Recent Advances in Inorganic Nanomaterials Synthesis Using Sonochemistry: A Comprehensive Review on Iron Oxide, Gold and Iron Oxide Coated Gold Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
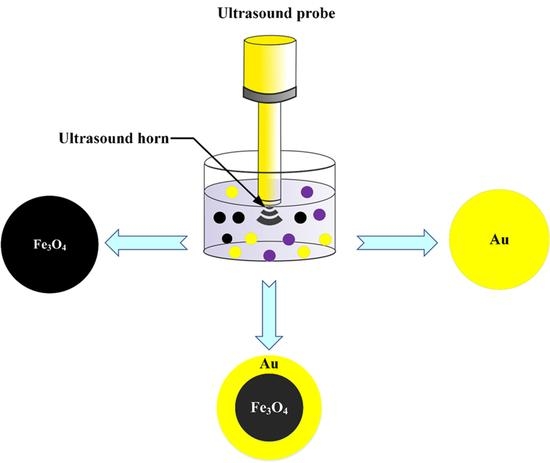
2. Sonochemical Formation of Fe3O4NPs, AuNPs and Fe3O4NPs@AuNPs
3. Nanomaterial Ultrasonic Synthesis
3.1. Fe3O4NPs
3.2. AuNPs
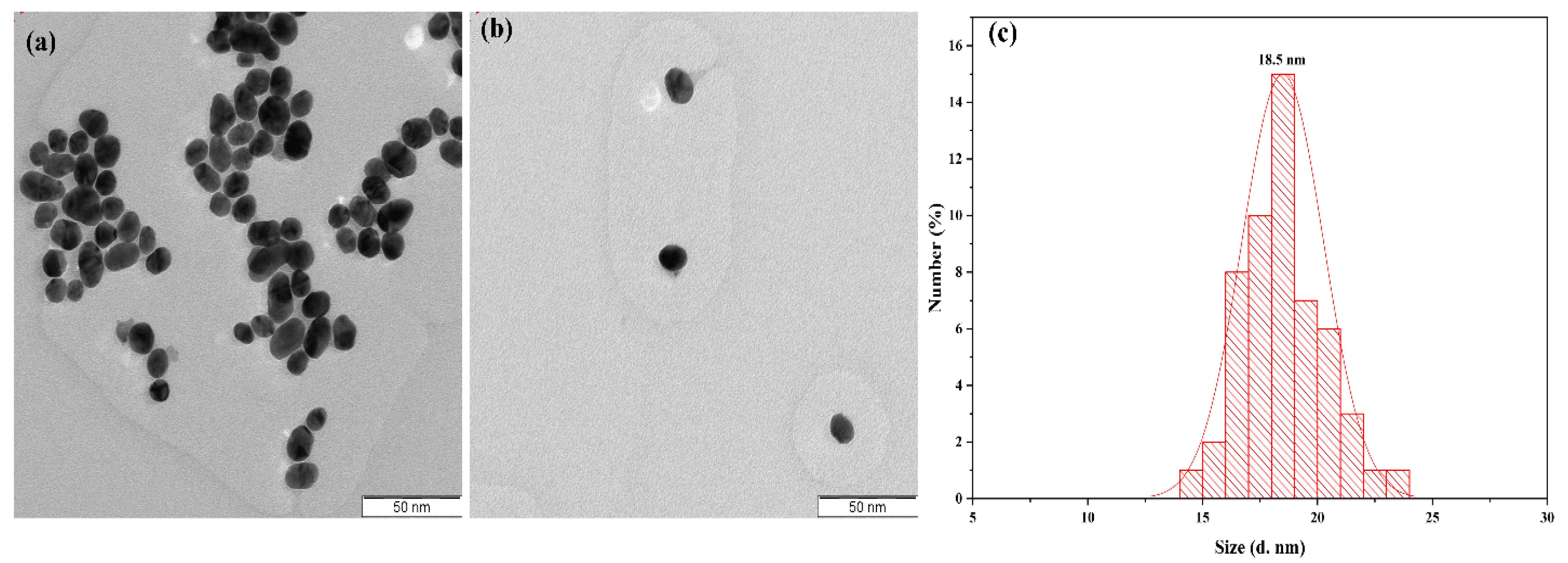
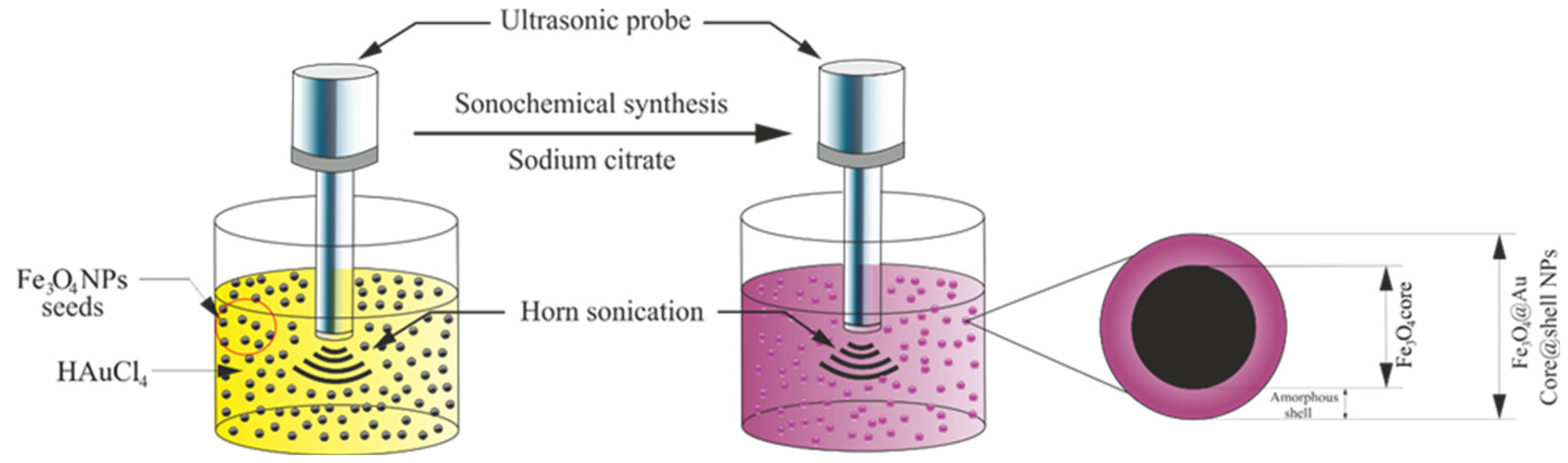
3.3. Fe3O4@AuNPs
| No. | Nanoparticles | Power or Frequency | Size and Shape | Media | Precursor Concentration | SPR | Magnetization | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fe3O4 | 130 kHz | 180 nm | NH4Cl | 0.5 mol/L | ………. | 20 mT | [50] |
| 2 | Fe3O4@GOS | 60 W | 96 nm spherical | sodium acetate Polyvinylpyrrolidone | 2 mg | ………. | ………. | [51] |
| 3 | Fe3O4 | ………. | 15 nm amorphous | NH4OH | 100 mg/L | 215 nm | 76.89 emu/g | [52] |
| 4 | Fe3O4@MWCNTs | 40 kHz | 20 nm amorphous | water/ethylene glycol | 40 mg | ………. | ………. | [53] |
| 5 | Fe3O4 | 40 kHz, 150 W | 22.41 nm Semi-spherical | ethylenediamine | ………. | ………. | 54.24 | [54] |
| 6 | Fe3O4 | 20 kHz 1500 W | 80 nm cubes | distilled water | 2.31 mg | 91 emu/g | [55] | |
| 7 | AuNPs | 20 kHz/17.9 W·cm2 | 18 nm semi-spherical | distilled water | 0.03 M | 520 nm | ………. | [80] |
| 8 | AuNPs | 495 kHz | 22 nm spherical | aqueous solution | 0.1 mM | 530 nm | ………. | [81] |
| 9 | Au–Ru NPs | 355 kHz | 15 nm spherical | polyethylene glycol perchloric acid | 5 × 10−5 M | 536 nm | ………. | [82] |
| 10 | GO-wrapped Au NPs | 200 W | 500 nm sphere | water and ethylene glycol | (8 mg, 0.02 mmol) | 546 nm | ………. | [83] |
| 11 | N_Au NPs | 750 W | 4.83 nm spherical | methanol | 0.1 mmol | ………. | ………. | [84] |
| 12 | AuNPs | 463 kHz | 14 nm nanorods | water | 0.2 mM | 650 nm | ………. | [85] |
| 13 | AuNPs | 20 kHz 40 W.cm−2 | 25 nm oval or spherical | dodecyl amine solutions or sodium dodecyl sulfate | 1 mmol/L | 523 nm | ………. | [86] |
| 14 | Fe3O4@AuNPs | 20 kHz/750 W | 21 nm spherical | water | 0.03 M | 541 nm | 42.2 emu/g | [109] |
| 15 | Fe3O4@AuNPs | 40 kHz | 20.8 nm spherical | water | 0.1 M | 538 nm | ………. | [104] |
| 16 | Fe3O4@AuNPs | 20 kHz and 750 w | 20 nm spherical | water | 0.3 M | 545 nm | 54 emu/g | [110] |
| 17 | Fe3O4-PZS-Au NPs | 40 kHz, 50 W | 253 nm spherical | NaBH4 | 24 mM | 526 nm | 24.2 emu/g | [115] |
| 18 | Fe3O4@Au NPs-BSA | 60 kHz | 9–25 nm spherical | sodium citrate | 15 mL (1% mass fraction) | 547 nm | ………. | [118] |
4. Shapes of Synthesis Nanomaterials Sonochemically
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsakalakos, T.; Ovid’ko, I.A.; Vasudevan, A.K. Nanostructures: Synthesis, Functional Properties and Application; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jameel, M.S.; Aziz, A.A.; Dheyab, M.A. Impacts of various solvents in ultrasonic irradiation and green synthesis of platinum nanoparticle. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 128, 108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameel, M.S.; Aziz, A.A.; Dheyab, M.A. Comparative analysis of platinum nanoparticles synthesized using sonochemical-assisted and conventional green methods. Nano Struct. Nano Objects 2020, 23, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, W.T.; Loomis, A.L. The Chemical Effects of High Frequency Sound Waves I. A preliminary survey. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1927, 49, 3086–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoli, C.U.; Kuttiyiel, K.A.; Cole, J.; McCutchen, J.; Tawfik, H.; Adzic, R.R.; Mahajan, D. Solvent effect in sonochemical synthesis of metal-alloy nanoparticles for use as electrocatalysts. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aufaure, R.; Lalatonne, Y.; Lièvre, N.; Heintz, O.; Motte, L.; Guénin, E. One pot microwave assisted synthesis of bisphosphonate alkene capped gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 59315–59322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangnier, A.P.; Aufaure, R.; Cheong, S.; Motte, L.; Palpant, B.; Tilley, R.D.; Guenin, E.; Wilhelm, C.; Lalatonne, Y. Raspberry-like small multicore gold nanostructures for efficient photothermal conversion in the first and second near-infrared windows. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 4055–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yang, H.; Huang, P.; Cui, D.