Alkali-Activated Hybrid Cements Based on Fly Ash and Construction and Demolition Wastes Using Sodium Sulfate and Sodium Carbonate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
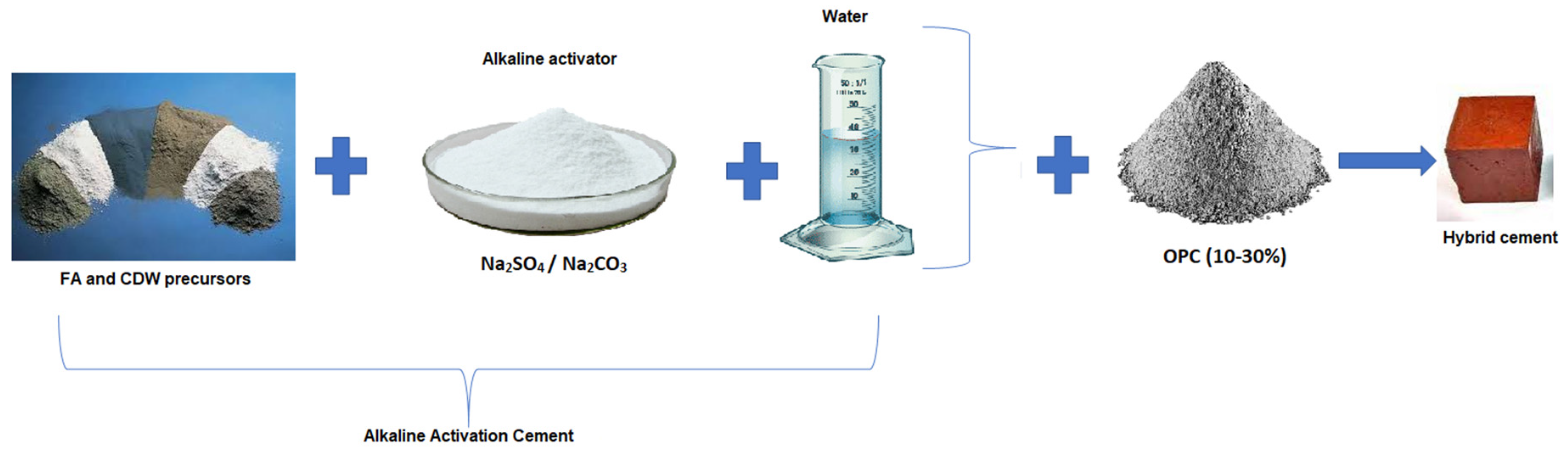
2. Materials and Experimental Methodology
- -
- Fourier transfer infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy was performed using an R-100 spectrometer (Perkin Elmer, Shelton, CT, USA) in transmittance mode with a frequency between 4000 and 450 cm−1. The samples were evaluated using compressed KBr pellets.
- -
- Scanning electron microscopy (SEM-EDS) was performed using a JSM 6490LV JEOL electron microscope (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) with an acceleration voltage of 20 kV. The samples were evaluated in low-vacuum mode with a Link-Isis X-ray spectrometer (Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, UK) coupled to the microscope.
3. Results and Analysis
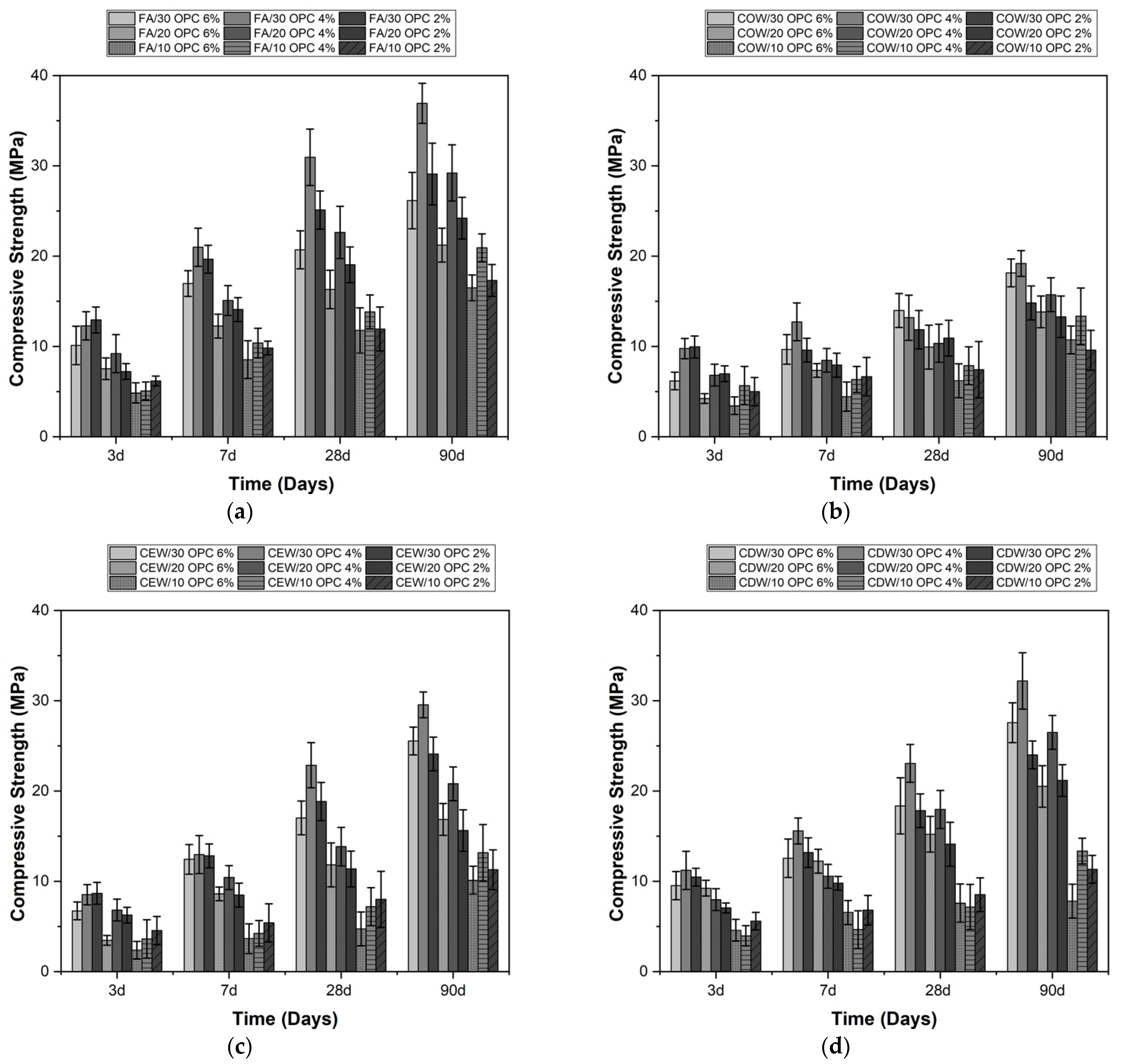
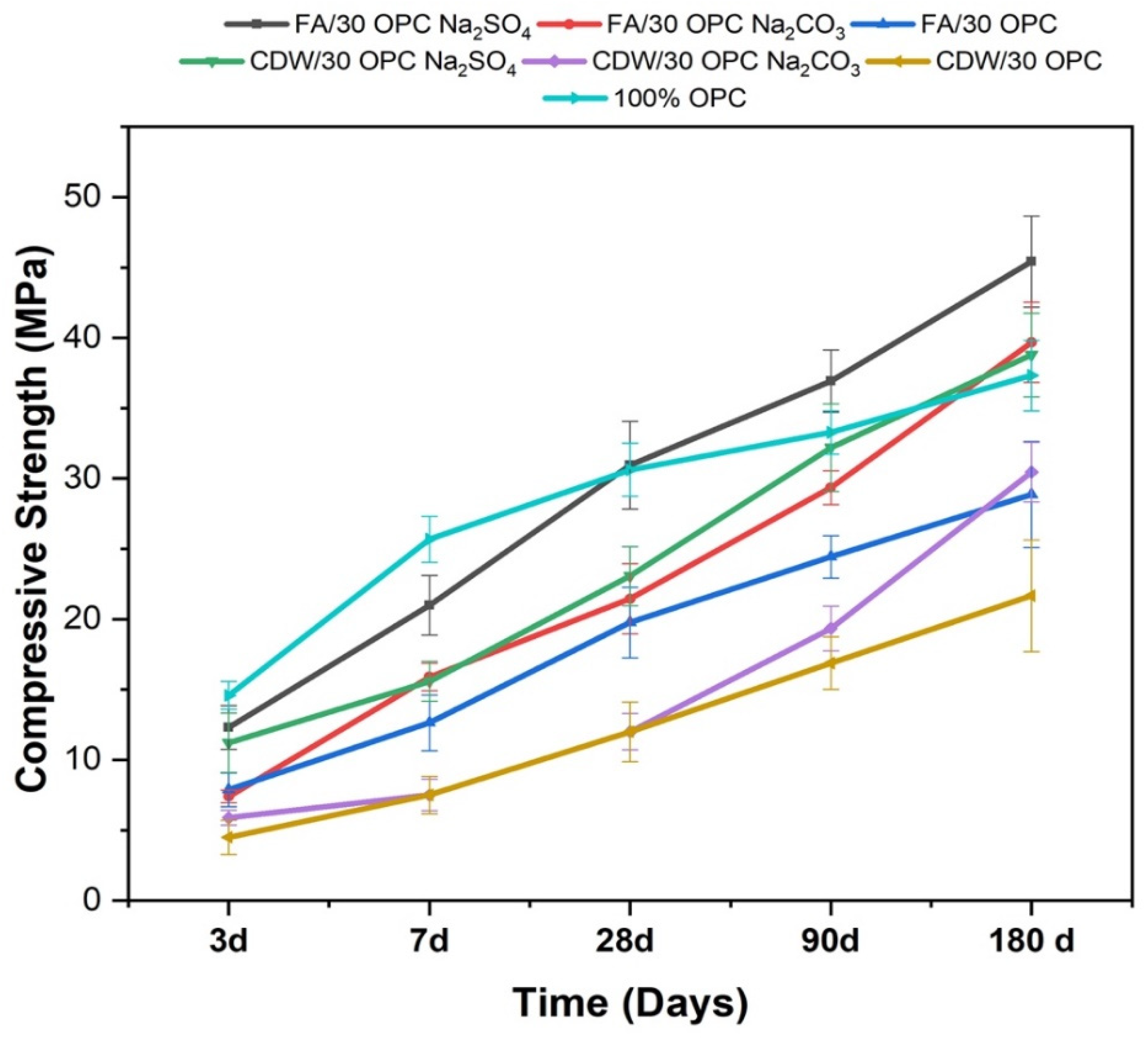
3.1. Characterization of Hybrid Cements Activated with Na2SO4 and Na2CO3
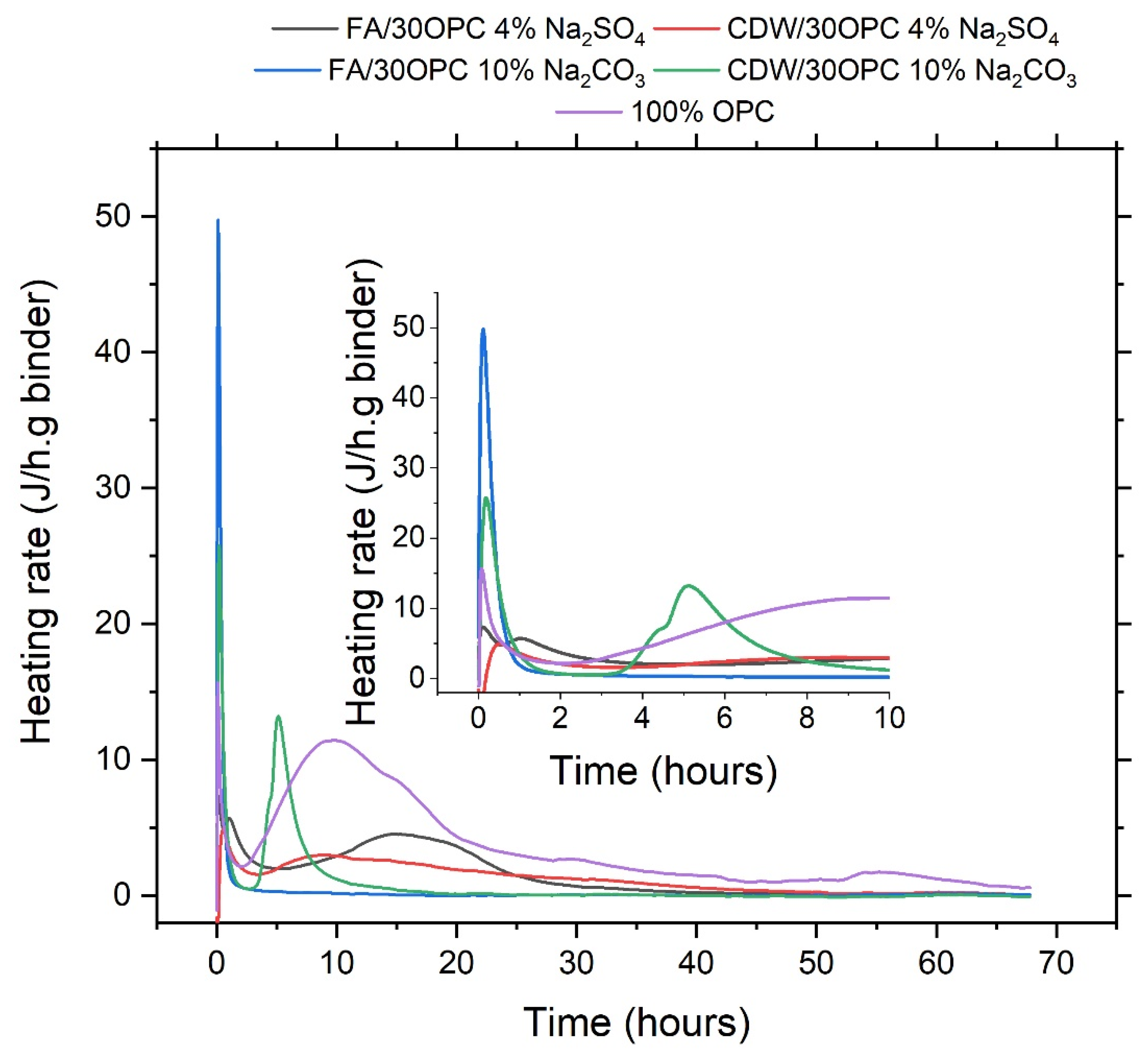
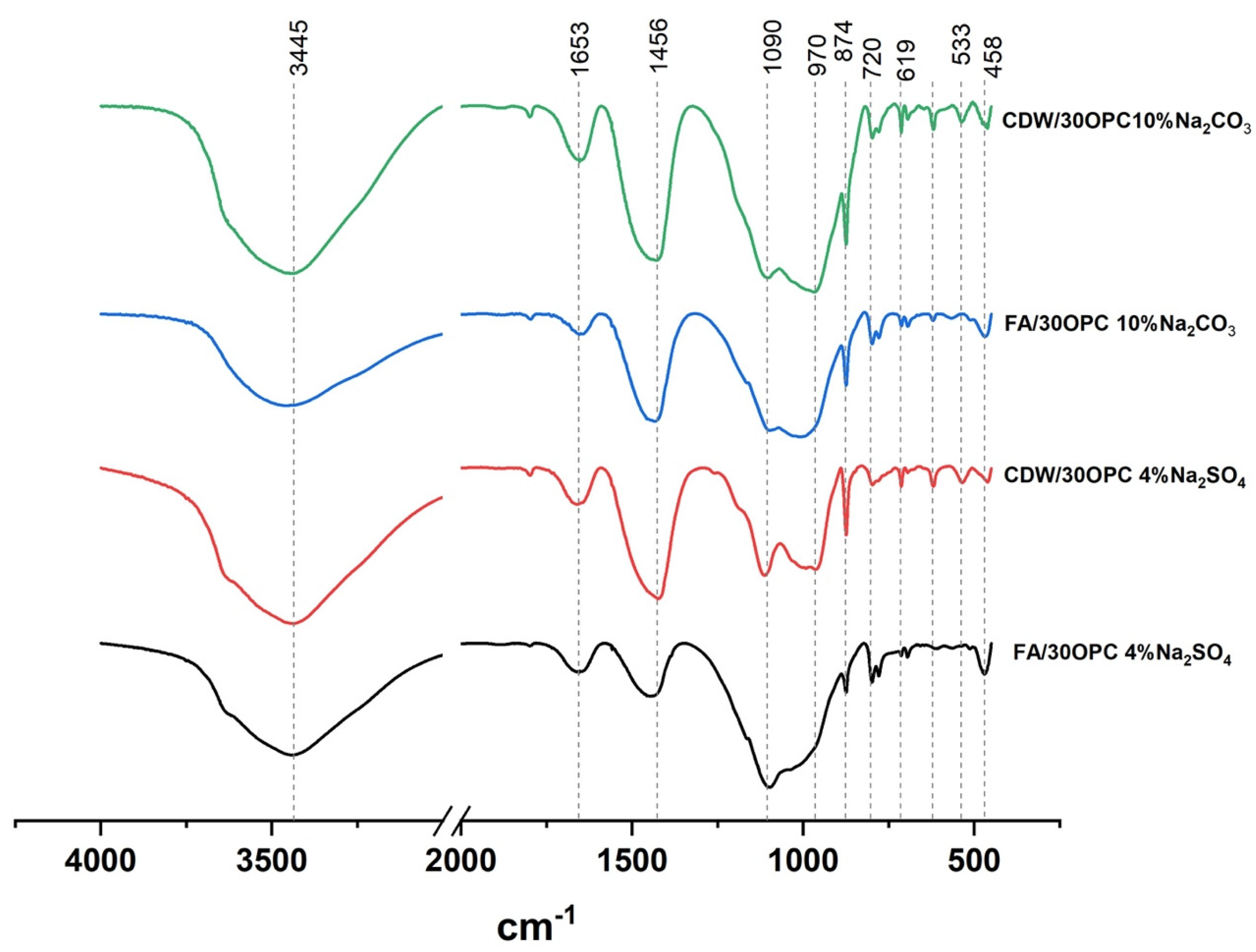
3.2. Reaction Monitoring and Characterization of Reaction Products
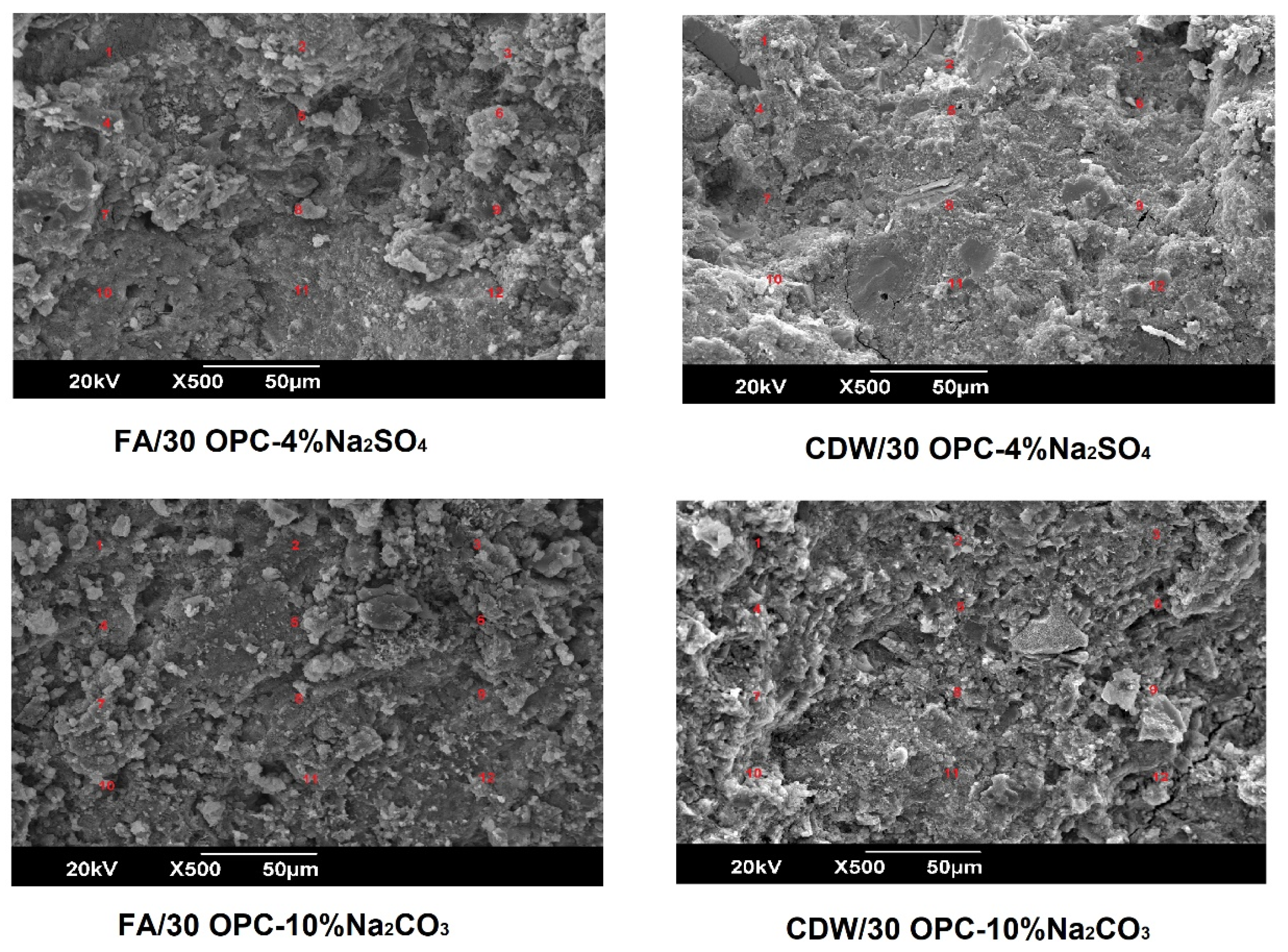
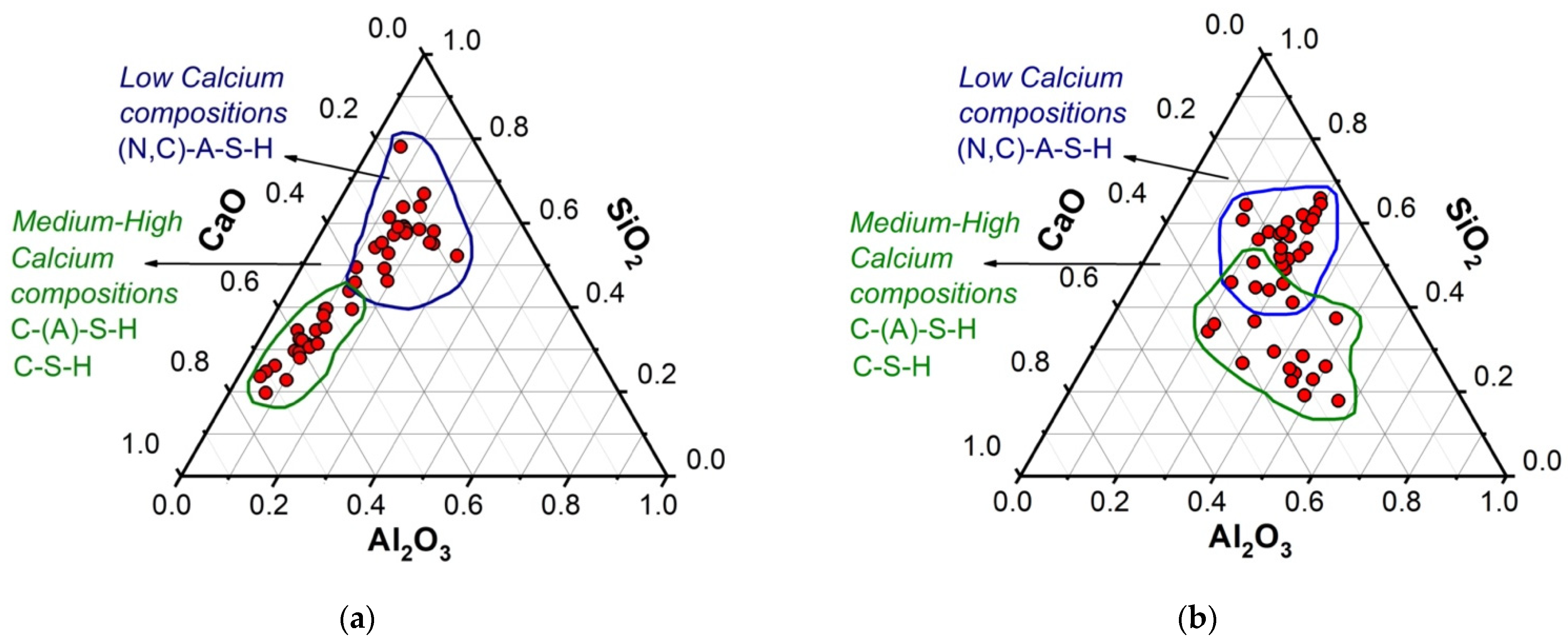
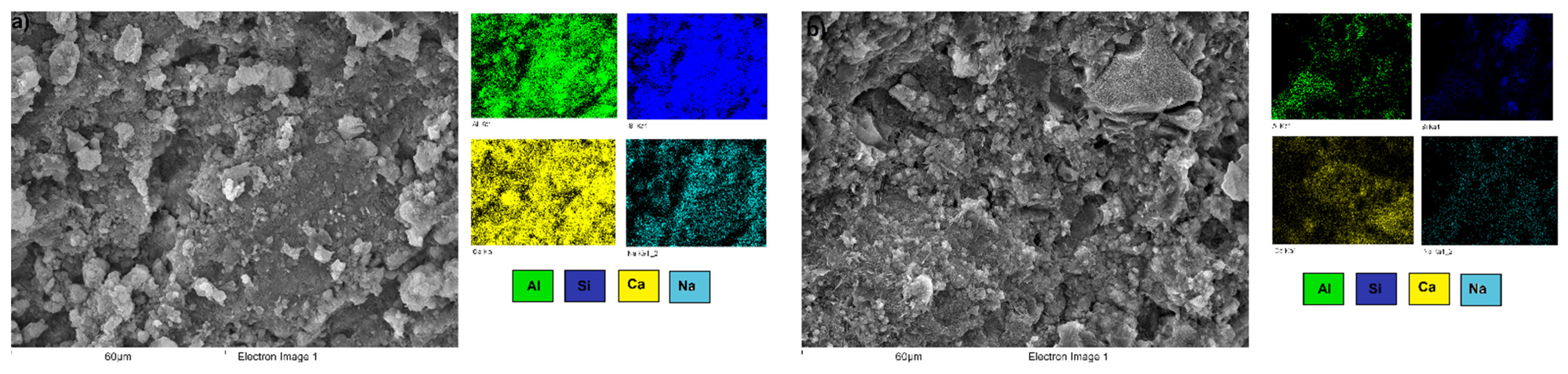
