Positron Emission Tomography Radiopharmaceuticals in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Iodine-Related PET Radiopharmaceuticals
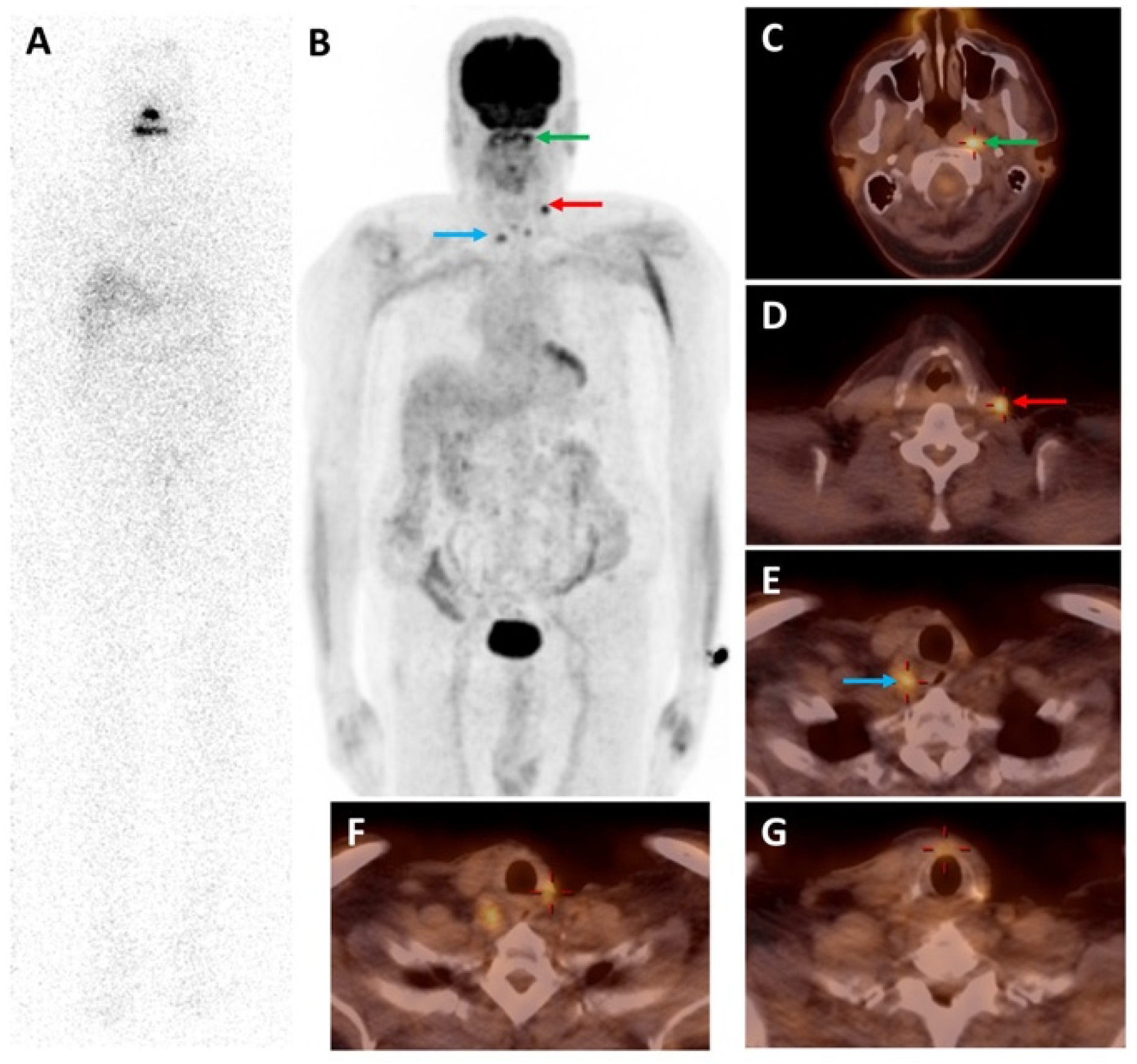
Iodine-124 (124I)
3. Non-Iodine-Related PET Radiopharmaceuticals
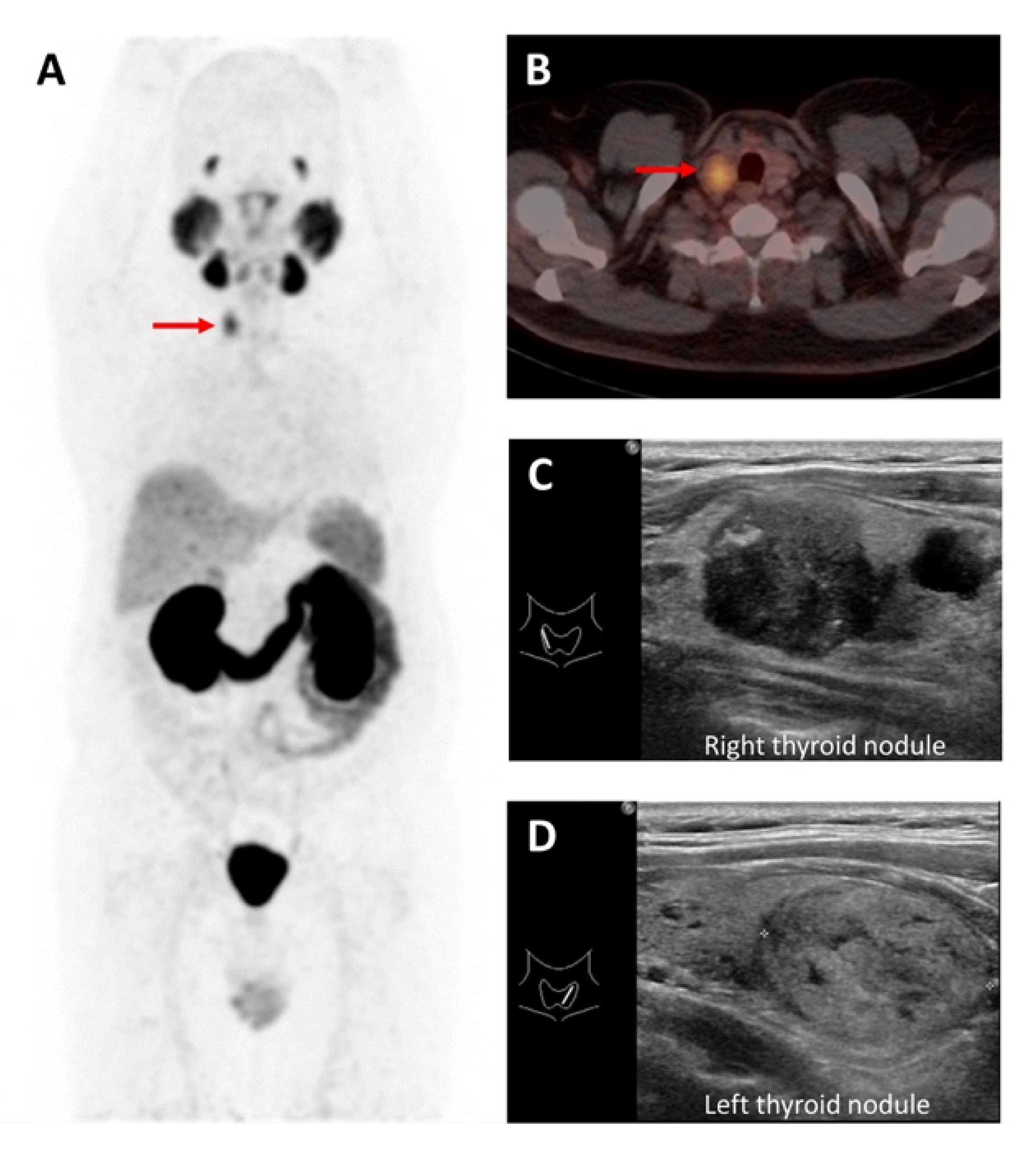
3.1. 18F Tetrafluoroborate ([18F]TFB)
3.2. 2-[18F]Fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose ([18F]FDG)
3.3. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen-Targeting Radiopharmaceuticals
3.4. Somatostatin Receptor-Targeting Radiopharmaceuticals
3.5. Fibroblast Activation Protein-Targeting Radiopharmaceuticals
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haugen, B.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Bible, K.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; Randolph, G.W.; Sawka, A.M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunlap, Q.; Davies, L. Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Incidence. In Surgery of the Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 174–180.e2. ISBN 978-0-323-66127-0. [Google Scholar]
- Seib, C.D.; Sosa, J.A. Evolving Understanding of the Epidemiology of Thyroid Cancer. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SEER*Explorer Surveillance Research Program, National Cancer Institute. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/application.html (accessed on 11 June 2022).
