Abstract
Polygonum capitatum as an ethnic medicine has been used to treat urinary tract infections, pyelonephritis and urinary calculi. In our previous study, P. capitatum was found to have anti-hyperuricemia effects. Nevertheless, the active constituents of P. capitatum for treating hyperuricemia were still unclear. In this study, an ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole/orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS) was used to comprehensively detect the chemical ingredients of P. capitatum and its absorbed constituents in the plasma of hyperuricemia rats for the first time. Xcalibur 3.0 and Compound Discoverer 2.0 software coupled to mzCloud and ChemSpider databases were utilized for qualitative analysis. A total of 114 chemical components including phenolics, flavonoids, tannins, phenylpropanoids, amino acids, amides and others were identified or tentatively characterized based on the exact mass, retention time and structural information. Compared to the previous P. capitatum study, an additional 66 different components were detected. Moreover, 68 related xenobiotics including 16 prototype components and 52 metabolites were found in the plasma of hyperuricemia rats. The metabolic pathways included ring fission, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydroxylation, methylation, glucuronidation and sulfation. This work may provide important information for further investigation on the active constituents of P. capitatum and their action mechanisms for anti-hyperuricemia effects.
1. Introduction
Hyperuricemia (HUA) is one of the most common metabolic conditions characterized by abnormally increased serum urate levels. Long-term HUA is a main etiologic factor for the deposition of monosodium urate crystals (MSU) in joints and soft tissues resulting in gout [1]. Moreover, HUA is associated with incidences of hypertension, diabetes, obesity and chronic kidney disease [2]. Allopurinol, febuxostat and benzbromarone were selected as anti-hyperuricemic agents, although these agents exhibited some adverse effects including hypersensitivity, cardiovascular mortality risk and hepatic toxicity [3,4,5].
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and ethnic medicine have been applied to treat hyperuricemia and gout for over thousands of years with their own unique advantages. TCM and ethnic medicine were considered important resources for discovering multitarget drugs for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. Polygonum capitatum Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don, named Touhualiao in Chinese, was utilized as Miao ethnic medicine in China to treat urinary tract infections, pyelonephritis and urinary calculi [6]. In our previous study, P. capitatum was found to reduce serum urate levels to treat hyperuricemia and gouty arthritis without renal toxicities. The underlying action mechanism of P. capitatum involved inhibiting the expression and function of xanthine oxidase and decreasing the expressions of glucose transporter 9 (GLUT9) and urate transporter 1 (URAT1) [7]. Despite the remarkable efficacy of P. capitatum for anti-hyperuricemia and anti-gouty arthritis, the active constituents of P. capitatum related to the pharmacological effect are still not clear.
A range of the active constituents of TCM and ethnic medicine is an essential prerequisite for executing pharmacological effects. Profiling the chemical ingredients, the absorbed constituents and metabolites is beneficial for elucidating the pharmacological materials of TCM and ethnic medicine. Traditional separation technologies have been used to isolate and obtain pure components from P. capitatum including triterpenes [8], phenolics [8,9,10], flavonoids [8,9,10], lignans [8,9], alkaloids [10] and tannins [11], although the technology was time-consuming and it was often difficult to acquire the substances at low concentrations. Only partial phenolics of P. capitatum were identified by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-photodiode array detection coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UHPLC-PDA-QqQ-MS) [12] and UHPLC with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-TOF-MS) [13]. These were not sufficient for the research on the active constituents and action mechanisms of P. capitatum for anti-hyperuricemia and anti-gouty arthritis. Therefore, it is necessary to comprehensively identify and characterize the chemical constituents of P. capitatum and its absorbed components in hyperuricemia rats.
UHPLC coupled with quadrupole/orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS) technology provided a sensitive and high-resolution platform for the analysis of chemical constituents at μg/kg concentration levels in complex matrix samples. The data-dependent acquisition mode of Q-Orbitrap HRMS provides MS/MS spectra with accurate mass data [14,15] which are beneficial for identifying and characterizing unknown compounds in TCM and ethnic medicine. Q-Orbitrap HRMS was also a powerful analytical technology for elucidating the metabolism of TCM and ethnic medicine in vivo due to its high sensitivity, high resolution and fast scanning capability.
In this study, a UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS method was employed to systematically clarify the chemical constituents of P. capitatum for the first time. Additionally, the prototypes and metabolites of P. capitatum in hyperuricemia rat plasma were also analyzed by the UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS technology based on neutral loss and metabolism types of representative components. Ultimately, 114 chemical constituents were tentatively identified or characterized from P. capitatum. Compared to the previous P. capitatum study using LC-MS, additional 66 different components were detected in this study. Among these, two new compounds were found, and 7 compounds were discovered in P. capitatum for the first time. A total of 68 related xenobiotics including 16 prototypes and 52 metabolites were detected in the hyperuricemia rats. Among them, 14 prototypes and 50 metabolites were reported for the first time. This study helped illustrate the active components and action mechanisms of P. capitatum for anti-hyperuricemia and anti-gouty arthritis.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS Analysis of P. capitatum Extract
UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS method was employed to profile the chemical constituents in P. capitatum extract. Under the optimized UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS conditions, the total ion current (TIC) chromatograms of P. capitatum extract in negative and positive ion modes are shown in Figure 1. The elemental compositions for the compound and the fragment ion were predicted within a mass tolerance of ±5 ppm. The chemical structures of the components in P. capitatum were elucidated by comparing their retention time, exact mass and structural information with those of authentic standards or available literature data. As a result, a total of 114 components from P. capitatum were unambiguously identified or tentatively characterized (Table S1 in Supplementary Materials), including 30 phenolic acids, 38 flavonoids, 16 phenylpropanoids, 10 tannins, 10 phenolics, 3 amino acids, 3 amides and 4 others. The chemical structures of the detected constituents were shown in Figure S1 in Supplementary Materials. Among these compounds, compounds 59, 77, 84, 96, 97, 110 and 112 were found in P. capitatum for the first time. Although positive and negative ion modes were employed, more peak signals and higher sensitivities were obtained in the negative ion mode. The fragment ions in the negative and positive ion modes are listed in Table S1.

Figure 1.
The TIC chromatograms of P. capitatum extract in negative (NEG) and positive (POS) ion modes.
