Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Inactivation Activity of the Polyphenol-Rich Tea Leaf Extract with Concentrated Theaflavins and Other Virucidal Catechins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
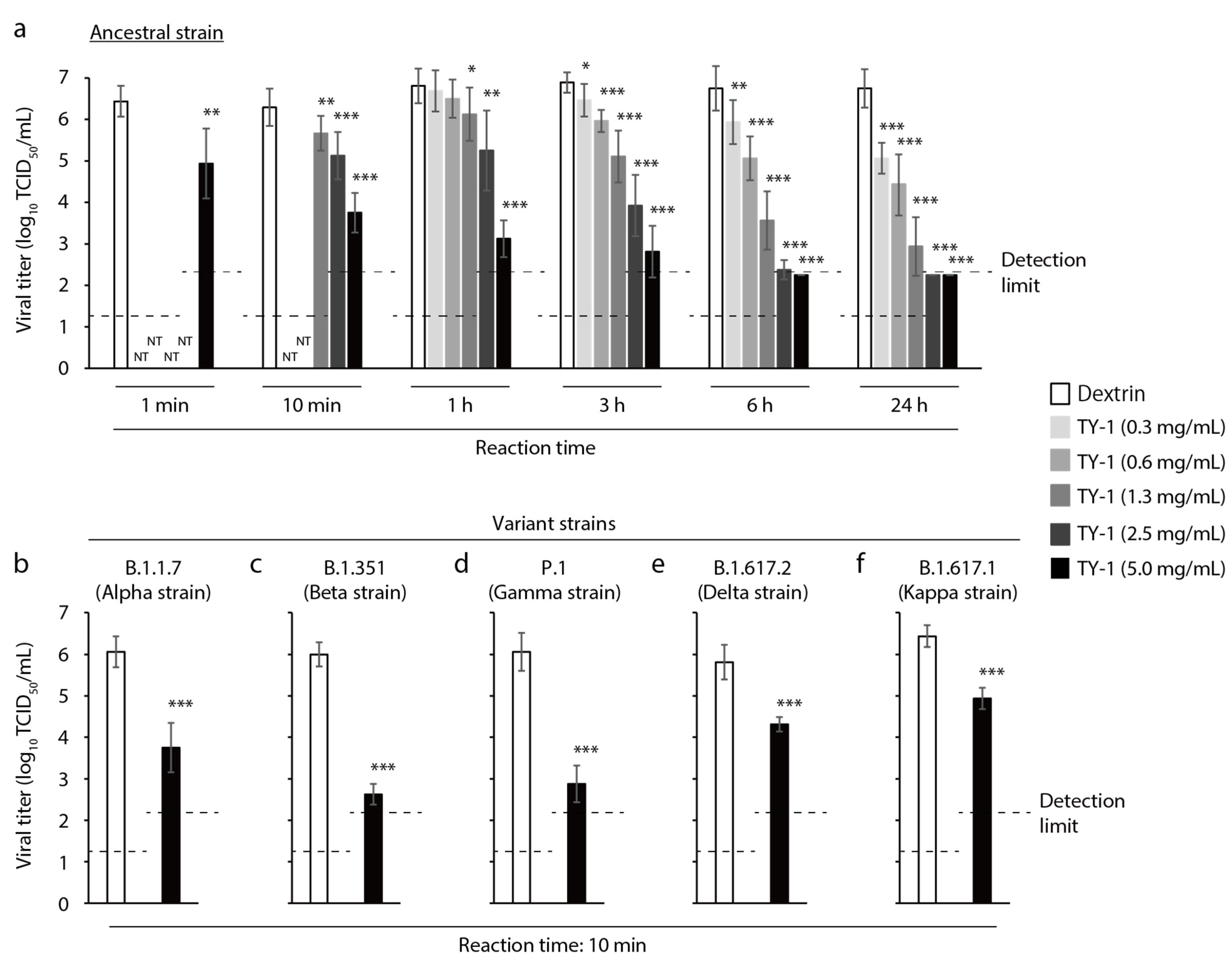
2.1. Virucidal Activity of TY-1 against SARS-CoV-2
2.2. Inhibitory Effects of TY-1 on SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Cells
2.3. Impact of TY-1 on SARS-CoV-2 Structural Proteins
2.4. Impact of TY-1 on the SARS-CoV-2 Genome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Viruses and Cells
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. Evaluation of the Virucidal Activity of TY-1 against SARS-CoV-2
4.4. Evaluation of the Inhibitory Effect of TY-1 on SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Cells
4.5. Evaluation of the Impact of TY-1 on SARS-CoV-2 Structural Proteins
4.6. Evaluation of the Impact of TY-1 on the SARS-CoV-2 Genome
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, K.; Antognini, D.; Combes, A.; Paden, M.; Zakhary, B.; Ogino, M.; Maclaren, G.; Brodie, D. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-2019) Situation Reports. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports (accessed on 12 May 2021).