- O’Malley, J.P.; Ziessman, H.A. Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging: The Requisites, 5th ed.; Elsevier Inc: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-323-53037-8. [Google Scholar]
- Glazer, D.I.; Brown, R.K.J.; Wong, K.K.; Savas, H.; Gross, M.D.; Avram, A.M. SPECT/CT Evaluation of Unusual Physiologic Radioiodine Biodistributions: Pearls and Pitfalls in Image Interpretation. RadioGraphics 2013, 33, 397–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascini, G.L.; Niccoli Asabella, A.; Notaristefano, A.; Restuccia, A.; Ferrari, C.; Rubini, D.; Altini, C.; Rubini, G. 124Iodine: A Longer-Life Positron Emitter Isotope—New Opportunities in Molecular Imaging. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 672094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahajan, S.; Divgi, C.R. The Role of Iodine-124 Positron Emission Tomography in Molecular Imaging. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2016, 4, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampella, E.; Klain, M.; Pace, L.; Cuocolo, A. PET/CT in the Management of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2021, 102, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avram, A.M.; Giovanella, L.; Greenspan, B.; Lawson, S.A.; Luster, M.; Van Nostrand, D.; Peacock, J.G.; Ovčariček, P.P.; Silberstein, E.; Tulchinsky, M.; et al. SNMMI Procedure Standard/EANM Practice Guideline for Nuclear Medicine Evaluation and Therapy of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Abbreviated Version. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 15N–35N. [Google Scholar]
- Klain, M.; Zampella, E.; Nappi, C.; Nicolai, E.; Ambrosio, R.; Califaretti, E.; Lamartina, L.; Schlumberger, M.; Deandreis, D.; Salvatore, D.; et al. Advances in Functional Imaging of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Plyku, D.; Kulkarni, K.; Garcia, C.; Atkins, F.; Tefera, E.; Burman, K.D.; Wartofsky, L.; Van Nostrand, D. Optimal Time for 124I PET/CT Imaging in Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhlmann, M.; Jentzen, W.; Ruhlmann, V.; Pettinato, C.; Rossi, G.; Binse, I.; Bockisch, A.; Rosenbaum-Krumme, S. High Level of Agreement between Pretherapeutic 124I PET and Intratherapeutic 131I Imaging in Detecting Iodine-Positive Thyroid Cancer Metastases. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Nostrand, D.; Moreau, S.; Bandaru, V.V.; Atkins, F.; Chennupati, S.; Mete, M.; Burman, K.; Wartofsky, L. 124I Positron Emission Tomography Versus 131I Planar Imaging in the Identification of Residual Thyroid Tissue and/or Metastasis in Patients Who Have Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2010, 20, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorjekar, G.R.; Van Nostrand, D.; Garcia, C.; O’Neil, J.; Moreau, S.; Atkins, F.B.; Mete, M.; Orquiza, M.H.; Burman, K.; Wartofsky, L. Do Negative 124I Pretherapy Positron Emission Tomography Scans in Patients with Elevated Serum Thyroglobulin Levels Predict Negative 131I Posttherapy Scans? Thyroid 2014, 24, 1394–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phan, H.T.T.; Jager, P.L.; Paans, A.M.J.; Plukker, J.T.M.; Sturkenboom, M.G.G.; Sluiter, W.J.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.R.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Links, T.P. The Diagnostic Value of 124I-PET in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capoccetti, F.; Criscuoli, B.; Rossi, G.; Ferretti, F.; Manni, C.; Brianzoni, E. The Effectiveness of 124I PET/CT in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 53, 536–545. [Google Scholar]
- De Pont, C.; Halders, S.; Bucerius, J.; Mottaghy, F.; Brans, B. 124I PET/CT in the Pretherapeutic Staging of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Comparison with Posttherapy 131I SPECT/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulec, S.A.; Kuker, R.A.; Goryawala, M.; Fernandez, C.; Perez, R.; Khan-Ghany, A.; Apaza, A.; Harja, E.; Harrell, M. 124I PET/CT in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Clinical and Quantitative Image Analysis. Thyroid 2016, 26, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kist, J.W.; de Keizer, B.; van der Vlies, M.; Brouwers, A.H.; Huysmans, D.A.; van der Zant, F.M.; Hermsen, R.; Stokkel, M.P.M.