Euphorbiasteroid Abrogates EGFR and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Impart Anticancer Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
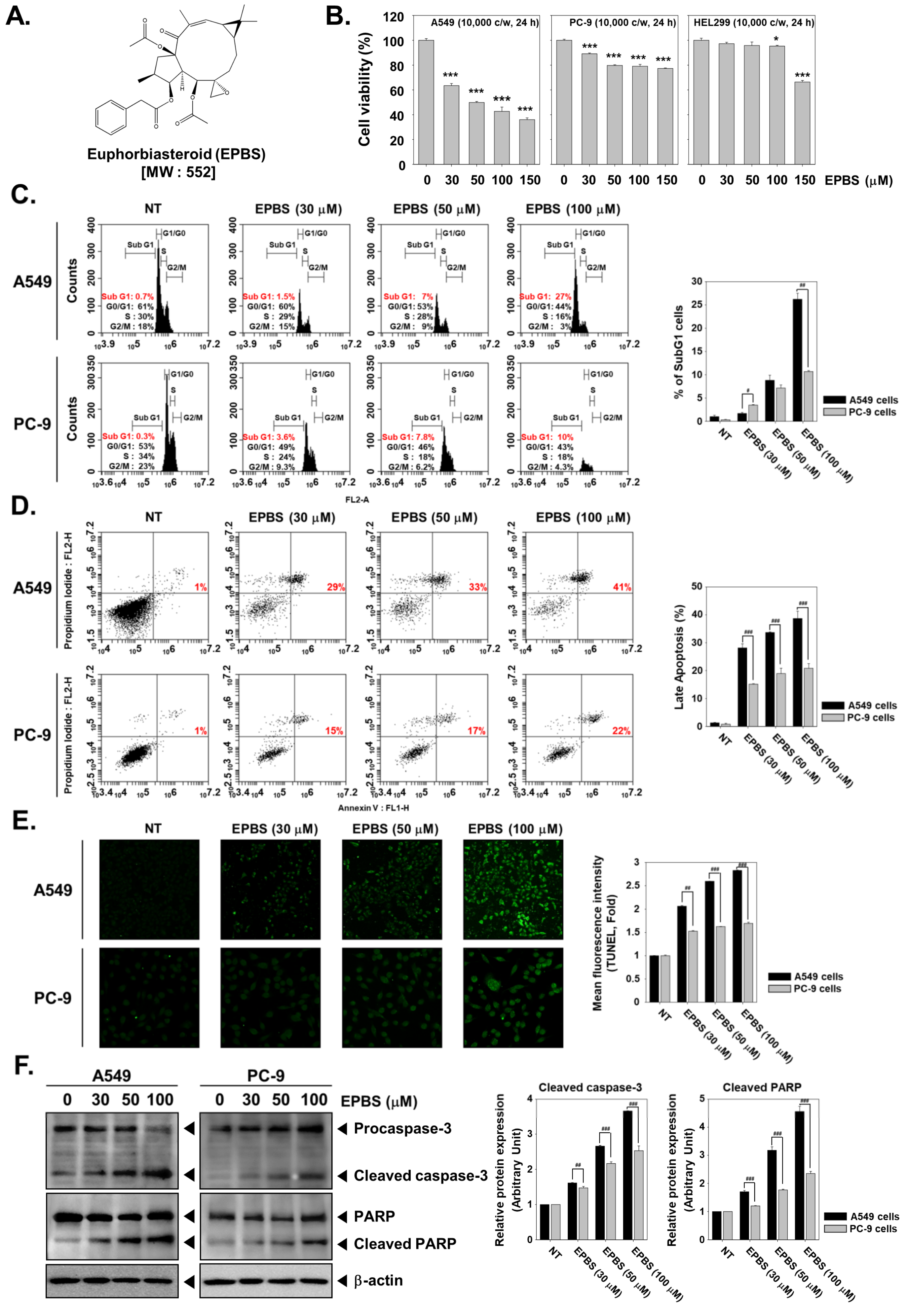
2.1. EPBS Has Preferential Cytotoxicity toward A549 Cells over PC-9 Cells
2.2. EPBS Increases the SubG1 Cell Population in NSCLC Cells
2.3. EPBS Induces Caspase-Mediated Apoptosis in NSCLC Cells
2.4. EPBS Downregulates the Expression of EGFR and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Proteins in NSCLC Cells
2.5. EPBS Modulates the Activity of GSK-3β in NSCLC Cells
2.6. EPBS Decreases the Nuclear Pool of β-Catenin in NSCLC Cells
2.7. EPBS Reverses the Lithium Chloride (LiCl)-Induced Inhibition of GSK-3β in NSCLC Cells
2.8. EPBS Decreases the LiCl Induced Nuclear Localization of β-Catenin in NSCLC Cells
2.9. EPBS Mitigates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Cascade in EGFR-Overexpressing NSCLC Cells
2.10. EPBS Modulates the Activity of GSK-3β in EGFR-Overexpressing NSCLC Cells
2.11. EPBS Modulates the Expression and Activity of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Proteins in EGFR-Knockdown NSCLC Cells
2.12. Overexpression and Knockdown of EGFR Modulates Apoptosis in NSCLC Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Immunocytochemistry for β-Catenin Localization
4.6. Cell-Cycle Analysis
4.7. Annexin/PI Staining Assay
4.8. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-Mediated dUTP Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
4.9. Transfection of pCMV3-EGFR Vector and pCMV-Untagged Vector in A549 Cells
4.10. Transfection of EGFR siRNA and Scrambled siRNA in PC-9 Cells
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- Lee, J.H.; Mohan, C.D.; Basappa, S.; Rangappa, S.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; et al. The IkappaB Kinase Inhibitor ACHP Targets the STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Cells. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ong, P.S.; Wang, L.; Chia, D.M.; Seah, J.Y.; Kong, L.R.; Thuya, W.L.; Chinnathambi, A.; Lau, J.Y.; Wong, A.L.; Yong, W.P.; et al. A novel combinatorial strategy using Seliciclib(®) and Belinostat(®) for eradication of non-small cell lung cancer via apoptosis induction and BID activation. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, T.; Dy, G.K.; Adjei, A.A. Small cell lung cancer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Syn, N.L.; Subhash, V.V.; Any, Y.; Thuya, W.L.; Cheow, E.S.H.; Kong, L.; Yu, F.; Peethala, P.C.; Wong, A.L.; et al. Pan-HDAC inhibition by panobinostat mediates chemosensitization to carboplatin in non-small cell lung cancer via attenuation of EGFR signaling. Cancer Lett. 2018, 417, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberg, A.J.; Ford, J.G.; Samet, J.M. Epidemiology of lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2007, 132, 29s–55s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulunay, O.E.; Hecht, S.S.; Carmella, S.G.; Zhang, Y.; Lemmonds, C.; Murphy, S.; Hatsukami, D.K. Urinary metabolites of a tobacco-specific lung carcinogen in nonsmoking hospitality workers. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedman, D.L.; Whitton, J.; Leisenring, W.; Mertens, A.C.; Hammond, S.; Stovall, M.; Donaldson, S.S.; Meadows, A.T.; Robison, L.L.; Neglia, J.P. Subsequent neoplasms in 5-year survivors of childhood cancer: The Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katanoda, K.; Sobue, T.; Satoh, H.; Tajima, K.; Suzuki, T.; Nakatsuka, H.; Takezaki, T.; Nakayama, T.; Nitta, H.; Tanabe, K.; et al. An association between long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and mortality from lung cancer and respiratory diseases in Japan. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lissowska, J.; Foretova, L.; Dabek, J.; Zaridze, D.; Szeszenia-Dabrowska, N.; Rudnai, P.; Fabianova, E.; Cassidy, A.; Mates, D.; Bencko, V.; et al. Family history and lung cancer risk: International multicentre case-control study in Eastern and Central Europe and meta-analyses. Cancer Causes Control CCC 2010, 21, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, M.S.; Cole, S.R.; Kirk, G.D.; Poole, C. A meta-analysis of the incidence of non-AIDS cancers in HIV-infected individuals. J. Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009, 52, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varela, G.; Thomas, P.A. Surgical management of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 6, S217–S223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackey, A.; Donington, J.S. Surgical Management of Lung Cancer. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 30, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shirvani, S.M.; Jiang, J.; Chang, J.Y.; Welsh, J.W.; Gomez, D.R.; Swisher, S.; Buchholz, T.A.; Smith, B.D. Comparative Effectiveness of Five Treatment Strategies for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Elderly. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, D.H. Locally Advanced, Unresectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: New Treatment Strategies. Chest 2000, 117, 123S–126S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, E., 3rd. Non-small cell lung cancer: Novel treatment strategies. Chest 1997, 112, 266S–268S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarelli, E.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Welsh, J.; Tang, C.; Tsao, A.S. Immunotherapy in lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burotto, M.; Manasanch, E.E.; Wilkerson, J.; Fojo, T. Gefitinib and erlotinib in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of toxicity and efficacy of randomized clinical trials. Oncologist 2015, 20, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köhler, J.; Schuler, M. Afatinib, Erlotinib and Gefitinib in the First-Line Therapy of EGFR Mutation-Positive Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Review. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2013, 36, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) activates nuclear factor-κB through IκBα kinase-independent but EGF receptor-kinase dependent tyrosine 42 phosphorylation of IκBα. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7324–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha-Lima, C.M.; Soares, H.P.; Raez, L.E.; Singal, R. EGFR targeting of solid tumors. Cancer Control 2007, 14, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, L.; Yang, J.; Cao, Z.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, S. Preclinical pharmacodynamic evaluation of drug candidate SKLB-178 in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhuvanalakshmi, G.; Basappa; Rangappa, K.S.; Dharmarajan, A.; Sethi, G.; Kumar, A.P.; Warrier, S. Breast Cancer Stem-Like Cells Are Inhibited by Diosgenin, a Steroidal Saponin, by the Attenuation of the Wnt β-Catenin Signaling via the Wnt Antagonist Secreted Frizzled Related Protein-4. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiremath, I.S.; Goel, A.; Warrier, S.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Garg, M. The multidimensional role of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human malignancies. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 199–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deldar Abad Paskeh, M.; Mirzaei, S.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Sethi, G. Wnt/β-Catenin signaling as a driver of hepatocellular carcinoma progression: An emphasis on molecular pathways. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlange, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Lienhard, S.; Huber, A.; Hynes, N.E. Autocrine WNT signaling contributes to breast cancer cell proliferation via the canonical WNT pathway and EGFR transactivation. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, R63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faivre, E.J.; Lange, C.A. Progesterone Receptors Upregulate Wnt-1 To Induce Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Transactivation and c-Src-Dependent Sustained Activation of Erk1/2 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W.; Cho, K.H. A hidden oncogenic positive feedback loop caused by crosstalk between Wnt and ERK Pathways. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4571–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Civenni, G.; Holbro, T.; Hynes, N.E. Wnt1 and Wnt5a induce cyclin D1 expression through ErbB1 transactivation in HC11 mammary epithelial cells. Embo Rep. 2003, 4, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, M.; Shigematsu, H.; Nakajima, T.; Kubo, R.; Motohashi, S.; Sekine, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Iizasa, T.; Hiroshima, K.; Nakatani, Y.; et al. Synchronous alterations of Wnt and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathways through aberrant methylation and mutation in non small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 6087–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.H.; Ha, I.J.; Lee, S.G.; Um, J.Y.; Ahn, K.S. Abrogation of STAT3 activation cascade by Ginkgolide C mitigates tumourigenesis in lung cancer preclinical model. J. Pharm Pharm. 2021, 73, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.S.; Zhao, L.P.; Huang, Z.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Xu, J.T.; Tai, W.C.; Tsim, K.W.K.; Chen, Y.T.; Xie, T. Ginkgetin derived from Ginkgo biloba leaves enhances the therapeutic effect of cisplatin via ferroptosis-mediated disruption of the Nrf2/HO-1 axis in EGFR wild-type non-small-cell lung cancer. Phytomedicine 2021, 80, 153370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.Y.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Narula, A.S.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.H.; Namjoshi, O.A.; Blough, B.E.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Oxymatrine Attenuates Tumor Growth and Deactivates STAT5 Signaling in a Lung Cancer Xenograft Model. Cancers 2019, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhai, T.; Li, S.; Hu, W.; Li, D.; Leng, S. Potential Micronutrients and Phytochemicals against the Pathogenesis of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Lung Cancer. Nutrients 2018, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.M.; Lee, J.H.; Sethi, G.; Kim, C.; Baek, S.H.; Nam, D.; Chung, W.S.; Kim, S.H.; Shim, B.S.; Ahn, K.S. Bergamottin, a natural furanocoumarin obtained from grapefruit juice induces chemosensitization and apoptosis through the inhibition of STAT3 signaling pathway in tumor cells. Cancer Lett. 2014, 354, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Chiang, S.Y.; Nam, D.; Chung, W.S.; Lee, J.; Na, Y.S.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Capillarisin inhibits constitutive and inducible STAT3 activation through induction of SHP-1 and SHP-2 tyrosine phosphatases. Cancer Lett. 2014, 345, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.M.; Nagulapalli Venkata, K.C.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Potential of neem (Azadirachta indica L.) for prevention and treatment of oncologic diseases. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 40–41, 100–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ahn, K.S.; Kim, C.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Siveen, K.S.; Arfuso, F.; Samym, R.P.; Deivasigamanim, A.; Lim, L.H.; Wang, L.; et al. Nimbolide-Induced Oxidative Stress Abrogates STAT3 Signaling Cascade and Inhibits Tumor Growth in Transgenic Adenocarcinoma of Mouse Prostate Model. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonito, M.C.; Cicala, C.; Marcotullio, M.C.; Maione, F.; Mascolo, N. Biological activity of bicyclic and tricyclic diterpenoids from Salvia species of immediate pharmacological and pharmaceutical interest. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 1934578X1100600839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.F.; Cheng, J.X.; Su, S.Z.; Zhang, C.F.; Akihisa, T.; Manosroi, J.; Manosroi, A.; Feng, F.; Liu, W.Y.; Zhang, J. Limonoids and tricyclic diterpenoids from Azadirachta indica and their antitumor activities. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 100, 103889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Kang, N.S.; Min, Y.K.; Kim, S.H. Euphorbiasteroid reverses P-glycoprotein-mediated multi-drug resistance in human sarcoma cell line MES-SA/Dx5. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Park, J.H.; Han, A.; Davaatseren, M.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Hur, H.J.; Sung, M.J.; Hwang, J.T.; Yang, H.J. Euphorbiasteroid, a component of Euphorbia lathyris L., inhibits adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2015, 33, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, G.; Xia, L.; Chao, Z.; Xia, R.; Meiyan, S.; Guosheng, J. Roles and mechanisms of Fas/FasL in the apoptosis of HL-60 cells induced by euphorbiasteroid. J. Int. Oncol. 2014, 41, 679. [Google Scholar]
