Neuroprotection of Cannabidiol, Its Synthetic Derivatives and Combination Preparations against Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Neurological Disorders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Effects of CBD on Neurological Disorders via Inhibiting Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation
2.1. Epilepsy
2.2. Multiple Sclerosis
2.3. Hypoxia Ischemia
2.4. Schizophrenia
2.5. Neuropathic Pain
2.6. Alzheimer’s Disease
3. Mechanisms of Action of CBD on Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammatory Genes and Pathways
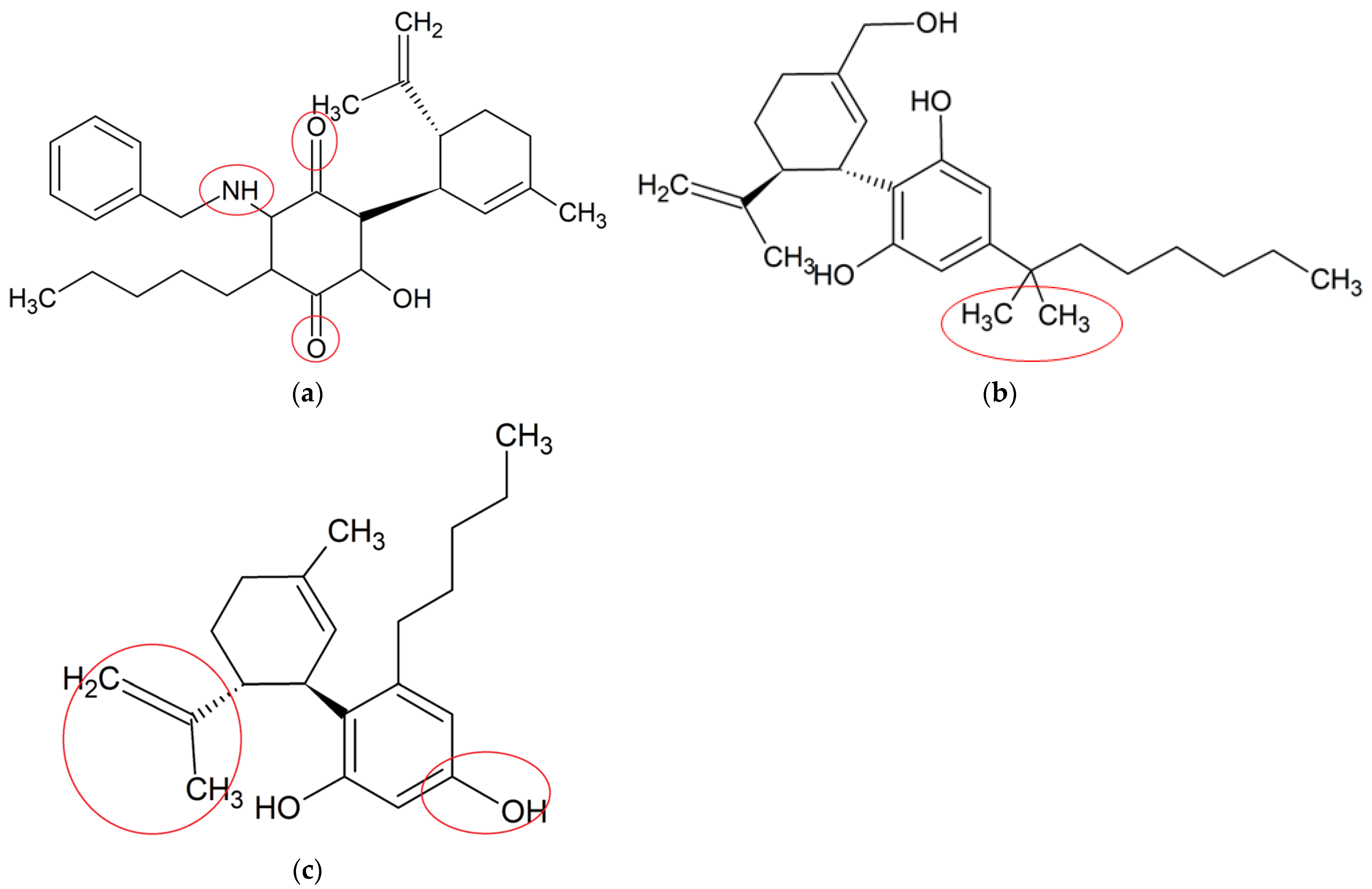
4. Neuroprotective Effects of Synthetic CBD Derivatives in Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation
| CBD Derivative | In Vitro/In Vivo Model | Key Findings | Pathways | Potential Targeted Disease/Therapeutic Potentials | Molecular Formula |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCE-004.8 [68] | MOG-induced EAE and TMEV-IDD in C57BL/6; LPS-induced BV-2 microglia and RAW264.7 cells | Ameliorated demyelination, axonal damage and neuroinflammation | Upregulated expressions of VEGFA and erythropoietin genes, reduced phenotype polarization, inhibited PGE2 and COX-2 pathways | MS | C28H35NO3 |
| Dimethylheptyl- cannabidiol (DMH-CBD) [72] | LPS-induced BV-2 microglia | Decreased proinflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress-related genes | Downregulated the expressions of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6; upregulated the expressions Trb3, p8, Slc7a11/xCT, Atf4, Hmox1 and Chop | Not specified | C25H38O2 |
| Abn-CBD [73] | LPS-activated astrocytic-microglial cocultures and astrocytic mono-culture | Reduced glial neuroinflammation and promoted astrocytic scar formation | Reduced productions of TNF-α and NO | Not specified | C21H30O2 |
5. Enhanced Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effects of CBD in Combination with Other Compounds
5.1. CBD in Combination with THC against MS
5.2. CBD in Combination with Beta-Caryophyllene against Ischemia
5.3. Enhanced Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effects of CBD in Combination with Dihydroartemisinin
| Combination Preparations of CBD | In Vitro/In Vivo Model | Key Findings | Modulated Neuroinflammatory Mediators | Potential Targeted Disease/Therapeutic Potentials |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBD-THC [74] | MOG-induced EAE in C57BL/6 female mice | Decreased neuroinflammation in murine EAE | Modulated the expression of miRNAs-mediated signalling pathways. Reduced CD4+ T cells, IL-6, IL-17, IL-1β, TBX21 and INF- γ, increased IL-4, IL-10, TGF-β, STAT5b and FoxP3 | MS |
| CBD-THC [75] | MOG-induced EAE in C57BL/6 female mice | Attenuated EAE severity and reduced neuroinflammation | Decreased the levels of IFN-γ and IL-17, increased the levels of TGF-β and IL-10, modulated gut microbiota | MS |
| CBD-BCP [77] | Photothrombosis-induced permanent ischemia in C57B/6 male mice | Improved motor performance, reduced infarct size, modulated microglial activation | Not determined | Permanent ischemia |
| CBD-DHA conjugation [79] | LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglia | Blocked neuroinflammation, eliminated neurotoxicity, improved therapeutic index | Inhibited NF-kB, IL-1β, iNOS and NO | Not specified |
6. Discussions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joy, E. A Prospective on the Biological Disease of Neurological & Psychiatric Disorders in Young people. J. Mult. Scler. 2021, 8, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chayasirisobhon, S. The Role of Cannabidiol in Neurological Disorders. Perm. J. 2021, 25, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Kim, B.S.; Im, H.I. Pathophysiological Role of Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Psychiatric Disorders. Int. Neurourol. J. 2016, 20, S2–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraju, S.; Zakaria, R.; Karuppan, M.K.M.; Al-Rahbi, B. The Role of Neuroinflammation in Cellular Damage in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 9231452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, J.; Nutma, E.; van der Valk, P.; Amor, S. Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology 2018, 154, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cervellati, C.; Trentini, A.; Pecorelli, A.; Valacchi, G. Inflammation in Neurological Disorders, The Thin Boundary Between Brain and Periphery. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 33, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, D.; Roth, T.L.; McGavern, D.B. Microglia development and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 367–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subhramanyam, C.S.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Dheen, S.T. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 94, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craft, J.M.; Watterson, D.M.; Van Eldik, L.J. Neuroinflammation: A potential therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2005, 9, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakan, Z. Cannabis, a complex plant: Different compounds and different effects on individuals. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 2, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, D.; Dai, K.; Xie, Z.; Chen, J. Secondary Metabolites Profiled in Cannabis Inflorescences, Leaves, Stem Barks, and Roots for Medicinal Purposes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, P.; Reggio, P.H.; Jagerovic, N. An Overview on Medicinal Chemistry of Synthetic and Natural Derivatives of Cannabidiol. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andre, C.M.; Hausman, J.F.; Guerriero, G. Cannabis sativa, The Plant of the Thousand and One Molecules. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mechoulam, R.; Shvo, Y.; Hashish, I. The structure of cannabidiol. Tetrahedron 1963, 19, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burstein, S. Cannabidiol (CBD) and its analogs: A review of their effects on inflammation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalay, S.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Cannabidiol. Antioxidants 2019, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGregor, I.S.; Cairns, E.A.; Abelev, S.; Cohen, R.; Henderson, M.; Couch, D.; Arnold, J.C.; Gauld, N. Access to cannabidiol without a prescription, A cross-country comparison and analysis. Int. J. Drug Policy 2020, 85, 102935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, L.; Arruza, L.; Rodríguez, M.J.; Aleo, E.; Vierge, E.; Criado, E.; Sobrino, E.; Vargas, C.; Ceprián, M.; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, A.; et al. Neuroprotection by cannabidiol and hypothermia in a piglet model of newborn hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology 2019, 146, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.C.; Fogaça, M.V.; Sonego, A.B.; Guimarães, F.S. Cannabidiol, neuroprotection and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 112, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, C.J.; Curran, H.V. Effects of cannabidiol on schizophrenia-like symptoms in people who use cannabis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2008, 192, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.C.; Fogaça, M.V.; Scarante, F.F.; Joca, S.R.L.; Sales, A.J.; Gomes, F.V.; Sonego, A.B.; Rodrigues, N.S.; Galve-Roperh, I.; Guimarães, F.S. Plastic and Neuroprotective Mechanisms Involved in the Therapeutic Effects of Cannabidiol in Psychiatric Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D.M.; Singh, N.