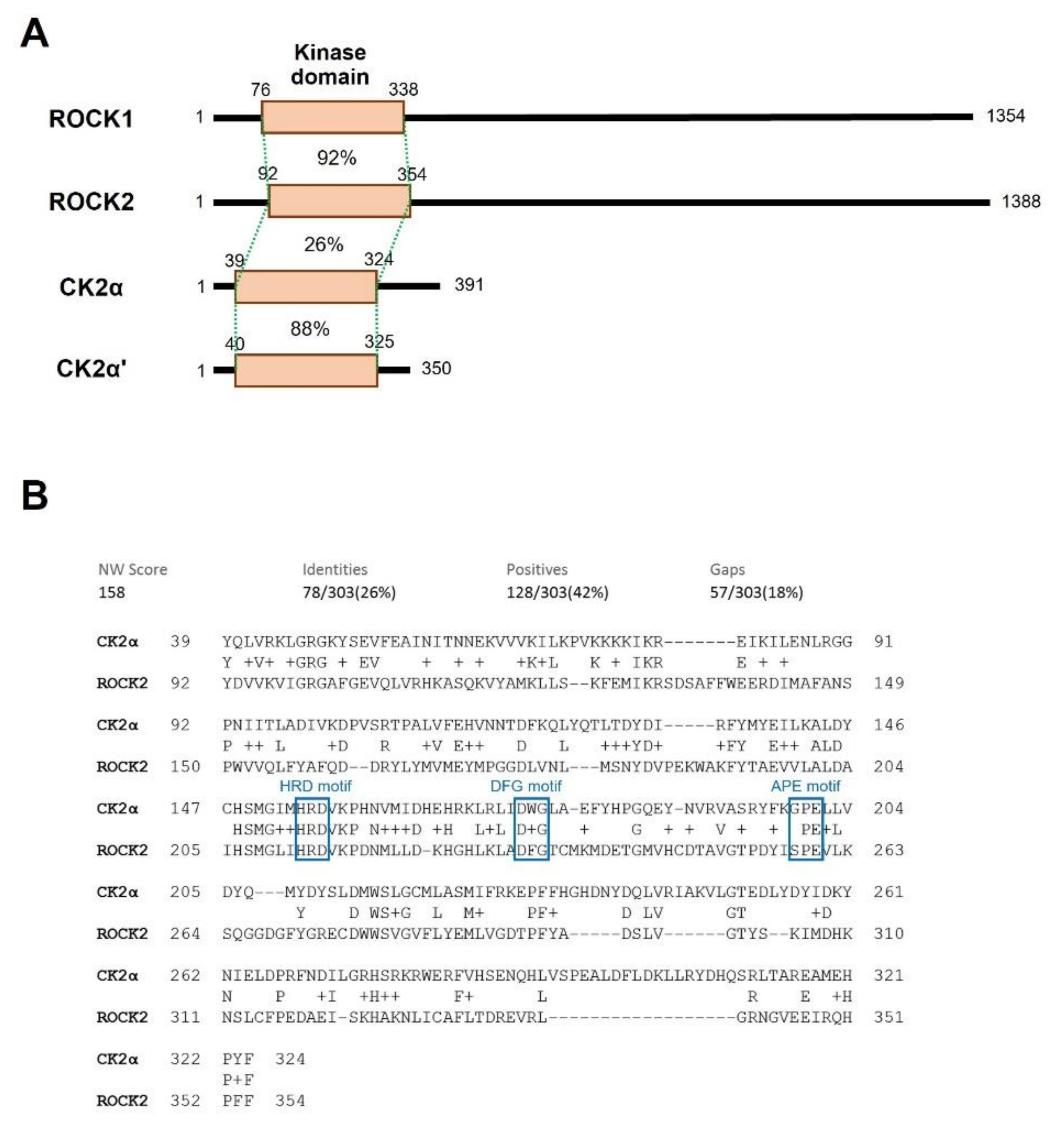
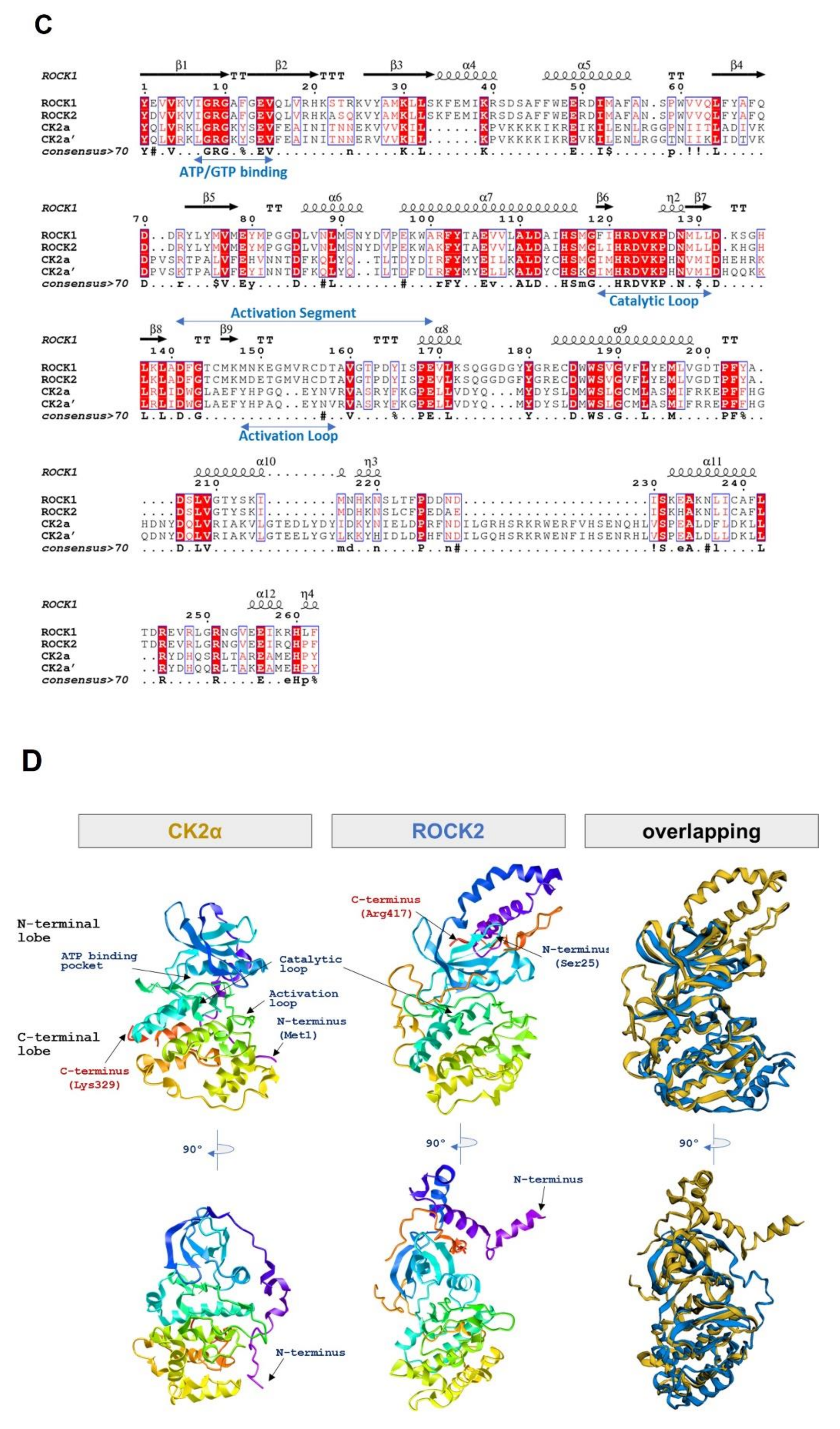
2.3. CK2α Shows Low Sequential and Structural Similarities with ROCK2
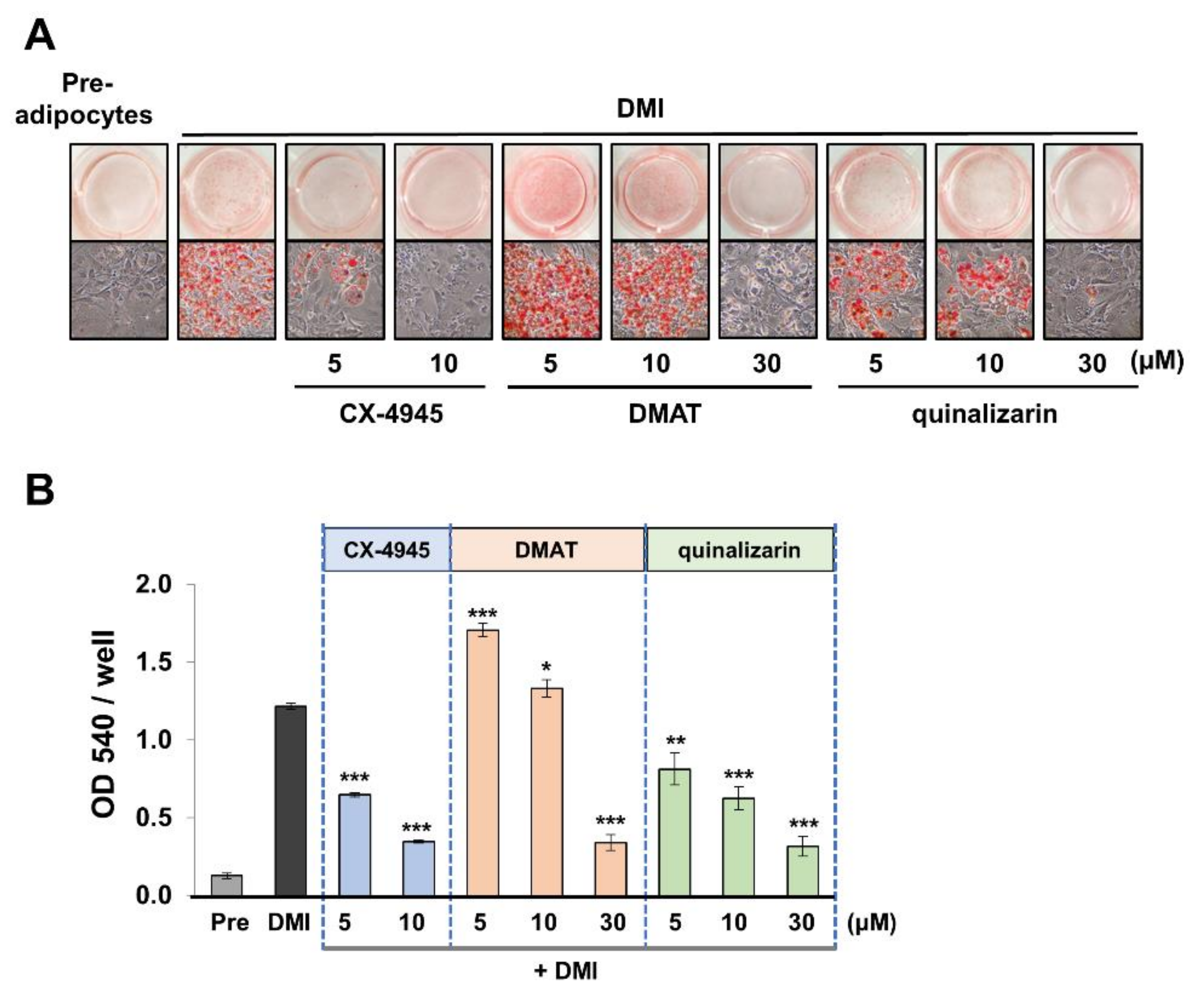
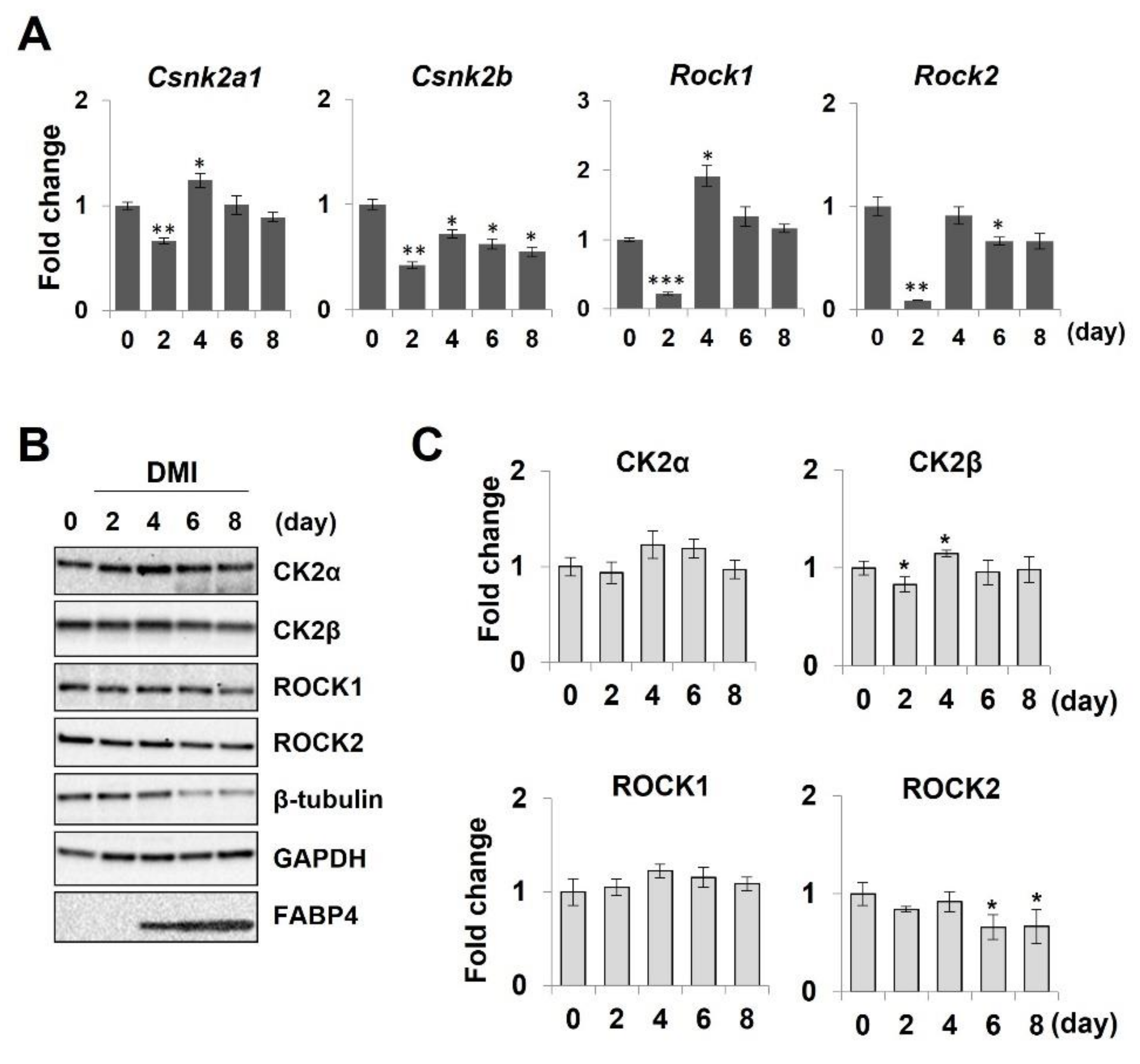
2.4. Downregulation of Adipocyte Differentiation ss Mediated by CK2 Inhibition
2.5. KD025 and CX-4945 Regulate the Intermediate Stage of Adipogenesis
2.6. CK2 Is a Key Regulator in Adipogenesis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Inhibitors
4.2. Drug-Kinase Binding Assay
4.3. Dissociation Constant Measurement
4.4. Sequence Alignment
4.5. Structural Alignment
4.6. CK2 Activity Assay
4.7. Cell Culture
4.8. Oil Red O Staining
4.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Leung, T.; Manser, E.; Tan, L.; Lim, L. A novel serine/threonine kinase binding the Ras-related RhoA GTPase which trans-locates the kinase to peripheral membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 29051–29054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishizaki, T.; Maekawa, M.; Fujisawa, K.; Okawa, K.; Iwamatsu, A.; Fujita, A.; Watanabe, N.; Saito, Y.; Kakizuka, A.; Morii, N.; et al. The small GTP-binding protein Rho binds to and activates a 160 kDa Ser/Thr protein kinase homologous to myotonic dystrophy kinase. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riento, K.; Ridley, A.J. ROCKs: Multifunctional kinases in cell behaviour. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lee, S.H.; Ye, C.; Lima, I.S.; Oh, B.C.; Lowell, B.B.; Zabolotny, J.M.; Kim, Y.B. ROCK1 in AgRP neurons regulates energy expenditure and locomotor activity in male mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3660–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.-H.; Araki, K.; Jee, Y.; Lee, D.-H.; Oh, B.-C.; Huang, H.; Park, K.S.; Lee, S.W.; Zabolotny, J.M.; Kim, Y.-B. Regulation of Glucose Transport by ROCK1 Differs from That of ROCK2 and Is Controlled by Actin Polymerization. