Orexins/Hypocretins and Cancer: A Neuropeptide as Emerging Target
Abstract
:1. Introduction
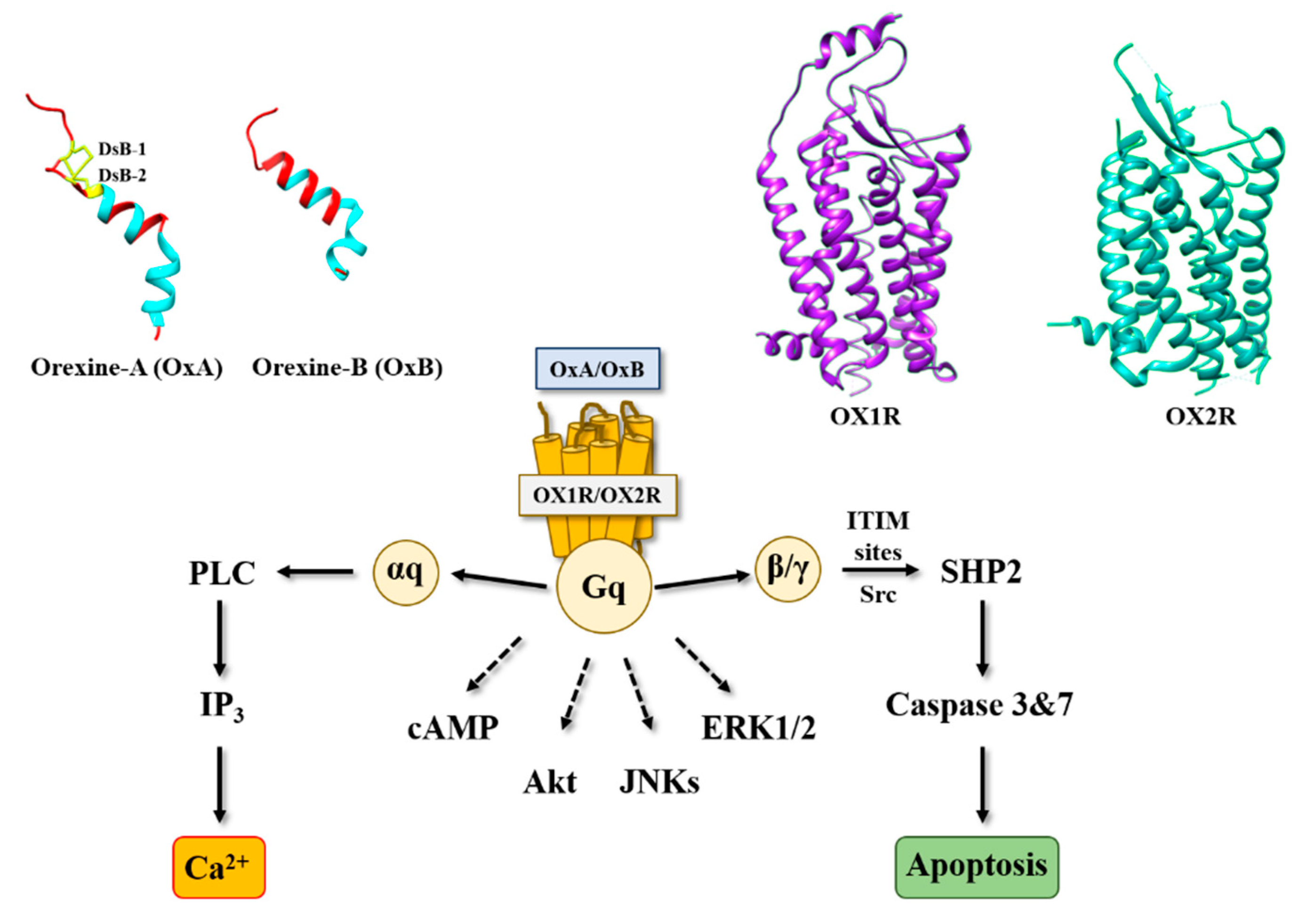
2. Orexins and Orexin Receptors
3. Orexins and Digestive Cancers
3.1. Colon Cancer
3.2. Pancreas Cancer
3.3. Gastric Cancer
4. Orexins and Other Cancers
4.1. Prostate Cancer
4.2. Other Cancers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, J.M.; Moore, R.; Thannickal, T.; Nienhuis, R. A brief history of hypocretin/orexin and narcolepsy. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 25, S14–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lecea, L.; Kilduff, T.S.; Peyron, C.; Gao, X.; Foye, P.E.; Danielson, P.E.; Fukuhara, C.; Battenberg, E.L.; Gautvik, V.T.; Bartlett, F.S., II; et al. The hypocretins: Hypothalamus-specific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakurai, T.; Amemiya, A.; Ishii, M.; Matsuzaki, I.; Chemelli, R.M.; Tanaka, H.; Williams, S.C.; Richardson, J.A.; Kozlowski, G.P.; Wilson, S.; et al. Orexins and orexin receptors: A family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 1998, 92, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couvineau, A.; Dayot, S.; Nicole, P.; Gratio, V.; Rebours, V.; Couvelard, A.; Voisin, T. The Anti-tumoral Properties of Orexin/Hypocretin Hypothalamic Neuropeptides: An Unexpected Therapeutic Role. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, S.B.; de Lecea, L. The hypocretin (orexin) system: From a neural circuitry perspective. Neuropharmacology 2020, 167, 107993–108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couvineau, A.; Voisin, T.; Nicole, P.; Gratio, V.; Abad, C.; Tan, Y.-V. Orexins as Novel Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berhe, D.F.; Gebre, A.K.; Assefa, B.T. Orexins role in neurodegenerative diseases: From pathogenesis to treatment. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2020, 194, 172929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, J.P.; Turunen, P.M. Cellular Signaling Mechanisms of Hypocretin/Orexin. Orexin Syst. Basic Sci. Role Sleep Pathol. 2021, 45, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouet-Benzineb, P.; Rouyer-Fessard, C.; Jarry, A.; Avondo, V.; Pouzet, C.; Yanagisawa, M.; Laboisse, C.; Laburthe, M.; Voisin, T. Orexins Acting at Native OX1 Receptor in Colon Cancer and Neuroblastoma Cells or at Recombinant OX1 Receptor Suppress Cell Growth by Inducing Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45875–45886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messal, N.; Fernandez, N.; Dayot, S.; Gratio, V.; Nicole, P.; Prochasson, C.; Chantret, I.; Leguilloux, G.; Jarry, A.; Couvelard, A.; et al. Ectopic expression of OX1R in ulcerative colitis mediates anti-inflammatory effect of orexin-A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3618–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becquet, L.; Abad, C.; Leclercq, M.; Miel, C.; Jean, L.; Riou, G.; Couvineau, A.; Boyer, O.; Tan, Y.-V. Systemic administration of orexin A ameliorates established experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by diminishing neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, D.; Hautot, C.; Mehio, M.; Jeandel, L.; Courel, M.; Voisin, T.; Couvineau, A.; Gobet, F.; Leprince, J.; Pfister, C.; et al. The orexin type 1 receptor is overexpressed in advanced prostate cancer with a neuroendocrine differentiation, and mediates apoptosis. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, T.; El Firar, A.; Fasseu, M.; Rouyer-Fessard, C.; Descatoire, V.; Walker, F.; Paradis, V.; Bedossa, P.; Henin, D.; Lehy, T.; et al. Aberrant Expression of OX1 Receptors for Orexins in Colon Cancers and Liver Metastases: An Openable Gate to Apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mogavero, M.P.; DelRosso, L.M.; Fanfulla, F.; Bruni, O.; Ferri, R. Sleep disorders and cancer: State of the art and future perspectives. Sleep Med. Rev. 2021, 56, 101409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soya, S.; Sakurai, T. Evolution of Orexin Neuropeptide System: Structure and Function. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicole, P.; Couvineau, P.; Jamin, N.; Voisin, T.; Couvineau, A. Crucial role of the orexin-B C-terminus in the induction of OX1 receptor-mediated apoptosis: Analysis by alanine scanning, molecular modelling and site-directed mutagenesis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 5211–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Tisdale, R.K.; Kilduff, T.S. Hypocretin/Orexin Receptor Pharmacology and Sleep Phases. Orexin Syst. Basic Sci. Role Sleep Pathol. 2021, 45, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muehlan, C.; Vaillant, C.; Zenklusen, I.; Kraehenbuehl, S.; Dingemanse, J. Clinical pharmacology, efficacy, and safety of orexin receptor antagonists for the treatment of insomnia disorders. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, C.D.; Breslin, M.J.; Whitman, D.B.; Schreier, J.D.; McGaughey, G.B.; Bogusky, M.J.; Roecker, A.J.; Mercer, S.P.; Bednar, R.A.; Lemaire, W.; et al. Discovery of the Dual Orexin Receptor Antagonist [(7R)-4-(5-Chloro-1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)-7-methyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl][5-methyl-2-(2H-1,2,3-triazol-2-yl)phenyl]methanone (MK-4305) for the Treatment of Insomnia. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5320–5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J. Lemborexant: First Approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvilliers, Y.; Zammit, G.; Fietze, I.; Mayleben, D.; Kinter, D.S.; Pain, S.; Hedner, J. Daridorexant, a New Dual Orexin Receptor Antagonist to Treat Insomnia Disorder. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Mobarec, J.C.; Kolb, P.; Rosenbaum, D.M. Crystal structure of the human OX2 orexin receptor bound to the insomnia drug suvorexant. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 519, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Babaoglu, K.; Brautigam, C.; Clark, L.; Shao, Z.; Scheuermann, T.H.; Harrell, C.M.; Gotter, A.L.; Roecker, A.J.; Winrow, C.; et al. Structure and ligand-binding mechanism of the human OX1 and OX2 orexin receptors. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, J.; Drabek, M.; Yin, J.; Gunera, J.; Pröll, T.; Kraus, F.; Langmead, C.J.; Hübner, H.; Weikert, D.; Kolb, P.; et al. Structure-based development of a subtype-selective orexin 1 receptor antagonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18059–18067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Byrne, N.J.; Zamlynny, B.; Tummala, S.; Xiao, L.; Shipman, J.M.; Partridge, A.T.; Minnick, C.; Breslin, M.J.; Rudd, M.T.; et al. Structures of active-state orexin receptor 2 rationalize peptide and small-molecule agonist recognition and receptor activation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G.; Bertotti, A.; Leto, S.M.; Vetrano, S. Patient-derived tumor models: A more suitable tool for pre-clinical studies in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerrito, M.; Grassilli, E. Identifying Novel Actionable Targets in Colon Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grothey, A.; Sargent, D.; Goldberg, R.M.; Schmoll, H.-J. Survival of Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancer Improves with the Availability of Fluorouracil-Leucovorin, Irinotecan, and Oxaliplatin in the Course of Treatment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Latif, M.; Townsend, K.; Dearman, C.; Shiu, K.