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Cannabidiol Attenuates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Model of Multiple Sclerosis Through Induction of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, F.J.; Lafuente, H.; Rey-Santano, M.C.; Mielgo, V.E.; Gastiasoro, E.; Rueda, M.; Pertwee, R.G.; Castillo, A.I.; Romero, J.; Martínez-Orgado, J. Neuroprotective effects of the nonpsychoactive cannabinoid cannabidiol in hypoxic-ischemic newborn piglets. Pediatr. Res. 2008, 64, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Valdepeñas, L.; Martínez-Orgado, J.A.; Benito, C.; Millán, A.; Tolón, R.M.; Romero, J. Cannabidiol reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced vascular changes and inflammation in the mouse brain: An intravital microscopy study. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schiavon, A.P.; Soares, L.M.; Bonato, J.M.; Milani, H.; Guimarães, F.S.; Weffort de Oliveira, R.M. Protective effects of cannabidiol against hippocampal cell death and cognitive impairment induced by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in mice. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 26, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozela, E.; Lev, N.; Kaushansky, N.; Eilam, R.; Rimmerman, N.; Levy, R.; Ben-Nun, A.; Juknat, A.; Vogel, Z. Cannabidiol inhibits pathogenic T cells, decreases spinal microglial activation and ameliorates multiple sclerosis-like disease in C57BL/6 mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ben-Shabat, S.; Hanus, L.O.; Katzavian, G.; Gallily, R. New cannabidiol derivatives: Synthesis, binding to cannabinoid receptor, and evaluation of their antiinflammatory activity. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, S.E. An update on PPAR activation by cannabinoids. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Victor, T.R.; Hage, Z.; Tsirka, S.E. Prophylactic administration of cannabidiol reduces microglial inflammatory response to kainate-induced seizures and neurogenesis. Neuroscience, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Assis Lima, I.V.; Bellozi, P.M.Q.; Batista, E.M.; Vilela, L.R.; Brandão, I.L.; Ribeiro, F.M.; Moraes, M.F.D.; Moreira, F.A.; de Oliveira, A.C.P. Cannabidiol anticonvulsant effect is mediated by the PI3Kγ pathway. Neuropharmacology 2020, 176, 108156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjadian, M.; Ragerdi Kashani, I.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Hassani, M.; Omidi, A.; Takzare, N.; Clarner, T.; Beyer, C.; Zendedel, A. Protective effects of cannabidiol on cuprizone-induced demyelination in C57BL/6 mice. J. Contemp. Med. Sci. 2017, 3, 278–283. [Google Scholar]
- Mecha, M.; Feliú, A.; Iñigo, P.M.; Mestre, L.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.J.; Guaza, C. Cannabidiol provides long-lasting protection against the deleterious effects of inflammation in a viral model of multiple sclerosis: A role for A2A receptors. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 59, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceprián, M.; Jiménez-Sánchez, L.; Vargas, C.; Barata, L.; Hind, W.; Martínez-Orgado, J. Cannabidiol reduces brain damage and improves functional recovery in a neonatal rat model of arterial ischemic stroke. Neuropharmacology 2017, 116, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.V.; Llorente, R.; Del Bel, E.A.; Viveros, M.P.; López-Gallardo, M.; Guimarães, F.S. Decreased glial reactivity could be involved in the antipsychotic-like effect of cannabidiol. Schizophr. Res. 2015, 164, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kong, W.; Chambers, C.R.; Yu, D.; Ganea, D.; Tuma, R.F.; Ward, S.J. The non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid cannabidiol (CBD) attenuates pro-inflammatory mediators, T cell infiltration, and thermal sensitivity following spinal cord injury in mice. Cell Immunol. 