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1649–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croft, D.R.; Olson, M.F. The Rho GTPase Effector ROCK Regulates Cyclin A, Cyclin D1, and p27 Kip1 Levels by Distinct Mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 4612–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kümper, S.; Mardakheh, F.; McCarthy, A.; Yeo, M.; Stamp, G.W.; Paul, A.; Worboys, J.; Sadok, A.; Jorgensen, C.; Guichard, S.; et al. Rho-associated kinase (ROCK) function is essential for cell cycle progression, senescence and tumorigenesis. eLife 2016, 5, e12203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, M.; Sahai, E.; Yeo, M.; Bosch, M.; Dewar, A.; Olson, M. Membrane blebbing during apoptosis results from caspase-mediated activation of ROCK I. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebbagh, M.; Renvoizé, C.; Hamelin, J.; Riché, N.; Bertoglio, J.; Bréard, J. Caspase-3-mediated cleavage of ROCK I induces MLC phosphorylation and apoptotic membrane blebbing. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBeath, R.; Pirone, D.M.; Nelson, C.M.; Bhadriraju, K.; Chen, C.S. Cell Shape, Cytoskeletal Tension, and RhoA Regulate Stem Cell Lineage Commitment. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sordella, R.; Jiang, W.; Chen, G.-C.; Curto, M.; Settleman, J. Modulation of Rho GTPase Signaling Regulates a Switch between Adipogenesis and Myogenesis. Cell 2003, 113, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baudry, A.; Yang, Z.Z.; Hemmings, B.A. PKBalpha is required for adipose differentiation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119 Pt 5, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Liao, K. Protein Kinase B/AKT 1 Plays a Pivotal Role in Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Signaling Induced 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 35914–35922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.H.; Huang, J.; Duvel, K.; Boback, B.; Wu, S.; Squillace, R.M.; Wu, C.L.; Manning, B.D. Insulin stimulates adipogenesis through the Akt-TSC2-mTORC1 pathway. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, M.; Hosoda, K.; Fujikura, J.; Fujimoto, M.; Iwakura, H.; Tomita, T.; Ishii, T.; Arai, N.; Hirata, M.; Ebihara, K.; et al. Genetic and Pharmacological Inhibition of Rho-associated Kinase II Enhances Adipogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29574–29583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, N.; Nobusue, H.; Shimizu, T.; Sugihara, E.; Yamaguchi-Iwai, S.; Onishi, N.; Kunitomi, H.; Kuroda, T.; Saya, H. ROCK Inhibition Induces Terminal Adipocyte Differentiation and Suppresses Tumorigenesis in Chemoresistant Osteosarcoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3088–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Kang, W.; Du, L.; Ge, S. Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 facilitates the proliferation, migration and pluripotency of human periodontal ligament stem cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3100–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvari, L.; Ojansivu, M.; Juntunen, M.; Kartasalo, K.; Miettinen, S.; Vanhatupa, S. Focal Adhesion Kinase and ROCK Signaling are switch-like regulators of human adipose stem cell differentiation towards osteogenic and adipogenic lineages. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 2190657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, D.T.V.; Duong, K.H.M.; Choi, H.; Jun, H.-S.; Chun, K.-H. KD025 (SLx-2119) suppresses adipogenesis at intermediate stage in human adipose-derived stem cells. Adipocyte 2019, 8, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diep, D.T.V.; Hong, K.; Khun, T.; Zheng, M.; Ul-Haq, A.; Jun, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-B.; Chun, K.