Pectin-Based Formulations for Controlled Release of an Ellagic Acid Salt with High Solubility Profile in Physiological Media
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. EALYS Preparation
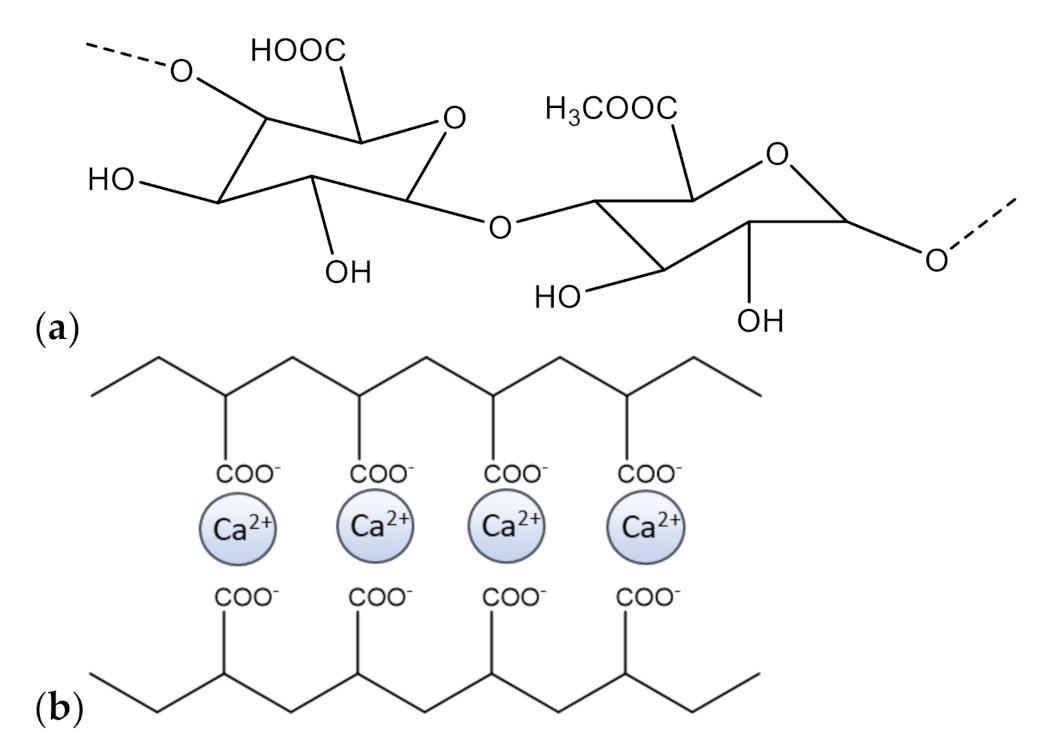
2.2. Optimization of Pectin Film Preparation
2.2.1. Degree of Esterification Determination
2.2.2. Rheological Analyses
2.3. Release Experiments
2.4. Release of EA from Pectin Films under Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions
2.5. Prebiotic Activity of EALYS-Containing Pectin Films
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Liquid Chromatography
3.3. Ellagic Acid–Lysine Salt (EALYS) Preparation
3.4. H-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H-NMR)
3.5. Solubility in CaCl2 Water Solution and in Phosphate Buffer Solution (PBS)
3.6. Determination of Degree of Esterification (DE) of Pectins
3.7. Pectin Gels Preparation and Casting
3.8. EALYS Pectin Gels Preparation and Casting
3.9. Rheological Analyses
3.10. Release Experiments
3.11. In Vitro Digestion
3.12. In Vitro Fermentation and SCFAs Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Khatib, M. Bioactive Compounds into Edible Syrian Plants: Pomegranate and Capper. Ph.D. Thesis, Università degli Studi di Firenze, Firenze, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Akkoyun, H.T.; Karadeniz, A. Investigation of the protective effect of ellagic acid for preventing kidney injury in rats exposed to nicotine during the fetal period. Biotech. Histochem. 2016, 91, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, P.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Yin, M.C. Anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulatory activities of caffeic acid and ellagic acid in cardiac tissue of diabetic mice. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Niño, W.R.; Zazueta, C. Ellagic acid: Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms involved in liver protection. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 97, 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Jagan Mohan Rao, L.; Shivanandappa, T. Isolation of ellagic acid from the aqueous extract of the roots of Decalepis hamiltonii: Antioxidant activity and cytoprotective effect. Food Chem. 2007, 103, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeram, N.P.; Zhang, Y.; McKeever, R.; Henning, S.M.; Lee, R.P.; Suchard, M.A.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Thames, G.; Zerlin, A.; et al. Pomegranate juice and extracts provide similar levels of plasma and urinary ellagitannin metabolites in human subjects. J. Med. Food 2008, 11, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Xing, D.M.; Xiang, L.; Zhao, Y.N.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.J.; Du, L.J. Pharmacokinetic study of ellagic acid in rat after oral administration of pomegranate leaf extract. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2003, 796, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Li, L.; Celver, J.; Killian, C.; Kovoor, A.; Seeram, N.P. Effects of fruit ellagitannin extracts, ellagic acid, and their colonic metabolite, urolithin A, on Wnt signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3965–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitley, A.C.; Sweet, D.H.; Walle, T. Site-specific accumulation of the cancer preventive dietary polyphenol ellagic acid in epithelial cells of the aerodigestive tract. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espín, J.C.; González-Barrio, R.; Cerdá, B.; López-Bote, C.; Rey, A.I.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. Iberian pig as a model to clarify obscure points in the bioavailability and metabolism of ellagitannins in humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10476–10485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sarrías, A.; García-Villalba, R.; Núñez-Sánchez, M.Á.; Tomé-Carneiro, J.; Zafrilla, P.; Mulero, J.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Espín, J.C. Identifying the limits for ellagic acid bioavailability: A crossover pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers after consumption of pomegranate extracts. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfei, S.; Marengo, B.; Zuccari, G. Oxidative Stress, Antioxidant Capabilities, and Bioavailability: Ellagic Acid or Urolithins? Antioxidants 2020, 9, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djedjibegovic, J.; Marjanovic, A.; Panieri, E.; Saso, L. Ellagic Acid-Derived Urolithins as Modulators of Oxidative Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyamba, I.; Lechanteur, A.; Semdé, R.; Evrard, B. Physical formulation approaches for improving aqueous solubility and bioavailability of ellagic acid: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verotta, L.; Panzella, L.; Antenucci, S.; Calvenzani, V.; Tomay, F.; Petroni, K.; Caneva, E.; Napolitano, A. Fermented pomegranate wastes as sustainable source of ellagic acid: Antioxidant properties, anti-inflammatory action, and controlled release under simulated digestion conditions. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mady, F.M.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponge for improvement of solubility and oral bioavailability of Ellagic acid. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 31, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pirzadeh-Naeeni, S.; Mozdianfard, M.R.; Shojaosadati, S.A.; Khorasani, A.C.; Saleh, T. A comparative study on schizophyllan and chitin nanoparticles for ellagic acid delivery in treating breast cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, R.; Kulkarni, G.T.; Ramana, M.V.; de Jesus Andreoli Pinto, T.; Kikuchi, I.S.; Molim Ghisleni, D.D.; de Souza Braga, M.; De Bank, P.; Dua, K. Dual crosslinked pectin–alginate network as sustained release hydrophilic matrix for repaglinide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, L.N.M.; Alcântara, A.C.S.; Darder, M.; Aranda, P.; Araújo-Moreira, F.M.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Pectin-coated chitosan-LDH bionanocomposite beads as potential systems for colon-targeted drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costas, L.; Pera, L.M.; López, A.G.; Mechetti, M.; Castro, G.R. Controlled release of sulfasalazine release from “smart” pectin gel microspheres under physiological simulated fluids. In Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 167, pp. 1396–1407. [Google Scholar]
- Günter, E.A.; Popeyko, O.V. Calcium pectinate gel beads obtained from callus cultures pectins as promising systems for colon-targeted drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, D.; Jung, K.; Winter, M.; Rogoll, D.; Melcher, R.; Kulozik, U.; Schwarz, K.; Richling, E. Encapsulation of anthocyanins from bilberries—Effects on bioavailability and intestinal accessibility in humans. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, I.; Bhardwaj, V.; Hariharan, S.; Kumar, M.N.V.R. Analytical methods for assay of ellagic acid and its solubility studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivica, V.; Bajza, A. Acidic attack of cement based materials—A review. Part 1. Principle of acidic attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2001, 15, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, G.D.; Lajolo, F.M. FT-IR spectroscopy as a tool for measuring degree of methyl esterification in pectins isolated from ripening papaya fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2002, 25, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Zafrilla, P.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. An in vitro method to simulate phenolic compound release from the food matrix in the gastrointestinal tract. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2002, 214, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDougall, G.J.; Dobson, P.; Smith, P.; Blake, A.; Stewart, D. Assessing potential bioavailability of raspberry anthocyanins using an in vitro digestion system. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5896–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Lin, Q.; Luo, F. Effects of Non-Starch Polysaccharides on Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Pan, L.-L.; Niu, W.; Fang, X.; Liang, W.