Structure Controlling Factors of Oxido-Bridged Dinuclear Iron(III) Complexes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Preparation of Complexes, 1, 2, and 3
2.2. Crystal Structures of Complexes, 1, 2, and 3
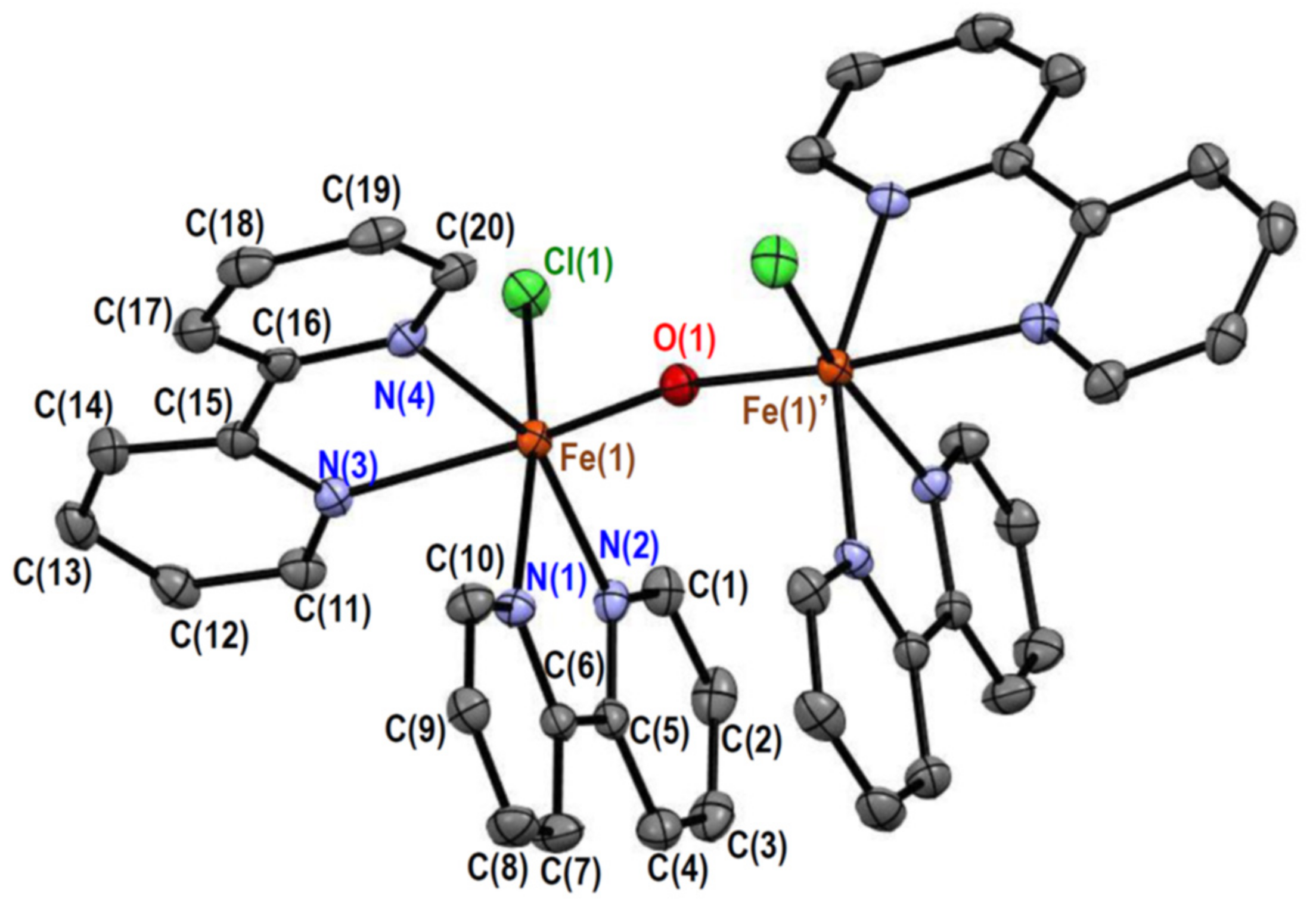
2.2.1. Crystal Structures of [Fe2OCl2(bpy)4][PF6]2 (1)
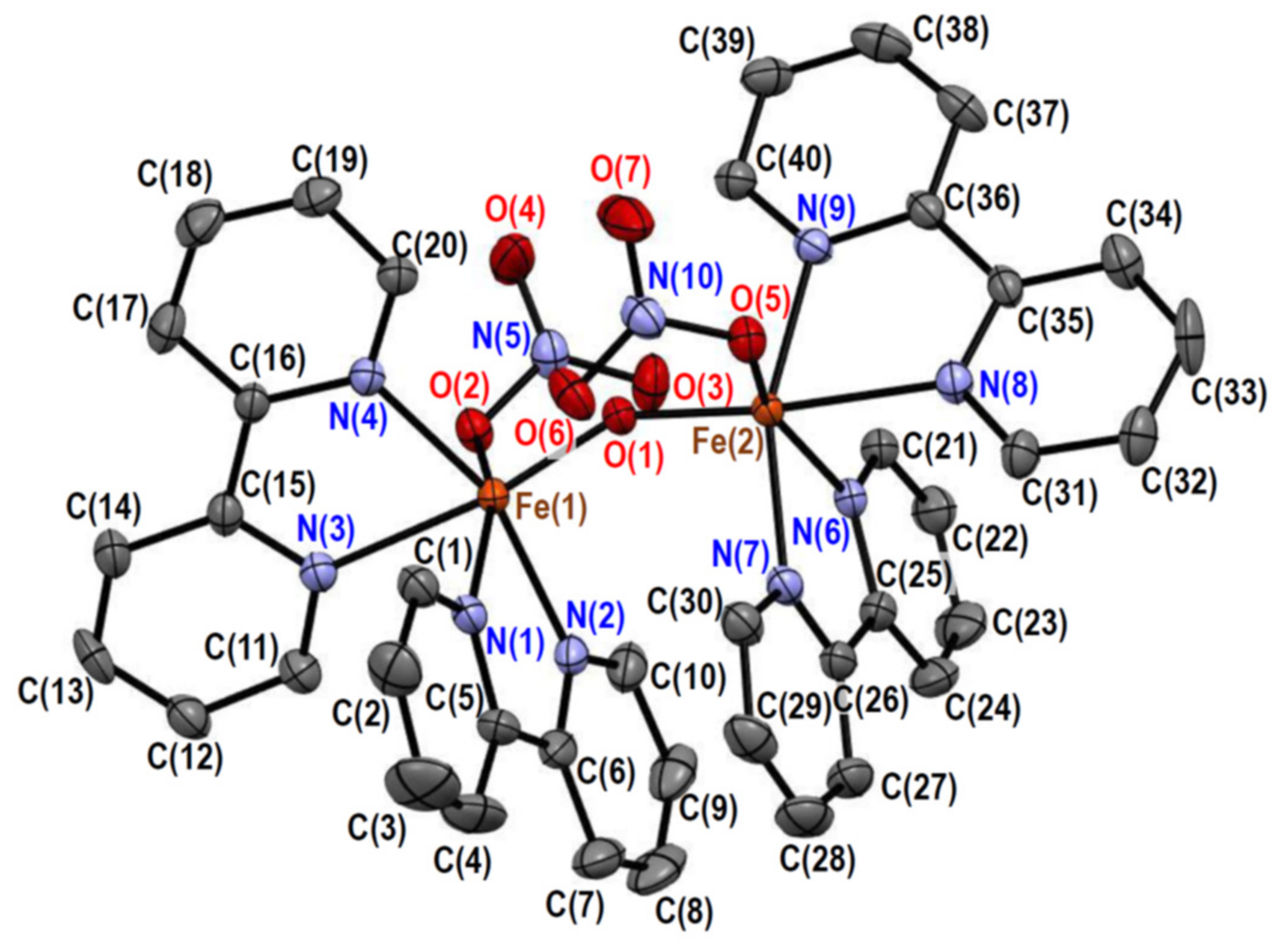
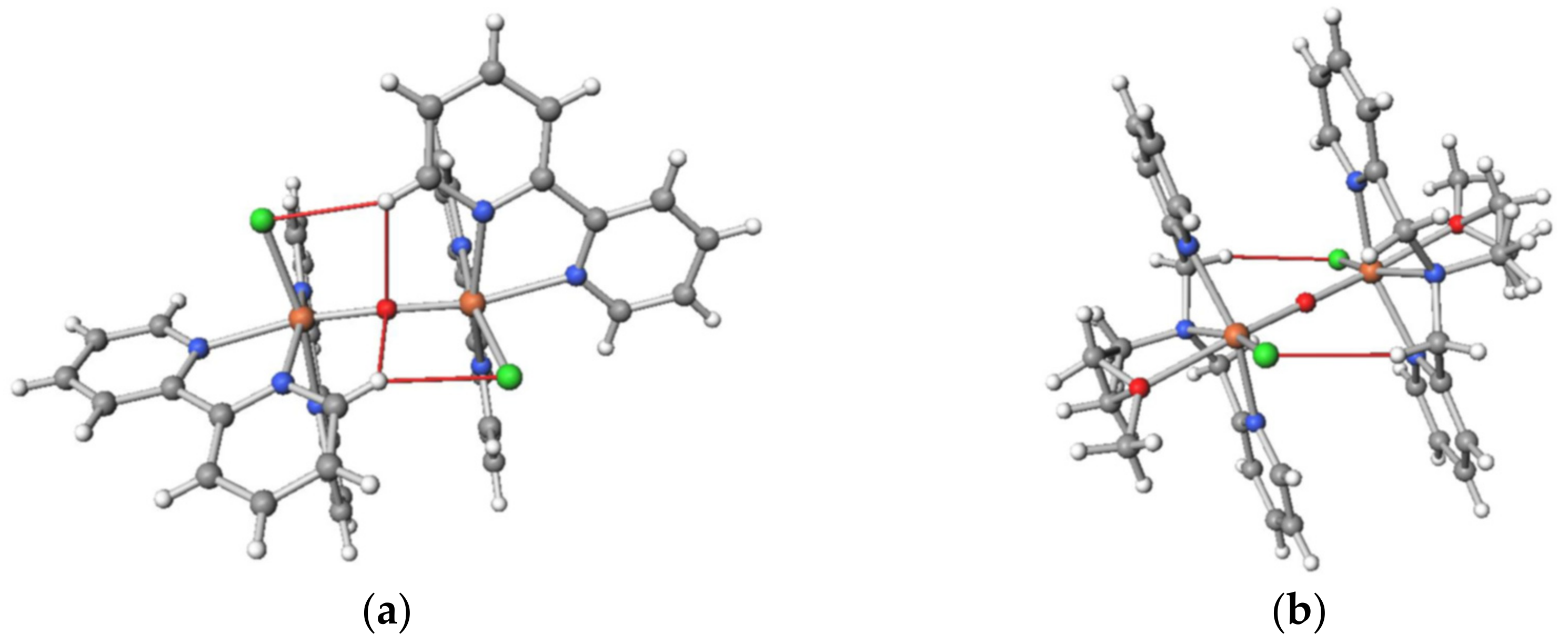
2.2.2. Crystal Structures of [Fe2O(NO3)2(bpy)4][PF6]2·0.6MeCN·0.2(2-PrOH) (2)
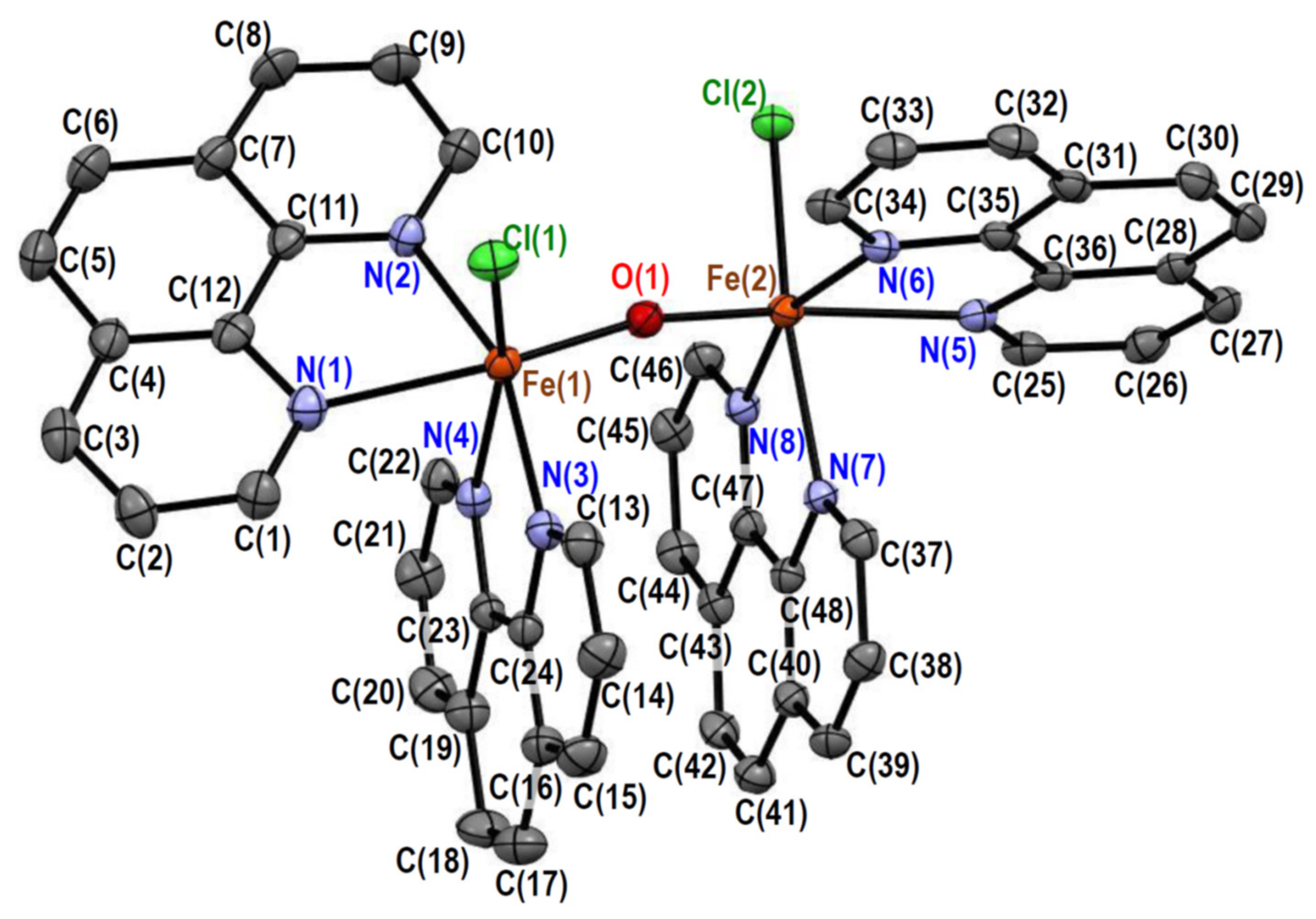
2.2.3. Crystal Structures of [Fe2OCl2(phen)4][PF6]2·MeCN·0.5H2O (3)
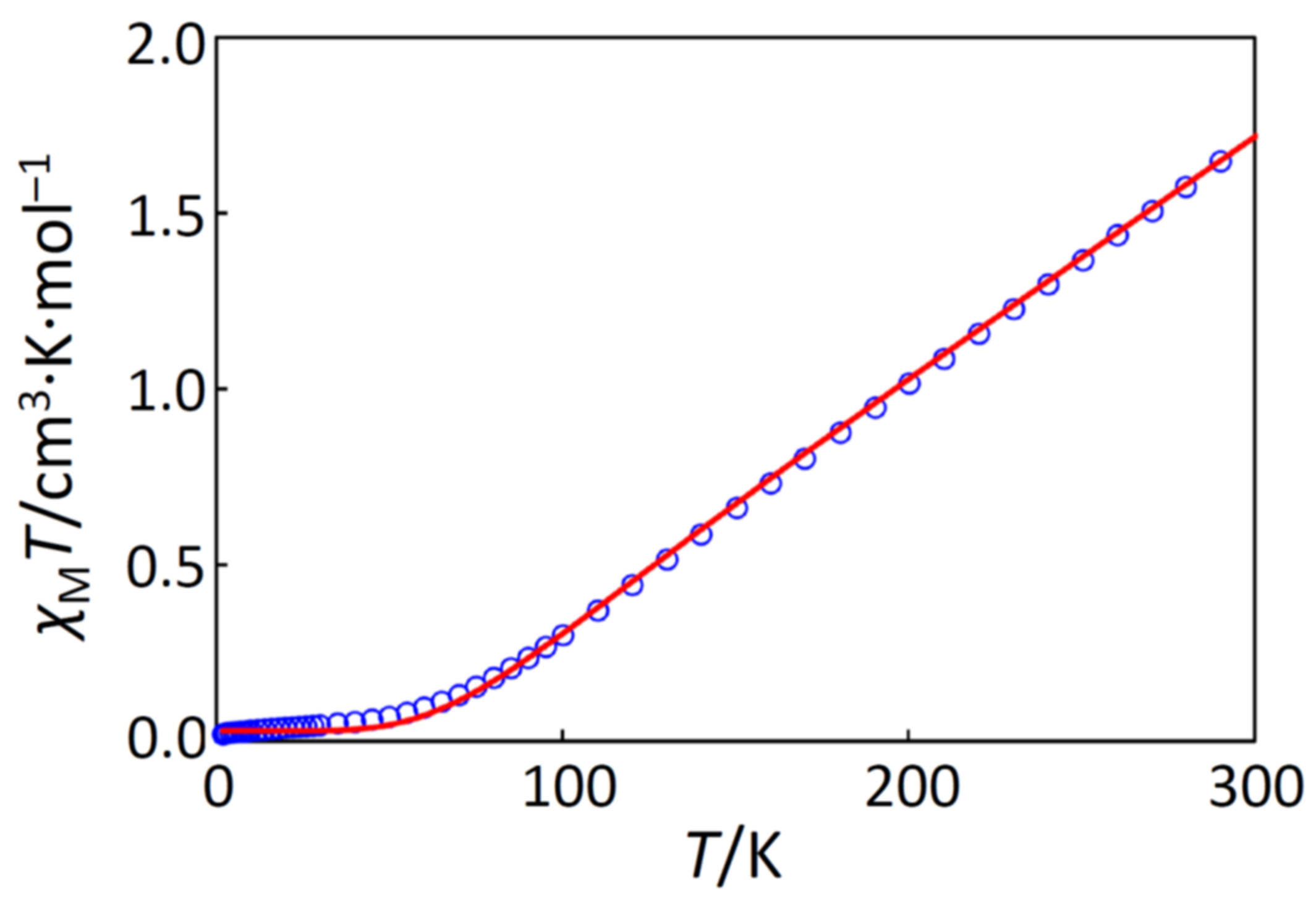
2.3. Magnetic Properties of Complexes, 1, 2, and 3
2.4. Electronic Spectra of Complexes, 1, 2, and 3
2.5. Factors in Controlling the Structures
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Measurements
3.2. Materials
3.3. Preparations
3.4. Crystallography
3.5. Computation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knight, R.J.; Sylva, R.N. Precipitation in hydrolysed iron (III) solutions. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1974, 36, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, A.F.; Venturelli, P. In situ study of the goethite-hematite phase transformation by real time synchrotron powder diffraction. Am. Mineral. 1999, 84, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Baik, M.-H.; Gherman, B.F.; Guallar, V.; Wirstam, M.; Murphy, R.B.; Lippard, S.J. How iron-containing proteins control dioxygen chemistry: A detailed atomic level description via accurate quantum chemical and mixed quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics calculations. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 238–239, 267–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, R.; Kawabata, T.; Sutoh, Y.; Nishida, N.; Okada, S. Oxidative renal tubular injuries induced by aminocarboxylate-type iron (III) coordination compounds as candidate renal carcinogens. Biometals 2006, 19, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooijman, H.; Son, M.; Tanase, S.; Bouwman, E.; Reedijk, J.; Spek, A.L. μ-Oxo-bis{chloro[N-(2-methoxyethyl)-N,N-bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine-κ4-N,N’,N”,O] iron(III)} bis(trifluoromethanesulfonate)acetonitrile disolvate. Acta Cryst. 