Nanoformulation and Evaluation of Oral Berberine-Loaded Liposomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
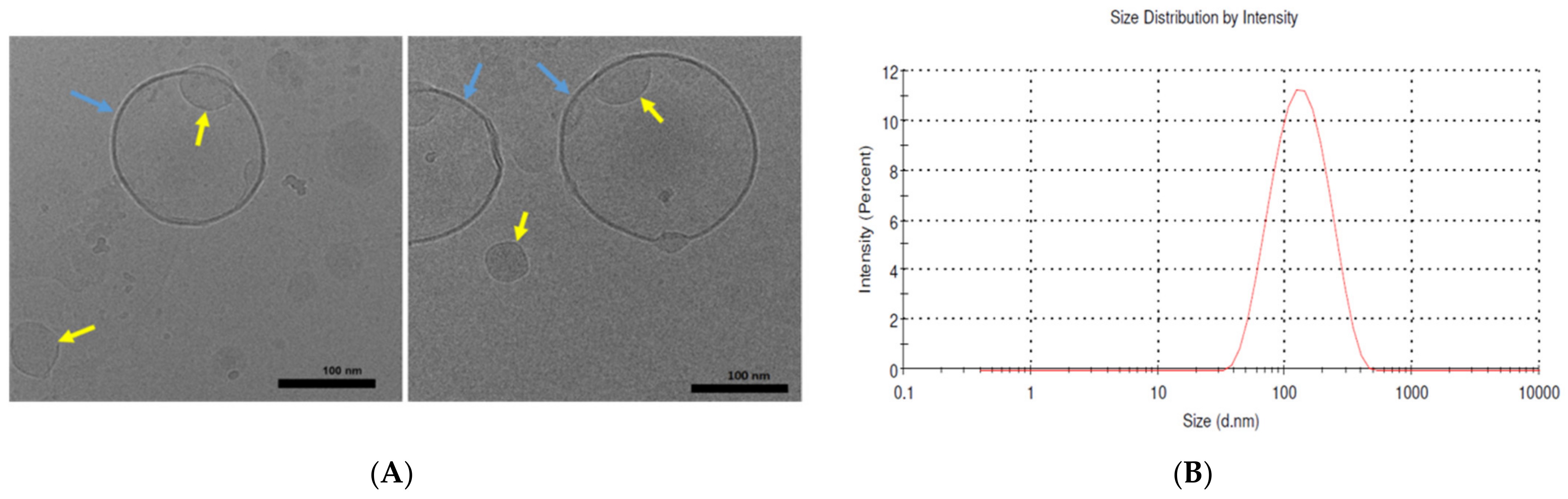
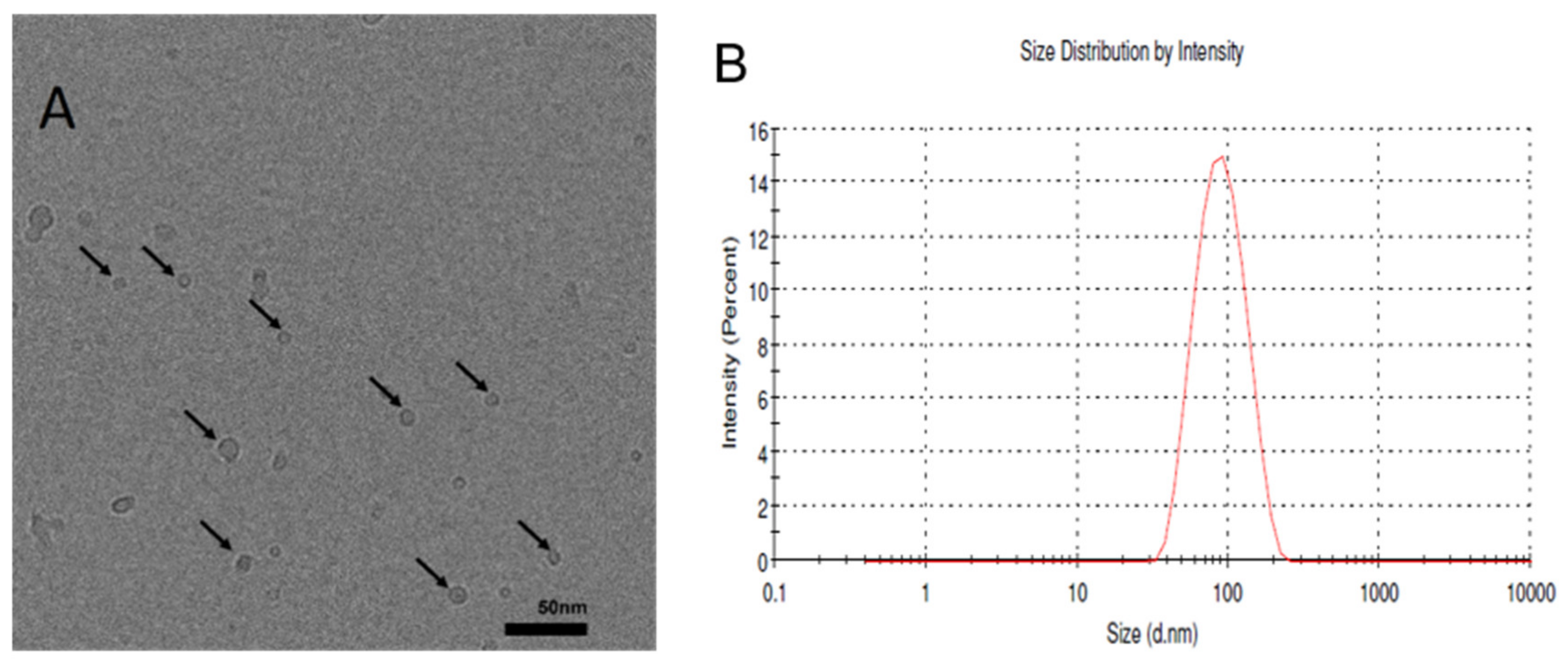
2.1. Size and Polydispersity Index (PDI) of BBR-Loaded Liposomes
2.2. Imaging of the Liposomes Generated by the Ethanol-Injection Method
2.3. Imaging of the Liposomes Generated by the Thin-Film Hydration Method
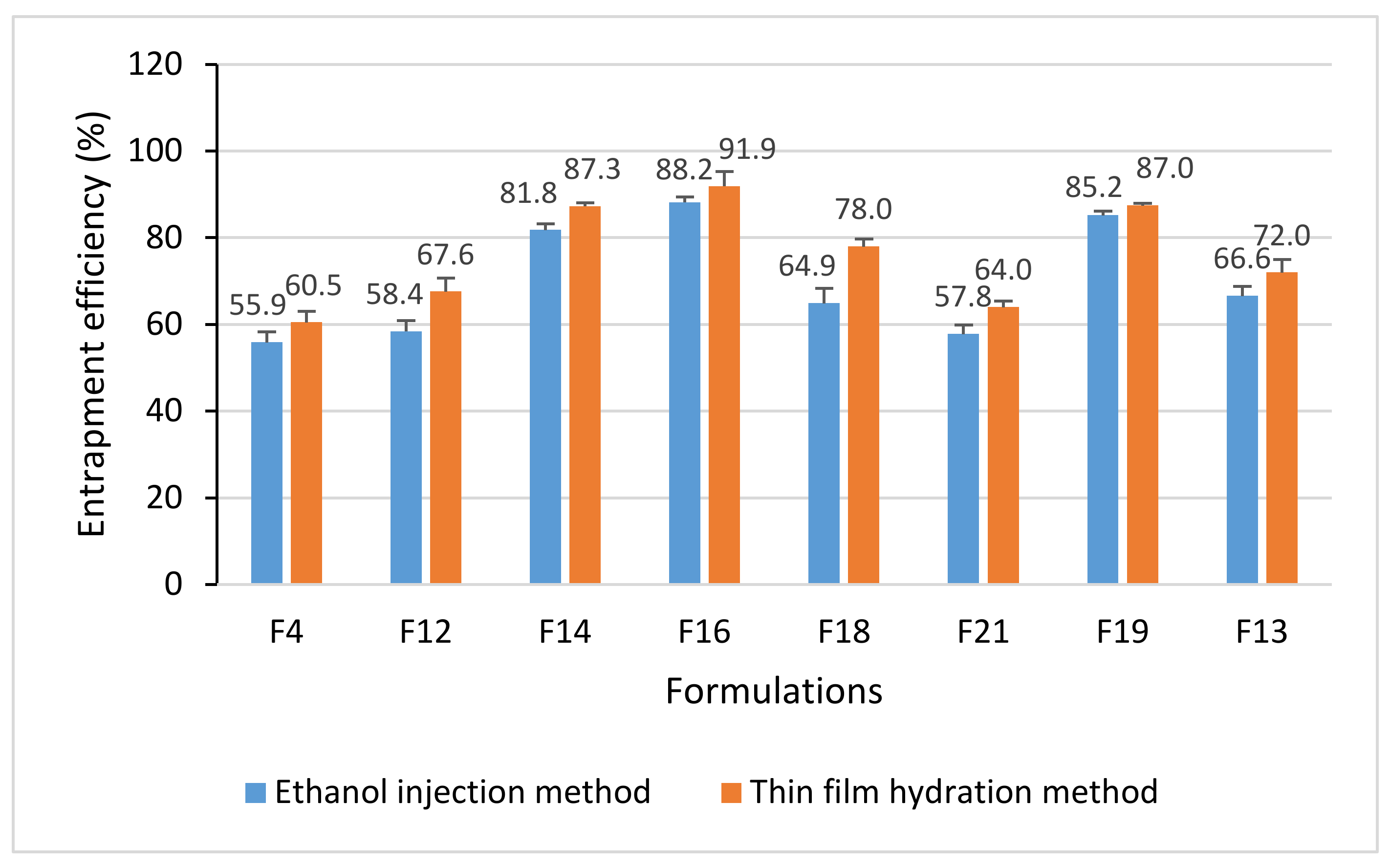
2.4. Entrapment Efficiency (EE) of Liposomes
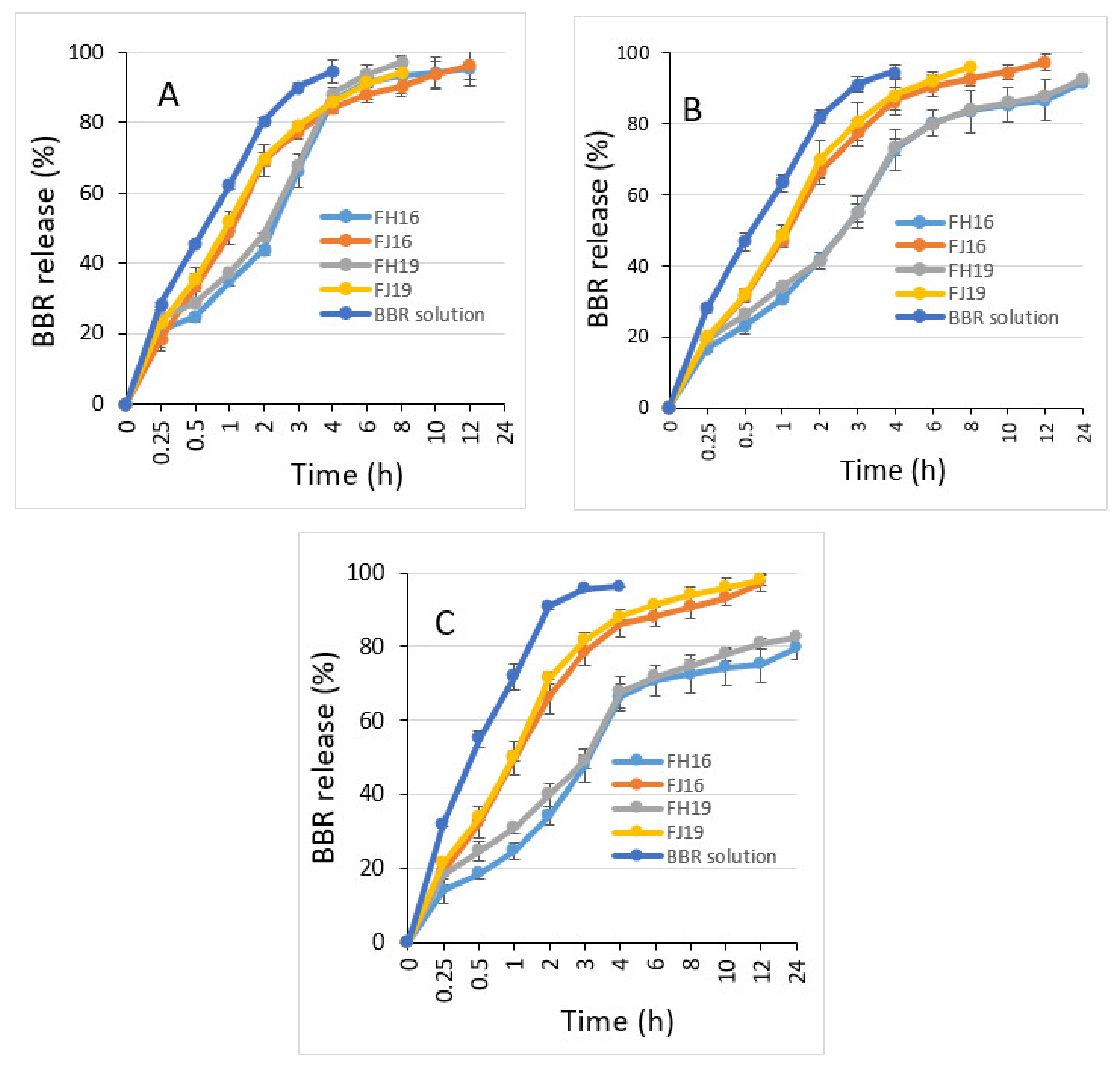
2.5. Drug Release In Vitro
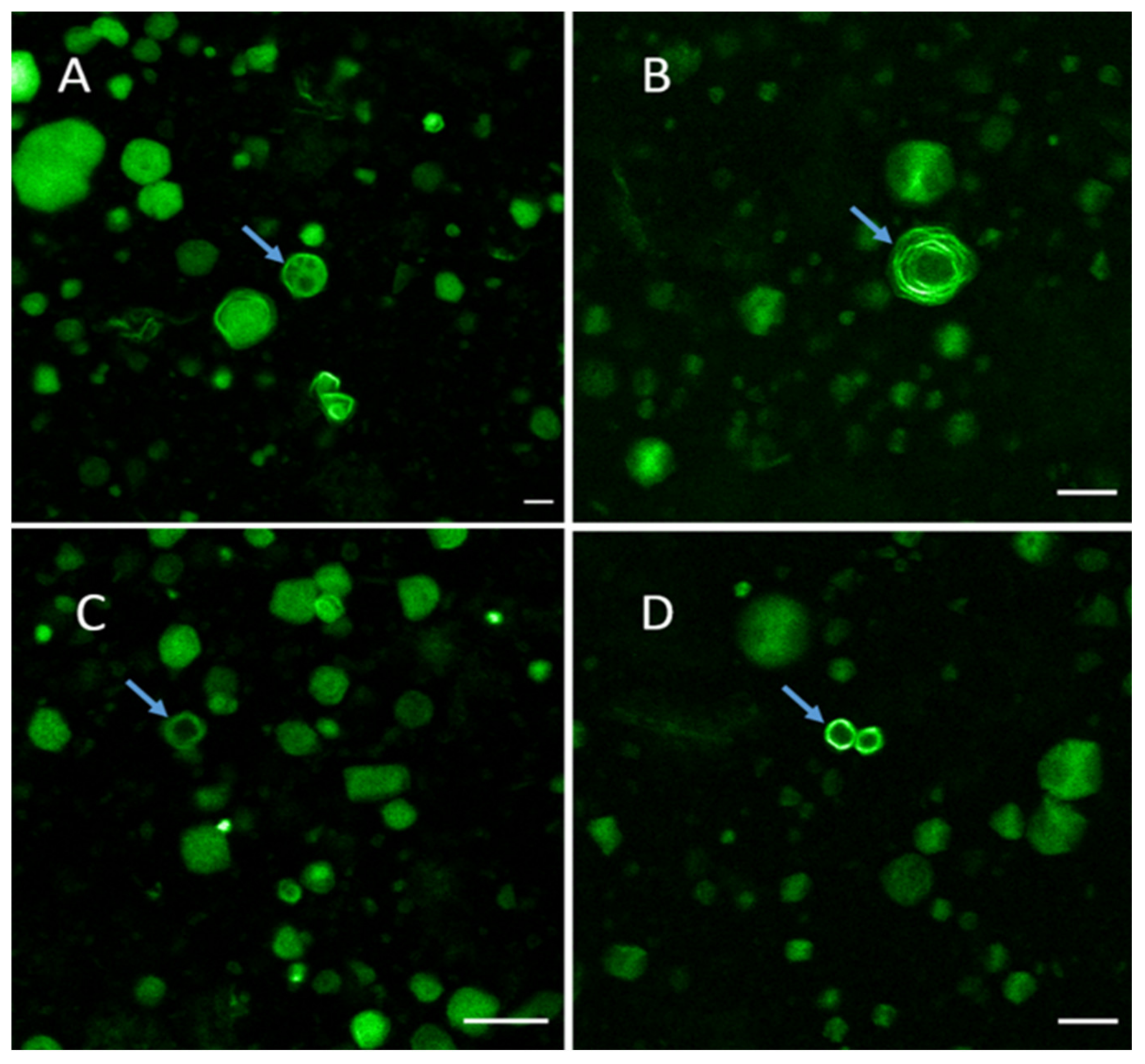
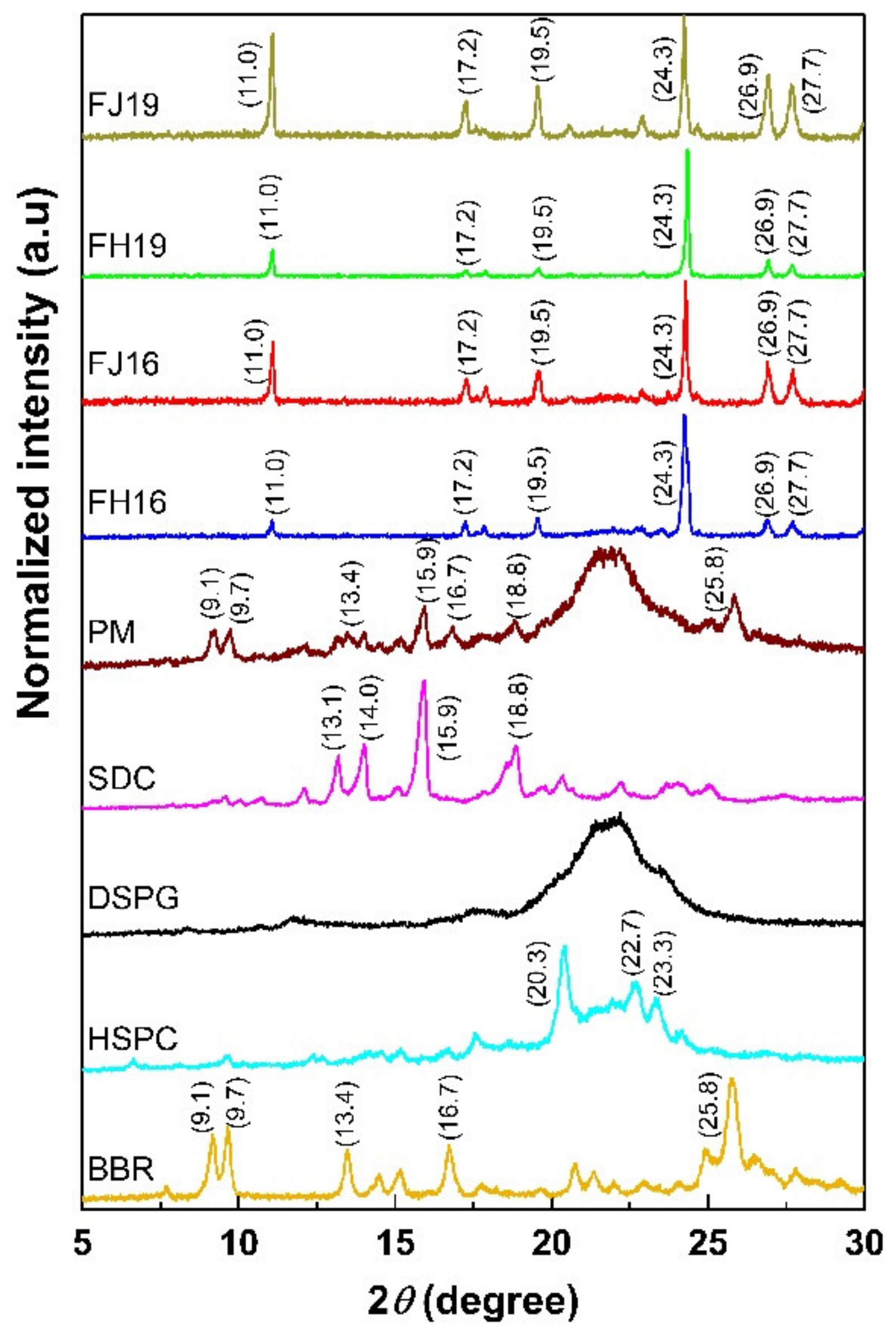
2.6. Physical Solid-State Properties of Liposomes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Liposomes by the Ethanol-Injection Method
4.3. Preparation of Liposomes by Thin-Film Hydration
4.4. Characterisation of Liposomes
4.4.1. Size and Polydispersity Index (PDI)
4.4.2. Microscopy Imaging
4.4.3. Determination of Entrapment Efficiency (EE)
4.4.4. Drug Release In Vitro
4.4.5. Physical Solid-State Properties
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zuo, F.; Nakamura, N.; Akao, T.; Hattori, M. Pharmacokinetics of berberine and its main metabolites in conventional and pseudo germ-free rats determined by liquid chromatography/ion trap mass spectrometry. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 2064–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernakova, M.; Kostalova, D. Antimicrobial activity of berberine—A constituent of Mahonia aquifolium. Folia Microbiol. 2002, 47, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.X.; Zhong, G.Q. Study progress of berberine in treating cardiovascular disease. Med. Recapitul. (Chin.) 2007, 13, 780–781. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, S. Berberine regulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and positive transcription elongation factor b expression in diabetic adipocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 649, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allijn, I.E.; Czarny, B.M.S.; Wang, X.; Chong, S.Y.; Weiler, M.; da Silva, A.E.; Metselaar, J.M.; Lam, C.S.P.; Pastorin, G.; de Kleijn, D.P.V. Liposome encapsulated berberine treatment attenuates cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction. J. Control Release 2017, 247, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Jo, B.W.; Kim, Y.C. Enhanced paclitaxel bioavailability after oral administration of paclitaxel or prodrug to rats pretreated with quercetin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.L.; Tsai, T.H. Hepatobiliary excretion of berberine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.T.; Hao, H.P.; Xie, H.G.; Lai, L.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.X.; Wang, G.J. Extensive intestinal first-pass elimination and predominant hepatic distribution of berberine explain its low plasma levels in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, F.; Jiang, J.; Gao, C.; Tan, Y. Intestinal absorption mechanisms of berberine, palmatine, jateorhizine, and coptisine: Involvement of P-glycoprotein. Xenobiotica 2011, 41, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sharma, U.S. Liposomes in drug delivery: Progress and limitations. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 154, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovska, O.; Simonovska, J.; Kavrakovski, Z.; Rafajlovska, V. An overview: Methods for preparation and characterization of liposomes as drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. Phytopharmacol. Res. (eIJPPR) 2013, 3, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ruozi, B.; Belletti, D.; Tombesi, A.; Tosi, G.; Bondioli, L.; Forni, F.; Vandelli, M.A. AFM, ESEM, TEM, and CLSM in liposomal characterization: A comparative study. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R. Light scattering: A review of particle characterization applications. Particuology 2015, 18, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirayil, C.J.; Abraham, J.; Mishra, R.K.; George, S.C.; Thomas, S. Instrumental techniques for the characterization of nanoparticles. In Thermal and Rheological Measurement Techniques for Nanomaterials Characterization; Thomas, S., Thomas, R., Zachariar, A.K., Mishra, R.K., Eds.; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Charman, W.N.A.; Stella, V.J. Estimating the maximal potential for intestinal lymphatic transport of lipophilic drug molecules. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 34, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailor, G.; Seth, A.K.; Parmar, G.; Chauhan, S.; Javia, A. Formulation and in vitro evaluation of berberine containing liposome optimized by 32 full factorial designs. J. Applied Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.X.; Huang, L.; Liu, L.; Elamin Abdalla, A.M.; Gauthier, M.; Yang, G. Chitosan-coated nano-liposomes for the oral delivery of berberine hydrochloride. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2014, 2, 7149–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Li, J.; Guo, L.