Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Heavy Metals in a Regulated E-Waste Recycling Site, Eastern China: Implications for Risk Management
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
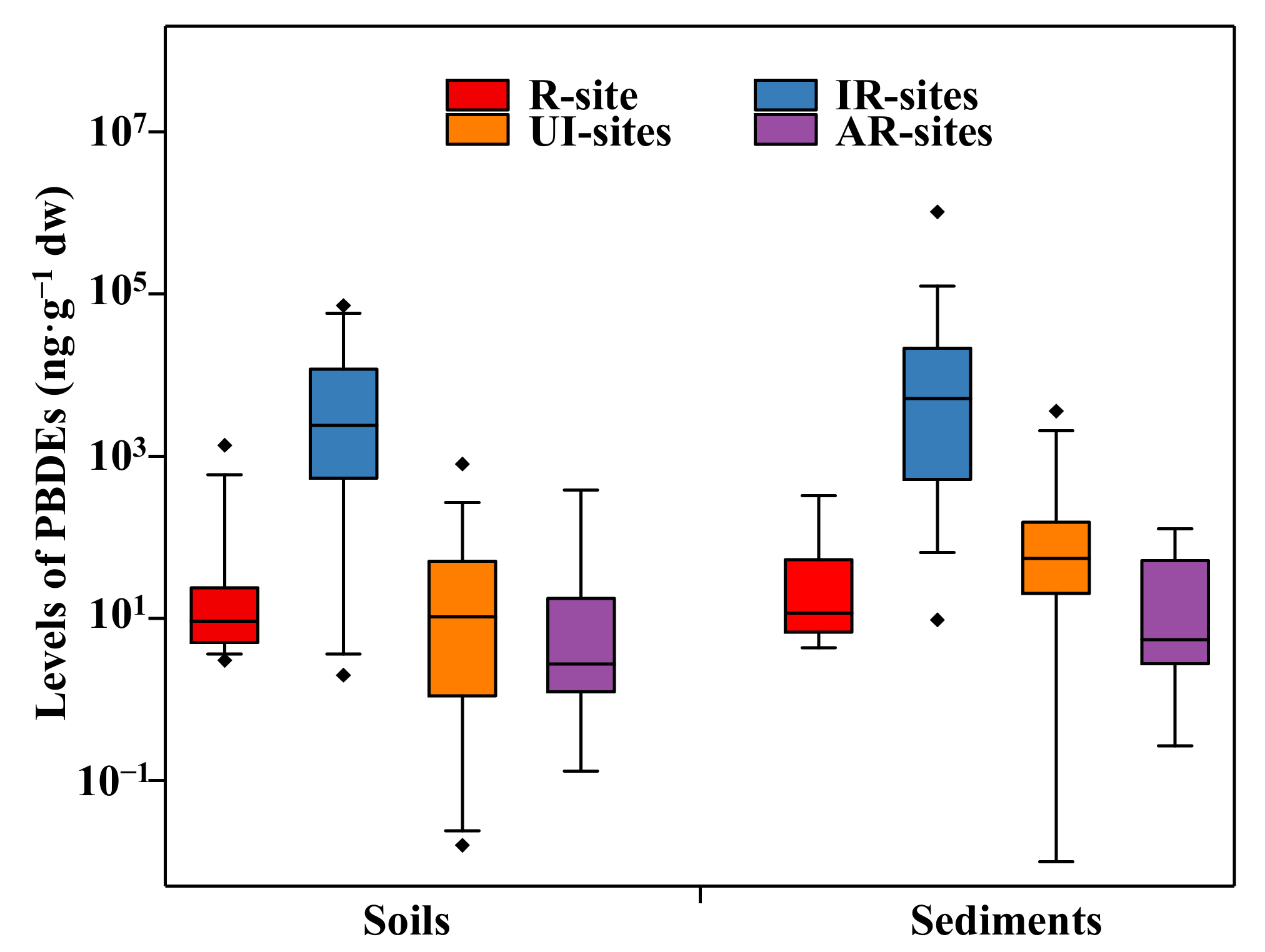
2.1. Contamination of PBDEs
2.2. Contamination of Heavy Metals
2.3. Health Risk Assessment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Sample Collection
3.3. Sample Analysis
3.4. Statistical Analysis and Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Baldé, C.P.; Wang, F.; Kuehr, R.; Huisman, J. The Global E-Waste Monitor 2014: Quantities, Flows and Resources; United Nations University, IAS–SCYCLE: Bonn, Germany, 2015; Available online: http://ewastemonitor.info/download/global-e-waste-monitor/ (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Baldé, C.P.; Forti, V.; Gray, V.; Kuehr, R.; Stegmann, P. The Global E-Waste Monitor 2017: Quantities, Flows and Resources. 2017. Available online: http://ewastemonitor.info/home-new-with-more-news/ (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Forti, V.; Baldé, C.P.; Kuehr, R.; Bel, G. The Global E-Waste Monitor 2020: Quantities, Flows and the Circular Economy Potential; 2020; Available online: http://ewastemonitor.info/ (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Ackah, M. Informal e-waste recycling in developing countries: Review of metal(loid)s pollution, environmental impacts and transport pathways. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24092–24101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Tang, Z.W.; Sun, J.Z.; Xing, X.Y.; Zhang, M.N.; Cheng, J.L. Heavy metals in soil contaminated through e-waste processing activities in a recycling area: Implications for risk management. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 125, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shaheen, S.M.; Jiang, Y.; Li, R.; Slaný, M.; Abdelrahman, H.; Kwon, E.; Bolan, N.; Rinklebe, J.; Zhang, Z. Fe/Mn- and P-modified drinking water treatment residuals reduced Cu and Pb phytoavailability and uptake in a mining soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Li, J. A systematic review of the human body burden of e-waste exposure in China. Environ. Int. 2014, 68, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adie, G.U.; Sun, L.; Zeng, X.; Zheng, L.; Osibanjo, O.; Li, J. Examining the evolution of metals utilized in printed circuit boards. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Wu, Y.X.; Simonnot, M.O. Soil contamination due to e-waste disposal and recycling activities: A review with special focus on China. Pedosphere 2012, 22, 434–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, T.; Popp, R.; Wolf, M.; van Eldik, R. Analysis of eco-relevant elements and noble metals in printed wiring boards using AAS, ICP-AES and EDXRF. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 375, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, B.H. E-waste: An assessment of global production and environmental impacts. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Marvin, C.H.; Hites, R.A. Dechlorane Plus and Other Flame Retardants in a Sediment Core from Lake Ontario. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6014–6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, D.; Walpita, J. Organic pollutants from E-waste and their electrokinetic remediation. Handb. Electron. Waste Manag. 2020, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, F.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Jamil, N.; Qadir, A.; Ali, M.I. Microbial and enzymatic degradation of PCBs from e-waste-contaminated sites: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 10474–10487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Zeng, X.; Li, J. Environmental pollution of electronic waste recycling in India: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morf, L.S.; Tremp, J.; Gloor, R.; Schuppisser, F.; Stengele, M.; Taverna, R. Metals, non-metals and PCB in electrical and electronic waste-actual levels in Switzerland. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvall, E.; Tostar, S.; Boldizar, A.; Foreman, M.R.; Möller, K. An analysis of the composition and metal contamination of plastics from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hu, M.; Wu, H.; Niu, Q.; Lu, X.; He, J.; Huang, F. Plasma polybrominated diphenyl ethers, urinary heavy metals and the risk of thyroid cancer: A case-control study in China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.L.; Liao, C.J.; Chang-Chien, G.P. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans in ash from different units in a municipal solid waste incinerator. Waste Manag. Res. 2010, 28, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Schnoor, J.L.; Zeng, E.Y. E-waste recycling: Where does it go from here? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10861–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Streicher-Porte, M.; Wang, M.Y.; Reuter, M.A. Informal electronic waste recycling: A sector review with special focus on China. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.L.; Williams, E.; Ju, M.T.; Shao, C.F. Managing e-waste in China: Policies, pilot projects and alternative approaches. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyi, A.A.; Oyeleke, P. Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil from e-waste dumpsites in Lagos and Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Health Pollut. 2017, 7, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaifie, A.; Schettgen, T.; Bertram, J.; Löhndorf, K.; Waldschmidt, S.; Felten, M.K.; Kraus, T.; Fobil, J.N.; Küpper, T. Informal e-waste recycling and plasma levels of non-dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (NDL-PCBs)—A cross-sectional study at Agbogbloshie, Ghana. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Liu, R.; Dietrich, K.N.; Reponen, T.; Xie, C.; Sucharew, H.; Huo, X.; et al. Birth outcomes associated with maternal exposure to metals from informal electronic waste recycling in Guiyu, China. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labunska, I.; Harrad, S.; Santillo, D.; Johnston, P.; Brigden, K. Levels and distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soil, sediment and dust samples collected from various electronic waste recycling sites within Guiyu town, southern China. Environ. Sci. Proc. Imp. 2013, 15, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeckel, C.; Breivik, K.; Nøst, T.H.; Sankoh, A.; Jones, K.C.; Sweetman, A. Soil pollution at a major West African e-waste recycling site: Contamination pathways and implications for potential mitigation strategies. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Leung, J.; Du, Y.; Kong, D.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, T. Trace metals in e-waste lead to serious health risk through consumption of rice growing near an abandoned e-waste recycling site: Comparisons with PBDEs and AHFRs. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, A.; Ray, J.G. Toxic heavy metals in human blood in relation to certain food and environmental samples in Kerala, South India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7946–7953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Cheng, J.; Tang, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhang, M. Global distribution and trends of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in human blood and breast milk: A quantitative meta-analysis of studies published in the period 2000–2019. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 280, 111696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Kayaga, S.; Smout, I. Regulating for e-waste in China: Progress and challenges. Munic. Eng. 2009, 162, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Zhao, K.; Liu, X.; Wendroth, O.; Xu, J. Ten-year regional monitoring of soil-rice grain contamination by heavy metals with implications for target remediation and food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wen, S.; Li, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. The human body burden of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and their relationships with thyroid hormones in the general population in Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Ding, J.; Xie, X.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Qin, L.; Han, C. Pollution status and human exposure of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in China. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3333–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Duan, Y.P.; Huang, F.; Yang, J.; Xiang, N.; Meng, X.Z.; Chen, L. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in e-waste: Level and transfer in a typical e-waste recycling site in Shanghai, Eastern China. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabi, O.A.; Bakare, A.A.; Xu, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, X. Comparative evaluation of environmental contamination and DNA damage induced by electronic-waste in Nigeria and China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 423, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Zeng, Y.; Luo, X.; Ren, Z.; Tang, B.; Lu, Q.; Gao, S.; Wang, S.; Mai, B. In situ microbial degradation of PBDEs in sediments from an e-waste site as revealed by positive matrix factorization and compound-specific stable carbon isotope analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Luo, C.; Li, J.; Yin, H.; Zhang, G. Plant selective uptake of halogenated flame retardants at an e-waste recycling site in southern China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Yang, F.; Li, J.G.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Hui, Y.; Wu, Y.N.; Zhao, Y.F.; Xu, Y. Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin and dibenzofurans (PCDD/Fs), polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) monitored by tree bark in an E-waste recycling area. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Cheng, J.; He, L.; Zhang, M.; Ren, S.; Sun, J.; Xing, X.; Tang, Z. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soils from Tianjin, North China: Distribution, health risk, and temporal trends. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.X.; Lu, Y.T.; Ruan, Q.Y.; Lai, C.; Sun, S.B.; Yao, H.; Zhang, Z.S. Occurrence, distribution, source, and health risk assessment of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in surface soil from the Shen-Fu Region, Northeast China. Environ. Sci. 2020, 41, 368–376. (In Chinse) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, B.; Chen, S.; Luo, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q.; Sheng, G.; Peng, P.; Fu, J.; Zeng, E.Y. Distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments of the Pearl River Delta and adjacent South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3521–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, W.L.; Chen, S.J.; Shi, D.L.; Zhao, H.; Ding, Y.; Huang, Y.R.; Li, N.; Ren, Y.; Mai, B.X. Occurrence, sources, and ecological risks of PBDEs, PCBs, OCPs, and PAHs in surface sediments of the Yangtze River Delta city cluster, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 5285–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, H.H.; Wang, X.T.; Cheng, H.X.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, R. Pine needles as biomonitors of polybrominated diphenyl ethers and emerging flame retardants in the atmosphere of Shanghai, China: Occurrence, spatial distributions, and possible sources. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 12171–12180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.X.; Zeng, L.Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, T.; Dong, L.; Huang, Y.R. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in camphor bark from speedy developing urban in Jiangsu Province. Environ. Sci. 2011, 32, 2654–2660. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Li, H.; Peng, Y.; Lou, X.; Liu, M.; Hu, J.; Liu, C.; Wei, B.; Jin, J. Concentrations and distributions of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in surface soils and tree bark in Inner Mongolia, northern China, and the risks posed to humans. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Z.; Lin, K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Cui, C.; Lin, J.; Dong, Q.; Huang, C. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in water, sediment, soil, and biological samples from different industrial areas in Zhejiang, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 197, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Meng, X.; Chen, L.; Yin, D. Contamination by persistent toxic substances in surface sediment of urban rivers in Chaohu City, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Pei, J.C.; Zheng, M.; Tang, L.; Bao, Y.Y.; Xu, B.T.; Sun, R.; Sun, Y.F.; Xu, G.; Lei, J.Q. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in soil and outdoor dust from a multi-functional area of Shanghai: Levels, compositional profiles and interrelationships. Chemosphere 2015, 118, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Pan, B.; Fu, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Lin, K. Distribution of metals and brominated flame retardants (BFRs) in sediments, soils and plants from an informal e-waste dismantling site, South China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 1020–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Cai, Z.W.; Wong, M.H. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in fish and sediment from river polluted by electronic waste. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 383, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Addink, R.; Yun, S.; Cheng, J.; Wang, W.; Kannan, K. Polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soil, vegetation, workshop-floor dust, and electronic shredder residue from an electronic waste recycling facility and in soils from a chemical industrial complex in eastern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7350–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Ma, W.L.; Jia, H.L.; Hong, W.J.; Moon, H.B.; Nakata, H.; Minh, N.H.; Sinha, R.K.; Chi, K.H.; Kannan, K.; et al. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in surface soils across five Asian countries: Levels, spatial distribution, and source contribution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12779–12788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Tang, Z.; Meng, T.; Zhang, M. Concentration profile, spatial distributions and temporal trends of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments across China: Implications for risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC). The Soil Background Value in China; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512–513, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, D.D.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Berger, T.A. Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Huang, Q. Concentrations and human health implications of heavy metals in market foods from a Chinese coal-mining city. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 50, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, G.; Li, X. Heavy metal contamination in soils and vegetables near an e-waste processing site, South China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Du, Y.; Huang, Z.; Gu, J.; Leung, J.; Mai, B.; Xiao, T.; Liu, W.; Fu, J. Vertical profile of soil/sediment pollution and microbial community change by e-waste recycling operation. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Luo, X.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X.; Yuan, J.; Chen, S.; Mai, B. Studies on heavy metal contamination by improper handling of e-waste and its environmental risk evaluation. IV. Heavy metal contamination of sediments in a small scale valley impacted by e-waste treating activities. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2008, 3, 343–349. Available online: http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STDL200804007.htm (accessed on 8 April 2021). (In Chinese).
