Antioxidant Activity of Deferasirox and Its Metal Complexes in Model Systems of Oxidative Damage: Comparison with Deferiprone
Abstract
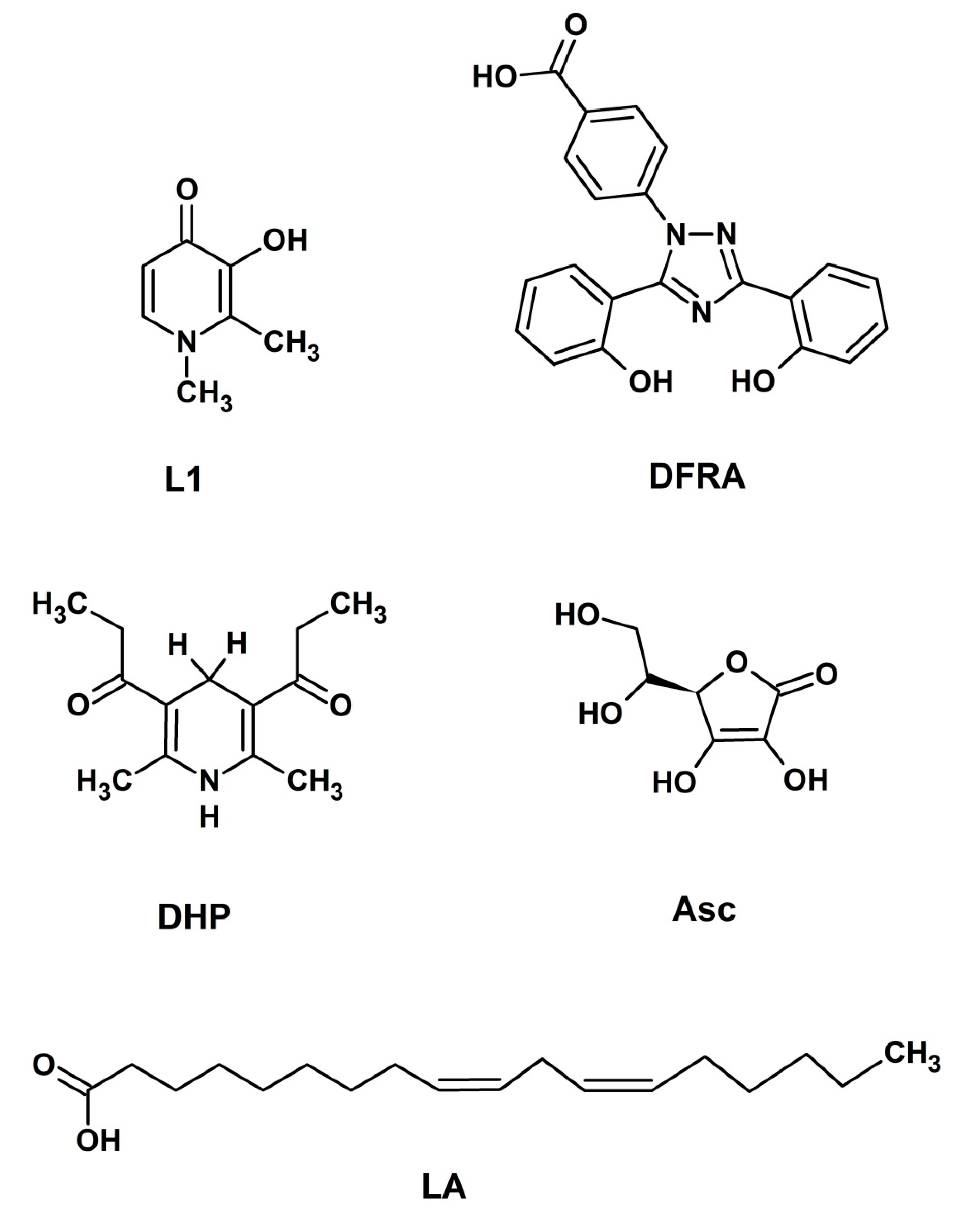
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. UV-Vis Spectroscopic Studies of the Influence of Deferasirox on the Oxidation of Ascorbic Acid by Iron and Copper Ions
2.2. NMR Studies of the Influence of Deferasirox and Deferiprone on Lipid Peroxidation of Linoleic Acid (LA) in the Presence of Iron and Copper Ions
2.3. NMR Studies of the Interaction of Deferasirox with Dihydropyridine
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. UV-Vis Optical Density Investigation of Ascorbic Acid Oxidation
4.2.2. The 1H-NMR Study of Lipid Peroxidation
4.2.3. The Study of Dihydropyridine Oxidation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| Asc | ascorbic acid |
| a.u. | arbitrary units |
| DFRA | deferasirox |
| DHP | dihydropyridine |
| H2O2 | hydrogen peroxide |
| LA | linoleic acid |
| L1 | deferiprone |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NADH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance |
| UV-Vis | ultraviolet-visible |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
References
- Weatherall, D.J.; Clegg, J.B. Inherited Haemoglobin Disorders: An Increasing Global Health Problem. Bull. World Health Organ. 2001, 79, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamoto, Y.; Lee, S.J. Late Effects of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica 2017, 102, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremers, E.M.P.; de Witte, T.; de Wreede, L.; Eikema, D.J.; Koster, L.; van Biezen, A.; Finke, J.; Socié, G.; Beelen, D.; Maertens, J.; et al. A Prospective Non-Interventional Study on the Impact of Transfusion Burden and Related Iron Toxicity on Outcome in Myelodysplastic Syndromes Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 2404–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurlo, M.G.; De Stefano, P.; Borgna-Pignatti, C.; Di Palma, A.; Melevendi, C.; Piga, A.; Di Gregorio, F.; Burattini, M.G.; Terzoli, S. Survival and Causes of Death in Thalassaemia Major. Lancet 1989, 2, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennell, D.J. T2* Magnetic Resonance and Myocardial Iron in Thalassemia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1054, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. How to Manage Iron Toxicity in Post-Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation? Expert Rev. Hematol. 2020, 13, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Chelation Protocols for the Elimination and Prevention of Iron Overload in Thalassaemia. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2018, 23, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Neocleous, K.; Kolnagou, A. Benefits and Risks of Deferiprone in Iron Overload in Thalassaemia and Other Conditions: Comparison of Epidemiological and Therapeutic Aspects with Deferoxamine. Drug Saf. 2003, 26, 553–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddaert, N.; Sang, K.H.L.Q.; Rötig, A.; Leroy-Willig, A.; Gallet, S.; Brunelle, F.; Sidi, D.; Thalabard, J.C.; Munnich, A.; Cabantchik, Z.I. Selective Iron Chelation in Friedreich Ataxia: Biologic and Clinical Implications. Blood 2007, 110, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin-Bastida, A.; Ward, R.J.; Newbould, R.; Piccini, P.; Sharp, D.; Kabba, C.; Patel, M.C.; Spino, M.; Connelly, J.; Tricta, F.; et al. Brain Iron Chelation by Deferiprone in a Phase 2 Randomised Double-Blinded Placebo Controlled Clinical Trial in Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzi, G.; Zibordi, F.; Chiapparini, L.; Bertini, E.; Russo, L.; Piga, A.; Longo, F.; Garavaglia, B.; Aquino, D.; Savoiardo, M.; et al. Iron-Related MRI Images in Patients with Pantothenate Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration (PKAN) Treated with Deferiprone: Results of a Phase II Pilot Trial. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1756–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.B.; Elalfy, M.S.; Taher, A.T.; Aydinok, Y.; Chan, L.L.; Lee, S.H.; Sutcharitchan, P.; Habr, D.; Martin, N.; El-Beshlawy, A. Efficacy and Safety of Deferasirox at Low and High Iron Burdens: Results from the EPIC Magnetic Resonance Imaging Substudy. Ann. Hematol. 2013, 92, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.; Eracleous, E.; Economides, C.; Kolnagou, A. Advances in Iron Overload Therapies. Prospects for Effective Use of Deferiprone (L1), Deferoxamine, the New Experimental Chelators ICL670, GT56-252, L1NAll and Their Combinations. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2663–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Efficacy and Safety of Iron-Chelation Therapy with Deferoxamine, Deferiprone, and Deferasirox for the Treatment of Iron-Loaded Patients with Non-Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia Syndromes. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baldari, S.; Di Rocco, G.; Toietta, G. Current Biomedical Use of Copper Chelation Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kontoghiorghe, C.N. Prospects for the Introduction of Targeted Antioxidant Drugs for the Prevention and Treatment of Diseases Related to Free Radical Pathology. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Advances on Chelation and Chelator Metal Complexes in Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Denisov, E.T.; Afanas’ev, I.B. Oxidation and Antioxidants in Organic Chemistry and Biology; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2005; ISBN 9780824753566. [Google Scholar]
- Korkina, L.G.; Afanas’Ev, I.B. Antioxidant and Chelating Properties of Flavonoids. Adv. Pharmacol. 1996, 38, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, S.; Mittal, M.; Mehta, A. Heavy Metal Induced Oxidative Stress & Its Possible Reversal by Chelation Therapy. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 501–523. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, A.S. Zinc: An Overview. Nutrition 1995, 11, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galaris, D.; Barbouti, A.; Pantopoulos, K. Iron Homeostasis and Oxidative Stress: An Intimate Relationship. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, E118535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eybl, V.; Caisová, D.; Koutenský, J.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Influence of Iron Chelators, 1,2-Dialkyl-3-Hydroxypyridin-4-Ones, on the Lipid Peroxidation and Glutathione Level in the Liver of Mice. Arch. Toxicol. Suppl. 1991, 14, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, P.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Characterization of the Neuroprotective Potential of Derivatives of the Iron Chelating Drug Deferiprone. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brar, S.; Henderson, D.; Schenck, J.; Zimmerman, E.A. Iron Accumulation in the Substantia Nigra of Patients with Alzheimer Disease and Parkinsonism. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallis, L.I.; Paley, M.N.J.; Graham, J.M.; Grünewald, R.A.; Wignall, E.L.; Joy, H.M.; Griffiths, P.D. MRI Assessment of Basal Ganglia Iron Deposition in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2008, 28, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapurkar, M.M.; Hegde, U.; Bhattacharya, A.; Alam, M.G.; Shah, S.V. Effect of Deferiprone, an Oral Iron Chelator, in Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Glomerular Disease. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2013, 23, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kolnagou, A.; Peng, C.T.; Shah, S.V.; Aessopos, A. Safety Issues of Iron Chelation Therapy in Patients with Normal Range Iron Stores Including Thalassaemia, Neurodegenerative, Renal and Infectious Diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2010, 9, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Jackson, M.J.; Lunec, J. In Vitro Screening of Iron Chelators Using Models of Free Radical Damage. Free Radic. Res. Commun. 1986, 2, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Prospects for Introducing Deferiprone as Potent Pharmaceutical Antioxidant. Front. Biosci. (Elite Ed.) 2009, 1, 161–178. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S.N.; Agarwal, S. Liposomes as Membrane Model for Study of Lipid Peroxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1988, 4, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, G.; Dunkley, W.L. Ascorbic Acid and Copper in Linoleate Oxidation. II. Ascorbic Acid and Copper as Oxidation Catalysts. J. Lipid Res. 1969, 10, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakır, T.; Sönmezoglu, İ.; Apak, R. Quantification of Antioxidant Ability against Lipid Peroxidation with an ‘Area under Curve’ Approach. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2017, 94, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterbauer, H. Estimation of Peroxidative Damage. A Critical Review. Pathol. Biol. 1996, 44, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell, B.; Chirico, S.; Crawford, M.A.; Bjerve, K.S.; Gey, K.F. Lipid Peroxidation: Its Mechanism, Measurement, and Significance. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1993, 57, 715S–725S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinchuk, I.; Lichtenberg, D. Analysis of the Kinetics of Lipid Peroxidation in Terms of Characteristic Time-Points. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2014, 178, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhauser, S.; Heinz, U.; Bartholomä, M.; Weyliermüller, T.; Nick, H.; Hegetschweiler, K. Complex Formation of ICL670 and Related Ligands with Fe III and Fe II. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 4177–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisponi, G.; Nurchi, V.M.; Crespo-Alonso, M.; Sanna, G.; Zoroddu, M.A.; Alberti, G.; Biesuz, R. A Speciation Study on the Perturbing Effects of Iron Chelators on the Homeostasis of Essential Metal Ions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Phytochelators Intended for Clinical Use in Iron Overload, Other Diseases of Iron Imbalance and Free Radical Pathology. Molecules 2015, 20, 20841–20872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Assessment Report: EXJADE International Non-Proprietary Name: Deferasirox; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Huang, X.; Ai, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L. Ascorbic Acid/Fe@Fe2O3: A Highly Efficient Combined Fenton Reagent to Remove Organic Contaminants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erdem, G.; Öner, C.; Önal, A.M.; Kisakürek, D.; Ögüs, A.Y. Free Radical Mediated Interaction of Ascorbic Acid and Ascorbate/Cu(II) with Viral and Plasmid DNAs. J. Biosci. 