Abstract
In this study, we provide the reader with an overview of quantum dot application in solar cells to replace dye molecules, where the quantum dots play a key role in photon absorption and excited charge generation in the device. The brief shows the types of quantum dot sensitized solar cells and presents the obtained results of them for each type of cell, and provides the advantages and disadvantages. Lastly, methods are proposed to improve the efficiency performance in the next researching.
1. Introduction
Solar cells have grown very rapidly over the past few decades, which are divided into three generations: the first generation is a monocrystalline and polycrystalline Si solar cell with an efficiency of 26.7% [1] and 21.9% [2], respectively. The 2nd generation solar cells are a thin film such as CdTe [3], amorphous Si [4], the cost is lower than the 1st generation, and the efficiency is 21.7% [5]. The 3rd generation solar cells include dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs), quantum dot sensitized solar cells (QDSSCs), perovskite cells with much lower cost than the 1st and the 2nd generation, and photoelectric conversion efficiency of over 40% according to the theoretical calculation. The highest yield obtained for DSSCs 11.9% lower than that of perovskite solar cells (19.7%) [6]. This shows the huge potential of the perovskite solar cell, it reaches an efficiency of 25.2% by 2020 [7], and it is predicted to reach 28% in the future. In addition to perovskite cells, QDSSCs are predicted to reach more than 40% efficiency according to theoretical calculations, this is also very potentially a 3rd generation solar cell.
One of the main reasons for the growing interest in quantum dots is their use in cheap solar cells, which have the possibility to increase the thermodynamic conversion efficiency above the Shockley–Queisser limit [8]. The thermodynamic limit of the light to electric power conversion efficiency, also known as Shockley–Queisser limit, originates from the fact that photons with energies below the band gap energy are not absorbed, while photons with energies above the band gap energy release the additional energy (Ephoton − Egap) mostly as heat. Third generation solar cells aim for conversion efficiencies beyond the Shockley–Queisser limit through advanced photovoltaic concepts such as multijunction cells, optical up and down converters, and multiple carrier generation by impact ionization. Their development has been based on different p–n junctions and the use of quantum dots (QDs) to replace dyes. Performance above 40% has been obtained [9].
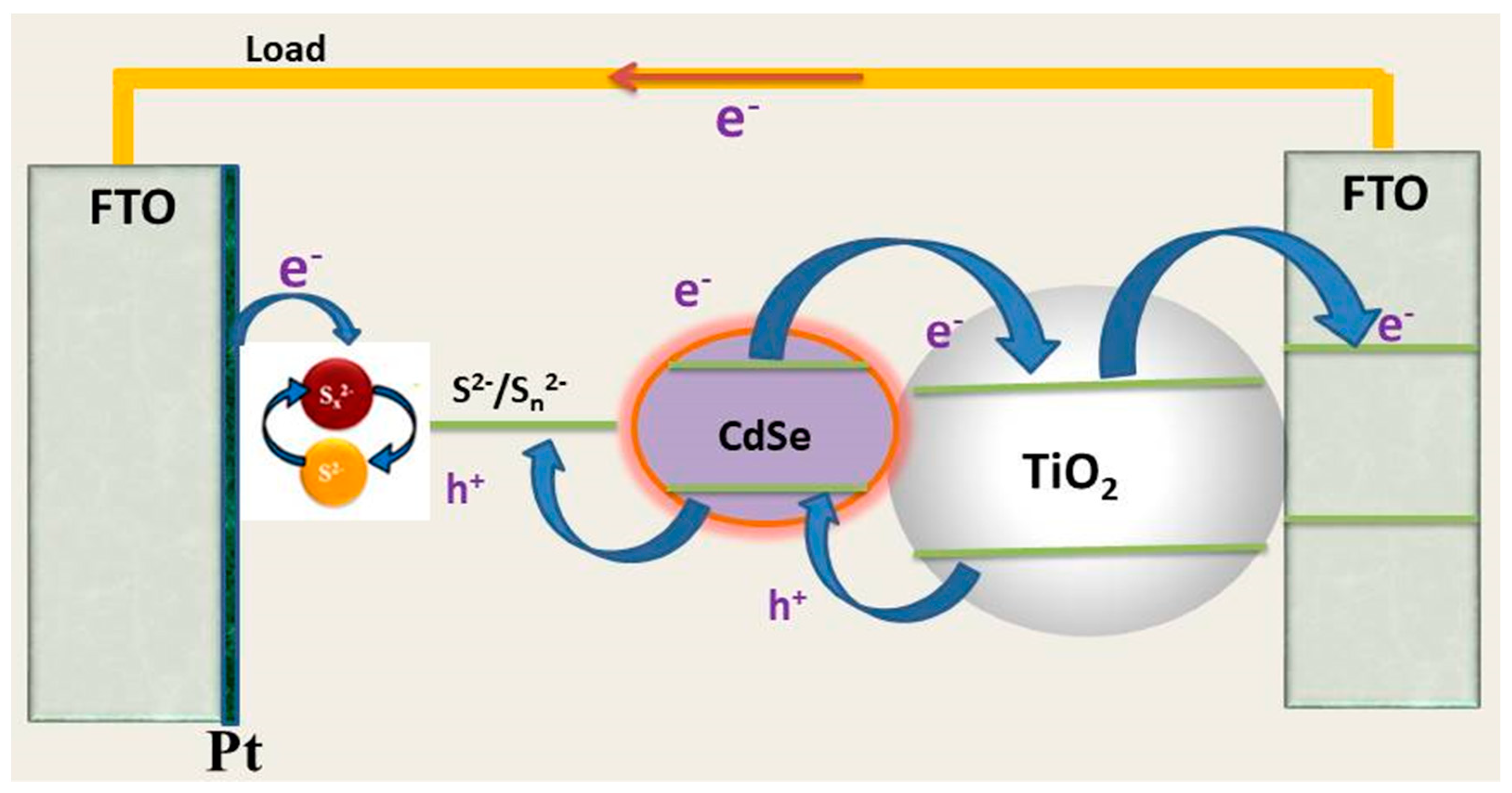
Now the focus is on the next generation solar cells with high efficiency at an economically viable cost [10,11]. QDs are drawing great attention as a material for the next generation solar cells due to high absorption coefficient, tunable band gap, and multiple exciton generation (MEG) effect [12,13]. Therefore, QDs have been used in dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) as the photosensitizer instead of organic dyes to form quantum dot sensitized solar cells (QDSSCs) [14,15,16]. The typical structure of the QDSSCs is similar to that of the DSSCs, which consists of mesoporous photo anode (TiO2 film), sensitizer (QDs), electrolyte (polysulfide), and the counter electrode [17,18,19,20]. During operation, photons are captured by QDs, yielding electron–hole pairs that are rapidly separated into electrons and holes at the interface between the nanocrystalline TiO2 and the QDs. The electrons inject into the TiO2 film and the holes are released by redox couples in the liquid polysulfide electrolyte [17,20,21].
Improving the power conversion efficiency (η) of QDSSCs has always been an overarching concern for all scientists. One of the approaches has been focused on constructing and fabricating nanostructural oxides, such as TiO2 [22], ZnO [23,24], and SnO2 [25] to harvest more amounts of QDs. On the other hand, many efforts have been concentrated on designing and synthesizing QDs to get high photoelectric performance [26,27,28].
In recent years, researchers have discovered the QDs, which can create the high performance of solar cells [29]. QDs can be changed in particle size, leading to a change in the absorption spectrum [30]. Controlling QDs size, we can change their absorption spectrum. Furthermore, in association with biological molecules, QDs can transfer charge faster while reducing losses and helping the passivated surface (reduced defect states) of them. In 1990, Vogel and his colleagues have used CdS QDs with the Pt cathode [31]. However, this is a new direction in QDSSCs research. Since then, there have been a large number of studies such as different QDs replacement, TiO2 semiconductor materials, electrolyte, and counter electrodes to enhance the photovoltaic performance [32,33,34]. Lee and his colleagues studied CdSe and CdTe QDs using the Pt counter electrode with an efficiency of under 1% [35]. One year later (2008), they went on investigating CdS and CdSe QDs and improved the performance efficiency to 1.2% with the use of polysulfide electrolyte [32]. Meanwhile, Lopez-Luke et al., Mora–Sero et al., Shen et al., and Tachibana et al. [36,37,38,39] synthesized CdS and CdSe QDs with the Pt counter electrode, but in different electrolyte systems (Na2S, NaOH + Na2S+S) and obtained a better performance efficiency of 2.2%. From 2009 to 2012, various QDSSCs were studied. Cheng et al. [40] examined CdS and CdSe cosensitized TiO2 nanowires and nanorods by using the Na2S+Na2SO3 electrolyte and obtained a high efficiency of 2.41%.
Recently, a few research showed that some doping ions in the sulfide QDs, such as Hg2+ into PbS [41], and Mn2+ into CdS [42], could increase the current density and efficiency of the solar cells. Compared with CdS and PbS QDs, CdSe are more attractive owing to its high potential for light harvesting in the visible light region [43,44]. The efficiency of CdSe QDs sensitized solar cells is much higher than that of the sulfide QDs sensitized solar cells [45,46,47,48,49]. Therefore, doping metal ions into CdSe QDs is considered a useful way for designing high efficiency solar cells [50,51].
In this study, a review on QDSSCs based on photoanodes with single quantum dot, with binding agents, with passive surfactant, with multilayer QDs, and with doped QDs, different counter electrodes, and different electrolytes are briefly provided.
2. Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells (QDSSCs) Based on Single Quantum Dots (QDs) Photoanode
2.1. A Review on QDSSCs Based on Single QDs
Single QDs are individual QDs synthesized by several methods such as colloidal QD, chemical bath deposition (CBD), successive ionic layer absorption and reaction (SILAR), etc. Those QDs are assembled on the surface of metal oxides, which have large electronic bandgaps such as TiO2, ZnO, SnO2, etc. Both QDs and metal oxide layers are put on top of fluorine doped tin oxide (FTO) substrates to form a complete photoanode, which is illustrated in Figure 1. Thus far, there are many QDs that have been attractive globally, for example, PbS [52,53], CuInS2 [54], AgInSe2 [55], PbSeS [56], Ag2Se [57], CdS [58], CdSe [59], CdTe [60], etc. Among them, CdS, CdSe, and CdTe QDs are prominent candidates because of their high stability in fabricated QDSSCs [61] and achieving the highest photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE) as illustrated in Table 1.
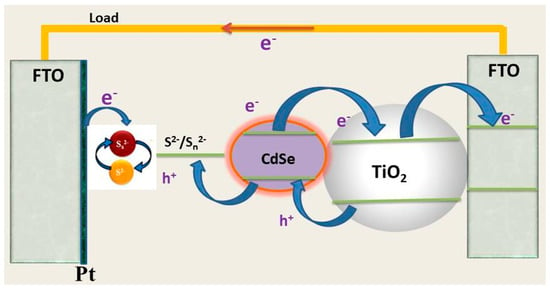
Figure 1.
Schematic of a QDSSC’s structure with a single QDs CdSe photoanode.

Table 1.
Review of the same field publications.
When a photon is absorbed, an excited electron is generated in the conduction band of a single QDs and transferred to the metal oxide layer to form a close electronic circuit. Several PCE of QDSSCs based on single QDs are shown in Table 1, whose efficiencies are relatively small, specifically, 1.31% and 1.03% [62], the highest PCE for CdS and CdSe QDs, respectively. These results are due to the absorption spectra of CdS and CdSe QDs being limited to 450 and 550 nm wavelength, respectively. This leads to the strong absorption of QDs with photons whose wavelengths are shorter than 550 nm. Otherwise, QDs are transparent to photons having wavelengths longer than 550 nm. Due to the restriction of QDs’ absorption spectra, the number of electrons produced after photo excitation is limited and greatly lost due to recombination centers (the material is imperfectly fabricated) resulting in low current density and clearly small PCE.
2.2. The Causes of Low QDSSCs’ PCE and Solutions
Based on the references and obtained results, there are some main reasons for the reduction of QDSSCs’ PCE, which are:
- a.
- Low fill factor
The fill factor (FF) is defined from the current density–voltage (J–V) characteristic measurement. FF depends on the value of open circuit potential, resistance of series-connected components, and recombination processes in the QDSSCs, which relate to the fabricated materials. Low FF may be caused by the small open circuit potential, which strongly depends on the photoanode, and excessive recombination in QDSSCs. Moreover, FF is also affected by series resistors and parallel resistors of QDSSCs. To achieve higher PCE and reduce recombination in QDSSCs, it is required to have smaller series resistance RS and larger parallel resistance RSH. From Table 1, RS values of QDSSCs based on CdSe QDs are relatively large, in the range of 27.4–732 Ω. This obstructs the electrons moving through the contact layers. Similarly, relatively small RSH values, which can be seen in Table 2, tend to reduce the performance of QDSSCs.

Table 2.
The resistance values of QDSSCs as calculated by physical approach.
- b.