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Vogel, W.V. 124I PET/CT to Predict the Outcome of Blind 131I Treatment in Patients with Biochemical Recurrence of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Results of a Multicenter Diagnostic Cohort Study (THYROPET). J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, B.Z.Y.; Dickie, G.; Garcia, P.; Scott, D.; Pattison, D.A. 124I-PET/CT–Guided Diagnosis and Personalized Treatment of Metastatic Papillary Thyroid Cancer to the Pancreas. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, M.; Binse, I.; Nagarajah, J.; Bockisch, A.; Herrmann, K.; Jentzen, W. The Role of 124I PET/CT Lesion Dosimetry in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 63, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhanam, P.; Taieb, D.; Solnes, L.; Marashdeh, W.; Ladenson, P.W. Utility of I-124 PET/CT in Identifying Radioiodine Avid Lesions in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 86, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobson, O.; Kiesewetter, D.O.; Chen, X. Fluorine-18 Radiochemistry, Labeling Strategies and Synthetic Routes. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Doherty, J.; Jauregui-Osoro, M.; Brothwood, T.; Szyszko, T.; Marsden, P.K.; O’Doherty, M.J.; Cook, G.J.R.; Blower, P.J.; Lewington, V. 18F-Tetrafluoroborate, a PET Probe for Imaging Sodium/Iodide Symporter Expression: Whole-Body Biodistribution, Safety, and Radiation Dosimetry in Thyroid Cancer Patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1666–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khoshnevisan, A.; Jauregui-Osoro, M.; Shaw, K.; Torres, J.B.; Young, J.D.; Ramakrishnan, N.K.; Jackson, A.; Smith, G.E.; Gee, A.D.; Blower, P.J. [18F]Tetrafluoroborate as a PET Tracer for the Sodium/Iodide Symporter: The Importance of Specific Activity. EJNMMI Res. 2016, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dittmann, M.; Gonzalez Carvalho, J.M.; Rahbar, K.; Schäfers, M.; Claesener, M.; Riemann, B.; Seifert, R. Incremental Diagnostic Value of [18F]Tetrafluoroborate PET-CT Compared to [131I]Iodine Scintigraphy in Recurrent Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 2639–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Samnick, S.; Al-Momani, E.; Schmid, J.-S.; Mottok, A.; Buck, A.K.; Lapa, C. Initial Clinical Investigation of [18F]Tetrafluoroborate PET/CT in Comparison to [124I]Iodine PET/CT for Imaging Thyroid Cancer. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2018, 43, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S. Review of 18F-FDG Synthesis and Quality Control. Biomed. Imaging Interv. J. 2006, 2, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, E.K.J.; Coumou, A.W.; Kostkiewicz, M.; Kairemo, K. [18F]Fluoro-2-Deoxy-D-Glucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Imaging in Oncology: Initial Staging and Evaluation of Cancer Therapy. Med. Princ. Pract. 2013, 22, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, V.; McCook, B.M.; Torok, F.S. An Introduction to PET-CT Imaging. RadioGraphics 2004, 24, 523–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feine, U.; Lietzenmayer, R.; Hanke, J.P.; Held, J.; Wöhrle, H.; Müller-Schauenburg, W. Fluorine-18-FDG and Iodine-131-Iodide Uptake in Thyroid Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 1996, 37, 1468–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Bongiovanni, M.; Paone, G.; Ceriani, L.; Pusztaszeri, M. Cellular and Molecular Basis for Thyroid Cancer Imaging in Nuclear Medicine. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2013, 1, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heydarzadeh, S.; Moshtaghie, A.A.; Daneshpoor, M.; Hedayati, M. Regulators of Glucose Uptake in Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelleira, E.; García Falcone, M.G.; Bueno, F.; Pitoia, F. Role of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer with Biochemical Incomplete or Indeterminate Response to Treatment. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2020, 67, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qichang, W.; Lin, B.; Gege, Z.; Youjia, Z.; Qingjie, M.; Renjie, W.; Bin, J. Diagnostic Performance of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in DTC Patients with Thyroglobulin Elevation and Negative Iodine Scintigraphy: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, R.; Bastos, C.R.G.; de Oliveira, I.A.G.; da Silva, R.M.; Fortes, C.P.D.D.; Pepe, V.L.E.; Reis, L.G.; Braga, J.U. Accuracy of Positron Emission Tomography and Positron Emission Tomography-CT in the Detection of Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Recurrence with Negative 131I Whole-Body Scan Results: A Meta-Analysis: PET and PET-CT in the Detection of Recurrent Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Head Neck 2016, 38, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrachimis, A.; Burg, M.C.; Wenning, C.; Allkemper, T.; Weckesser, M.; Schäfers, M.; Stegger, L. [18F]FDG PET/CT Outperforms [18F]FDG PET/MRI in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dai, H.; Li, Q.; Shen, G.; Shi, L.; Tian, R. Investigating 18F-FDG PET/CT Parameters as Prognostic Markers for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 648658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, D.; Dondi, F.; Mazzoletti, A.; Bellini, P.; Rodella, C.; Bertagna, F. Prognostic Role of 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT Metabolic Volume Parameters in Patients Affected by Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma with High Thyroglobulin Level, Negative 131I WBS and Positive 2-[18F]-FDG PET/CT. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. The Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the Follow-up of Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer with Negative Thyroglobulin but Positive and/or Elevated Antithyroglobulin Antibody. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2016, 37, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-J.; Lee, S.-W.; Pak, K.; Shim, S.-R. Diagnostic Performance of PET in Thyroid Cancer with Elevated Anti-Tg Ab. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, E.; Aras, G.; Kucuk, N.O. Correlation of 18F-FDG PET/CT Findings with Histopathological Results in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients Who Have Increased Thyroglobulin or Antithyroglobulin Antibody Levels and Negative 131I Whole-Body Scan Results. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2013, 38, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, E.; Soydal, C.; Araz, M.; Aras, G.; Ibis, E. The Additive Clinical Value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Defining the Recurrence of Disease in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Who Have Isolated Increased Antithyroglobulin Antibody Levels. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 37, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Leijer, J.F.; Metman, M.J.H.; van der Hoorn, A.; Brouwers, A.H.; Kruijff, S.; van Hemel, B.M.; Links, T.P.; Westerlaan, H.E. Focal Thyroid Incidentalomas on 18F-FDG PET/CT: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Prevalence, Risk of Malignancy and Inconclusive Fine Needle Aspiration. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 723394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccardo, A.; Puntoni, M.; Bertagna, F.; Treglia, G.; Foppiani, L.; Arecco, F.; Giubbini, R.; Naseri, M.; Cistaro, A.; Cabria, M.; et al. 18F-FDG Uptake as a Prognostic Variable in Primary Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Incidentally Detected by PET/CT: A Multicentre Study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 1482–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presotto, L.; Bettinardi, V.; De Bernardi, E.; Belli, M.L.; Cattaneo, G.M.; Broggi, S.; Fiorino, C. PET Textural Features Stability and Pattern Discrimination Power for Radiomics Analysis: An “Ad-Hoc” Phantoms Study. Phys. Med. 2018, 50, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherghe, M.; Lazar, A.M.; Mutuleanu, M.-D.; Stanciu, A.E.; Martin, S. Radiomics Analysis of [18F]FDG PET/CT Thyroid Incidentalomas: How Can It Improve Patients’ Clinical Management? A Systematic Review from the Literature. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciappuccini, R.; Saguet-Rysanek, V.; Giffard, F.; Licaj, I.; Dorbeau, M.; Clarisse, B.; Poulain, L.; Bardet, S. PSMA Expression in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Association with Radioiodine, 18FDG Uptake, and Patient Outcome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 3536–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhn-Heath, C.; Salavati, A.; Behr, S.C.; Rowe, S.P.; Calais, J.; Fendler, W.P.; Eiber, M.; Emmett, L.; Hofman, M.S.; Hope, T.A. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen PET in Prostate Cancer. Radiology 2021, 299, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martiniova, L.; De Palatis, L.; Etchebehere, E.; Ravizzini, G. Gallium-68 in Medical Imaging. Curr. Radiopharm. 