2.1.1. Phenolic Acids
The mass signals for phenolic acids in negative ion mode were observed. The quasi-molecular ions of phenolic acids preferred to produce the corresponding product ions by neutral loss of H2O, CO and CO2. Compounds 4 and 14 were unambiguously identified as gallic acid and protocatechuic acid, respectively, by comparing their retention time and mass data with those of reference standards. The [M − H]− of gallic acid at m/z 169.0133 lost a unit of CO2 to form the product ion at m/z 125.0233 and subsequently discarded a H2O unit and a CO group to yield the ions at m/z 107.0126 and 97.0283. The [M − H]− ion of compound 55 was 14.0158 Da (CH2) more massive than that of gallic acid. The ions at m/z 168.0055 and 165.0187 were formed from the [M − H]− ion through losing ·CH3 and H2O. Moreover, the prominent ion at m/z 139.0390 was assigned as [M − H − CO2]−. Compound 55 was tentatively identified as the reported 4-O-methylgallic acid [12]. Similarly, compounds 50 and 52 gave the [M − H]− ions at m/z 197.0448 and 197.0449 with the same predicted molecular formulae (C9H9O5−), which was C2H4 moiety more massive than that of gallic acid. Notably, the product ions at m/z 169.0133 of compound 50 corresponding to [M − H − C2H4]− indicated the existence of ethyl moiety. The fragment ion at m/z 125.0233 ([M − H − C2H4 − CO2]−) was also observed in the tandem mass spectrometry (MS2) of compound 50. Therefore, compound 50 was tentatively identified as the reported ethyl gallate [16]. Different from the fragmentation pattern of compound 50, compound 52 generated the product ions at m/z 182.0212 ([M − H − CH3·]−) and 166.9976 ([M − H − 2 × CH3·]−) suggesting the presence of two methyl groups in compound 52. Compound 52 was assigned as syringic acid [17]. Compounds 17 and 35 eluted at 3.20 min and 7.07 min showed additional hexoside groups (162 Da) compared to compounds 52 and 50. The fragmentation pathways of the aglycone ions were similar to those of compounds 52 and 50. Compounds 17 and 35 were tentatively identified as syringic acid-O-hexoside and ethyl gallate-O-hexoside. Compound 13 gave a [M − H]− ion at m/z 329.0858 and exhibited the fragment ions at m/z 167.0341 ([M − H − hexose sugar]−), 152.0105 ([M − H − hexose sugar − CH3·]−), 123.0440 ([M − H − hexose sugar − CO2]−) and 108.0205 ([M − H − hexose sugar-CO2 − CH3·]−) assigned as the moiety of vanillic acid. Based on the above observation, compound 13 was tentatively identified as vanillic acid-O-hexoside. Compound 34 exhibited the quasi-molecular ion at m/z 481.0985 ([M − H]−) which was 152.0127 Da (C7H4O4) more massive than that of compound 13. The [M − H]− ion of compound 34 lost a vanillic acid residue and a dehydrated hexose moiety in succession to form the ions at m/z 313.0564 and 169.0133. Notably, the characteristic fragment ions at m/z 169.0133, 125.0232 and 97.0282 assigned as gallic acid were observed in the MS2 spectrum of compound 34, which primarily implied a galloyl residue connected to the vanillic acid-O-hexoside. Due to the existences of vanillic acid [17] and 2-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenol-1-O-β-d-(6′-O-galloyl) glucopyranoside [10] in P. capitatum, compound 34 was tentatively identified as vanillic acid-4-O-(6′-O-galloyl)-glucopyranoside.
2.1.2. Flavonoids
Flavonoids refer to a class of natural compounds possessing a chemical skeleton of C6-C3-C6. A total of 38 flavonoids were detected in P. capitatum, including flavonols, flavan-3-ols and flavanones. Compounds 26, 67, 69, 75, 76, 93, 105 and 107 were confirmed as (+)-catechin, myricetrin, quercetin-3-O-(2″-O-galloyl)-β-d-glucopyranoside, rutin, quercetin-3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside, quercitrin, quercetin and 3″-O-galloylquercitrin compared by authentic reference standards.
Generally, flavonoid O-glycosides usually lose saccharide moieties to produce the corresponding aglycone ions. Most of the flavonoid O-glycosides in P. capitatum were characterized by galloyl groups attached to monosaccharide residues. In the MS2 spectra, the loss of a galloyl moiety (152 Da) was the characteristic fragmentation pattern of flavonoid O-glycosides in P. capitatum. For flavonoid aglycones, retro-diels-alder (RDA) fragmentation reaction and neutral losses of H2O (18 Da), CO (28 Da) were involved. As the isomers of quercetin-3-O-(2″-O-galloyl)-β-d-glucopyranoside (compound 69), compounds 79 and 97 showed the [M − H]− ions at m/z 615.0987 (err. 1.02 ppm) and 615.0988 (err. 1.23 ppm) with the same predicted molecular formulae (C28H23O16−). Compound 79 gave a similar fragment pattern to that of compound 69, where the [M − H]− ion continuously lost a galloyl unit and a hexose residue to form the ion at m/z 463.0886 and 301.0352. The fragment ions at m/z 151.0027 and 107.0126 were generated from the aglycone ion through the RDA fragmentation reaction. Compound 79 was tentatively identified as the reported quercetin-3-O-(3″-O-galloyl)-β-d-glucopyranoside [18]. The MS2 spectrum for compound 97 showed the product ions at m/z 463.0881 and 316.0223 resulting from the loss of a galloyl unit and a rhamnosyl residue in succession. The fragment ions observed at m/z 164.0104 and 151.0027 were assigned as the [1,3A]− and [1,3B]− products of the RDA fragmentation pathway. The observed ions at m/z 463.0881, 316.0223, 164.0104 and 151.0027 were characteristic of myricetin-O-rhamnoside. Myricetin-3-O-rhamnoside-gallate has been identified as a main chemical constituent of Polygonum neofiliforme as homologous plant of P. capitatum [19]. Moreover, the compounds quercetin-3-O-(2″-O-galloyl)-rhamnopyranoside and quercetin-3-O-(3″-O-galloyl)-rhamnopyranoside were present in P. capitatum [18]. Compound 97 was tentatively identified as myricetin-3-O-(2″-O-galloyl)-rhamnopyranoside or myricetin-3-O-(3″-O-galloyl)-rhamnopyranoside. The proposed mass fragmentation pathway of compound 97 is shown in Figure 2.
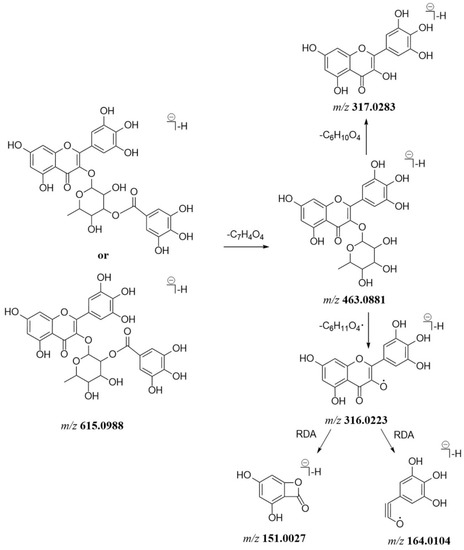
Figure 2.
The proposed mass fragmentation pathway of compound 97.
Compound 87 detected at 14.50 min showed a quasi-molecular ion at m/z 629.0785 (C28H21O17−) and lost a galloyl moiety to generate the product ions at m/z 477.0678. The above [M − H]− ion and product ions of compound 87 were 13.9797 Da higher than the corresponding ions of compound 79. The observed ions at m/z 327.0357 and 175.0240 of compound 87 suggested a glucuronic acid moiety was connected to the galloyl group. Furthermore, the ions at m/z 301.0353, 151.0027 and 107.0126 were assigned as quercetin. Therefore, compound 87 was tentatively identified as a new compound, quercetin 3-O-galloylglucuronide. Similarly, compounds 102 and 104 were tentatively identified as the reported quercetin-3-O-(6″-O-trans-feruloyl)-β-d-galactopyranoside [20] and quercetin-3-O-(4″-O-acetyl)-α-l-rhamnopyranoside [21], respectively. Compound 49 eluted at 8.63 min exhibited an [M − H]− ion at m/z 735.1563 and gave the product ions at m/z 583.1091 and 447.0930 through losing a protocatechuoyl moiety and a galloyl group in succession, suggesting the existence of protocatechuoyl and galloyl residues. In addition, the characteristic ions at m/z 447.0930, 301.0348 and 243.0295 in the MS2 spectra implied the presence of quercetin-O-rhamnoside. Although the positions of the protocatechuoyl moiety and the galloyl group were unclear, the finding of quercetin-3-O-(2″-O-protocatechuoyl)-rhamnoside and 3″-O-galloylquercitrin in this plant implied the protocatechuoyl and galloyl moieties were connected to the monosaccharide residue of compound 49. Therefore, compound 49 was tentatively identified as a new compound, quercetin-3-O-(protocatechuoyl-galloyl)-rhamnoside.