1994, 19, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martell, A.E. Chelates of Ascorbic Acid: Formation and Catalytic Properties. In Ascorbic Acid: Chemistry, Metabolism, and Uses; Advances in Chemistry Series; Seib, P.A., Tolbert, B.M., Eds.; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; pp. 153–178. ISBN 9780841206328. [Google Scholar]
- Bielski, B.H.J. Chemistry of Ascorbic Acid Radicals. In Ascorbic Acid: Chemistry, Metabolism, and Uses; Advances in Chemistry Series; Seib, P.A., Tolbert, B.M., Eds.; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1982; pp. 81–100. ISBN 9780841206328. [Google Scholar]
- Muneta, P.; Kaisaki, F. Ascorbic Acid-Ferrous Iron (Fe++)Complexes and after Cooking Darkening of Potatoes. Am. Potato J. 1985, 62, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, S.; Ohno, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Soma, G.I.; Inoue, M. High-Dose Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) Therapy in the Treatment of Patients with Advanced Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Cullen, J.J.; Buettner, G.R. Ascorbic Acid: Chemistry, Biology and the Treatment of Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2012, 1826, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kolnagou, A.; Kontoghiorghe, C.N.; Mourouzidis, L.; Timoshnikov, V.A.; Polyakov, N.E. Trying to Solve the Puzzle of the Interaction of Ascorbic Acid and Iron: Redox, Chelation and Therapeutic Implications. Medicines 2020, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, H.-S. Advances in NMR Spectroscopy for Lipid Oxidation Assessment; Springer Briefs in Food, Health, and Nutrition; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-54195-2. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshnikov, V.A.; Kobzeva, T.; Selyutina, O.Y.; Polyakov, N.E.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Effective Inhibition of Copper-Catalyzed Production of Hydroxyl Radicals by Deferiprone. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.F.; Budin, I.; Szostak, J.W. Preparation of Fatty Acid Micelles. Methods Enzymol. 2013, 533, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koppenol, W.H.; Hider, R.H. Iron and Redox Cycling. Do’s and Don’ts. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J.; Kontoghiorghe, C.N. Iron and Chelation in Biochemistry and Medicine: New Approaches to Controlling Iron Metabolism and Treating Related Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taraban, M.B.; Kruppa, A.I.; Polyakov, N.E.; Leshina, T.V.; Lūsis, V.; Muceniece, D.; Duburs, G. The Mechanisms of the Oxidation of NADH Analogues 1. Photochemical Oxidation of N-Unsubstituted 1,4-Dihydropyridines by Various Acceptors. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 1993, 73, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruppa, A.I.; Taraban, M.B.; Polyakov, N.E.; Leshina, T.V.; Lusis, V.; Muceniece, D.; Duburs, G. The Mechanisms of the Oxidation of NADH Analogues 2. N-Methyl-Substituted 1,4-Dihydropyridines. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 1993, 73, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshnikov, V.A.; Kobzeva, T.V.; Polyakov, N.E.