-H. Anti-adipogenic effects of KD025 (SLx-2119), a ROCK2-specific inhibitor, in 3T3-L1 cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, B.; Madsen, L.; Petersen, R.K.; Techer, N.; Kopperud, R.; Ma, T.; Døskeland, S.O.; Ailhaud, G.; Wang, J.; Amri, E.-Z.; et al. Activation of Protein Kinase A and Exchange Protein Directly Activated by cAMP Promotes Adipocyte Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loirand, G. Rho Kinases in Health and Disease: From Basic Science to Translational Research. Pharmacol. Rev. 2015, 67, 1074–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Lograsso, P.V.; Defert, O.; Li, R. Rho Kinase (ROCK) Inhibitors and Their Therapeutic Potential. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 59, 2269–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerma, M.; Fu, Q.; Wang, J.; Loose, D.S.; Bartolozzi, A.; Ellis, J.L.; McGonigle, S.; Paradise, E.; Sweetnam, P.; Fink, L.M.; et al. Comparative gene expression profiling in three primary human cell lines after treatment with a novel inhibitor of Rho kinase or atorvastatin. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2008, 19, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Zheng, Y.; Von Bornstadt, D.; Wei, Y.; Balcioglu, A.; Daneshmand, A.; Yalcin, N.; Yu, E.; Herisson, F.; Atalay, Y.B.; et al. Selective ROCK 2 inhibition in focal cerebral ischemia. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2013, 1, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanin-Zhorov, A.; Weiss, J.M.; Nyuydzefe, M.S.; Chen, W.; Scher, J.U.; Mo, R.; Depoil, D.; Rao, N.; Liu, B.; Wei, J.; et al. Selective oral ROCK2 inhibitor down-regulates IL-21 and IL-17 secretion in human T cells via STAT3-dependent mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16814–16819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 7 October 2020).