- Impaired electrolyte
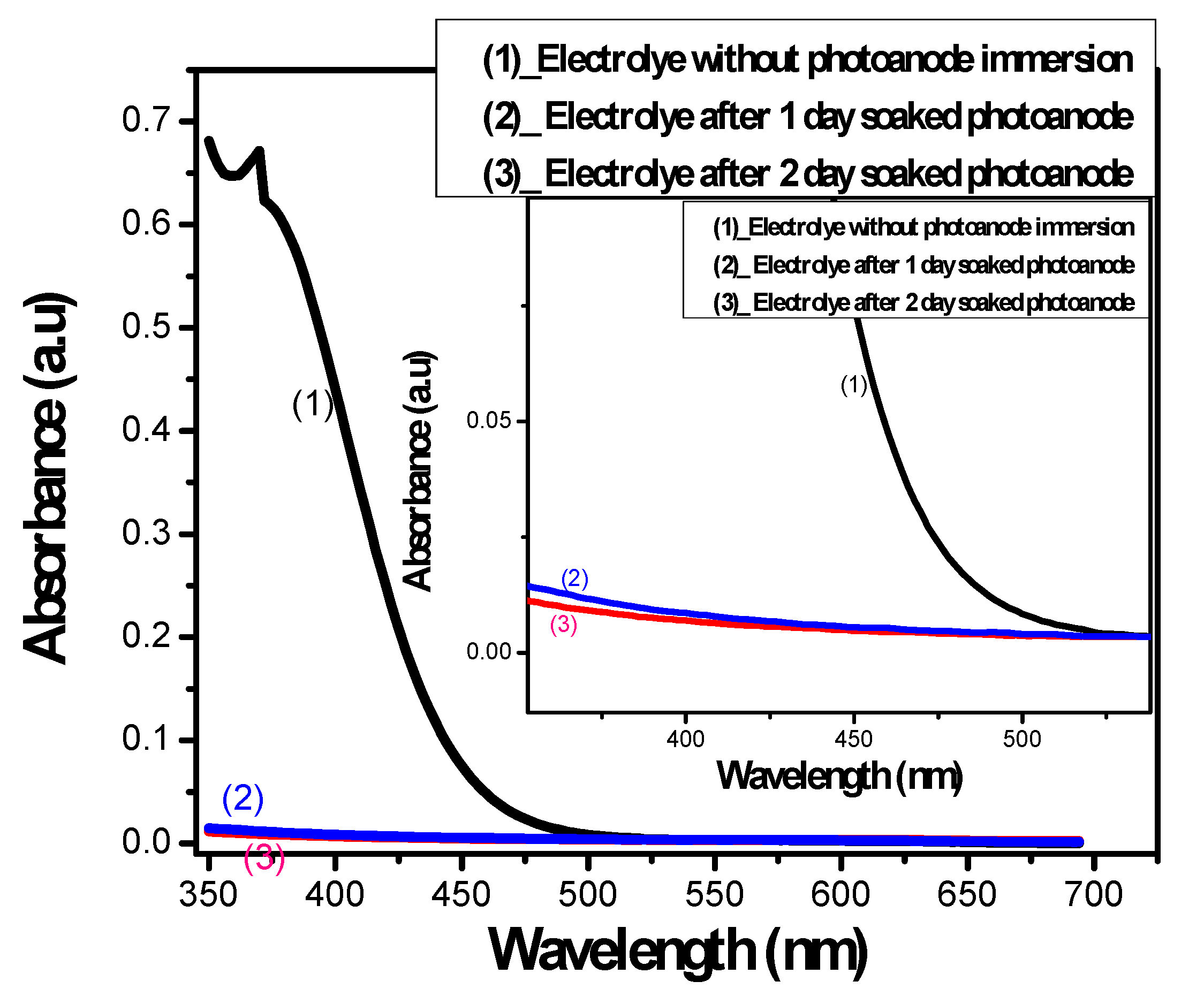
To investigate the factors that can cause a reduction in QDSSCs’ PCE, the reduced absorption ability of the electrolyte after photoanode immersion is studied. According to Kamat et al., the electrolyte is in direct contact with the TiO2/CdSe membrane, so, in operation, CdSe QDs react with the electrolyte and generate byproducts, which impair both the electrolyte and CdSe QDs. Those reactions are described by the following equations:
- A dynamic balance is existed in the S2−/Sn2− aqueous electrolyte:
S2− + H2O ↔ HS− + OH−
- Electron–hole pairs are generated after CdSe QDS are photoexcited by possibly the following equations:
CdSe + hν → CdSe (e + h) → CdSe + hν’
CdSe (e + h) + TiO2 → CdSe (h) + TiO2 (e)
- Reaction at the CdSe/electrolyte interface:
CdSe (h) + S2− → CdSe + S−*
- The S2−/Sn2− strongly obstructs the hole movement from CdSe QDs into the electrolyte [27] as described in Equation (4) and S−* is in an excited ion.
As can be seen in Figure 2, the absorption of the electrolyte was dramatically decreased after 2 days of immersion. This proves the large influence of the electronic exchange reactions between CdSe QDs and the electrolyte, as generated byproducts from Equations (1)–(4) impaired the electrolyte absorbance and reduced the QDSSCs’ PCE.
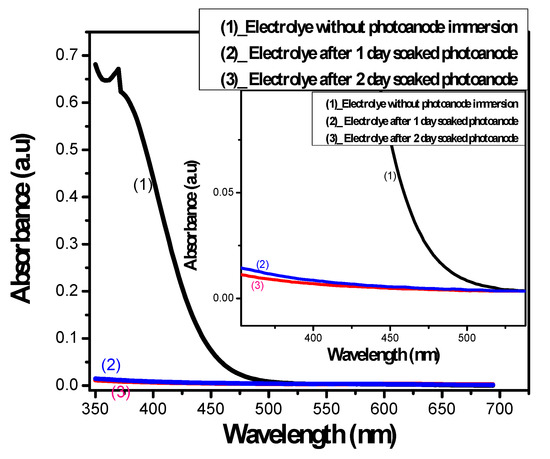
Figure 2.
The absorption spectrum of polysulfide electrolyte before and at specific times after photoanode immersion.
- c.
- Strong recombination processes
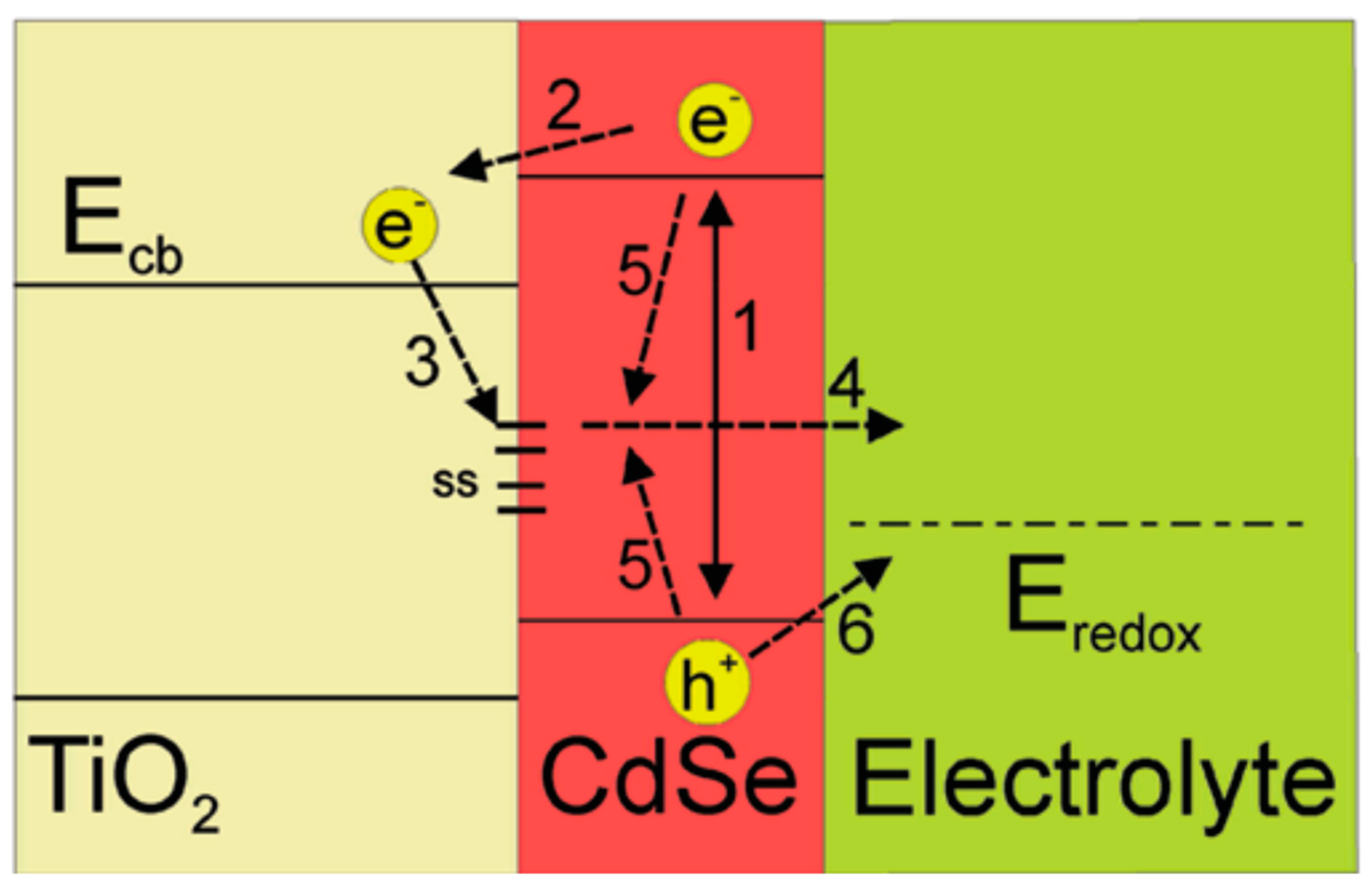
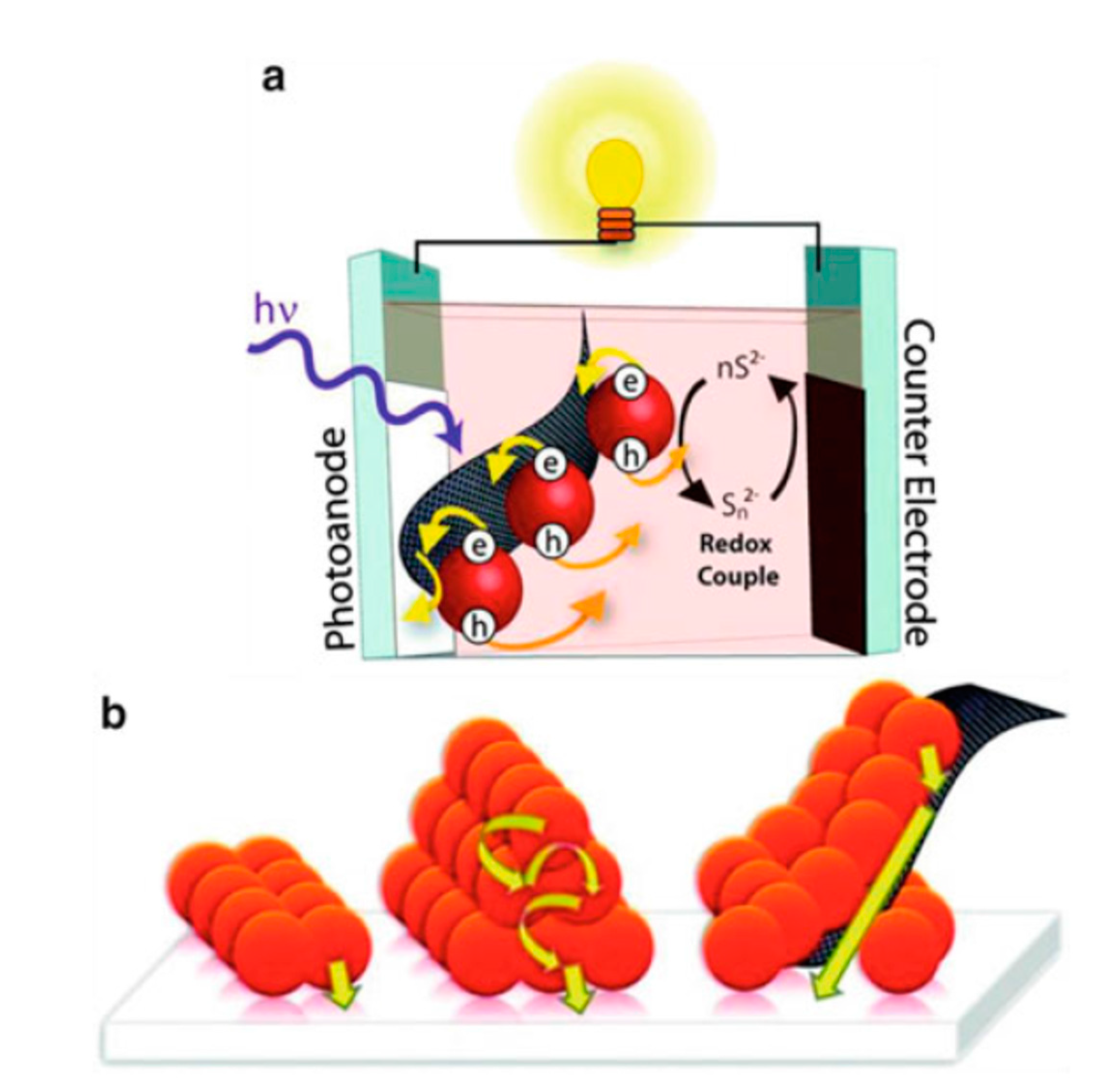
A typical structure of QDSSCs includes the photoanode, counter electrode, and polysulfide electrolyte. Under the light condition, the operated processes happening inside QDSSCs are shown in Figure 3. These processes are indicated by arrows. When the photoanode surface is illuminated, exciton generation and electron–hole recombination are exhibiting simultaneously inside CdSe QDs (1). Free electrons in the conduction band of CdSe QDs are easily transferred to the TiO2 conduction band (2). Those electrons, however, may be trapped in surface states due to CdSe QDs imperfection (3) and diffused into the electrolyte afterward (4), or recombined with holes inside CdSe QDs. The recombination of free electrons in the conduction band (CB) with CdSe QDs surface state and the recombination of electrons in the electrolyte and holes in CdSe QDs valence band (VB) are indicated as (5) and (6) processes, respectively. The (1), (2), and (6) processes are useful in QDSSCs operation. In contrast, the remaining processes cause a reduction in QDSSCs’ performance.
