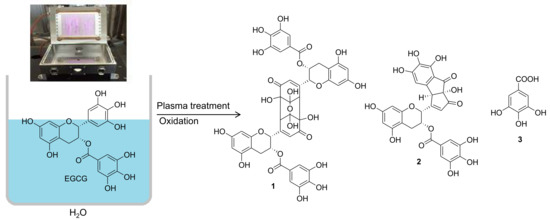
Plasma-Induced Oxidation Products of (–)-Epigallocatechin Gallate with Digestive Enzymes Inhibitory Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
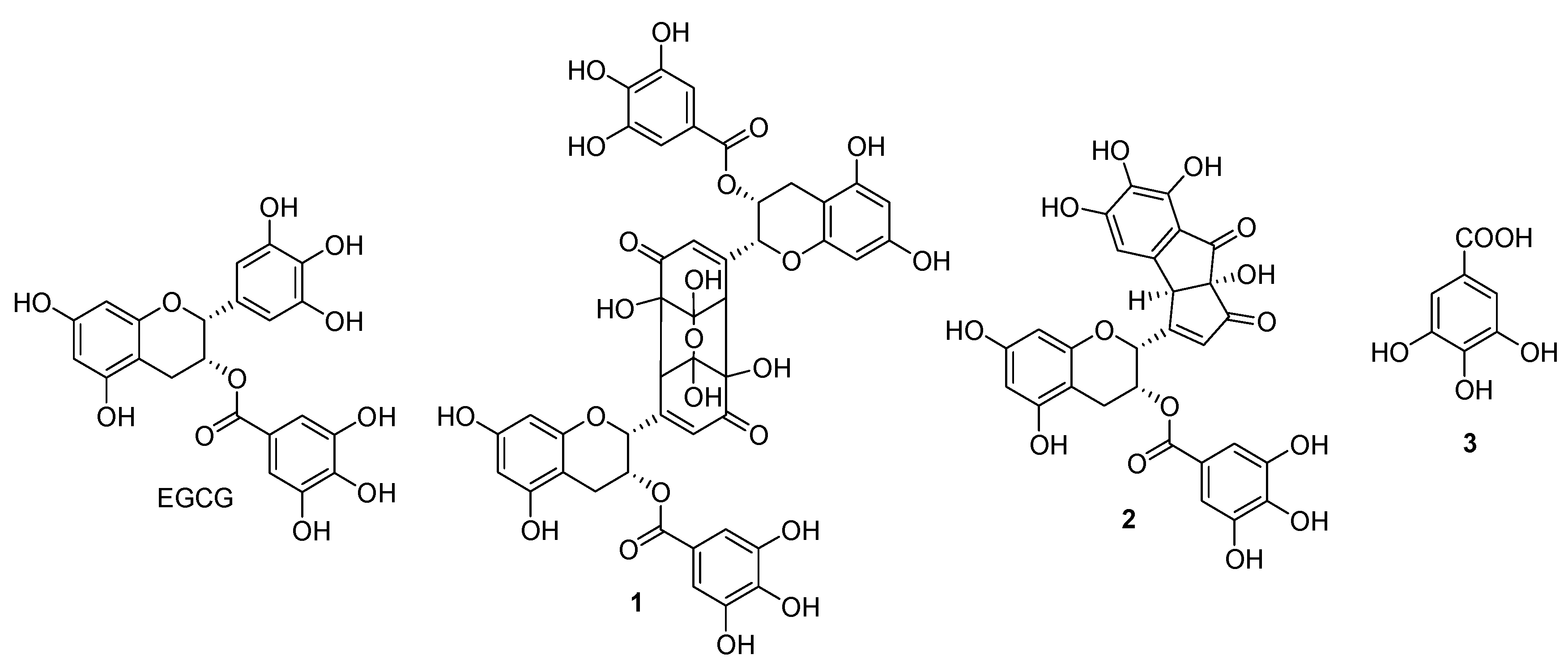
2.1. Characterization of Oxidation Products
2.2. Inhibitory Effects of α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase
2.3. Quantitative Analysis of Newly Generated Products
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Nonthermal Plasma Irradiation
3.3. Isolation of Oxidation Products
3.4. HPLC Analysis and Quantitation of Newly Generated Products
3.5. Inhibitory Effects of α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Mellitus, D. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, S5–S10. [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy, L.; Casas, J.P.; Hingorani, A.D.; Williams, D. Type 2 diabetes mellitus after gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2009, 373, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasson, J.L.; Josse, R.G.; Gomis, R.; Hanefeld, M.; Karasik, A.; Laakso, M.; STOP-NIDDM Trial Research Group. Acarbose for prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus: The STOP-NIDDM randomised trial. Lancet 2020, 359, 2072–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tundis, R.; Loizzo, M.R.; Menichini, F. Natural products as α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibitors and their hypoglycaemic potential in the treatment of diabetes: An update. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Liu, D.; Xiang, Q.; Ahn, J.; Chen, S.; Ye, X.; Ding, T. Inactivation mechanisms of non-thermal plasma on microbes: A review. Food Control. 2017, 75, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendero, C.; Tixier, C.; Tristant, P.; Desmaison, J.; Leprince, P. Atmospheric pressure plasmas: A review. Spectrochim. Acta B 2006, 61, 2–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, M.; Orange, N.; Feuilloley, M.G.J. Non-thermal plasma technologies: New tools for bio-decontamination. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, J.; Yong, H.I.; Yum, S.J.; Jeong, H.G.; Jo, C. Increase in nitrite content and functionality of ethanolic extracts of Perilla frutescens following treatment with atmospheric pressure plasma. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Han, I.; Baik, H.K.; Lee, M.H.; Han, D.W.; Park, J.C.; Lee, I.S.; Song, K.M.; Lim, Y.S. Analysis of sterilization effect by pulsed dielectric barrier discharge. J. Electrostat. 2006, 64, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Jeong, G.H.; Lee, K.B.; Jo, C.; Kim, T.H. A green chemical oligomerization of phloroglucinol induced by plasma as novel α-glucosidase inhibitors. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 2059–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.H.; Park, E.K.; Kim, T.H. Anti-diabetic effects of trans-resveratrol byproducts induced by plasma treatment. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.H.; Jeong, G.H.; Jeong, Y.H.; Kim, T.H. Identification of sesamol byproducts produced by plasma treatment with inhibition of advanced glycation end products formation and ONOO− scavenging activities. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.H.