2005, E61, m1042–m1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.F.; Tan, X.S.; Zhang, S.W.; Han, Y.; Yu, K.B.; Tang, W.X. Synthesis, crystal structure and properties of [Fe2O(bipy)4C12](ClO4)2·0.25CH3CN·0.25CH3OH·0.25H2O, a μ-Oxo diiron(III) complex. Polyhedron 1998, 17, 2095–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Okuno, T.; Itoh, H.; Ohba, S.; Matsushima, H.; Tokii, T.; Nishida, Y. Chemical basis for high activity in oxygenation of cyclohexane catalyzed by dinuclear iron(III) complexes with ethereal oxygen containing ligand and hydrogen peroxide system. Z. Naturforsch. 1997, 52b, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Okuno, T.; Matsushima, H.; Tokii, T.; Nishida, Y. Chemical origin of high activity in oxygenation of cyclohexane by H2O2 catalysed bydinuclear iron(III) complexes with amide-containing ligands. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1996, 4479–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, A.; Jensen, K.B.; McKenzie, C.J.; Toftlund, H. Synthesis and reactivity of (μ-oxo)diiron(III) complexes of tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine. X-ray crystal structures of [tpa(OH)FeOFe(H2O)tpa](C1O4)3 and [tpa(Cl)FeOFe(Cl)tpa](C1O4)2. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 3127–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.R.; Allen, F.H.; Brown, I.D. The crystallographic information file (CIF): A new standard archive file for crystallography. Acta Cryst. 1991, A47, 655–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, R.N.; Stack, T.D.P.; Holm, R.H. Angle dependence of the properties of the [Fe2X]4+ bridge unit (X = O, S): Structures, antiferromagnetic coupling, and properties in solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 1850–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, S.H.; Pawlik, M.J.; Skowyra, J.; Kennedy, J.R.; Anderson, O.P.; Spartalian, K.; Dye, J.L. Comparison of the molecular and electronic structures of (μ-oxo)bis[(5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrinato)iron(III)] and (μ-oxo)bis[(7,8-dihydro-5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrinato)iron(III)]. Inorg. Chem. 1987, 26, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowman, J.E.; Loehr, T.M.; Schauer, C.K.; Anderson, O.P. Crystal and molecular structure of the (μ-oxo)bis[aquobis(phenanthroline)iron(III)] complex, a Raman spectroscopic model for the binuclear iron site in hemerythrin and ribonucleotide reductase. Inorg. Chem. 1984, 23, 3553–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiff, W.M.; Baker, W.A., Jr.; Erickson, N.E. Binuclear, oxygen-bridged complexes of iron(III). New iron(III)-2,2′,2″-terpyridine complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1968, 90, 4794–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippard, S.J.; Schugar, H.J.; Walling, C. The crystal and molecular structure of an oxo-bridged binuclear iron(III) complex, [(HEDTA)FeOFe(HEDTA)]2−. Inorg. Chem. 1967, 6, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, E.; Hawkinson, S. The structure of two seven-coordinate complexes of iron(III). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 720–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzyaloshinsky, I. A thermodynamic theory of “weak” ferromagnetism of antiferromagnetics. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1958, 4, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, T. Theory of magnetism of NiF2. Phys. Rev. 1960, 117, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshikawa, R.; Mitsuhashi, R.; Mikuriya, M.; Sakiyama, H. Crystal structure of a mononuclear iron(II) complex, tris(1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N,N’)iron(II) bis(hexafluoridophosphate). X-ray Struct. Anal. Online 2019, 35, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorun, S.M.; Lippard, S.J. Magnetostructural correlations in magnetically coupled (μ-oxo)diiron(III) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 1991, 30, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, W.J. The use of conductivity measurements in organic solvents for the characterisation of coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 7, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäffer, C.E. The angular overlap model of the ligand field: Theory and applications. Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 24, 361–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, R.E.; Holz, R.C.; Menage, S.; O’Connor, C.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Que, L., Jr. Structures and properties of dibridged (μ-oxo)diiron(III) complexes. Effects of the Fe-O-Fe angle. Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, 4629–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reem, R.C.; McCormick, J.M.; Richardson, D.E.; Devlin, F.J.; Stephens, P.J.; Musselman, R.L.; Solomon, E.I. Spectroscopic studies of the coupled binuclear ferric active site in methemerythrins and oxyhemerythrin: The electronic structure of each iron center and the iron-oxo and iron-peroxide Bonds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 4688–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, R.L.; Hessevick, R.E.; Zoltai, T.; Finger, L.W. Refinement of the hematite structure. Am. Mineral. 1966, 51, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. Sect. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. Sect. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.W.; Baldridge, K.K.; Boatz, J.A.; Elbert, S.T.; Gordon, M.S.; Jensen, J.H.; Koseki, S.; Matsunaga, N.; Nguyen, K.A.; Su, S.; et al. General atomic and molecular electronic structure system. J. Comput. Chem. 1993, 14, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.S.; Schmidt, M.W. Advances in Electronic Structure Theory; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tawada, Y.; Tsuneda, T.; Yanagisawa, S.; Yanai, T.; Hirao, K. A long-range-corrected time-dependent density functional theory. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 8425–8433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Atom–Atom 1 | Distance/Å | Atom–Atom | Distance/Å |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe(1)–Cl(1) | 2.3119(5) | Fe(1)–O(1) | 1.7819(3) |
| Fe(1)–N(1) | 2.2169(15) | Fe(1)–N(2) | 2.1446(15) |
| Fe(1)–N(3) | 2.2279(15) | Fe(1)–N(4) | 2.1357(15) |
| Fe(1)···Fe(1)′ | 3.5407(5) |
| Atom–Atom–Atom | Angle/° | Atom–Atom–Atom | Angle/° |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cl(1)–Fe(1)–O(1) | 99.35(4) | Cl(1)–Fe(1)–N(1) | 166.69(4) |
| Cl(1)–Fe(1)–N(2) | 97.75(4) | Cl(1)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 86.33(4) |
