Ancient Wheat and Quinoa Flours as Ingredients for Pasta Dough—Evaluation of Thermal and Rheological Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Proximate Composition of Flours
2.2. Phase Transition Behavior of Flours
2.3. Pasting Characteristics of Flours
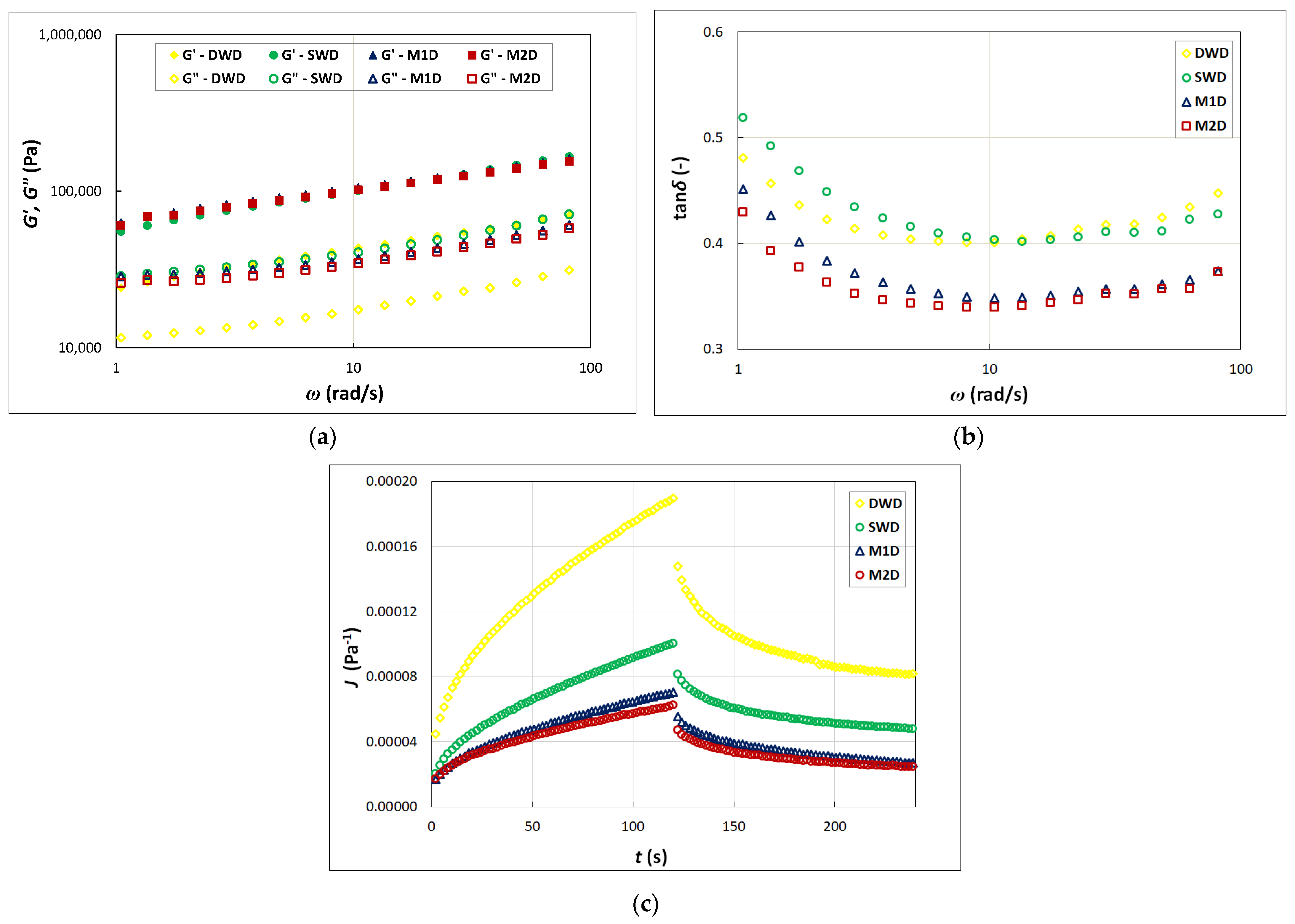
2.4. Rheological Properties of Pasta Dough
2.5. Pasting Characteristics of Dry Pasta
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Determination of Proximate Composition of Flours
3.2.2. Determination of Phase Transition Behavior of Flours
3.2.3. Determination of Pasting Characteristics of Flours
3.2.4. Preparation of Pasta Dough—Mixtures of Flours with Water
3.2.5. Determination of Rheological Properties of Pasta Dough
3.2.6. Preparation of Dry Pasta
3.2.7. Determination of Pasting Characteristics of Dry Pasta
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Van Boxstael, F.; Aerts, H.; Linssen, S.; Latré, J.; Christiaens, A.; Haesaert, G.; Dierickx, I.; Brusselle, J.; De Keyzer, W. A comparison of the nutritional value of Einkorn, Emmer, Khorasan and modern wheat: Whole grains, processed in bread, and population-level intake implications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4108–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukid, F.; Folloni, S.; Sforza, S.; Vittadini, E.; Prandi, B. Current Trends in Ancient Grains-Based Foodstuffs: Insights into Nutritional Aspects and Technological Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammed, A.M.; Simsek, S. Hulled wheats: A review of nutritional properties and processing methods. Cereal Chem. 2014, 91, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewry, P.R. Do ancient types of wheat have health benefits compared with modern bread wheat? J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzani, A.; Ashraf, M. Cultivated Ancient Wheats (Triticum spp.): A Potential Source of Health-Beneficial Food Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belcar, J.; Sobczyk, A.; Sobolewska, M.; Stankowski, S.; Gorzelany, J. Characteristics of Technological Properties of Grain and Flour from Ancient Varieties of Wheat (Einkorn, Emmer and Spelt). Acta Univ. Cibiniensis Ser. E Food Technol. 2020, 24, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisslitz, S.; Longin, C.F.H.; Scherf, K.A.; Koehler, P. Comparative study on gluten protein composition of ancient (einkorn, emmer and spelt) and modern wheat species (durum and common wheat). Foods 2019, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, E.; Encina-Zelada, C.; Barros, L.; Gonzales-Barron, U.; Cadavez, V.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Chemical and nutritional characterization of Chenopodium quinoa Willd (quinoa) grains: A good alternative to nutritious food. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frakolaki, G.; Giannou, V.; Topakas, E.; Tzia, C. Chemical characterization and breadmaking potential of spelt versus wheat flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 79, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goranova, Z.; Marudova, M.; Baeva, M. Influence of functional ingredients on starch gelatinization in sponge cake batter. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruisi, P.; Ingraffia, R.; Urso, V.; Giambalvo, D.; Alfonzo, A.; Corona, O.; Settanni, L.; Frenda, A.S. Influence of grain quality, semolinas and baker’s yeast on bread made from old landraces and modern genotypes of Sicilian durum wheat. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczyk, A.; Pycia, K.; Stankowski, S.; Jaworska, G.; Kuźniar, P. Evaluation of the rheological properties of dough and quality of bread made with the flour obtained from old cultivars and modern breeding lines of spelt (Triticum aestivum ssp. spelta). J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 77, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiga, B.H.; Kumcuoglu, S.; Vatansever, M.; Tavman, S. Thermal and pasting properties of Quinoa—Wheat flour blends and their effects on production of extruded instant noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 97, 103120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquistucci, R.; Melini, V.; Galli, V. Durum wheat grain and pasta from locally-grown crops: A case-study on Saragolla (Triticum turgidum ssp. turanicum) and Senatore Cappelli (Triticum turgidum ssp. durum) wheats. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2020, 32, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójtowicz, A.; Oniszczuk, A.; Kasprzak, K.; Olech, M.; Mitrus, M.; Oniszczuk, T. Chemical composition and selected quality characteristics of new types of precooked wheat and spelt pasta products. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Corke, H. Gelatinization, pasting, and gelling properties of sweetpotato and wheat starch blends. Cereal Chem. 2011, 88, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, A.; Cini, E.; Guerrini, L.; Masella, P.; Angeloni, G.; Parenti, A. Predictive models of the rheological properties and optimal water content in doughs: An application to ancient grain flours with different degrees of refining. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 83, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecka-Jóźwiak, K.; Słowik, E.; Rozmierska, J.; Chabłowska, B. Characteristic of organic flour produced from einkorn wheat and rheological properties of einkorn dough in terms of bread obtaining. J. Res. Appl. Agric. Eng. 2015, 60, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, H.; Mueller, K.J.; Koehler, P. Studies on the protein composition and baking quality of einkorn lines. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 229, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konvalina, P.; Bradová, J.; Capouchová, I.; Stehno, Z.; Moudrý, J. Baking quality and high molecular weight glutenin subunit composition of Emmer wheat, old and new varieties of bread wheat. Rom. Agric. Res. 2013, 30, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Witczak, T.; Gałkowska, D. Sorption and thermal characteristics of ancient grain pasta of various compositions. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 137, 110433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, F. Formulation and Quality Attributes of Quinoa Food Products. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2016, 9, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneel, C.; Pareyt, B.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. The impact of the protein network on the pasting and cooking properties of dry pasta products. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Jubete, L.; Arendt, E.K.; Gallagher, E. Nutritive value and chemical composition of pseudocereals as gluten-free ingredients. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 60, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzani, A. Emmer (Triticum turgidum ssp. dicoccum) flour and bread. In Flour and Breads and Their Fortification in Health and Disease Prevention; Preedy, V.R., Watson, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 89–98. ISBN 9780128146392. [Google Scholar]
- Mastromatteo, M.; Danza, A.; Lecce, L.; Spinelli, S.; Lampignano, V.; Laverse, J.; Contò, F.; Del Nobile, M.A. Effect of durum wheat varieties on bread quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 49, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Bajaj, R.; Kaur, A. Wheat starch production, structure, functionality and applications—A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, S.; Singh, N.; Isono, N.; Noda, T. Relationship of granule size distribution and amylopectin structure with pasting, thermal, and retrogradation properties in wheat starch. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffolani, M.E.; León, A.E.; Pérez, G.T. Study of the physicochemical and functional characterization of quinoa and kañiwa starches. Starch/Staerke 2013, 65, 976–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Yasui, T.; Matsuki, J. Effect of amylose content on gelatinization, retrogradation, and pasting properties of starches from waxy and nonwaxy wheat and their F1 seeds. Cereal Chem. 2000, 77, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziobro, R.; Witczak, T.; Juszczak, L.; Korus, J. Supplementation of gluten-free bread with non-gluten proteins. Effect on dough rheological properties and bread characteristic. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gałkowska, D.; Witczak, T.; Korus, J.; Juszczak, L. Characterization of Some Spelt Wheat Starches as a Renewable Biopolymeric Material. ISRN Polym. Sci. 2014, 2014, 361069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shyu, Y.S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Huang, T.C.; Sung, W.C. Effect of Resistant Starch on Physicochemical Properties of Wheat Dough and Bread. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 6, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, F. Physicochemical properties of quinoa flour as affected by starch interactions. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hamaker, B.R. A three component interaction among starch, protein, and free fatty acids revealed by pasting profiles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 2797–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, A.; Sindhu, R.; Khatkar, B.S. Effect of fats and oils on pasting and textural properties of wheat flour. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3836–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, A.; Brandolini, A.; Gazza, L. Influence of steaming treatment on chemical and technological characteristics of einkorn (Triticum monococcum L. ssp. monococcum) wholemeal flour. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.; Alamprese, C.; Pagani, M.A.; Lucisano, M. Effect of puffing on ultrastructure and physical characteristics of cereal grains and flours. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohajdová, Z.; Karovičová, J. Chemical Characteristics and Pasting Properties of Commercial Slovak Common and Spelt Wheat Flours. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2009, 74, 313–317. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, E.; Krzeminska-Fiedorowicz, L.; Khachatryan, G.; Fiedorowicz, M. Comparison of molecular structure and selected physicochemical properties of spelt wheat and common wheat starches. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 53, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Brandolini, A.; Hidalgo, A.; Moscaritolo, S. Chemical composition and pasting properties of einkorn (Triticum monococcum L. subsp. monococcum) whole meal flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, D.B.; Singh, R.; Rani, S.; Upadhyay, A.; Kaur, B.P.; Kumar, N.; Thangalakshmi, S. Evaluation of structural, chemical and digestibility properties of multigrain pasta. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Shevkani, K.; Katyal, M.; Singh, N.; Ahlawat, A.K.; Singh, A.M. Physicochemical and rheological properties of starch and flour from different durum wheat varieties and their relationships with noodle quality. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2127–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srichuwong, S.; Curti, D.; Austin, S.; King, R.; Lamothe, L.; Gloria-Hernandez, H. Physicochemical properties and starch digestibility of whole grain sorghums, millet, quinoa and amaranth flours, as affected by starch and non-starch constituents. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, C.; Mutungi, C.; Unbehend, G.; Lindhauer, M.G. Rheological and baking characteristics of batter and bread prepared from pregelatinised cassava starch and sorghum and modified using microbial transglutaminase. J. Food Eng. 2010, 97, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, C.; Mutungi, C.; Unbehend, G.; Lindhauer, M.G. Creep-recovery parameters of gluten-free batter and crumb properties of bread prepared from pregelatinised cassava starch, sorghum and selected proteins. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 2493–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Huang, J.; Tian, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhu, Q.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Ma, S.; Wang, X. Effects of insoluble dietary fiber from wheat bran on noodle quality. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2021, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, N.M.; Dexter, J.E.; Scanlon, M.G. Starch participation in durum dough linear viscoelastic properties. Cereal Chem. 2002, 79, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, M.E.; Iturriaga, L.B. Viscoelastic properties of amaranth starch gels and pastes. Creep compliance modeling with Maxwell model. Starch/Stärke 2016, 68, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, T.; Salvador, A.; Hernández, M.J. Creep-Recovery and Oscillatory Rheology of Flour-Based Systems. In Advances in Food Rheology and Its Applications; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Ahmed, J., Ptaszek, P., Basu, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 277–295. ISBN 9780081004326. [Google Scholar]
- Crockett, R.; Ie, P.; Vodovotz, Y. Effects of soy protein isolate and egg white solids on the physicochemical properties of gluten-free bread. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, C.; Rosell, C.M. Breadmaking performance of protein enriched, gluten-free breads. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 227, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronda, F.; Villanueva, M.; Collar, C. Influence of acidification on dough viscoelasticity of gluten-free rice starch-based dough matrices enriched with exogenous protein. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witczak, T.; Juszczak, L.; Ziobro, R.; Korus, J. Rheology of gluten-free dough and physical characteristics of bread with potato protein. J. Food Process Eng. 2017, 40, e12491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez, M.A.; Drago, S.R.; De Greef, D.; Gonzalez, R.J.; Lobo, M.O.; Samman, N.C. Rheological, functional and nutritional properties of wheat/broad bean (Vicia faba) flour blends for pasta formulation. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.; Duizer, L.; Seetharaman, K. The effect of drying and whole grain content on the pasting, physicochemical and qualitative properties of pasta. Starch/Staerke 2013, 65, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti, A.; Seetharaman, K.; Pagani, M.A. Rheological Approaches Suitable for Investigating Starch and Protein Properties Related to Cooking Quality of Durum Wheat Pasta. J. Food Qual. 2013, 36, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamadevan, V.; Bertoft, E. Structure-function relationships of starch components. Starch/Stärke 2015, 67, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 21st ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019; ISBN 0935584544.
- EN ISO 21415-1:2006. Wheat and Wheat Flour—Gluten Content—Part 1: Determination of Wet Gluten by a Manual Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10520:1997. Native Starch—Determination of Starch Content—Ewers Polarimetric Method; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Perten Instrument RVA Method 01.05 General Pasting Method. Available online: https://www.perten.com/Global/Application%20notes/RVA/General%20Pasting%20Method%20-%20RVA%2001.05.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2018).