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, T.H. Plasma-induced dimerization of phloridzin as a new class of anti-adipogenic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4889–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ho, C.T.; Zhou, J.; Santos, J.S.; Armstrong, L.; Granato, D. Chemistry and biological activities of processed Camellia sinensis teas: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F. 2019, 18, 1474–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chakrawarti, L.; Agrawal, R.; Dang, S.; Gupta, S.; Gabrani, R. Therapeutic effects of EGCG: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Chen, P.; Ling, T.; Wang, Y.; Dong, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Han, M.; Wang, D.; Wan, X.; et al. Certain (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) auto-oxidation products (EAOPs) retain the cytotoxic activities of EGCG. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, H.; Okuda, K.; Kunihira, Y.; Inada, A.; Miyagi, C.; Matsuo, Y.; Saito, Y.; Tanaka, T. Oligomerization mechanism of tea catechins during tea roasting. Food Chem. 2019, 285, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfili, L.; Cuccioloni, M.; Mozzicafreddo, M.; Cecarini, V.; Angeletti, M.; Eleuteri, A.M. Identification of an EGCG oxidation derivative with proteasome modulatory activity. Biochimie 2011, 93, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcic, S.; Muders, A.; Jacobsen, N.E.; Liebler, D.C.; Timmermann, B.N. Antioxidant chemistry of green tea catechins. Identification of products of the reaction of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate with peroxyl radicals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 1999, 12, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Li, Y.; Watarumi, S.; Tanaka, T.; Kouno, I. Production and degradation mechanism of theacitrin C, a black tea pigment derived from epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate via a bicyclo [3.2.1] octane-type intermediate. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanwitheesuk, A.; Teerawutgulrag, A.; Kilburn, J.D.; Rakariyatham, N. Antimicrobial gallic acid from Caesalpinia mimosoides Lamk. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Kwon, C.S.; Son, K.H. Inhibition of alpha-glucosidase and amylase by luteolin, a flavonoid. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 2458–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justino, A.B.; Miranda, N.C.; Franco, R.R.; Martins, M.M.; da Silva, N.M.; Espindola, F.S. Annona muricata Linn. leaf as a source of antioxidant compounds with in vitro anti-diabetic and inhibitory potential against α-amylase, α-glucosidase, lipase, non-enzymatic glycation and lipid peroxidation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 100, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcic, S.; Burr, J.A.; Timmermann, B.N.; Liebler, D.C. Antioxidant chemistry of green tea catechins. New oxidation products of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate and (−)-epigallocatechin from their reactions with peroxyl radicals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2000, 13, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, Y.; Okuda, K.; Morikawa, H.; Oowatashi, R.; Saito, Y.; Tanaka, T. Stereochemistry of the black tea pigments theacitrins A and C. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Kouno, I. A novel black tea pigment and two new oxidation products of epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 7571–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Watarumi, S.; Matsuo, Y.; Kamei, M.; Kouno, I. Production of theasinensins A and D, epigallocatechin gallate dimers of black tea, by oxidation–reduction dismutation of dehydrotheasinensin A. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 7939–7947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankaj, S.K.; Wan, Z.; Keener, K.M. Effects of cold plasma on food quality: A review. Foods 2018, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.J.; Yong, H.I.; Park, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, T.H.; Choe, W.; Jo, C. Effect of atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge plasma on the biological activity of naringin. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.J.; Jo, C. Plasma-induced degradation of quercetin associated with the enhancement of biological activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6929–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Wang, M.H.; Rhee, H.I. A novel α-glucosidase inhibitor from pine bark. Carbohyd. Res. 2004, 339, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura-Konishi, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Saito, M.; Nakajima, N.; Sakaki, T.; Katayama, T.; Enomoto, T. Isolation of a new phlorotannin, a potent inhibitor of carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzymes, from the brown alga Sargassum patens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 5565–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| IC50 Value (μg/mL) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Plasma Irradiation Time (min) | α-Glucosidase | α-Amylase |
| 0 (control) | 44.5 ± 1.2 a | 34.5 ± 0.9 a |
| 20 | 40.5 ± 1.1 a | 29.5 ± 0.6 b |
| 40 | 28.6 ± 0.9 b | 19.2 ± 0.8 c |
| 60 | 20.1 ± 0.6 c | 16.5 ± 0.7 d |
| IC50 Value (μM) 1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compounds | α-Glucosidase | α-Amylase |
| EGCG | 97.2 ± 1.2 b | 75.5 ± 1.3 b |
| 1 | 15.9 ± 0.3 d | 18.7 ± 0.3 d |
| 2 | 20.7 ± 0.5 c | 25.3 ± 0.6 c |
| 3 | >300 a | >300 a |
| Acarbose 2 | 169.0 ± 1.8 a | 70.7 ± 1.4 b |
| Compounds | Absolute Content (mg/g) 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| tR (min) | 20 Min-Reactant | 40 Min-Reactant | 60 Min-Reactant | |
| EGCG | 15.6 | 730.9 ± 2.1 a | 465.3 ± 1.5 b | 345.7 ± 1.1 c |
| 1 | 15.0 | 126.0 ± 0.9 e | 266.7 ± 1.1 d | 321.8 ± 1.2 c |
| 2 | 16.2 | nd 2 | nd | 40.8 ± 0.2 f |
| 3 | 8.0 | nd | 65.7 ± 0.4 f | 101.5 ± 0.5 e |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, G.H.; Kim, T.H. Plasma-Induced Oxidation Products of (–)-Epigallocatechin Gallate with Digestive Enzymes Inhibitory Effects. Molecules 2021, 26, 5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26195799
Jeong GH, Kim TH. Plasma-Induced Oxidation Products of (–)-Epigallocatechin Gallate with Digestive Enzymes Inhibitory Effects. Molecules. 2021; 26(19):5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26195799
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Gyeong Han, and Tae Hoon Kim. 2021. "Plasma-Induced Oxidation Products of (–)-Epigallocatechin Gallate with Digestive Enzymes Inhibitory Effects" Molecules 26, no. 19: 5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26195799
APA StyleJeong, G. H., & Kim, T. H. (2021). Plasma-Induced Oxidation Products of (–)-Epigallocatechin Gallate with Digestive Enzymes Inhibitory Effects. Molecules, 26(19), 5799. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26195799