2.1.3. Phenylpropanoids
Phenylpropanoids in P. capitatum were divided into phenylpropanoid sucrose esters, lignans and chromones derivatives. Compound 111 (tR = 18.36 min) produced an [M − H]− ion at m/z 735.2141 (C34H39O18−, err. 1.31). In the MS2 spectrum, the fragment ions at m/z 559.1661 (C24H31O15−) and 175.0392 (C10H7O3−) were produced via the loss of the dehydrated feruloyl group. The ion at m/z 559.1661 lost an acetylated hexosyl residue to generate the ion at m/z 337.0931, and subsequently discarded another hexosyl residue to form a feruloyl moiety (m/z 193.0498, C10H9O4−). Compound 111 was tentatively identified as the reported bistoroside B [22]. Compared to compound 111, compound 84 (tR = 14.16 min, m/z 559.1665, [M − H]−, C24H31O15−) exhibited the absence of a feruloyl residue and showed a similar mass fragmentation pathway in compound 111. Compound 84 was tentatively identified as 6′-acetyl-6(or 3)-feruloylsucrose. This compound was firstly found in the Polygonum genus. The mass data and the fragmentation pathway of 6′-acetyl-6(or 3)-feruloylsucrose was proposed for the first time in this study (Figure 3A). Similarly, compound 112 (tR = 18.36 min, m/z 777.2244, [M − H]−, C36H41O19−) showed an additional acetyl moiety (42.0103 Da) compared to compound 111. Based on the reported mass data [23], compoumd 112 was tentatively identified as smilaside A. Compound 110 possessed an [M − H]− ion at m/z 705.2040 (C33H37O17−) and gave the product ions at m/z 559.1662 (C24H31O15−), 163.0389 (C9H7O3−) and 145.0284 (C9H5O2−), suggesting the existence of a coumaroyl moiety. The characteristic ions of 6′-acetyl-6(or 3)-feruloylsucrose at m/z 559.1662, 337.0943, 193.0499 and 175.0392 were also observed in the MS2 spectrum of compound 110. Compound 110 was tentatively identified as 6′-acetyl-3(or 6)-feruloyl-6(or 3)-coumaroylsucrose (Figure 3B).
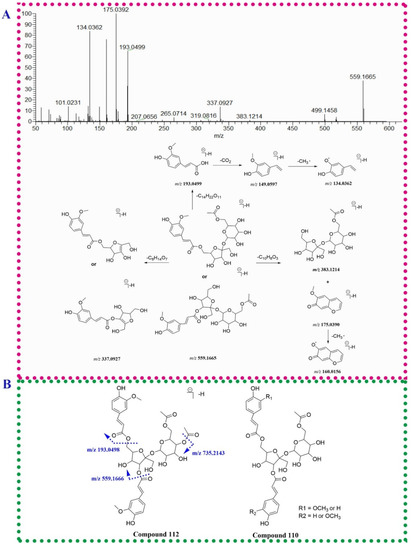
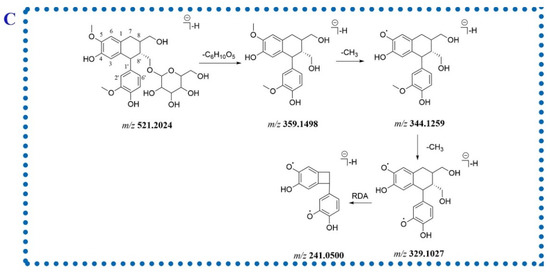
Figure 3.
The fragmentation patterns of compounds 84 (A), 110 (B) and 77 (C).
Two isomeric compounds, 77 and 90, were eluted at 13.20 and 14.83 min possessing identical molecular formulae (C26H33O11−). For compound 77, the fragment ions at m/z 359.1498, 344.1259 and 329.1027 in the MS2 spectrum were generated via losing a hexosyl moiety and subsequent discarding two methyl groups. The RDA fragment ion at m/z 241.0500 was corresponding to the cleavage of 8-8′ bond (Figure 3C). Due to the presence of isolariciresinol-9′-O-β-d-xylopyranoside in P. capitatum, compound 77 was tentatively identified as isolariciresinol-9′-O-glucopyranoside. Compound 90 neutrally lost a pentose residue (132 Da) to form the aglycone ion at m/z 389.1605 and lost three methyl groups in succession to generate the ions at m/z 374.1370, 359.1136 and 344.0892, respectively, implying the existence of three methoxy groups in the aglycone moiety. Therefore, compound 90 was tentatively identified as 3(or 5′)-methoxyisolariciresinol-9′-O-xylopyranoside.
2.1.4. Tannins
Tannins identified in P. capitatum in this study were classified into proanthocyanidins and ellagitannins. Proanthocyanidins were condensed tannins composed of oligomers and polymers of flavan-3-ol moieties linked mainly through 4-8′ bonds. RDA reaction, heterocyclic ring fission (HRF) and quinone methide (QM) cleavage were the main mass fragmentation patterns of proanthocyanidins [24]. Ellagitannins belonging to hydrolyzable tannins consisted of hexahydroxydiphenoyl (HHDP) groups and related acyl groups. The characteristic fragment ion at m/z 300.9991 (C14H5O8−) in the MS2 spectrum of ellagitannin was corresponding to an ellagic acid moiety.
A pair of isomer compounds 25 and 32 both showed the deprotonated ions at m/z 577.1348 ([M − H]−, C30H25O12−) and the fragment ions at m/z 425.0877, 451.1039 and 289.0717 generated through RDA fragment reaction, HRF fragmentation and QM cleavage, respectively (Figure 4A), which suggested that compounds 25 and 32 were the reported procyanidin B1/B2 [25]. Compounds 43, 51 and 53 all produced the deprotonated ions at m/z 729.1458 (C37H29O16−) and lost a galloyl group to generate the fragment ions at m/z 577.1352 (C30H25O12−). The subsequent fragmentation pathways of the ion at m/z 577.1352 were similar to those of compounds 25 and 32. Compounds 43, 51 and 53 exhibited an additional galloyl residue compared to compounds 25 and 32. Since catechin-3-O-gallate had been found in P. capitatum, compounds 43, 51 and 53 were tentatively identified as 3(or 3′)-O-galloyl(epi)catechin-(4,8′)-(epi)catechin.

Figure 4.
The fragmentation pathways of compounds 25 or 32 (A), 64 (B) and 33 (C). The dotted purple and green lines represent the cleavage positions of compound 33 in MS2 spectrum.
Compound 64 (tR = 11.36 min) had a [M − H]− ion at m/z 937.0953 (C41H29O26−) and gave the fragment ions at 893.1055 and 785.0838 generated from the loss of a CO2 unit and a galloyl residue, respectively. The product ion at m/z 785.0838 continuously discarded a galloyl residue to form the ion at m/z 615.0617. In addition, the ions at m/z 300.9991and 275.0198 were assigned to the moieties of ellagic acid and urolithin M5. Compound 64 was tentatively identified as davidiin. The proposed mass fragment pathway of compound 64 was shown in Figure 4B. Compound 33 (tR = 6.71 min) exhibited an [M − H]− ion at m/z 925.0955 (C40H29O26−). The MS2 spectra for compound 33 revealed the intense product ion at m/z 605.0789 resulting from the neutral loss of a dehydrated HHDP residue (C14H8O9). The characteristic fragment ions at 615.0638 and 309.0245 were generated through losing a C13H9O9 moiety, which implies the existence of the residue region composed of D- and E-rings. Compound 33 was tentatively attributed to phyllanthusiin C. The MS2 fragmentation pathway (Figure 4C) of phyllanthusiin C was proposed for the first time.
