HR-MAS NMR Applications in Plant Metabolomics
Abstract
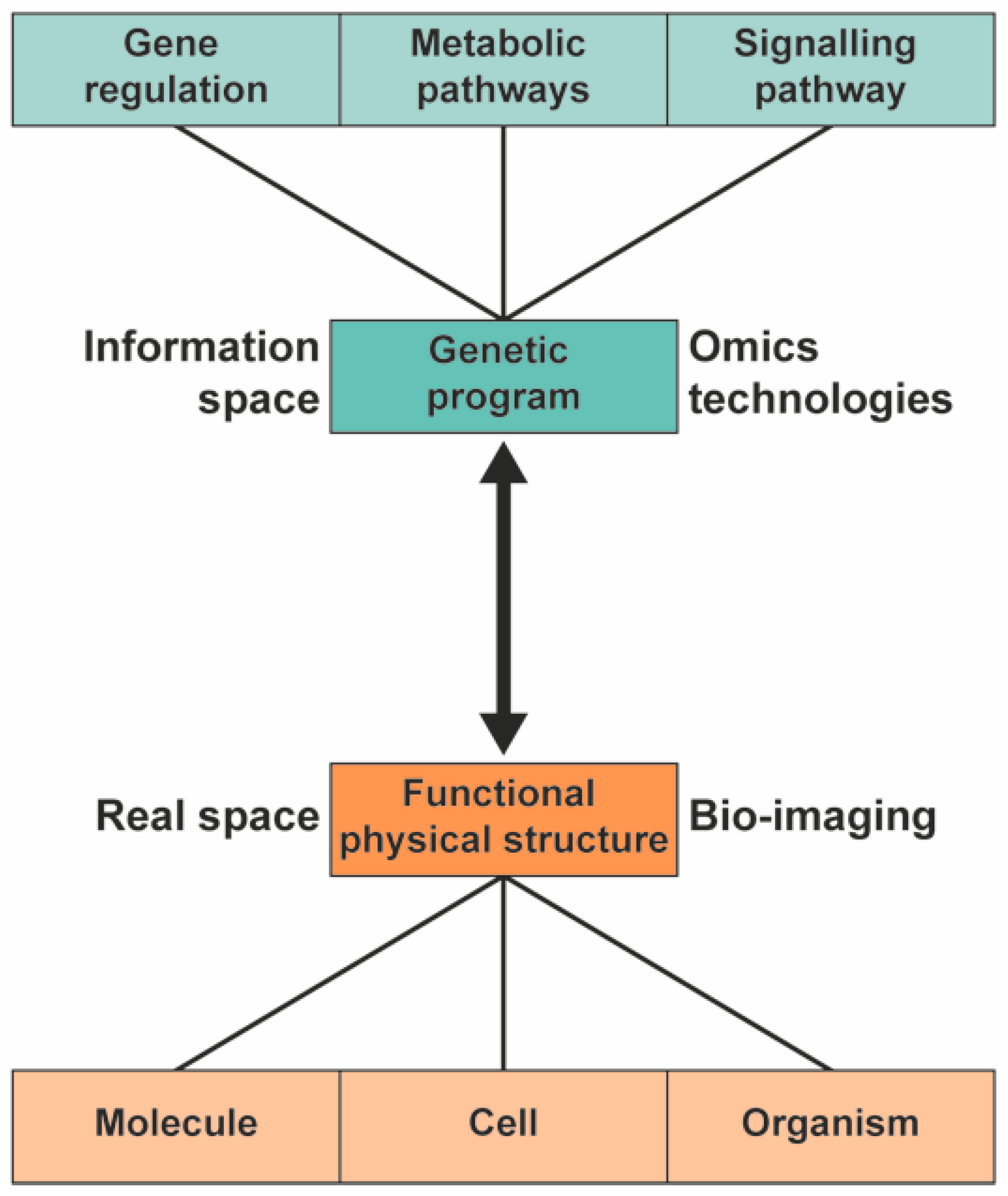
1. Introduction
2. Analytical Techniques in Metabolomics
3. Theoretical Background of HR-MAS NMR
4. HR-MAS NMR-Based Workflow
5. Harvesting Plant Material and Sample Preparation
6. Pulse Sequences Used in Metabolomics
7. Pre-Processing of One-Dimensional HR-MAS NMR Spectra
7.1. Spectral Alignment
7.2. Baseline Correction
7.3. Bucketing
7.4. Normalisation
7.5. Scaling
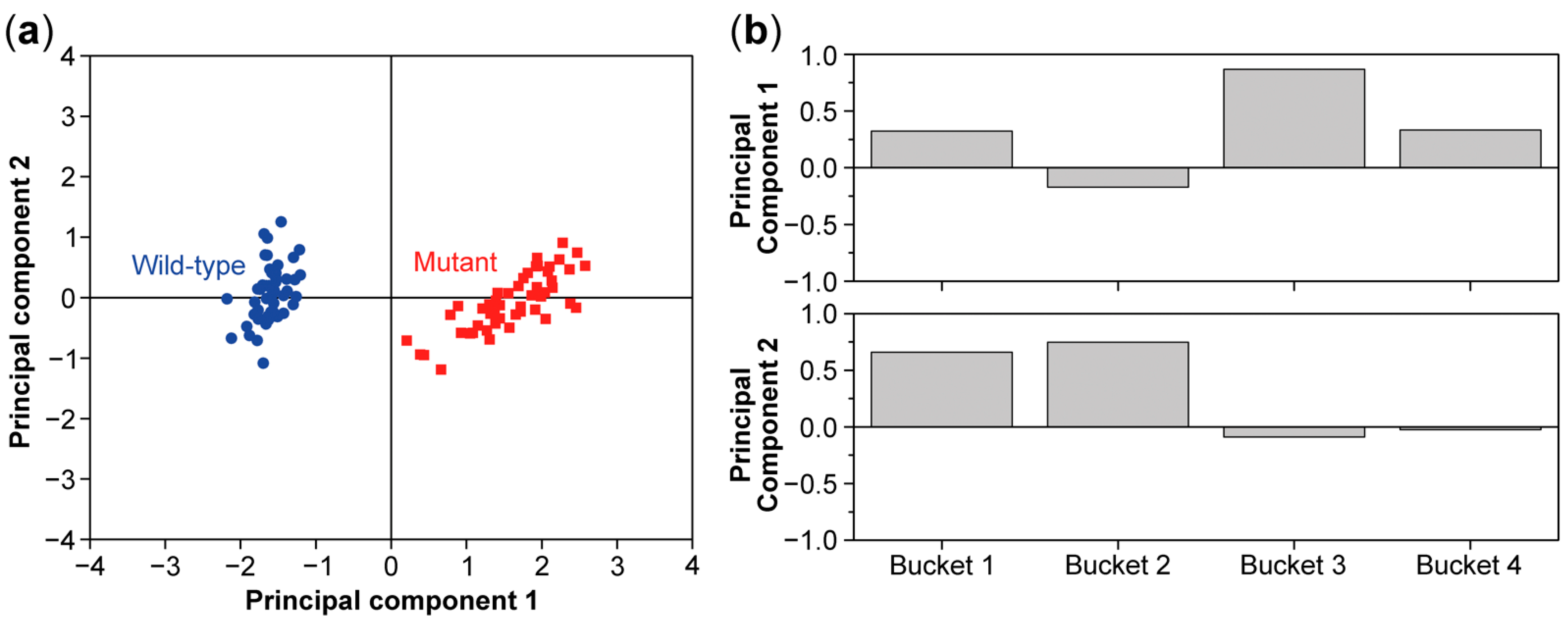
8. Multivariate Analysis
9. Applications of HR-MAS NMR in Plant Metabolomics
10. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, R.; Bohra, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Pandey, M.K.; Kumar, A. Metabolomics for Plant Improvement: Status and Prospects. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.H. The strengths and weaknesses of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry with particular focus on metabolomics research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1277, 161–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.-H.M.; Salek, R.M.; Griffin, J.L.; Merzaban, J. NMR-based metabolomics in human disease diagnosis: Applications, limitations, and recommendations. Metabolomics 2013, 9, 1048–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markley, J.L.; Brüschweiler, R.; Edison, A.S.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Powers, R.; Raftery, D.; Wishart, D.S. The future of NMR-based metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 43, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, F. Technical Challenges in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 5, S0052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckonert, O.; Coen, M.; Keun, H.C.; Wang, Y.; Ebbels, T.M.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K. High-resolution magic-angle-spinning NMR spectroscopy for metabolic profiling of intact tissues. Nat. Protoc 2010, 5, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alia, A.; Ganapathy, S.; de Groot, H.J. Magic Angle Spinning (MAS) NMR: A new tool to study the spatial and electronic structure of photosynthetic complexes. Photosynth Res. 2009, 102, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mazzei, P.; Piccolo, A. HRMAS NMR spectroscopy applications in agriculture. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2017, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermathen, M.; Marzorati, M.; Vermathen, P. Exploring high-resolution magic angle spinning (HR-MAS) NMR spectroscopy for metabonomic analysis of apples. Chimisty 2012, 66, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deborde, C.; Moing, A.; Roch, L.; Jacob, D.; Rolin, D.; Giraudeau, P. Plant metabolism as studied by NMR spectroscopy. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 2017, 102, 61–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, I.S.; Martinelli, B.C.B.; Pinto, V.S.; Queiroz, L.H.K., Jr.; Lião, L.A.-O. Important issues in plant tissues analyses by HR-MAS NMR. Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazaki, K.; Fukushima, A.; Nakabayashi, R.; Okazaki, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Mori, T.; Nishizawa, T.; Reyes-Chin-Wo, S.; Michelmore, R.W.; Saito, K.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming in Leaf Lettuce Grown Under Different Light Quality and Intensity Conditions Using Narrow-Band LEDs. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Liao, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; An, R.; Zeng, Q.; Li, X.e. A Widely Metabolomic Analysis Revealed Metabolic Alterations of Epimedium Pubescens Leaves at Different Growth Stages. Molecules 2019, 25, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustijn, D.; Roy, U.; van Schadewijk, R.; de Groot, H.J.; Alia, A. Metabolic Profiling of Intact Arabidopsis thaliana Leaves during Circadian Cycle Using 1H High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning NMR. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, K.-B.; Lu, Z.-G.; Ren, S.-X.; Jiang, H.-R.; Cui, J.-W.; Chen, G.; Teng, N.-J.; Lam, H.-M.; Jin, B. Differential physiological, transcriptomic and metabolomic responses of Arabidopsis leaves under prolonged warming and heat shock. BMC Plant. Biol. 2020, 20, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustijn, D.; Tol, N.V.; van der Zaal, B.J.; de Groot, H.J.M.; Alia, A. High-resolution magic angle spinning NMR studies for metabolic characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana mutants with enhanced growth characteristics. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustijn, D.; de Groot, H.J.M.; Alia, A. A robust circadian rhythm of metabolites in Arabidopsis thaliana mutants with enhanced growth characteristics. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas-Torres, C.; Bernard, T.; Huber, G.; Berthault, P.; Nishiyama, Y.; Kandiyal, P.S.; Elena-Herrmann, B.; Molin, L.; Solari, F.; Bouzier-Sore, A.-K.; et al. General Guidelines for Sample Preparation Strategies in HR-µMAS NMR-based Metabolomics of Microscopic Specimens. Metabolites 2020, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk, J.; Doskocz, M.; Jodlowska, E.; Zacharzewska, A.; Lakomiec, J.; Czaja, K.; Kujawski, J. NMR Techniques in Metabolomic Studies: A Quick Overview on Examples of Utilization. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2017, 48, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elena-Herrmann, B. CHAPTER 2 NMR Pulse Sequences for Metabolomics. In NMR-Based Metabolomics; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 22–38. [Google Scholar]
- Le Guennec, A.; Tayyari, F.; Edison, A.S. Alternatives to Nuclear Overhauser Enhancement Spectroscopy Presat and Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill Presat for NMR-Based Metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 8582–8588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dona, A.C.; Kyriakides, M.; Scott, F.; Shephard, E.A.; Varshavi, D.; Veselkov, K.; Everett, J.R. A guide to the identification of metabolites in NMR-based metabonomics/metabolomics experiments. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.N.; Laukens, K. Getting your peaks in line: A review of alignment methods for NMR spectral data. Metabolites 2013, 3, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, C.; Viant, M.R. Two-dimensional J-resolved NMR spectroscopy: Review of a key methodology in the metabolomics toolbox. Phytochem. Anal. 2010, 21, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.-H.; Saccenti, E.; Gao, X.; McKay, R.T.; Dos Santos, V.A.P.M.; Roy, R.; Wishart, D.S. Recommended strategies for spectral processing and post-processing of 1D (1)H-NMR data of biofluids with a particular focus on urine. Metab. Off. J. Metab. Soc. 2018, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liland, K.H. Multivariate methods in metabolomics—From pre-processing to dimension reduction and statistical analysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 827–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, T.; Sinnaeve, D.; Van Gasse, B.; Rietzschel, E.R.; De Buyzere, M.L.; Langlois, M.R.; Bekaert, S.; Martins, J.C.; Van Criekinge, W. Evaluation of standard and advanced preprocessing methods for the univariate analysis of blood serum 1H-NMR spectra. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euceda, L.R.; Giskeodegard, G.F.; Bathen, T.F. Preprocessing of NMR metabolomics data. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2015, 75, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska, A.; Blanchet, L.; Buydens, L.M.; Wijmenga, S.S. NMR and pattern recognition methods in metabolomics: From data acquisition to biomarker discovery: A review. Anal. Chim Acta 2012, 750, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, R.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Smilde, A.K.; van der Werf, M.J. Centering, scaling, and transformations: Improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worley, B.; Powers, R. Multivariate Analysis in Metabolomics. Curr Metab. 