Production and Characterization of Cross-Linked Aggregates of Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCR11 Thermoalkaliphilic Recombinant Lipase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of LipMatCCR11-CLEA Production
2.2. Biochemical Characterization
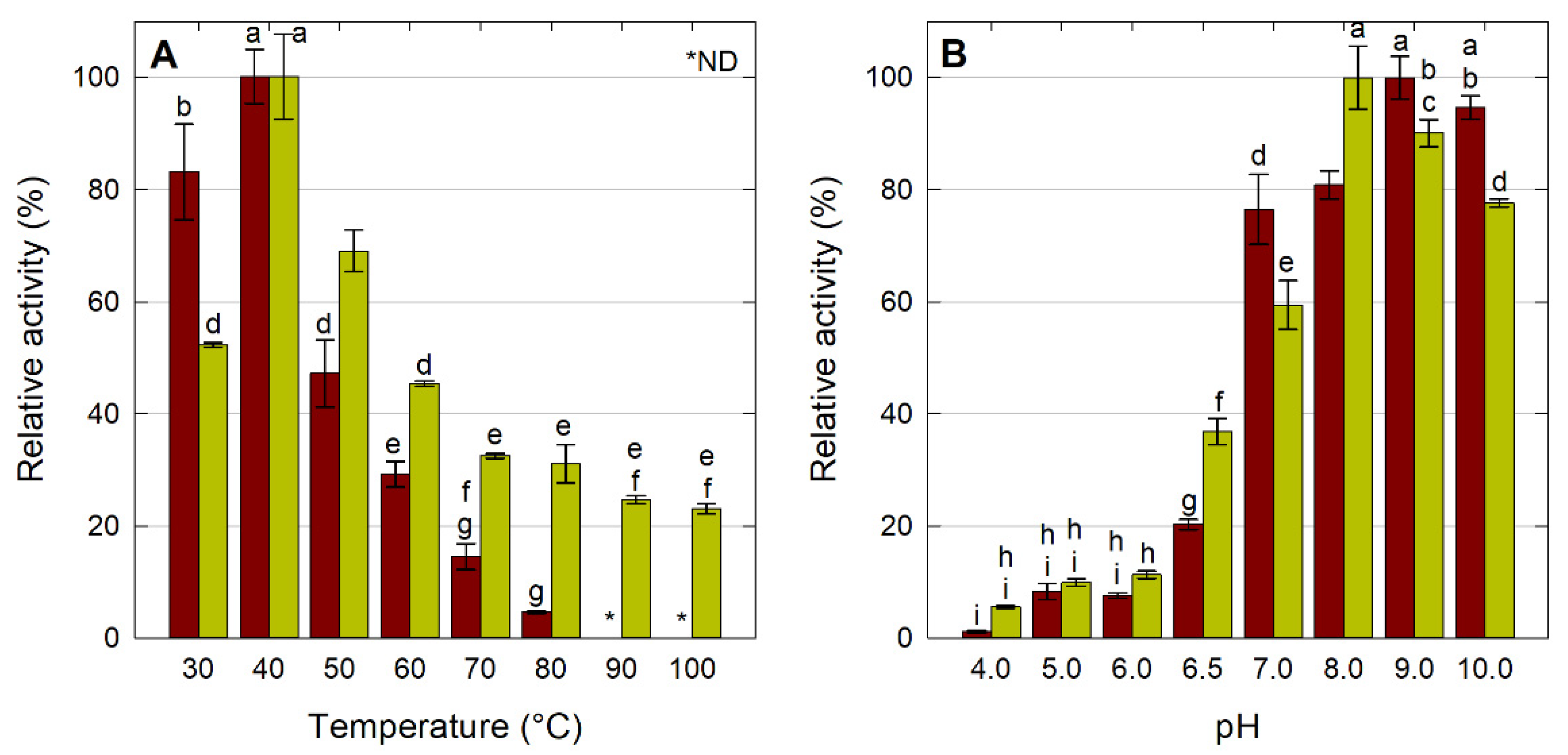
2.2.1. Effect of Temperature and pH on LipMatCCR11-CLEA Activity
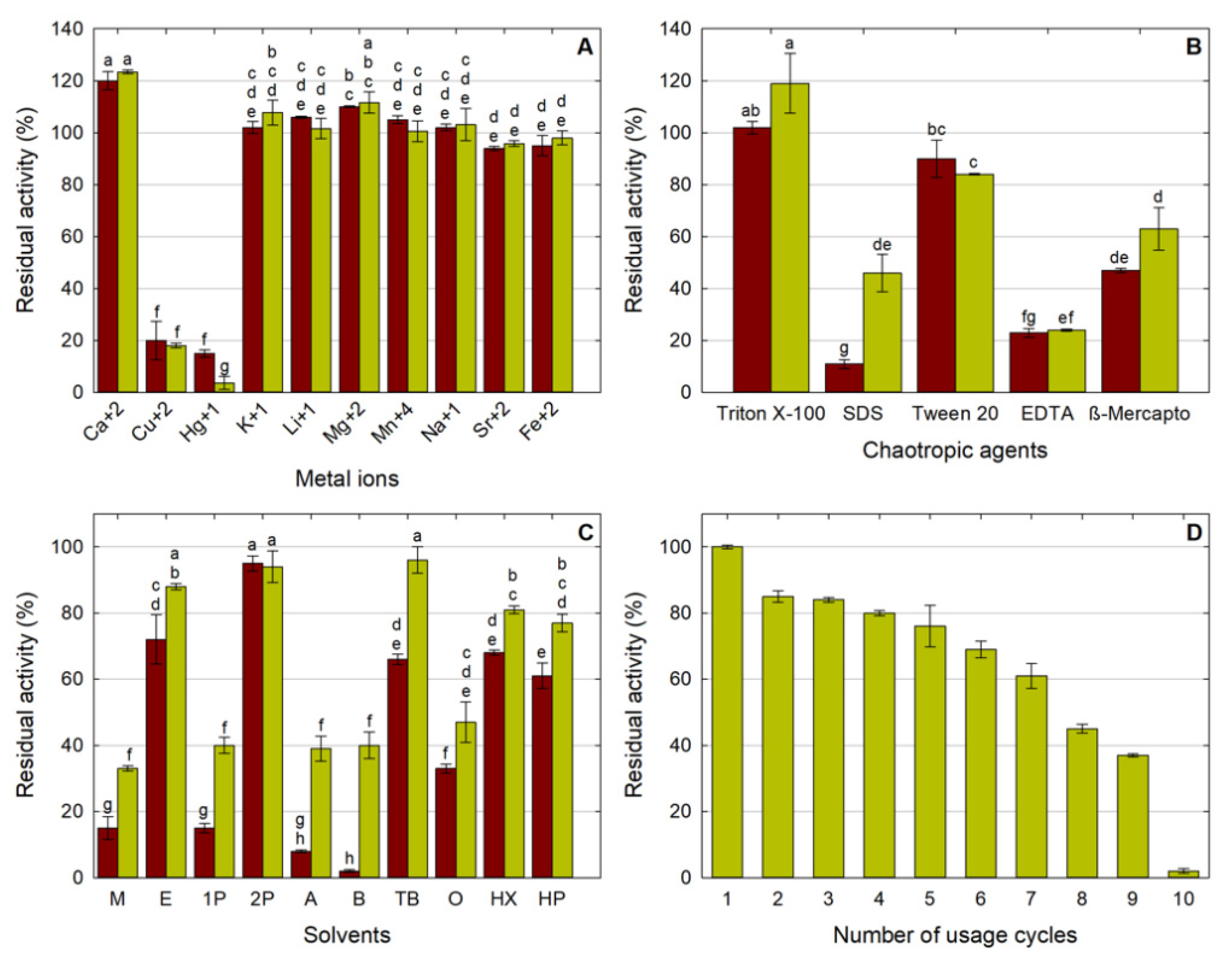
2.2.2. Effect of Metal Ions on LipMatCCR11-CLEA Activity
2.2.3. Stability in Chaotropic Agents
2.2.4. Stability in Organic Solvents
2.2.5. Reusability of Immobilized Lipase Test
2.2.6. Storage Stability of LipMatCCR1-CLEAs
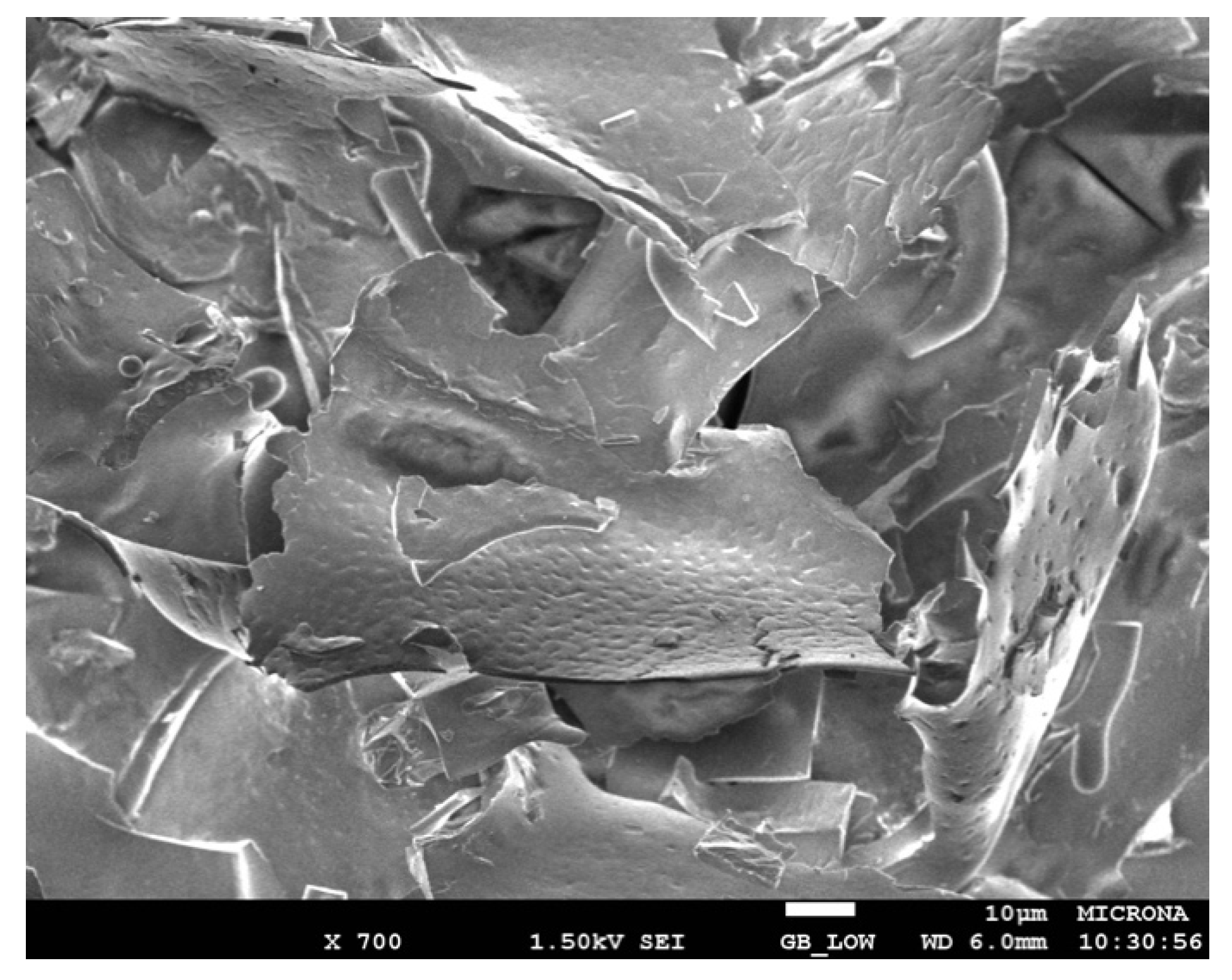
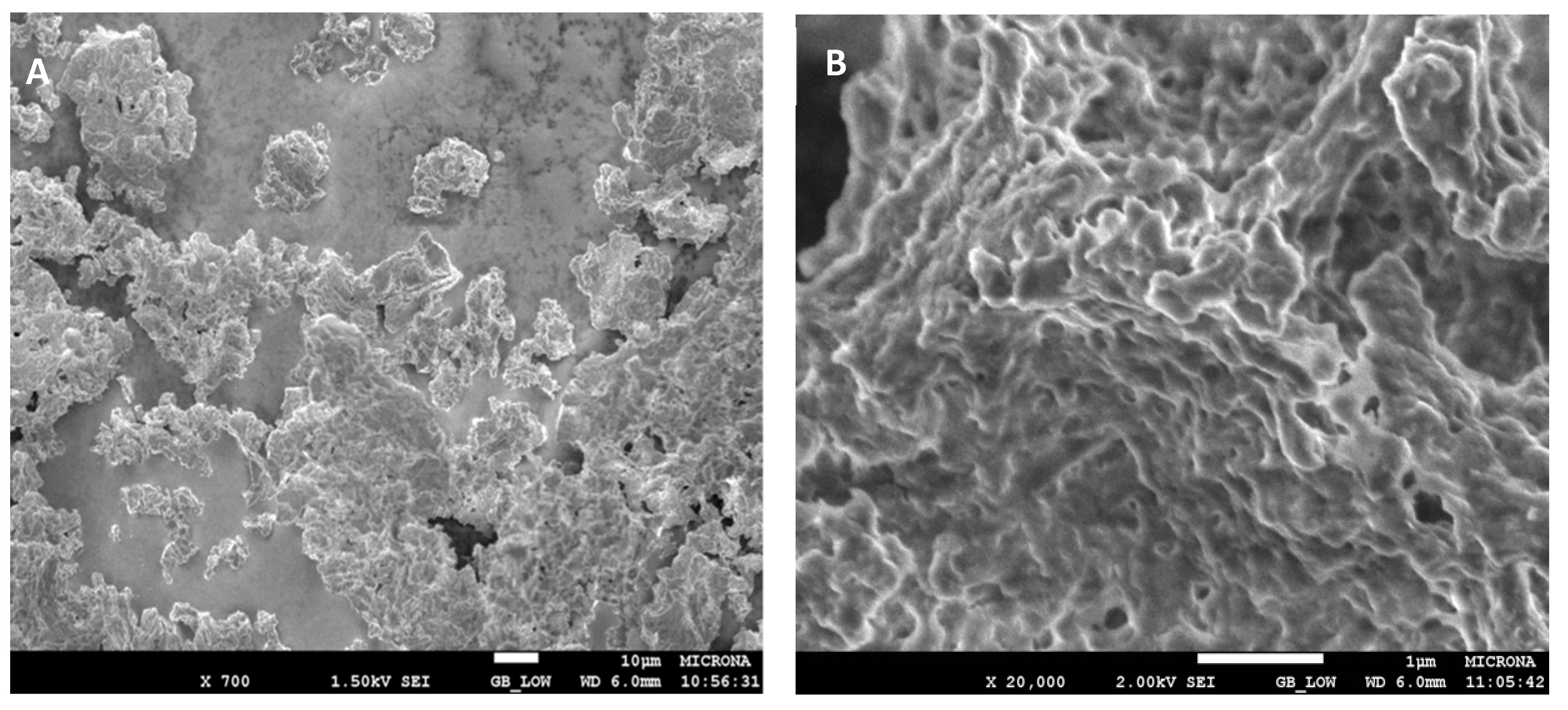
2.2.7. Morphological Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Production and Recovery of the LipMatCCR11 Lipase
3.2. Lipolytic Activity and Protein Concentration
3.3. Synthesis of the LipMatCCR11-CLEAs
3.4. Optimization of LipMatCCR11-CLEA Production
3.5. Characterization of the LipMatCCR11-CLEAs
3.5.1. Effect of pH and Temperature on Lipase Activity
3.5.2. Effect of pH and Temperature on Enzyme Stability
3.5.3. Effect of Metallic Ions and Chaotropic Agents on Enzyme Stability
3.5.4. Effect of Organic Solvents on Lipase Activity
3.5.5. Reutilization of LipMatCCR11-CLEAs
3.6. Microstructural Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Guncheva, M.; Zhiryakova, D. Catalytic properties and potential applications of Bacillus lipases. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym 2011, 68, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.; Gupta, M.N. Lipase promiscuity and its biochemical applications. Proc. Biochem. 