- Wang, F.; Leung, A.O.; Wu, S.C.; Yang, M.S.; Wong, M.H. Chemical and ecotoxicological analyses of sediments and elutriates of contaminated rivers due to e-waste recycling activities using a diverse battery of bioassays. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2082–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, K.H.; Yan, X.; Chen, S.J.; Hu, G.C.; Peng, X.W.; Yuan, J.G.; Mai, B.X.; Yang, Z.Y. Heavy metals in food, house dust, and water from an e-waste recycling area in South China and the potential risk to human health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 96, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.S.; Yu, S.; Zhu, Y.G.; Li, X.D. Trace metal contamination in urban soils of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xia, T.; Jia, X.; Wang, S. Heavy metal pollution and human health risk assessment at mercury smelting sites in Wanshan district of Guizhou Province, China. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23066–23079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Li, X.; Ai, Y.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; et al. Potentially toxic metals and the risk to children’s health in a coal mining city: An investigation of soil and dust levels, bioaccessibility and blood lead levels. Environ. Int. 2020, 141, 105788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.M.; Wen, H.H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.S.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Niu, J.; Tang, Z. Distribution and speciation of heavy metals in sediments from the mainstream, tributaries, and lakes of the Yangtze River catchment of Wuhan, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 166, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Fang, H.L.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, X.X.; Liu, Y.D. Heavy metal in leaves of twelve plant species from seven different areas in Shanghai, China. Urban. For. Urban. Gree. 2017, 27, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, R.; Fu, S.; Wu, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, H. Spatial heterogeneity of heavy metal contamination in soils and plants in Hefei, China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, C.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jia, J.; Bao, X. Heavy metals and lead isotopes in soils, road dust and leafy vegetables and health risks via vegetable consumption in the industrial areas of Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Q.; Fu, W.J.; Zhang, M.J.; Zhao, K.L.; Tunney, H.; Guan, Y.D. Potentially hazardous metals contamination in soil-rice system and it’s spatial variation in Shengzhou City, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 167, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, T.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Johnson, D.; Huang, Y. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in the lotus root of rural ponds in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2557–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, X.; Qin, J.; Li, H. Distribution of heavy metals in soils and vegetables and health risk assessment in the vicinity of three contaminated sites in Guangdong Province, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 1901–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Ma, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Yu, Y. Halogenated and organophosphorous flame retardants in surface soils from an e-waste dismantling park and its surrounding area: Distributions, sources, and human health risks. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, M. Risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls and heavy metals in soils of an abandoned e-waste site in China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). China County Statistics Yearbook-2018 (Township Volume); China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019; p. 268. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Ministry of Environmental Protection (CMEP). Technical Guidelines for Investigation on Soil Contamination of Land for Construction. Available online: http://kjs.mee.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/jcffbz/201912/t20191209_748223.shtml (accessed on 25 December 2020). (In Chinese)
- Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China (MLRC). Specification on Geochemical Reconnaissance Survey (1:50000) (DZ/T 0011–2015). 2015. Available online: http://www.jianbiaoku.com/webarbs/book/82739/2260214.shtml (accessed on 25 December 2020). (In Chinese).