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, T.; Deng, Y. Preparation of berberine hydrochloride long-circulating liposomes by ionophore A23187-mediated ZnSO4 gradient method. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sahdev, A.K.; Sethi, B.; Sheokand, R.; Rawat, S.L. A study on liposomes: Classification techniques and importance. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 2, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Batzri, S.; Korn, E.D. Single bilayer liposomes prepared without sonication. BBA-Biomembr. 1973, 298, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deamer, D.; Bangham, A.D. Large volume liposomes by an ether vaporization method. BBA-Nucleic Acids Protein Synth. 1976, 443, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.H.; Chung, S.J.; Shim, C.K. Enhanced intestinal absorption of salmon calcitonin (sCT) from proliposomes containing bile salts. J. Control. Release 2005, 106, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, P.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Niu, M.; Lian, R.; Hu, F.; Wu, W. Enhanced oral bioavailability of cyclosporine A by liposomes containing a bile salt. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 965–974. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Zhou, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y. Development of Liposome containing sodium deoxycholate to enhance oral bioavailability of itraconazole. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 12, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, K.; Ono, S.; Narioka, K.; Kakemi, M.; Morimoto, K.; Yamashita, S.; Nango, N.; Oku, N. Oral delivery of insulin by using surface coating liposomes: Improvement of stability of insulin in GI tract. Int. J. Pharm. 