2012, 47, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Otero, M.G.; Quintana-Castro, R.; Mora-González, P.C.; Márquez-Molina, O.; Valerio-Alfaro, G.; Oliart-Ros, R.M. Enzymatic reactions and synthesis of n-butyl caproate: Esterification, transesterification and aminolysis using a recombinant lipase from Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCR11. Environ. Technol. 2010, 10, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Park, G.D.; Patel, S.K.S.; Kondaveeti, S.; Otari, S.; Anwar, M.Z.; Kalia, V.C.; Singh, Y.; Kim, S.C.; Cho, B.K.; et al. SiO2 microparticles with carbon nanotube derived mesopores as an efficient support for enzyme immobilization. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treichel, H.; de Oliveira, D.; Mazutti, M.A.; Di Luccio, M.; Oliveira, J.V. A Review on Microbial Lipases Production. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2010, 3, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-López, C.; Godoy, C.; de Las Rivas, B.; Fernández-Lorente, G.; Palomo, J.M.; Guisán, J.M.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Martínez-Ripoll, M.; Hermoso, J.A. Activation of bacterial thermo alkalophilic lipases is spurred by dramatic structural rearrangements. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 4365–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skjold-Jorgensen, J.; Vind, J.; Moroz, O.V.; Blagova, E.; Bhatia, V.K.; Svendsen, A.; Wilson, K.S.; Bjerrum, M.J. Controlled lid-opening in Thermomyces lanuginosus lipase—An engineered switch for studying lipase function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1865, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, R.V.; Branco, R.V.; Peixoto, B.; da Silva, L.C.; Alqueres, S.M.C.; Freire, D.M.G. Immobilization of a recombinant thermostable esterase (Pf2001) from Pyrococcus furiosus on microporous polypropylene: Isotherms, hyperactivation and purification. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 39, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Lorente, G.; Cabrera, Z.; Godoy, C.; Fernández-Lafuente, R.; Palomo, J.M.; Guisán, J.M. Interfacially activated lipases against hydrophobic supports: Effect of the support nature on the biocatalytic properties. Proc. Biochem. 2008, 43, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timucin, E.; Sezerman, O.U. The Conserved Lid Tryptophan, W211, Potentiates Thermostability and Thermoactivity in Bacterial Thermoalkalophilic Lipases. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Guo, S.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. State-of-the-art protein engineering approaches using biological macromolecules: A review from immobilization to implementation viewpoint. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Wu, G.; Liu, Z. Synthesis and characterization of cross-linked enzyme aggregates of serine hydroxyl methyltransferase from Idiomerinaleihiensis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Zhang, S.; Wu, G.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, J.; Baskaran, R.; Liu, Z. Cellulose binding domain assisted immobilization of lipase (GSlip~CBD) onto cellulosic nanogel: Characterization and application in organic medium. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gricajeva, A.; Sadauskas, M.; Malunavicius, V.; Kamyab, H.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, T.; Pant, D. Microbial lipolytic enzymes—Promising energy-efficient biocatalysts in bioremediation. Energy 2020, 192, 116674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kanwar, S.S. Synthesis of ethyl ferulate in organic medium usingcelite-immobilized lipase. Biores. Technol. 