Evaluation of the Saponin Content in Panax vietnamensis Acclimatized to Lam Dong Province by HPLC–UV/CAD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Assessing the Quantitative Performance of UV and CAD
2.2. The Change in Weight of Underground Parts of VG with Age
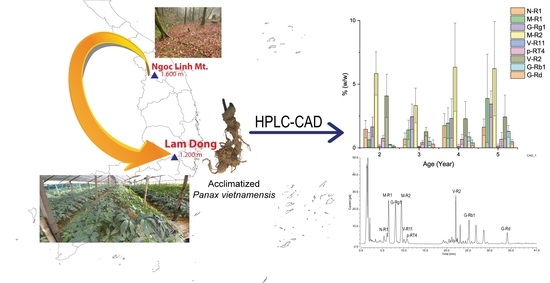
2.3. The Saponin Content of VG Main Roots at Different Ages
2.4. The Saponin Content of VG Rhizomes at Different Ages
2.5. The Saponin Accumulation Pattern in Various Parts of VG at Different Ages
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Sample and Standard Preparation
3.4. HPLC Analysis
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Duc, N.M.; Nham, N.T.; Kasai, R.; Ito, A.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. Collected in central Vietnam. I. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 2010–2014. [Google Scholar]
- Duc, N.M.; Nham, N.T.; Kasai, R.; Ito, A.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese Ginseng, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. Collected in central Vietnam. II. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Duc, N.M.; Nham, N.T.; Kasai, R.; Ito, A.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. collected in central Vietnam. III. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 634–640. [Google Scholar]
- Konoshima, T.; Takasaki, M.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H.; Duc, N.M.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Anti-tumor-promoting Activity of Majonoside-R2 from Veitnamese Ginseng, Panax vietnamensis HA et GRUSHV.(I). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 21, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huong, N.T.T.; Matsumoto, K.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K.; Watanabe, H. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity of Vietnamese Ginseng Saponin and Its Components. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 21, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yobimoto, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Huong, N.T.T.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K.; Watanabe, H. Suppressive effects of Vietnamese ginseng saponin and its major component majonoside-R2 on psychological stress-induced enhancement of lipid peroxidation in the mouse brain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2000, 66, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.T.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Duc, N.M.; Nham, N.T.; Watanabe, H.J.P.B.; Behavior. Majonoside-R2, a major constituent of Vietnamese ginseng, attenuates opioid-induced antinociception. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1997, 57, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.T.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Duc, N.M.; Nham, N.T.; Watanabe, H.J.P.B.; Behavior. Crude sponin extracted from Vietnamese ginseng and its major constituent majonoside-R2 attenuate the psychological stress-and foot-shock stress-induced antinociception in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1995, 52, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Huynh, K.L.; Le, T.H.V.; Nguyen, H.T.; Kim, H.M.; Kang, K.S.; Park, J.H.; Nguyen, M.D. Increase in protective effect of Panax vietnamensis by heat processing on cisplatin-induced kidney Cell Toxicity. Molecules 2019, 24, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.; Lee, J.; Vu-Huynh, K.L.; Van Le, T.H.; Tuoi Do, T.H.; Hwang, G.S.; Park, J.H.; Kang, K.S.; Nguyen, M.D.; Yamabe, N. Protective Effect of Panaxynol Isolated from Panax vietnamensis against Cisplatin-Induced Renal Damage: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minh Nguyen, H.; Truong Nguyen, H.; Win, N.; Piow Wong, C.; Vu Huynh, K.L.; Hoang, N.N.; Do, K.M.; Thi Nguyen, H.; Viet Ho, D.; Duc Nguyen, M.J.C.; et al. Antimelanogenic Activity of Ocotillol-Type Saponins from Panax vietnamensis. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e2000037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samukawa, K.; Yamashita, H.; Matsuda, H.; Kubo, M. Simultaneous analysis of ginsenosides of various Ginseng radix by HPLC. Yakugaku Zasshi J. Pharm. Soc. Jpn. 1995, 115, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wu, J.-A.; Osinski, J.; Yuan, C.-S. Determination of major ginsenosides in Panax quinquefolius (American ginseng) using high-performance liquid chromatography. Phytochem. Anal. 2005, 16, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L. Investigation of ginsenosides in different parts and ages of Panax ginseng. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.N.; Ha, Y.W.; Shin, H.; Son, S.H.; Wu, S.J.; Kim, Y.S. Simultaneous quantification of 14 ginsenosides in Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer (Korean red ginseng) by HPLC-ELSD and its application to quality control. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Balan, P.; Popovich, D.G. Ginsenosides analysis of New Zealand–grown forest Panax ginseng by LC-QTOF-MS/MS. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.-F.; Wang, Z.-L.; Dai, J.-G.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.-N. Determination of total ginsenosides in ginseng extracts using charged aerosol detection with post-column compensation of the gradient. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 12, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; In, G.; Han, S.T.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, K.T.; Cho, B.G.; Han, G.H.; Chang, I.M. Simultaneous determination of 30 ginsenosides in Panax ginseng preparations using ultra performance liquid chromatography. J. Ginseng. Res. 2013, 37, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vervoort, N.; Daemen, D.; Török, G. Performance evaluation of evaporative light scattering detection and charged aerosol detection in reversed phase liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1189, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Li, J.; Yunusova, N.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, J. A new application of Charged Aerosol Detection in liquid chromatography for the simultaneous determination of polar and less polar ginsenosides in Ginseng products. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 24, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Huynh, K.L.; Nguyen, H.T.; Van Le, T.H.; Ma, C.T.; Lee, G.J.; Kwon, S.W.; Park, J.H.; Nguyen, M.D. Accumulation of saponins in underground parts of Panax vietnamensis at different ages analyzed by HPLC-UV/ELSD. Molecules 2020, 25, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health. Vietnamese Pharmacopoeia V, Part 2; Medical Publishing House: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2017.






| Compounds | Calibration Curve | R2 | Range (mg/mL) | LOD (mg/mL) | LOQ (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV | |||||
| N-R1 | y = 31.0544x + 0.095 | 0.9997 | 0.008–0.53 | 0.0024 | 0.0073 |
| M-R1 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| G-Rg1 | y = 89.4402x + 0.2917 | 0.9999 | 0.019–1.24 | 0.0024 | 0.0073 |
| M-R2 | y = 1.4089x + −0.0086 | 0.9965 | 0.238–1.24 | 0.0312 | 0.0945 |
| V-R11 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| p-RT4 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| V-R2 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |