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, F.; Lian, J.; Shi, D. Unique role of ionic liquid in microwave-assisted synthesis of monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3866–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiruba, V.S.A.; Dakshinamurthy, A.; Selvakumar, P.M. Eco-Friendly Biocidal Silver-Activated Charcoal Nanocomposite: Antimicrobial Application in Water Purification. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Chem. 2013, 43, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyetade, O.; Oyeleke, G.; Adegoke, B.; Akintunde, A. Stability studies on ascorbic acid (vitamin C) from different sources. J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 2, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hinman, J.J.; Suslick, K.S. Nanostructured Materials Synthesis Using Ultrasound. Sonochemistry 2017, 59–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhuang, T.; Dong, J.; Wang, L.; Xia, J.; Wang, H.; Cui, X.; Wang, Z. Sonochemical fabrication of inorganic nanoparticles for applications in catalysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 71, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Cui, X.; Wang, Z. Sonochemical catalysis as a unique strategy for the fabrication of nano-/micro-structured inorganics. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 41–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zeiger, B.W.; Suslick, K.S. Sonochemical synthesis of nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suslick, K.S.; Flannigan, D.J. Inside a Collapsing Bubble: Sonoluminescence and the Conditions During Cavitation. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2008, 59, 659–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Abu Noqta, O.; Mehrdel, B. Synthesis and coating methods of biocompatible iron oxide/gold nanoparticle and nanocomposite for biomedical applications. Chin. J. Phys. 2020, 64, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.H.; Suslick, K.S. Applications of Ultrasound to the Synthesis of Nanostructured Materials. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1039–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Jameel, M.S.; Ahmed, N.M.; Ali, A.T. Distinct advantages of using sonochemical over laser ablation methods for a rapid-high quality gold nanoparticles production. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 8, 015009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Movahedirad, S.; Shahhosseini, S. CFD study of the flow pattern in an ultrasonic horn reactor: Introducing a realistic vibrating boundary condition. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 35, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabbina, P.K.; Karabiyik, M.; Al-Amin, C.; Pala, N.; Das, S.; Choi, W.; Saxena, T.; Shur, M. Controlled Synthesis of Single-Crystalline ZnO Nanoflakes on Arbitrary Substrates at Ambient Conditions. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2013, 31, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristl, M.; Ban, I.; Danč, A.; Danč, V.; Drofenik, M. A sonochemical method for the preparation of cadmium sulfide and cadmium selenide nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2010, 17, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, D.A.; Mendoza, L.; Vizuete, K.; Debut, A.; Arias, M.T.; Gavilanes, A.; Terencio, T.; Ávila, E.; Jeffryes, C.; Dahoumane, S.A. Sugar-Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Selenide Semiconductor Nanocrystals under Ultrasound Irradiation. Molecules 2020, 25, 5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Smita, K.; Cumbal, L.; Debut, A.; Pathak, R.N. Sonochemical Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Starch: A Comparison. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2014, 2014, 784268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukoshi, Y.; Oshima, R.; Maeda, Y.; Nagata, Y. Preparation of Platinum Nanoparticles by Sonochemical Reduction of the Pt(II) Ion. Langmuir 1999, 15, 2733–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.T.; Petru, M.; Militký, J.; Azeem, M.; Ashraf, M.A. One-Pot Sonochemical Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic Applications, Modelling and Optimization. Materials 2019, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taghavinezhad, P.; Haghighi, M.; Alizadeh, R. Sonosynthesis of VOx/MCM-41 nanocatalyst enhanced by various metal oxides (Mg, AL, Zr) for CO2-oxidative dehydrogenation of ethane to ethylene. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 261, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, A.P.C.; Klingebiel, B.; Luysberg, M.; Carius, R. Sonochemical synthesis of hydrogenated amorphous silicon nanoparticles from liquid trisilane at ambient temperature and pressure. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y. Tailoring catalytic performance of carbon nanotubes confined CuOCeO2 catalysts for CO preferential oxidation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 18211–18219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-H.; Tsao, Y.-H.; Wu, M.-H.; Chou, T.-M.; Lin, Z.-H.; Wu, J.M. Single-and few-layers MoS2 nanocomposite as piezo-catalyst in dark and self-powered active sensor. Nano Energy 2017, 31, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sostaric, J.Z.; Mulvaney, P.; Grieser, F. Sonochemical dissolution of MnO2 colloids. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1995, 91, 2843–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makino, K.; Mossoba, M.M.; Riesz, P. Chemical effects of ultrasound on aqueous solutions. Evidence for hydroxyl and hydrogen free radicals (.cntdot.OH and.cntdot.H) by spin trapping. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1982, 104, 3537–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B. Mechanisms of effective gold shell on Fe3O4 core nanoparticles formation using sonochemistry method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 64, 104865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Price, G.J. Applications of Ultrasound to Materials Chemistry. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1999, 29, 295–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, Y.-J.; Kang, S.-H.; Do, C.; Moon, S.Y.; Kim, T.-H. Water-Redispersible and Highly Stable Gold Nanoparticles Permanently Capped by Charge-Controllable Surfactants for Potential Medical Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 7924–7932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimzadeh, I.; Aghazadeh, M.; Dalvand, A.; Doroudi, T.; Kolivand, P.H.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P. Effective electrosynthesis and in situ surface coating of Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles with polyvinyl alcohol for biomedical applications. Mater. Res. Innov. 2017, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadiyan, Z.; Shameli, K.; Miyake, M.; Teow, S.-Y.; Peh, S.-C.; Mohamad, S.E.; Taib, S.H.M. Green fabrication of biologically active magnetic core-shell Fe3O4/Au nanoparticles and their potential anticancer effect. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Chen, H.; Tang, J.; Nie, L. Sonochemical synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of air-stable Fe3O4/Au nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 145609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, M. The characterization of acoustic cavitation bubbles—An overview. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2011, 18, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S.; Didenko, Y.; Fang, M.M.; Hyeon, T.; Kolbeck, K.J.; McNamara, W.B.; Mdleleni, M.M.; Wong, M. Acoustic cavitation and its chemical consequences. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1999, 357, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolloch, L.; Kost, J. The importance of microjet vs shock wave formation in sonophoresis. J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhar, A.; Nomura, K.-I.; Kalia, R.K.; Nakano, A.; Vashishta, P. Nanobubble Collapse on a Silica Surface in Water: Billion-Atom Reactive Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 184503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doktycz, S.J.; Suslick, K.S. Interparticle collisions driven by ultrasound. Science 1990, 247, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Putterman, S. Sonoluminescence: Sound into light. Sci. Am. 1995, 272, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S. The Chemistry of Ultrasound; Encyclopaedia Britannica: Chicago, IL, USA, 1994; pp. 138–155. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Stabilization, Vectorization, Physicochemical Characterizations, and Biological Applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, F.; Enomoto, N.; Hojo, J.; Enpuku, K. Sonochemical synthesis of monodispersed magnetite nanoparticles by using an ethanol–water mixed solvent. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchegiani, G.; Imperatori, P.; Mari, A.; Pilloni, L.; Chiolerio, A.; Allia, P.M.E.I.; Tiberto, P.; Suber, L. Sonochemical synthesis of versatile hydrophilic magnetite nanoparticles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2012, 19, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafi, K.V.; Ulman, A.; Yan, X.; Yang, N.L.; Estournes, C.; White, H.; Rafailovich, M. Sonochemical Synthesis of Functionalized Amorphous Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5093–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukh-Qasem, R.A.; Gedanken, A. Sonochemical synthesis of stable hydrosol of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 284, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüdtke-Buzug, K.; Penxová, Z. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: An Evaluation of the Sonochemical Synthesis Process. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 5, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, B.; Govindasamy, M.; Wanga, S.-F.; Ramalingam, R.J.; Al-Lohedanb, H.; Maiyalagan, T. Novel sonochemical synthesis of Fe3O4 nanospheres decorated on highly active reduced graphene oxide nanosheets for sensitive detection of uric acid in biological samples. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villegas, V.A.R.; Ramírez, J.I.D.L.; Guevara, E.H.; Sicairos, S.P.; Ayala, L.A.H.; Sanchez, B.L. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles for photocatalysis of nitrobenzene. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, G.; Zhu, J.-J. Sonochemical synthesis of Fe3O4/carbon nanotubes using low frequency ultrasonic devices and their performance for heterogeneous sono-persulfate process on inactivation of Microcystis aeruginosa. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boustani, K.; Shokri, A.; Shayesteh, S.F.; Jafari, A. Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis and Tuning the Magnetic and Structural Features of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles by Using Ethylenediamine as a Precipitating Agent. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2020, 33, 1879–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kim, C. Facile sonochemical synthesis of high-moment magnetite (Fe3O4) nanocube. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2012, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penders, J.; Stolzoff, M.; Hickey, D.J.; Andersson, M.; Webster, T.J. Shape-dependent antibacterial effects of non-cytotoxic gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2457–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owaid, M.N.; Rabeea, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Dheyab, M.A. Mushroom-assisted synthesis of triangle gold nanoparticles using the aqueous extract of fresh Lentinula edodes (shiitake), Omphalotaceae. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2019, 12, 100270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Owaid, M.N.; Rabeea, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S. Mycosynthesis of gold nanoparticles by the Portabello mushroom extract, Agaricaceae, and their efficacy for decolorization of Azo dye. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Du Toit, H.; Ben Jaber, S.; Wu, G.; Panariello, L.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Parkin, I.P.; Gavriilidis, A. Rapid synthesis of gold nanoparticles with carbon monoxide in a microfluidic segmented flow system. React. Chem. Eng. 2019, 4, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golub, D.; Ivanič, A.; Majerič, P.; Tiyyagura, H.R.; Anžel, I.; Rudolf, R. Synthesis of Colloidal Au Nanoparticles through Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis and Their Use in the Preparation of Polyacrylate-AuNPs’ Composites. Materials 2019, 12, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adekoya, J.A.; Ogunniran, K.O.; Siyanbola, T.O.; Dare, E.O.; Revaprasadu, N. Band Structure, Morphology, Functionality, and Size-Dependent Properties of metal Nanoparticles. In Noble and Precious Metals—Properties, Nanoscale Effects and Applications; Seehra, M., Bristow, A.D., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; pp. 15–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrdel, B.; Othman, N.; Aziz, A.A.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Jameel, M.S.; Dheyab, M.A.; Amiri, I.S. Identifying Metal Nanoparticle Size Effect on Sensing Common Human Plasma Protein by Counting the Sensitivity of Optical Absorption Spectra Damping. Plasmonics 2019, 15, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, S.; Sehrig, F.Z.; Farkhani, S.M.; Goloujeh, M.S.; Akbarzadeh, A. Current methods for synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2014, 44, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Jiao, Y.; Chai, Q. Applications of Gold Nanoparticles in Biosensors. Nano Life 2016, 6, 1642001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.M.; Vig, K.; Dennis, V.A.; Singh, S.R. Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2011, 1, 31–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ning, C.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Tan, G.; Mao, C. Nanomaterials as photothermal therapeutic agents. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 99, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Ge, S. Application of Antimicrobial Nanoparticles in Dentistry. Molecules 2019, 24, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balhaddad, A.A.; Kansara, A.A.; Hidan, D.; Weir, M.D.; Xu, H.H.; Melo, M.A.S. Toward dental caries: Exploring nanoparticle-based platforms and calcium phosphate compounds for dental restorative materials. Bioact. Mater. 2019, 4, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchomel, P.; Kvitek, L.; Prucek, R.; Panacek, A.; Halder, A.; Vajda, S.; Zboril, R. Simple size-controlled synthesis of Au nanoparticles and their size-dependent catalytic activity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mieszawska, A.J.; Mulder, W.J.M.; Fayad, Z.A.; Cormode, D.P. Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Diagnosis and Therapy of Disease. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 831–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Rashid, R.; Murtaza, G.; Zahra, A. Gold Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications in Drug Delivery. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majerič, P.; Jenko, D.; Friedrich, B.; Rudolf, R. Formation mechanisms for gold nanoparticles in a redesigned Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabeea, M.A.; Owaid, M.N.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Dheyab, M.A. Mycosynthesis of gold nanoparticles using the extract of Flammulina velutipes, Physalacriaceae, and their efficacy for decolorization of methylene blue. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariq, M.; Friedrich, B.; Budic, B.; Hodnik, N.; Ruiz-Zepeda, F.; Majerič, P.; Rudolf, R. Successful synthesis of gold nanoparticles through ultrasonic spray pyrolysis from a gold (III) nitrate precursor and Their interaction with a high electron beam. ChemistryOpen 2018, 7, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, W.Y. A Perspective on the Flame Spray Synthesis of Photocatalyst Nanoparticles. Materials 2013, 6, 3194–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffiths, M.B.E.; Pallister, P.J.; Mandia, D.J.; Barry, S.T. Atomic Layer Deposition of Gold Metal. Chem. Mater. 2015, 28, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palgrave, R.G.; Parkin, I.P. Aerosol Assisted Chemical Vapor Deposition of Gold and Nanocomposite Thin Films from Hydrogen Tetrachloroaurate (III). Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4639–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Daanen, N.N.; Rugen, E.E.; Chen, D.P.; Skrabalak, S.E. Simple Reactor for Ultrasonic Spray Synthesis of Nanostructured Materials. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Takada, N.; Machmudah, S.; Wahyudiono; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Ultrasonic-Enhanced Fabrication of Metal Nanoparticles by Laser Ablation in Liquid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 7512–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Oglat, A.A. Rapid Sonochemically-Assisted Synthesis of Highly Stable Gold Nanoparticles as Computed Tomography Contrast Agents. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, K.; Sato, T.; Asakura, Y. Size-controlled synthesis of gold nanoparticles by ultrafine bubbles and pulsed ultrasound. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 217, 115527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.S.; Manivel, A.; Anandan, S.; Zhou, M.; Grieser, F.; Ashokkumar, M. Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of gold–ruthenium bimetallic nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 356, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhou, D.; Sui, Z.; Han, B. Sonochemical Synthesis of Graphene Oxide-Wrapped Gold Nanoparticles Hybrid Materials: Visible Light Photocatalytic Activity. Chin. J. Chem. 2014, 33, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Natan, M.