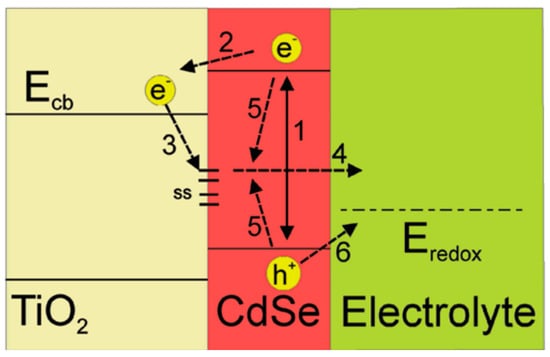
Figure 3.
Schematic of the energy levels of different material layers and main processes in an operating QDSSC: (1) exciton generation in CdSe QDs, (2) electrons transferring from CdSe QDs into TiO2 layer, (3) electron trapping causing by QDs’ surface trap states, (4) electrons diffusion from CdSe QDs into electrolyte, (5) relaxation in CdSe QDs, and (6) recombination of electrons in electrolyte and holes in CdSe QDs by reduction reaction at the QDs/electrolyte interface. It was obtained from Mora-Sero and co-works, 2009 [79].
- d.
- Shortage of binding agents between QDs and TiO2 membrane
Among QDSSCs, which are prepared based on TiO2, the membrane is soaked directly into TOP organic solvents, where CdSe QDs are dissolved. The solvents, however, create unsustainable chemical bonding with TiO2 molecules. Consequently, it reduces the carrier transport efficiency in QDSSCs.
3. QDSSCs Based on Photoanode Binding Agents
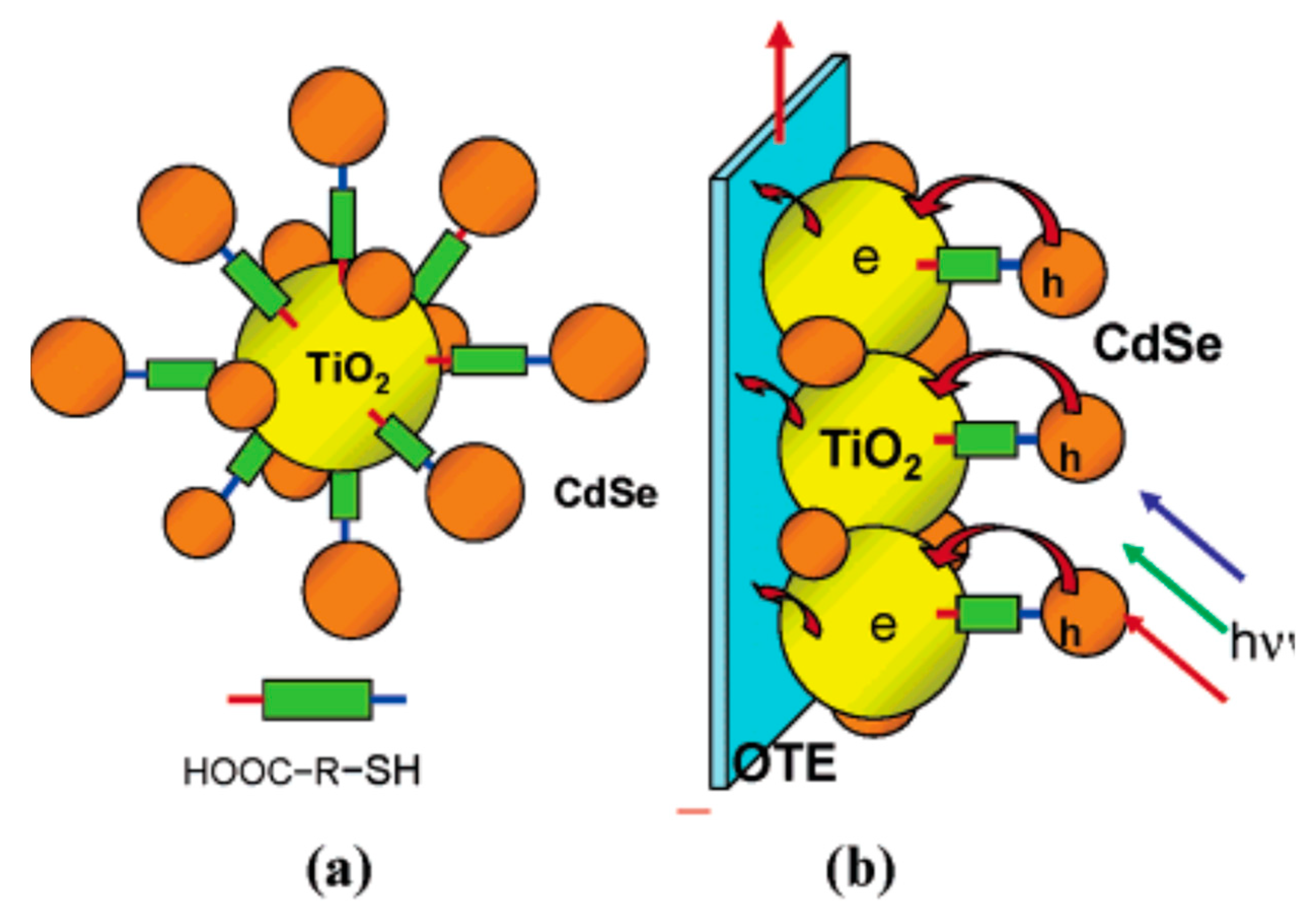
The single QDs presented in the last section are directly absorbed onto the metal oxide membrane. It is difficult to achieve perfect absorption at the QDs/TiO2 interface, hence electronic trap states have consequently arisen. To reduce the recombination at QDs/metal oxide interface, binding agents, such as mercaptopropionic acid (MPA), trioctylphosphine, or trioctylphosphine oxide [82,83], thiolacetid acid (TAA), or mercaptohexadecanoic acid [84], are frequently used. With the formation of COOH-R-SH, the COOH- (carboxyl) group of binding agents can establish chemical bonding with metal oxides, while -SH (thiol) group is linked to single QDs, as illustrated in Figure 4. The presence of binding agents supports the electron transport from the CB of QDs into the metal oxide layer, consequently, the current density enhancement in QDSSCs has been observed.
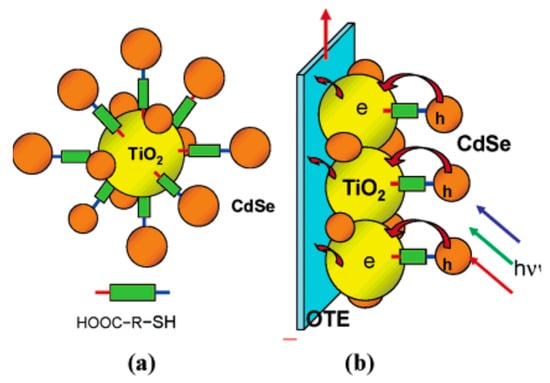
Figure 4.
(a) The absorption of single CdSe QDs onto the metal oxide membrane supported by binding agents and (b) photoanode is formed by coating system (a) with the FTO glass substrate [84].
4. QDSSCs Based on a Photoanode with a Passive Surfactant
The actual PCE of the majority of QDSSCs, which have a single QDs photoanode, is less than from the theoretical calculation due to the strong recombination inside QDs and at QDs/TiO2 interface or direct contact of QDs with the different electrolyte systems. To limit the number of surface trap states, materials with large band gaps, such as ZnS, SiO2, MgO, or Al2O3 (shown in Table 3), have been frequently used as a passivation layer [85,86,87,88,89,90]. The passivation layer is covered on the surface of QDs to create a boundary that prevents the direct contact of QDs with the electrolyte and hence the dark current, i.e., stimulated electron transport from QDs to the electrolyte. One can imagine that the excited electrons are blocked by the presence of this passivation layer and only able to move from QDs to TiO2 and then to the outer circuit.

Table 3.
Review on QDSSCs with passive surfactant.
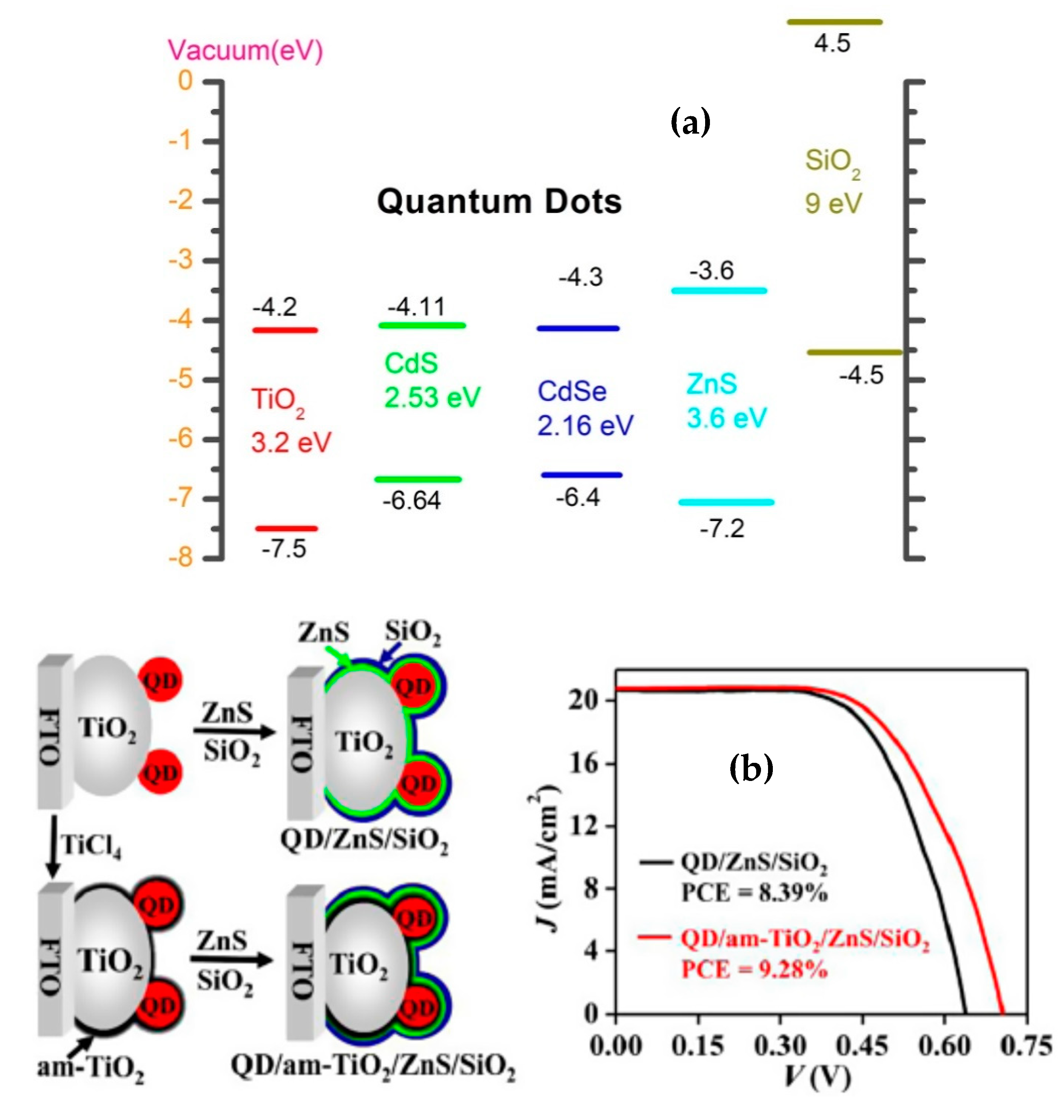
Currently, ZnS has been widely used as the most effective passive surfactant for QDSSCs since this semiconductor has a large band gap of approximately 3.6 eV and CB level (−3.6 eV) of nanocrystal ZnS is higher than that of CdSe (−4.3 eV) and CdS (−4.11 eV), which is studied by Tung et al. and illustrated in Figure 5a. The efficiency was significantly increased by 150% with the presence of a passivation layer. In addition, Tung and colleagues reported an efficiency enhancement from 1.64% to 3.77% on QDSSCs based CdS/CdSe:Mn photoanode and from 1.64% to 4.22% on CdS/CdSe:Cu-based photoanode with the presence of ZnS passivation layer [99,100,101,102]. As reported by Hachiya et al. [95], a significant improvement of excited electron transport from QDs into TiO2 layer and a dramatic reduction of surface trap states at the QDs/TiO2 interface by covering ZnS nanocrystals on PbS QDs were observed and proved by transient grating (TG) spectra. Apart from ZnS, other materials, such as ZnSe [103], Al2O3 [104], or SiO2 [101], have been used as a passivation layer for QDSSCs. According to Tung et al., the QDSSCs efficiency was sharply increased by 375% when a SiO2 passivation layer was absorbed onto the surface of CdS/CdSe QDs. Since SiO2 conduction level in a vacuum (4.5 eV) was much higher than those of CdSe (−4.3 eV) and CdS (−4.11 eV), the dark current was mostly suppressed in QDSSCs leading to the PCE enhancement. Furthermore, the combination of ZnS and SiO2 as a passivation layer has shown promising efficiency in recent studies. The passivation layer of ZnS/SiO2 covered on the surface of CdSexTe1−x QDs, in particular, leads to the significantly increased efficiency from 6.37% to 8.55% [103].
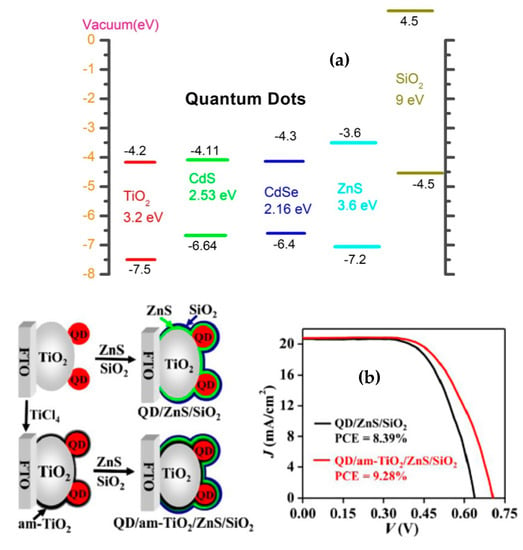
Figure 5.