2.1.5. Other Phenolics
Ten phenolics with a small molecular mass (<350 Da) and less than 15 carbons were tentatively identified in P. capitatum. The common fragment characteristic of phenolics is a successive or simultaneous loss of H2O and CO groups in their MS2 spectra. Compound 29 at tR 5.58 min gave a deprotonated ion at m/z 247.0246 (C12H7O6−). The MS2 spectrum of compound 29 showed the fragment ions at m/z 219.0293 and 203.0343 resulting from the neutral loss of CO and CO2 unit from quasi-molecular ion, respectively. Furthermore, the ion at m/z 219.0293 went on losing a CO and a CO2 unit in succession to form the ions at 191.0342 and 147.0440. Since brevifolin has previously been found in P. capitatum in the reported literature [20], compound 29 was tentatively identified as brevifolin. Compound 46 gave a quasi-molecular ion at m/z 275.0197 ([M − H]−, C13H7O7−) and the fragment ions at m/z 257.0089 ([M − H − H2O]−), 247.0243 ([M − H − CO]−), 231.0291 ([M − H − CO2]−), 229.0138 ([M − H − H2O − CO]−) and 203.0343 ([M − H − CO − CO2]−). A lactone moiety or a carboxyl group was implied to be present in compound 46. In addition, the ion at m/z 191.0341 was generated through an RDA fragmentation reaction from the ion at m/z 231.0291. Compound 46 was tentatively identified as urolithin M5. Urolithin M5 was an intestinal bacterial metabolite of ellagitannin davidiin from P. capitatum [26] and was also found in natural higher plants from diverse families [27,28]. The compound might be biosynthesized through the polyketide pathway [29,30] by endophytic fungi residing in raw P. capitatum. Compound 8 (tR = 2.09 min) gave an [M − H]− ion at m/z 243.0507 (C10H11O7−) and exhibited the characteristic ions of gallic acid moiety at m/z 169.0134, 125.0233 and 107.0125. The glycerol residue at m/z 91.0388 was found in the spectrum of compound 8. Based on the reported literature [31], compound 8 was tentatively identified as galloyl-glycerol.
2.1.6. Amino Acids and Amides
Three Amino acids and 3 amides were identified or characterized in P. capitatum. Compound 6 (tR = 2.03 min, [M + H]+, m/z 166.0864) was tentatively identified as the reported phenylalanine [12]. Compound 12 (tR = 2.37 min) gave an [M + H]+ ion at m/z 328.1386 (C15H23O7N+) and lost a fructose moiety to form the characteristic ion of phenylalanine (m/z 166.0859 and 120.0808). Comparing the mass information of compound 12 to those in the reported literature [32], compound 12 was tentatively identified as fructose-phenylalanine. Compound 96 eluted at 15.82 min showed a quasi-molecular ion at m/z 330.1335 (C18H20NO5+) and gave the base-peak ion at m/z 177.0547 assigned to ferulic acid through neutral loss of an octopamine residue. The ions at m/z 145.0284 and 117.0338 were formed through successively losing CH4O and CO from the ion at m/z 177.0547. Moreover, the ion at m/z 194.0815 was generated through carbon-nitrogen bond cleavage (Figure 5A). Compound 96 was tentatively assigned as N-feruloyloctopamine. For compound 101 (tR = 17.58 min, [M + H]+, C18H20NO4+), a tyramine moiety replaced the octopamine moiety compared to 96. The MS2 data of compound 101 was similar to that of compound 96. Compound 101 was tentatively assigned as N-feruloyltyramine (Figure 5A).
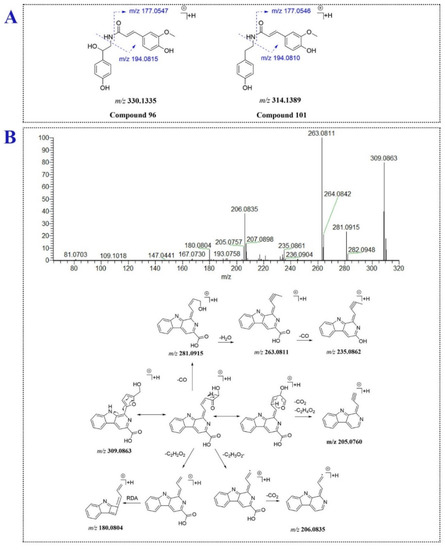
Figure 5.
The fragmentation patterns of compounds 96, 101 (A) and 106 (B).
2.1.7. Others
Compound 106 eluted at 17.80 min produced an [M + H]+ ion at m/z 309.0863 (C17H13O4N2+), suggesting compound 106 might be an alkaloid. In the MS/MS analysis, the fragment ions at m/z 281.0919, 263.0811 and 235.0862 were generated via ring fission and lost CO, H2O and CO units in succession. Furthermore, the [M + H]+ ion of compound 106 lost a C2H2O2 moiety of hydroxymethylfuran ring and underwent RDA fragment reaction to yield the fragment ion at m/z 180.0804. The product ion at m/z 206.0835 was formed though losing C2H3O2· and CO2 from the [M + H]+ ion. Compound 106 was tentatively assigned as flazin. The proposed mass fragment pathway of flazin was shown for the first time in the study (Figure 5B). Compound 41 (tR = 7.67 min, [M − H]−, m/z 387.1660) generated the aglycone ion at m/z 207.1021 (C12H15O3−) through losing hexose sugar, and further lost one molecule of CO2 to form the ion at m/z 163.1118. Compound 41 was tentatively identified as the reported 12-hydroxyjasmonic acid glucoside [10].
2.2. UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS Analysis of the Prototype Compounds in Hyperuricemia Rat Plasma
The TIC chromatograms and mass data of rat plasma from hyperuricemia and drug-treated groups were compared to analyze P. capitatum-related exogenous components. The peaks that appeared at the same positions in the TIC chromatograms of both the dosed rat plasma and the herb extract but not in the chromatogram of the model rat plasma were regarded as prototype constituents. As a result, 16 prototype components of P. capitatum were found in hyperuricemia rat plasma. The detailed mass information is shown in Table S1. Among these, ellagic acid, 5,7-dihydroxychromone, quercetin-3-O-glucuronide, quercitrin, 3,3′-di-O-methylellagic acid, flazin, salidroside, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenol-1-O-β-d-glucopyranoside, fructose-phenylalanine, nudiposide, quercetin-3-O-β-d-galactoside, quercetin-3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside, kaempferol-4-O′-rutinoside, N-feruloyltyramine and afzelin were found in rat plasma after oral administration of P. capitatum extracts for the first time.
2.3. UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS Analysis of P. capitatum Metabolites in Hyperuricemia Rat Plasma
The procedures for identification of metabolites included speculating probable metabolites according to the biotransformation rules of original compounds, extracting the [M − H]− or [M + H]+ ions of probable metabolites from dosed plasma in full-scan mass mode and analyzing the MS2 information of the detected peak. The detected metabolic mechanism of P. capitatum in hyperuricemia rats involved ring fission, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydroxylation, methylation, glucuronidation and sulfation. In this study, a total of 52 metabolites of P. capitatum in rat plasma were tentatively identified. Among them, 50 metabolites were revealed for the first time. The details of the characterized metabolites are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
The metabolites of P. capitatum in hyperuricemia rat plasma.
2.3.1. Characterization of Phenolic-Related Metabolites
A total of 22 constituents were identified as phenolic-related metabolites, including 14 gallic acid-related (M1–M3, M5–M6, M7–M12, M14, M20 and M24), 3 syringic acid/ethyl gallate-related (M18, M19 and M26), 2 dimethylellagic acid-related (M43 and M47), a vanillic acid-related (M17) and a protocatechuic acid-related (M4) metabolites.