2013, 1, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qi, X.; Duan, L.-X. Plant metabolomics: Methods and Applications. In Plant Metabolomics: Methods and Applications; Qi, X., Chen, X., Wang, Y., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trygg, J.; Wold, S. Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS). J. Chemom. 2002, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trygg, J.; Holmes, E.; Lundstedt, T. Chemometrics in metabonomics. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylesjö, M.; Rantalainen, M.; Cloarec, O.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Trygg, J. OPLS discriminant analysis: Combining the strengths of PLS-DA and SIMCA classification. J. Chemom. 2006, 20, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellinger, J.J.; Chylla, R.A.; Ulrich, E.L.; Markley, J.L. Databases and Software for NMR-Based Metabolomics. Curr Metab. 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, S.; Johansson, E.; Sjostrom, L.; Mellerowicz, E.J.; Edlund, U.; Shockcor, J.P.; Gottfries, J.; Moritz, T.; Trygg, J. Visualization of GC/TOF-MS-based metabolomics data for identification of biochemically interesting compounds using OPLS class models. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, S.; Karlsson, M.; Antti, H.; Johnels, D.; Sjostrom, M.; Wingsle, G.; Edlund, U. A new metabonomic strategy for analysing the growth process of the poplar tree. Plant. Biotechnol. J. 2005, 3, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bylesjo, M. Extracting meaningful information from metabonomic data using multivariate statistics. Methods Mol. Biol 2015, 1277, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, O.P.; Annarao, S.; Pathre, U.; Snehi, S.K.; Raj, S.K.; Roy, R.; Tuli, R.; Khetrapal, C.L. Metabolic and histopathological alterations of Jatropha mosaic begomovirus-infected Jatropha curcas L. by HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging. Planta 2010, 232, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, G.; Righi, V.; Simoni, A.; Schenetti, L.; Mucci, A.; Tugnoli, V.; Muzzi, E.; Francioso, O. Effect of a peat humic acid on morphogenesis in leaf explants of Pyrus communis and Cydonia oblonga. Metabolomic analysis at an early stage of regeneration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4979–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.I.; Figueiredo, P.I.; Barros, A.S.; Dias, M.C.; Santos, C.; Duarte, I.F.; Gil, A.M. Changes in the metabolome of lettuce leaves due to exposure to mancozeb pesticide. Food Chem. 2014, 154, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, P.; Vinale, F.; Woo, S.L.; Pascale, A.; Lorito, M.; Piccolo, A. Metabolomics by Proton High-Resolution Magic-Angle-Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance of Tomato Plants Treated with Two Secondary Metabolites Isolated from Trichoderma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3538–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, C.; Khelalfa, F.; Reynaud, S.; Fauvelle, F.; Raveton, M. Effect of organochlorine pesticides exposure on the maize root metabolome assessed using high-resolution magic-angle spinning (1)H NMR spectroscopy. Environ. Pollut 2016, 214, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, P.; Cozzolino, V.; Piccolo, A. High-Resolution Magic-Angle-Spinning NMR and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Spectroscopies Distinguish Metabolome and Structural Properties of Maize Seeds from Plants Treated with Different Fertilizers and Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 2580–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, C.S.; Lião, L.M.; Alcantara, G.B. Metabolic response of soybean plants to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum infection. Phytochemistry 2019, 167, 112099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taglienti, A.; Tiberini, A.; Ciampa, A.; Piscopo, A.; Zappia, A.; Tomassoli, L.; Poiana, M.; Dell’Abate, M.T. Metabolites response to onion yellow dwarf virus (OYDV) infection in ‘Rossa di Tropea’ onion during storage: A (1) H HR-MAS NMR study. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winning, H.; Viereck, N.; Wollenweber, B.; Larsen, F.H.; Jacobsen, S.; Sondergaard, I.; Engelsen, S.B. Exploring abiotic stress on asynchronous protein metabolism in single kernels of wheat studied by NMR spectroscopy and chemometrics. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, O.N.A.; Folegatti, M.V.; Dutra, L.M.; Andrade, I.P.d.S.; Fanaya, E.D.; Lena, B.P.; Barison, A.; Santos, A.D.d.C. Tracking lipid profiles of Jatropha curcas L. seeds under different pruning types and water managements by low-field and HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 109, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagter, M.; Yde, C.C.; Kjaer, K.H. Metabolic Fingerprinting of Dormant and Active Flower Primordia of Ribes nigrum Using High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning NMR. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10123–10130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, I.D.; Moraes, T.B.; Mertz-Henning, L.M.; Nepomuceno, A.L.; Giordani, W.; Marcolino-Gomes, J.; Santagneli, S.; Colnago, L.A. Integrating High-Resolution and Solid-State Magic Angle Spinning NMR Spectroscopy and a Transcriptomic Analysis of Soybean Tissues in Response to Water Deficiency. Phytochem Anal. 2017, 28, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.M.; Duarte, I.F.; Delgadillo, I.; Colquhoun, I.J.; Casuscelli, F.; Humpfer, E.; Spraul, M. Study of the compositional changes of mango during ripening by use of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1524–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.M.S.; Iglesias, M.J.; Ortiz, F.L.; Pérez, I.S.; Galera, M.M. Study of the suitability of HRMAS NMR for metabolic profiling of tomatoes: Application to tissue differentiation and fruit ripening. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermathen, M.; Marzorati, M.; Diserens, G.; Baumgartner, D.; Good, C.; Gasser, F.; Vermathen, P. Metabolic profiling of apples from different production systems before and after controlled atmosphere (CA) storage studied by (1)H high resolution-magic angle spinning (HR-MAS) NMR. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.; Choi, B.R.; Ma, S.; Lee, J.W.; Jo, I.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, G.S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.Y. Metabolomics for Age Discrimination of Ginseng Using a Multiplex Approach to HR-MAS NMR Spectroscopy, UPLC-QTOF/MS, and GC × GC-TOF/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, A.; Parenti, F.; Righi, V.; Schenetti, L. Citron and lemon under the lens of HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3167–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, V.; Parenti, F.; Tugnoli, V.; Schenetti, L.; Mucci, A. Crocus sativus Petals: Waste or Valuable Resource? The Answer of High-Resolution and High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8439–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Badshah, G.; Da Ros Montes D’Oca, C.; Ramos Campos, F.; Nagata, N.; Khan, A.; de Fátima Costa Santos, M.; Barison, A. High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning (HR-MAS) NMR-Based Fingerprints Determination in the Medicinal Plant Berberis laurina. Molecules 2020, 25, 3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choze, R.; Alcantara, G.B.; Alves Filho Ede, G.; e Silva, L.M.; Faria, J.C.; Liao, L.M. Distinction between a transgenic and a conventional common bean genotype by 1H HR-MAS NMR. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2841–2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C.S.; Carlos, E.F.; Vieira, L.G.; Liao, L.M.; Alcantara, G.B. HR-MAS NMR metabolomics of ‘Swingle’ citrumelo rootstock genetically modified to overproduce proline. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2014, 52, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritota, M.; Marini, F.; Sequi, P.; Valentini, M. Metabolomic characterization of Italian sweet pepper (Capsicum annum L.) by means of HRMAS-NMR spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2010, 58, 9675–9684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritota, M.; Casciani, L.; Han, B.Z.; Cozzolino, S.; Leita, L.; Sequi, P.; Valentini, M. Traceability of Italian garlic (Allium sativum L.) by means of HRMAS-NMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Food Chem 2012, 135, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marseglia, A.; Acquotti, D.; Consonni, R.; Cagliani, L.R.; Palla, G.; Caligiani, A. HR MAS (1)H NMR and chemometrics as useful tool to assess the geographical origin of cocoa beans–Comparison with HR (1)H NMR. Food Res. Int. 2016, 85, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero-Leon, E.; De Rudder, O.; Maquet, A. Metabolomics for organic food authentication: Results from a long-term field study in carrots. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallamace, D.; Corsaro, C.; Salvo, A.; Cicero, N.; Macaluso, A.; Giangrosso, G.; Ferrantelli, V.; Dugo, G. A multivariate statistical analysis coming from the NMR metabolic profile of cherry tomatoes (The Sicilian Pachino case). Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2014, 401, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsaro, C.; Mallamace, D.; Vasi, S.; Ferrantelli, V.; Dugo, G.; Cicero, N. (1)H HR-MAS NMR Spectroscopy and the Metabolite Determination of Typical Foods in Mediterranean Diet. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2015, 2015, 175696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, N.; Corsaro, C.; Salvo, A.; Vasi, S.; Giofre, S.V.; Ferrantelli, V.; Di Stefano, V.; Mallamace, D.; Dugo, G. The metabolic profile of lemon juice by proton HR-MAS NMR: The case of the PGI Interdonato Lemon of Messina. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1894–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Pérez, E.M.; García López, J.; Iglesias, M.J.; López Ortiz, F.; Toresano, F.; Camacho, F. HRMAS-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy characterization of tomato “flavor varieties” from Almería (Spain). Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 3212–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daolio, C.; Beltrame, F.L.; Ferreira, A.G.; Cass, Q.B.; Cortez, D.A.; Ferreira, M.M. Classification of commercial Catuaba samples by NMR, HPLC and chemometrics. Phytochem Anal. 2008, 19, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, S.K.; Bhatia, A.; Tewari, S.K.; Sidhu, O.P.; Roy, R. Application of HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy for studying chemotype variations of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal. Magn. Reson Chem. 2011, 49, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermathen, M.; Marzorati, M.; Baumgartner, D.; Good, C.; Vermathen, P. Investigation of different apple cultivars by high resolution magic angle spinning NMR. A feasibility study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 12784–12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Goni, T.; Campo, S.; Martin-Sitjar, J.; Cabanas, M.E.; San Segundo, B.; Arus, C. Assessment of a 1H high-resolution magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy procedure for free sugars quantification in intact plant tissue. Planta 2013, 238, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, E.H.; Kim, H.J.; Jeong, J.; Chung, H.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Bang, E.; Hong, Y.S. A (1)H HR-MAS NMR-Based Metabolomic Study for Metabolic Characterization of Rice Grain from Various Oryza sativa L. Cultivars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3009–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.; Fonseca, F.A.; Dutra, L.M.; Santos, M.F.C.; Menezes, L.R.A.; Campos, F.R.; Nagata, N.; Ayub, R.; Barison, A. (1)H HR-MAS NMR-based metabolomics study of different persimmon cultivars (Diospyros kaki) during fruit development. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, D.; Choi, B.-R.; Kim, Y.-C.; Oh, S.M.; Kim, H.-G.; Kim, J.-U.; Baek, N.-I.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.Y. Comparative Analysis of Panax ginseng Berries from Seven Cultivars Using UPLC-QTOF/MS and NMR-Based Metabolic Profiling. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvo, A.; Rotondo, A.; Mangano, V.; Grimaldi, M.; Stillitano, I.; D’Ursi, A.M.; Dugo, G.; Rastrelli, L. High-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS-NMR) as quick and direct insight of almonds. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, I.S.; Martinelli, B.C.B.; Lião, L.M. High-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS NMR) as a tool in the determination of biomarkers of Passiflora-based herbal medicines. Fitoterapia 2020, 142, 104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.; Lucas-Torres, C. CHAPTER 5 High-resolution Magic-angle Spinning (HR-MAS) NMR Spectroscopy. In NMR-Based Metabolomics; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 133–150. [Google Scholar]
- Shet, K.; Siddiqui, S.M.; Yoshihara, H.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Ries, M.; Li, X. High-resolution magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy of human osteoarthritic cartilage. NMR Biomed. 2012, 25, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarou-Kanian, V.; Joudiou, N.; Louat, F.; Yon, M.; Szeremeta, F.; Même, S.; Massiot, D.; Decoville, M.; Fayon, F.; Beloeil, J.-C. Metabolite localization in living drosophila using High Resolution Magic Angle Spinning NMR. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Lucas-Torres, C. Simultaneous metabolic mapping of different anatomies by (1)H HR-MAS chemical shift imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Torres, C.; Wong, A. Intact NMR spectroscopy: Slow high-resolution magic angle spinning chemical shift imaging. Analyst 2020, 145, 2520–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Torres, C.; Wong, A. Current Developments in µMAS NMR Analysis for Metabolomics. Metabolites 2019, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas-Torres, C.; Huber, G.; Ichikawa, A.; Nishiyama, Y.A.-O.; Wong, A.A.-O. HR-μMAS NMR-Based Metabolomics: Localized Metabolic Profiling of a Garlic Clove with μg Tissues. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13736–13743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salon, C.; Avice, J.C.; Colombie, S.; Dieuaide-Noubhani, M.; Gallardo, K.; Jeudy, C.; Ourry, A.; Prudent, M.; Voisin, A.S.; Rolin, D. Fluxomics links cellular functional analyses to whole-plant phenotyping. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2083–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.; Kromer, J.O. Fluxomics—Connecting ‘omics analysis and phenotypes. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1901–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölling, K.; Müller, A.; Flütsch, P.; Zeeman, S.C. A device for single leaf labelling with CO2 isotopes to study carbon allocation and partitioning in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant. Methods 2013, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratcliffe, R.G.; Shachar-Hill, Y. Measuring multiple fluxes through plant metabolic networks. Plant. J. 2006, 45, 490–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondi, M.; Liò, P. Multi-omics and metabolic modelling pipelines: Challenges and tools for systems microbiology. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 171, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Tagkopoulos, I. Data integration and predictive modeling methods for multi-omics datasets. Mol. Omics 2018, 14, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.D.; Holzinger, E.R.; Li, R.; Pendergrass, S.A.; Kim, D. Methods of integrating data to uncover genotype-phenotype interactions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| NMR Spectroscopy | Mass Spectrometry | |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Low sensitivity, but can be improved with higher field strength and cryo- or microprobes | High sensitivity, can reach the detection limit of attomolar (10–18) concentrations |