(a) Schematic diagram of the energy level of an QDSSC’s photoanode [101] and (b) the enhancement in QDSSCs performance by using a passive surfactant from Ren and co-work, 2015 [105].
5. QDSSCs Based on a Photoanode with Multilayer QDs
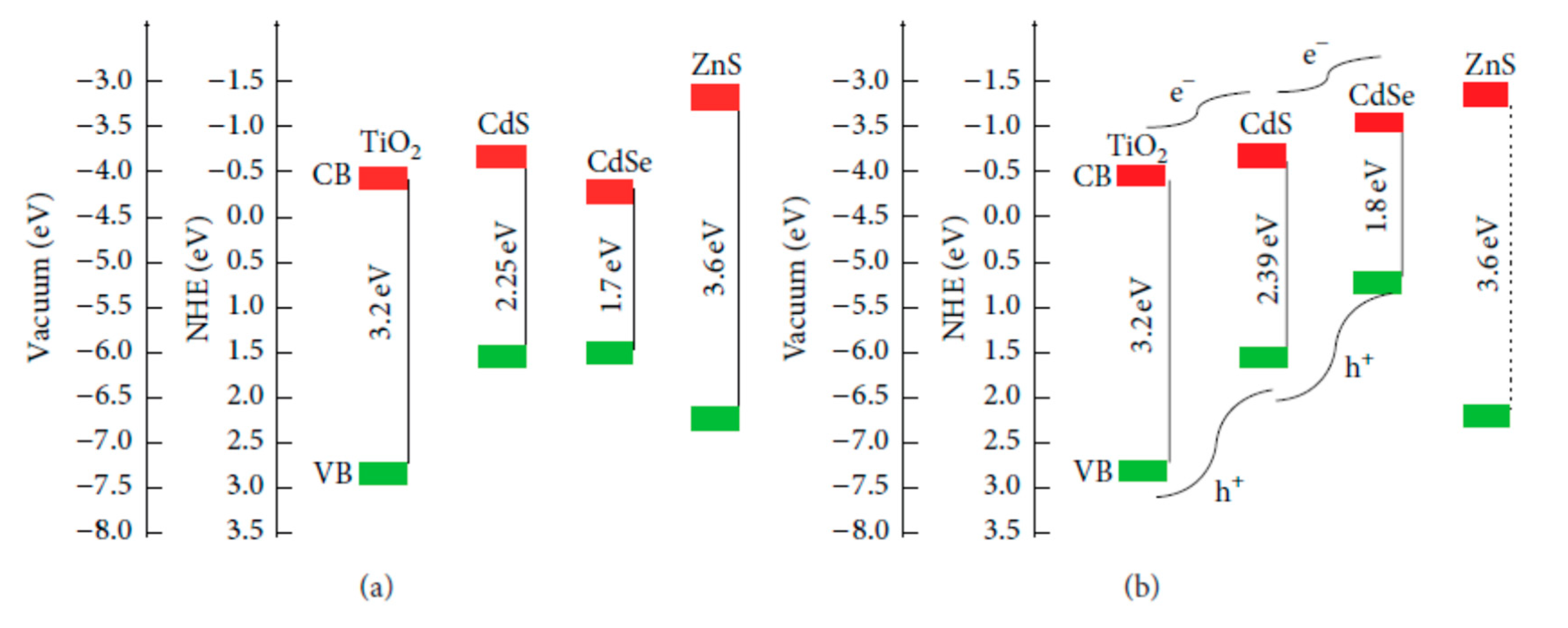
QDSSCs based on single QDs have limited absorption spectra in the visible region. To overcome CdS, CdSe, CdTe, and PbS QDs are combined to be able to absorb photons with different wavelengths in the visible region. Recently, photoanodes with multilayer QDs, such as CdS/CdSe [105], CdS/CdTe [106], CdS/PbS [107], CdS/CdSe/PbS [108], CdSe/CdTe [109], or ZnTe/CdSe [110], have been studied. Osada et al. reported a 70% increasement in PCE of QDSSCs by covering a CdS layer prior to TiO2, i.e., CdS acts as a buffer layer, while only 50% enhancement with CdSe prior covering. This result has good agreement with others reported by Tung and colleagues [111]. Specifically, they observed a raise from 0.6% to 1.05% in QDSSC’ PCE when a CdS layer is sandwiched between TiO2 and CdSe outer layers. Several publications on the electric transport researched inside QDSSCs based on TG spectra have proved that the tandem (or parallel or cophotosensitive) structure, as can be seen in Figure 5a, leads to more photon absorption and hence more exciton generation [112,113].
In Figure 6a, TiO2, CdS, and CdSe are in bulk scale, so the CB level of bulk CdSe is lower than those of bulk TiO2 and CdS. This structure obstructs the electron movement from the CB of CdS and CdSe QDs into the TiO2 layer. However, when CdS and CdSe are in the nanoscale, their band gap can be manipulated. As can be seen in Figure 6b, the band gaps of CdS and CdSe nanocrystals were 2.39 and 1.8 eV, respectively. Due to quantum confinement, the conduction energy levels of both CdS and CdSe nanocrystals were higher than that of bulk TiO2. This yielded a tandem structure at the photoanode energy, which is favorable for electron transport from QDs into TiO2. Moreover, with the tandem structure shown in Figure 6, light propagates in order through FTO, TiO2, CdS, CdSe, and ZnS layers. FTO glass substrate is transparent, so light energy is preserved when reaching the TiO2 layer. Due to the large bandgap of 3.2 eV, the TiO2 layer just absorbed photons with wavelengths less than 400 nm. Other longer wavelength photons were continuously propagated and then those with wavelengths less than 450 nm and 650 nm were absorbed by CdS and CdSe QDs, respectively. Therefore, the tandem structure of photoanode energy led to a broader absorption spectrum from the ultraviolet region to 650 nm in the visible region and more exciton generation, consequently, PCE of QDSSCs may be enhanced. However, the excited electrons can be trapped by a number of surface states at TiO2/CdS/CdSe/ZnS interface due to the imperfect synthesis process, which affects the performance of QDSSCs [100].
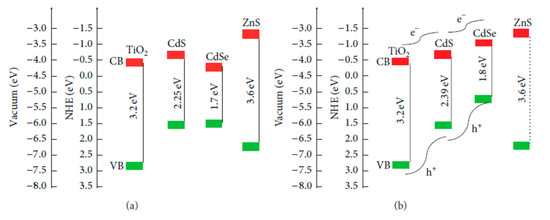
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram of the energy level of a photoanode with (a) CdS CdSe in bulk scale and (b) CdS CdSe in the nanoscale from Grätzel, 2001 [114].
6. QDSSCs Based on a Photoanode with Doped QDs
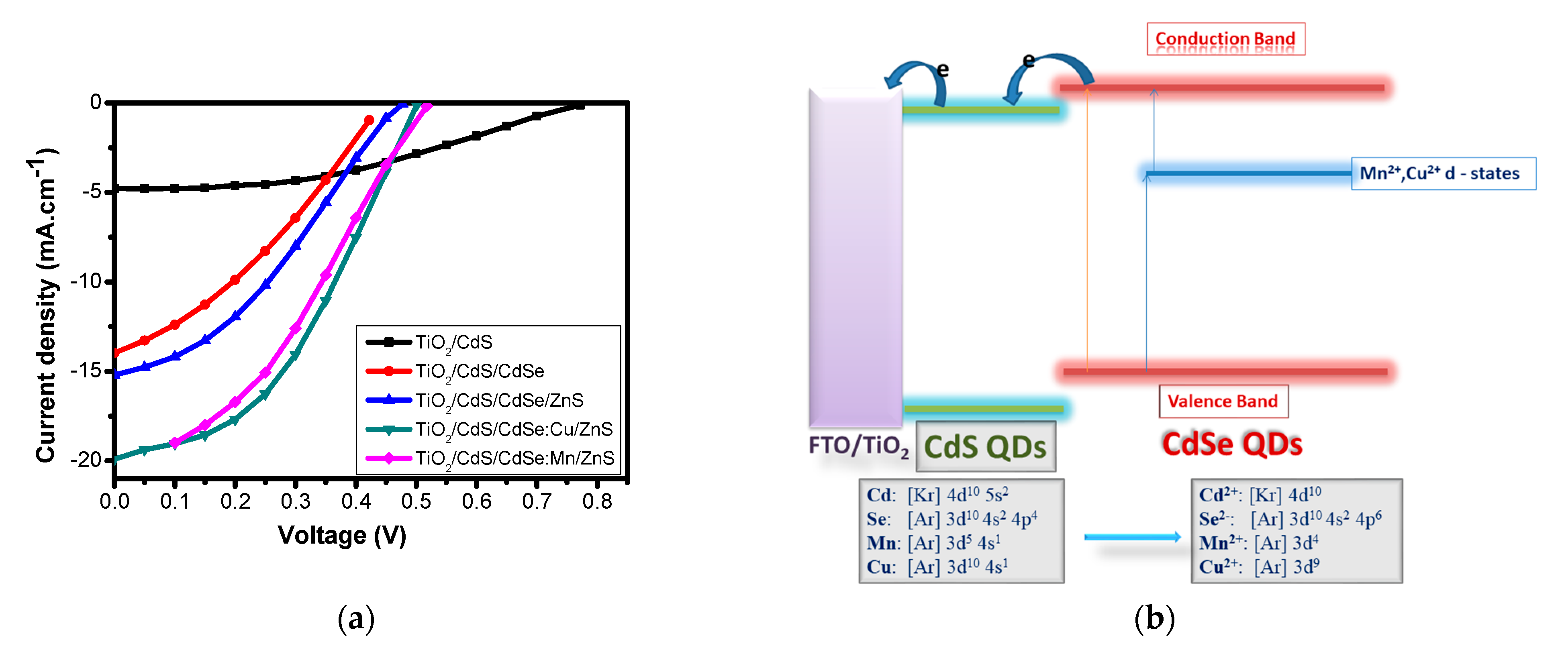
In recent years, CdSe QDs has been attractively researched and applied in QDSSCs fabrication due to their simple synthesis, low cost, and high chemical stability. The resistance, however, of CdSe was relatively high and the CB level of this material in the bulk state was slightly slower than that of TiO2, which obstructed the movement of photoexcited electrons from the CB of CdSe QDs into TiO2. To improve the current density and hence the PCE of QDSSCs, several research have been carried out on doping metals, such as Mg [115], Mn [99], Cu [100], Ag [116], Hg [117], Co [118], or Eu [119], into CdS, CdSe or PbS QDs.
As reported by Tung et al., by doping Mn and Cu into CdSe QDs, the efficiencies of QDSSCs were increased from 2.55% with pure tandem-structure photoanode to 3.77% and 4.22% with Mn- and Cu-doped photoanode, respectively. These results have good agreement with those in Reference [97]. The current density enhancement in QDSSCs with the doped photoanode was due to the presence of doping metal energy level in the bandgap of pure QDs, as can be seen in Figure 7b. Hence, one can manipulate the bandgap of QDs, for instance, CdSe:Cu2+ QDs, by controlling the doping concentration and layer thickness. Without doping, photons whose energy was less than the pure QDs bandgap cannot be absorbed. However, by the presence of doping energy levels inside the pure QDs bandgap, those aforementioned photons were able to be absorbed. This led to a significant improvement of the photoexcited electron density and hence the current density of QDSSCs [120,121,122]. Moreover, by doping metals into pure QDs, the resistance of different components in QDSSCs, such as TiO2/QDs interface and TiO2 diffusion layer resistance (Rct2) or electrolyte/counter electrode resistance (Rct1), were dramatically decreased, while the significant increasement of photoexcited electron lifetime in the QDs CB was observed [100].
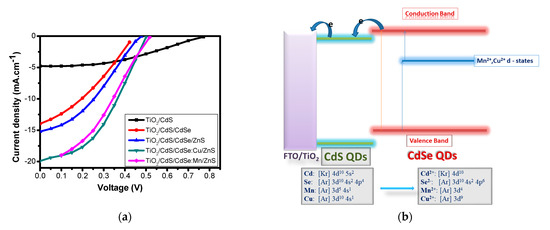
Figure 7.
(a) Current density–voltage (J–V) curves of QDSSCs with different photoanodes and (b) schematic diagram of the energy level of a photoanode with CdSe QDs doped Mn or Cu from Phuc, D.H and co-works, 2019 [120].