| G-Rb1 | y = 66.7414x + 0.1563 | 1.0000 | 0.015–0.98 | 0.0013 | 0.0041 |
| G-Rd | y = 71.789x + 0.2697 | 1.0000 | 0.21–1.36 | 0.0021 | 0.0065 |
| CAD | |||||
| N-R1 | log(y) = 0.8795 × log(x) + 0.8698 | 0.9983 | 0.008–0.53 | 0.0053 | 0.0159 |
| M-R1 | log(y) = 0.8053 × log(x) + 1.1228 | 0.9985 | 0.018–1.13 | 0.0092 | 0.0278 |
| G-Rg1 | log(y) = 0.8136 × log(x) + 1.1613 | 0.9981 | 0.019–1.24 | 0.0093 | 0.0281 |
| M-R2 | log(y) = 0.8565 × log(x) + 1.0409 | 0.9975 | 0.019–1.24 | 0.0076 | 0.0229 |
| V-R11 | log(y) = 0.8254 × log(x) + 1.3789 | 0.9961 | 0.010–0.67 | 0.0045 | 0.0138 |
| p-RT4 | log(y) = 0.8649 × log(x) + 1.0157 | 0.9970 | 0.018–1.13 | 0.0071 | 0.0214 |
| V-R2 | log(y) = 0.7981 × log(x) + 1.0384 | 0.9970 | 0.016–1.00 | 0.0064 | 0.0195 |
| G-Rb1 | log(y) = 0.8161 × log(x) + 1.2291 | 0.9983 | 0.015–0.98 | 0.0078 | 0.0236 |
| G-Rd | log(y) = 0.8165 × log(x) + 1.2531 | 0.9987 | 0.21–1.36 | 0.0079 | 0.0240 |
| Age | Saponin Content (% w/w) | Total Saponin Content | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-R1 | M-R1 | G-Rg1 | M-R2 | V-R11 | p-RT4 | V-R2 | G-Rb1 | G-Rd | ||
| 2 | 1.46 ± 0.69 | 0.63 ± 0.58 | 1.64 ± 0.78 | 5.84 ± 1.7 | 0.14 ± 0.14 | 0.75 ± 0.24 | 4.08 ± 1.7 | 0.24 ± 0.03 | 0.13 ± 0.09 | 14.92 ± 0.69 |
| 3 | 0.7 ± 0.47 | 1.41 ± 0.77 * | 2.44 ± 1 | 3.33 ± 1.36 | 0.09 ± 0.06 | 0.41 ± 0.15 | 1.27 ± 0.34 * | 0.51 ± 0.32 | 0.3 ± 0.33 | 10.46 ± 0.47 |
| 4 | 1.74 ± 0.94 | 1.94 ± 2.72 | 2.31 ± 1.54 | 6.34 ± 3.46 | 0.11 ± 0.17 | 0.67 ± 0.4 | 2.29 ± 1.35 | 0.86 ± 0.35 | 0.39 ± 0.23 | 16.65 ± 0.94 |
| 5 | 1.62 ± 0.64 | 3.88 ± 3.47 * | 3.44 ± 1.04 | 6.23 ± 3.71 | 0.14 ± 0.16 | 0.67 ± 0.54 | 2.43 ± 1.72 | 1.3 ± 0.47 * | 0.48 ± 0.19 * | 20.18 ± 0.64 |
| Age | Saponin Content (% w/w) | Total Saponin Content | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N-R1 | M-R1 | G-Rg1 | M-R2 | V-R11 | p-RT4 | V-R2 | G-Rb1 | G-Rd | ||
| 2 | 2.05 ± 0.98 | 1.01 ± 0.87 | 2.95 ± 1.3 | 8.76 ± 2.37 | 0.37 ± 0.35 | 1.32 ± 0.37 | 6.39 ± 2.42 | 0.36 ± 0.12 | 0.24 ± 0.09 | 23.44 ± 0.98 |
| 3 | 1.51 ± 0.62 | 2.57 ± 1.34 * | 4.68 ± 1.03 | 5.75 ± 1.03 | 0.21 ± 0.21 | 0.88 ± 0.13 | 2.66 ± 0.52 * | 0.89 ± 0.38 | 0.67 ± 0.75 | 19.82 ± 0.62 |
| 4 | 2.25 ± 1.04 | 2.58 ± 3.37 | 3.14 ± 1.69 | 8.88 ± 4.82 | 0.19 ± 0.22 | 1.21 ± 0.65 | 3.76 ± 2.06 | 1.12 ± 0.35 | 0.83 ± 0.22 | 23.94 ± 1.04 |
| 5 | 1.59 ± 0.51 | 4.22 ± 3.94 * | 3.84 ± 1.29 | 6.7 ± 3.17 | 0.17 ± 0.19 | 0.87 ± 0.41 | 2.82 ± 1.83 | 1.4 ± 0.3 * | 0.8 ± 0.52 * | 22.42 ± 0.51 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.T.; Vu-Huynh, K.L.; Nguyen, H.M.; Le, H.T.; Le, T.H.V.; Park, J.H.; Nguyen, M.D. Evaluation of the Saponin Content in Panax vietnamensis Acclimatized to Lam Dong Province by HPLC–UV/CAD. Molecules 2021, 26, 5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175373
Nguyen HT, Vu-Huynh KL, Nguyen HM, Le HT, Le THV, Park JH, Nguyen MD. Evaluation of the Saponin Content in Panax vietnamensis Acclimatized to Lam Dong Province by HPLC–UV/CAD. Molecules. 2021; 26(17):5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175373
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Huy Truong, Kim Long Vu-Huynh, Hien Minh Nguyen, Huong Thuy Le, Thi Hong Van Le, Jeong Hill Park, and Minh Duc Nguyen. 2021. "Evaluation of the Saponin Content in Panax vietnamensis Acclimatized to Lam Dong Province by HPLC–UV/CAD" Molecules 26, no. 17: 5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175373
APA StyleNguyen, H. T., Vu-Huynh, K. L., Nguyen, H. M., Le, H. T., Le, T. H. V., Park, J. H., & Nguyen, M. D. (2021). Evaluation of the Saponin Content in Panax vietnamensis Acclimatized to Lam Dong Province by HPLC–UV/CAD. Molecules, 26(17), 5373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175373