Response Surface Optimisation of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) on Borosilicate Glass and Stainless Steel (SS316) to Increase Hydrophobicity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Experimental Design of Surface Coating via the Central Composite Rotatable Design (CCRD)
2.3. Dairy Product Preparation
2.4. Water Contact Angle Measurement
2.5. Surface Tension of Milk Products
2.6. The Work of Adhesion for Milk Products
2.7. Morphological Surface Analysis: Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
2.8. Functional Groups Profiling: Fourier Transform Infrared-Attenuated Total Reflectance (FTIR-ATR)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
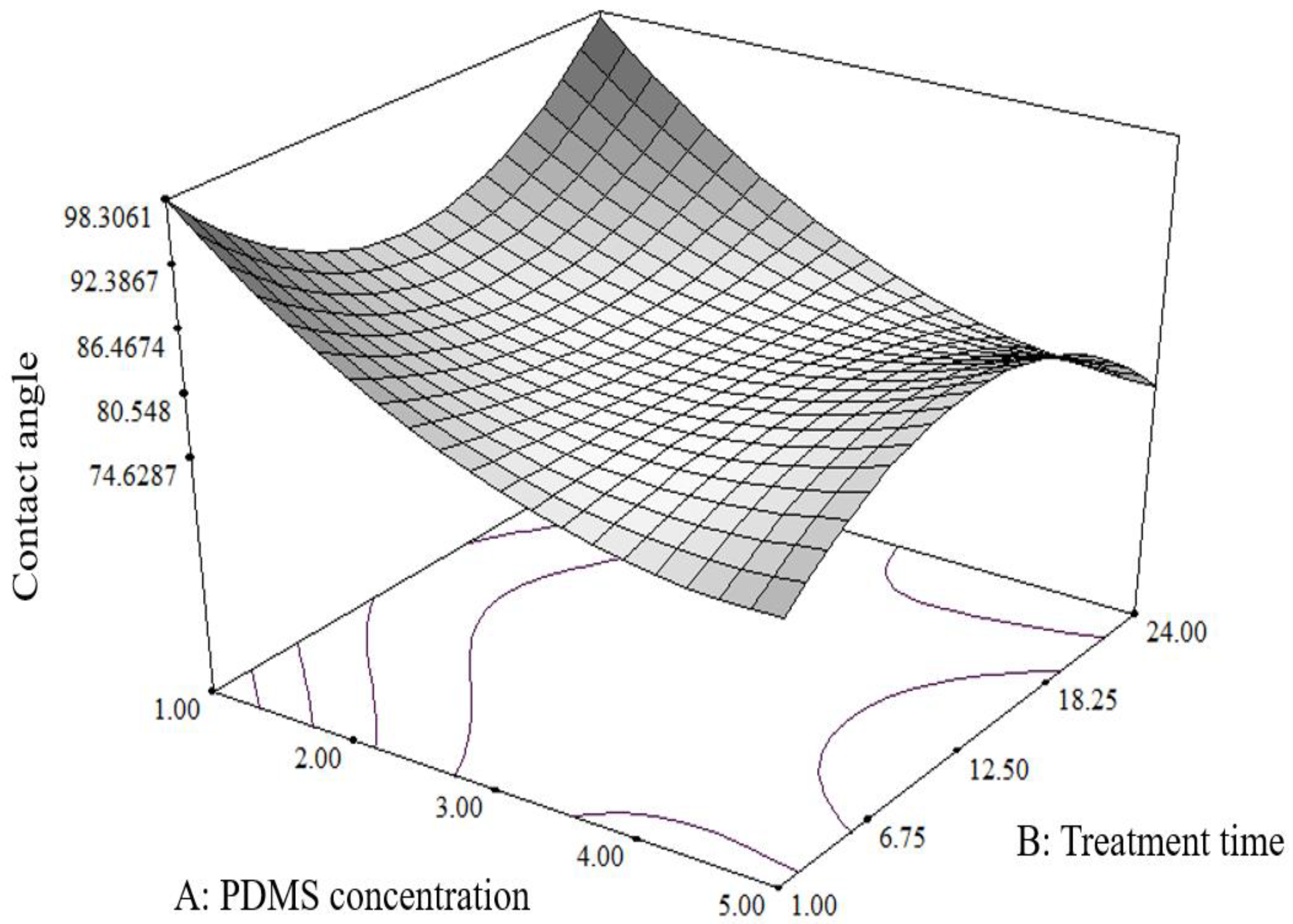
3.1. Optimisation of PDMS Treatment on Stainless Steel and Borosilicate Glass
3.2. Determination of the Model Validity
3.3. Surface Morphology of Borosilicate Glass and Stainless Steel Substrates
3.4. Determination of Functional Groups on the Surface of the Borosilicate Glass and Stainless Steel Substrates
3.5. Differences of Contact Angle and Milk Surface Tension
3.6. Differences in Adhesion Work
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, K.; Goddard, J.M. Influence of fluid milk product composition on fouling and cleaning of Ni-PTFE modified stainless steel heat exchanger surfaces. J. Food Eng. 2015, 158, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Kuffel, E. Formation of hydrophobic coating on glass surface using atmospheric pressure non-thermal plasma in ambient air. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2004, 37, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuck, P.; Méjean, S.; Dolivet, A.; Jeantet, R. Thermohygrometric sensor: A tool for optimizing the spray drying process. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2005, 6, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, B.; Howes, T. Relating the Stickiness Property of Foods Undergoing Drying and Dried Products to their Surface Energetics. Dry. Technol. 2005, 23, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.W.; Daud, W.R.W.; Tasirin, S.M.; Talib, M.Z.M. Controlling food powder deposition in spray dryers: Wall surface energy manipulation as an alternative. J. Food Eng. 2009, 94, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Fei, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q. Preparation of a durable superhydrophobic membrane by electrospinning poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) mixed with epoxy—Siloxane modified SiO2 nanoparticles: A possible route to superhydrophobic surfaces with low water sliding angle and high water contact angle. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 359, 380–388. [Google Scholar]