7. QDSSCs Based on Different Counter Electrodes
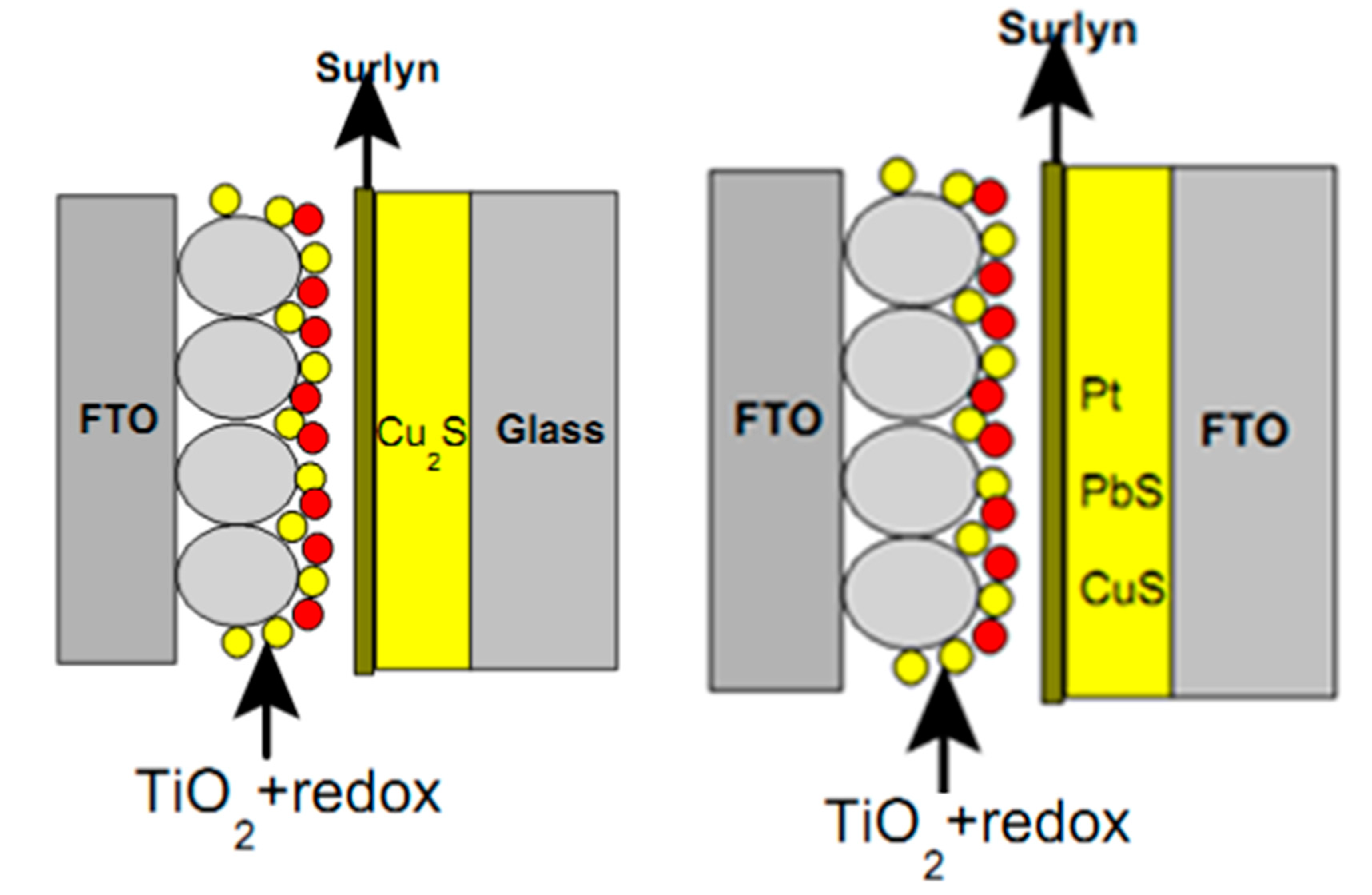
Counter electrode has a large contribution on the operation of QDSSCs, so choosing the suitable material for counter electrode fabrication is strongly required. The reduction reaction of the electrolyte system is occurred at the counter electrode surface, hence the counter electrode material must have low resistance and high electrochemical catalyst activity, i.e., to reduce the redox potential of the electrolyte. Pt was previously used as the cathode material due to its compatibility with the I3−/I− electrolyte as a Figure 9. However, the resistance of the counter electrode/electrolyte interface is relatively high, which reduces the electron transport efficiency through the cathode surface [123]. For QDSSCs, QDs are easily corroded in the I3−/I− electrolyte and hence limit the light absorption ability of those QDs. Several cathode materials, such as nanocarbon tubes, CuS, nanocarbon tube–Cu2S, NiS, or Au (Figure 8 and Figure 9) [124,125,126], have been studied in QDSSCs with a polysulfide electrolyte. Among them, nanocarbon tube, Au and NiS are suitable for the polysulfide electrolyte but have high resistance at the counter electrode/electrolyte interface, hence limiting the electron movement from counter electrode to electrolyte and reduce the efficiency of QDSSCs. CoS and NiS materials have been studied for better results, but they leave impurities in the electrolyte and counter electrode, which affect QDSSCS in the long-term operation [127,128].
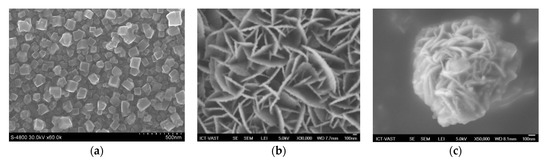
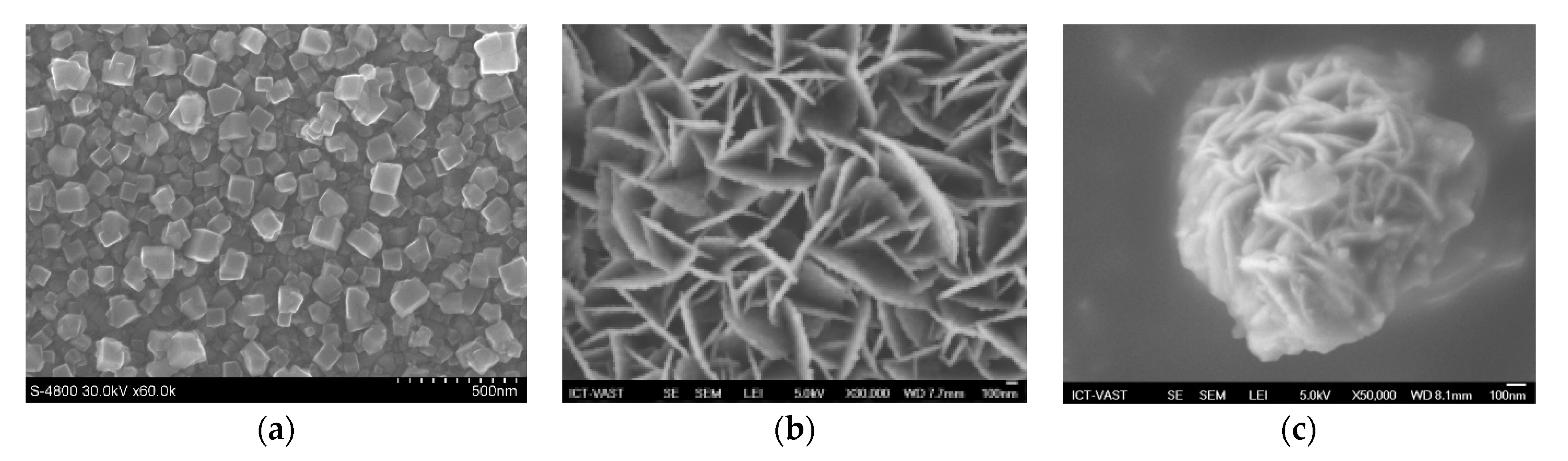
Figure 8.
FE-SEM images of counter electrodes based on different materials: (a) PbS, (b) CuS, and (c) Cu2S from Tung HT and co-works, 2014 [129].
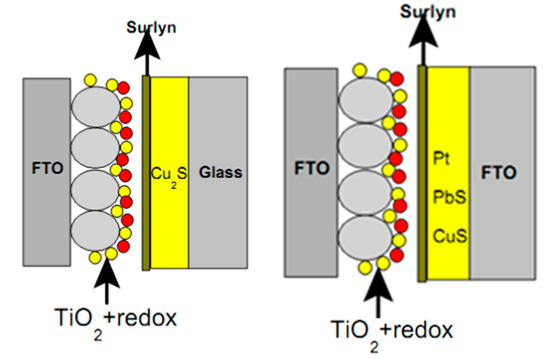
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram of QDSSCs’ structure with different counter electrode materials: Cu2S (left) and Pt, CuS, and PbS (right).
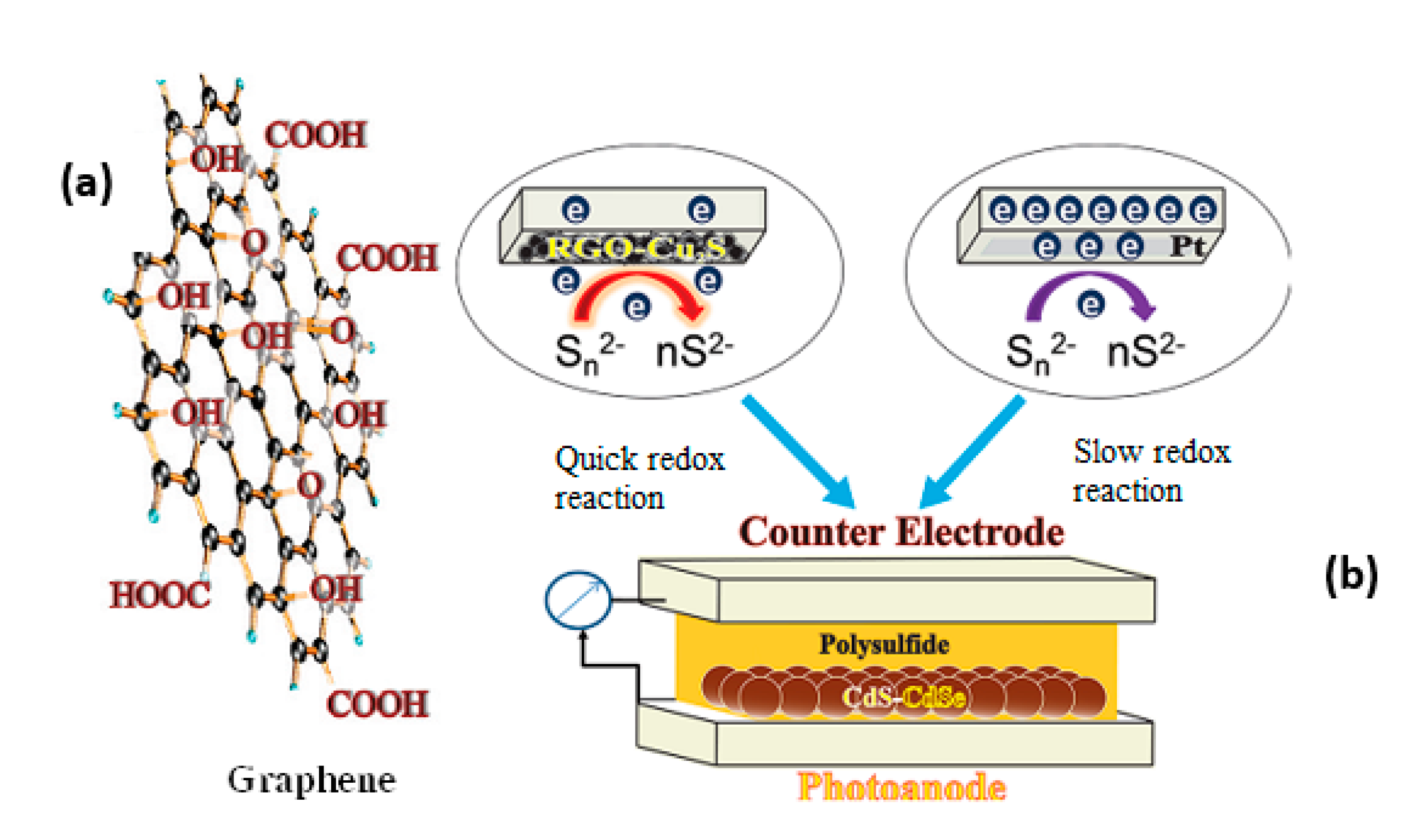
Graphene is a two-dimensional single layer of carbon atoms, which has a large surface area and high electronic mobility of 1.5 × 104 cm2 V−1 s−1 so having prominent electrical, optical, thermal dynamics, and mechanical properties [130,131,132]. Therefore, graphene has become promising for science and technology revolution. Moreover, graphene oxide is more applicable due to possessing -COOH and -OH function groups lying between horizontal lattices and on the corner of the horizontal plane, which can form carbonyl or carboxylic (Figure 10) to easily establish chemical bonding with inorganic materials, such as CuxS, on counter electrodes of QDSSCs.
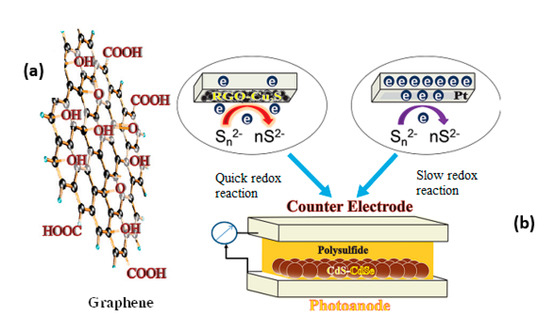
Figure 10.
(a) Graphene with functional groups and (b) structure of a QDSSC from Tachan and co-works, 2011 [133].
CuxS and its compounds have superior absorption and decompose chemical reaction ability, which lead to efficiency enhancement, so they have been widely used as counter electrode materials in QDSSCs [134]. Lee et al. studied the composite of Cu2S and nanocarbon tube, but only 0.08% efficiency was achieved due to the carrier mobility of the nanocarbon tube is much lower than that of graphene [135].
8. QDSSCs Based on Different Electrolytes
As discussed in Section 6, QDSSCs derived from the previous type of solar cells, which had dye molecules as photo absorbers, so keep using the I−/I3− electrolyte. This electrolyte, however, is the main cause of corrosion and functional degradation of QDs and hence low efficiency, for instance, 1.52% PCE of QDSSCs based on CdS/CdSe QDs [123]. Therefore, seeking for a more compatible electrolyte with QDs to improve QDSSCs performance is the main challenge. The electrolyte, according to recent reports (Table 4), can now be divided into three categories, which are liquid, pseudo-solid, and solid electrolytes.

Table 4.
Review on QDSSCS based on different counter electrodes.
