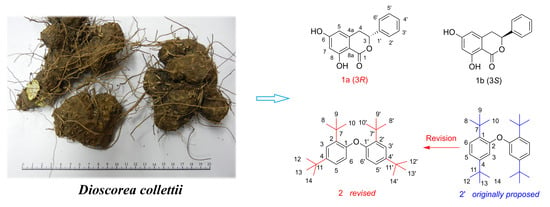
Dihydroisocoumarins and Dihydroisoflavones from the Rhizomes of Dioscorea collettii with Cytotoxic Activity and Structural Revision of 2,2′-Oxybis(1,4-di-tert-butylbenzene)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
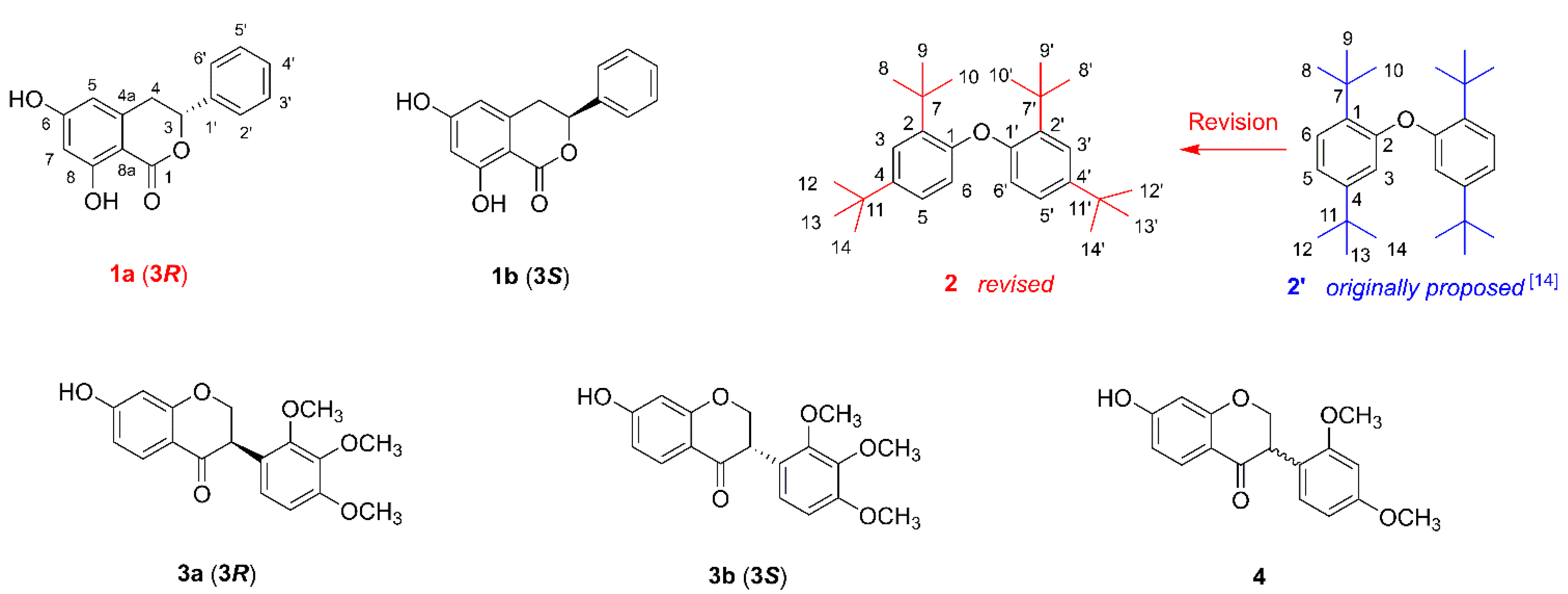
2.1. Structural Elucidation of the Compounds
2.2. Cytotoxic Activity against NCI-H460 Cell Line
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
3.2. Materials
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.3.1. (−)-Montroumarin (1a)
3.3.2. Montroumarin (1b)
3.3.3. 1,1′-Oxybis(2,4-di-tert-butylbenzene) (2)
3.3.4. (3R)-3′-O-Methylviolanone (3a)
3.3.5. (3S)-3′-O-Methylviolanone (3b)
3.3.6. (RS)-Sativanone (4)
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhu, L.; Dong, Y.; Na, S.; Han, R.; Wei, C.; Chen, G. Saponins extracted from Dioscorea collettii rhizomes regulate the expression of urate transporters in chronic hyperuricemia rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; He, X.; Wang, G.; Na, S.; Lv, L.; Chen, G. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of total saponin of Dioscorea. Chin. J. Clin. Pharm. Therap. 2020, 25, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Yao, X. Methyl protogracillin (NSC-698792): The spectrum of cytotoxicity against 60 human cancer cell lines in the National Cancer Institute’s anticancer drug screen panel. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2001, 12, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.-C.; Shen, T.-S.; Wu, C.-C.; Chang, I.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-P.; Cheng, C.-H.; Chen, C.-L. Methyl protodioscin induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells by caspase-dependent and MAPK signaling pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2670–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Sha, N.; Chen, G. Effect of total saponin of Dioscorea on NALP3 inflammasome signaling pathway with acute gouty in rats. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 2017, 33, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, Y. Steroidal sapogenins in Dioscorea collettii. Planta Med. 1983, 49, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Ge, S.; Li, B. Studies on the Constituents of Dioscorea Plants. II. Isolation and Identification of Steroidal Saponins from Dioscorea collettii Hook. F. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1983, 18, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.-S.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.-M.; Li, X.; Li, X.-J.; Zhao, C.-C.; Sun, J.-C.; Qiu, P.-Y.; Man, S.-L.; Gao, W.-Y. Diocollettines A, an unusual tricyclic diarylheptanoid derivative from the rhizomes of Dioscorea collettii. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 3215–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.-S.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.-J.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.