| Type of Flour | Moisture (g/100 g) | Wet Gluten (g/100 g) | Protein (g/100 g, d.w.b.) | Starch (g/100 g, d.w.b.) | Fat (g/100 g, d.w.b.) | Ash (g/100 g, d.w.b.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DW | 13.9 e ± 0.33 | 27.2 b ± 0.3 | 13.7 c ± 0.01 | 79.4 d ± 0.65 | 1.92 a ± 0.02 | 1.04 a ± 0.04 |
| SW | 10.9 b ± 0.36 | 30.9 c ± 0.1 | 14.0 d ± 0.03 | 73.5 c ± 0.00 | 2.00 a ± 0.08 | 1.31 b ± 0.02 |
| EkW | 12.5 c ± 0.16 | 27.4 b ± 0.2 | 13.0 a ± 0.04 | 71.6 b ± 0.64 | 3.30 c ± 0.08 | 1.69 d ± 0.03 |
| EmW | 13.3 d ± 0.19 | 25.5 a ± 0.8 | 13.4 b ± 0.04 | 74.4 c ± 0.25 | 2.60 b ± 0.05 | 1.53 c ± 0.02 |
| Qn | 9.6 a ± 0.04 | n.d. | 14.3 e ± 0.06 | 65.2 a ± 0.68 | 7.46 d ± 0.07 | 2.37 e ± 0.06 |
| ANOVA—p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Parameter | Unit | Type of Flour | ANOVA—p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DW | SW | EkW | EmW | Qn | |||
| Glass transition | |||||||
| TgO | °C | 48.7 ± 1.2 | 48.2 ± 0.8 | 48.8 ± 0.9 | 48.9 ± 1.3 | 49.6 ± 1.8 | 0.655 |
| TgM | °C | 50.8 ± 0.9 | 50.7 ± 0.9 | 51.3 ± 0.9 | 51.5 ± 1.3 | 52.0 ± 1.9 | 0.559 |
| TgE | °C | 53.1 ± 1.2 | 53.2 ± 0.9 | 53.8 ± 1.4 | 53.7 ± 1.6 | 54.3 ± 2.3 | 0.792 |
| Gelatinization | |||||||
| TOg | °C | 58.2 c ± 0.1 | 57.7 b ± 0.1 | 60.2 e ± 0.0 | 59.0 d ± 0.1 | 56.0 a ± 0.0 | <0.001 |
| TPg | °C | 65.0 a ± 0.1 | 65.3 a ± 0.5 | 66.7 b ± 0.1 | 65.4 a ± 0.1 | 65.0 a ± 0.1 | 0.004 |
| TEg | °C | 73.1 a ± 0.1 | 73.0 a ± 0.1 | 73.3 a ± 0.4 | 72.4 b ± 0.1 | 73.3 a ± 0.1 | 0.030 |
| ΔHg | J/g, d.w.b. | 8.74 c ± 0.06 | 6.43 a ± 0.53 | 8.20 b,c ± 0.41 | 7.74 b ± 0.04 | 6.43 a ± 0.23 | 0.002 |
| Retrogradation | |||||||
| TOr | °C | 45.7 ± 0.1 | 45.7 ± 0.3 | 47.5 ± 1.5 | 47.3 ± 0.4 | 47.1 ± 0.4 | 0.137 |
| TPr | °C | 56.5 ± 0.0 | 56.8 ± 0.2 | 57.9 ± 0.6 | 56.8 ± 1.6 | 58.4 ± 1.1 | 0.298 |
| TEr | °C | 65.1 ± 0.1 | 66.1 ± 1.5 | 66.1 ± 0.0 | 66.4 ± 0.1 | 66.8 ± 1.1 | 0.419 |
| ΔHr | J/g, d.w.b. | 1.37 b,c ± 0.24 | 2.08 c ± 0.67 | 0.80 a,b ± 0.04 | 1.05 a,b,c ± 0.48 | 0.41 a ± 0.17 | 0.029 |
| DR | % | 16 | 29 | 10 | 14 | 6 | - |
| Pasting | |||||||
| PT | °C | 65.1 a ± 0.03 | 64.6 a ± 0.46 | 69.38 d ± 0.08 | 66.6 b ± 0.52 | 67.5 c ± 0.45 | <0.001 |
| PV | mPa·s | 4860 d ± 74 | 4137 b ± 34 | 4121 b ± 66 | 3853 a ± 34 | 4468 c ± 41 | <0.001 |
| MV | mPa·s | 3478 d ± 27 | 2510 b ± 20 | 2843 b ± 99 | 2216 a ± 35 | 4136 c ± 44 | <0.001 |
| BD | mPa·s | 1383 c ± 49 | 1627 d ± 23 | 1278 b ± 34 | 1637 d ± 13 | 332 a ± 44 | <0.001 |
| FV | mPa·s | 7013 e ± 26 | 5010 b ± 37 | 6097 d ± 125 | 5449 c ± 44 | 4169 a ± 7 | <0.001 |
| SB | mPa·s | 3535 c ± 5 | 2501 a ± 25 | 3254 b ± 61 | 3233 b ± 9 | n.d. | <0.001 |
| Parameter | Unit | Type of Pasta Dough | ANOVA—p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWD | SWD | M1D | M2D | |||