- Yoon, J.-H.; Nguyen, T.-T.-L.; Duong, V.-A.; Chun, K.-H.; Maeng, H.-J. Determination of KD025 (SLx-2119), a Selective ROCK2 Inhibitor, in Rat Plasma by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Its Pharmacokinetic Application. Molecules 2020, 25, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, R.; Ursu, O.; Gaulton, A.; Bento, A.P.S.F.F.; Donadi, R.S.; Bologa, C.G.; Karlsson, A.; Al-Lazikani, B.; Hersey, A.; Oprea, T.I.; et al. A comprehensive map of molecular drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgo, C.; Milan, G.; Favaretto, F.; Stasi, F.; Fabris, R.; Salizzato, V.; Cesaro, L.; Belligoli, A.; Sanna, M.; Foletto, M.; et al. CK2 modulates adipocyte insulin-signaling and is up-regulated in human obesity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwind, L.; Wilhelm, N.; Kartarius, S.; Montenarh, M.; Gorjup, E.; Gotz, C. Protein kinase CK2 is necessary for the adipo-genic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853 10 Pt A, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar]
- Schwind, L.; Schetting, S.; Montenarh, M. Inhibition of Protein Kinase CK2 prevents adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells like C3H/10T1/2 Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sommercorn, J.; Krebs, E.G. Induction of casein kinase II during differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 3839–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, N.; Kostelnik, K.; Götz, C.; Montenarh, M. Protein kinase CK2 is implicated in early steps of the differentiation of pre-adipocytes into adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 365, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozza, G.; Venerando, A.; Sarno, S.; Pinna, L.A. The Selectivity of CK2 Inhibitor Quinalizarin: A Reevaluation. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cozza, G.; Mazzorana, M.; Papinutto, E.; Bain, J.; Elliott, M.; Di Maira, G.; Gianoncelli, A.; Pagano, M.A.; Sarno, S.; Ruzzene, M.; et al. Quinalizarin as a potent, selective and cell-permeable inhibitor of protein kinase CK2. Biochem. J. 2009, 421, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarno, S.; Papinutto, E.; Franchin, C.; Bain, J.; Elliott, M.; Meggio, F.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Orzeszko, A.; Zanotti, G.; Battistutta, R.; et al. ATP site-directed inhibitors of protein kinase CK2: An update. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, M.A.; Bain, J.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Sarno, S.; Ruzzene, M.; Di Maira, G.; Elliott, M.; Orzeszko, A.; Cozza, G.; Meggio, F.; et al. The selectivity of inhibitors of protein kinase CK2: An update. Biochem. J. 2008, 415, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, P.S.; Gupta, S.; Chang, E.; Song, L.; Stirzaker, R.A.; Liao, J.K.; Bhagat, G.; Pernis, A.B. Phosphorylation of IRF4 by ROCK2 regulates IL-17 and IL-21 production and the development of autoimmunity in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3280–3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flynn, R.; Paz, K.; Du, J.; Reichenbach, D.K.; Taylor, P.A.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Vulic, A.; Luznik, L.; MacDonald, K.K.; Hill, G.R.; et al. Targeted Rho-associated kinase 2 inhibition suppresses murine and human chronic GVHD through a Stat3-dependent mechanism. Blood 2016, 127, 2144–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zandi, S.; Nakao, S.; Chun, K.-H.; Fiorina, P.; Sun, D.; Arita, R.; Zhao, M.; Kim, E.; Schueller, O.; Campbell, S.; et al. ROCK-Isoform-Specific Polarization of Macrophages Associated with Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.H.; Shi, J.; Jeoung, N.H.; Kim, M.S.; Zabolotny, J.M.; Lee, S.W.; White, M.F.; Wei, L.; Kim, Y.-B. Targeted Disruption of ROCK1 Causes Insulin Resistance in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 11776–11780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chun, K.-H.; Choi, K.-D.; Lee, D.-H.; Jung, Y.; Henry, R.R.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Kim, Y.-B. In vivo activation of ROCK1 by insulin is impaired in skeletal muscle of humans with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2011, 300, E536–E542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.-H.; Huang, H.; Choi, K.; Lee, D.H.; Shi, J.; Liu, T.; Chun, K.H.; Seo, J.A.; Lima, I.S.; Zabolotny, J.M.; et al. ROCK1 isoform-specific deletion reveals a role for diet-induced insulin resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2014, 306, E332–E343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kato, Y.; Ozaki, N.; Yamada, T.; Miura, Y.; Oiso, Y. H-89 potentiates adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells by activating insulin sig-naling independently of protein kinase A. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Surma, M.; Yang, Y.; Tersey, S.; Shi, J. ROCK2 inhibition enhances the thermogenic program in white and brown fat tissue in mice. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 474–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Chun, K.-H. Identification of novel functions of the ROCK2-specific inhibitor KD025 by bioinformatics analysis. Gene 2020, 737, 144474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez de Villavicencio-Diaz, T.; Rabalski, A.J.; Litchfield, D.W. Protein Kinase CK2: Intricate relationships within regulatory cellular networks. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shinoda, K.; Ohyama, K.; Hasegawa, Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Ogura, M.; Sato, A.; Hong, H.; Hosono, T.; Sharp, L.Z.; Scheel, D.W.; et al. Phosphoproteomics Identifies CK2 as a Negative Regulator of Beige Adipocyte Thermo-genesis and Energy Expenditure. Cell. Metab. 2015, 22, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, S.E.; Kwon, S.; Seok, S.; Xiao, Z.; Lee, K.-W.; Kang, Y.; Li, X.; Shinoda, K.; Kajimura, S.; Kemper, B.; et al. Obesity-Linked Phosphorylation of SIRT1 by Casein Kinase 2 Inhibits Its Nuclear Localization and Promotes Fatty Liver. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 37, e00006-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eom, G.H.; Cho, Y.K.; Ko, J.-H.; Shin, S.; Choe, N.; Kim, Y.; Joung, H.; Kim, H.-S.; Nam, K.-I.; Kee, H.J.; et al. Casein Kinase-2α1 Induces Hypertrophic Response by Phosphorylation of Histone Deacetylase 2 S394 and its Activation in the Heart. Circulation 2011, 123, 2392–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, S.-C.; Seto, E. Regulation of Histone Deacetylase 2 by Protein Kinase CK2. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 31826–31833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabian, M.A.; Biggs, W.H.; Treiber, D.K.; Atteridge, C.E.; Azimioara, M.D.; Benedetti, M.G.; Carter, T.A.; Ciceri, P.; Edeen, P.T.; Floyd, M.; et al. A small molecule-kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, C.; Jensen, S.M.; Gerhard, D.; Streibig, J.C. Dose-Response Analysis Using, R. PLoS ONE 2019, 10, 0146021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, J.S.; Agarwala, R. COBALT: Constraint-based alignment tool for multiple protein sequences. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Jaroszewski, L.; Iyer, M.; Sedova, M.; Godzik, A. FATCAT 2.0: Towards a better understanding of the structural diversity of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W60–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