M18 (tR = 5.67 min) and M19 (tR = 5.94 min) exhibited the same quasi-molecular ion at m/z 373.0775 ([M − H]−, C15H17O11−) and the same fragment ion at m/z 197.0448 by the cleavage of a dehydrated glucuronic acid moiety, suggesting the two metabolites were the glucuronidation products. Furthermore, M18 showed the characteristic fragment ions at m/z 197.0448, 169.0144 and 125.0233 of ethyl gallate, while M19 showed the fragment ions at m/z 197.0447, 182.0208, 166.9976 assigned to syringic acid. Therefore, M18 and M19 were identified as ethyl gallate glucuronide and syringic acid glucuronide, respectively. M20 (tR = 6.20 min) and M26 (tR = 7.02 min) exhibited the quasi-molecular ions [M-H]− at m/z 277.0022 which were 79.9573 Da (SO3) more than that of 3,4-O-dimethylgallic acid or syringic acid and yielded the characteristic product ions of the two isomers at m/z 197.0449, 182.0213 and 166.9977. M20 and M26 were preliminarily assigned as 3,4-O-dimethylgallic acid sulfate or syringic acid-4-O-sulfate. To elucidate the exact conjugation site of M20 and M26, their ClogP values were calculated through ChemBioDraw Ultra 20.0 software. Generally, compounds with larger ClogP values tend to form longer retention times in reverse-phase chromatography. The ClogP value of 3,4-O-dimethylgallic acid sulfate (−0.53863) is smaller than that of syringic acid-4-O-sulfate (−0.18863). Thus, M20 and M26 were speculated as 3,4-O-dimethylgallic acid sulfate and syringic acid-4-O-sulfate. M2 and M19 presented [M − H]− ions at m/z 359.0620 (C14H15O11−) and lost a dehydrated glucuronic acid residue, a methyl group and a CO2 unit to form the ions at m/z 183.0292, 168.0068 and 124.0154, implying M2 and M19 were the methylated and glucuronidated products of gallic acid. Considering both 4-O-methylgallic acid and the 3-O-methylgallic acid were the main methylated metabolites of gallic acid [33] and 3-OH position was easier to be glucuronidated due to the smaller steric hindrance, M2 with higher peak intensity was speculated as 4-O-methylgallic acid-3-O-glucuronide. M19 was tentatively identified as 3-O-methylgallic acid-4-O-glucuronide. Similarly, M7 lost an SO3 group to yield the aglycone ion assigned to methylated gallic acid. M7 was tentatively identified as methylgallic acid sulfate.
M43 (tR = 13.95 min, m/z 505.0623, [M − H]−) and M47 (tR = 16.48 min, m/z 408.9866, [M − H]−) showed the same aglycone fragment ion at m/z 329.0303 through the loss of a dehydrated glucuronic acid and an SO3 unit, respectively. The ion at m/z 329.0303 discarded two methyl group in succession to yield the ions at m/z 314.0048 and 298.9833. The fragmentation behaviors of the aglycone ion at m/z 329.0303 was consistent with that of 3,3′-di-O-methylellagic acid. M43 and M47 was considered as 3,3′-di-O-methylellagic acid glucuronide and 3,3′-di-O-methylellagic acid sulfates.
2.3.2. Characterization of Flavonoid-Related Metabolites
Six flavonols-related, 2 flavanone-related and 7 flavanols-related metabolites of P. capitatum were detected in dosed rat plasma. Sulfation, glucuronidation and methylation were the main metabolic pathways of the flavonoid. Moreover, ring fission and dehydroxylation were observed in the metabolic fate of flavanols (catechin or epicatechin).
M44 and M49 exhibited [M − H]− ions at m/z 461.0726 (C21H17O12−) and 364.9972 (C15H9O9S−), respectively. The same fragment ions at m/z 285.0402 of M44 and M49 were corresponding to the loss of a dehydrated glucuronic acid and an SO3 group from their [M − H]− ions, respectively. The ion at m/z 285.0402 furtherly lost a CH2O moiety to form the ion at m/z 255.0293. The fragment pattern of the aglycone ion was consistent with that of kaempferol in P. capitatum extract. According to the reported literature [34], M44 and M49 were identified as kaempferol glucuronide and kaempferol sulfate, respectively. M41 (tR = 13.07 min) produced a [M − H]− ion at m/z 571.0396 (C22H19O16S−) and dissociated into the fragment ions at m/z 491.0832 (C22H19O13−) and 315.0511 (C16H11O7−) ascribed to the continuous losses of an SO3 unit and a glucuronic acid residue. The ion at m/z 315.0511 lost a methyl group to yield the product ion at m/z 300.0275 and furtherly was subjected to an RDA fragmentation reaction to form the ion at m/z 148.0155. The cracking path of the ion at m/z 315.0511 was similar to 3-O-methylquercetin [35]. M41 was speculated as glucuronidation and sulfation of 3-O-methylquercetin.
Ring cleavage was a common metabolic pathway of (epi)catechin in vivo [36,37]. These metabolites generated through ring cleavage were further bio-transformed through sulfation or glucuronidation. M13 (tR = 4.32 min) showed an [M − H]− ion at m/z 230.9964 (C8H7O6S−) and an aglycone ion at 151.0393 through loss of an SO3 unit. The [M − H]− ion produced the fragment ions at m/z 187.0063 (C7H7O4S−) and 107.0490 (C7H7O−) by discarding a CO2 group and an SO3 group in succession, which was in high accordance with mass fragment pattern of 3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid sulfate [36]. M13 was considered the metabolite of (epi)catechin through dehydroxylation, ring cleavage and sulfation (3-hydroxyphenylacetic acid sulfate). M25 (tR = 6.88 min) showed an [M − H]− ion at m/z 287.0233 (C11H11O7S−) and an [aglycone − H]− ion at m/z 207.0504 generated by the loss of an SO3 moiety. The ion at m/z 163.0764 was yielded from the [aglycone − H]− ion through losing a CO2 unit. According to the reported metabolic pathway of (epi)catechin [38], M25 was tentatively characterized as 5-(3′,4′-dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone sulfate. Compared to M25, M30 exhibited the absence of an oxygen atom (16 Da) and a similar fragment pattern to M25. M30 was tentatively assigned as 5-(3′-hydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone sulfate or 5-(4′-hydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone sulfate. Similarly, 5-(3′,4′-hydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone glucuronide (M21, C17H19O10−) was tentatively identified in spite of no fragment ions obtained in the MS2 spectrum [36]. M16 (tR = 5.50 min) produced a [M − H]− ion at m/z 242.9966 (C9H7O6S−). In the MS2 spectrum, the fragment ions at m/z 163.0392 ([M − H − SO3]−), 135.0443 ([M − H − SO3 − CO]−) and 119.0491 ([M − H − SO3 − CO2]−) were consistent with the fragment pathway of m-coumaric acid or p-coumaric acid [39]. M16 was tentatively assigned as m-coumaric acid sulfate or p-coumaric acid sulfate. Based on the above data, the possible metabolic pathways of (epi)catechin in hyperuricemia rats administered orally with P. capitatum extract are shown in Figure 6A.
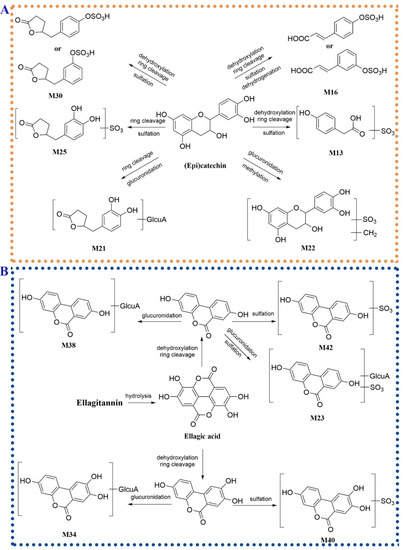
Figure 6.