Among them, liquid polysulfide electrolyte has been widely used due to its compatibility with QDs and counter electrodes, which greatly improve the QDSSCS performance [144]. This electrolyte, unfortunately, causes oxidation of the QDs and makes the open circuit potential (VOC) and FF low [145]. To protect from corrosion, QDs are frequently covered by a layer of passivation surfactants, such as ZnS or SiO2, as discussed above. In addition to the polysulfide electrolyte, the pseudo-solid [146] or solid [147] electrolyte has been used in the combination with organic compounds, such as polyethylene glycol [148] and guanidine thiocyanate [149].
9. Opportunities and Challenges
Currently, QDs have been made with high purity, quality, less defects, manipulated bandgap energy, and good optical properties to replace photosensitive molecules. However, the PCE of QCSSCs has not exceeded 10%, which is much lower than that from theoretical calculations. There are two major issues one has to overcome:
Firstly, substantial excitation electron loss in QDSSCs. There are many types of losses in QDSSCs operation, such as the recombination process inside QDs or on their surfaces due to imperfect fabrication, electron loss when transported through the QDs/TiO2 interface, electron diffusion process inside the TiO2 membrane, and QDs corrosion by electrolyte or electron loss due to redox reaction at the electrolyte/counter electrode interface. Among them, the losses due to internal and surface defects of QDs are limited for those QDs synthesized by the colloidal process at high temperature or extended for those made by the CBD or SILAR method. Losses due to electrolyte corrosion can be improved by using passivation surfactants, such as ZnS or SiO2, to limit the contact between QDs and electrolytes. However, more defects are observed in the multilayer photoanodes with tandem structure.
Secondly, researching on the new kind of QDs materials.
- a.
- QDSSCs based on QDs possessing intermediate band (IB)
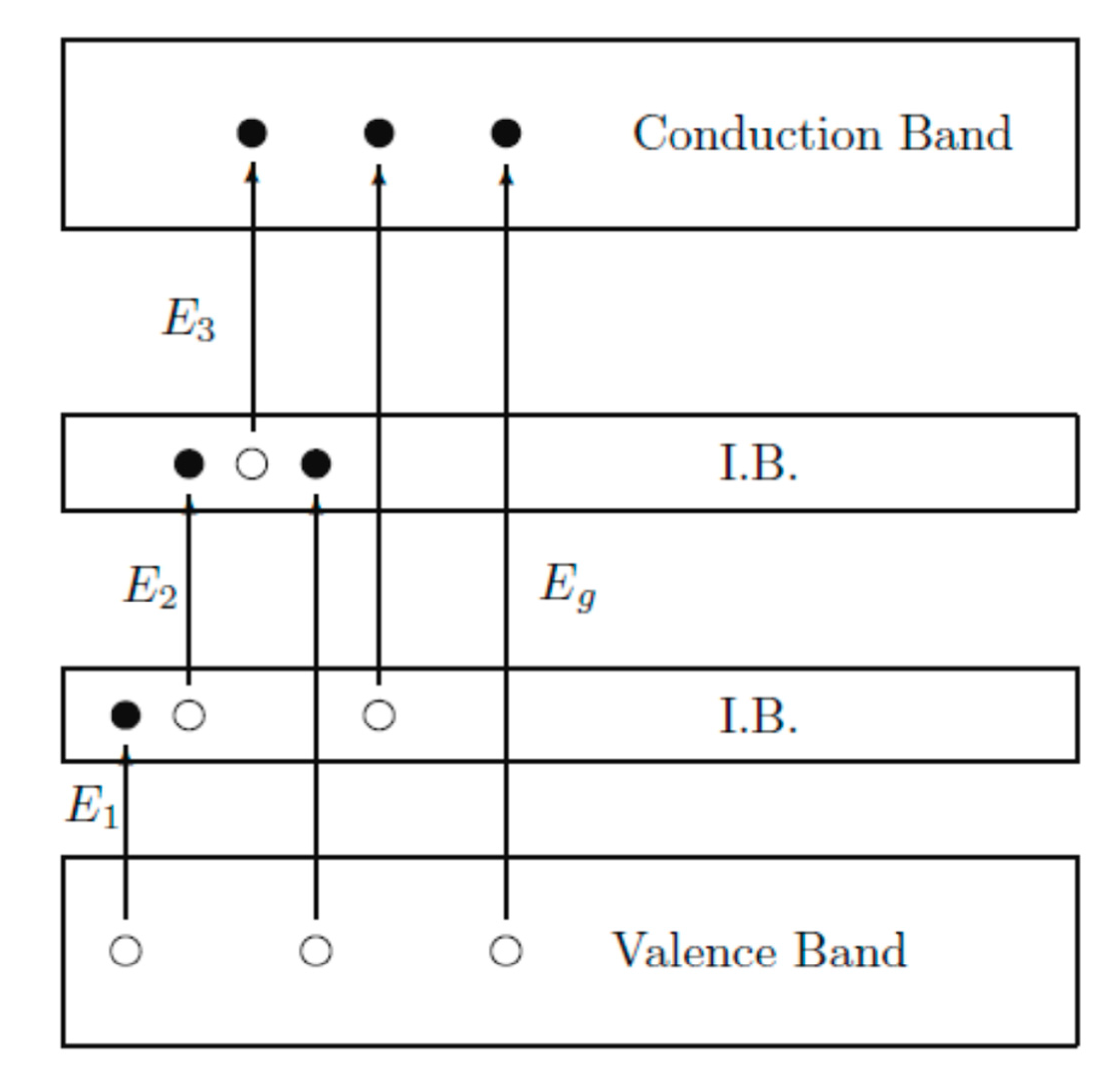
Limitations in traditional solar cells, such as a narrow absorption spectrum of photosensitive materials, leads to the degradation of absorbed photon density, current density, and open circuit potential. Those photons, which have energy larger or equal than the photosensitive material bandgap, are absorbed. For materials with IB structure, this issue is overcome since the material is a compound of two or more materials with different bandgap energies. As can be seen in Figure 11, photons with different energies E1, E2, and E3 are absorbed, corresponding to the energy gap between two VBs of the two materials, valence and CBs of the narrower bandgap material and two CBs of the two materials, respectively. These absorptions result in the enhancement of the excited electron concentration in the CB of a wider bandgap material, which is then collected and transferred to an external circuit and creates the electric current density. These IB structure materials have great potential to replace traditional photosensitive materials due to predicted PCE in QDSSCs up to 46% [150].
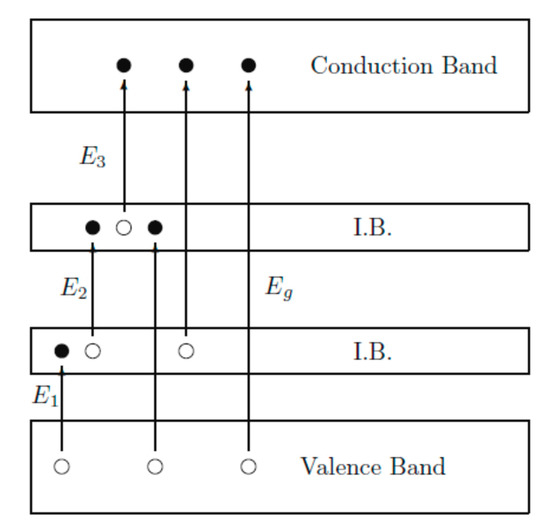
Figure 11.
Schematic diagram of energy levels of an IB structure material from Wu and co-works, 2012 [151].
- b.
- Graphene thin film with QDs for photoanode fabrication
Graphene is a two-dimensional single layer of carbon atoms, which has a large surface area and high electronic mobility of 1.5 × 104 cm2 V−1 s−1 so having prominent electrical, optical, thermal dynamics, and mechanical properties [151,152,153]. Carbon-based graphene materials have outstanding properties, especially graphene quantum dots with extremely effective electron transport properties, and other interesting phenomena due to the quantum confinement effect [154]. Therefore, graphene has become promising for science and technology revolution. Several reports on this kind of material have been observed. Dutta et al. synthesized graphene QDs and then absorbed onto the surface of ZnO fibers by chemical deposition method, resulting in a 0.8 V open circuit potential [154]. Zhong and colleagues combined graphene QDs with CdSe QDs covering the TiO2 membrane for 6% conversion efficiency [155]. Graphene QDs combined with other QDs, such as CdSe, CdS, or CdTe, is an effective method to improve PCE of QDSSCs.
Figure 12 shows a schematic diagram of a QDSSCs based on a photoanode with graphene. Core–shell structure CdSe/ZnS QDs absorbed on a graphene membrane has demonstrated the faster electron transportation from QDs to the TiO2 layer [156]. The superiority of graphene is demonstrated in another report, which studied the transient absorption spectrum of pure and CdTe QDs absorbed graphene resulting in a significant increase of relaxation time from 50 ps in pure QDs to 200 ps in absorbed graphene and hence increases the excitation electron density in the CB of QDs and is the basis for increasing the current density in QDSSCs [157].
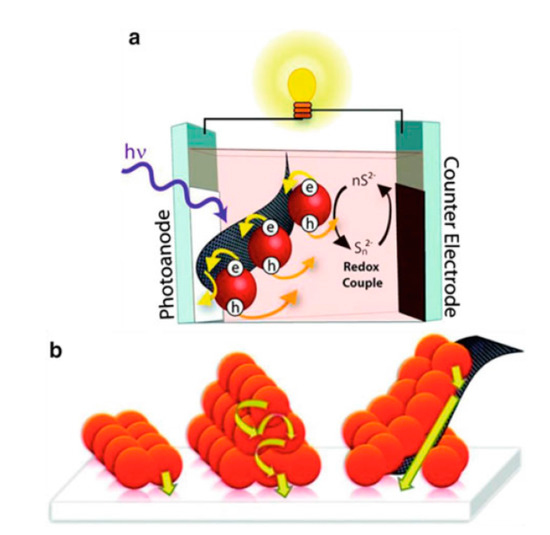
Figure 12.
(a) Structure of QDSSCs based on graphene/CdSe QDs photoanode and (b) schematic of a photoanode that has graphene/CdSe QDs absorbing on the FTO substrate.