- Arkles, B. Hydrophobicity, Hydrophilicity and Silane Surface Modification; Gelest, Inc.: Morrisville, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsoulis, D.E.; Schmidt, R.G.; Zank, G.A. Siloxanes and silicones. In Advances in Silicone Technologies 2000–2015; Lee, V.Y., Ed.; Academic Press: Midland, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 301–322. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Liu, F.; Du, F. Synthesis and properties of a green and self-cleaning hard protective coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 94, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Xie, A.; Shen, Y.; Duan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. A simple method for preparation of transparent hydrophobic silica-based coatings on different substrates. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Processing 2012, 106, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlan, N.; Mohd Zamri, N.W.; Maskat, M.Y.; Zubairi, S.I. Effects of Chemical Surface Coating (Rain-ZTM) on the Powder Yield of Spray-Drying: A Preliminary Approach. Acta Hortic. 2017, 1152, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, Z.S.; Hasan, N.S.; Zubairi, S.I. Response Surface Optimization of Rotenone Using Natural Alcohol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent as Additive in the Extraction Medium Cocktail. J. Chem. 2017, 9434168, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramlan, N.; Mohd Zamri, N.W.; Maskat, M.Y.; Aizad, S.; Zubairi, S.I. Effect of Plasma Treatment (He/CH4) on the Glass Surface during Drying to Reduce Powder Flux Adhesion. Sains Malays. 2018, 47, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshani, S.; Wan Daud, W.R.; Meng Wai Woo, M.W.; Nourouzi, M.M.; Meor Talib, M.Z.; Chuah, A.L.; Russly, A.R. Reducing the deposition of fat and protein covered particles with low energy surfaces. J. Food Eng. 2013, 116, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, A.M. The effect of teflon liquid sprayed silicate glass coating on improving its hydrophobicity. Pros. Simp. Nas. Polim. VI 2006, 98–104. Available online: https://digilib.batan.go.id/ppin/katalog/file/1410-8720-2006-1-098.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- El Dessouky, W.I.; Abbas, R.; Sadik, W.A.; El Demerdash, A.G.M.; Hefnawy, A. Improved adhesion of superhydrophobic layer on metal surfaces via one step spraying method. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubairi, S.I.; Bismarck, A.; Mantalaris, A. The Effect of Surface Heterogeneity on Wettability of Porous Three Dimensional (3-D) Scaffolds of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyric Acid) (PHB) and Poly(3-Hydroxybutyric-co-3-Hydroxyvaleric Acid) (PHBV). J. Teknol. 2015, 75, 1, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zubairi, S.I.; Ishak, N.; Sani, N.A.; Kassim, Z.; Nurzahim, Z. Yogurt Drink Spoilage Profiles: Characterization of Physico-Chemical Properties and Coliform Potability Analysis. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavana, H.; Neumann, A.W. Recent progress in the determination of solid surface tensions from contact angles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 132, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubairi, S.I.; Mantalaris, A.; Bismarck, A. Pore Interconnectivity Analysis of Porous Three Dimensional Scaffolds of Poly (3-Hydroxybutyric Acid) (PHB) and Poly(3-Hydroxybutyric-co-3-Hydroxyvaleric Acid) (PHBV) Through Non-Invasive Color Staining Method. Sains Malays. 