The possible metabolic pathways of (epi)catechin (A) and ellagitannins (B) in hyperuricemia rats administered orally with P. capitatum extract.
2.3.3. Characterization of Phenylpropanoid-Related Metabolites
A total of 8 phenylpropanoid-related metabolites were detected in rat plasma, mainly from the products of isolariciresinol and 5,7-dihydroxychromone. M31 (tR = 8.39 min), M32 (tR = 8.55 min), M35 (tR = 9.65 min) and M36 (tR = 9.86 min) showed the same quasi-molecular ion [M − H]− at m/z 535.1823 (C26H31O12−) and gave the fragment ions at m/z 359.1497 ([M − H − glucuronyl unit]−), 344.1266 ([M − H − glucuronyl unit − CH3·]−) and 329.1036 ([M − H − glucuronyl unit − 2 × CH3·]−) in their MS2 spectra. The ion at m/z 241.0507 was formed from the ion at m/z 329.1036 through an RDA fragmentation pathway. M31, M32, M35 and M36 were preliminarily assigned as glucuronidation of isolariciresinol. The conjugation sites of the four metabolites were speculated by ClogP values. M31 (ClogP = −1.3851) and M32 (ClogP = −1.3851) were tentatively identified as isolariciresinol-4 (or 4′)-O-glucuronide. M35 (ClogP = −0.7404) and M36 (ClogP = −0.7404) were tentatively identified as isolariciresinol-9 (or 9′)-O-glucuronide.
2.3.4. Characterization of Tannis-Related Metabolites
According to the reported literature, although ellagitannins were not absorbed in vivo, ellagitannins located at the distal segment of the gastrointestinal tract could be bio-transformed by the intestinal bacteria into dibenzo-α-pyrones derivatives [40]. Compared to the base peak chromatography (BPC) of the plasma from the hyperuricemia group, a peak with high intensity at 10.13 min (M38) was detected in the BPC of dosed rat plasma. M38 exhibited an [M − H]− ion at m/z 403.0669 (C19H15O10−) and lost a dehydrated glucuronic acid residue to form the ions at m/z 227.0345 ([M − H − glucuronyl unit]−) and 175.0239 (glucuronyl unit), suggesting the M38 was a glucuronic conjugate. The aglycone ion at m/z 227.0345 furtherly lost a CO group and a CO2 unit to generate the fragment ions at m/z 199.0388 and 183.0446, respectively. The ion at m/z 155.0491 was formed through the combined loss of CO and CO2 from the aglycone ion. The fragment pattern of the aglycone ion was consistent with that of urolithin A [41]. M38 was tentatively identified as urolithin A glucuronide. M42 (m/z 306.9917, [M − H]−, C13H7O7S−) lost an SO3 group to yield the aglycone ion at m/z 227.0345 assigned to urolithin A. M42 was identified as urolithin A sulfate. Similarly, M23 (tR = 6.74 min) lost an SO3 group and a dehydrated glucuronic acid moiety to form the aglycone fragment of urolithin A. M23 was speculated as glucuronidation and sulfation product of urolithin A. Compared to the quasi-molecular ions and the corresponding fragment ions of M38 and M42, M34 and M40 showed an additional oxygen atom (15.9951 Da). M34 and M40 were identified as urolithin C glucuronide and urolithin C sulfate, respectively. The possible metabolic pathways of ellagitannins in hyperuricemia rats orally administered with P. capitatum were shown in Figure 6B.
2.3.5. Characterization of Alkaloid-Related Metabolites
M52 (tR = 20.68 min) showed an [M + H]+ ion at m/z 323.1024 (C18H15O4N2+) that was more 14.0161 Da (CH2 moiety) than that of flazin. The MS2 spectrum of M52 in positive ion mode showed the fragment ions at m/z 263.0814, 206.0837 and 180.0806 assigned to flazin as discussed above. Furthermore, M52 detected at m/z 321.0880 ([M − H]−) in negative ion mode yielded the fragment ions at 291.0775 and 277.0612 by losing CH2O and C2H4O, suggesting the existence of a methoxy group in M52. The ion at m/z 277.0612 furtherly lost a CO2 group and a molecule of H2O to form the ion at m/z 233.0719 and 259.0511. M52 was tentatively identified as flazin methyl ether.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material and Reagents
The herb of P. capitatum was collected from Qianxi county, Guizhou province, China and was identified by Qingde Long (Guizhou Medical University) as the whole plant of Polygonum capitatum Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don. The voucher specimen of P. capitatum (No.: PC20201103) was deposited in the Herbarium of Guizhou Medical University.
The reference standards of gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, (+)-catechin, rutin, quercitrin, quercetin and emodin were purchased from Chengdu Chroma-Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Chengdu, China). The pure materials of myricitrin, quercetin-3-O-(2″-O-galloyl)-β-d-glucopyranoside, quercetin-3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside, cis-N-caffeoyltyramine and 3″-O-galloylquercitrin were obtained in our laboratory. The purities of the reference standards were determined to be more than 98% by HPLC (-DAD. Hypoxanthine and potassium oxonate were purchased from the Beijing Solarbio Science and Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China). Urate assay kits were purchased from Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China).
HPLC-grade methanol and acetonitrile were acquired from Honeywell Burdick & Jackson Company (Morristown, NJ, USA). Formic acid (MS grade) was obtained from Fisher Scientific (Madrid, Spain). Deionized water for HPLC analysis was prepared using a Milli-Q water purification system (Millipore, Milford, MA, USA). All other reagents were of analytical grade.
3.2. Preparation of Mixed Standard Solutions
The stock solutions of standards were prepared by weighting appropriate amounts of 13 reference substances individually and dissolving them in methanol at a concentration of 1.0 mg/mL. The final mixed standard solution (200 ng/mL) was obtained by mixing the appropriate volumes of the stock solutions and diluting with 60% methanol before qualitative analysis.
3.3. Preparation of P. capitatum Samples
The dried raw herb of P. capitatum (1453 g) was weighed and crushed into power. The obtained powder was immersed in a ten-fold volume of distilled water for 30 min and decocted three times by boiling for 1 h. The decoctions were filtered to remove the herbal residue. The supernatants were merged together and concentrated to yield the extract residue (291.1 g, the extraction rate 20.03%).
10 mg of the obtained extract residue was dissolved in 1 mL of 60% (v/v) methanol and ultrasonicated for 30 min at 100 kHz. After centrifuging at 12,000 rpm for 10 min, 10 µL of the supernatant was used for UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS analysis.
3.4. Animal Treatment and Drug Administration
A total of 18 male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats (weighing 200 ± 20 g) were obtained from Changsha Tianqin Biotechnology Company (Hunan, China). The rats were housed under a standard 12-h light-dark cycle at 25 ± 2 °C and 60 ± 5% humidity with free access to water and a normal diet for 7 days. All of the experiments were approved by the Animal Care Welfare Committee of Guizhou Medical University (approval number 2100138) and performed according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Institutes of Health).
Rats were randomly divided into three groups with six animals per group (control, hyperuricemia and drug-treated groups). Hyperuricemia was induced in the rats according to the described method previously [42]. Briefly, except for the control group, intragastric hypoxanthine (500 mg/kg/day) and intraperitoneal injection of potassium oxonate (100 mg/kg/day) were given to the rats for 7 days. The animals in the control group received physiological saline in a similar fashion. On the 4th day of hyperuricemia induction, the P. capitatum extract (5 g/kg/day) was administered orally to the rats in the drug-treated group at 1 h after dosing of the modeling agents for 3 days. The serum urate levels in the control and hyperuricemia rat groups were detected by urate assay kits during the experimental period. The serum urate levels in the hyperuricemia rat group significantly increased compared to those of the control rats (p < 0.05), indicating the successful establishment of the hyperuricemia model.