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, W.; Liu, S.; Jacobi, G.; Perelshtein, I.; Gedanken, A.; Banin, E.; Jiang, X. Small molecule-decorated gold nanoparticles for preparing antibiofilm fabrics. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.S.M.; AshokKumar, M. Sonochemical Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles by Using High Intensity Focused Ultrasound. ChemPhysChem 2015, 16, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radziuk, D.; Grigoriev, D.; Zhang, W.; Su, D.; Möhwald, H.; Shchukin, D. Ultrasound-Assisted Fusion of Preformed Gold Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 1835–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B. Sonochemical-assisted synthesis of highly stable gold nanoparticles catalyst for decoloration of methylene blue dye. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 127, 108551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Göksu, H.; Gerengi, H.; Arikan, K.; Ahamed, M.I.; Şen, F. Magnetic Nanomaterials for Hydrogen Storage. Mater. Appl. 2020, 66, 236. [Google Scholar]
- Rajkumar, S.; Prabaharan, M. Multi-functional core-shell Fe3O4@ Au nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Colloids Surf. B. 2019, 174, 252–259. [Google Scholar]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Abu Noqta, O.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B. Simple rapid stabilization method through citric acid modification for magnetite nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaniabadi, P.M.; Shahbazi-Gahrouei, D.; Aziz, A.A.; Dheyab, M.A.; Khaniabadi, B.M.; Mehrdel, B.; Jameel, M.S. Trastuzumab conjugated porphyrin-superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle: A potential PTT-MRI bimodal agent for herceptin positive breast cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 31, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baskakov, A.; Solov’Eva, A.; Ioni, Y.V.; Starchikov, S.; Lyubutin, I.; Khodos, I.; Avilov, A.; Gubin, S. Magnetic and interface properties of the core-shell Fe3O4/Au nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 422, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, H.; Tian, Z.; Han, D.; Gu, F. Strong metal–support interaction in novel core–shell Au–CeO2 nanostructures induced by different pretreatment atmospheres and its influence on CO oxidation. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5865–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Yu, S.; Zeng, Q.; Yang, M. Core–shell interaction and its impact on the optical absorption of pure and doped core-shell CdSe/ZnSe nanoclusters. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 134307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.M.; Govindaiah, P.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cheong, I.W. Multifunctional Fe3O4 nanoparticles-embedded poly (styrene)/poly (thiophene) core/shell composite particles. Synth. Met. 2013, 175, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, D.; Tang, D.; Niessner, R. Bioanalytical applications of biomolecule-functionalized nanometer-sized doped silica particles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 647, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.B.; Annamanedi, M.; Prashad, M.D.; Arunasree, K.M.; Mastai, Y.; Gedanken, A.; Paik, P. Synthesis of mesoporous SiO 2–ZnO nanocapsules: Encapsulation of small biomolecules for drugs and “SiOZO-plex” for gene delivery. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudome, T.; Kaneda, K. Advanced Core-Shell Nanoparticle Catalysts for Efficient Organic Transformations. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pustovalov, V.; Astafyeva, L.; Fritzsche, W. Optical properties of core–shell gold–silver and silver–gold nanoparticles for near UV and visible radiation wavelengths. Plasmonics 2012, 7, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Toni, A.M.; Habila, M.A.; Labis, J.P.; Alothman, Z.A.; Alhoshan, M.; Elzatahry, A.A.; Zhang, F. Design, synthesis and applications of core–shell, hollow core, and nanorattle multifunctional nanostructures. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2510–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.-H.; Doong, R.-A. Bifunctional Au−Fe3O4 Heterostructures for Magnetically Recyclable Catalysis of Nitrophenol Reduction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 6591–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Fu-Bing, X.; Hong-Wei, L.; Feng, W.; Di-Zhao, C.; Zhao-Yang, W. A novel H2O2 biosensor based on Fe3O4–Au magnetic nanoparticles coated horseradish peroxidase and graphene sheets–Nafion film modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 109, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamipour, S.; Sadjadi, M.; Farhadyar, N. Fabrication and spectroscopic studies of folic acid-conjugated Fe3O4@Au core–shell for targeted drug delivery application. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 148, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B.; Khaniabadi, B.M. Gold-coated iron oxide nanoparticles as a potential photothermal therapy agent to enhance eradication of breast cancer cells. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1497, 012003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Cai, H.; Sun, W.; Shen, M.; Zhang, G.; Shi, X. Facile One-Pot Synthesis of Fe3O4@Au Composite Nanoparticles for Dual-Mode MR/CT Imaging Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10357–10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wu, B.; Xing, D. Bio-modified Fe3O4core/Au shell nanoparticles for targeting and multimodal imaging of cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; McKeague, M.; DeRosa, M.C. Synthesis, transfer, and characterization of core-shell gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles. MethodsX 2019, 6, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostevšek, N.; Rožman, K.Ž.; Arshad, M.S.; Spreitzer, M.; Kobe, S.; Šturm, S. Multimodal Hybrid FePt/SiO2/Au Nanoparticles for Nanomedical Applications: Combining Photothermal Stimulation and Manipulation with an External Magnetic Field. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 16374–16382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S.; Abu Noqta, O.; Khaniabadi, P.M.; Mehrdel, B. Excellent relaxivity and X-ray attenuation combo properties of Fe3O4@Au CSNPs produced via Rapid sonochemical synthesis for MRI and CT imaging. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheyab, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S. Synthesis and optimization of the sonochemical method for functionalizing gold shell on Fe3O4 core nanoparticles using response surface methodology. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 12, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.R.; Walter, D.G.; Natan, M.J. Seeding of Colloidal Au Nanoparticle Solutions. 2. Improved Control of Particle Size and Shape. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.-P.; Yao, G.-H.; Fan, L.-X.; Qiu, J.-D. Magnetic Fe3O4@Au composite-enhanced surface plasmon resonance for ultrasensitive detection of magnetic nanoparticle-enriched α-fetoprotein. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 737, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.-D.; Peng, H.-P.; Liang, R.-P.; Xia, X.-H. Facile preparation of magnetic core–shell Fe3O4@Au nanoparticle/myoglobin biofilm for direct electrochemistry. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.; Fan, Q.; Suzuki, M.; Suzuki, I.S.; Engelhard, M.H.; Lin, Y.; Kim, N.; Wang, J.Q. Monodispersed core—shell Fe3O4@ Au nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2005, 109, 21593–21601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Meng, L.; Niu, L.; Lu, Q. Facile Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4@polyphosphazene@Au Shells for Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 4586–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodipo, B.K.; Aziz, A.A.; Mustapa, M. Facile synthesis and characteristics of gold coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via sonication. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 2015, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Luo, J.; Maye, M.M.; Fan, Q.; Rendeng, Q.; Engelhard, M.H.; Wang, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhong, C.-J. Iron oxide–gold core–shell nanoparticles and thin film assembly. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.-P.; Wang, X.-N.; Wang, L.; Qiu, J.-D. Enantiomeric separation by microchip electrophoresis using bovine serum albumin conjugated magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@Au nanocomposites as stationary phase. Electrophoresis 2014, 35, 2824–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, I.A.; Ahmad, T. Size and shape dependant antifungal activity of gold nanoparticles: A case study of Candida. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 101, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, W.-S.; Park, S.-H.; Kadam, A.N.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.