-S.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, C.-C.; Huang, L.-Q.; Gao, W.-Y. Phytochemical and chemotaxonomic studies on Dioscorea collettii. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2017, 71, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qu, Z.; Jing, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Man, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W. Dioscin-6′-O-acetate inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation via inducing cell cycle arrest and caspase-dependent apoptosis. Phytomedicine 2019, 53, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, L.; Zheng, L.; Xu, L.; Yin, L.; Han, X.; Qi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Peng, J. Dioscin suppresses human laryngeal cancer cells growth via induction of cell-cycle arrest and MAPK-mediated mitochondrial-derived apoptosis and inhibition of tumor invasion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 774, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Jing, S.; Man, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W. A new acetylated spirostanol saponin and other constituents from the rhizomes of Dioscorea althaeoides R. Knuth (Dioscoreaceae). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2016, 65, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Jing, S.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Man, S.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W. Novel phenanthrene and isocoumarin from the rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica Makino subsp. rosthornii (Prain et Burkill) CT Ting (Dioscoreaceae). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3595–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.-N.; Shen, H.-D.; Wu, H.-X.; Cui, F.; Yao, L.-X.; Cheng, Z.-Q.; Diao, Y. Chemical Constituents of Onchidium struma from Chongming Island, Shanghai. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2014, 26, 987–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, C.; Mishina, Y.; Litaudon, M.; Cosson, J.-P.; Furukawa, H. Xanthone and dihydroisocoumarin from Montrouziera sphaeroidea. Phytochemistry 2000, 53, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraschos, S.; Magiatis, P.; Kalpoutzakis, E.; Harvala, C.; Skaltsounis, A.-L. Three New Dihydroisocoumarins from the Greek Endemic Species Scorzonera cretica. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1585–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-J.; Wang, Z.-B.; Zhu, D.-L.; Yu, Y.; Lei, Y.-T.; Liu, Y. Two new cyanogenic glucosides from the leaves of Hydrangea macrophylla. Molecules 2012, 17, 5396–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Xue, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Civelli, O.; Liang, X. Amide alkaloids from Scopolia tangutica. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perlatti, B.; Lan, N.; Earp, C.E.; AghaAmiri, S.; Vargas, S.H.; Azhdarinia, A.; Bills, G.F.; Gloer, J.B. Arenicolins: C-glycosylated depsides from Penicillium arenicola. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köck, M.; Lindel, T.; Junker, J. Incorporation of 4J-HMBC and NOE Data into Computer-Assisted Structure Elucidation with WEBCOCON. Molecules 2021, 26, 4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wang, P.; Lucardi, R.D.; Su, Z.; Li, S. Natural sources and bioactivities of 2, 4-di-tert-butylphenol and its analogs. Toxins 2020, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, C.; Gu, Q.; Fang, Y. Isolation and identification of a phenolic derivative from the ascidian. J. Ocean. Univ. Qingdao 1999, 29, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Huang, X.-l.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.-h.; Zhang, J. Chemical Constituents from Sauropus spatulifolius. Chin. Med. Mater. 2019, 7, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, I.d.S.; Gottlieb, O.R.; Andrade, C.S.; Magalhaes, M.T. Flavonoids from Dalbergia cearensis. Phytochemistry 1975, 14, 1452–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doran, R.; Carroll, M.P.; Akula, R.; Hogan, B.F.; Martins, M.; Fanning, S.; Guiry, P.J. A stereoselective switch: Enantiodivergent approach to the synthesis of isoflavanones. Chem.-Eur. J. 2014, 20, 15354–15359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Lee, J.W.; Jin, Q.; Jang, D.S.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, D.; Hong, J.T.; Kim, Y.; Lee, M.K.; Hwang, B.Y. Inhibitory constituents of the heartwood of Dalbergia odorifera on nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4263–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Mei, W.; Gong, M.; Zuo, W.; Bai, H.; Dai, H. Antibacterial activity of the flavonoids from Dalbergia odorifera on Ralstonia solanacearum. Molecules 2011, 16, 9775–9782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Umehara, K.; Nemoto, K.; Matsushita, A.; Terada, E.; Monthakantirat, O.; De-Eknamkul, W.; Miyase, T.; Warashina, T.; Degawa, M.; Noguchi, H. Flavonoids from the heartwood of the Thai medicinal plant Dalbergia parviflora and their effects on estrogenic-responsive human breast cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2163–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.-C.; Chang, Y.-S.; Wang, J.-P.; Chen, S.-C.; Kuo, S.-C. Three new flavonoids and antiallergic, anti-inflammatory constituents from the heartwood of Dalbergia odorifera. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Obidiegwu, J.E.; Lyons, J.B.; Chilaka, C.A. The Dioscorea Genus (Yam)—An appraisal of nutritional and therapeutic potentials. Foods 2020, 9, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sautour, M.; Mitaine-Offer, A.-C.; Lacaille-Dubois, M.-A. The Dioscorea genus: A review of bioactive steroid saponins. J. Nat. Med.-Tokyo 2007, 61, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
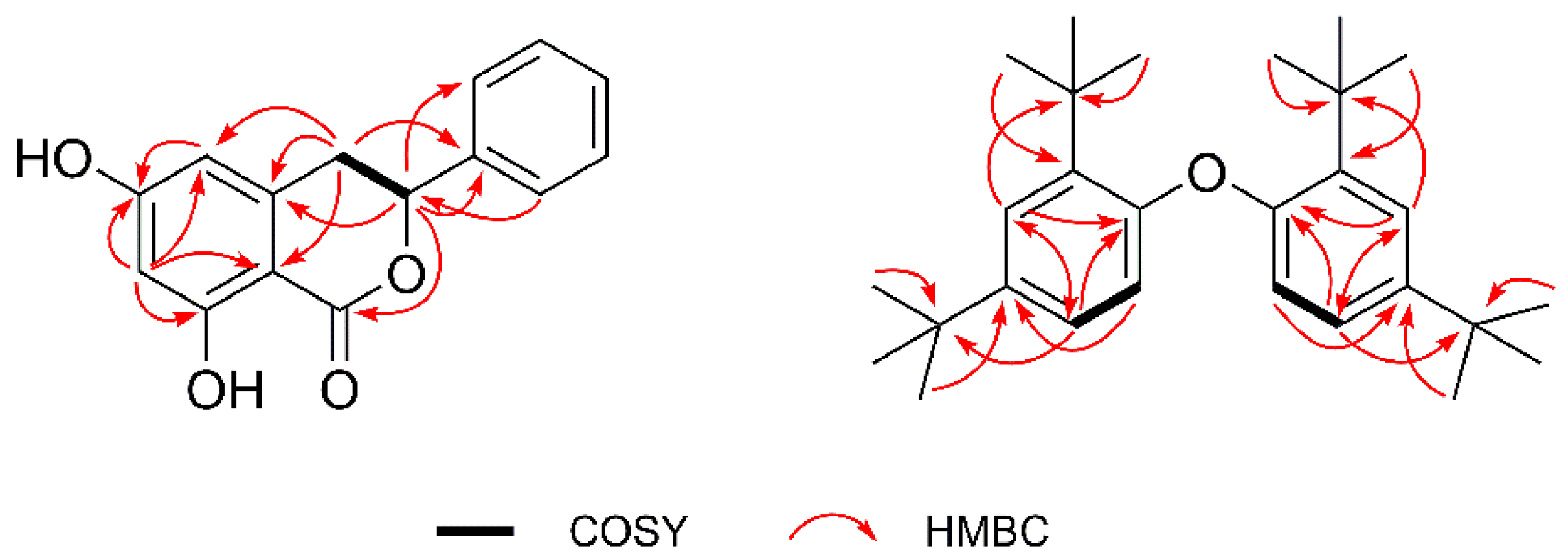

