Ellagitannin–Lipid Interaction by HR-MAS NMR Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of the Lipids in E. coli Lipid Extract
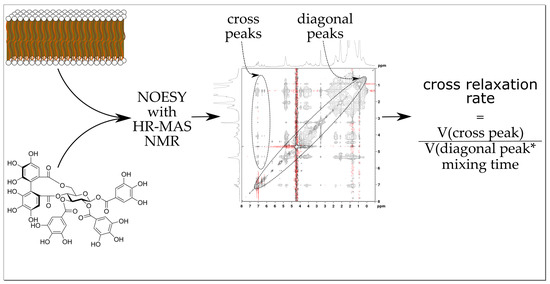
2.2. ET–Lipid Interaction Measurements by HR-MAS NMR
2.2.1. H Chemical Shift Deltas of E. coli Lipid Extract in the Presence of Tannins
2.2.2. NOESY Cross Relaxation Rates of the Aromatic Protons of Tannins
2.2.3. Effect of ET Concentration on the ET–Lipid Interaction
2.2.4. Effect of Lipid Batch on the ET–Lipid Interaction
2.3. Analysis of Stability of ET–Lipid Solution with UPLC-DAD-MS
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Isolation of Ellagitannins and Pentagalloylglucose
3.3. NMR Analyses
3.4. UPLC-DAD-MS Analyses
3.5. Data Analysis and Software
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

Appendix B



References
- Waghorn, G.C.; McNabb, W.C. Consequences of plant phenolic compounds for productivity and health of ruminants. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Harvey, I.; Bee, G.; Dohme-Meier, F.; Hoste, H.; Karonen, M.; Kölliker, R.; Lüscher, A.; Niderkorn, V.; Pellikaan, W.F.; Salminen, J.P.; et al. Benefits of condensed tannins in forage legumes fed to ruminants: Importance of structure, concentration, and diet composition. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 861–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baert, N.; Pellikaan, W.F.; Karonen, M.; Salminen, J.-P.P. A study of the structure-activity relationship of oligomeric ellagitannins on ruminal fermentation in vitro. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 8041–8052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoste, H.; Jackson, F.; Athanasiadou, S.; Thamsborg, S.M.; Hoskin, S.O. The effects of tannin-rich plants on parasitic nematodes in ruminants. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karonen, M.; Ahern, J.R.; Legroux, L.; Suvanto, J.; Engström, M.T.; Sinkkonen, J.; Salminen, J.-P.; Hoste, H. Ellagitannins Inhibit the Exsheathment of Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis Larvae: The Efficiency Increases Together with the Molecular Size. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 4176–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engström, M.T.; Karonen, M.; Ahern, J.R.; Baert, N.; Payré, B.; Hoste, H.; Salminen, J.P. Chemical Structures of Plant Hydrolyzable Tannins Reveal Their in Vitro Activity against Egg Hatching and Motility of Haemonchus contortus Nematodes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puljula, E.; Walton, G.; Woodward, M.J.; Karonen, M. Antimicrobial Activities of Ellagitannins against Clostridiales perfringens, Escherichia coli, Lactobacillus plantarum and Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2020, 25, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karonen, M.; Oraviita, M.; Mueller-Harvey, I.; Salminen, J.P.; Green, R.J. Ellagitannins with Glucopyranose Cores Have Higher Affinities to Proteins than Acyclic Ellagitannins by Isothermal Titration Calorimetry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12730–12740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engström, M.T.; Arvola, J.; Nenonen, S.; Virtanen, V.T.J.; Leppä, M.M.; Tähtinen, P.; Salminen, J.P. Structural Features of Hydrolyzable Tannins Determine Their Ability to Form Insoluble Complexes with Bovine Serum Albumin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 6798–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moilanen, J.; Salminen, J.-P. Ecologically neglected tannins and their biologically relevant activity: Chemical structures of plant ellagitannins reveal their in vitro oxidative activity at high pH. Chemoecology 2008, 18, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Hao, Y.Q.; Jin, L.; Xu, Z.J.; McAllister, T.A.; Wang, Y. Anti-Escherichia coli O157:H7 properties of purple prairie clover and sainfoin condensed tannins. Molecules 2013, 18, 2183–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawrisch, K.; Eldho, N.V.; Polozov, I.V. Novel NMR tools to study structure and dynamics of biomembranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2002, 116, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polenova, T.; Gupta, R.; Goldbourt, A. Magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy: A versatile technique for structural and dynamic analysis of solid-phase systems. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5458–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheidt, H.A.; Pampel, A.; Nissler, L.; Gebhardt, R.; Huster, D. Investigation of the membrane localization and distribution of flavonoids by high-resolution magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2004, 1663, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidt, H.A.; Huster, D. The interaction of small molecules with phospholipid membranes studied by 1H NOESY NMR under magic-angle spinning. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salminen, J.P.; Karonen, M. Chemical ecology of tannins and other phenolics: We need a change in approach. Funct. Ecol. 2011, 25, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Z.H.; Kouno, I. Relationship between hydrophobicity and structure of hydrolyzable tannins, and association of tannins with crude drug constituents in aqueous solution. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Virtanen, V.; Karonen, M. Partition coefficients (logP) of hydrolysable tannins. Molecules 2020, 25, 3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salminen, J.P.; Ossipov, V.; Loponen, J.; Haukioja, E.; Pihlaja, K. Characterisation of hydrolysable tannins from leaves of Betula pubescens by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 864, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, J.-P.; Ossipov, V.; Haukioja, E.; Pihlaja, K. Seasonal variation in the content of hydrolysable tannins in leaves of Betula pubescens. Phytochemistry 2001, 57, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Wakamatsu, H.; Omar, M.; Tanaka, T. Reinvestigation of the Stereochemistry of the C-Glycosidic Ellagitannins, Vescalagin and Castalagin. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grélard, A.; Loudet, C.; Diller, A.; Dufourc, E.J. NMR spectroscopy of lipid bilayers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 654, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Virtanen, V.; Räikkönen, S.; Puljula, E.; Karonen, M. Ellagitannin–Lipid Interaction by HR-MAS NMR Spectroscopy. Molecules 2021, 26, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020373
Virtanen V, Räikkönen S, Puljula E, Karonen M. Ellagitannin–Lipid Interaction by HR-MAS NMR Spectroscopy. Molecules. 2021; 26(2):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020373
Chicago/Turabian StyleVirtanen, Valtteri, Susanna Räikkönen, Elina Puljula, and Maarit Karonen. 2021. "Ellagitannin–Lipid Interaction by HR-MAS NMR Spectroscopy" Molecules 26, no. 2: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020373
APA StyleVirtanen, V., Räikkönen, S., Puljula, E., & Karonen, M. (2021). Ellagitannin–Lipid Interaction by HR-MAS NMR Spectroscopy. Molecules, 26(2), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020373