2011, 102, 2162–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Galan, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Rodrigues, R.C. Potential of Different Enzyme Immobilization Strategies to Improve Enzyme Performance. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2885–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Berenguer-Murcia, B.; Carballares, D.; Morellon-Sterling, R.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Stabilization of enzymes via immobilization: Multipoint covalent attachment and other stabilization strategies. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 52, 10782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Kiyota, Y.; Miyazaki, M. Techniques for Preparation of Cross-Linked Enzyme Aggregates and Their Applications in Bioconversions. Catalysts 2018, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoevaart, R.; Wolbers, M.W.; Golubovic, M.; Ottens, M.; Kieboom, A.P.; van Rantwijk, F.; van der Wielen, L.A.; Sheldon, R.A. Preparation, optimization, and structures of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs). Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 87, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, R.A. Characteristic features and biotechnological applications of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 92, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Tailoring Multipurpose Biocatalysts via Protein Engineering Approaches: A Review. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 2204–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. Synthesis and characterization of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs) of thermostable xylanase from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans X1. Process Biochem. 2019, 80, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talekar, S.; Joshi, G.; Joshi, A.; Kamat, P. Parameters in preparation and characterization of cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs). RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 12485–12511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmod, S.S.; Yusof, F.; Jami, M.S.; Khanahmadi, S. Optimizing the preparation conditions and characterization of a stable and recyclable cross-linked enzyme aggregate (CLEA)-protease. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2016, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Migneault, I.; Dartiguenave, C.; Bertrand, M.J.; Waldron, K.C. Glutaraldehyde: Behavior in aqueous solution, reaction with proteins, and application to enzyme crosslinking. Biotechniques 2004, 37, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Zhao, C.; Ding, J.; Chen, Y.; Guo, H. Preparation of nano-enzyme aggregates by crosslinking lipase with sodium tripolyphosphate. Process Biochem. 2020, 97, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, E.; Cao, H.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Q.; Ye, Y.; He, J.; Huang, L.; Yin, D. Cross-linked protein crystals by glutaraldehyde and their applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 26163–26174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytar, B.S.; Ufuk, B. Preparation of cross-linked tyrosinase aggregates. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, F.; Kilinc, A. Crosslinked aggregates of Rhizopus oryzae lipase as industrial biocatalysts: Preparation, optimization, characterization, and application for enantioselective resolution reactions. Biotechnol. Prog. 2012, 28, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, F.; Janssen, M.H.; Hollmann, F.; Sheldon, R.A.; Kılınc, A. Improved esterification activity of Candida rugosa lipase in organic solvent by immobilization as cross-linked enzyme aggregates (CLEAs). J. Mol. Catals. B Enzym. 2011, 71, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Dutt, K.; Misra, S.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Saxena, R.K. Characterization of cross-linked immobilized lipase from thermophilic mould Thermomyces lanuginosa using glutaraldehyde. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4074–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhavathi Devi, B.L.A.; Guo, Z.; Xu, X. Characterization of Cross-Linked Lipase Aggregates. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2009, 86, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana-Castro, R.; Díaz, P.; Valerio-Alfaro, G.; García, H.S.; Oliart-Ros, R.M. Gene cloning, expression, and characterization of the Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCR11 thermoalkaliphilic lipase. Mol. Biotechnol. 2009, 42, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badillo-Zeferino, G.L.; Ruiz-López, I.I.; Oliart-Ros, R.M.; Sánchez-Otero, M.G. Improved expression and immobilization of Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCR11 thermostable recombinant lipase. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2017, 64, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SABLE. Available online: http://sable.cchmc.org/ (accessed on 23 October 2021).