| Sample measurement | In one measurement with a detectable concentration can be detected | Need chromatography techniques for different classes of metabolites |
| Sample recovery | Non-destructive technique Several analyses can be performed on the same extracted sample | Destructive technique |
| Reproducibility | Very high | Moderate |
| Quantification | Absolute quantitation of metabolites possible by adding one standard with known concentration | Quantification is possible with authentic standards, which are not available for newly identified compounds. Ionisation efficiencies, ion suppression and matrix effects have influences on the concentration. |
| Targeted or untargeted approach | Untargeted and targeted approach | Untargeted and targeted approach, mainly used for targeted analysis |
| Scaling Method | Formula |
|---|---|
| Autoscaling | |
| Range scaling | |
| Vast scaling | |
| Pareto scaling |
| Plant | Research Objective | Magnetic Field Strength (MHz) | Pulse Sequences | Multivariate Models |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influences of Biotic or Abiotic Stress | ||||
| Winter wheat (Triticum aestivum) [49] | Evaluate the influences of different drought treatments | 400 | 1D | PCA |
| Jatropha curcas [50] | Determine the impacts of pruning procedures and water management | 400 | Zg | - |
| Ribes nigrum [51] | Determine the effect of seasonal asymmetric warming | 600 | CPMG, HSQC | PCA |
| Soybean [52] | Determine the influences of water deficiency | 600 | CPMG, NOESY | PLS-DA |
| Jatropha curcas [41] | Studying the effect of Jatropha mosaic virus on the metabolic profile | 400 | NOESY, CPMG, COSY | - |
| Pear (Pyrus communis) and quince (Cydonia oblonga) [42] | Study the effect of humic acid on the morphogenesis of pear and quince | 400 | 13C, CPMG, 1D LED, COSY, TOCSY, HSQC | PCA |
| Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) [43] | Influences of the fungicide mancozeb on the leaves at different growth stages | 800 | NOESY, TOCSY, HSQC | PCA, PLS-DA |
| Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) [44] | Study the influences of 6-pentyl-2H-pyran-2-one and harzianic acid on the leaves | 400 | CPMG, COSY, TOCSY, J-res, HSQC, HMBC | PCA |
| Maize (Zea mays) [45] | Determine the toxic effects on maize root tips of organo-chlorine pesticides | 600 | CPMG | OPLS-DA |
| Maize (Zea mays) [46] | Determine the effect of mineral or compost fertilisation and inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi | 400 | CPMG, COSY, TOCSY, J-res, HSQC, HMBC | PCA |
| Soybean [47] | Determine the metabolic alternation caused by S. sclerotiorum infection | 500 | CPPR, TOCSY, HSQC | PCA |
| Onion (Allium cepa L.) [48] | Evaluate the effect of onion yellow dwarf virus on the metabolites of onions | 400 | Zgpr | PLS-DA |
| Study the Ripening and Storage of Fruits | ||||
| Mango fruit (Mangifera indica) [53] | Studying the metabolic profile of mango pulp during ripening | 400 | 1H 1D, 1H-13C correlation, TOCSY, J-res | - |
| Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) [54] | Studying different tissues of the tomato during fruit ripening | 500 | NOESY, TOCSY, HMQC | PCA |
| Golden delicious apples [55] | Determine the impact of storage time and production systems | 500 | NOESY, COSY, TOCSY | PCA, PLS-DA |
| Ginseng [56] | Distinguish the age of ginseng based on metabolomics | 600 | CPMG | PCA, PLS-DA, OPLS-DA |
| Studying Different Cell Types of Plants | ||||
| Lemon (Citrus limon) and citron (Citrus medica) [57] | The metabolic profile of different parts of the lemon and citron are studied | 400 | 1H, CPMG, COSY, TOCSY, HSQC | - |