3.3. Microstructural Characterization of Alkali-Activated Hybrid Cements by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM-EDS)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adesina, A.; Rodrigue Kaze, C. Physico-mechanical and microstructural properties of sodium sulfate activated materials: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Jin, G.; Ji, T. Effect of combined activator of Ca(OH)2 and Na2CO3 on workability and compressive strength of alkali-activated ferronickel slag system. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 123, 104179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.A. Advances in near-neutral salts activation of blast furnace slags. RILEM Tech. Lett. 2016, 1, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, C.B.; Tan, L.E.; Ramli, M. Recent advances in slag-based binder and chemical activators derived from industrial by-products—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M.; Bai, Y.; Basheer, P.A.M.; Milestone, N.B.; Collier, N.C. Hydration and properties of sodium sulfate activated slag. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 37, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdalqader, A.F.; Jin, F.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Characterisation of reactive magnesia and sodium carbonate-activated fly ash/slag paste blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Z. Understanding the roles of activators towards setting and hardening control of alkali-activated slag cement. Compos. Part B 2019, 171, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Yu, Q.L.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Reaction kinetics, reaction products and compressive strength of ternary activators activated slag designed by Taguchi method. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lyu, X.; Wang, L.; Cao, X.; Liu, Q.; Zang, H. Influence of the combination of calcium oxide and sodium carbonate on the hydration reactivity of alkali-activated slag binders. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 171, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y. Preliminary study on combined-alkali–slag paste materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Alrefaei, Y.; Dai, J.G. Roles of hybrid activators in improving the early-age properties of one-part geopolymer pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 306, 124880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L.; Myers, R.J.; San Nicolas, R.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Role of carbonates in the chemical evolution of sodium carbonate-activated slag binders. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, N.T.; Hooper, T.J.N.; Unluer, C. Accelerating the reaction kinetics and improving the performance of Na2CO3-activated GGBS mixes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 126, 105927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donatello, S.; Fernández-Jimenez, A.; Palomo, A. Very High Volume Fly Ash Cements. Early Age Hydration Study Using Na2SO4 as an Activator. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhane, A.; Tweedley, S.; Kailas, S.; Marzke, R.; Neithalath, N. Mechanical and microstructural characterization of alkali sulfate activated high volume fly ash binders. Mater. Des. 2017, 122, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristelo, N.; Garcia-Lodeiro, I.; Rivera, J.F.; Miranda, T.; Palomo, A.; Coelho, J.; Fernández-Jimenez, A. One-part hybrid cements from fly ash and electric arc furnace slag activated by sodium sulphate or sodium chloride. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaquirán-Caicedo, M.A.; Mejía de Gutiérrez, R. Comparison of different activators for alkaline activation of construction and demolition wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 281, 122599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Ali, B.; Qureshi, L.A.; Aslam, H.M.U.; Hussain, I.; Masood, B.; Raza, S.S. Effect of sulfate activator on mechanical and durability properties of concrete incorporating low calcium fly ash. Case Stud. Constr. Mat. 2020, 13, e00407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Snellings, R.; Cizer, Ö. Activation of Portland cement blended with high volume of fly ash using Na2SO4. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 104, 103417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.I.E.; Campos-Venegas, K.; Gorokhovsky, A.; Fernández, A. Cementitious composites of pulverised fuel ash and blast furnace slag activated by sodium silicate: Effect of Na2O concentration and modulus. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2006, 105, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Z.; Sun, X.; Xing, J. Effect of sodium sulfate on the hydration and mechanical properties of lime-slag based eco-friendly binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalqader, A.F.; Jin, F.