2016, 9, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennrich, U.; Eder, M. [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11: The First FDA-Approved 68Ga-Radiopharmaceutical for PET Imaging of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourni, E.; Henriksen, G. Metal-Based PSMA Radioligands. Molecules 2017, 22, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Basuli, F.; Phelps, T.E.; Zhang, X.; Woodroofe, C.C.; Roy, J.; Choyke, P.L.; Swenson, R.E.; Jagoda, E.M. Fluorine-18 Labeled Urea-Based Ligands Targeting Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) with Increased Tumor and Decreased Renal Uptake. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bychkov, A.; Vutrapongwatana, U.; Tepmongkol, S.; Keelawat, S. PSMA Expression by Microvasculature of Thyroid Tumors—Potential Implications for PSMA Theranostics. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmani, S.; Al-Turkait, D.; Al-Kandari, F.; Ahmed, N. Thyroid Cancer Detected on 68Ga-PMSA PET/CT. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2021, 71, 1511–1512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Horneman, R.; Nagra, N.K. More than the Prostate: Intrapancreatic Accessory Spleen and Papillary Thyroid Cancer Detected with 18F-PSMA PET/CT. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 21, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhn-Heath, C.; Yom, S.S.; Liu, C.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Aslam, M.; Smith, R.; Narwal, M.; Juarez, R.; Behr, S.C.; Pampaloni, M.H.; et al. Gallium-68 Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen ([68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11) PET for Imaging of Thyroid Cancer: A Feasibility Study. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitalua-Cortes, Q.; García-Perez, F.O.; Vargas-Ahumada, J.; Gonzalez-Rueda, S.; Gomez-Argumosa, E.; Ignacio-Alvarez, E.; Soldevilla-Gallardo, I.; Torres-Agredo, L. Head-to-Head Comparison of 68Ga-PSMA-11 and 131I in the Follow-Up of Well-Differentiated Metastatic Thyroid Cancer: A New Potential Theragnostic Agent. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 794759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alçın, G.; Arslan, E.; Aksoy, T.; Çermik, T.F. 68Ga-PSMA Uptake in a Radioiodine-Refractory Metastatic Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patient. Rev. Esp. Med. Nucl. Imagen Mol. 2021, 41, S42–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Malhotra, G.; Meshram, V.; Chandak, A.; Sonavane, S.; Lila, A.R.; Bandgar, T.R.; Asopa, R.V. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Expression in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer with Thyroglobulin Elevation and Negative Iodine Scintigraphy Using 68Ga-PSMA-HBED-CC PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, e406–e409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, L.H.; Lodewijk, L.; Braat, A.J.A.T.; Krijger, G.C.; Valk, G.D.; Lam, M.G.E.H.; Borel Rinkes, I.H.M.; Vriens, M.R.; de Keizer, B. 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT in Radioactive Iodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and First Treatment Results with 177Lu-PSMA-617. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.S.; Windhorst, A.D.; Zeglis, B.M. (Eds.) Radiopharmaceutical Chemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-3-319-98946-4. [Google Scholar]
- Johnbeck, C.B.; Knigge, U.; Kjær, A. PET Tracers for Somatostatin Receptor Imaging of Neuroendocrine Tumors: Current Status and Review of the Literature. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 2259–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klagge, A.; Krause, K.; Schierle, K.; Steinert, F.; Dralle, H.; Fuhrer, D. Somatostatin Receptor Subtype Expression in Human Thyroid Tumours. Horm. Metab. Res. 2010, 42, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazaitou-Panayiotou, K.; Tiensuu Janson, E.; Koletsa, T.; Kotoula, V.; Stridsberg, M.; Karkavelas, G.; Karayannopoulou, G. Somatostatin Receptor Expression in Non-Medullary Thyroid Carcinomas. Hormones 2012, 11, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, M.; Demirci, E.; Kabasakal, L.; Aygun, A.; Tutar, R.O.; Araman, A.; Kanmaz, B. Evaluation and Comparison of Ga-68 DOTA-TATE and Ga-68 DOTA-NOC PET/CT Imaging in Well-Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2013, 34, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodei, L.; Mueller-Brand, J.; Baum, R.P.; Pavel, M.E.; Hörsch, D.; O’Dorisio, M.S.; O’Dorisio, T.M.; Howe, J.R.; Cremonesi, M.; Kwekkeboom, D.J.; et al. Erratum to: The Joint IAEA, EANM, and SNMMI Practical Guidance on Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRNT) in Neuroendocrine Tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 41, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosberg, J.; El-Haddad, G.; Wolin, E.; Hendifar, A.; Yao, J.; Chasen, B.; Mittra, E.; Kunz, P.L.; Kulke, M.H.; Jacene, H.