| Characterising of Plant | ||||
| Crocus sativus [58] | Establish the main metabolites present in C. sativus petals | 400 | 1H, COSY, TOCSY, HSQC, HMBC | - |
| Berberis laurina (Berberidaceae) [59] | Establish the main metabolites present in Berberis laurina leaves, stems and roots | 400 | Zg, HSQC, HMBC | PCA |
| Understanding Transgenic Plants | ||||
| Poplar tree (Populus tremula) [39] | Studying the time- and growth-related metabolic profile of PttMYB76 and wild-type poplar tree | 500 | CPMG | PCA, PLS-DA |
| Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) [60] | Distinction between conventional and transgenic common beans | 500 | CPMG | PCA |
| “Swingle” citrumelo [61] | Evaluate the metabolic profile of non-transgenic and transgenic citrumelo | 500 | 1H, HSQC, TOCSY | PCA, PLS-DA |
| Geographical Origin of Plants | ||||
| Sweet peppers (Capsicum annum) [62] | Discriminate sweet peppers according to their geographical origin | 400 | NOESY, 1D 13C, TOCSY | PLS-DA |
| Garlic (Allium sativum) [63] | Characterisation of two varieties garlic cropped in different Italian regions | 400 | NOESY, 13C, TOCSY, HMQC | PLS-DA |
| Cocoa beans [64] | Assess the geographical origins of fermented and dried cocoa beans | 400 | 1H | PCA, PLS-DA, OPLS-DA |
| Cherry tomatoes of Pachino [66] | Determine the major metabolites present in cherry tomatoes of Pachino | 700 | 1H | PCA |
| PGI cherry tomato of Pachino, PGI inter-donato lemon of Messina, red garlic of Nubia [67] | Identify and quantify metabolites from three typical food products of the Mediterranean diet | 700 | 1H | PCA |
| PGI inter-donato lemon of Messina [68] | Determine metabolites unique for PGI interdonato lemon of messina | 700 | 1H, COSY, TOCSY, HSQC | - |
| Tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) [69] | Establish the metabolic differences between commercially available varieties | 500 | NOESY, HSQC | PCA |
| Distinguish between Different Cultivars | ||||
| Trichilia catigua [70] | Classification of commercial samples of Catuaba | 400 | CPMG | PCA, HCA |
| Withania somnifera [71] | Evaluate metabolic profile of 4 different chemotypes of W. somnifera | 800 | NOESY, CPMG, COSY, HSQC | PCA |
| Apples [72] | Discriminate three different apple cultivars by their metabolic profile | 500 | NOESY, COSY, TOCSY | PCA, PLS-DA |
| Melon (Cucumis melo) [73] | Quantification of sugars and compare two varieties | 400 | 1H | - |
| Rice (Oryza sativa) [74] | Determine the metabolic variation of diverse rice cultivars | 700 | CPMG, TOCSY, HSQC, STOCSY | PCA, OPLS-DA |
| Persimmon (Diospyros kaki) [75] | Follow the metabolic changes during development of different cultivars | 400 | NOESY | PCA |
| Seven cultivars of Panax ginseng [76] | Study the primary metabolites of the seven cultivars of ginseng berries | 600 | CPMG | PCA, PLS-DA, OPLS-DA |
| Almonds (seeds of Prunus dulcis) [77] | Establish the difference between seven different types of almonds | 500 | Zg, COSY | PCA |
| Curtis (Passiflora alata) [78] | Seven herbal medicines containing leaf extract of some Passiflora species | 500 | Zg, COSY | PCA, KNN |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Augustijn, D.; de Groot, H.J.M.; Alia, A. HR-MAS NMR Applications in Plant Metabolomics. Molecules 2021, 26, 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040931
Augustijn D, de Groot HJM, Alia A. HR-MAS NMR Applications in Plant Metabolomics. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):931. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040931
Chicago/Turabian StyleAugustijn, Dieuwertje, Huub J. M. de Groot, and A. Alia. 2021. "HR-MAS NMR Applications in Plant Metabolomics" Molecules 26, no. 4: 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040931
APA StyleAugustijn, D., de Groot, H. J. M., & Alia, A. (2021). HR-MAS NMR Applications in Plant Metabolomics. Molecules, 26(4), 931. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040931