2018, 329, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Moreno, A.M.; Reigada, D.; Ramírez, B.G.; Mechoulam, R.; Innamorato, N.; Cuadrado, A.; de Ceballos, M.L. Cannabidiol and other cannabinoids reduce microglial activation in vitro and in vivo: Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 79, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozela, E.; Pietr, M.; Juknat, A.; Rimmerman, N.; Levy, R.; Vogel, Z. Cannabinoids Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol differentially inhibit the lipopolysaccharide-activated NF-kappaB and interferon-beta/STAT proinflammatory pathways in BV-2 microglial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Chen, N.; Liu, Y.; Godlewski, G.; Kaplan, H.J.; Shrader, S.H.; Song, Z.H.; Shao, H. Studies of involvement of G-protein coupled receptor-3 in cannabidiol effects on inflammatory responses of mouse primary astrocytes and microglia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos-Santos-Pereira, M.; Guimarães, F.S.; Del-Bel, E.; Raisman-Vozari, R.; Michel, P.P. Cannabidiol prevents LPS-induced microglial inflammation by inhibiting ROS/NF-κB-dependent signaling and glucose consumption. Glia 2020, 68, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Garcia, C.; Zeleke, H.; Rojas, A. Impact of Stress on Epilepsy, Focus on Neuroinflammation—A Mini Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhanova, E.D.; Kozlov, A.A.; Litovchenko, A.V. Mechanisms of drug resistance in the pathogenesis of epilepsy: Role of neuroinflammation. A literature review. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Balosso, S.; Ravizza, T. Neuroinflammatory pathways as treatment targets and biomarkers in epilepsy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pracucci, E.; Pillai, V.; Lamers, D.; Parra, R.; Landi, S. Neuroinflammation, A Signature or a Cause of Epilepsy? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billakota, S.; Devinsky, O.; Marsh, E. Cannabinoid therapy in epilepsy. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 32, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szaflarski, J.P.; Bebin, E.M.; Cutter, G.; DeWolfe, J.; Dure, L.S.; Gaston, T.E.; Kankirawatana, P.; Liu, Y.; Singh, R.; Standaert, D.G. Cannabidiol improves frequency and severity of seizures and reduces adverse events in an open-label add-on prospective study. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 87, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoedel, K.A.; Szeto, I.; Setnik, B.; Sellers, E.M.; Levy-Cooperman, N.; Mills, C.; Etges, T.; Sommerville, K. Abuse potential assessment of cannabidiol (CBD) in recreational polydrug users: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Epilepsy Behav. 2018, 88, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silvestro, S.; Mammana, S.; Cavalli, E.; Bramanti, P.; Mazzon, E. Use of cannabidiol in the treatment of epilepsy: Efficacy and security in clinical trials. Molecules 2019, 24, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rocha, L.; Frías-Soria, C.L.; Ortiz, J.G.; Auzmendi, J.; Lazarowski, A. Is cannabidiol a drug acting on unconventional targets to control drug-resistant epilepsy? Epilepsia Open 2020, 5, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazurkiewicz-Bełdzińska, M.; Zawadzka, M. Use of cannabidiol in the treatment of epilepsy. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2022, 56, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleti, A.P.d.A.; Frihling, B.E.F.; E Silva, P.S.; Cardoso, P.H.d.O.; de Moraes, L.F.R.; Rodrigues, T.A.A.; Biembengute, M.E.F.; Koolen, H.H.F.; Migliolo, L. Biochemical aspects and therapeutic mechanisms of cannabidiol in epilepsy. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 132, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morano, A.; Fanella, M.; Albini, M.; Cifelli, P.; Palma, E.; Giallonardo, A.T.; Di Bonaventura, C. Cannabinoids in the treatment of epilepsy: Current status and future prospects. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2020, 16, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franco, V.; Bialer, M.; Perucca, E. Cannabidiol in the treatment of epilepsy, Current evidence and perspectives for further research. Neuropharmacology 2021, 185, 108442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friese, M.A.; Schattling, B.; Fugger, L. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and axonal dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemka-Nalecz, M.; Jaworska, J.; Zalewska, T. Insights into the Neuroinflammatory Responses after Neonatal Hypoxia-Ischemia. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 76, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Reis Marques, T.; Howes, O.D. Schizophrenia-An Overview. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskaris, L.E.; Di Biase, M.A.; Everall, I.; Chana, G.; Christopoulos, A.; Skafidas, E.; Cropley, V.L.; Pantelis, C. Microglial activation and progressive brain changes in schizophrenia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Kuner, R.; Jensen, T.S. Neuropathic Pain, From Mechanisms to Treatment. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 259–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, G.A., III; Gamez, N.; Escobedo, G., Jr.; Calderon, O.; Moreno-Gonzalez, I. Modifiable Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: Where do we go from here? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, W.J.; Mrak, R.E.; Griffin, W.S.T. Microglia and neuroinflammation: A pathological perspective. J. Neuroinflamm. 2004, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carabotti, M.; Scirocco, A.; Maselli, M.A.; Severi, C. The gut-brain axis: Interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous systems. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2015, 28, 203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dopkins, N.; Miranda, K.; Wilson, K.; Holloman, B.L.; Nagarkatti, P.; Nagarkatti, M. Effects of Orally Administered Cannabidiol on Neuroinflammation and Intestinal Inflammation in the Attenuation of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroel-Vicente, C.; Gutiérrez-Palomo, S.; Ferri, J.; Cortes, D.; Cabedo, N. Natural products and analogs as preventive agents for metabolic syndrome via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, An overview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 221, 113535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgaz, S.; García, C.; Gómez-Cañas, M.; Rolland, A.; Muñoz, E.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Neuroprotection with the Cannabidiol Quinone Derivative VCE-004.8 (EHP-101) against 6-Hydroxydopamine in Cell and Murine Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Molecules 2021, 26, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.P.; Yang, M.H.; Tseng, K.F.; Lee, O.K. Hypoxia-induced secretion of TGF-β1 in mesenchymal stem cell promotes breast cancer cell progression. Cell Transpl. 2013, 22, 1869–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Kim, W.J.; Lok, J.; Lee, S.R.; Besancon, E.; Luo, B.H.; Stins, M.F.; Wang, X.; Dedhar, S.; Lo, E.H. Neuroprotection via matrix-trophic coupling between cerebral endothelial cells and neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7582–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, Q.; Goderie, S.K.; Jin, L.; Karanth, N.; Sun, Y.; Abramova, N.; Vincent, P.; Pumiglia, K.; Temple, S. Endothelial cells stimulate self-renewal and expand neurogenesis of neural stem cells. Science 2004, 304, 1338–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarrete, C.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.; Palomares, B.; Mecha, M.; Jiménez-Jiménez, C.; Mestre, L.; Feliú, A.; Bellido, M.L.; Fiebich, B.L.; Appendino, G.; et al. Hypoxia mimetic activity of VCE-004.8, a cannabidiol quinone derivative: Implications for multiple sclerosis therapy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, T.J.; Silbereis, J.C.; Griveau, A.; Chang, S.M.; Daneman, R.; Fancy, S.P.J.; Zahed, H.; Maltepe, E.; Rowitch, D.H. Oligodendrocyte-encoded HIF function couples postnatal myelination and white matter angiogenesis. Cell 2014, 158, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleszka, K.; Leu, T.; Quinting, T.; Jastrow, H.; Pechlivanis, S.; Fandrey, J.; Schreiber, T. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α is crucial for proper brain development. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, N.M.; Peters, M.; Mechoulam, R. Cannabinoid Quinones-A Review and Novel Observations. Molecules 2021, 26, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juknat, A.; Kozela, E.; Kaushansky, N.; Mechoulam, R.; Vogel, Z. Anti-inflammatory effects of the cannabidiol derivative dimethylheptyl-cannabidiol—Studies in BV-2 microglia and encephalitogenic T cells. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardinal von Widdern, J.; Hohmann, T.; Dehghani, F. Abnormal Cannabidiol Affects Production of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators and Astrocyte Wound Closure in Primary Astrocytic-Microglial Cocultures. Molecules 2020, 25, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Ghezi, Z.Z.; Miranda, K.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Combination of Cannabinoids, Δ9- Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol, Ameliorates Experimental Multiple Sclerosis by Suppressing Neuroinflammation Through Regulation of miRNA-Mediated Signaling Pathways. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghezi, Z.Z.; Busbee, P.B.; Alghetaa, H.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Combination of cannabinoids, delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), mitigates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) by altering the gut microbiome. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 82, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Al Kaabi, J.M.; Nurulain, S.M.; Goyal, S.N.; Kamal, M.A.; Ojha, S. Polypharmacological Properties and Therapeutic Potential of β-Caryophyllene, A Dietary Phytocannabinoid of Pharmaceutical Promise. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 3237–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokubaitis, C.G.; Jessani, H.N.; Li, H.; Amodea, A.K.; Ward, S.J. Effects of Cannabidiol and Beta-Caryophyllene Alone or in Combination in a Mouse Model of Permanent Ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malami, I.; Bunza, A.M.; Alhassan, A.M.; Muhammad, A.; Abubakar, I.B.; Yunusa, A.; Waziri, P.M.; Etti, I.C. Dihydroartemisinin as a potential drug candidate for cancer therapy: A structural-based virtual screening for multitarget profiling. J. Biomol. Struct Dyn. 2020, 40, 1347–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Li, M.; Lin, C.; Jin, S.; Li, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Cannabidiol-dihydroartemisinin conjugates for ameliorating neuroinflammation with reduced cytotoxicity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2021, 39, 116131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, K.A.; Grob, D.; Hirsch, M.; Metternich, B.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Jacobs, J. Efficacy and Tolerance of Synthetic Cannabidiol for Treatment of Drug Resistant Epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devinsky, O.; Cross, J.H.; Wright, S. Trial of Cannabidiol for Drug-Resistant Seizures in the Dravet Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheffer, I.E.; Hulihan, J.; Messenheimer, J.; Ali, S.; Keenan, N.; Griesser, J.; Gutterman, D.L.; Sebree, T.; Sadleir, L.G. Safety and Tolerability of Transdermal Cannabidiol Gel in Children With Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathies, A Nonrandomized Controlled Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2123930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, C.; Ehler, E.; Waberzinek, G.; Alsindi, Z.; Davies, P.; Powell, K.; Notcutt, W.; O’Leary, C.; Ratcliffe, S.; Nováková, I.; et al. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of Sativex, in subjects with symptoms of spasticity due to multiple sclerosis. Neurol. Res. 2010, 32, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovà, J.; Essner, U.; Akmaz, B.; Marinelli, M.; Trompke, C.; Lentschat, A.; Vila, C. Sativex(®) as add-on therapy vs. further optimized first-line ANTispastics (SAVANT) in resistant multiple sclerosis spasticity: A double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised clinical trial. Int. J. Neurosci. 