-K.; Khan, K. Immunotherapy in gastrointestinal cancer: The current scenario and future perspectives. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 88, 102030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, S.; Khawer, M.; Rafique, S.; Naz, Z.; Saleem, K. The current status of anti-GPCR drugs against different cancers. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arang, N.; Gutkind, J.S. G Protein-Coupled receptors and heterotrimeric G proteins as cancer drivers. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 4201–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, T.; El Firar, A.; Rouyer-Fessard, C.; Gratio, V.; Laburthe, M. A hallmark of immunoreceptor, the tyrosine-based inhibitory motif ITIM, is present in the G protein-coupled receptor OX1R for orexins and drives apoptosis: A novel mechanism. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Firar, A.; Voisin, T.; Rouyer-Fessard, C.; Ostuni, M.A.; Couvineau, A.; Laburthe, M. Discovery of a functional immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif in a 7-transmembrane-spanning receptor: Role in the orexin receptor OX1R-driven apoptosis. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 4069–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laburthe, M.; Voisin, T.; El Firar, A. Orexins/hypocretins and orexin receptors in apoptosis: A mini-review. Acta Physiol. 2010, 198, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchene, J.; Schanstra, J.P.; Pecher, C.; Pizard, A.; Susini, C.; Esteve, J.-P.; Bascands, J.-L.; Girolami, J.-P. A Novel Protein-Protein Interaction between a G Protein-coupled Receptor and the Phosphatase SHP-2 Is Involved in Bradykinin-induced Inhibition of Cell Proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 40375–40383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferjoux, G.; Lopez, F.; Esteve, J.-P.; Ferrand, A.; Vivier, E.; Vely, F.; Saint-Laurent, N.; Pradayrol, L.; Buscail, L.; Susini, C. Critical Role of Src and SHP-2 in sst2 Somatostatin Receptor-mediated Activation of SHP-1 and Inhibition of Cell Proliferation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 3911–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vatinel, S.; Ferrand, A.; Lopez, F.; Kowalski-Chauvel, A.; Estève, J.-P.; Fourmy, D.; Dufresne, M.; Seva, C. An ITIM-like motif within the CCK2 receptor sequence required for interaction with SHP-2 and the activation of the AKT pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2006, 1763, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arihara, Z.; Takahashi, K.; Murakami, O.; Totsune, K.; Sone, M.; Satoh, F.; Ito, S.; Mouri, T. Immunoreactive orexin-A in human plasma. Peptides 2001, 22, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, S.; Nishijima, T.; Takahashi, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Arihara, Z.; Takahashi, K. Clinical Significance of Daytime Plasma Orexin-A-Like Immunoreactivity Concentrations in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Hypopnea Syndrome. Respiration 2004, 71, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.; Dudeja, V. The war against pancreatic cancer in 2020—advances on all fronts. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuzillet, C.; Tijeras-Raballand, A.; Bourget, P.; Cros, J.; Couvelard, A.; Sauvanet, A.; Vullierme, M.-P.; Tournigand, C.; Hammel, P. State of the art and future directions of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 155, 80–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherri, S.; Noventa, S.; Zaniboni, A. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Beyond first line, where are we? World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 1847–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting Cancer Incidence and Deaths to 2030: The Unexpected Burden of Thyroid, Liver, and Pancreas Cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singhi, A.D.; Wood, L.D. Early detection of pancreatic cancer using DNA-based molecular approaches. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visani, M.; Acquaviva, G.; De Leo, A.; Sanza, V.; Merlo, L.; Maloberti, T.; Brandes, A.A.; Franceschi, E.; Di Battista, M.; Masetti, M.; et al. Molecular alterations in pancreatic tumors. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 2710–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, C.; Xie, K.-P. Therapeutic resistance of pancreatic cancer: Roadmap to its reversal. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerg. 2021, 1875, 188461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayot, S.; Speisky, D.; Couvelard, A.; Bourgoin, P.; Gratio, V.; Cros, J.; Rebours, V.; Sauvanet, A.; Bedossa, P.; Paradis, V.; et al. In vitro, in vivo and ex vivo demonstration of the antitumoral role of hypocretin-1/orexin-A and almorexant in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 6952–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.H.; Shimano, T.; Chu, T.M. Differential Localization of Human Pancreas Cancer-Associated Antigen and Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Homologous Pancreatic Tumoral Xenograft23. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1981, 67, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slosky, L.M.; Caron, M.G.; Barak, L.S. Biased Allosteric Modulators: New Frontiers in GPCR Drug Discovery. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Guo, L. Effect of orexin A on apoptosis in BGC-823 gastric cancer cells via OX1R through the AKT signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 3439–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.; Yang, Z.; Feng, H.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y. A Combination of Species Identification and STR Profiling Identifies Cross-contaminated Cells from 482 Human Tumor Cell Lines. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, F.; Chen, C.; Qin, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, C. Genetic profiling reveals an alarming rate of cross-contamination among human cell lines used in China. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 4268–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rebello, R.J.; Oing, C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Loeb, S.; Johnson, D.C.; Reiter, R.E.; Gillessen, S.; Van der Kwast, T.; Bristow, R.G. Prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.H.; Sokolova, A.O.; Schaeffer, E.M.; Small, E.J.; Higano, C.S. Germline and Somatic Mutations in Prostate Cancer for the Clinician. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wengner, A.M.; Scholz, A.; Haendler, B. Targeting DNA Damage Response in Prostate and Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swami, U.; McFarland, T.R.; Nussenzveig, R.; Agarwal, N. Advanced Prostate Cancer: Treatment Advances and Future Directions. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, E.; Karachaliou, G.S.; Kao, C.; Harrison, M.R.; Hoimes, C.J.; George, D.J.; Armstrong, A.J.; Zhang, T. Novel therapies are changing treatment paradigms in metastatic prostate cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Fong, L. Immunotherapy for Prostate Cancer: Where Do We Go From Here?-PART 2: Checkpoint Inhibitors, Immunotherapy Combinations, Tumor Microenvironment Modulation, and Cellular Therapies. Oncology 2018, 32, e65–e73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fay, E.K.; Graff, J.N. Immunotherapy in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Z.