-W. Direct hydrothermal synthesis of amine-functionalized cubic hematite (C-Fe2O3) and sonochemical deposition of nanosized Au for its application as a visible-light photocatalyst. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 2924–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandramohan, J.; Anandan, S.; Sivasankar, T. A simple approach for the sonochemical synthesis of Fe3O4-guargum nanocomposite and its catalytic reduction of p-nitroaniline. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okitsu, K.; Nunota, Y. One-pot synthesis of gold nanorods via autocatalytic growth of sonochemically formed gold seeds: The effect of irradiation time on the formation of seeds and nanorods. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1928–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, D.M.A.; Freire, R.M.; Gallo, J.; Freire, T.M.; Queiroz, D.C.; Ricardo, N.M.P.S.; Vasconcelos, I.F.; Mele, G.; Carbone, L.; Mazzetto, S.E.; et al. Rapid Sonochemical Approach Produces Functionalized Fe3O4 Nanoparticles with Excellent Magnetic, Colloidal, and Relaxivity Properties for MRI Application. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 24206–24222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Van Phong, L.; Jeong, J.-R.; Kim, C. A facile route to sonochemical synthesis of magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 8277–8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, F.; Yamamoto, N.; Todoriki, M.; Jin, J. Sonochemical preparation of gold nanoparticles for sensitive colorimetric determination of nereistoxin insecticides in environmental samples. Talanta 2018, 188, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagvenkar, A.P.; Perelshtein, I.; Piunno, Y.; Mantecca, P.; Gedanken, A. Sonochemical One-Step Synthesis of Polymer-Capped Metal Oxide Nanocolloids: Antibacterial Activity and Cytotoxicity. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 13631–13639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammadi, M.K.; Hayati, P.; Jafari, S.; Karimi, M.; Gutierrez, A. Sonication-assisted synthesis of a new rod-like metal-organic coordination polymer compound; novel precursor to produce pure phase nano-sized lead(II) oxide. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1176, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.; Aghaei, H.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A.; Monajemi, M.; Bazrafshan, A.A. Synthesis of nanocomposites of iron oxide/gold (Fe3O4/Au) loaded on activated carbon and their application in water treatment by using sonochemistry: Optimization study. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 41, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


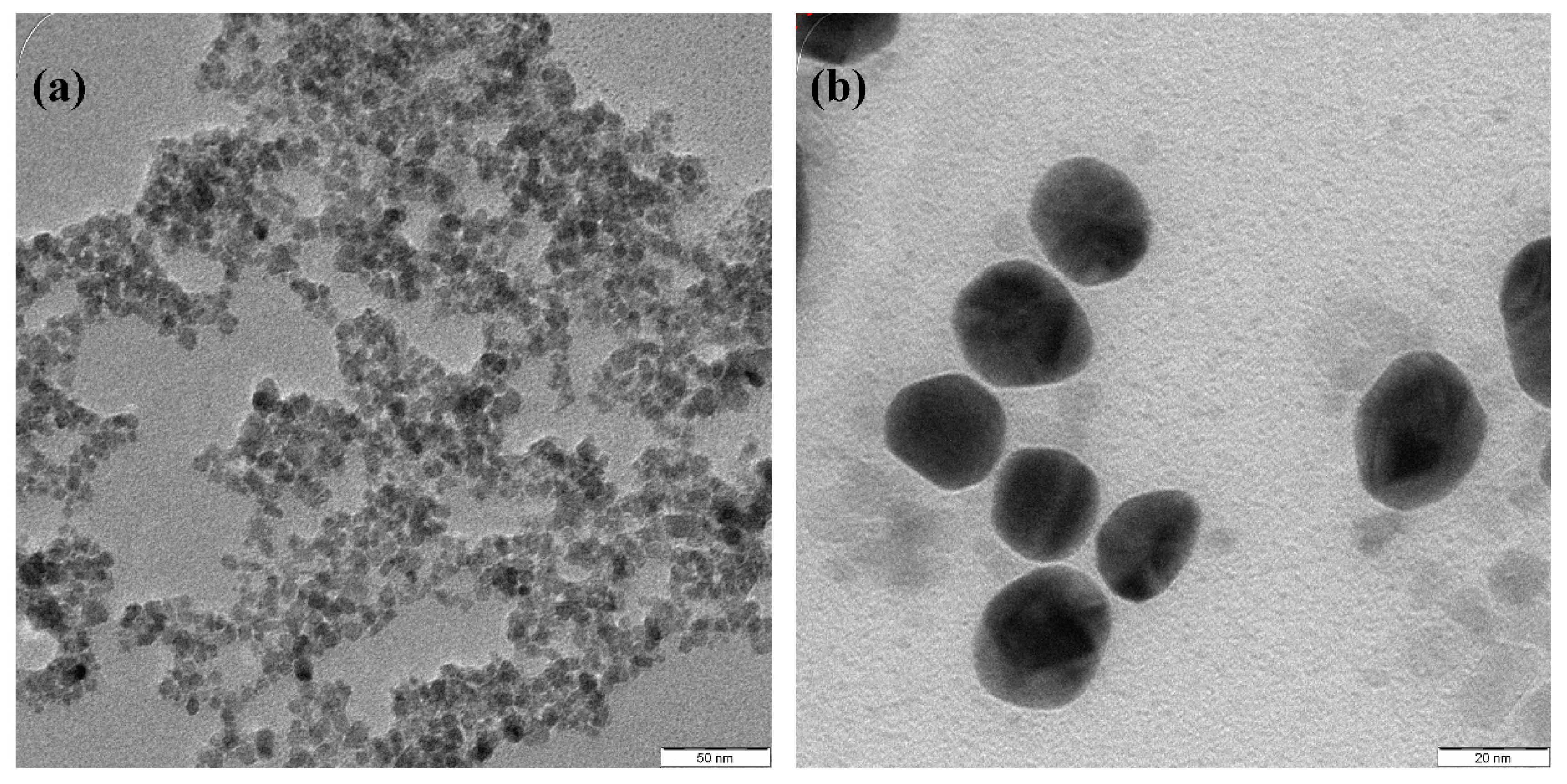
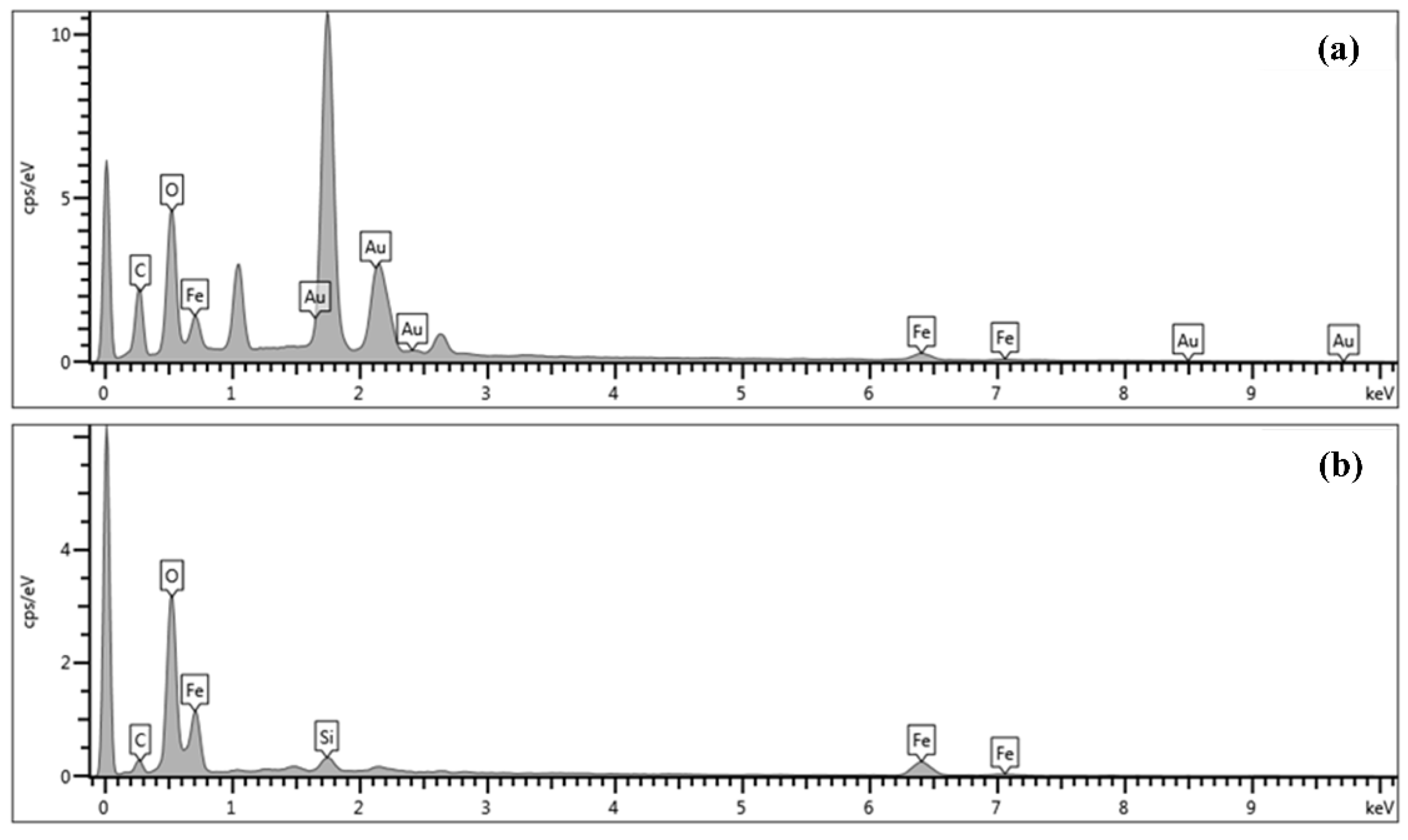
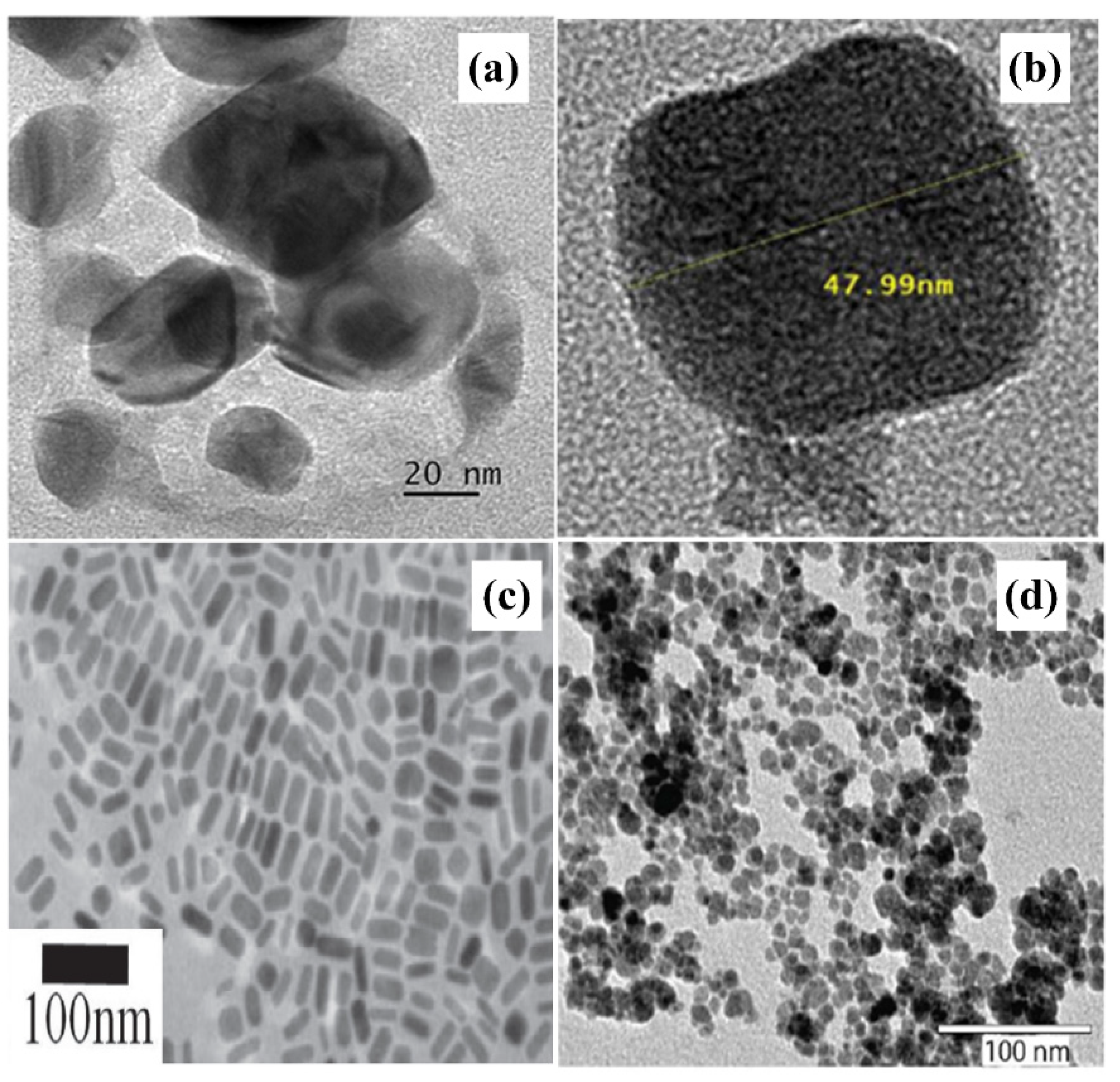
| No | Particles Shape | Particles Size (nm) | Ultrasonic Power | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | nanodiscs | 30 | ………. | [119] |
| 2 | nanocubic | 433 | (300 W, 20 kHz) | [120] |
| 3 | nanocube | 43 | ………. | [121] |
| 4 | nanorods | 34 | [122] | |
| 5 | nanosphere | 9–11 | (585 W, 20 kHz) | [123] |
| 6 | nanosphere | 11 | ………. | [124] |
| 7 | nanosphere | 15–20 | 430 kHz | [125] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali Dheyab, M.; Aziz, A.A.; Jameel, M.S. Recent Advances in Inorganic Nanomaterials Synthesis Using Sonochemistry: A Comprehensive Review on Iron Oxide, Gold and Iron Oxide Coated Gold Nanoparticles. Molecules 2021, 26, 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092453
Ali Dheyab M, Aziz AA, Jameel MS. Recent Advances in Inorganic Nanomaterials Synthesis Using Sonochemistry: A Comprehensive Review on Iron Oxide, Gold and Iron Oxide Coated Gold Nanoparticles. Molecules. 2021; 26(9):2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092453
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli Dheyab, Mohammed, Azlan Abdul Aziz, and Mahmood S. Jameel. 2021. "Recent Advances in Inorganic Nanomaterials Synthesis Using Sonochemistry: A Comprehensive Review on Iron Oxide, Gold and Iron Oxide Coated Gold Nanoparticles" Molecules 26, no. 9: 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092453
APA StyleAli Dheyab, M., Aziz, A. A., & Jameel, M. S. (2021). Recent Advances in Inorganic Nanomaterials Synthesis Using Sonochemistry: A Comprehensive Review on Iron Oxide, Gold and Iron Oxide Coated Gold Nanoparticles. Molecules, 26(9), 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092453