3.5. Collection and Preparation of Plasma Sample
Blood samples were collected at 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 and 24 h after the last administration from the retro-orbital plexus into heparinized tubes. Plasma was obtained through centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 10 min. All plasma samples at different time points from each group of rats were combined to produce the pooled sample for eliminating the individual variability. A 500 µL volume of the pooled plasma sample was added with 1.5 mL of acetonitrile and vortexed for 1.0 min to precipitate protein. The sample was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm and 4 °C for 10 min. The supernatant was evaporated to dryness under a gentle flow of nitrogen at room temperature. The residue was redissolved with 200 µL of 60% methanol in water and centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min. The supernatant was injected into the UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS system for analysis.
3.6. UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS Conditions
A Dionex Ultimate 3000 UHPLC system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) consisted of a quaternary solvent delivery system, a column compartment and a refrigerated auto-sampler. The sample separation was performed on an ACQUITY UPLC® BEH C18 column (2.1 mm × 100 mm, 1.7 µm) eluted with acetonitrile (A) and 0.1% aqueous formic acid (B). The flow rate was set at 0.3 mL/min with an initial mobile phase of 5% (A). The chromatographic elution program was set: 5–5% A at 0–1.0 min, 5–10% A at 1.0–4.0 min, 10–12% A at 4.0–9.0 min, 12–20% A at 9.0–14.0 min, 20–45% A at 14.0–19.0 min, 45–70% A at 19.0–20.0 min, 70–100% A at 20.0–22.0 min, 100–5% A at 22.0–22.1 min, 5–5% A at 22.1–25.0 min. The injection volume was 10 µL.
A Q-Exactive™ Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) equipped with a heated electrospray ionization source (HESI) was used for qualitative analysis. The analysis was carried out both in positive and negative ion modes. The collision and nebulizing gases were ultra-high purity helium (He) and high purity nitrogen (N2). The parameters were set as follows: ion spray voltage: +3.0 kV and −2.5 kV, capillary temperature: 320 °C, S-lens RF level: 60%. The flow rates of sheath gas and auxiliary gas were set to 35 and 10 arbitrary units, respectively. A full MS/dd-MS2 acquisition program was executed with resolutions of 70,000 and 17,500 FWHM. For the full MS experiments, the scan range was from 80 to 1200 m/z, the automatic gain control (AGC) target was defined as 1e6 and the maximum injection time (IT) was set as auto. For the dd-MS2 experiments, AGC target: 2e5, maximum IT: auto, loop count: 1, the isolation window was 3.0 m/z. The stepped normalized collision energies (NCE) were 20, 40, and 60 eV.
3.7. Data Analysis
The information of chemical constituents from P. capitatum, including CAS number, molecular formula and molecular weight, were obtained by retrieving SciFinder Scholar and Dictionary of Natural Product databases. An in-house library containing potential compounds from P. capitatum extract was established. Data analysis was performed through Xcalibur 3.0 software (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and Compound Discoverer 2.0 software coupled to mzCloud© and ChemSpider© databases. The data processing workflow for the identification of chemical ingredients from P. capitatum and its metabolites was shown in Figure 7.
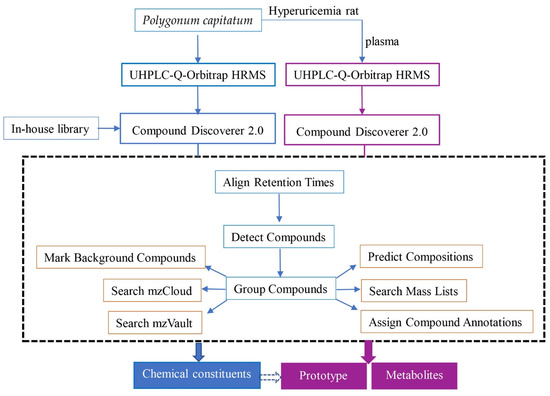
Figure 7.
The data processing workflow for identification of chemical ingredients from P. capitatum and its absorbed constituents in hyperuricemia rat plasma.
4. Conclusions
In this study, a sensitive and accurate UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS method was utilized to systematically analyze the chemical constituents of P. capitatum and its absorbed components in hyperuricemia rats. A total of 114 compounds including phenolic acids, flavonoids, phenylpropanoids, tannins, phenolics, amino acids, amides and others were identified or characterized. At the same time, 68 P. capitatum-related xenobiotics were found in the hyperuricemia rats’ plasma. These exogenous components in hyperuricemia rats might be the potential active constituents of P. capitatum for anti-hyperuricemia and anti-gouty arthritis. The detected metabolic pathway of P. capitatum in hyperuricemia rats included ring fission, hydrolysis, decarboxylation, dehydroxylation, methylation, glucuronidation and sulfation. This study not only supplied a basis for the further investigation of the active components and pharmacokinetics of P. capitatum, but also provided insight into the anti-hyperuricemia mechanism and quality control of P. capitatum.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules27113521/s1, Table S1: Chemical constituents identified and characterized in P. capitatum by UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS in negative and positive ion modes. Figure S1: The chemical structures of the constituents from P. capitatum analyzed by UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap HRMS.
Author Contributions
S.L. and H.G. conceived and designed the research. H.G., P.L., Q.W., F.Z., D.W., M.Z. (Mei Zhou), M.Z. (Meng Zhou) and X.H. participated in the experiment operation. H.G. and P.L. analyzed the data. W.P. and S.L. supervise the research. H.G. and P.L. wrote and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. U1812403-5-1), the Postdoctoral Workstation of the Key Laboratory of Chemistry for Natural Products of Guizhou Province and Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant No. Qiankehe Talent Platform [2019]5627), the High-level Innovative Talents Project of Guizhou Province ([2020]6011), the Science and Technology Innovation Talent Team Project in Guizhou Province ([2020]5006).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Animal Care Welfare Committee of Guizhou Medical University (approval number: 2100138 and approval date: 5 March 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
References
- Benn, C.L.; Dua, P.; Gurrell, R.; Loudon, P.; Pike, A.; Storer, R.I.; Vangjeli, C. Physiology of hyperuricemia and urate-lowering treatments. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.H.; Ruan, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.W. Pallidifloside D, a saponin glycoside constituent from Smilax riparia, resist to hyperuricemia based on URAT1 and GLUT9 in hyperuricemic mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 157, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.J.; Ahn, H.S.; Oh, S.W.; Han, K.H.; Um, T.H.; Cho, C.R.; Han, S.Y. Renoprotective effects of febuxostat compared with allopurinol in patients with hyperuricemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 36, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, J.D.; Dalbeth, N.; Mikuls, T.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Guyatt, G.; Abeles, A.M.; Gelber, A.C.; Harrold, L.R.; Khanna, D.; King, C.; et al. 2020 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Gout. Arthritis Care Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 744–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardin, T.; Richette, P. The role of febuxostat in gout. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.G.; Zhang, L.J.; Sun, F.; Zhang, J.J.; Chen, A.Y.; Lan, Y.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, A.M.; He, X.; Xiong, Y.; et al. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of extracts and fractions from Polygonum capitatum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.L.; Zhang, J.J.; Zhu, Q.F.; Guan, H.Y.; Yang, Y.X.; He, X.; Fu, Y.; Chen, T.X.; Dong, L.; Yang, X.S.; et al. Antihyperuricemia and antigouty arthritis effects of Persicaria capitata herba in mice. Phytomedicine 2021, 93, 153765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.H.; Gao, Y.; Wu, Z.J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, D.D.; Chen, W.S.; Sun, L.N. Chemical constituents from Polygonum capitatum Buch-Ham. ex D. Don. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2015, 59, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Chen, W. Chemical Constituents of Polygonum capitatum. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2015, 51, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.B.; Lu, W.Q.; Wu, Z.J.; Chen, W.S. A new hydroxyjasmonic acid derivative from Polygonum capitatum. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2017, 53, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.; Zhou, X.; Fu, J.; Hu, T.; Or, P.M.; Feng, R.; He, C.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. Metabolite profiling analysis of FR429, an ellagitannin purified from Polygonum capitatum, in rat and human liver microsomes, cytosol and rat primary hepatocytes in vitro. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 220, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.G.; Zhang, L.J.; Sun, F.; Wang, Z.; He, X.; Wang, A.M.; Li, Y.J.; Huang, Y.; Lan, Y.Y.; Zhang, B.L.; et al. Identification and characterisation of phenolics in Polygonum capitatum by ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection and tandem mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2013, 24, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xie, L.M.; Qiu, L.F.; Wang, J.R.; Ma, S.B.; Jiang, Z.H.; Tang, J.W. Analysis of alcohol extract and water extract of Polygonum capitatum by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Chin. J. Chin. Mat. Med. 2017, 42, 3557–3563. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H.; Xian, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Bai, W.; Zeng, X. Analysis of heterocyclic aromatic amine profiles in Chinese traditional bacon and sausage based on ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-Orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap-HRMS). Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou, E.A.M.; Nguyen, K.H.; Ebele, A.J.; Atia, N.N.; Ali, H.R.H.; Harrad, S. A single run, rapid polarity switching method for determination of 30 pharmaceuticals and personal care products in waste water using Q-Exactive Orbitrap high resolution accurate mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1588, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.X.; Bai, H.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, A.Q. Chemical constituents from Polygonum capitatum. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2011, 23, 262–266. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Wei, S.; Jing, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, A. Development and validation of HPLC coupled with triple quadrupole MS for the simultaneous determination of six phenolic acids, six flavonoids, and a lignan in Polygonum capitatum. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, Y.; Long, Q.; Liao, S. Study on the chemical constituents of the active fraction of Polygonum capitatum. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2012, 35, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Ogwuru, N.; Adamczeski, M. Bioactive natural products derived from Polygonum species of plants: Their structures and mechanisms of action. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2000; Volume 22, pp. 607–642. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.P.; Cao, F.; Yang, X.W. Chemical constituents in aerial parts of Polygonum capitatum. Chin. Tradit. Herb Drug 2013, 44, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.G.; Zhang, L.J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, F.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, A.M.; Huang, Y.; Lan, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.L. Electrospray ionization and collision-induced dissociation tandem mass spectrometric discrimination of polyphenolic glycosides: Exact acylation site determination of the O-acylated monosaccharide residues. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 2483–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; He, Y.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, J.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Zhang, S.; Mo, F. Mechanism underlying Polygonum capitatum effect on Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis based on network pharmacology. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 114, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Yuan, M.; Dong, G.; Luo, P.; Yan, Z. Rapid discrimination of raw and sulfur-fumigated Smilax glabra based on chemical profiles by UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS coupled with multivariate statistical analysis. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Kelm, M.A.; Hammerstone, J.F.; Zhang, Z.; Beecher, G.; Holden, J.; Haytowitz, D.; Prior, R.L. Liquid chromatographic/electrospray ionization mass spectrometric studies of proanthocyanidins in foods. J. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 38, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y.; Teka, T.; Pan, G.; Dou, Z.; Gao, X.; He, J.; Han, L. An effective strategy for distinguishing the processing degree of Polygonum multiflorum based on the analysis of substance and taste by LC-MS, ICP-OES and electronic tongue. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 205, 114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Ma, J.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, Y.; Feng, R.; Chen, Y.C.; Tan, X.S.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, Y.P.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Identification of metabolites of FR429, a potential antitumor ellagitannin, transformed by rat intestinal bacteria in vitro, based on liquid chromatography-ion trap-time of flight mass spectrometry analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 71, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaoka, Y.; Suzuki, S.; Kato, N.; Hayakawa, C.; Kawabe, S.; Ganeko, N.; Uemura, T.; Ito, H. Characterization and Identification of Bioactive Polyphenols in the Trapabispinosa Roxb. Pericarp Extract. Molecules 2021, 26, 5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garazd, Y.L.; Garazd, M.M. Natural dibenzo[b,d]pyran-6-ones: Structural diversity and biological activity. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Sun, W.; Fu, L.; Luo, H.; Lai, D.; Zhou, L. Natural dibenzo-alpha-pyrones and their bioactivities. Molecules 2014, 19, 5088–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davinelli, S.; De Stefani, D.; De Vivo, I.; Scapagnini, G. Polyphenols as caloric restriction mimetics regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and mitophagy. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sang, M.; Liu, E.; Banahene, P.O.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, L.; Gao, X. Rapid profiling and pharmacokinetic studies of major compounds in crude extract from Polygonum multiflorum by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS and UPLC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 140, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Z.; Tan, G.; Li, H.; Mei, Q.; Qian, Z. Analysis of antioxidants in Chrysanthemum indici flos by online gradient extraction and HPLC-FRAP. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 2283–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, J.M.; Morton, L.W.; Puddey, I.B.; Beilin, L.J.; Croft, K.D. Gallic acid metabolites are markers of black tea intake in humans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2276–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, M.; Shi, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Jiang, H.; Wu, J.; Tong, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. In vivo exposure of kaempferol is driven by phase II metabolic enzymes and efflux transporters. AAPS J. 2016, 18, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottone, A.; Masullo, M.; Montoro, P.; Pizza, C.; Piacente, S. HR-LC-ESI-Orbitrap-MS based metabolite profiling of Prunus dulcis Mill. (Italian cultivars Toritto and Avola) husks and evaluation of antioxidant activity. Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Xiong, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Yu, N.; Hu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Tsao, R. Phenolics of green pea (Pisum sativum L.) Hulls, their plasma and urinary metabolites, bioavailability, and in vivo antioxidant activities in a rat model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 11955–11968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.Y.; Zeng, J.X.; Dai, Z.Q.; Chen, M.H.; Ye, M.N.; Yao, Z.H.; Dai, Y.; Yao, X.S. Identification and characterization of chemical constituents in Qi-Lin pills and their metabolites in rat bio-samples after oral administration using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 188, 113402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, G.; van der Hooft, J.J.J.; Crozier, A. A comprehensive evaluation of the [2-(14)C](-)-epicatechin metabolome in rats. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 99, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourino, S.; Perez-Jimenez, J.; Mateos-Martin, M.L.; Fuguet, E.; Vinardell, M.P.; Cascante, M.; Torres, J.L. Metabolites in contact with the rat digestive tract after ingestion of a phenolic-rich dietary fiber matrix. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5955–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas-Barberan, F.A.; Gonzalez-Sarrias, A.; Garcia-Villalba, R.; Nunez-Sanchez, M.A.; Selma, M.V.; Garcia-Conesa, M.T.; Espin, J.C. Urolithins, the rescue of “old” metabolites to understand a “new” concept: Metabotypes as a nexus among phenolic metabolism, microbiota dysbiosis, and host health status. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1500901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Li, Q.; Zhou, B. The tannins from Sanguisorba officinalis L. (Rosaceae): A systematic study on the metabolites of rats based on HPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap MS2 analysis. Molecules 2021, 26, 4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, F.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W. Study of the Treatment Effects of Compound Tufuling Granules in Hyperuricemic Rats Using Serum Metabolomics. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 3458185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).