-X.; Guo, D.-Y.; Tao, Y.-X. Regulation of prostate cancer by hormone-responsive G protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 191, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-F.; Fu, S.-Q.; Yan, Y.-C.; Gong, B.-B.; Xie, W.-J.; Yang, X.-R.; Sun, T.; Ma, M. Progress in Clinical Research on Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor Antagonists for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiante, S.; Liguori, G.; Tafuri, S.; Campese, R.; Monaco, R.; Paino, S.; Laforgia, V.; Staiano, N.; Vittoria, A. Expression of orexin A and its receptor 1 in the human prostate. J. Anat. 2013, 222, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiante, S.; Liguori, G.; Tafuri, S.; Pavone, L.M.; Campese, R.; Monaco, R.; Iachetta, G.; Assisi, L.; Mirabella, N.; Forte, M.; et al. Expression and potential role of the peptide orexin-A in prostate cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chartrel, N.; Anouar, Y.; Jeandel, L.; Alexandre, D.; Leprince, J.; Couvineau, A.; Voisin, T. Methods and Pharmaceutical Compositions Using Orexins (OXA, OXB) for the Treatment of Prostate Cancers. U.S. Patent Application, WO2016087889A1, 3 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kukkonen, J.P. Orexin/Hypocretin Signaling. Behav. Neurosci. Orexin/Hypocretin 2016, 33, 17–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediavilla, C. Bidirectional gut-brain communication: A role for orexin-A. Neurochem. Int. 2020, 141, 104882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehan, P.; Canon, C.; Trooskens, G.; Rehli, M.; Munaut, C.; Van Criekinge, W.; Delvenne, P. Expression of Type 2 Orexin Receptor in Human Endometrium and Its Epigenetic Silencing in Endometrial Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wenzel, J.; Grabinski, N.; Knopp, C.A.; Dendorfer, A.; Ramanjaneya, M.; Randeva, H.S.; Ehrhart-Bornstein, M.; Dominiak, P.; Joehren, O. Hypocretin/orexin increases the expression of steroidogenic enzymes in human adrenocortical NCI H295R cells. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 297, R1601–R1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzocchi, G.; Malendowicz, L.K.; Aragona, F.; Rebuffat, P.; Gottardo, L.; Nussdorfer, G.G. Human pheochromocytomas express orexin receptor type 2 gene and display an in vitro secretory response to orexins A and B. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4818–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogavero, M.; Silvani, A.; DelRosso, L.; Salemi, M.; Ferri, R. Focus on the Complex Interconnection between Cancer, Narcolepsy and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Possible Case of Orexin-Dependent Inverse Comorbidity. Cancers 2021, 13, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graybill, N.L.; Weissig, V. A review of orexin’s unprecedented potential as a novel, highly-specific treatment for various localized and metastatic cancers. SAGE Open Med. 2017, 5, 2050312117735774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alain, C.; Pascal, N.; Valérie, G.; Thierry, V. Orexins/Hypocretins and Cancer: A Neuropeptide as Emerging Target. Molecules 2021, 26, 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164849
Alain C, Pascal N, Valérie G, Thierry V. Orexins/Hypocretins and Cancer: A Neuropeptide as Emerging Target. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164849
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlain, Couvineau, Nicole Pascal, Gratio Valérie, and Voisin Thierry. 2021. "Orexins/Hypocretins and Cancer: A Neuropeptide as Emerging Target" Molecules 26, no. 16: 4849. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164849