2015, 44, 1351–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubairi, S.I.; Ab Kadir, I.A.; Nurzahim, Z. Evaluation of poly(L-lactic acid) (PLLA) rapid indicator film on deterioration degree of Refined, Bleached and Deodorised Malaysian Tenera Palm Olein oil (RBDPO) during long-term repetitive deep-fat frying. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñeiro, G.; Perelman, S.; Guerschman, J.P.; Paruelo, J.M. How to evaluate models: Observed vs. predicted or predicted vs. observed? Ecol. Model. 2008, 216, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogihara, H.; Katayama, T.; Saji, T. One-step electrophoretic deposition for the preparation of superhydrophobic silica particle/trimethylsiloxysilicate composite coatings. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 362, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, H.; Xiao, B.; Yan, L.; Jiang, B. A simple route to prepare crack-free thick antireflective silica coatings with improved antireflective stability. Mater. Lett. 2012, 69, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkles, B. Silane Coupling Agents: Connecting across Boundaries; Gelest, Inc.: Morrisville, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bodas, D.; Khan-Malek, C. Hydrophilization and hydrophobic recovery of PDMS by oxygen plasma and chemical treatment-an SEM investigation. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashokkumar, S.; Adler-Nissen, J.; Moller, P. Factors affecting the wettability of different surface materials with vegetable oil at high temperatures and its relation to cleanability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 263, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, J.D.; Sarkar, D.K.; Perron, J.; Audibert-Hayet, A.; Melot, D. Nano-micro structured superhydrophobic zinc coating on steel for prevention of corrosion and ice adhesion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 447, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenojar, J.; Martínez, M.A.; Encinas, N.; Velasco, F. Modification of glass surfaces adhesion properties by atmospheric pressure plasma torch. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L. The Adhesion of Poly(Dimethyl Siloxane) to Silica Substrates. Master’s Thesis, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mahadik, S.A.; Kavale, M.S.; Mukherjee, S.K.; Rao, A.V. Transparent superhydrophobic silica coatings on glass by sol-gel method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guermeur, C.; Lambard, J.; Gerard, J.-F.; Sanchez, C. Hybrid polydimethylsiloxane-zirconium oxo nanocomposites. Part 1 Characterization of the matrix and the siloxane-zirconium oxo interface. J. Mater. Chem. 1999, 9, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Zerafat, M.; Shokri Doodeji, M.; Sabbaghi, S. Investigation of dip-coating parameters effect on the performance of alumina-polydimethylsiloxane nanofiltration membranes for desalination. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2017, 2, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.; Li, H.; Lai, X.; Zhang, L.; Liang, T.; Feng, Y.; Zeng, X. Polydimethylsiloxane-based surfaces on steel substrate: Fabrication, reversibly extreme wettability and oil–water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 3131–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.M.; Jones, J.R.; Paterson, A.H.J.; Pearce, D.L. Milks and Milk Concentrates: Surface Tension Measurement. Int. J. Food Eng. 2005, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, C.M.S.; Andre, P.S.; Ferreira, R.A.S. Simple measurement of surface free energy using a web cam. Revista Brasileira de Ensino de Física 2012, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernardes, P.; Araújo, E.; Pires, A.C.; José, F.Q.F.; Lelis, C.; de Andrade, N.J. Work of adhesion of dairy products on stainless steel surface. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, B.; Howes, T.; Bhandari, B.R.; Truong, V. Stickiness in foods: A review of mechanisms and test methods. Int. J. Food Prop. 2001, 4, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosmaninho, R.; Rizzo, G.; Müller-Steinhagen, H.; Melo, L.F. Deposition from a milk mineral solution on novel heat transfer surfaces under turbulent flow conditions. J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, J.A.S.; Rosario, L.M.D.; Lee, H.V.; Ramos, H.J.; Tumlos, R.B. Hydrophobic coating on glass surfaces via application of silicone oil and activated using a microwave atmospheric plasma jet. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 259, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Run | X1 (x1) (%, w/v) | X2 (x2) (h) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.00 (1.000) | 24.00 (1.000) |
| 2 | 1.00 (−1.000) | 1.00 (−1.000) |
| 3 * | 3.00 (0.000) | 12.50 (0.000) |
| 4 * | 3.00 (0.000) | 12.50 (0.000) |
| 5 * | 3.00 (0.000) | 12.50 (0.000) |
| 6 | 3.00 (0.000) | −3.76 (−1.414) |
| 7 | 3.00 (0.000) | 28.76 (1.414) |
| 8 | 0.17 (−1.414) | 12.50 (0.000) |
| 9 | 1.00 (−1.000) | 24.00 (1.000) |
| 10 | 5.00 (1.000) | 1.00 (−1.000) |
| 11 * | 3.00 (0.000) | 12.50 (0.000) |
| 12 * | 3.00 (0.000) | 12.50 (0.000) |
| 13 | 5.83 (1.414) | 12.50 (0.000) |
| Composition | Whole Milk (%) |
|---|---|
| Fat | 26 |
| Protein | 22.8 |
| Lactose | 42.4 |
| Moisture | 4 |
| Run | X1 | X2 | Contact Angle (°) (Y) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borosilicate Glass | Stainless Steel | |||
| 1 | 5.00 | 24.00 | 78.48 | 76.72 |
| 2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 90.75 | 97.82 |
| 3 * | 3.00 | 12.50 | 78.47 | 77.51 |
| 4 * | 3.00 | 12.50 | 76.74 | 80.53 |
| 5 * | 3.00 | 12.50 | 80.37 | 81.23 |
| 6 | 3.00 | −3.76 | 82.5 | 83.54 |
| 7 | 3.00 | 28.76 | 77.02 | 78.16 |
| 8 | 0.17 | 12.50 | 87.27 | 90.93 |
| 9 | 1.00 | 24.00 | 96.69 | 99.93 |
| 10 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 81.14 | 76.13 |
| 11 * | 3.00 | 12.50 | 77.56 | 80.93 |
| 12 * | 3.00 | 12.50 | 77.23 | 78.92 |
| 13 | 5.83 | 12.50 | 88.83 | 91.55 |
| Substrate | Response | Model Equation | Model Significance | Lack of Fit | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borosilicate glass | Contact angle | Actual equation 1.0/Y = 0.011374 − 1.22587 × 10−3X1 + 9.25626 × 10−4X12 − 1.24670 × 10−4X13 Coded equation 1.0/y = 0.013 + 1.924 × 10−3x1 − 7.856 × 10−4x12 − 9.974 × 10−4 | 0.0006 (Significant) | 0.0797 (Not significant) | 0.8416 |