| K′ | Pa·sn′ | 24861 a ± 1135 | 56905 b ± 3980 | 65068 c ± 4883 | 62818 b,c ± 2775 | <0.001 |
| n’ | - | 0.236 b ± 0.014 | 0.244 b ± 0.003 | 0.207 a ± 0.004 | 0.205 a ± 0.014 | 0.003 |
| R2 | - | >0.997 | >0.998 | >0.996 | >0.988 | |
| K″ | Pa·sn″ | 10687 a ± 520 | 26434 c ± 1842 | 25919 b,c ± 1866 | 23472 b ± 1394 | <0.001 |
| n″ | - | 0.227 c ± 0.012 | 0.206 b ± 0.003 | 0.173 a ± 0.002 | 0.186 a ± 0.011 | <0.001 |
| R2 | - | >0.977 | >0.973 | >0.955 | >0.951 | |
| tanδ (at 1 rad/s) | - | 0.481 c ± 0.004 | 0.519 d ± 0.007 | 0.451 b ± 0.008 | 0.429 a ± 0.007 | <0.001 |
| J0 × 104 | Pa | 0.453 c ± 0.041 | 0.208 b ± 0.019 | 0.174 a,b ± 0.031 | 0.144 a ± 0.027 | <0.001 |
| η0 × 10−4 | Pa·s | 147 a ± 5 | 252 a ± 40 | 489 b ± 141 | 474 b ± 42 | 0.001 |
| J1 × 104 | Pa | 0.644 c ± 0.069 | 0.320 b ± 0.027 | 0.286 a,b ± 0.044 | 0.228 a ± 0.027 | <0.001 |
| λret | s | 30.7 a ± 3.8 | 32.3 a ± 2.4 | 42.9 b ± 4.5 | 28.5 a ± 3.0 | 0.005 |
| R2 | - | >0.997 | >0.997 | >0.994 | >0.987 | |
| Parameter | Unit | Type of Pasta | ANOVA—p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DWP | SWP | M1P | M2P | |||
| PT | °C | 80.6 a ± 0.28 | 81.4 b ± 0.03 | 82.4 c ± 0.53 | 83.3 d ± 0.56 | <0.001 |
| PV | mPa·s | 2299 a ± 39 | 1530 b ± 15 | 1736 c ± 33 | 1841 d ± 8 | <0.001 |
| MV | mPa·s | 1363 c ± 14 | 982 b ± 3 | 946 a ± 9 | 947 a ± 14 | <0.001 |
| BD | mPa·s | 936 c ± 33 | 548 a ± 13 | 790 b ± 31 | 893 c ± 8 | <0.001 |
| FV | mPa·s | 2915 c ± 36 | 2193 b ± 2 | 2085 a ± 13 | 2213 b ± 21 | <0.001 |
| SB | mPa·s | 1552 d ± 24 | 1211 b ± 4 | 1139 a ± 8 | 1266 c ± 10 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gałkowska, D.; Witczak, T.; Witczak, M. Ancient Wheat and Quinoa Flours as Ingredients for Pasta Dough—Evaluation of Thermal and Rheological Properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 7033. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26227033
Gałkowska D, Witczak T, Witczak M. Ancient Wheat and Quinoa Flours as Ingredients for Pasta Dough—Evaluation of Thermal and Rheological Properties. Molecules. 2021; 26(22):7033. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26227033
Chicago/Turabian StyleGałkowska, Dorota, Teresa Witczak, and Mariusz Witczak. 2021. "Ancient Wheat and Quinoa Flours as Ingredients for Pasta Dough—Evaluation of Thermal and Rheological Properties" Molecules 26, no. 22: 7033. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26227033
APA StyleGałkowska, D., Witczak, T., & Witczak, M. (2021). Ancient Wheat and Quinoa Flours as Ingredients for Pasta Dough—Evaluation of Thermal and Rheological Properties. Molecules, 26(22), 7033. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26227033