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Pan, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; et al. Modulation of Gut Microbiota by Low Methoxyl Pectin Attenuates Type 1 Diabetes in Non-obese Diabetic Mice. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Heath, A.L.; Galland, B.; Rehrer, N.; Drummond, L.; Wu, X.Y.; Bell, T.J.; Lawley, B.; Sims, I.M.; Tannock, G.W. Substrate use prioritization by a coculture of five species of gut bacteria fed mixtures of arabinoxylan, xyloglucan, β-glucan, and pectin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Besten, G.; Van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bialonska, D.; Ramnani, P.; Kasimsetty, S.G.; Muntha, K.R.; Gibson, G.R.; Ferreira, D. The influence of pomegranate by-product and punicalagins on selected groups of human intestinal microbiota. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 140, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Terao, J. Role of Intestinal Microbiota in the Bioavailability and Physiological Functions of Dietary Polyphenols. Molecules 2019, 24, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, J.T.; Rao, M.A. Rheology and structure development during gelation of low-methoxyl pectin gels: The effect of sucrose. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbits, C.W.; MacDougall, A.J.; Ring, S.G. Calcium binding and swelling behaviour of a high methoxyl pectin gel. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 310, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzella, L.; Pérez-Burillo, S.; Pastoriza, S.; Martín, M.Á.; Cerruti, P.; Goya, L.; Ramos, S.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Napolitano, A.; D’Ischia, M. High Antioxidant Action and Prebiotic Activity of Hydrolyzed Spent Coffee Grounds (HSCG) in a Simulated Digestion-Fermentation Model: Toward the Development of a Novel Food Supplement. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 6452–6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sample | Acetic Acid | Propionic Acid | Butyric Acid |
|---|---|---|---|
| HM Pectin + 10% EALYS | 4.37 ± 0.09 a | 3.01 ± 0.06 a | 0.300 ± 0.007 a |
| HM Pectin | 3.89 ± 0.08 b | 2.06 ± 0.05 b | 0.220 ± 0.006 b |
| LM Pectin + 10% EALYS | 4.0 ± 0.1 b | 2.83 ± 0.09 c | 0.44 ± 0.02 c |
| LM Pectin | 2.89 ± 0.06 c | 1.73 ± 0.03 d | 0.280 ± 0.009 d |
| Blank | 1.01 ± 0.02 d | 0.94 ± 0.02 e | - |
| EALYS Salt | Weight (mg) | Water (mL) | Water Solubility (mg/mL) | CaCl2 Water Solution Solubility (mg/mL) | PBS Solubility (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 20.1 | 15 | Insoluble | ------ | ------ |
| 1:2 | 23.6 | 15 | Insoluble | ------ | ------ |
| 1:3 | 19.8 | 15 | Insoluble | ------ | ------ |
| 1:4 | 22.4 | 1.7 | 12.99 | 0.31 | 8.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortenzi, M.A.; Antenucci, S.; Marzorati, S.; Panzella, L.; Molino, S.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Napolitano, A.; Verotta, L. Pectin-Based Formulations for Controlled Release of an Ellagic Acid Salt with High Solubility Profile in Physiological Media. Molecules 2021, 26, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020433
Ortenzi MA, Antenucci S, Marzorati S, Panzella L, Molino S, Rufián-Henares JÁ, Napolitano A, Verotta L. Pectin-Based Formulations for Controlled Release of an Ellagic Acid Salt with High Solubility Profile in Physiological Media. Molecules. 2021; 26(2):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020433
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtenzi, Marco Aldo, Stefano Antenucci, Stefania Marzorati, Lucia Panzella, Silvia Molino, José Ángel Rufián-Henares, Alessandra Napolitano, and Luisella Verotta. 2021. "Pectin-Based Formulations for Controlled Release of an Ellagic Acid Salt with High Solubility Profile in Physiological Media" Molecules 26, no. 2: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020433
APA StyleOrtenzi, M. A., Antenucci, S., Marzorati, S., Panzella, L., Molino, S., Rufián-Henares, J. Á., Napolitano, A., & Verotta, L. (2021). Pectin-Based Formulations for Controlled Release of an Ellagic Acid Salt with High Solubility Profile in Physiological Media. Molecules, 26(2), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020433