- Tang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Cheng, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, W.; Nie, Z.; Zeng, N.; Jin, L. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in soils, sediments, and human hair in a plastic waste recycling area: A neglected heavily polluted area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Cheng, J.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chai, M. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) and heavy metals in road dusts from a plastic waste recycling area in north China: Implications for human health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of Geo-Accumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Child-Specific Exposure Factors Handbook, EPA-600-P-00-002B; National Center for Environmental Assessment: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/si/si_public_record_report.cfm?Lab=NCEA&dirEntryId=55145 (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (EPA/540/1-89/002). Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part. A); Office of Emergency and Remedial Response: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; Volume 1. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/rags_a.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Baseline Human Health Risk Assessment Vasquez Boulevard and I-70 superfund site Denver; Denver (Co); 2001. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/documents/hhra_vbi70-ou1.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Beijing Municipal Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision (BMBQTS). Environmental Site Assessment Guideline (DB11/T 656–2009); BMBQTS: Beijing, China. Available online: https://www.baidu.com/link?url=V_DFtVvt6IPOY1rE8yRzPcRze-thX5Iehk2IHdQwQaJjH1eiAyXEoLMjpbms94iS-1Izhtj_Fcjk7wOIORT9VKt9wtu3WtMYWfv7tuTO5I-hj3xHk_NcnwSI2FjD2KVHYRC2I6meKP9RGI_3-Bks4VyEYqqI1xLRQaFeCxldTau7o6h4rX2prhW98uGe0X3rygS9Wqp_yBUUmFAAStpgwLkZlkudFA7gP0KMR-2x-yw0D-MOziCKHN0yiXGFmSGB&wd=&eqid=af84f9d00001ea5d00000003606f0895 (accessed on 8 April 2021). (In Chinese).
- Smith, R.L. Use of Monte Carlo Simulation for Human Exposure Assessment at a Superfund Site. Risk Anal. 1994, 14, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund: Volume III-Part A, Process for Conducting Probabilistic Risk Assessment; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-09/documents/rags3adt_complete.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Health Canada (HC). Federal Contaminated Site Risk Assessment in Canada-Part II: Health Canada Toxicological Reference Values (TRVs) and Chemical-Specific Factors; Government of Canada: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2004. Available online: http://publications.gc.ca/site/eng/387683/publication.html (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- Integrated Risk Information System (USEPA IRIS). 2,2′,4,4′-Tetrabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-47) (CASRN 5436-43-1); US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/toxreviews/1010tr.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Integrated Risk Information System (USEPA IRIS). 2,2′,4,4′,5-Pentabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-99) (CASRN 60348-60-9); US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/1008_summary.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Integrated Risk Information System (USEPA IRIS). 2,2′,4,4′,5,5′-Hexabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-153) (CASRN 68631-49-2); US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/1009_summary.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Integrated Risk Information System (USEPA IRIS). 2,2′,3,3′,4,4′,5,5′,6,6′-Decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) (CASRN 1163-19-5); US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/iris_documents/documents/subst/0035_summary.pdf (accessed on 31 January 2021).