| Cl(1)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 97.71(4) | O(1)–Fe(1)–N(1) | 92.71(5) |
| O(1)–Fe(1)–N(2) | 99.01(6) | O(1)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 168.39(5) |
| O(1)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 94.71(6) | N(1)–Fe(1)–N(2) | 74.65(6) |
| N(1)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 82.83(5) | N(1)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 86.81(6) |
| N(2)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 90.17(5) | N(2)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 157.33(6) |
| N(3)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 74.40(6) | Fe(1)–O(1)–Fe(1)′ | 166.95(11) |
| Atom–Atom | Distance/Å | Atom–Atom | Distance/Å |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe(1)–O(1) | 1.792(19) | Fe(1)–O(2) | 2.028(2) |
| Fe(1)–N(1) | 2.167(2) | Fe(1)–N(2) | 2.135(3) |
| Fe(1)–N(3) | 2.247(2) | Fe(1)–N(4) | 2.131(2) |
| Fe(2)–O(1) | 1.791(19) | Fe(2)–O(5) | 2.021(2) |
| Fe(2)–N(6) | 2.166(2) | Fe(2)–N(7) | 2.128(2) |
| Fe(2)–N(8) | 2.228(2) | Fe(2)–N(9) | 2.120(2) |
| Fe(1)···Fe(2) | 3.4729(5) |
| Atom–Atom–Atom | Angle/° | Atom–Atom–Atom | Angle/° |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(1)–Fe(1)–O(2) | 99.96(9) | O(1)–Fe(1)–N(1) | 101.14(10) |
| O(1)–Fe(1)–N(2) | 100.97(9) | O(1)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 170.72(9) |
| O(1)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 96.46(9) | O(2)–Fe(1)–N(1) | 158.06(9) |
| O(2)–Fe(1)–N(2) | 94.65(10) | O(2)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 80.20(9) |
| O(2)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 91.38(9) | N(1)–Fe(1)–N(2) | 75.51(10) |
| N(1)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 79.94(9) | N(1)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 92.15(9) |
| N(2)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 88.24(9) | N(2)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 160.25(9) |
| N(3)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 74.27(9) | O(1)–Fe(2)–O(5) | 101.38(9) |
| O(1)–Fe(2)–N(6) | 98.66(9) | O(1)–Fe(2)–N(7) | 98.77(9) |
| O(1)–Fe(2)–N(8) | 172.76(9) | O(1)–Fe(2)–N(9) | 98.07(9) |