Author Contributions
N.T.K.C.: Formal analysis; funding acquisition; investigation, writingreview & editing. P.T.N.: Formal analysis; writingreview & editing. H.T.T.: Conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; funding acquisition; investigation; methodology; writing-original draft; writingreview & editing. D.H.P.: Conceptualization; data curation; formal analysis; funding acquisition; investigation; methodology; writing-original draft; writing-review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by Thu Dau Mot University under grant number: DT.21.1-028.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yoshikawa, K.; Kawasaki, H.; Yoshida, W.; Irie, T.; Konishi, K.; Nakano, K.; Uto, T.; Adachi, D.; Kanematsu, M.; Uzu, H.; et al. Silicon heterojunction solar cell with interdigitated back contacts for a photoconversion efficiency over 26%. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Benick, J.; Feldmann, F.; Fell, A.; Hermle, M.; Glunz, S.W. n-Type Si solar cells with passivating electron contact: Identifying sources for efficiency limitations by wafer thickness and resistivity variation. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 173, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ren, S.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Li, B. Exploring window buffer layer technology to enhance CdTe solar cell performance Back contact Window layer 40 nm. Sol. Energy 2018, 164, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Hama, T.; Sakai, H.; Harashima, K. Production technology for amorphous silicon-based # exible solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 66, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T.; Handa, A.; Yagioka, T.; Matsuura, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Higashi, S. Enhanced Efficiency of Cd-Free Cu (In, Ga)(Se, S)2 Minimodule Via (Zn, Mg) O Second Buffer Layer and Alkali Metal Post-Treatment. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2017, 7, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; Noh, J.H.; Jeon, N.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Ryu, S.; Seo, J.; Seok, S.I. Highperformance photovoltaic perovskite layers fabricated through intramolecular exchange. Science 2015, 348, 1234–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolterfoht, M.; Grischek, M.; Caprioglio, P.; Wolff, C.M.; Gutierrez-Partida, E.; Peña-Camargo, F.; Rothhardt, D.; Zhang, S.; Raoufi, M.; Wolansky, J.; et al. How to Quantify the Efficiency Potential of Neat Perovskite Films: Perovskite Semiconductors with an Implied Efficiency Exceeding 28%. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozik, A.J. Quantum Dot Solar Cells. Physica E 2002, 14, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.A.; Emery, K.; Hishikawa, Y.; Warta, W. Improved optical transmission and current matching of a triple-junction solar cell utilizing sub-wavelength structures. Prog. Photovolt. 2009, 17, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graetzel, M.; Janssen, R.A.J.; Mitzi, D.B.; Sargent, E.H. Materials interface engineering for solution processed photovoltaics. Nature 2012, 488, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Dy, J.T.; Uchida, S.; Kubo, T.; Segawa, H. Wideband dye-sensitized solar cells employing a phosphine-coordinated ruthenium sensitizer. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Voznyy, O.; Zhitomirsky, D.; Sargent, E.H. Colloidal quantum dot materials and devices: A quarter-century of advances. Adv. Mater. 2015, 25, 4986–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Zhang, Q.; Uchaker, E.; Gao, R.; Qu, X.; Zhang, S.; Cao, G. ZnO/TiO2 nanocable structured photoelectrodes for CdS/CdSe quantum dot co-sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuc, D.H.; Tung, H.T. Quantum dot sensitized solar cell based on the different photoelectrodes for the enhanced performance. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 196, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, H.T.; Phuc, D.H.; Chung, N.T.K.; Thuy, N.T.N. Enhanced light absorption and charge recombination control in quantum dot sensitized solar cells using Copper and Manganese doped cadmium sulfide quantum dots. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2021, e13650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, T.H.; Vinh, L.Q.; Dat, H.T. The Dynamic Resistance of CdS/CdSe/ZnS Co-Sensitized TiO2 Solar Cells. Braz. J. Phys. 2014, 44, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuc, D.H.; Tung, H.T. The effect of thickness on the performance of CdSe: Cu 2+—quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Appl. Phys. 2018, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.L.; Lee, Y.L.; Teng, H. High-performance quantum dot-sensitized solar cells based on sensitization withCuInS2 quantum dots/CdS heterostructure. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5315–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugaya, T.; Numakami, O.; Oshima, R.; Furue, S.; Komaki, H.; Amano, T.; Matsubara, K.; Okano, Y.; Niki, S. Type II GaSb quantum ring solar cells under concentrated sunlight. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6233–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.V. Quantum Dot Solar Cells. Semiconductor Nanocrystals as Light Harvesters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 18737–18753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.V. Quantum Dot Solar Cells. The Next Big Thing in Photovoltaics. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, F.A.; Poro, A.; Rezaee, M.; Sameni, M. Enhancement in power conversion efficiency of CdS quantum dot sensitized solar cells through a decrease in light reflection. Opt. Mater. 2020, 108, 110248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, J.; Gupta, H.; Purohit, L.P. Cascade Structured ZnO/TiO2/CdS quantum dot sensitized solar cell. Solid State Sci. 2020, 102, 106176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.J.; Zhang, Q.F.; Zhang, L.L.; Gao, R.; Shen, L.F.; Zhang, S.G.; Qu, X.H.; Cao, G.Z. Architectured ZnO photoelectrode for high efficiency quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Jennings, J.R.; Koh, Z.Y.; Wang, Q. CdSe-sensitized mesoscopic TiO2 solar cells exhibiting >5% efficiency: Redundancy of CdS buffer layer. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 3172–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, A.; Nath, S.S.; Srivastava, V.M. Enhanced efficiency in swift 100 mev ni ion irradiated zns quantum dot sensitized solar cell. Chalcogenide Lett. 2020, 17, 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Marandi, M.; Abadi, S.H. Aqueous synthesis of colloidal CdSexTe1−x–CdS core–shell nanocrystals and effect of shell formation parameters on the efficiency of corresponding quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Sol. Energy 2020, 209, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, L.; Gou, Y.; Fang, J.; Feng, R.; Lei, Y.; Song, X.; Yang, Z. CdS-derived CdS1−xSex nanocrystals within TiO2 films for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells prepared through hydrothermal anion exchange reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 356, 136845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robel, I.; Kuno, M.; Kamat, P.V. Size-dependent electron injection from excited CdSe quantum dots into TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 4136–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.W.; Peng, X.G. Formation of high-quality CdS and other II–VI semiconductor nanocrystals in noncoordinating solvents: Tunable reactivity of monomers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2368–2371. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, R.; Pohl, K.; Weller, H. Sensitization of highly porous, polycrystalline TiO2 electrodes by quantum sized CdS. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1990, 174, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Kim, D.-Y.; Yoo, J.-S.; Bang, J.; Kim, S.; Park, S.-M. Anchoring cadmium chalcogenide quantum dots (QD) onto stable oxide semiconductor for QD sensitized solar cells. Bull. Kor. Chem. Soc. 2008, 28, 953–958. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-J.; Yum, J.-H.; Leventis, H.C.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Haque, S.A.; Chen, P.; Seok, S.I.; Gratzel, M.; Nazeeruddin, M.-K. CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells exceeding efficiency 1% at full sun intensity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 11600–11608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Kang, S.H.; Min, S.-K.; Sung, Y.-E.; Han, S.-H. Co-sensitization of vertically aligned TiO2 nanotubes with two different sizes of CdSe quantum dots for broad spectrum. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, K.; Coates, N.E.; Moses, D.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Dante, M.; Heeger, A.J. Efficient tandem polymer solar cells fabricated by all solution processing. Science 2007, 317, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.R.; Zhu, K.; Norman, A.G.; Ferrere, S.; Frank, A.J.; Nozik, A.J. Nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cells sensitized with InAs quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 50, 25451–25454. [Google Scholar]
- Giménez, S.; Iván, M.-S.; Lorena, M.; Nestor, G.; Teresa, L.-V.; Roberto, G.; Diguna, L.J.; Shen, Q.; Toyoda, T.; Bisquert, J. Improving the performance of colloidal quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells. Nanotechnology 2009, 29, 295204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diguna, L.J.; Shen, Q.; Kobayashi, J.; Toyoda, T. High efficiency of CdSe quantum-dot-sensitized TiO2 inverse opal solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 023116. [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana, Y.; Umekita, K.; Otsuka, Y.; Kuwabata, S. Performance improvement of CdS quantum dots sensitized TiO2 solar cells by introducing a dense TiO2 blocking layer. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Fu, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.; Zhao, H.; Sun, M.; Yang, L. Photoelectrochemical performance ofmultiple semiconductors (CdS/CdSe/ZnS) cosensitized TiO2 photoelectrodes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 2615–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Ho, Y.C.; Yang, R.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Huang, C.M. Electrode posited AgInSe2 onto TiO2 films for semiconductor- sensitized solar cell application: The influence of electrode posited time. J. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 58, 6558–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huazheng, L.; Lu, W.; Song, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, G.; Han, G. The design of Mn2+ & Co2+ co-doped CdTe quantum dot sensitized solar cells with much higher efficiency. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 35701–35708. [Google Scholar]
- Dongho, L.; Choi, W.; Yang, J. Investigation of the Trap-Induced Power Conversion Limit for CdS/CdSe Cascade Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells Fabricated by Using the Successive Ionic Layer Adsorption and Reaction Process. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2020, 76, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, S.; Dehghani, M.; Parand, P.; Najafi, M.N.; Parvazian, E. Photovoltaic performance and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis of CdS/CdSe-sensitized solar cell based on surfactant-modified ZnS treatment. Appl. Phys. A 2020, 126, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Huashang, R.; Zhou, M.; Pan, Z.; Zhong, X. Quantum dot materials engineering boosting the quantum dot sensitized solar cell efficiency over 13%. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 10233–10241. [Google Scholar]
- Yunlong, D.; Lu, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ma, F.; Peng, S. Enhanced performance of CdS/CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells by long-persistence phosphors structural layer. Sci. China Mater. 2020, 63, 516–523. [Google Scholar]
- Nideep, T.K.; Ramya, M.; Kailasnath, M. An investigation on the photovoltaic performance of quantum dot solar cells sensitized by CdTe, CdSe and CdS having comparable size. Superlattices Microstruct. 2020, 141, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elibol, E. Quantum dot sensitized solar cell design with surface passivized CdSeTe QDs. Sol. Energy 2020, 206, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrapani, V.; Baker, D.; Kamat, P.V. Understanding the Role of the Sulfide Redox Couple (S2−/Sn2−) in Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 9607–9615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, A.; Nath, S.S. Mn-doped CdS quantum dots as sensitizers in solar cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2020, 255, 114532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadim, F.L. Impedance Spectroscopy Applications to Electrochemical and Dielectric Phenomena; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Archana, T.; Vijayakumar, K.; Subashini, G.; Grace, A.N.; Arivanandhan, M.; Jayavel, R. Facile synthesis of CdS Quantum dots for QDSSC with high photo current density. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulac, R.; Archer, P.I.; Ochsenbein, S.T.; Gamelin, D.R. Mn2+-Doped CdSe Quantum Dots: New Inorganic Materials for Spin-Electronics and Spin-Photonics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 3873–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, N.S.; Sarma, D.D.; Kadam, R.M.; Pradhan, N. Doping transition metal (Mn or Cu) ions in semiconductor nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 2863–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria, G.P.; Sima, C.; Marzari, G.; Boix, P.P.; Giménez, S.; Shen, Q.; Dittrich, T.; Mora-Seró, I. High performance PbS Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells exceeding 4% efficiency: The role of metal precursors in the electron injection and charge separation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 13835–13843. [Google Scholar]
- Santra, P.K.; Kamat, P.V. Mn-doped quantum dot sensitized solar cells: A strategy to boost efficiency over 5%. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2508–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Pan, L.; Xu, T.; Sun, Z. CdS/CdSe-Cosensitized TiO2 Photoanode for Quantum-Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells by a Microwave-Assisted Chemical Bath Deposition Method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3146–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Im, S.H.; Chang, J.A.; Lee, J.H.; Seok, S.I. CdSe-sensitized inorganic-organic heterojunction solar cells: The effect of molecular dipole interface modification and surface passivation. Org. Electron. 2012, 13, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryam, O.; Dehghani, H. Improving the photovoltaic performance of CdSe0.2S0.8 alloyed quantum dot sensitized solar cells using CdMnSe outer quantum dot. Sol. Energy 2020, 199, 901–910. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Z.; Zhao, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhong, X. Near infrared absorption of CdSexTe1-x alloyed quantum dot sensitized solar cells with more than 6% efficiency and high stability. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5215–5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radich, J.G.; Peeples, N.R.; Santra, P.K.; Kamat, P.V. Charge transfer mediation through CuxS. The hole story of CdSe in polysulfide. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 16463–16471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Shen, Q.; Mora-Sero, I.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z.X.; Zhao, K.; Kuga, Y.; Zhong, X.H.; Bisquert, J. Band engineering in core/shell ZnTe/CdSe for photovoltage and efficiency enhancement in exciplex quantum dot sensitized solar cells. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 908–915. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Kamat, P.V. Photoelectrochemical behaviour of thin CdSe and coupled TiO2/CdSe semiconductor films. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 10769–10773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wu, J.; Lu, X.; Shen, Y.; Lu, Z. Sensitization of nanocrystalline TiO2 electrode with quantum sized CdSe and ZnTcPc molecules. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1997, 270, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, L.M.; Riley, D.J.; Tull, E.Z.; Wijayantha, K.G.U. Photosensitization of nanocrystalline TiO2 by self-assembled layers of CdS quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2002, 10, 1030–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kwak, W.-C.; Min, S.K.; Lee, J.-C.; Chae, W.-S.; Sung, Y.-M.; Han, S.-H. Spectral broadening in quantum dots-sensitized photoelectrochemical solar cells based on CdSe and Mg-doped CdSe nanocrystals. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1699–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Kongkanand, A.; Tvrdy, K.; Takechi, K.; Kuno, M.; Kamat, P.V. Quantum dot solar cells. Tuning photoresponse through size and shape control of CdSe-TiO2 architecture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 4007–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Luke, T.; Wolcott, A.; Xu, L.-P.; Chen, S.; Wen, Z.; Li, J.; Rosa, E.D.L.; Zhang, J.Z. Nitrogen-doped and CdSe quantum-dot-sensitized nanocrystalline TiO2 films for solar energy conversion applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Sero, I.; Gimenez, S.; Moehl, T.; Fabregat-Santiago, F.; Lana-Villareal, T.; Gomez, R.; Bisquert, J. Factors determining the photovoltaic performance of a CdSe quantum dot sensitized solar cell: The role of the linker molecule and of the counter electrode. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 424007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.-L. Assembly of CdS quantum dots onto mesoscopic TiO2 films for quantum dot-sensitized solar cell application. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 045602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, D.W.; Song, J.L.; Sun, X.W.; Deng, W.Q.; Liu, X.W.; Lei, W. Directly assembled CdSe quantum dots on TiO2 in aqueous solution by adjusting pH value for quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 2265–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.-Y.; Lei, B.-X.; Kuang, D.-B.; Su, C.-Y. High performance and reduced charge recombination of CdSe/CdS quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12058–12063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.W.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, W.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Choi, C.-J.; Ahn., K.-S. Enhanced electron lifetime in CdS quantum dot-sensitized solar cells with nanoporous-layer-covered TiO2 nanotube arrays. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 054301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, W.; Wu, S. CdS and PbS quantum dots co sensitized TiO2 nanorod arrays with improved performance for solar cells. Appl. Mater. Sci. Semicond Process 2013, 16, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Li, D.; Luo, Y.; Meng, Q. Aqueous colloidal CuInS2 for quantum dot sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerathangam, K.; Pandian, M.S.; Ramasamy, P. Photovoltaic performance of Pb-doped CdS quantum dots for solar cell application. Mater. Lett. 2018, 220, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaos, B.; Vassilios, D.; Kyriakos, B.; Panagiotis, L. Quantum dot sensitized solar cells based on an optimized combination of ZnS, CdS and CdSe with CoS and CuS counter electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 91, 246–252. [Google Scholar]