- Leung, A.O.W.; Luksemburg, W.J.; Wong, A.S.; Wong, M.H. Spatial Distribution of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Polychlorinated Dibenzo-p-dioxins and Dibenzofurans in Soil and Combusted Residue at Guiyu, an Electronic Waste Recycling Site in Southeast China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.F.; Tang, Z.W.; Shen, H.Y.; Huang, Q.F.; Tao, Y. Characterization of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in dismantling and burning sites in electronic waste polluted area, south China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 36, 84–89. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Yu, Y.J.; Han, M.; Yang, S.W.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y. Estimated PBDE and PBB Congeners in Soil from an Electronics Waste Disposal Site. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 83, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, K.; Wu, M.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Occurrence, compositional profiles and possible sources of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in urban soils of Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Fu, S.; Yang, Z.Z.; Xu, X.B. Composition, Distribution and Characterization of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) in the Soil in Taiyuan, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 81, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, K.; Wu, M.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Occurrence, compositional patterns, and possible sources of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in agricultural soil of Shanghai, China. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Pan, L.; Zhan, Y.; Lu, H.; Tsang, D.C.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, L. Contamination of phthalate esters, organochlorine pesticides and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in agricultural soils from the Yangtze River Delta of China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 544, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ran, Y. Distribution and partitioning of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments from the Pearl River Delta and Guiyu, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J. Study on the accumulation of dechorane plus: Compared with polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediment from the Yongning River with an e-waste dismantling plant in Taizhou, Southeastern China. Master’s Dissertation, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, China, 2015. Available online: http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10337-1016036270.htm (accessed on 8 April 2021). (In Chinese).
- Xiong, J.; An, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, G. Pollution profiles and risk assessment of PBDEs and phenolic brominated flame retardants in water environments within a typical electronic waste dismantling region. Environ. Geochem. Heal. 2015, 37, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhou, H.; Han, N.; Zhu, H.; Uchimiya, M. Spatial distribution, source analysis, and ecological risk assessment of PBDEs in river sediment around Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, C.; Wang, R.; Huang, Q.; Mao, J.; Xie, L.; Xue, C.; Zhang, L. Sediment Records of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers (PBDEs) from the Anhui Province Section of Yangtze River, China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, C.; Wang, R.; Ye, J.; Yang, S. Sediment records of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in Huaihe River, China: Implications for historical production and household usage of PBDE-containing products. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.L.; Chen, Z.X.; Ni, H.G.; Zeng, H. PBDEs as indicator chemicals of urbanization along an urban/rural gradient in South China. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Qin, X.F.; Li, Y.; Liu, P.Y.; Tian, M.; Yan, S.S.; Qin, Z.F.; Xu, X.B.; Yang, Y.J. Diffusion of polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDE) from an e-waste recycling area to the surrounding regions in Southeast China. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Chen, S.J.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Luo, X.J.; Mai, B.X. Plant Uptake of Atmospheric Brominated Flame Retardants at an E-Waste Site in Southern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2708–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Z.; Zhao, X.R.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, Z.F.; Qin, X.F.; Xu, X.B.; Jin, Z.X.; Xu, C.X. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers in Leaves and Soil from Typical Electronic Waste Polluted Area in South China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 80, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, S.; Christie, P. Plant uptake and dissipation of PBDEs in the soils of electronic waste recycling sites. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Mai, B. Studies on heavy metal contamination by improper handling of e-waste and its environmental risk evaluation I. Heavy metal contamination in e-waste open burning sites. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2008, 3, 34–41. Available online: https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-STDL200801008.htm (accessed on 8 April 2021). (In Chinese).
- Luo, Y.; Luo, X.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X.; Yuan, J.; Chen, S.; Mai, B. Studies on heavy metal contamination by improper handling of e-waste and its environmental risk evaluation. II. Heavy metal contamination in surface soils on e-waste disassembling workshops within villages and the adjacent agricultural soils. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2008, 3, 123–129. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=97bb4a53b576730d0e9eec5d88acfda0&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 8 April 2021). (In Chinese).
