New 4-Aminoproline-Based Small Molecule Cyclopeptidomimetics as Potential Modulators of α4β1 Integrin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
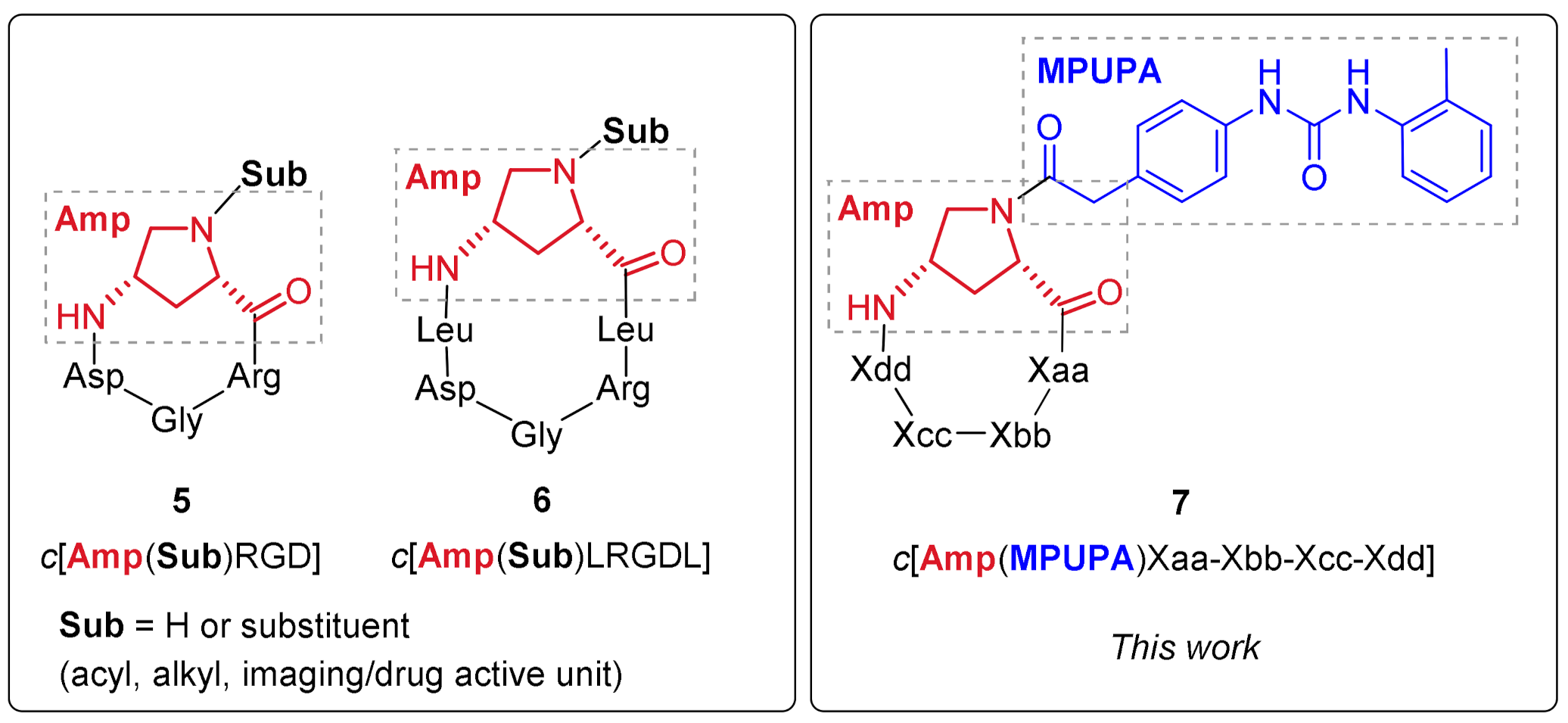
2.1. Design of Novel α4β1 Ligands
2.2. Synthesis of Novel α4β1 Ligands
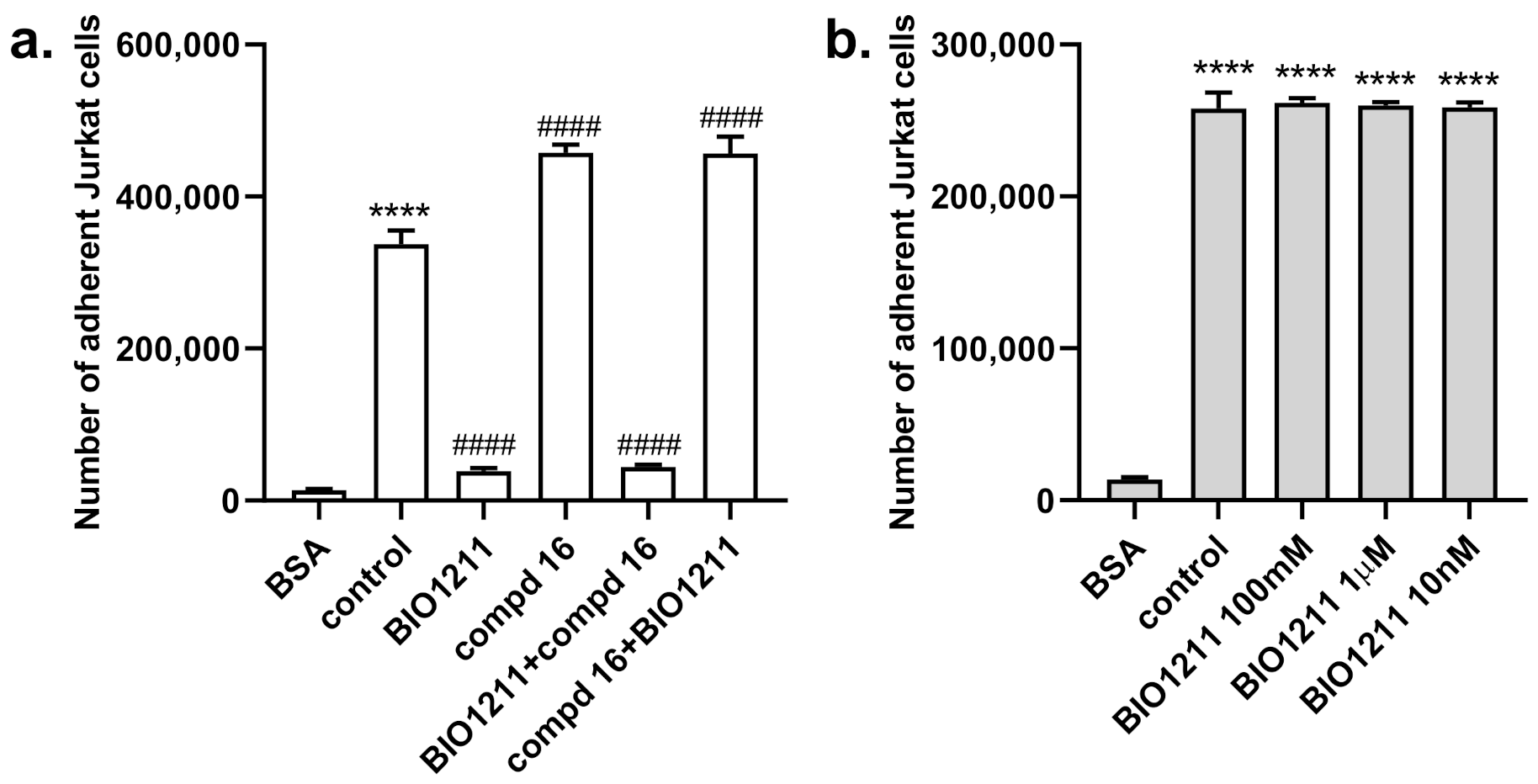
2.3. Biological Evaluation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
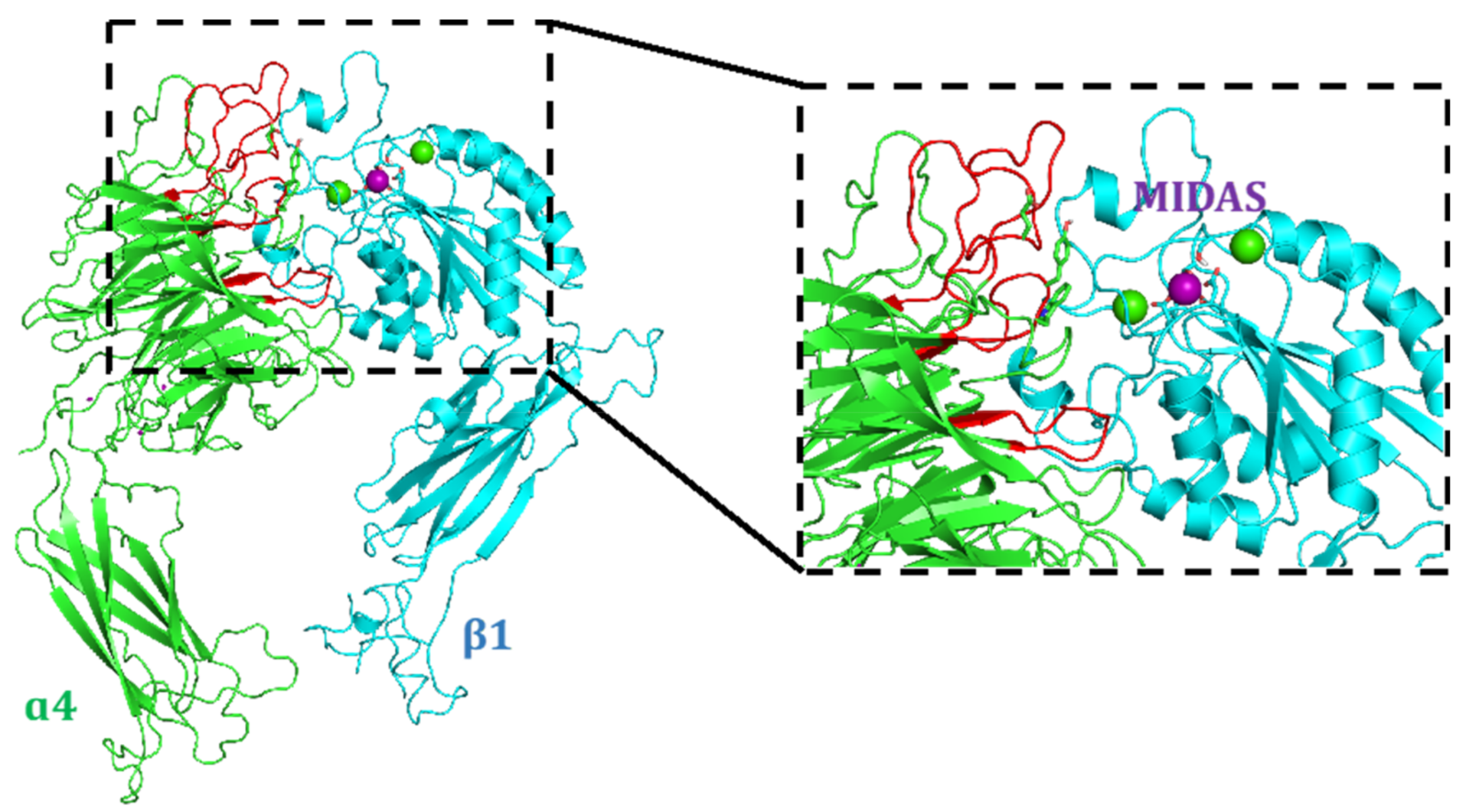
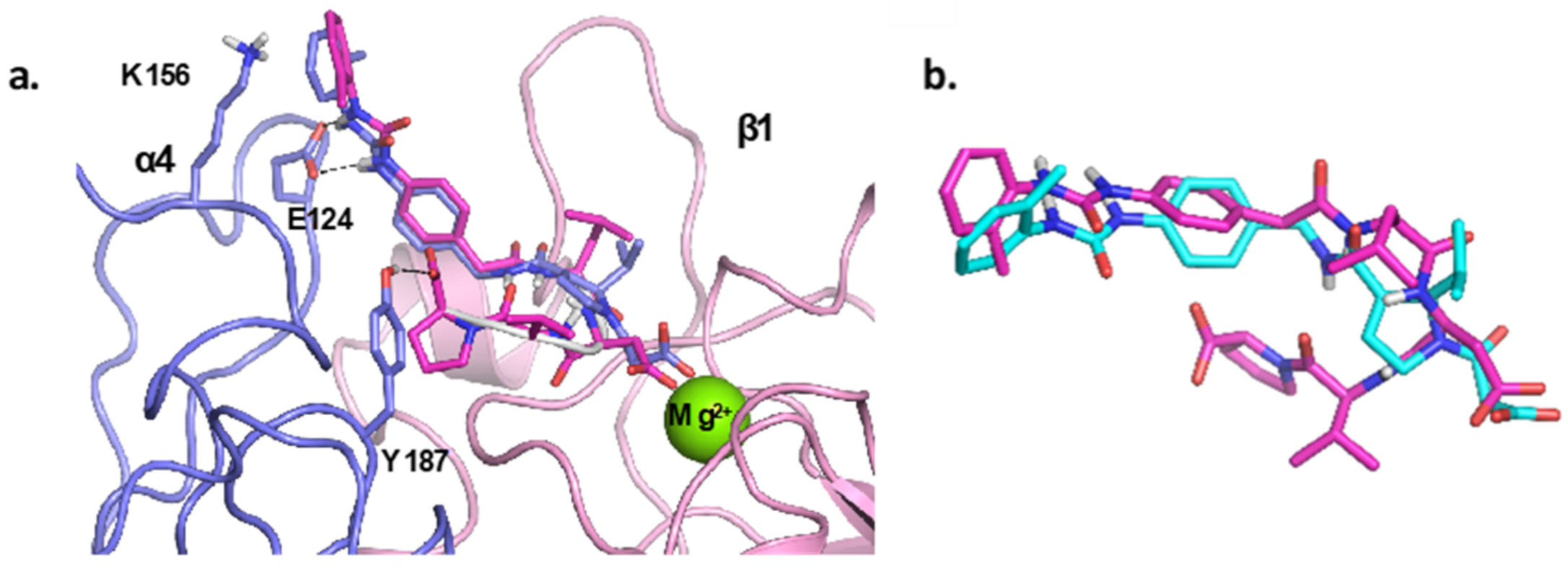
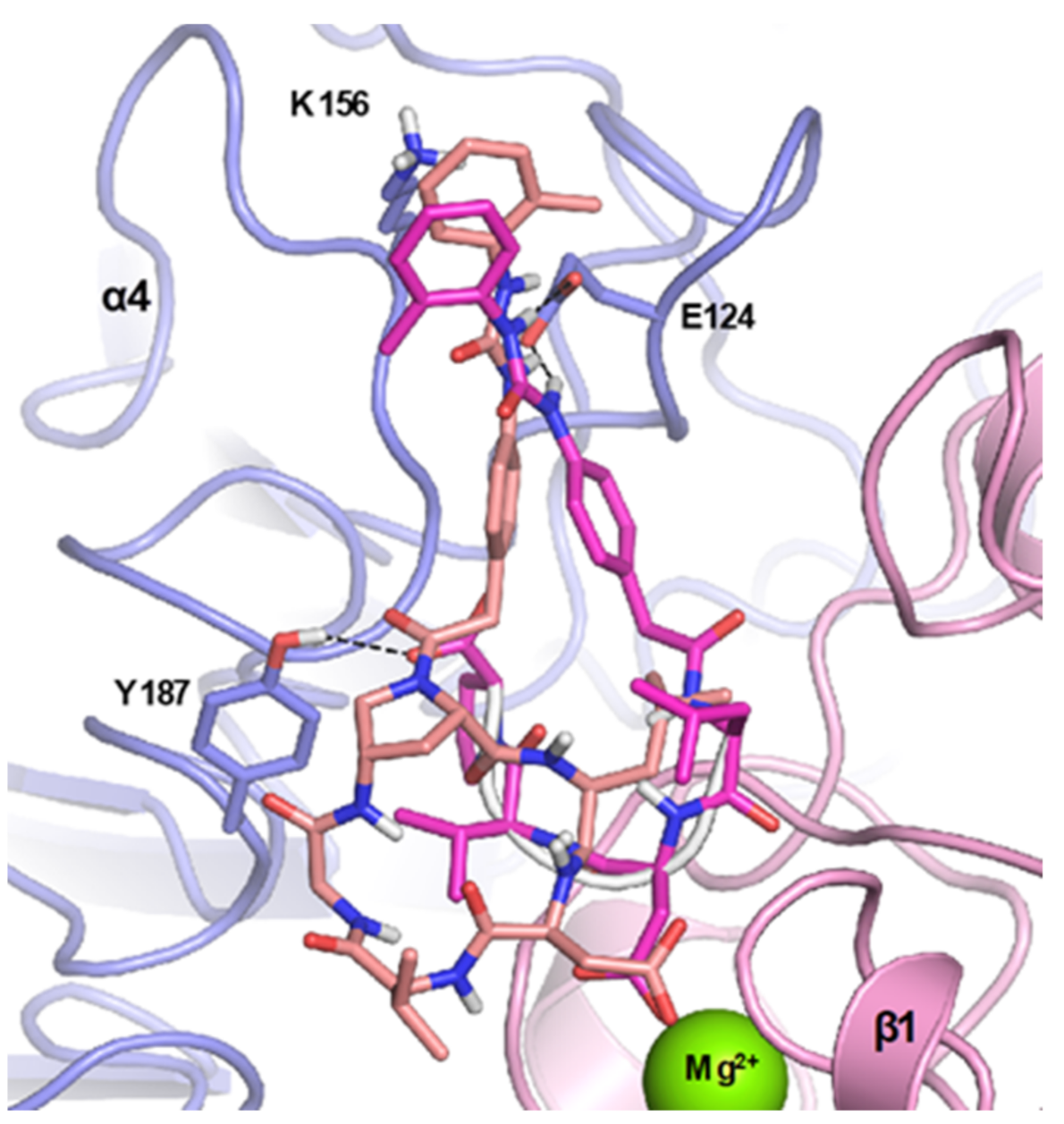
4.1. Docking Studies
4.1.1. Protein Setup
4.1.2. Ligand Docking Calculations
4.2. Chemistry
General Information
4.3. Experimental Synthetic Procedures and Characterization Data
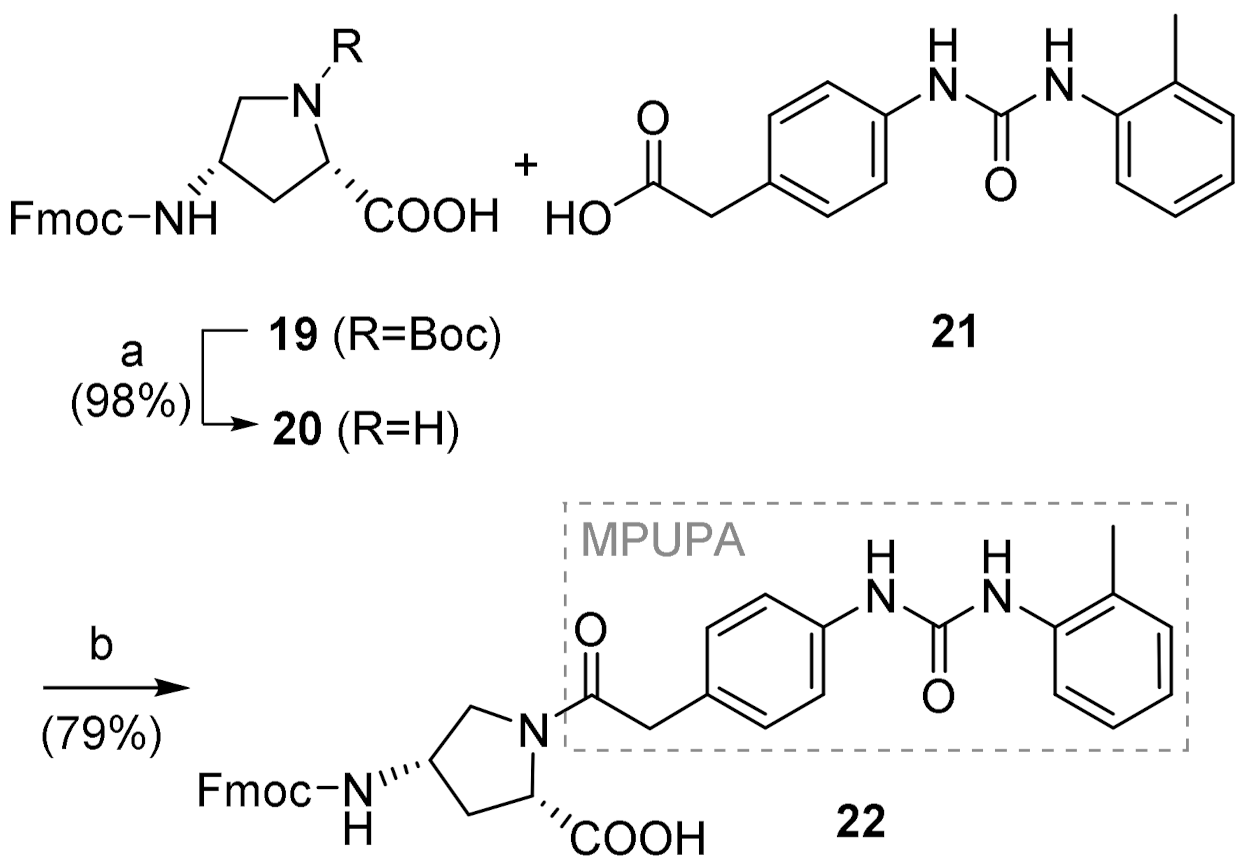
4.3.1. (2S,4S)-1-(MPUPA)-4-(Fmoc)aminoproline [Fmoc-(MPUPA)Amp-OH] (22)
4.3.2. General Procedure for Fmoc-Based SPPS
4.3.3. General Procedure for Cyclization Reaction
4.3.4. General Procedure for Deprotection Reaction
4.3.5. H-Val-1-(MPUPA)Amp-Leu-Asp(tBu)-OH (23)
4.3.6. H-Val-1-(MPUPA)Amp-Leu-Glu(tBu)-OH (24)
4.3.7. H-Val-Gly-1-(MPUPA)Amp-Leu-Asp(tBu)-OH (25)
4.3.8. H-Val-Gly-1-(MPUPA)Amp-Leu-Glu(tBu)-OH (26)
4.3.9. H-Leu-1-(MPUPA)Amp-Val-Asp(tBu)-OH (27)
4.3.10. H-Leu-1-(MPUPA)Amp-Val-Glu(tBu)-OH (28)
4.3.11. H-Asp(tBu)-1-(MPUPA)Amp-Arg(Pmc)-Gly-OH (29)
4.3.12. c[(MPUPA)Amp-Leu-Asp-Val-Gly] (12)
4.3.13. c[(MPUPA)Amp-Leu-Glu-Val-Gly] (13)
4.3.14. c[(MPUPA)Amp-Leu-Asp-Val] (14)
4.3.15. c[(MPUPA)Amp-Leu-Glu-Val] (15)
4.3.16. c[(MPUPA)Amp-Val-Asp-Leu] (16)
4.3.17. c[(MPUPA)Amp-Val-Glu-Leu] (17)
4.3.18. c[(MPUPA)Amp-Arg-Gly-Asp] (18)
4.4. Biology
4.4.1. Cell Culture
4.4.2. Cell Adhesion Assays
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnaout, M.A.; Goodman, S.L.; Xiong, J.P. Structure and mechanics of integrin-based cell adhesion. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cox, D.; Brennan, M.; Moran, N. Integrins as therapeutic targets: Lessons and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 804–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, K.; Rivera-Nieves, J.; Sandborn, W.J.; Shattil, S. Integrin-based therapeutics: Biological basis, clinical use and new drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamidi, H.; Pietilä, M.; Ivaska, J. The complexity of integrins in cancer and new scopes for therapeutic targeting. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abram, C.L.; Lowell, C.A. The ins and outs of leukocyte integrin signaling. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Deng, H.; et al. Platelet integrin αIIbβ3: Signal transduction, regulation, and its therapeutic targeting. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanderslice, P.; Woodside, D.G. Integrin antagonists as therapeutics for inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2006, 15, 1235–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, S.J.; Moran, N. Cell adhesion molecules: Therapeutic targets for inhibition of inflammatory states. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2015, 41, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiula, M.; Spampinato, S.; Gentilucci, L.; Tolomelli, A. Novel ligands targeting α4β1 integrin: Therapeutic applications and perspectives. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Bryant, R.V.; Travis, S. Interfering with leukocyte trafficking in Crohn’s disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 38, 101617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herter, J.; Zarbock, A. Integrin regulation during leukocyte recruitment. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4451–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dattoli, S.D.; Baiula, M.; de Marco, R.; Bedini, A.; Anselmi, M.; Gentilucci, L.; Spampinato, S. DS-70, a novel and potent α4 integrin antagonist, is an effective treatment for experimental allergic conjunctivitis in guinea pigs. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 3891–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murata, M. Inflammation and cancer. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2018, 23, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Avraamides, C.J.; Garmy-Susini, B.; Varner, J.A. Integrins in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuphal, S.; Bauer, R.; Bosserhoff, A.-K. Integrin signaling in malignant melanoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2005, 24, 195–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemke, M.; Weschenfelder, T.; Konstandin, M.H.; Samstag, Y. High affinity interaction of integrin α4β1 (VLA-4) and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) enhances migration of human melanoma cells across activated endothelial cell layers. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 212, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderslice, P.; Biediger, R.J.; Woodside, D.G.; Brown, W.S.; Khounlo, S.; Warier, N.D.; Gundlach, C.W.; Caivano, A.R.; Bornmann, W.G.; Maxwell, D.S.; et al. Small molecule agonist of very late antigen-4 (VLA-4) integrin induces progenitor cell adhesion. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19414–19428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komoriya, A.; Green, L.; Mervic, M.; Yamada, S.; Yamada, K.; Humphries, M. The minimal essential sequence for a major cell type-specific adhesion site (CS1) within the alternatively spliced type III connecting segment domain of fibronectin is leucine-aspartic acid-valine. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 15075–15079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Pepinsky, R.B.; Stehle, T.; Liu, J.H.; Karpusas, M.; Browning, B.; Osborn, L. The crystal structure of an N-terminal two-domain fragment of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1): A cyclic peptide based on the domain 1 C-D loop can inhibit VCAM-1-alpha 4 integrin interaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5714–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, D.Y. Alpha 4 Integrin Antagonists. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2002, 8, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-C.; Ateeq, H.S.; Hsiung, S.H.; Chong, L.T.; Zimmerman, C.N.; Castro, A.; Lee, W.-C.; Hammond, C.E.; Kalkunte, S.; Chen, L.-L.; et al. Selective, tight-binding inhibitors of integrin α4β1 that inhibit allergic airway responses. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 920–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.-C.; Castro, A.C. Very late antigen 4 (VLA4) antagonists as anti-inflammatory agents. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1998, 2, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Liu, R.; Marik, J.; Wang, X.; Takada, Y.; Lam, K.S. Combinatorial chemistry identifies high-affinity peptidomimetics against α4β1 integrin for in vivo tumor imaging. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.; Li, Y.; Roxin, Á.; Schaffer, P.; Adam, M.J.; Perrin, D.M. Facile synthesis and 18 F-radiolabeling of α 4 β 1 -specific LLP2A-aryltrifluoroborate peptidomimetic conjugates. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5126–5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaino, W.; Anderson, C.J. PET Imaging of very late antigen-4 in melanoma: Comparison of 68Ga- and 64Cu-labeled NODAGA and CB-TE1A1P-LLP2A conjugates. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, D.; Ma, B.; He, C.; Liu, R.; Farmer, D.; Lam, K.S.; Wang, A. Surface modification of polymeric electrospun scaffolds via a potent and high-affinity integrin α4β1 ligand improved the adhesion, spreading and survival of human chorionic villus-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A new insight for fetal tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, R.; Tolomelli, A.; Juaristi, E.; Gentilucci, L. Integrin ligands with α/β-hybrid peptide structure: Design, bioactivity, and conformational aspects. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 389–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderslice, P.; Woodside, D.G.; Caivano, A.R.; Decker, E.R.; Munsch, C.L.; Sherwood, S.J.; LeJeune, W.S.; Miyamoto, Y.J.; McIntyre, B.W.; Tilton, R.G.; et al. Potent in vivo suppression of inflammation by selectively targeting the high affinity conformation of integrin α4β1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 400, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardi, F.; Burreddu, P.; Rassu, G.; Auzzas, L.; Battistini, L.; Curti, C.; Sartori, A.; Nicastro, G.; Menchi, G.; Cini, N.; et al. Discovery of subnanomolar arginine-glycine-aspartate-based αVβ3/αVβ5 integrin binders embedding 4-aminoproline residues. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battistini, L.; Burreddu, P.; Carta, P.; Rassu, G.; Auzzas, L.; Curti, C.; Zanardi, F.; Manzoni, L.; Araldi, E.M.V.; Scolastico, C.; et al. 4-Aminoproline-based arginine-glycine-aspartate integrin binders with exposed ligation points: Practical in-solution synthesis, conjugation and binding affinity evaluation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugatti, K.; Bruno, A.; Arosio, D.; Sartori, A.; Curti, C.; Augustijn, L.; Zanardi, F.; Battistini, L. Shifting towards α V β 6 integrin ligands using novel aminoproline-based cyclic peptidomimetics. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 13468–13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, V.; Bianchini, F.; Portioli, E.; Peppicelli, S.; Lulli, M.; Bani, D.; Del Sole, R.; Zanardi, F.; Sartori, A.; Fiammengo, R. Gold nanoparticles functionalized with RGD-semipeptides: A simple yet highly effective targeting system for αVβ3 integrins. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 12093–12100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilkington-Miksa, M.; Arosio, D.; Battistini, L.; Belvisi, L.; De Matteo, M.; Vasile, F.; Burreddu, P.; Carta, P.; Rassu, G.; Perego, P.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel cRGD–paclitaxel conjugates for integrin-assisted drug delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battistini, L.; Burreddu, P.; Sartori, A.; Arosio, D.; Manzoni, L.; Paduano, L.; D’Errico, G.; Sala, R.; Reia, L.; Bonomini, S.; et al. Enhancement of the uptake and cytotoxic activity of doxorubicin in cancer cells by novel cRGD-semipeptide-anchoring liposomes. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2280–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, A.; Bianchini, F.; Migliari, S.; Burreddu, P.; Curti, C.; Vacondio, F.; Arosio, D.; Ruffini, L.; Rassu, G.; Calorini, L.; et al. Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of a novel, selective 111In-labelled aminoproline-RGD-peptide for non-invasive melanoma tumor imaging. MedChemComm 2015, 6, 2175–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, A.; Portioli, E.; Battistini, L.; Calorini, L.; Pupi, A.; Vacondio, F.; Arosio, D.; Bianchini, F.; Zanardi, F. Synthesis of novel c(AmpRGD)–sunitinib dual conjugates as molecular tools targeting the αvβ3 integrin/VEGFR2 couple and impairing tumor-associated angiogenesis. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, F.; Portioli, E.; Ferlenghi, F.; Vacondio, F.; Andreucci, E.; Biagioni, A.; Ruzzolini, J.; Peppicelli, S.; Lulli, M.; Calorini, L.; et al. Cell-targeted c(AmpRGD)-sunitinib molecular conjugates impair tumor growth of melanoma. Cancer Lett. 2019, 446, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, A.; Corno, C.; De Cesare, M.; Scanziani, E.; Minoli, L.; Battistini, L.; Zanardi, F.; Perego, P. Efficacy of a selective binder of αVβ3 Integrin linked to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor sunitinib in ovarian carcinoma preclinical models. Cancers 2019, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchini, F.; De Santis, A.; Portioli, E.; Krauss, I.R.; Battistini, L.; Curti, C.; Peppicelli, S.; Calorini, L.; D’Errico, G.; Zanardi, F.; et al. Integrin-targeted AmpRGD sunitinib liposomes as integrated antiangiogenic tools. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 18, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capuano, A.; Fogolari, F.; Bucciotti, F.; Spessotto, P.; Nicolosi, P.A.; Mucignat, M.T.; Cervi, M.; Esposito, G.; Colombatti, A.; Doliana, R. The α4β1/EMILIN1 interaction discloses a novel and unique integrin-ligand type of engagement. Matrix Biol. 2018, 66, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Mi, L.-Z.; Walz, T.; Sun, H.; Chen, J.; Springer, T.A. Structural specializations of α4β7, an integrin that mediates rolling adhesion. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagae, M.; Re, S.; Mihara, E.; Nogi, T.; Sugita, Y.; Takagi, J. Crystal structure of α5β1 integrin ectodomain: Atomic details of the fibronectin receptor. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 197, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, D.Y.; Quan, C.; Artis, D.R.; Rawson, T.; Blackburn, B.; Struble, M.; Fitzgerald, G.; Chan, K.; Mullins, S.; Burnier, J.P.; et al. Potent α4β1 peptide antagonists as potential anti-inflammatory agents. J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 3359–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotouhi, N.; Joshi, P.; Tilley, J.W.; Rowan, K.; Schwinge, V.; Wolitzky, B. Cyclic thioether peptide mimetics as VCAM–VLA-4 antagonists. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 1167–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolomelli, A.; Baiula, M.; Viola, A.; Ferrazzano, L.; Gentilucci, L.; Dattoli, S.D.; Spampinato, S.; Juaristi, E.; Escudero, M. Dehydro-β-proline Containing α4β1 Integrin Antagonists: Stereochemical recognition in ligand–receptor interplay. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irie, A.; Kamata, T.; Puzon-McLaughlin, W.; Takada, Y. Critical amino acid residues for ligand binding are clustered in a predicted β-turn of the third N-terminal repeat in the integrin alpha 4 and alpha 5 subunits. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 5550–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasem, A.R.; Bucolo, C.; Baiula, M.; Spartà, A.; Govoni, P.; Bedini, A.; Fascì, D.; Spampinato, S. Contribution of α4β1 integrin to the antiallergic effect of levocabastine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiula, M.; Galletti, P.; Martelli, G.; Soldati, R.; Belvisi, L.; Civera, M.; Dattoli, S.D.; Spampinato, S.M.; Giacomini, D. New β-lactam derivatives modulate cell adhesion and signaling mediated by RGD-binding and leukocyte integrins. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 9221–9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, R.; Greco, A.; Calonghi, N.; Dattoli, S.D.; Baiula, M.; Spampinato, S.; Picchetti, P.; De Cola, L.; Anselmi, M.; Cipriani, F.; et al. Selective detection of α4β1 integrin (VLA-4)-expressing cells using peptide-functionalized nanostructured materials mimicking endothelial surfaces adjacent to inflammatory sites. Pept. Sci. 2018, 110, e23081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, G.; Baiula, M.; Caligiana, A.; Galletti, P.; Gentilucci, L.; Artali, R.; Spampinato, S.M.; Giacomini, D. Could dissecting the molecular framework of β-lactam integrin ligands enhance selectivity? J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 10156–10166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, T.J.; Maxwell, D.S.; Kogan, T.P.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Kassir, J.; Holland, G.W.; Dixon, R.A. A 3D Structure model of integrin α4β1 complex: I. construction of a homology model of β1 and ligand binding analysis. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, J.; Abraham, W.M.; Adams, S.P.; Van Vlijmen, H.; Liao, Y.; Lee, W.C.; Cornebise, M.; Harris, M.; Shu, I.H.; Gill, A.; et al. Identification of potent and novel α4β1 antagonists using in silico screening. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2988–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangapandian, S.; John, S.; Sakkiah, S.D.; Lee, K.W. Discovery of potential integrin VLA-4 antagonists using pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening and molecular docking studies. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2011, 78, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutt, O.E.; Saubern, S.; Winkler, D.A. Modeling the molecular basis for α4β1 integrin antagonism. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 5903–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Schyman, P. Treatment of Halogen Bonding in the OPLS-AA Force Field: Application to Potent Anti-HIV Agents. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3895–3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


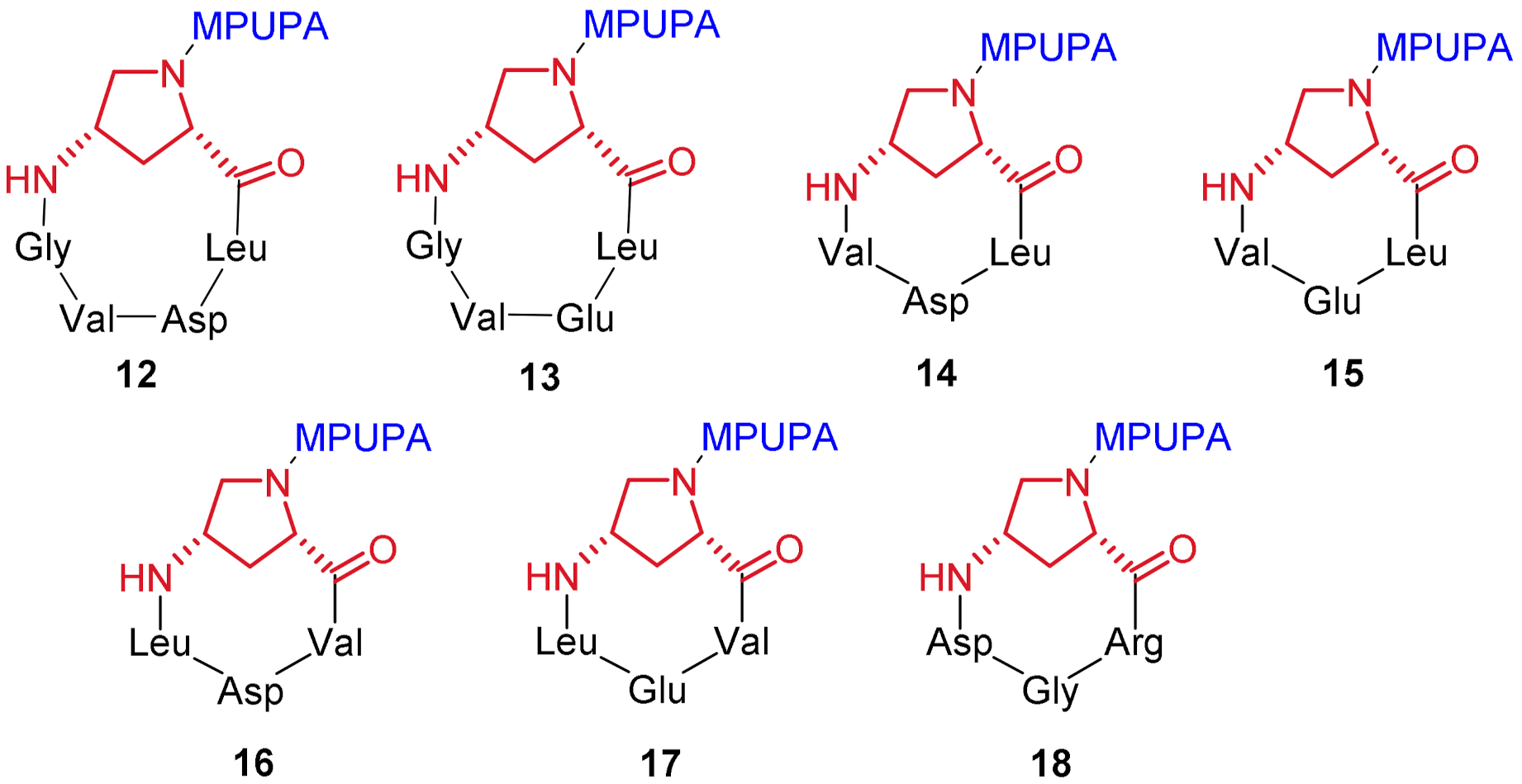

| Compound | Structure [a] | EC50/IC50 (μM) [b] |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | c[Amp(MPUPA)Leu-Asp-Val-Gly] | >100 |
| 13 | c[Amp(MPUPA)Leu-Glu-Val-Gly] | >100 |
| 14 | c[Amp(MPUPA)Leu-Asp-Val] | >100 |
| 15 | c[Amp(MPUPA)Leu-Glu-Val] | >100 |
| 16 | c[Amp(MPUPA)Val-Asp-Leu] | 0.37 ± 0.09 agonist |
| 17 | c[Amp(MPUPA)Val-Glu-Leu] | >100 |
| 18 | c[Amp(MPUPA)Arg-Gly-Asp] | >100 |
| 1 | MPUPA-Leu-Asp-Val-Pro | 0.0046 ± 0.0030 [c] antagonist |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sartori, A.; Bugatti, K.; Portioli, E.; Baiula, M.; Casamassima, I.; Bruno, A.; Bianchini, F.; Curti, C.; Zanardi, F.; Battistini, L. New 4-Aminoproline-Based Small Molecule Cyclopeptidomimetics as Potential Modulators of α4β1 Integrin. Molecules 2021, 26, 6066. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196066
Sartori A, Bugatti K, Portioli E, Baiula M, Casamassima I, Bruno A, Bianchini F, Curti C, Zanardi F, Battistini L. New 4-Aminoproline-Based Small Molecule Cyclopeptidomimetics as Potential Modulators of α4β1 Integrin. Molecules. 2021; 26(19):6066. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196066
Chicago/Turabian StyleSartori, Andrea, Kelly Bugatti, Elisabetta Portioli, Monica Baiula, Irene Casamassima, Agostino Bruno, Francesca Bianchini, Claudio Curti, Franca Zanardi, and Lucia Battistini. 2021. "New 4-Aminoproline-Based Small Molecule Cyclopeptidomimetics as Potential Modulators of α4β1 Integrin" Molecules 26, no. 19: 6066. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196066
APA StyleSartori, A., Bugatti, K., Portioli, E., Baiula, M., Casamassima, I., Bruno, A., Bianchini, F., Curti, C., Zanardi, F., & Battistini, L. (2021). New 4-Aminoproline-Based Small Molecule Cyclopeptidomimetics as Potential Modulators of α4β1 Integrin. Molecules, 26(19), 6066. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26196066