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Redox Interactions of Vitamin c and Iron: Inhibition of the pro-Oxidant Activity by Deferiprone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polyakov, N.E.; Leshina, T.V.; Konovalova, T.A.; Kispert, L.D. Carotenoids as Scavengers of Free Radicals in a Fenton Reaction: Antioxidants or pro-Oxidants? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 31, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, P.; Uribe, D. Study of the Complexes of the Ascorbic Acid-Iron(III) System. Z. Naturforsch. Sect. J. Chem. Sci. 1982, 37, 1446–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zümreoglu-Karan, B. The Coordination Chemistry of Vitamin C: An Overview. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2006, 250, 2295–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keypour, H.; Silver, J.; Wilson, M.T.; Hamed, M.Y. Studies on the Reactions of Ferric Iron with Ascorbic Acid. A Study of Solution Chemistry Using Mössbauer Spectroscopy and Stopped-Flow Techniques. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1986, 125, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Toyoshima, Y.; Kurata, T. Identification of 3,4-Dihydroxy-2-Oxo-Butanal (L-Threosone) as an Intermediate Compound in Oxidative Degradation of Dehydro-L-Ascorbic Acid and 2,3-Diketo-L-Gulonic Acid in a Deuterium Oxide Phosphate Buffer. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, G.L.W.; Ortwerth, B.J. The Non-Oxidative Degradation of Ascorbic Acid at Physiological Conditions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2000, 1501, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pham, A.N.; Xing, G.; Miller, C.J.; Waite, T.D. Fenton-like Copper Redox Chemistry Revisited: Hydrogen Peroxide and Superoxide Mediation of Copper-Catalyzed Oxidant Production. J. Catal. 2013, 301, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Cao, W.; Jia, Y.; Lu, N. The Application of Ferroptosis in Diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.Y.; Dixon, S.J. Mechanisms of Ferroptosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2195–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoyanovsky, D.A.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Shrivastava, I.; Bahar, I.; Tyurin, V.A.; Protchenko, O.; Jadhav, S.; Bolevich, S.B.; Kozlov, A.V.; Vladimirov, Y.A.; et al. Iron Catalysis of Lipid Peroxidation in Ferroptosis: Regulated Enzymatic or Random Free Radical Reaction? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, S.; Canário, S.; Carrasco, M.P.; Mira, L.; Santos, M.A. Hydroxy(Thio)Pyrone and Hydroxy(Thio)Pyridinone Iron Chelators: Physico-Chemical Properties and Anti-Oxidant Activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 114, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, C.E.; Mcguire, W.P.; Liss, R.H.; Ifrim, I.; Grotzinger, K.; Young, R.C. Adriamycin: The Role of Lipid Peroxidation in Cardiac Toxicity and Tumor Response. Science 1977, 197, 165–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.; Berk, M.; Carvalho, A.F.; Maes, M.; Walker, A.J.; Puri, B.K. Why Should Neuroscientists Worry about Iron? The Emerging Role of Ferroptosis in the Pathophysiology of Neuroprogressive Diseases. Behav. Brain Res. 2018, 341, 154–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahdar, A.; Hajinezhad, M.R.; Sargazi, S.; Bilal, M.; Barani, M.; Karimi, P.; Kyzas, G.Z. Biochemical Effects of Deferasirox and Deferasirox-Loaded Nanomicellesin Iron-Intoxicated Rats. Life Sci. 2021, 270, 119146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenky, P.; Bogan, K.L.; Brenner, C. NAD+ Metabolism in Health and Disease. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, N.; Dölle, C.; Ziegler, M. The Power to Reduce: Pyridine Nucleotides—Small Molecules with a Multitude of Functions. Biochem. J. 2007, 402, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshnikov, V.A.; Kobzeva, T.V.; Polyakov, N.E.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Inhibition of Fe2+- and Fe3+- Induced Hydroxyl Radical Production by the Iron-Chelating Drug Deferiprone. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 78, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.M.; Spear, N.H.; Aust, S.D. Effects of Deferrioxamine on Iron-Catalyzed Lipid Peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1992, 295, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroh, A.; Zimmer, C.; Gutzeit, C.; Jakstadt, M.; Marschinke, F.; Jung, T.; Pilgrimm, H.; Grune, T. Iron Oxide Particles for Molecular Magnetic Resonance Imaging Cause Transient Oxidative Stress in Rat Macrophages. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, N.E.; Kruppa, A.I.; Leshina, T.V.; Lusis, V.; Muceniece, D.; Duburs, G. The Mechanism of Oxidation of NADH Analogues 4. Photooxidation of N-Acetyl-Substituted 1,4-Dihydropyridine in the Presence of Quinones. J. Photochem. Photobiol. Chem. 1997, 111, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Metal Ions | Concentration of Metal Ions, ×10−5 M | Concentration of DFRA, ×10−5 M | k, M−1 s−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3+ | 5 | 0 | 832 ± 1 |
| 5 | 5 | 7.6 ± 0.9 | |
| 5 | 10 | 7.0 ± 0.6 | |
| Cu2+ | 2 | 0 | 2808 ± 144 |
| 2 | 2 | 86 ± 1.0 | |
| 2 | 4 | 82 ± 2.25 |
| Effect of Iron Ions | Initiation Rate Constant, ×10−5 s−1 | Termination Rate Constant, ×10−5 s−1 |
|---|---|---|
| LA | 24.0 ± 1 | 17.0 ± 2 |
| LA + DFRA | 3.8 ± 0.5 | 3.5 ± 0.2 |
| LA + L1 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.03 |
| Effect of Copper Ions | ||
| LA | 10.0 ± 2 * | 4.2 ± 0.8 * |
| LA + DFRA | 3.0 ± 1 | 13.0 ± 5 |
| LA + L1 | 0.02 ± 0.01 * | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| After 15 h | After 2.5 Days | |
|---|---|---|
| DHP | <1% | 4% |
| DHP + Cu2+ | 57% | 84% |
| DHP + Cu2+ + DFRA | 9% | 14% |
| DHP + Fe3+ | 96% | >99% |
| DHP + Fe3+ + DFRA | 5% | 7% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Timoshnikov, V.A.; Kichigina, L.A.; Selyutina, O.Y.; Polyakov, N.E.; Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Antioxidant Activity of Deferasirox and Its Metal Complexes in Model Systems of Oxidative Damage: Comparison with Deferiprone. Molecules 2021, 26, 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165064
Timoshnikov VA, Kichigina LA, Selyutina OY, Polyakov NE, Kontoghiorghes GJ. Antioxidant Activity of Deferasirox and Its Metal Complexes in Model Systems of Oxidative Damage: Comparison with Deferiprone. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165064
Chicago/Turabian StyleTimoshnikov, Viktor A., Lilia A. Kichigina, Olga Yu. Selyutina, Nikolay E. Polyakov, and George J. Kontoghiorghes. 2021. "Antioxidant Activity of Deferasirox and Its Metal Complexes in Model Systems of Oxidative Damage: Comparison with Deferiprone" Molecules 26, no. 16: 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165064
APA StyleTimoshnikov, V. A., Kichigina, L. A., Selyutina, O. Y., Polyakov, N. E., & Kontoghiorghes, G. J. (2021). Antioxidant Activity of Deferasirox and Its Metal Complexes in Model Systems of Oxidative Damage: Comparison with Deferiprone. Molecules, 26(16), 5064. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165064