1997, 157, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, F.J.; Sánchez-Migallón, M.P.; Gómez-Fernández, J.C. Influence of α-tocopherol incorporation on Ca2+-induced fusion of phosphatidylserine vesicles. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 333, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, P.J. The effect of tocopherol on the structure and permeability of phosphatidylcholine liposomes. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.S.; Fang, X.Q.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.J. Preparation and quality assessment of itraconazole transfersomes. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, R.; Dogdas, B.; Keough, E.; Haas, R.M.; Wepukhulu, W.; Krotzer, S.; Burke, P.A.; Sepp-Lorenzino, L.; Bagchi, A.; Howell, B.J. Analysis of lipid nanoparticles by Cryo-EM for characterizing siRNA delivery vehicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 403, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berclaz, N.; Blöchliger, E.; Müller, M.; Luisi, P.L. Matrix effect of vesicle formation as investigated by cryotransmission electron microscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetefeld, J.; McKenna, S.A.; Patel, T.R. Dynamic light scattering: A practical guide and applications in biomedical sciences. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, J.; Kotarek, J.; Marszal, E.; Topp, E.M. Analyzing subvisible particles in protein drug products: A comparison of dynamic light scattering (DLS) and resonant mass measurement (RMM). AAPS J. 2014, 16, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaumet, M.; Vargas, A.; Gurny, R.; Delie, F. Nanoparticles