Hydrazones of 4-(Trifluoromethyl)benzohydrazide as New Inhibitors of Acetyl- and Butyrylcholinesterase
Abstract
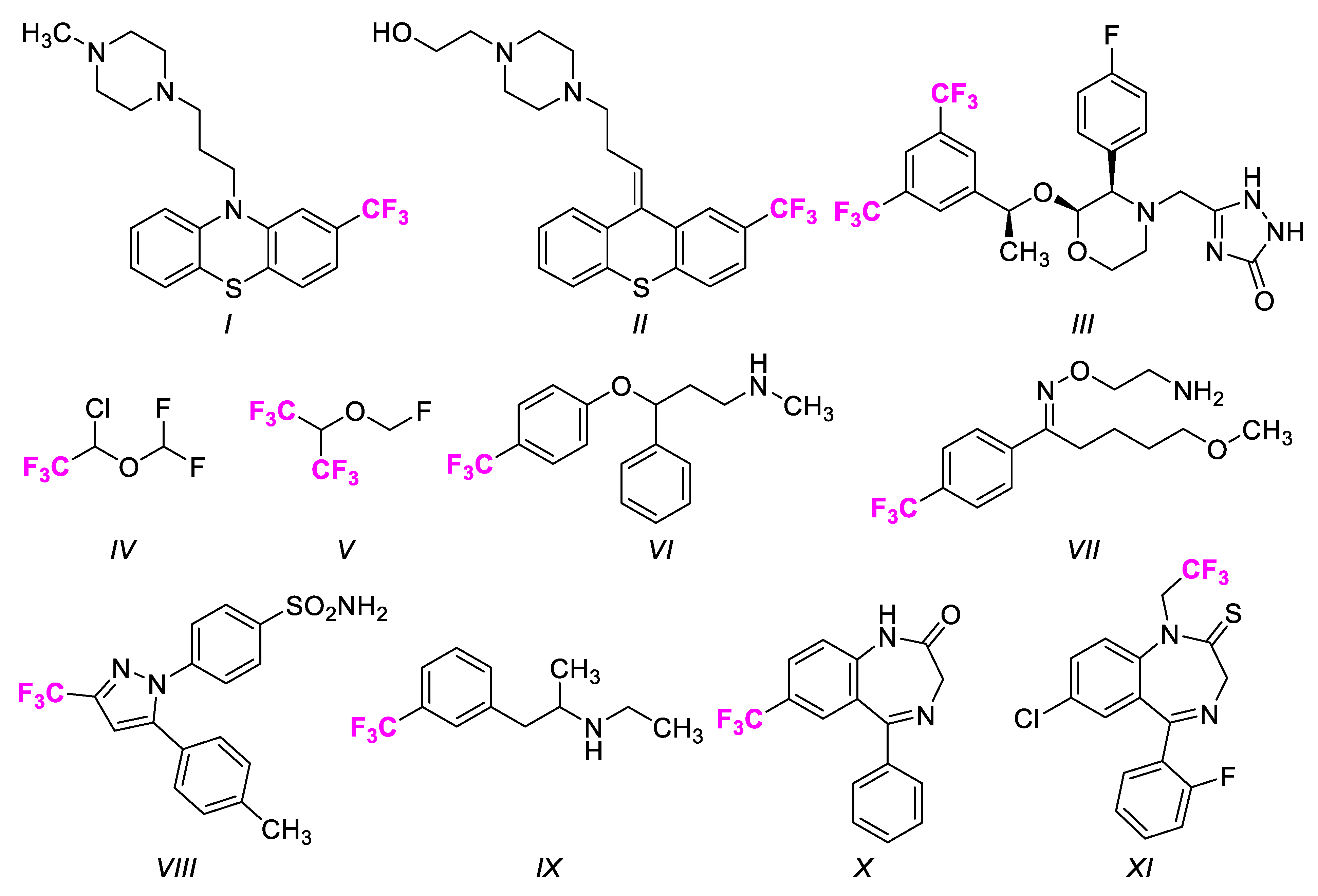
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
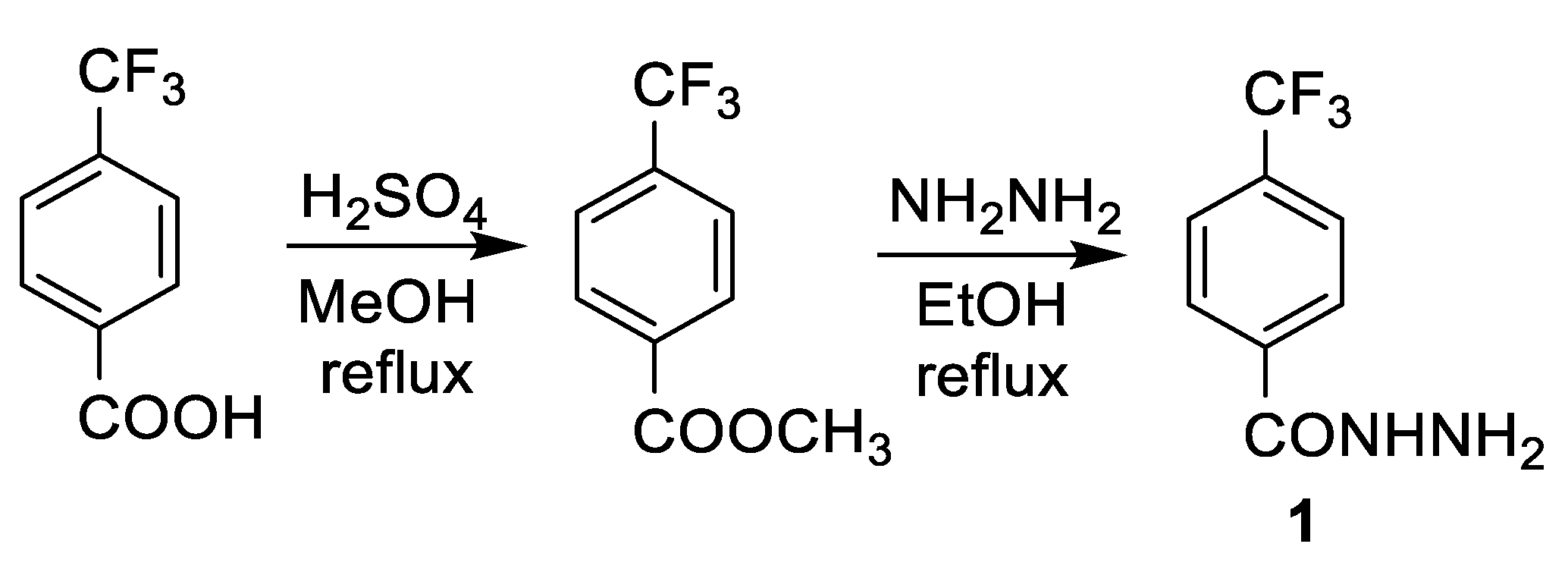
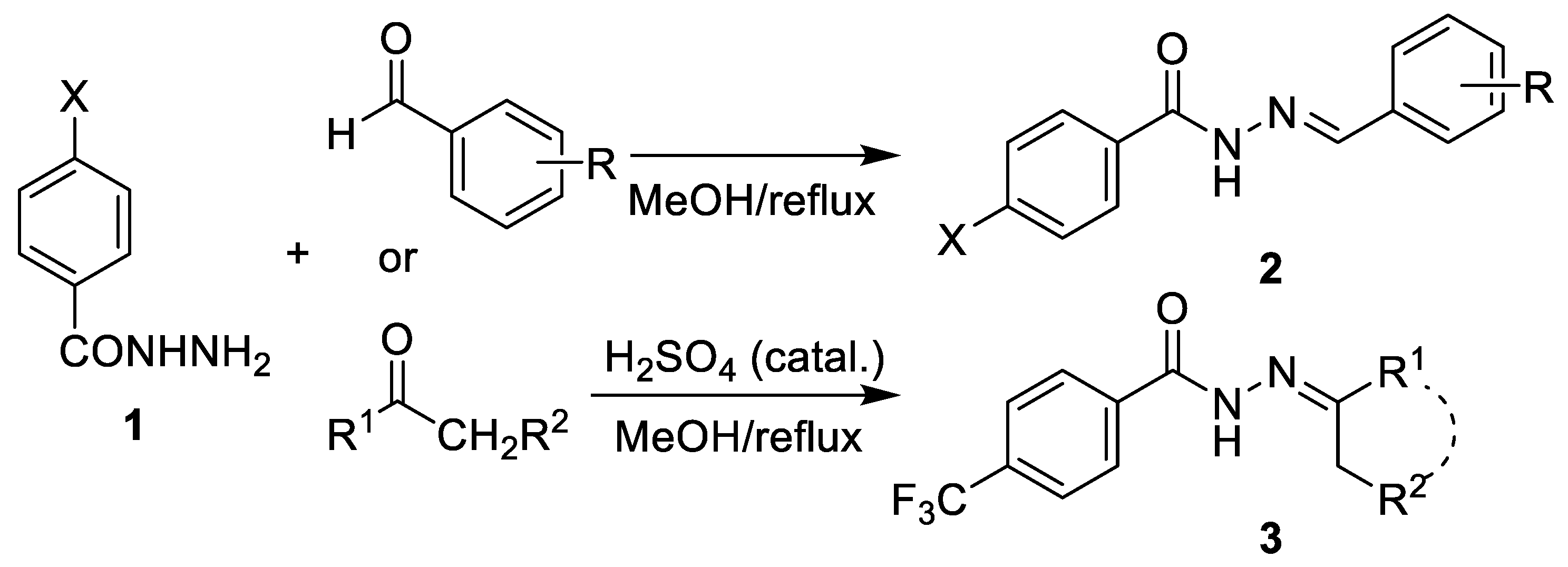
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Inhibition of Acetyl- and Butyrylcholinesterase
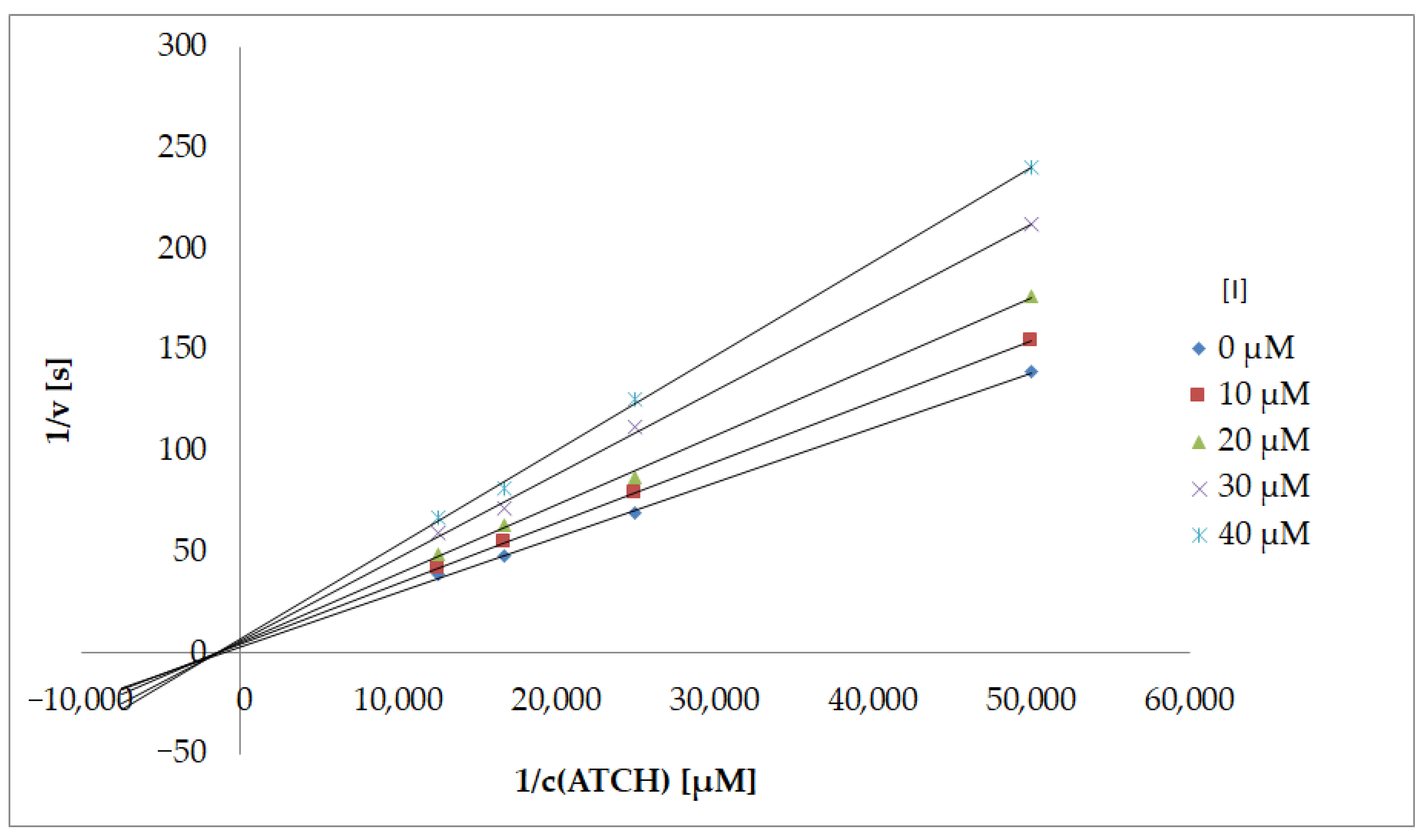
Type of Inhibition
2.3. Prediction of BBB Permeability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Evaluation of Acetyl- and Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibition
3.3. Determination of Parameters for CNS Delivery
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Isanbor, C.; O’Hagan, D. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry: A review of anticancer agents. J. Fluorine Chem. 2006, 127, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sanchez-Rosello, M.; Acena, L.J.; del Pozo, C.; Sorochinsky, A.E.; Fustero, S.; Soloshonok, V.A.; Liu, H. Fluorine in pharmaceutical industry: Fluorine-containing drugs introduced to the market in the last decade (2001–2011). Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 2432–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojima, I. Strategic incorporation of fluorine into taxoid anticancer agents for medicinal chemistry and chemical biology studies. J. Fluor. Chem. 2017, 198, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meanwell, N.A. Fluorine and fluorinated motifs in the design and application of bioisosteres for drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 611, 45822–45880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluorine in Pharmaceutical and Medicinal Chemistry: From Biophysical Aspects to Clinical Applications. Available online: https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/pdf/10.1142/9781848166363_fmatter (accessed on 2 January 2021).
- Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Gu, Z.; Acena, J.L.; Izawa, K.; Liu, H.; Soloshonok, V.A. Recent advances in the trifluoromethylation methodology and new CF3-containing drugs. J. Fluor. Chem. 2014, 167, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yale, H.L. The Trifluoromethyl Group in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Pharm. Chem. 1959, 1, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purser, S.; Moore, P.R.; Swallow, S.; Gouverneur, V. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagmann, W.K. The many roles for fluorine in medicinal chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4359–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollas, S.; Küçükgüzel, S.G. Biological activities of hydrazone derivatives. Molecules 2007, 12, 1910–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, G.; Marella, A.; Shaquiquzzaman, M.; Akhtar, M.; Ali, M.R.; Alam, M.M. A review exploring biological activities of hydrazones. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2014, 6, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krátký, M.; Bősze, S.; Baranyai, Z.; Stolaříková, J.; Vinšová, J. Synthesis and biological evolution of hydrazones derived from 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzohydrazide. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 5185–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.-Y.; Qiu, X.-Y.; Cheng, J.-Y.; Liu, S.-J.; Wu, S.-M. Synthesis, characterization and crystal structures of vanadium(V) complexes derived from halido-substituted tridentate hydrazone compounds with antimicrobial activity. Polyhedron 2018, 156, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-S.; Su, M.-M.; Zhang, X.-P.; Liu, Q.-X.; He, Z.-X.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.-L. Developing potential Helicobacter pylori urease inhibitors from novel oxoindoline derivatives: Synthesis, biological evaluation and in silico study. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 3182–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-S.; Su, M.-M.; Xu, J.-F.; Liu, Q.-X.; Bai, L.-F.; Hu, X.-W.; Zhu, H.-L. Discovery of novel oxoindolin derivatives as atypical dual inhibitors for DNA Gyrase and FabH. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 93, 103309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Q.-D.; Li, D.; Sun, Y.; Han, X.-Y.; Yi, F.; Sha, Y.; Ren, Y.-L.; Ding, M.-W.; Feng, L.-L.; Wan, J. Design and syntheses of novel N′-((4-oxo-4H-chromen-3-yl)methylene)benzohydrazide as inhibitors of cyanobacterial fructose-1,6-/sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaman, N.; Sıcak, Y.; Taşkın-Tok, T.; Öztürk, M.; Karaküçük-İyidoğan, A.; Dikmen, M.; Koçyiğit-Kaymakçıoğlu, B.; Oruç-Emre, E.E. New piperidine-hydrazone derivatives: Synthesis, biological evaluations and molecular docking studies as AChE and BChE inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktar, B.S.K.; Sıcak, Y.; Tok, T.T.; Oruç-Emre, E.E.; Yağlıoğlu, A.S.; Iyidoğan, A.K.; Öztürk, M.; Demirtaş, I. Designing heterocyclic chalcones, benzoyl/sulfonyl hydrazones: An insight into their biological activities and molecular docking study. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1211, 128059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, S.; Saad, S.M.; Zafar, H.; Malik, R.; Khan, K.M.; Choudhary, M.I.; Rahman, A.U. Thymidine phosphorylase and prostrate cancer cell proliferation inhibitory activities of synthetic 4-hydroxybenzohydrazides: In vitro, kinetic, and in silico studies. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Aldhamin, E.A.J.; Almandil, N.B.; Anouar, E.; Uddin, N.; Alomari, M.; Rahim, F.; Adalat, B.; Ibrahim, M.; Nawaz, F.; et al. Synthesis of indole based acetohydrazide analogs: Their in vitro and in silico thymidine phosphorylase studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 98, 103745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, M.; Raines, D.J.; Castillo, C.E.; Duhme-Klair, A.K. Inhibition of xanthine oxidase by thiosemicarbazones, hydrazones and dithiocarbazates derived from hydroxy-substituted benzaldehydes. ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniak, H.; Talma, M.; Matyja, K.; Trusek, A.; Giurg, M. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship studies of hydrazide-hydrazones as inhibitors of laccase from Trametes versicolor. Molecules 2020, 25, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krátký, M.; Baranyai, Z.; Štěpánková, Š.; Svrčková, K.; Švarcová, M.; Stolaříková, J.; Horváth, L.; Bősze, S.; Vinšová, J. N-Alkyl-2-[4-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl]hydrazine-1-carboxamides and their analogues: Synthesis and multitarget biological activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krátký, M.; Štěpánková, Š.; Brablíková, M.; Svrčková, K.; Švarcová, M.; Vinšová, J. Novel iodinated hydrazide-hydrazones and their analogues as acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 2106–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lineweaver, H.; Burk, D. The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Zoete, V. A boiled-egg to predict gastrointestinal absorption and brain penetration of small molecules. ChemMedChem. 2016, 7, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankovic, Z. CNS drug design: Balancing physicochemical properties for optimal brain exposure. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 2584–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Ott, G.R.; Hudkins, R.L. Technically extended multiparameter optimization (TEMPO): An advanced robust scoring scheme to calculate central nervous system druggability and monitor lead optimization. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mikitsh, J.L.; Chacko, A.M. Pathways for small molecule delivery to the central nervous system across the blood-brain barrier. Perspect. Medicin. Chem. 2014, 6, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdrazilova, P.; Stepankova, S.; Komers, K.; Ventura, K.; Cegan, A. Half-inhibition concentrations of new cholinesterase inhibitors. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2004, 59, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
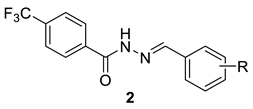 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Code | R | IC50 AChE (µM) | IC50 BuChE (µM) | Selectivity BuChE/AChE | IC50 (HepG2) [12] |
| 2a | H | 75.90 ± 1.6 | 651.3 ± 31.5 | 8.7 | >100 |
| 2b | 4-Cl | 88.5 ± 1.4 | 253.8 ± 3.3 | 2.9 | >100 |
| 2c | 3-Cl | 77.1 ± 0.03 | 260.9 ± 40.7 | 3.4 | >100 |
| 2d | 2-Cl | 128.5 ± 10.0 | 63.6 ± 0.9 | 0.5 | >100 |
| 2e | 4-OH | 101.9 ± 3.8 | 229.2 ± 14.5 | 2.3 | >100 |
| 2f | 3-OH | 70.4 ± 2.8 | 249.7 ± 7.5 | 3.5 | >100 |
| 2g | 2-OH | 47.4 ± 1.8 | 881.1 ± 8.0 | 18.6 | >100 |
| 2h | 2-OH-5-Cl | 137.7 ± 3.0 | 287.2 ± 12.6 | 2.1 | >100 |
| 2i | 4-CH3 | 91.4 ± 6.2 | 253.1 ± 9.6 | 2.8 | >100 |
| 2j | 4-CH3O | 108.5 ± 2.2 | 279.1 ± 2.9 | 2.6 | >100 |
| 2k | 4-Br | 62.1 ± 0.02 | 342.3 ± 11.3 | 5.5 | >100 |
| 2l | 4-CF3 | 46.8 ± 2.1 | 175.0 ± 8.3 | 3.7 | >100 |
| 2m | 4-NO2 | 60.0 ± 0.4 | 190.6 ± 1.1 | 3.2 | >100 |
| 2n | 3-Br | 96.9 ± 1.3 | 166.3 ± 0.8 | 1.7 | ND |
| 2o | 2-Br | 62.6 ± 3.2 | 54.2 ± 0.1 | 0.9 | ND |
| 2p | 3-CF3 | 49.9 ± 1.4 | 63.6 ± 2.8 | 1.3 | ND |
| 2q | 2-CF3 | 50.0 ± 1.6 | 19.1 ± 0.5 | 0.4 | ND |
| 2r | 3-NO2 | 81.3 ± 2.6 | 132.9 ± 10.2 | 1.6 | ND |
| 2s | 2-NO2 | 59.7 ± 5.8 | 93.1 ± 4.9 | 1.6 | ND |
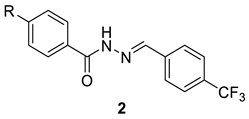 | |||||
| 2t | H | 62.9 ± 0.8 | 189.8 ± 1.7 | 3.0 | ND |