- Tang, X.; Shen, C.; Shi, D.; Cheema, S.A.; Khan, M.I.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y. Heavy metal and persistent organic compound contamination in soil from Wenling: An emerging e-waste recycling city in Taizhou area, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, X.; Yutong, Z.; Shenggao, L. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risk in urban soils of steel industrial city (Anshan), Liaoning, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 120, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.M.; Chen, T.B.; He, J.Z. Multivariate geostatistical analysis of heavy metals in topsoils from Beijing, China. J. Soils Sediments 2007, 8, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.K.; Ke, Z.X. Heavy metals, phosphorus and some other elements in urban soils of Hangzhou city, China. Pedosphere 2004, 14, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Chen, Z.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Bi, C.; Teng, J. Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Yang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Li, Y.; Hou, Q.; Yu, T. Soil heavy metal concentrations and their typical input and output fluxes on the southern Song-nen Plain, Heilongjiang Province, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Mao, R.; Shao, H.; Gao, Y. An investigation on the distribution of eight hazardous heavy metals in the suburban farmland of China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.P. On Heavy metal pollution status and its assessment for the farmland soil of Henan Province. J. Environ. Manage. Coll. Chin. 2007, 3, 44–46. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.M.; Wang, W.B.; Wen, C.P.; Yi, Z.Y.; Tang, S.M. Concentrations and distributions of selenium and heavy metals in Hainan paddy soil and assessment of ecological security. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 3477–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, W.; Huang, B.; Shi, X.; Ji, J. Spatial interrelations and multi-scale sources of soil heavy metal variability in a typical urban–rural transition area in Yangtze River Delta region of China. Geoderma 2010, 156, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Fang, H.G.; Wang, L.J. Present situation of soil environmental quality and protection countermeasures in Ji County. Till. Cultivation 2012, 2, 36–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Y.; Guo, J.; Chai, S.; Cai, J.; Xue, L.; Zhang, Q. Source identification of eight heavy metals in grassland soils by multivariate analysis from the Baicheng–Songyuan area, Jilin Province, Northeast China. Chemosphere 2015, 134, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Yang, F.; Xu, C.; Yang, H.; Liu, W. Status of metal accumulation in farmland soils across China: From distribution to risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, S.X.; Yan, B.; Lei, C.; Yang, F.; Li, N.; Xiao, X.M.; Fu, J.M. Distribution of heavy metal pollution in sediments from an acid leaching site of e-waste. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 499, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yu, C.; Shen, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, L.; Shen, K.; Tang, X.; Chen, Y. Study on adverse impact of e-waste disassembly on surface sediment in East China by chemical analysis and bioassays. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wu, Q.; Kong, D.; Shi, Y.; Huang, X.; Luo, D.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, T.; Leung, J.Y. Accumulation and translocation of heavy metals in water hyacinth: Maximising the use of green resources to remediate sites impacted by e-waste recycling activities. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; He, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, S. Content, enrichment, and regional geochemical baseline of antimony in the estuarine sediment of the Daliao river system in China. Geochem. 2012, 72, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Cai, A.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Wu, T.; Pan, B.; Song, N.; Li, F.; Lu, M. Heavy metals in the riverbed surface sediment of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 24768–24780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Liu, L.; Yan, N.; Li, F.; Tao, H.; Ye, H.; Wen, H. Factors controlling the accumulation and ecological risk of trace metal(loid)s in river sediments in agricultural field. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Wang, D.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S. Accumulation and risk assessment of heavy metals in water, sediments, and aquatic organisms in rural rivers in the Taihu Lake region, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 6721–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Qin, C.; Hong, X.; Kang, G.; Qin, M.; Yang, D.; Pang, B.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Dick, R.P. Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of Yellow River irrigation in China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 633, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wang, R.; Zhu, B.; Rudstam, L.G.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xin, W.; Chen, Y. Heavy metal gradients from rural to urban lakes in central China. Ecol. Process. 2020, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soils | Sediments | Vegetables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min–Max | Median | Min–Max | Median | Min–Max | Median | |