- Kratzel, A.; Todt, D.; V’kovski, P.; Steiner, S.; Gultom, M.; Thao, T.T.N.; Ebert, N.; Holwerda, M.; Steinmann, J.; Niemeyer, D.; et al. Inactivation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 by WHO-recommended hand rub formulations and alcohols. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1592–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Uchiumi, H.; Matsuda, S.; Ogawa, H. Acidic electrolyzed water potently inactivates SARS-CoV-2 depending on the amount of free available chlorine contacting with the virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 530, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.-H.; Sridhar, S.; Zhang, R.R.; Chu, H.; Fung, A.Y.-F.; Chan, G.; Chan, J.F.-W.; To, K.K.-W.; Hung, I.F.-N.; Cheng, V.C.-C.; et al. Factors affecting stability and infectivity of SARS-CoV-2. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 106, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerowitz, E.A.; Richterman, A.; Gandhi, R.T.; Sax, P.E. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A review of viral, host, and environmental factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ita, K. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Current status and prospects for drug and vaccine development. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, J.G.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Mehra, M.R.; Lavie, C.J.; Rizk, Y.; Forthal, D.N. Pharmaco-immunomodulatory therapy in COVID-19. Drugs 2020, 80, 1267–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, S.A.K.; Tulio, D.O. New SARS-CoV-2 variants-clinical, public health, and vaccine implications. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1866–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibmer, C.K.; Ayres, F.; Hermanus, T.; Madzivhandila, M.; Kgagudi, P.; Oosthuysen, B.; Lambson, B.E.; de Oliveira, T.; Vermeulen, M.; van der Berg, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 501Y.V2 escapes neutralization by South African COVID-19 donor plasma. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, R.; Sharma, B.; Kanwar, S.S. Antiviral phytochemicals: An overview. Biochem. Physiol. Open Access 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildiyal, R.; Prakash, V.; Chaudhary, V.K.; Gupta, V.; Gabrani, R. Phytochemicals as antiviral agents: Recent updates. In Plant-Derived Bioactives; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 279–295. [Google Scholar]
- Musarra-Pizzo, M.; Pennisi, R.; Ben-Amor, I.; Mandalari, G.; Sciortino, M.T. Antiviral activity exerted by natural products against human viruses. Viruses 2021, 13, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, W. A review of the antiviral role of green tea catechins. Molecules 2017, 22, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tong, T.; Liu, Y.J.; Kang, J.; Zhang, C.M.; Kang, S.G. Antioxidant activity and main chemical components of a novel fermented tea. Molecules 2019, 24, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Hua, J.; Wang, B.; Yuan, H.; Ma, H. Effects of variety, season, and region on theaflavins content of fermented Chinese Congou black tea. J. Food Qual. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lu, H.; Zhao, Q.; He, Y.; Niu, J.; Debnath, A.K.; Wu, S.; Jiang, S. Theaflavin derivatives in black tea and catechin derivatives in green tea inhibit HIV-1 entry by targeting gp41. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2005, 1723, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhatre, S.; Srivastava, T.; Naik, S.; Patravale, V. Antiviral activity of green tea and black tea polyphenols in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: A review. Phytomedicine 2020, 85, 153286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, M. Manufacturing Method for Theaflavins Using Raw Tea Leaves. Japanese Patent No 4,817,206, 9 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Utsunomiya, H.; Ichinose, M.; Uozaki, M.; Tsujimoto, K.; Yamasaki, H.; Koyama, A.H. Antiviral activities of coffee extracts in vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1919–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, Y.; Kurihara, S.; Higashi, N.; Morikawa, S.; Kase, T.; Maeda, A.; Arisaka, H.; Shibahara, S.; Akiyama, Y. Combined administration of L-cystine and L-theanine enhances immune functions and protects against influenza virus infection in aged mice. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakayama, M.; Suzuki, K.; Toda, M.; Okubo, S.; Hara, Y.; Shimamura, T. Inhibition of the infectivity of influenza virus by tea polyphenols. Antiviral Res. 1993, 21, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukoyama, A.; Ushijima, H.; Nishimura, S.; Koike, H.; Toda, M.; Hara, Y.; Shimamura, T. Inhibition of rotavirus and enterovirus infections by tea extracts. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 1991, 44, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohba, M.; Oka, T.; Ando, T.; Arahata, S.; Ikegaya, A.; Takagi, H.; Ogo, N.; Zhu, C.; Owada, K.; Kawamori, F.; et al. Antiviral effect of theaflavins against caliciviruses. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, P.; Sahuc, M.E.; Rouillé, Y.; Rivière, C.; Bonneau, N.; Vandeputte, A.; Brodin, P.; Goswami, M.; Bandyopadhyay, T.; Dubuisson, J.; et al. Theaflavins, polyphenols of black tea, inhibit entry of hepatitis C virus in cell culture. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeda, Y.; Murata, T.; Jamsransuren, D.; Suganuma, K.; Kazami, Y.; Batkhuu, J.; Badral, D.; Ogawa, H. Saxifraga spinulosa-derived components rapidly inactivate multiple viruses including SARS-CoV-2. Viruses 2020, 12, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knox, Y.M.; Hayashi, K.; Suzutani, T.; Ogasawara, M.; Yoshida, I.; Shiina, R.; Tsukui, A.; Terahara, N.; Azuma, M. Activity of anthocyanins from fruit extract of Ribes nigrum L. against influenza A and B viruses. Acta Virol. 2001, 45, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Amoros, M.; Simōes, C.M.O.; Girre, L.; Sauvager, F.; Cormier, M. Synergistic effect of flavones and flavonols against herpes simplex virus type 1 in cell culture. Comparison with the antiviral activity of propolis. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudzynski, K.; Maldonado-Alvarez, L. Polyphenol-protein complexes and their consequences for the redox activity, structure and function of honey. A current view and new hypothesis—A review. Polish J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2015, 65, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zu, M.; Yang, F.; Zhou, W.; Liu, A.; Du, G.; Zheng, L. In vitro anti-influenza virus and anti-inflammatory activities of theaflavin derivatives. Antiviral Res. 2012, 94, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Jamsransuren, D.; Matsuda, S.; Crea, R.; Ogawa, H. The SARS-CoV-2-inactivating activity of hydroxytyrosol-rich aqueous olive pulp extract (HIDROX®) and its use as a virucidal cream for topical application. Viruses 2021, 13, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Lan, Q.; Feng, S.; Qi, F.; Bao, L.; Du, L.; Liu, S.; et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 (previously 2019-nCoV) infection by a highly potent pan-coronavirus fusion inhibitor targeting its spike protein that harbors a high capacity to mediate membrane fusion. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xu, X.F.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.W. Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: Potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, H.; Maeda, M.; Okuda, S.; Shimamura, T. Role of hydrogen peroxide in bactericidal action of catechin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, A.; Oikawa, S.; Murata, M.; Hiraku, Y.; Kawanishi, S. (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate causes oxidative damage to isolated and cellular DNA. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikigai, H.; Nakae, T.; Hara, Y.; Shimamura, T. Bactericidal catechins damage the lipid bilayer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1993, 1147, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nao, N.; Sato, K.; Yamagishi, J.; Tahara, M.; Nakatsu, Y.; Seki, F.; Katoh, H.; Ohnuma, A.; Shirogane, Y.; Hayashi, M.; et al. Consensus and variations in cell line specificity among human metapneumovirus strains. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kärber, G. Beitrag zur kollektiven behandlung pharmakologischer reihenversuche. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1931, 162, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirato, K.; Nao, N.; Katano, H.; Takayama, I.; Saito, S.; Kato, F.; Katoh, H.; Sakata, M.; Nakatsu, Y.; Mori, Y.; et al. Development of genetic diagnostic methods for detection for novel coronavirus 2019(nCoV-2019) in Japan. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, N.; Pérez, P.; Kato, T.; Mikami, Y.; Okuda, K.; Gilmore, R.C.; Conde, C.D.; Gasmi, B.; Stein, S.; Beach, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of the oral cavity and saliva. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxford, J.S.; Lambkin, R.; Guralnik, M.; Rosenbloom, R.A.; Petteruti, M.P.; DiGian, K.; LeFante, C. Preclinical in vitro activity of QR-435 against influenza a virus as a virucide and in paper masks for prevention of viral transmission. Am. J. Ther. 2007, 14, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takeda, Y.; Tamura, K.; Jamsransuren, D.; Matsuda, S.; Ogawa, H. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Inactivation Activity of the Polyphenol-Rich Tea Leaf Extract with Concentrated Theaflavins and Other Virucidal Catechins. Molecules 2021, 26, 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164803
Takeda Y, Tamura K, Jamsransuren D, Matsuda S, Ogawa H. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Inactivation Activity of the Polyphenol-Rich Tea Leaf Extract with Concentrated Theaflavins and Other Virucidal Catechins. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164803
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakeda, Yohei, Kyohei Tamura, Dulamjav Jamsransuren, Sachiko Matsuda, and Haruko Ogawa. 2021. "Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Inactivation Activity of the Polyphenol-Rich Tea Leaf Extract with Concentrated Theaflavins and Other Virucidal Catechins" Molecules 26, no. 16: 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164803
APA StyleTakeda, Y., Tamura, K., Jamsransuren, D., Matsuda, S., & Ogawa, H. (2021). Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Inactivation Activity of the Polyphenol-Rich Tea Leaf Extract with Concentrated Theaflavins and Other Virucidal Catechins. Molecules, 26(16), 4803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164803