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of 177Lu-Dotatate for Midgut Neuroendocrine Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.Y.; Kim, Y. Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy in Patients with Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2020, 45, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesel, F.L.; Kratochwil, C.; Lindner, T.; Marschalek, M.M.; Loktev, A.; Lehnert, W.; Debus, J.; Jäger, D.; Flechsig, P.; Altmann, A.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Biodistribution and Preliminary Dosimetry Estimate of 2 DOTA-Containing FAP-Targeting Agents in Patients with Various Cancers. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kratochwil, C.; Flechsig, P.; Lindner, T.; Abderrahim, L.; Altmann, A.; Mier, W.; Adeberg, S.; Rathke, H.; Röhrich, M.; Winter, H.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Tracer Uptake in 28 Different Kinds of Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindner, T.; Giesel, F.L.; Kratochwil, C.; Serfling, S.E. Radioligands Targeting Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP). Cancers 2021, 13, 5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Pu, Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, C.; Yang, F.; Pu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y. FAPI-PET/CT in Cancer Imaging: A Potential Novel Molecule of the Century. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 854658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Sun, L.; Wu, H.; Guo, W.; Qiu, S.; Chen, H. 68Ga Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor PET/CT in the Detection of Metastatic Thyroid Cancer: Comparison with 18F-FDG PET/CT. Radiology 2022, 304, 212430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Yao, S.; Miao, W. 68Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT Imaging in Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (RR-DTC) Patients. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2022, 36, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ou, L.; Zhang, C. Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in Metastases of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocrine 2021, 73, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Fu, J.; Huang, J.; Pang, Y.; Chen, H. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT Versus 18F-FDG PET/CT for Detecting Metastatic Lesions in a Case of Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Moon, E.S.; Roesch, F.; Kumari, S.; Agarwal, S.; Tripathi, M.; Sahoo, R.K.; Mangu, B.S.; Tupalli, A.; et al. Novel Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor-Based Targeted Theranostics for Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients: A Pilot Study. Thyroid 2021, 32, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakulpisuti, C.; Charoenphun, P.; Chamroonrat, W. Positron Emission Tomography Radiopharmaceuticals in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Molecules 2022, 27, 4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154936
Sakulpisuti C, Charoenphun P, Chamroonrat W. Positron Emission Tomography Radiopharmaceuticals in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Molecules. 2022; 27(15):4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154936
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakulpisuti, Chaninart, Putthiporn Charoenphun, and Wichana Chamroonrat. 2022. "Positron Emission Tomography Radiopharmaceuticals in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer" Molecules 27, no. 15: 4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154936
APA StyleSakulpisuti, C., Charoenphun, P., & Chamroonrat, W. (2022). Positron Emission Tomography Radiopharmaceuticals in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Molecules, 27(15), 4936. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154936