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Development of greener alkali-activated cement: Utilisation of sodium carbonate for activating slag and fly ash mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velandia, D.F.; Lynsdale, C.J.; Provis, J.L.; Ramirez, F.; Gomez, A.C. Evaluation of activated high volume fly ash systems using Na2SO4, lime and quicklime in mortars with high loss on ignition fly ashes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 128, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.M.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, H.K. Binder chemistry of sodium carbonate-activated CFBC fly ash. Mater. Struct. 2018, 51, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alehyen, S.; Achouri, M.E.L.; Taibi, M. Characterization, microstructure and properties of fly ash-based geopolymer. J. Mater. Env. Sci. 2017, 8, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Murillo, L.M.; Delvasto, S.; Gordillo, M. 11—A study of a hybrid binder based on alkali-activated ceramic tile wastes and portland cement. In Sustainable and Nonconventional Construction Materials Using Inorganic Bonded Fiber Composites; Savastano Junior, H., Fiorelli, J., dos Santos, S.F., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; pp. 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaquirán-Caicedo, M.A. Studying different silica sources for preparation of alternative waterglass used in preparation of binary geopolymer binders from metakaolin/boiler slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawrah, M.F.; Gado, R.A.; Feltin, N.; Ducourtieux, S.; Devoille, L. Recycling and utilization assessment of waste fired clay bricks (Grog) with granulated blast-furnace slag for geopolymer production. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 103, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robayo-Salazar, R.A.; Valencia-Saavedra, W.; Mejía de Gutiérrez, R. Construction and Demolition Waste (CDW) Recycling—As Both Binder and Aggregates—In Alkali-Activated Materials: A Novel Re-Use Concept. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Lodeiro, I.; Macphee, D.E.; Palomo, A.; Fernández-Jiménez, A. Effect of alkalis on fresh C–S–H gels. FTIR analysis. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, H.; Neithalath, N. Novel synthesis of lightweight geopolymer matrices from fly ash through carbonate-based activation. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 17, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Papale, F.; Lamanna, G.; Bollino, F. Geopolymer/PEG Hybrid Materials Synthesis and Investigation of the Polymer Influence on Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Song, J.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, L.; Qin, Y.; Liu, D.; Hou, W.; Du, N. Synthesis and thermal properties of ZnAl layered double hydroxide by urea hydrolysis. Powder Technol. 2014, 253, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panias, D.; Giannopoulou, I.P.; Perraki, T. Effect of synthesis parameters on the mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymers. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 301, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djobo, J.N.Y.; Tchakouté, H.K.; Ranjbar, N.; Elimbi, A.; Tchadjié, L.N.; Njopwouo, D. Gel Composition and Strength Properties of Alkali-Activated Oyster Shell-Volcanic Ash: Effect of Synthesis Conditions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lodeiro, I.; Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Variation in hybrid cements over time. Alkaline activation of fly ash–portland cement blends. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 52, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregziabiher, B.S.; Thomas, R.J.; Peethamparan, S. Temperature and activator effect on early-age reaction kinetics of alkali-activated slag binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega, E.A.; Cheeseman, C.; Knight, J.; Loizidou, M. Properties of alkali-activated clinoptilolite. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Material | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | SO3 | TiO2 | LOI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precursors | FA | 59.03 | 23.97 | 5.98 | 0.74 | 0.31 | 0.19 | 0.55 | 0.95 | 6.35 |
| COW | 36.13 | 8.33 | 6.78 | 28.66 | 1.85 | 0.64 | 1.16 | 0.35 | 15.94 | |
| CEW | 59.63 | 16.10 | 5.48 | 9.79 | 0.77 | 0.45 | 0.35 | 0.72 | 4,07 | |
| MAW | 59.04 | 18.42 | 7.76 | 5.37 | 2.39 | 1.05 | 0.21 | 0.80 | 2.92 | |
| CDW | 51.60 | 14.28 | 6.67 | 14.61 | 1.67 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 7.64 | |
| OPC | 19.13 | 4.42 | 4.32 | 57.70 | 1.60 | - | 2.32 | - | 9.78 | |