| O(5)–Fe(2)–N(6) | 159.31(9) | O(5)–Fe(2)–N(7) | 95.86(9) |
| O(5)–Fe(2)–N(8) | 80.12(9) | O(5)–Fe(2)–N(9) | 92.21(9) |
| N(6)–Fe(2)–N(7) | 75.94(9) | N(6)–Fe(2)–N(8) | 80.64(9) |
| N(6)–Fe(2)–N(9) | 90.02(9) | N(7)–Fe(2)–N(8) | 88.07(9) |
| N(7)–Fe(2)–N(9) | 159.49(9) | N(8)–Fe(2)–N(9) | 74.75(9) |
| Fe(1)–O(1)–Fe(2) | 151.44(12) |
| Atom–Atom | Distance/Å | Atom–Atom | Distance/Å |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe(1)–Cl(1) | 2.3315(10) | Fe(1)–O(1) | 1.791(2) |
| Fe(1)–N(1) | 2.246(3) | Fe(1)–N(2) | 2.134(3) |
| Fe(1)–N(3) | 2.156(3) | Fe(1)–N(4) | 2.192(3) |
| Fe(2)–Cl(2) | 2.297(10) | Fe(2)–O(1) | 1.786(2) |
| Fe(2)–N(5) | 2.283(3) | Fe(2)–N(6) | 2.137(3) |
| Fe(2)–N(7) | 2.212(3) | Fe(2)–N(8) | 2.165(3) |
| Fe(1)···Fe(2) | 3.5501(7) |
| Atom–Atom–Atom | Angle/° | Atom–Atom–Atom | Angle/° |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cl(1)–Fe(1)–O(1) | 100.59(8) | Cl(1)-Fe(1)–N(1) | 88.26(7) |
| Cl(1)–Fe(1)–N(2) | 93.74(8) | Cl(1)-Fe(1)–N(3) | 94.93(8) |
| Cl(1)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 167.13(8) | O(1)-Fe(1)–N(1) | 167.95(11) |
| O(1)–Fe(1)–N(2) | 95.65(11) | O(1)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 98.64(11) |
| O(1)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 90.06(10) | N(1)–Fe(1)–N(2) | 75.45(11) |
| N(1)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 88.63(10) | N(1)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 82.32(10) |
| N(2)–Fe(1)–N(3) | 161.61(11) | N(2)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 92.37(10) |
| N(3)–Fe(1)–N(4) | 76.16(10) | Cl(2)–Fe(2)–O(1) | 101.91(8) |
| Cl(2)–Fe(2)–N(5) | 86.96(8) | Cl(2)–Fe(2)–N(6) | 95.77(9) |
| Cl(2)–Fe(2)–N(7) | 162.27(8) | Cl(2)–Fe(2)–N(8) | 93.54(8) |
| O(1)–Fe(2)–N(5) | 166.51(11) | O(1)–Fe(2)–N(6) | 94.16(11) |
| O(1)–Fe(2)–N(7) | 94.29(11) | O(1)–Fe(2)–N(8) | 102.05(11) |
| N(5)–Fe(2)–N(6) | 74.67(11) | N(5)–Fe(2)–N(7) | 78.49(11) |
| N(5)–Fe(2)–N(8) | 87.34(11) | N(6)–Fe(2)–N(7) | 90.14(11) |
| N(6)–Fe(2)–N(8) | 159.21(11) | N(7)–Fe(2)–N(8) | 75.87(11) |
| Fe(1)–O(1)–Fe(2) | 165.87(15) |
| Complex | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| J/cm–1 | –205 | –205 | –207 |