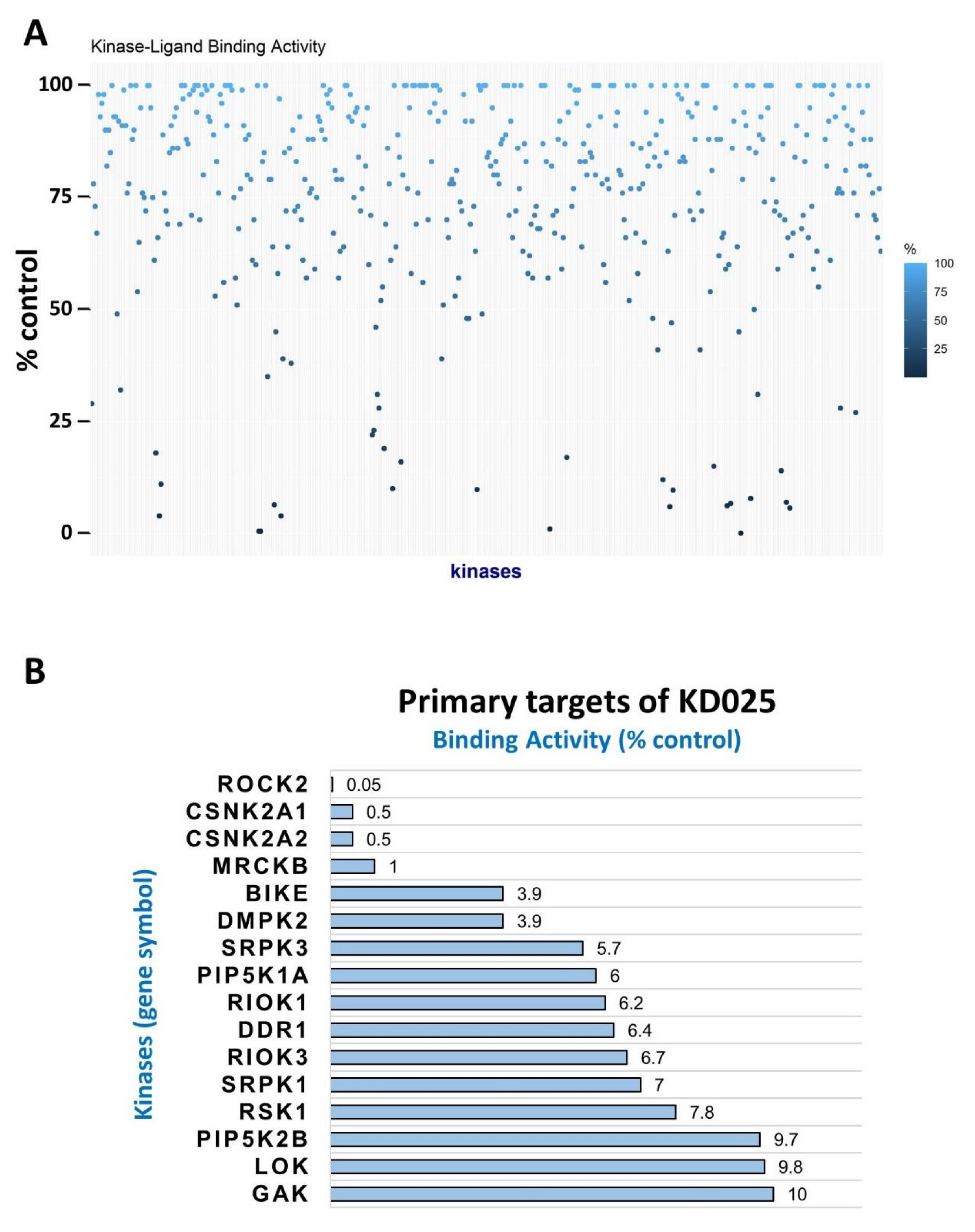
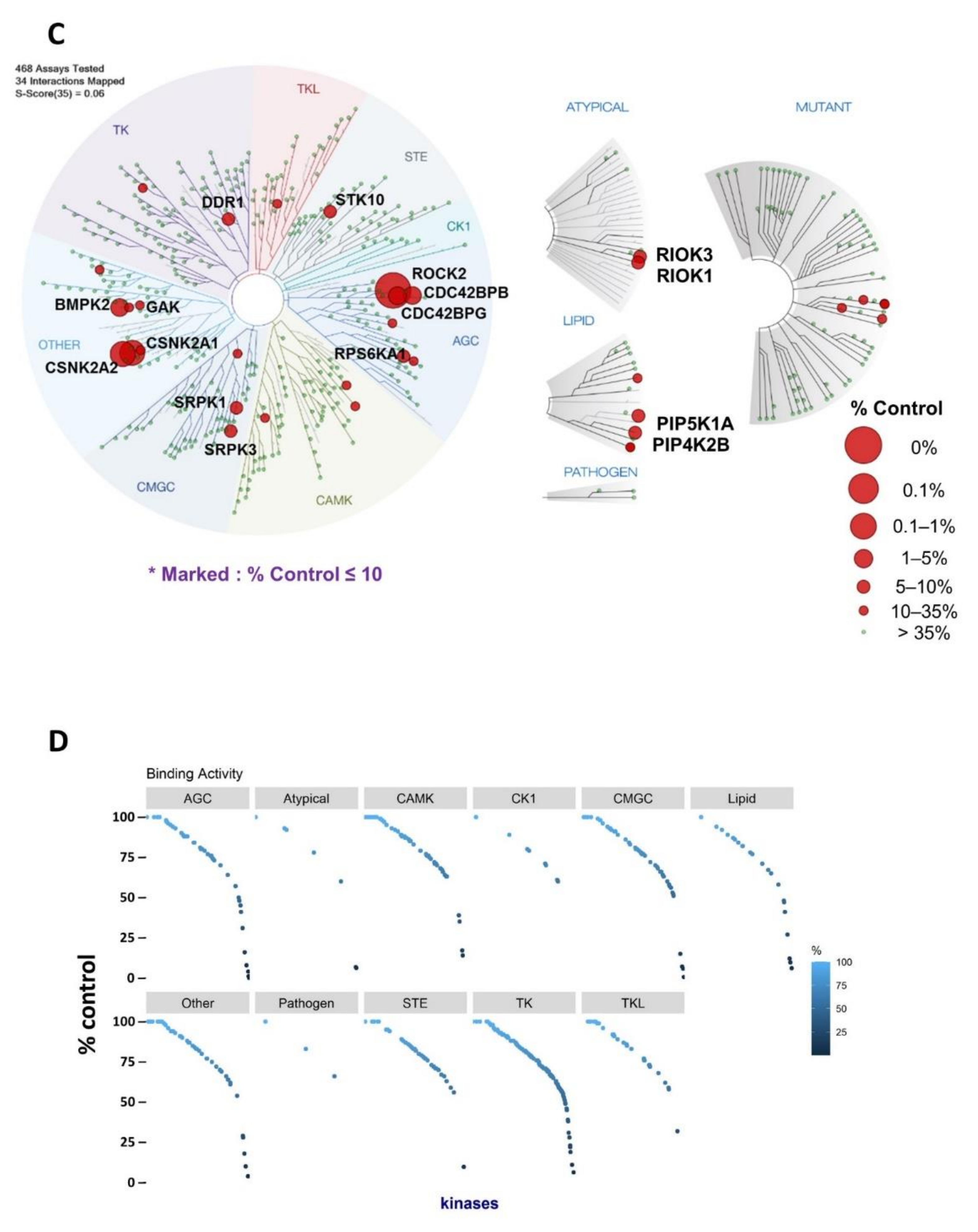
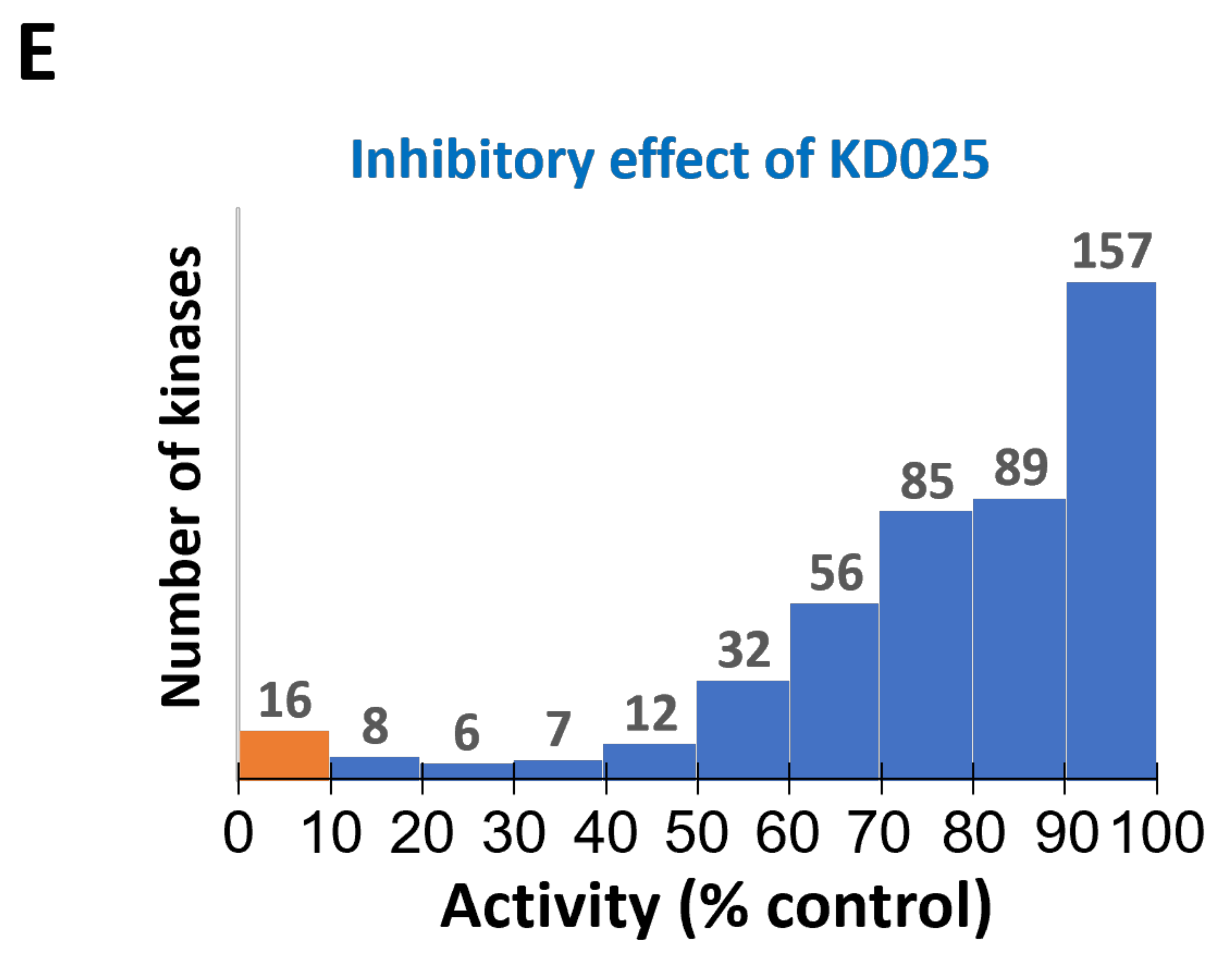
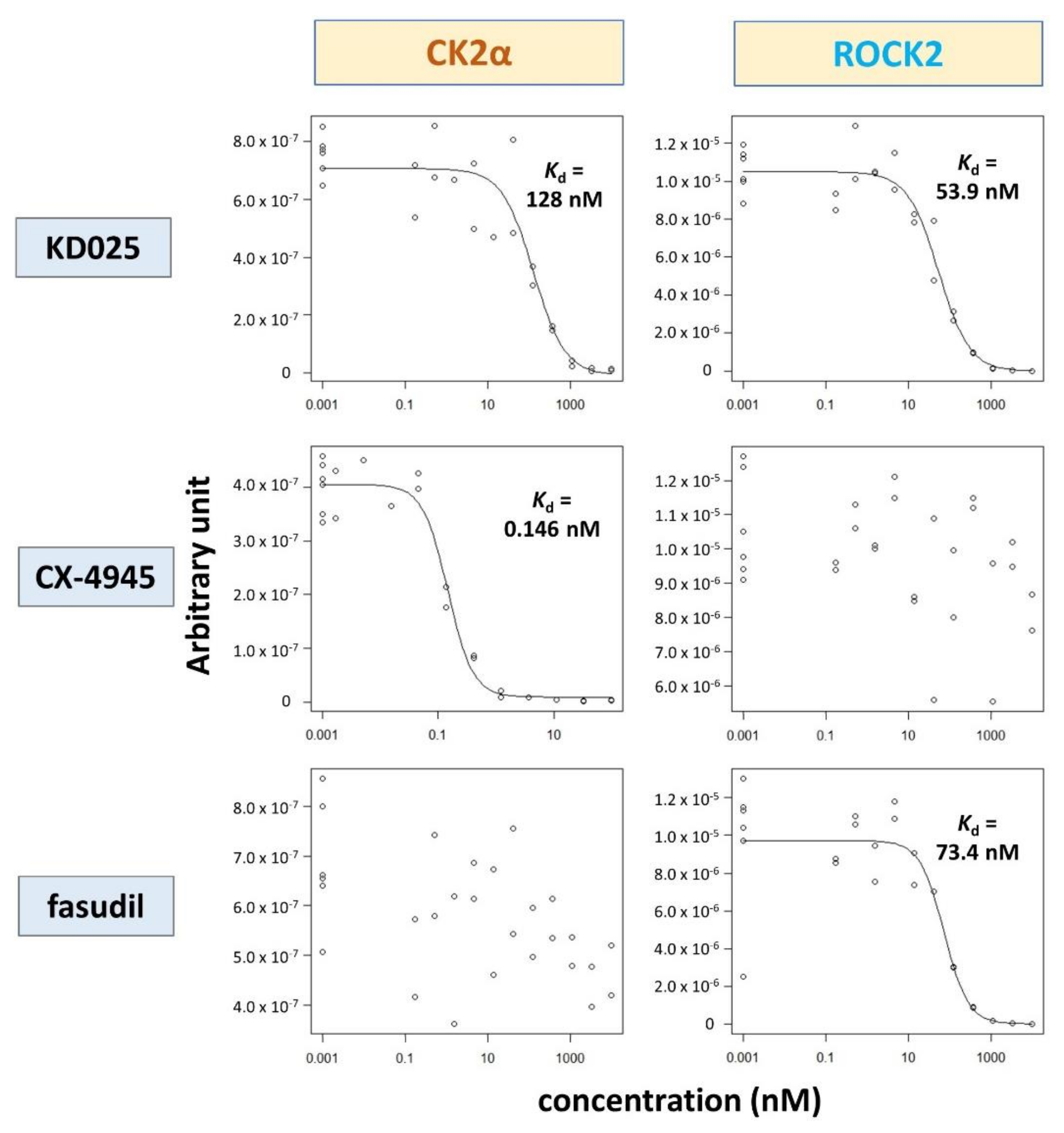


| Kinase | NCBI ID | Length (Residues) | Molecular Weight (kDa) | Kinase Domain # | Catalytic Loop | Activation Segment | PDB ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROCK1 | NP_005397.1 | 1354 | 158 | 76–338 | 194–206 | 216–244 | 6E9W |
| ROCK2 | NP_004841.2 | 1388 | 161 | 92–354 | 210–222 | 216–244 | 7JOV |
| CK2α | NP_001886.1 | 391 | 45 | 39–324 | 152–164 | 175–201 | 6YPN |
| CK2α’ | NP_001887.1 | 350 | 41 | 40–325 | 153–165 | 176–202 | 6TGU |
| Type | Gene | Primer | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ROCKs | Rock1 | forward | TGCTAACCAAAGATATTGAAATGCT |
| reverse | TTTATTTCTTCCTCCTTCTTCAATTT | ||
| Rock2 | forward | AATCTCATATGTGCCTTCTTAACAGA | |
| reverse | CCCAATTCCATTGATCATTCTT | ||
| CK2 | Csnk2a1 | forward | GCCGCCATATTGTCTGTGTG |
| reverse | CCCTTTTTCTTCACACTGCGG | ||
| Csnk2b | forward | TCCTTGGAAGCACAGCTCC | |
| reverse | AGTCTTCATCCACCTCACAGA | ||
| Adipogenic genes | Pparg | forward | TGCTGTTATGGGTGAAACTC |
| reverse | CTGTGTCAACCATGGTAATT | ||
| Cepba | forward | AGCTGCCTGAGAGCTCCTT | |
| reverse | GACCCGAAACCATCCTCTG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, N.N.Q.; Chun, K.-H. ROCK2-Specific Inhibitor KD025 Suppresses Adipocyte Differentiation by Inhibiting Casein Kinase 2. Molecules 2021, 26, 4747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164747
Tran NNQ, Chun K-H. ROCK2-Specific Inhibitor KD025 Suppresses Adipocyte Differentiation by Inhibiting Casein Kinase 2. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):4747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164747
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Nhu Nguyen Quynh, and Kwang-Hoon Chun. 2021. "ROCK2-Specific Inhibitor KD025 Suppresses Adipocyte Differentiation by Inhibiting Casein Kinase 2" Molecules 26, no. 16: 4747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164747
APA StyleTran, N. N. Q., & Chun, K.-H. (2021). ROCK2-Specific Inhibitor KD025 Suppresses Adipocyte Differentiation by Inhibiting Casein Kinase 2. Molecules, 26(16), 4747. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164747