- Bharathkumar, H.; Paricharak, S.; Dinesh, K.R.; Siveen, K.S.; Fuchs, J.E.; Rangappa, S.; Mohan, C.D.; Mohandas, N.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation and in silico and in vitro mode-of-action analysis of novel dihydropyrimidones targeting PPAR-γ. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 45143–45146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.Y.; Jung, Y.Y.; Yang, M.H.; Chinnathambi, A.; Govindasamy, C.; Narula, A.S.; Namjoshi, O.A.; Blough, B.E.; Ahn, K.S. Tanshinone IIA exerts autophagic cell death through down-regulation of beta-catenin in renal cell carcinoma cells. Biochimie 2022, 200, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Attri, B.K.; Gill, R.K.; Bariwal, J. Review on EGFR Inhibitors: Critical Updates. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1134–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigismund, S.; Avanzato, D.; Lanzetti, L. Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roskoski, R. Small molecule inhibitors targeting the EGFR/ErbB family of protein-tyrosine kinases in human cancers. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Di Maria, M.V.; Veve, R.; Bremmes, R.M.; Baron, A.E.; Zeng, C.; Franklin, W.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas: Correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and impact on prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3798–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanini, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Vignati, S.; Chine, S.; Lucchi, M.; Silvestri, V.; Mussi, A.; De Placido, S.; Tortora, G.; Bianco, A.R.; et al. Evaluation of epidermal growth factor-related growth factors and receptors and of neoangiogenesis in completely resected stage I-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer: Amphiregulin and microvessel count are independent prognostic indicators of survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 241–249. [Google Scholar]
- Ciardiello, F.; De Vita, F.; Orditura, M.; Tortora, G. The role of EGFR inhibitors in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2004, 16, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Qin, N.; Su, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, J. The prognostic role of EGFR-TKIs for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, C.-H.; Hung, H.-W.; Hung, P.-H.; Shieh, Y.-S. Epidermal growth factor receptor regulates β-catenin location, stability, and transcriptional activity in oral cancer. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, T.; Li, C. Convergence between Wnt-beta-catenin and EGFR signaling in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Pan, Q.; Fuhler, G.M.; Smits, R.; Peppelenbosch, M.P. Action and function of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the progression from chronic hepatitis C to hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamamoto, J.; Yasuda, H.; Aizawa, K.; Nishino, M.; Nukaga, S.; Hirano, T.; Kawada, I.; Naoki, K.; Betsuyaku, T.; Soejima, K. Non-small cell lung cancer PC-9 cells exhibit increased sensitivity to gemcitabine and vinorelbine upon acquiring resistance to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3559–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, M.C.; Wu, M.Y.; Hwang, M.H.; Chang, Y.T.; Huang, H.J.; Lin, A.M.; Yang, J.C. Chloroquine enhances gefitinib cytotoxicity in gefitinib-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.H.; Lee, J.H.; Chang, Y.J.; Tsai, H.H.; Lin, Y.L.; Lin, A.M.; Yang, J.C. MEK inhibitors reverse resistance in epidermal growth factor receptor mutation lung cancer cells with acquired resistance to gefitinib. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.M.; Lee, H.-J.; Jung, J.H.; Sim, D.Y.; Hwang, J.; Park, J.E.; Shim, B.S.; Kim, S.