| Stainless steel | Contact angle | Actual equation Y = 114.65007 − 15.60827X1 − 3.42166X2 + 1.52731X12 + 0.13671X22 + 1.06516X1X2 − 0.043267X1X22 Coded equation y = 79.82 + 0.22x1 − 0.61x2 + 6.11x12 + 0.91x22 − 0.38x1x2 − 11.44x1x22 | 0.0004 (Significant) | 0.1216 (Not significant) | 0.9644 |
| Contact Angle | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | F | Prob < F | |
| BOROSILICATE GLASS | |||
| Independent variables | |||
| PDMS concentration, x1 | 1.924 × 10−3 | 18.10 | 0.0021 |
| Treatment time, x2 | - | - | - |
| Interactions | |||
| x11 | –7.856 × 10−4 | 26.71 | 0.0006 |
| x111 | –9.974 × 10−4 | 12.16 | 0.0069 |
| STAINLESS STEEL | |||
| Independent variables | |||
| PDMS concentration, x1 | 0.22 | 0.04 | 0.8467 |
| Treatment time, x2 | –0.61 | 0.64 | 0.4548 |
| Interactions | |||
| x11 | 6.11 | 55.04 | 0.0003 |
| x12 | –0.38 | 0.12 | 0.7384 |
| x22 | 0.91 | 1.23 | 0.3094 |
| x122 | –11.44 | 55.52 | 0.0003 |
| Substrate | Optimum PDMS Concentration (%, v/v) | Optimum Treatment Time (h) | Projected Contact Angle Value (°) | Contact Angle Value from the Repeated Experiment (°) | RMSD | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replication 1 | Replication 2 | Replication 3 | |||||
| Borosilicate glass | 1 | 4.92 | 90.91 | 88.83 | 91.83 | 91.39 | 1.64 |
| Stainless steel | 1 | 1 | 98.31 | 99.82 | 100.94 | 101.98 | 3.37 |
| Liquid Product | Substrate Surface | Contact Angle (°) | Surface Tension (mJ/m2) | Adhesion Work (mJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole milk | Borosilicate glass | 68.30 ± 0.38 e | 59.68 ± 0.28 a | 81.75 ± 0.33 a |
| PDMS-borosilate glass | 102.81 ± 0.35 a | 59.63 ± 0.19 a | 46.41 ± 0.21 d | |
| Stainless steel | 82.03 ± 1.30 d | 61.90 ± 0.09 a | 70.48 ± 1.30 b | |
| PDMS-stainless steel | 103.24 ± 2.50 a | 54.11 ± 1.51 b | 41.69 ± 1.14 ed |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramlan, N.; Zubairi, S.I.; Maskat, M.Y. Response Surface Optimisation of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) on Borosilicate Glass and Stainless Steel (SS316) to Increase Hydrophobicity. Molecules 2022, 27, 3388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113388
Ramlan N, Zubairi SI, Maskat MY. Response Surface Optimisation of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) on Borosilicate Glass and Stainless Steel (SS316) to Increase Hydrophobicity. Molecules. 2022; 27(11):3388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113388
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamlan, Nadiah, Saiful Irwan Zubairi, and Mohamad Yusof Maskat. 2022. "Response Surface Optimisation of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) on Borosilicate Glass and Stainless Steel (SS316) to Increase Hydrophobicity" Molecules 27, no. 11: 3388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113388
APA StyleRamlan, N., Zubairi, S. I., & Maskat, M. Y. (2022). Response Surface Optimisation of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) on Borosilicate Glass and Stainless Steel (SS316) to Increase Hydrophobicity. Molecules, 27(11), 3388. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27113388