for drug delivery: The need for precision in reporting particle size parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, K.A.; Baeumner, A.J. Analysis of liposomes. Talanta 2006, 68, 1432–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxa, U. Imaging of Liposomes by Transmission Electron Microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol 2018, 1682, 73–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Turker, M.S.; Chi, E.Y.; Sela, S.; Martin, G.M. Preparation of multivesicular liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 728, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, P.; Helm, F.; Hofhaus, G.; Brings, S.; Kaufman, C.; Leotta, K.; Urban, S.; Haberkorn, U.; Mier, W.; Fricker, G. A liposomal formulation for the oral application of the investigational hepatitis B drug Myrcludex, B. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 103, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battu, S.K.; Repka, M.A.; Maddineni, S.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Avery, M.A.; Majumdar, S. Physicochemical characterization of berberine chloride: A perspective in the development of a solution dosage form for oral delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010, 11, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.X.; Li, X.Y.; Li, N.; Ju, R.J.; Shi, J.F.; Sun, M.G.; Zhao, W.Y.; Mu, L.M. Modulation of drug-resistant membrane and apoptosis proteins of breast cancer stem cells by targeting berberine liposomes. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 4452–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Woo Joo, S.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wu, W. Adapting liposomes for oral drug delivery. Acta. Pharm. Sin. B. 2019, 9, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Yang, M.X.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.M.; Gao, D.H.; Ou, Z.M.; Li, Z.P.; Liu, S.H.; Li, X.J.; Yang, S.Y. Characterization, pharmacokinetics, and hypoglycemic effect of berberine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4677–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, A.D.; Standish, M.M.; Watkins, J.C. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J. Mol. Biol. 1965, 13, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, M.P.; Pardo, J.; Cebolla, V.; Gálvez, E.M. Berberine: A fluorescent alkaloid with a variety of applications from medicine to chemistry. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2010, 7, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Exp. | Formulation Codes | Ethanol-Injection | Thin-Film Hydration | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Size (d.nm) | PDI | Mean Size (d.nm) | PDI | ||
| 1 | FJ4, FH4 | 133.6 ± 1.1 | 0.209 ± 0.008 | 248.7 ± 3.3 | 0.272 ± 0.053 |
| 2 | FJ21, FH21 | 117.3 ± 1.3 | 0.186 ± 0.004 | 236.0 ± 2.0 | 0.248 ± 0.009 |
| 3 | FJ17 | 82.3 ± 1.3 | 0.113 ± 0.004 | – | – |
| 4 | FJ13, FH13 | 149.1 ± 0.8 | 0.220 ± 0.008 | 182.8 ± 2.6 | 0.297 ± 0.022 |
| 5 | FJ12, FH12 | 120.4 ± 1.1 | 0.243 ± 0.001 | 292.0 ± 3.9 | 0.181 ± 0.033 |
| 6 | FH11 | – | – | 209.0 ± 1.1 | 0.317 ± 0.037 |
| 7 | FJ14, FH14 | 243.6 ± 4.1 | 0.195 ± 0.012 | 208.2 ± 3.2 | 0.312 ± 0.031 |
| 8 | FJ16, FH16 | 91.2 ± 2.0 | 0.232 ± 0.015 | 448.5 ± 6.6 | 0.276 ± 0.016 |
| 9 | FJ18, FH18 | 50.9 ± 1.2 | 0.259 ± 0.009 | 239.2 ± 2.4 | 0.243 ± 0.009 |
| 10 | FJ19, FH19 | 146.5 ± 2.7 | 0.186 ± 0.007 | 111.5 ± 3.7 | 0.285 ± 0.011 |