- Hodes, G.; Manassen, J.; Cahen, D. Electrocatalytic electrodes for the polysulfide redox system. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1980, 127, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora-Seró, I.; Bisquert, J. Breakthroughs in the development of semiconductor-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 3046–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthamilselvi, V.; Saravanakumar, K.; Begum, N.J.; Anandhi, R.; Ravichandran, A.T.; Sakthivel, B. Photovoltaic properties of nanocrystalline CdS films deposited by SILAR and CBD techniques—A comparative study. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2012, 23, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliev, R.B.; Dorofeev, S.G.; Dirin, D.N.; Belov, D.A.; Kuznetsova, T.A. Synthesis and optical properties of PbSe and CdSe colloidal quantum dots capped with oleic acid. Mendeleev Commun. 2004, 14, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Bai, Y.Q.; Guan, X.N.; Chen, J.W.; Zeng, J.H. Phosphating passivation layer for quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Thin Solid Films. 2021, 138678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, N.; Lana-Villarreal, T.; Mora-Sero, I.; Bisquert, J.; Gόmez, R. CdSe quantum dot-sensitized TiO2 electrodes: Effect of quantum dot coverage and mode of attachment. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 4208–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- István, R.; Subramanian, V.; Kuno, M.; Kamat, P.V. Quantum dot solar cells. Harvesting light energy with CdSe nanocrystals molecularly linked to mesoscopic TiO2 films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.M.; Huang, C.H.; Zhai, J.; Wang, Z.S.; Jiang, L. High photostability and quantum yield of nanoporous TiO2 thin film electrodes Co-sensitized with capped sulfides. J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishanav, S.K.; Jyoti, K.; Nagwanshi, R.; Karbhal, I.; Dewangan, L.; Ghosh, K.K.; Satnami, M.L. Interaction of Folic Acid with Mn2+ Doped CdTe/ZnS Quantum Dots: In Situ Detection of Folic Acid. J. Fluoresc. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Kobayashi, J.; Diguna, L.J.; Toyoda, T. Effect of ZnS coating on the photovoltaic properties of CdSe quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 084304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachan, Z.; Hod, I.; Shalom, M.; Grinis, L.; Zaban, A. The importance of the TiO2/quantum dots interface in the recombination processes of quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 3841–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Miyauchi, M.; Uemura, Y.; Cui, Y.; Hara, K.; Zhao, Z.; Sunahara, K.; Furube, A. Enhancing the performance of quantum dots sensitized solar cell by SiO2 surface coating. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 233107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, T.P.; Trejo, O.; Roelofs, K.E.; Xu, J.; Prinz, F.B.; Bent, S.F. Efficiency enhancement of solid-state PbS quantum dot-sensitized solar cells with Al2O3 barrier layer. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 7566–7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grätzel, M. Mesoscopic Solar Cells for Electricity and Hydrogen Production from Sunlight. Chem. Lett. 2005, 34, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, X.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Li, D.; Luo, Y.; Shen, Q.; Toyoda, T.; Meng, Q. Highly efficient CdS/CdSe-sensitized solar cells controlled by the structural properties of compact porous TiO2 photoelectrodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4659–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Pan, Z.; Mora-Seró, I.; Cánovas, E.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Gong, X.; Wang, J.; Bonn, M.; Bisquert, J.; et al. Boosting Power Conversion Efficiencies of Quantum-Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells Beyond 8% by Recombination Control. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5602–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simi, N.J.; Bernadsha, S.B.; Thomas, A.; Ison, V.V. Quantum Dot Sensitized Solar Cells using Type-II CdSe-Cu2Se Core-Shell QDs. Results Opt. 2021, 100088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Wang, J.; Shen, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhong, X. Surface engineering of PbS quantum dot sensitized solar cells with a conversion efficiency exceeding 7%. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 7214–7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mora-Seró, I.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhong, X.; Bisquert, J. Core/Shell Colloidal Quantum Dot Exciplex States for the Development of Highly Efficient Quantum-Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15913–15922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, B.D.; Lin, C.; Shawon, S.M.Z.; Soliz-Martinez, A.J.; Huq, H.; Uddin, M.J. A photoanode with hierarchical nanoforest TiO2 structure and silver plasmonic nanoparticles for flexible dye sensitized solar cell. Sci. Rep. 2011, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Thanh, T.H.; Quang, V.L.; Thanh, D.H. Determination of the dynamic resistance of the quantum dots solar cells by one I–V curve and electrochemical impedance spectra. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 143, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, T.N.; Phuong, H.N.; Tung, H.T.; Phat, N.T.; Dat, H.T.; Vinh, L.Q. The enhanced current density of the quantum dots solar cells based on CdSe: Mn2+ crystalline. Opt. Mater. 2018, 84, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Ha, T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Ho, N.P.; Huynh, T.D.; Lam, Q.V. Effect of Cu2+ ions doped on the photovoltaic features of CdSe quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 282, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, H.T.; Thao, N.T.; Vinh, L.Q. The Reduced Recombination and the Enhanced Lifetime of Excited Electron in QDSSCs Based on Different ZnS and SiO2 Passivation. Int. J. Photoenergy 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.W.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, R.Q.; Pan, Z.X.; Gong, X.Q.; Zhong, X.H. Effects of metal oxyhydroxide coatings on photoanode in quantum dot sensitized solar cells. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Tian, H.; Yuan, C.; Fu, Y.; Qin, H.; Sun, L.; Ågren, H. Solar cells sensitized with type-II ZnSe-CdS core/shell colloidal quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1536–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, K.E.; Brennan, T.P.; Dominguez, J.C.; Bailie, C.D.; Margulis, G.Y.; Hoke, E.T.; McGehee, M.D.; Bent, S.F. Effect of Al2O3 Recombination Barrier Layers Deposited by Atomic Layer Deposition in Solid-State CdS Quantum Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 5584–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Mora-Sero, I.; Bisquert, J.; Zhong, X. Amorphous TiO2 buffer layer boosts efficiency of quantum dot sensitized solar cells to over 9%. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 8398–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-H.M.; Brown, P.R.; Bulović, V.; Bawendi, M.G. Improved performance and stability in quantum dot solar cells through band alignment engineering. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Stavrinadis, A.; Lasanta, T.; So, D.; Konstantatos, G. The role of surface passivation for efficient and photostable PbS quantum dot solar cells. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, R.; Oh, S.-H.; Jang, S.-Y. High-Efficiency Colloidal Quantum Dot Photovoltaic Devices Using Chemically Modified Heterojunctions. ACS Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-H.; De Arquer, F.P.G.; Yoon, Y.J.; Lan, X.; Liu, M.; Voznyy, O.; Jagadamma, L.K.; Abbas, A.S.; Yang, Z.; Fan, F.; et al. Correction to High-Efficiency Colloidal Quantum Dot Photovoltaics via Robust Self-Assembled Monolayers. Nano Lett. 2015, 16, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Franceschetti, A.; Lusk, M.T. Size Dependence of the Multiple Exciton Generation Rate in CdSe Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 2503–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, T.H.; Lam, Q.V.; Nguyen, T.H.; Huynh, T.D. Performance of CdS/CdSe/ZnS quantum dot-sensitized TiO2 mesopores for solar cells. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2013, 11, 72501–72504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, P.; Min, X. Bio-templated CdSe quantum dots green synthesis in the functional protein, lysozyme, and biological activity investigation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, R.; Gómez, H.; Schrebler, R.; Cury, P.; Orellana, M.; Grez, P.; Leinen, D.; Ramos-Barrado, J.R.; Del Río, R. Electrosynthesis and Electrochemical Characterization of a Thin Phase of CuxS (x→2) on ITO Electrode. Langmuir 2002, 18, 8647–8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grätzel, M. Photoelectrochemical cells. Nature 2001, 414, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grätzel, M. Dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C: Photochem. Rev. 2003, 4, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, H.T.; Van Thuan, D.; Kiat, J.H.; Phuc, D.H. Ag+ ion doped on the CdSe quantum dots for quantum-dot-sensitized solar cells’ application. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Son, D.Y.; Ahn, T.K.; Shin, H.W.; Kim, I.Y.; Hwang, S.J.; Ko, M.J.; Sul, S.; Han, H.; Park, N.G. Quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell with unprecedentedly high photocurrent. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.-Q.; Cao, R.-J.; Xi, Y.-X.; Gao, M.; Wang, M.-D.; Kima, D.-H. CdSe quantum dots as cosensitizers of organic dyes in solar cells for red-shifted light harvesting. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid. Commun. 2009, 10, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-L.; Huang, B.-M.; Chien, H.-T. Highly efficient CdSe-sensitized TiO2 photoelectrode for quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell applications. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6903–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezhkam, M.; Zakery, A.; Keshavarz, A. Intersubband, interband transitions, and optical properties of two vertically coupled hemispherical quantum dots with wetting layers. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2016, 14, 121904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jung, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, C.J.; Ahn, K.S. ZnS over layer on in situ chemical bath deposited CdS quantum dot assembled TiO2 films for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2012, 12, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewdu, T.; Clifford, J.N.; Hernández, J.P.; Palomares, E. Photo-induced charge transfer dynamics in efficient TiO2/CdS/CdSe sensitized solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.T.; Chi, C.H.; Vy, N.T.; Thoa, N.T.P.; Huynh, T.D.; Lam, Q.V. Improving the performance of QDSSCs based on TiO2/CdS (Silar)/CdSe(Colloid)/Zns(Silar) photoanodes. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 1774–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodes, G.; Manassen, J.; Cahen, D. Photo-electrochemical energy conversion: Electrocatalytic sulphur electrodes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1977, 7, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, M.A.; Abbas, M.A.; Naeem, H.M.; Ali, I.; Jang, E.; Bang, J.H.; Park, T.J. Ultrathin TiO2-coated SiO2 nanoparticles as light scattering centers for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Res. Bull. 2020, 127, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.R.; Du, J.H.; Guo, S.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Matsumoto, Y. CoS thin films prepared with modified chemical bath deposition. Thin Solid Films 2002, 415, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, M.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Hua, Q.; Dong, L.; Pan, C. Flexible quantum dot-sensitized solar cells employing CoS nanorod arrays/graphite paper as effective counter electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 13661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-Y.; Teng, C.Y.; Li, T.L.; Lee, Y.L.; Teng, H. Photoactive p-type PbS as a counter electrode for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, H.T.; Thanh, D.H.; Lam, V.Q. The CdS/CdSe/ZnS Photoanode Co-sensitized Solar Cells Based on Pt, CuS, Cu2S, and PbS Counter Electrodes. Adv. Optoelectron. 2014, 2014, 397681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-S.; Feng, X.L.; Müllen, K. Graphene-metal oxide hybrids for lithium ion batteries and electrochemical capacitors. In Nanocarbon-Inorganic Hybrids; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 319–340. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.D.; Dong, F.; Xiong, T.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis of BiOBr–graphene and BiOBr–graphene oxide nanocomposites with enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 9003–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.Y.; Jin, J.; Yusoh, K.; Rafiq, R.; Song, M. High performance polyurethane/functionalized graphene nanocomposites with improved mechanical and thermal properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2012, 72, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachan, Z.; Shalom, M.; Hod, I.; Ruhle, S.; Tirosh, S.; Zaban, A. PbS as a highly catalytic counter electrode for polysulfide-based quantum dot solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 6162–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Pan, H.; Lou, Y.; Qiu, X.; Zhu, J.; Burda, C. Plasmonic Cu2−xS Nanocrystals: Optical and Structural Properties of Copper-Deficient Copper(I) Sulfides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4253–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yoon, S.W.; Kim, E.J.; Park, J. In situ growth of coppersulfide nanocrystals on multi walled carbon Nano tubes and their application as novel solar cell and amperometric glucose sensor materials. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.L.; Lo, Y.S. Highly efficient quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell based on co-sensitization of CdS/CdSe. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Xu, S.J.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, Z.X.; Luo, Y.P. Modulation doping of absorbent cotton derived carbon dots for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 26133–26145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Peng, W.X.; Yang, C.; Zhong, X.H. Quantum dot sensitized solar cells with efficiency up to 8.7% based on heavily copper-deficient copper selenide counter electrode. Nano Energy 2016, 23, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yu, B.B.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.H.; Sun, J.K.; Zhong, X.H.; Hu, J.-S.; Song, W.G.; Wan, L.-J. Boosting the open circuit voltage and fill factor of QDSSCs using hierarchically assembled ITO@ Cu2S nanowire array counter electrodes. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 3088–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, M.S.; Park, K.; Cabán-Acevedo, M.; Santra, P.K.; Jin, S. Earth-abundant cobalt pyrite (CoS2) thin film on glass as a robust, high-performance counter electrode for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radich, J.G.; Dwyer, R.; Kamat, P.V. Cu2S reduced graphene oxide composite for high-efficiency quantum dot solar cells. Overcoming the redox limitations of S2–/Sn2–at the counter electrode. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zheng, H.; Wu, M. Designing Metal-Sulfide-Sphere Counter-Electrode Catalysts for ZnO-Nanorod-Array-Based Quantum-Dot-Sensitized Solar Cells. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 32, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Sun, H.; Huang, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, D.; Meng, Q. Composite counter electrode based on nanoparticulate PbS and carbon black: Towards quantum dot-sensitized solar cells with both high efficiency and stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 6162–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Q.; He, B.; Yu, L. Recent advances in critical materials for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17497–17510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Ayuzawa, Y.; Katayama, K.; Sawada, T.; Toyoda, T. Separation of ultrafast photoexcited electron and hole dynamics in CdSe quantum dots adsorbed onto nanostructured TiO2 films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 263113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, C.; Belaidi, A.; Ogacho, A.; Dittrich, T. Inorganic solid state solar cell with ultra-thin nanocomposite absorber based on nanoporous TiO2 and In2S3. Energy Environ. Sci. 2009, 2, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hwang, I.; Yong, K. Highly durable and efficient quantum dot-sensitized solar cells based on oligomer gel electrolytes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 11245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Meng, X.; Zhao, K.; Li, Y.; Zhong, X. Performance enhancement of quantum dot sensitized solar cells by adding electrolyte additives. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17091–17097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.Y.; Lee, C.P.; Vittal, R.; Ho, K.C. Efficient quantum dot-sensitized solar cell with polystyrene-modified TiO2 photoanode and with guanidine thiocyanate in its polysulfide electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 6595–6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, S.; Gilmore, R. Quantum dot solar cell: Materials that produce two intermediate bands. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2010, 2, 13111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-S.; Zhou, G.; Yin, L.-C.; Ren, W.; Li, F.; Cheng, H.-M. Graphene/metal oxide composite electrode materials for energy storage. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chang, X.; Gondal, M.A.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Ji, G. Synthesis and photocatalytic activity of graphene/BiOBr composites under visible light. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 7826–7832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Cho, J.W. Functionalized graphene nanoplatelets for enhanced mechanical and thermal properties of polyurethane nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 266, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, M.; Sarkar, S.; Ghosh, T.; Basak, D. ZnO/Graphene Quantum Dot Solid-State Solar Cell. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 20127–20131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Pan, D.; Wang, L.; Zhong, X. Graphene quantum dots assisted photovoltage and efficiency enhancement in CdSe quantum dot sensitized solar cells. J. Energy Chem. 2015, 24, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Berciaud, S.; Nuckolls, C.; Heinz, T.F.; Brus, L.E. Energy Transfer from Individual Semiconductor Nanocrystals to Graphene. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2964–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaniyankandy, S.; Rawalekar, S.; Ghosh, H.N. Ultrafast Charge Transfer Dynamics in Photoexcited CdTe Quantum Dot Decorated on Graphene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 16271–16275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).