| 2u | CH3 | 75.3 ± 1.5 | 244.9 ± 7.0 | 3.3 | ND |
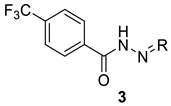 | |||||
| 3a | propan-2-ylidene | 69.7 ± 5.2 | 424.3 ± 1.4 | 6.1 | >100 |
| 3b | cyclopentylidene | 69.2 ± 1.0 | 199.8 ± 13.2 | 2.9 | >100 |
| 3c | cyclohexylidene | 61.2 ± 1.3 | 74.7 ± 2.7 | 1.2 | >100 |
| 3d | 1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo-[2.2.1]heptan-2-ylidene | 59.3 ± 1.8 | 57.2 ± 3.4 | 1.0 | >100 |
| 1 [23] | - | 69.4 ± 1.4 | 204.0 ± 2.7 | 2.9 | >100 |
| Galantamine | 1.54 ± 0.02 | 2.77 ± 0.15 | 1.8 | ND | |
| Code | Mw | log P | H-Bond Donors | H-Bond Acceptors | tPSA (Å2) | Rotatable Bonds | BOILED-Egg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | 292.26 | 3.66 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2b | 326.70 | 4.19 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2c | 326.70 | 4.20 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2d | 326.70 | 4.37 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2e | 308.26 | 3.26 | 2 | 4 | 61.69 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2f | 308.26 | 3.26 | 2 | 4 | 61.69 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2g | 308.26 | 3.43 | 2 | 4 | 61.69 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2h | 342.70 | 4.01 | 2 | 4 | 61.69 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2i | 306.28 | 4.00 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2j | 322.28 | 3.67 | 1 | 4 | 50.69 | 6 | ✔ |
| 2k | 371.15 | 4.28 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2l | 360.25 | 4.72 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 6 | - |
| 2m | 337.25 | 3.06 | 1 | 5 | 87.28 | 6 | - |
| 2n | 371.15 | 4.29 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2o | 371.15 | 4.45 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2p | 360.25 | 4.71 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 6 | - |
| 2q | 360.25 | 4.77 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 6 | - |
| 2r | 337.25 | 3.05 | 1 | 5 | 87.28 | 6 | - |
| 2s | 337.25 | 3.23 | 1 | 5 | 87.28 | 6 | - |
| 2t | 292.26 | 3.65 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 5 | ✔ |
| 2u | 306.28 | 3.91 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 5 | ✔ |
| 3a | 244.21 | 2.93 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 4 | ✔ |
| 3b | 270.25 | 3.35 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 4 | ✔ |
| 3c | 284.28 | 3.69 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 4 | ✔ |
| 3d | 338.37 | 4.60 | 1 | 3 | 41.46 | 4 | ✔ |
| 1 | 204.15 | 1.70 | 2 | 3 | 55.12 | 3 | ✔ |
| Breakpoint [29] | ≤500 | ≤6.0 | <5 | <10 | ≤90 | ≤5 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krátký, M.; Svrčková, K.; Vu, Q.A.; Štěpánková, Š.; Vinšová, J. Hydrazones of 4-(Trifluoromethyl)benzohydrazide as New Inhibitors of Acetyl- and Butyrylcholinesterase. Molecules 2021, 26, 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040989
Krátký M, Svrčková K, Vu QA, Štěpánková Š, Vinšová J. Hydrazones of 4-(Trifluoromethyl)benzohydrazide as New Inhibitors of Acetyl- and Butyrylcholinesterase. Molecules. 2021; 26(4):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040989
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrátký, Martin, Katarína Svrčková, Quynh Anh Vu, Šárka Štěpánková, and Jarmila Vinšová. 2021. "Hydrazones of 4-(Trifluoromethyl)benzohydrazide as New Inhibitors of Acetyl- and Butyrylcholinesterase" Molecules 26, no. 4: 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040989
APA StyleKrátký, M., Svrčková, K., Vu, Q. A., Štěpánková, Š., & Vinšová, J. (2021). Hydrazones of 4-(Trifluoromethyl)benzohydrazide as New Inhibitors of Acetyl- and Butyrylcholinesterase. Molecules, 26(4), 989. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26040989