| Exp. | Formulation Code | Molar Ratio (BBR:Lipid:SDC α-TP) | Lipid Molar Ratio (HSPC:DSPG) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F04 | 9:9:2:0 | 7:3 |
| 2 | F21 | 9:9:0:3 | 7:3 |
| 3 | F17 | 8:9:2:2 | 7:3 |
| 4 | F13 | 8:9:2:2 | 6:4 |
| 5 | F12 | 8:9:2:0 | 7:3 |
| 6 | F11 | 8:9:2:0 | 4:6 |
| 7 | F14 | 6:9:2:0 | 6:4 |
| 8 | F16 | 6:9:2:0 | 4:6 |
| 9 | F18 | 6:9:2:0 | 7:3 |
| 10 | F19 | 8:9:2:2 | 4:6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duong, T.T.; Isomäki, A.; Paaver, U.; Laidmäe, I.; Tõnisoo, A.; Yen, T.T.H.; Kogermann, K.; Raal, A.; Heinämäki, J.; Pham, T.-M.-H. Nanoformulation and Evaluation of Oral Berberine-Loaded Liposomes. Molecules 2021, 26, 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092591
Duong TT, Isomäki A, Paaver U, Laidmäe I, Tõnisoo A, Yen TTH, Kogermann K, Raal A, Heinämäki J, Pham T-M-H. Nanoformulation and Evaluation of Oral Berberine-Loaded Liposomes. Molecules. 2021; 26(9):2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092591
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuong, Thuan Thi, Antti Isomäki, Urve Paaver, Ivo Laidmäe, Arvo Tõnisoo, Tran Thi Hai Yen, Karin Kogermann, Ain Raal, Jyrki Heinämäki, and Thi-Minh-Hue Pham. 2021. "Nanoformulation and Evaluation of Oral Berberine-Loaded Liposomes" Molecules 26, no. 9: 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092591
APA StyleDuong, T. T., Isomäki, A., Paaver, U., Laidmäe, I., Tõnisoo, A., Yen, T. T. H., Kogermann, K., Raal, A., Heinämäki, J., & Pham, T.-M.-H. (2021). Nanoformulation and Evaluation of Oral Berberine-Loaded Liposomes. Molecules, 26(9), 2591. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092591