-H. Inhibition of Wnt3a/FOXM1/β-Catenin Axis and Activation of GSK3β and Caspases are Critically Involved in Apoptotic Effect of Moracin D in Breast Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augello, G.; Emma, M.R.; Cusimano, A.; Azzolina, A.; Montalto, G.; McCubrey, J.A.; Cervello, M. The Role of GSK-3 in Cancer Immunotherapy: GSK-3 Inhibitors as a New Frontier in Cancer Treatment. Cells 2020, 9, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, A.; Yoshida, R.; Yamaguchi, R.; Yamauchi, M.; Tamada, Y.; Fujita, A.; Shimamura, T.; Imoto, S.; Higuchi, T.; Nomura, M.; et al. Elevated β-catenin pathway as a novel target for patients with resistance to EGF receptor targeting drugs. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galli, C.; Piemontese, M.; Lumetti, S.; Manfredi, E.; Macaluso, G.M.; Passeri, G. GSK3b-inhibitor lithium chloride enhances activation of Wnt canonical signaling and osteoblast differentiation on hydrophilic titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2013, 24, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Shair, O.H.M.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Farnesol abrogates epithelial to mesenchymal transition process through regulating Akt/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Lee, S.G.; Yang, W.M.; Arfuso, F.; Um, J.Y.; Kumar, A.P.; Bian, J.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Formononetin-induced oxidative stress abrogates the activation of STAT3/5 signaling axis and suppresses the tumor growth in multiple myeloma preclinical model. Cancer Lett. 2018, 431, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baburajeev, C.P.; Dhananjaya Mohan, C.; Ananda, H.; Rangappa, S.; Fuchs, J.E.; Jagadish, S.; Sivaraman Siveen, K.; Chinnathambi, A.; Ali Alharbi, S.; Zayed, M.E.; et al. Development of Novel Triazolo-Thiadiazoles from Heterogeneous “Green” Catalysis as Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B Inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nandeesh, K.N.; Swarup, H.A.; Sandhya, N.C.; Mohan, C.D.; Pavan Kumar, C.S.; Kumara, M.N.; Mantelingu, K.; Ananda, S.; Rangappa, K.S. Synthesis and antiproliferative efficiency of novel bis(imidazol-1-yl)vinyl-1,2,4-oxadiazoles. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 2823–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.T.; Yang, M.H.; Baek, S.H.; Um, J.Y.; Ahn, K.S. Genistin attenuates cellular growth and promotes apoptotic cell death breast cancer cells through modulation of ERalpha signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2020, 263, 118594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.; Kim, S.H.; Sethi, G.; Ahn, K.S. Farnesol inhibits tumor growth and enhances the anticancer effects of bortezomib in multiple myeloma xenograft mouse model through the modulation of STAT3 signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2015, 360, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, N.Y.; Mohan, C.D.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Sethi, G.; Rangappa, K.S.; Ahn, K.S. Euphorbiasteroid Abrogates EGFR and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Impart Anticancer Activity. Molecules 2022, 27, 3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123824
Kim NY, Mohan CD, Chinnathambi A, Alharbi SA, Sethi G, Rangappa KS, Ahn KS. Euphorbiasteroid Abrogates EGFR and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Impart Anticancer Activity. Molecules. 2022; 27(12):3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123824
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Na Young, Chakrabhavi Dhananjaya Mohan, Arunachalam Chinnathambi, Sulaiman Ali Alharbi, Gautam Sethi, Kanchugarakoppal S. Rangappa, and Kwang Seok Ahn. 2022. "Euphorbiasteroid Abrogates EGFR and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Impart Anticancer Activity" Molecules 27, no. 12: 3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123824
APA StyleKim, N. Y., Mohan, C. D., Chinnathambi, A., Alharbi, S. A., Sethi, G., Rangappa, K. S., & Ahn, K. S. (2022). Euphorbiasteroid Abrogates EGFR and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells to Impart Anticancer Activity. Molecules, 27(12), 3824. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123824