| No. | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δC | HMBC (H→C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 171.5, C | ||
| 3 | 5.56, dd (12.0, 3.0) | 81.8, CH | C-1, C-4, C-4a, C-1′, C-2′, C-6′ |
| 4 | 3.21, dd (16.3, 12.2) 3.06, dd (16.4, 3.2) | 36.0, CH2 | C-3, C-4a, C-5, C-8a, C-1′ |
| 4a | 143.4, C | ||
| 5 | 6.26, br s | 108.0, CH | C-4, C-6, C-7, C-8a |
| 6 | 166.4, C | ||
| 7 | 6.24, d (1.8) | 102.4, CH | C-5, C-6, C-8, C-8a |
| 8 | 165.7, C | ||
| 8a | 101.7, C | ||
| 1′ | 140.1, C | ||
| 2′, 6′ | 7.48, d (7.5) | 127.3, CH | C-3, C-3′, C-4′, C-5′ |
| 3′, 5′ | 7.41, t (7.5) | 129.7, CH | C-1′, C-3′, C-5′ |
| 4′ | 7.36, t (7.0) | 129.7, CH | C-2′, C-6′ |
| No. | δH, mult (J in Hz) | δC | HMBC (H→C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (1′) | 147.8 (147.8), C | ||
| 2 (2′) | 138.6 (138.7), C | ||
| 3 (3′) | 7.36, t (2.5) | 124.6, CH | C-7, C-11, C-5, C-1 (C-7′, C-11′, C-5′, C-1′) |
| 4 (4′) | 147.2, C | ||
| 5 (5′) | 7.13, dd (8.6, 2.5) | 124.1, CH | C-11, C-6, C-3, C-1 (C-11′, C-6′, C-3′, C-1′) |
| 6 (6′) | 7.54, d (8.6) | 119.3, CH | C-2, C-4 (C-2′, C-4′) |
| 7 (7′) | 35.0, C | ||
| 8/9/10 (8′/9′/10′) | 1.33, s | 30.4, CH3 | C-7, C-2 (C-7′, C-2′) |
| 11 (11′) | 34.7, C | ||
| 12/13/14 (12′/13′/14′) | 1.28, s | 31.6, CH3 | C-11, C-4 (C-11′, C-4′) |
| Sample | IC50 (μM) | Sample | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound 1a | 33.37 | Compound 1b | 32.06 |
| Compound 2 | >100 | Compound 3a | 57.83 |
| Compound 3b | 59.34 | Compound 4 | 64.01 |
| Cisplatin | 1.27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jing, S.; Qu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, W. Dihydroisocoumarins and Dihydroisoflavones from the Rhizomes of Dioscorea collettii with Cytotoxic Activity and Structural Revision of 2,2′-Oxybis(1,4-di-tert-butylbenzene). Molecules 2021, 26, 5381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175381
Jing S, Qu Z, Zhao C, Li X, Guo L, Liu Z, Zheng Y, Gao W. Dihydroisocoumarins and Dihydroisoflavones from the Rhizomes of Dioscorea collettii with Cytotoxic Activity and Structural Revision of 2,2′-Oxybis(1,4-di-tert-butylbenzene). Molecules. 2021; 26(17):5381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175381
Chicago/Turabian StyleJing, Songsong, Zhuo Qu, Chengcheng Zhao, Xia Li, Long Guo, Zhao Liu, Yuguang Zheng, and Wenyuan Gao. 2021. "Dihydroisocoumarins and Dihydroisoflavones from the Rhizomes of Dioscorea collettii with Cytotoxic Activity and Structural Revision of 2,2′-Oxybis(1,4-di-tert-butylbenzene)" Molecules 26, no. 17: 5381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175381
APA StyleJing, S., Qu, Z., Zhao, C., Li, X., Guo, L., Liu, Z., Zheng, Y., & Gao, W. (2021). Dihydroisocoumarins and Dihydroisoflavones from the Rhizomes of Dioscorea collettii with Cytotoxic Activity and Structural Revision of 2,2′-Oxybis(1,4-di-tert-butylbenzene). Molecules, 26(17), 5381. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175381