| Sample | Initial Setting Time (min) | Final Setting Time (min) | Heat of Reaction (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA/30OPC-4%Na2SO4 | 88 | 146 | 94.03 |
| CDW/30OPC-4%Na2SO4 | 350 | 570 | 80.13 |
| FA/30OPC-10%Na2CO3 | 90 | 116 | 24.90 |
| CDW/30OPC-10%Na2CO3 | 92 | 115 | 53.70 |
| 100% OPC | - | - | 234.62 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valencia-Saavedra, W.; Robayo-Salazar, R.; Mejía de Gutiérrez, R. Alkali-Activated Hybrid Cements Based on Fly Ash and Construction and Demolition Wastes Using Sodium Sulfate and Sodium Carbonate. Molecules 2021, 26, 7572. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247572
Valencia-Saavedra W, Robayo-Salazar R, Mejía de Gutiérrez R. Alkali-Activated Hybrid Cements Based on Fly Ash and Construction and Demolition Wastes Using Sodium Sulfate and Sodium Carbonate. Molecules. 2021; 26(24):7572. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247572
Chicago/Turabian StyleValencia-Saavedra, William, Rafael Robayo-Salazar, and Ruby Mejía de Gutiérrez. 2021. "Alkali-Activated Hybrid Cements Based on Fly Ash and Construction and Demolition Wastes Using Sodium Sulfate and Sodium Carbonate" Molecules 26, no. 24: 7572. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247572
APA StyleValencia-Saavedra, W., Robayo-Salazar, R., & Mejía de Gutiérrez, R. (2021). Alkali-Activated Hybrid Cements Based on Fly Ash and Construction and Demolition Wastes Using Sodium Sulfate and Sodium Carbonate. Molecules, 26(24), 7572. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26247572