| g (fixed) | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| TIP/cm3·mol–1 (fixed) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ρ | 0.0017 | 0.0011 | 0.0035 |
| Component | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9410 (3.74) | 9870 (18.4) | 9370 (2.21) |
| 2 | 11,000 (7.53) | 12,100 (11.4) | 10,900 (6.78) |
| 3 | 16,400 (87.9) | 16,100 (171) | 17,200 (91.5) |
| 4 | 18,500 (103) | 17,800 (179) | 19,000 (88.0) |
| 5 | 21,400 (320) | 20,900 (683) | 20,200 (438) |
| 6 | 23,700 (683) | ||
| 7 | 25,800 (3940) | 26,300 (2370) | 25,300 (5150) |
| 8 | 30,100 (10,800) | 31,000 (10,600) | 30,700 (5020) |
| 9 | 32,300 (2680) 35,200 (49,600) | 32,200 (4410) 35,500 (53,800) | 34,500 (24,100) 37,700 (92,400) |
| 10 | 39,100 (28,300) | 39,100 (28,900) | |
| 11 | 40,800 (14,700) 42,500 (53,800) | 40,800 (17,700) 42,600 (64,400) | 44,200 (110,000) |
| Parameter/Term | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 804 | 867 | 966 |
| C | 3500 | 3500 | 2940 |
| eσ,av1 | 5790 | 5960 | 5200 |
| 6A1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2T2 | 9410 | 9870 | 9370 |
| 4T1 | 11,000 | 12,100 | 10,900 |
| 4T2 | 16,400 | 16,100 | 17,200 |
| 2A2 | 23,100 | 28,400 | 21,600 |
| 2T1 | 23,400 | 28,500 | 22,000 |
| 2T2 | 25,100 | 30,100 | 23,800 |
| 4A1 | 25,600 | 30,900 | 24,400 |
| 2E | 27,000 | 32,000 | 25,600 |
| 4T2 | 28,300 | 32,700 | 28,000 |
| 4E | 31,200 | 35,000 | 31,100 |
| 2T1 | 32,000 | 35,600 | 31,300 |
| Parameter/Term | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| B | 739 | 547 | 864 |
| C | 3830 | 5220 2 | 3390 |
| eσ,av1 | 9440 | 11400 | 8980 |
| 2T2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6A1 | 9410 | 9870 | 9370 |
| 4T1 | 11,000 | 12,100 | 10,900 |
| 4T2 | 16,400 | 16,100 | 17,200 |
| 2A2 | 24,000 | 28,900 | 22,800 |
| 2T1 | 24,300 | 29,100 | 23,100 |
| 2T2 | 26,200 | 30,700 | 25,300 |
| Complex | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C40H32Cl2F12Fe2N8OP2 | C41.8H35.4F12Fe2N10.6O7.2P2 | C50H36Cl2F12Fe2N9O1.5P2 |
| Formula weight | 1113.27 | 1203.04 | 1259.42 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Triclinic | Triclinic |
| Space group | C2/c | P | P |
| a/Å | 24.5777(8) | 12.7471(2) | 12.0156(8) |
| b/Å | 9.6680(3) | 13.6863(3) | 13.0997(8) |
| c/Å | 18.2923(5) | 14.9623(3) | 17.0918(11) |