| BDE-28 | <0.002 | <0.002 | <0.002–0.043 | <0.002 | <0.003–0.18 | 0.05 |
| BDE-47 | <0.003–0.11 | <0.003 | <0.003–0.81 | <0.003 | 0.005–1.27 | 0.26 |
| BDE-66 | <0.006–0.03 | <0.006 | <0.006–0.62 | <0.006 | <0.007–0.19 | 0.05 |
| BDE-85 | <0.013 | <0.013 | <0.013 | <0.013 | <0.013–0.18 | <0.013 |
| BDE-99 | <0.007–0.22 | <0.007 | <0.007–0.31 | <0.007 | <0.007–0.30 | 0.110 |
| BDE-100 | <0.010 | <0.010 | <0.010–1.26 | <0.010 | <0.010–0.36 | 0.02 |
| BDE-138 | <0.005 | <0.005 | <0.005 | <0.005 | <0.005–0.06 | <0.005 |
| BDE-153 | <0.008–0.33 | <0.008 | <0.008–0.23 | <0.008 | <0.008–0.20 | <0.008 |
| BDE-154 | <0.022–14.0 | <0.022 | <0.022–0.93 | 0.12 | <0.022–0.76 | 0.20 |
| BDE-183 | <0.018–0.81 | <0.018 | <0.018–0.13 | <0.018 | <0.019–0.30 | 0.019 |
| BDE-190 | <0.035 | <0.035 | <0.035 | <0.035 | <0.035 | <0.035 |
| BDE-196 | <0.054–1.09 | <0.054 | <0.054 | <0.054 | <0.054–0.44 | <0.054 |
| BDE-197 | <0.073–1.04 | <0.073 | <0.073–0.70 | <0.073 | <0.073–0.37 | <0.073 |
| BDE-201 | <0.002–0.74 | <0.002 | <0.002–0.73 | <0.002 | <0.003–0.46 | <0.003 |
| BDE-202 | <0.002–0.55 | <0.002 | <0.002–0.54 | <0.002 | <0.003–0.37 | <0.003 |
| BDE-203 | <0.105–1.56 | <0.105 | <0.105 | <0.105 | <0.105–0.37 | <0.105 |
| BDE-205 | <0.079 | <0.079 | <0.079 | <0.079 | <0.079 | <0.079 |
| BDE-206 | <0.045–8.70 | <0.045 | <0.045–1.74 | <0.045 | 0.34–1.76 | 0.89 |
| BDE-207 | <0.081–3.96 | <0.081 | <0.081–4.12 | <0.081 | <0.082–1.12 | 0.61 |
| BDE-208 | <0.183–1.99 | <0.183 | <0.183–1.81 | <0.183 | <0.184–1.24 | 0.54 |
| BDE-209 | 3.05–1,331 | 8.09 | 4.27–314 | 10.8 | 90.2–419 | 201 |
| Σ21PBDEs | 3.05–1,336 | 9.23 | 4.31–327 | 11.6 | 93.9–425 | 204 |
| Sampling Sites | Statistics | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Mn | Ni | Pb | Sb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soils (n = 21) | Range | 11.2–31.3 | 0.08–0.22 | 73.2–159 | 14.9–101 | 0.02–0.09 | 1077–2991 | 21.8–52.4 | 23.7–63.3 | 0.96–8.07 | 32.2–170 |
| Mean | 20.0 | 0.12 | 104 | 27.9 | 0.04 | 1839 | 38.9 | 33.4 | 2.11 | 54.0 | |
| Background values 1 | 9.30 | 0.08 | 66.0 | 24.0 | 0.019 | 644 | 25.8 | 25.8 | 0.90 | 63.5 | |
| Risk screening values | 60 2 | 65 2 | 18,000 2 | 38 2 | – | 900 2 | 800 2 | – | – | ||
| 25 3 | 0.6 3 | 250 3 | 100 3 | 3.4 3 | – | 190 3 | 170 3 | – | 300 3 | ||
| Sediments (n = 7) | Range | 7.41–18.0 | 0.11–1.53 | 98.1–294 | 17.5–132 | 0.03–4.95 | 780–1684 | 27.3–61.8 | 26.3–226 | 1.52–123 | 52.9–1071 |
| Mean | 12.0 | 0.42 | 144 | 41.6 | 0.76 | 1145 | 40.7 | 62.3 | 20.7 | 226 | |
| TEC 4 | 9.79 | 0.99 | 43.4 | 31.6 | 0.18 | 22.7 | 35.8 | 121 | |||
| PEC 4 | 33.0 | 4.98 | 111 | 149 | 1.06 | 48.6 | 128 | 459 | |||
| Vegetables (n = 8) | Range | 0.49–1.72 | 0.03–0.31 | 3.28–13.4 | 4.00–16.5 | 0.05–0.37 | 86.7–284 | 1.30–6.14 | 1.09–9.93 | 0.06–2.76 | 21.8–73.7 |
| Mean | 0.95 | 0.14 | 5.49 | 9.99 | 0.17 | 177 | 3.39 | 3.94 | 0.62 | 42.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, H.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Meng, T.; Tang, Z. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Heavy Metals in a Regulated E-Waste Recycling Site, Eastern China: Implications for Risk Management. Molecules 2021, 26, 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082169
Yin H, Ma J, Li Z, Li Y, Meng T, Tang Z. Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Heavy Metals in a Regulated E-Waste Recycling Site, Eastern China: Implications for Risk Management. Molecules. 2021; 26(8):2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082169
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Hongmin, Jiayi Ma, Zhidong Li, Yonghong Li, Tong Meng, and Zhenwu Tang. 2021. "Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Heavy Metals in a Regulated E-Waste Recycling Site, Eastern China: Implications for Risk Management" Molecules 26, no. 8: 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082169
APA StyleYin, H., Ma, J., Li, Z., Li, Y., Meng, T., & Tang, Z. (2021). Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Heavy Metals in a Regulated E-Waste Recycling Site, Eastern China: Implications for Risk Management. Molecules, 26(8), 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26082169