- Eswar, N.; Eramian, D.; Webb, B.; Shen, M.Y.; Sali, A. Protein structure modeling with MODELLER. In Structural Proteomics: High-Throughput Methods, 1st ed.; Kobe, B., Guss, M., Huber, T., Eds.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.H.L.; Rabaça, M. Cross-linked enzyme aggregates of naringinase: Novel biocatalysts for naringin hydrolysis. Enzyme Res. 2011, 2011, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cruz, J.; Barbosa, O.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Torres, R.; Ortiz, C. Optimized preparation of CALB-CLEAs by response surface methodology: The necessity to employ a feeder to have an effective crosslinking. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2012, 80, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmod, S.S.; Yusof, F.; Jami, M.S.; Khanahmadi, S.; Shah, H. Development of an immobilized biocatalyst. with lipase and protease activities as a multipurpose cross-linked enzyme aggregate (multi-CLEA). Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 2144–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudrant, J.; Woodley, J.M.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Parameters necessary to define an immobilized enzyme preparation. Process Biochem. 2020, 90, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanahmadi, S.; Yusof, F.; Amid, A.; Mahmod, S.S.; Mahat, M.K. Optimized preparation and characterization of CLEA-lipase from cocoa pod husk. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 202, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Ochoa, L.D.; Rodríguez-Gómez, C.; Valerio-Alfaro, G.; Oliart-Ros, R.M. Screening, purification and characterization of the thermoalkaliphilic lipase produced by Bacillus thermoleovorans CCR11. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2005, 37, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Luna, G.; Sánchez-Otero, M.G.; Quintana-Castro, R.; Matus-Toledo, R.E.; Oliart-Ros, R.M. Gene Cloning and Characterization of the Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCR11 Carboxylesterase CaesCCR11, a New Member of Family XV. Mol. Biotechnol. 2016, 58, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchini, F.D.A.; Pereira, M.G.; Vici, A.C.; Filice, M.; Pessela, B.C.; Guisan, J.M.; Fernandez-Lorente, G.; Polizeli, M.D.L. Immobilization Effects on the Catalytic Properties of Two Fusarium Verticillioides Lipases: Stability, Hydrolysis, Transesterification and Enantioselectivity Improvement. Catalysts 2018, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahadevan, G.D.; Neelagund, S.E. Thermostable lipase from Geobacillus sp. Iso5: Bioseparation, characterization and native structural studies. J. Basic Microbiol. 2010, 54, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crichton, R.R. Basic coordination chemistry for biologist. In Biological Inorganic Chemistry: A New Introduction to Molecular Structure and Function, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kanmani, P.; Ramya, S.; Dhivya, R.; Iswarya, M.K.; Sree, V.N.; Subashini, D.; Swetha, K.V. Rice Bran Lipase: Partial Purification, Immobilization in Calcium Alginate Beads, Characterization and Application as a Detergent Additive. World Appl. Sci. J. 2015, 33, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.B.; Fraga, L.P.; Fleuri, L.F.; Macedo, G.A. Lipase and esterase: To what extent can this classification be applied accurately. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 31, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Ni, H.; Xiao, A.; Li, L.; Cai, H. Molecular cloning and characterization of a thermostable lipase from deep-sea thermophile Geobacillus sp. EPT9. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussamara, R.; Dall’agnol, L.; Schrank, A.; Fernandes, K.F.; Vainstein, M.H. Optimal Conditions for continuous immobilization of Pseudozyma hubeiensis (Strain HB85A) lipase by adsorption in a packed-bed reactor by response surface methodology. Enzyme Res. 2012, 2012, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussein, A.H.; Lisowsk, B.K.; Leak, D.J. The Genus Geobacillus and their Biotechnological Potential. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 92, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Muthukumar, K. Isolation of thermo-stable and solvent-tolerant Bacillus sp. lipase for the production of biodiesel. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2011, 166, 1095–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illanes, A. Enzyme Biocatalysis Principles and Applications, 1st ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; p. 391. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z. Activity and stability of cross-linked tyrosinase aggregates in aqueous and nonaqueous media, J. Biotechnol. 2011, 152, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusof, F.; Khanahmadi, S.; Amid, A.; Mahmod, S.S. Cocoa pod husk, a new source of hydrolase enzymes for preparation of cross-linked enzyme aggregate. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1621–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Run-Tian, M.; Yan-Ping, S. Recent advances on support materials for lipase immobilization and applicability as biocatalysts in inhibitors screening methods—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1101, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamwal, S.; Dharela, R.; Gupta, R.; Ahn, J.H.; Chauhan, G.S. Synthesis of crosslinked lipase aggregates and their use in the synthesis of aspirin. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 97, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zheng, P.; Ni, Y.; Sun, Z. Highly efficient biosynthesis of sucrose-6-acetate with cross-linked aggregates of Lipozyme TL 100 L. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 161, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, L.M.; Johnson, R.E.; Oldroyd, M.E.; Ahmed, S.S.; Joseph, L.; Saracovan, I.; Sinha, S. Characterizing the freeze–drying behavior of model protein formulations. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawani, N.; Rajvinder, R.; Kaur, J. Immobilization and stability studies of a lipase from thermophilic Bacillus sp.: The effect of process parameters on immobilization of enzyme. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 9, 1–7. Available online: https://scielo.conicyt.cl/pdf/ejb/v9n5/a11.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein Measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1953, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serrano, P.; Cao, L.; Van-Rantwijk, F.; Sheldon, R.A. Cross-linked enzyme aggregates with enhanced activity: Application to lipases. Biotechnol. Lett. 2002, 24, 1379–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Lin, D.; Winker, P. Uniform design: Theory and application. Technometrics 2000, 42, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Otero, M.G.; Valerio-Alfaro, G.; García-Galindo, H.S.; Oliart-Ros, R.M. Immobilization in the presence of Triton X-100: Modifications in activity and thermostability of Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCR11 lipase. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 35, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Factor | Code | Levels * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (−1) | 2 (−1/2) | 3 (0) | 4 (1/2) | 5 (1) | ||
| Protein concentration (mg/mL) | x1 | 1 | 3.25 | 5.5 | 7.75 | 10 |
| Ammonium sulfate (% sat) | x2 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| pH | x3 | 6.5 | 7.125 | 7.75 | 8.375 | 9 |
| Glutaraldehyde (mM) | x4 | 40 | 105 | 170 | 235 | 300 |
| Temperature (°C) | x5 | 4 | 9.25 | 14.5 | 19.75 | 25 |
| Incubation time (h) | x6 | 2 | 7.5 | 13 | 18.5 | 24 |
| Treatment | x1 | x2 | x3 | x4 | x5 | x6 | y (U/g) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 80 ± 22 e |
| 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 5485 ± 626 b |
| 3 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2458 ± 344 c |
| 4 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 85 ± 31 e |
| 5 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 710 ± 12 d |
| 6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 165 ± 6 de |
| 7 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 60 ± 0 e |
| 8 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 7755 ± 144 a |
| 9 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 63 ± 15 e |
| 10 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 25 ± 6 e |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliart-Ros, R.-M.; Badillo-Zeferino, G.-L.; Quintana-Castro, R.; Ruíz-López, I.-I.; Alexander-Aguilera, A.; Domínguez-Chávez, J.-G.; Khan, A.A.; Nguyen, D.D.; Nadda, A.K.; Sánchez-Otero, M.-G. Production and Characterization of Cross-Linked Aggregates of Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCR11 Thermoalkaliphilic Recombinant Lipase. Molecules 2021, 26, 7569. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247569
Oliart-Ros R-M, Badillo-Zeferino G-L, Quintana-Castro R, Ruíz-López I-I, Alexander-Aguilera A, Domínguez-Chávez J-G, Khan AA, Nguyen DD, Nadda AK, Sánchez-Otero M-G. Production and Characterization of Cross-Linked Aggregates of Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCR11 Thermoalkaliphilic Recombinant Lipase. Molecules. 2021; 26(24):7569. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247569
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliart-Ros, Rosa-María, Giselle-Lilian Badillo-Zeferino, Rodolfo Quintana-Castro, Irving-Israel Ruíz-López, Alfonso Alexander-Aguilera, Jorge-Guillermo Domínguez-Chávez, Azmat Ali Khan, Dinh Duc Nguyen, Ashok Kumar Nadda, and María-Guadalupe Sánchez-Otero. 2021. "Production and Characterization of Cross-Linked Aggregates of Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCR11 Thermoalkaliphilic Recombinant Lipase" Molecules 26, no. 24: 7569. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247569
APA StyleOliart-Ros, R.-M., Badillo-Zeferino, G.-L., Quintana-Castro, R., Ruíz-López, I.-I., Alexander-Aguilera, A., Domínguez-Chávez, J.-G., Khan, A. A., Nguyen, D. D., Nadda, A. K., & Sánchez-Otero, M.-G. (2021). Production and Characterization of Cross-Linked Aggregates of Geobacillus thermoleovorans CCR11 Thermoalkaliphilic Recombinant Lipase. Molecules, 26(24), 7569. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247569