| α/° | 90 | 75.554(2) | 99.7840(10) |
| β/° | 102.781(3) | 78.197(2) | 97.4510(10) |
| γ/° | 90 | 76.516(2) | 104.7590(10) |
| V/Å3 | 4238.9(2) | 2428.25(9) | 2521.1(3) |
| Z | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| Crystal dimensions/mm | 0.125 × 0.074 × 0.045 | 0.190 × 0.180 × 0.070 | 0.400 × 0.340 × 0.220 |
| T/K | 105 | 102 | 90 |
| λ/Å | 0.71073 | 0.71073 | 0.71073 |
| ρcalcd/g·cm−3 | 1.744 | 1.645 | 1.659 |
| µ/mm−1 | 0.985 | 0.771 | 0.841 |
| F(000) | 2240 | 1216 | 1270 |
| 2θmax/◦ | 55 | 57 | 55 |
| No. of reflections measured | 15,350 | 61,890 | 15,982 |
| No. of independent reflections | 4853 (Rint = 0.0268) | 12079 (Rint = 0.0403) | 11291 (Rint = 0.0165) |
| Data/restraints/parameters | 4853/0/303 | 12,079/240/790 | 11,291/0/783 |
| R1 1 [I > 2.00 σ(I)] | 0.0306 | 0.0534 | 0.0522 |
| wR2 2 (all reflections) | 0.0780 | 0.1609 | 0.1265 |
| Goodness of fit indicator | 1.039 | 1.064 | 1.126 |
| Highest peak, deepest hole/e Å−3 | 0.393, −0.334 | 1.690, −0.634 | 0.855, −0.496 |
| CCDC deposition number | 2052873 | 2052876 | 2052878 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoshikawa, R.; Yoshida, K.; Mitsuhashi, R.; Mikuriya, M.; Okuno, T.; Sakiyama, H. Structure Controlling Factors of Oxido-Bridged Dinuclear Iron(III) Complexes. Molecules 2021, 26, 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040897
Hoshikawa R, Yoshida K, Mitsuhashi R, Mikuriya M, Okuno T, Sakiyama H. Structure Controlling Factors of Oxido-Bridged Dinuclear Iron(III) Complexes. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):897. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040897
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoshikawa, Ryusei, Kosuke Yoshida, Ryoji Mitsuhashi, Masahiro Mikuriya, Takashi Okuno, and Hiroshi Sakiyama. 2021. "Structure Controlling Factors of Oxido-Bridged Dinuclear Iron(III) Complexes" Molecules 26, no. 4: 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040897
APA StyleHoshikawa, R., Yoshida, K., Mitsuhashi, R., Mikuriya, M., Okuno, T., & Sakiyama, H. (2021). Structure Controlling Factors of Oxido-Bridged Dinuclear Iron(III) Complexes. Molecules, 26(4), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040897