2019, 129, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, D.T.; Makela, P.; Robson, P.; House, H.; Bateman, C. Do cannabis-based medicinal extracts have general or specific effects on symptoms in multiple sclerosis? A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study on 160 patients. Mult. Scler. 2004, 10, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.H.; Cullen, B.D.; Tang, M.; Fang, Y. The Effectiveness of Topical Cannabidiol Oil in Symptomatic Relief of Peripheral Neuropathy of the Lower Extremities. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 21, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, M.H.; Zuardi, A.W.; Tumas, V.; Pena-Pereira, M.A.; Sobreira, E.T.; Bergamaschi, M.M.; dos Santos, A.C.; Teixeira, A.L.; Hallak, J.E.; Crippa, J.A. Effects of cannabidiol in the treatment of patients with Parkinson’s disease: An exploratory double-blind trial. J. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 28, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leehey, M.A.; Liu, Y.; Hart, F.; Epstein, C.; Cook, M.; Sillau, S.; Klawitter, J.; Newman, H.; Sempio, C.; Forman, L.; et al. Safety and Tolerability of Cannabidiol in Parkinson Disease, An Open Label, Dose-Escalation Study. Cannabis. Cannabinoid. Res. 2020, 5, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consroe, P.; Laguna, J.; Allender, J.; Snider, S.; Stern, L.; Sandyk, R.; Kennedy, K.; Schram, K. Controlled clinical trial of cannabidiol in Huntington’s disease. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 40, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gofshteyn, J.S.; Wilfong, A.; Devinsky, O.; Bluvstein, J.; Charuta, J.; Ciliberto, M.A.; Laux, L.; Marsh, E.D. Cannabidiol as a Potential Treatment for Febrile Infection-Related Epilepsy Syndrome (FIRES) in the Acute and Chronic Phases. J. Child Neurol. 2017, 32, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sands, T.T.; Rahdari, S.; Oldham, M.S.; Caminha Nunes, E.; Tilton, N.; Cilio, M.R. Long-Term Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of Cannabidiol in Children with Refractory Epilepsy, Results from an Expanded Access Program in the US. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szaflarski, J.P.; Bebin, E.M.; Comi, A.M.; Patel, A.D.; Joshi, C.; Checketts, D.; Beal, J.C.; Laux, L.C.; De Boer, L.M.; Wong, M.H.; et al. Long-term safety and treatment effects of cannabidiol in children and adults with treatment-resistant epilepsies, Expanded access program results. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crippa, J.A.; Derenusson, G.N.; Ferrari, T.B.; Wichert-Ana, L.; Duran, F.L.; Martin-Santos, R.; Simões, M.V.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Fusar-Poli, P.; Atakan, Z.; et al. Neural basis of anxiolytic effects of cannabidiol (CBD) in generalized social anxiety disorder: A preliminary report. J. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 25, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares, I.M.; Zuardi, A.W.; Pereira, L.C.; Queiroz, R.H.; Mechoulam, R.; Guimarães, F.S.; Crippa, J.A. Cannabidiol presents an inverted U-shaped dose-response curve in a simulated public speaking test. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2019, 41, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuardi, A.W.; Rodrigues, N.P.; Silva, A.L.; Bernardo, S.A.; Hallak, J.E.C.; Guimarães, F.S.; Crippa, J.A.S. Inverted U-Shaped Dose-Response Curve of the Anxiolytic Effect of Cannabidiol during Public Speaking in Real Life. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Santi, L.; Polimeni, G.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E.; Sessa, E.; Annunziata, P.; Bramanti, P. Neuroinflammation and neuroprotection: An update on (future) neurotrophin-related strategies in multiple sclerosis treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmogne, M.; Klein, R.S. Neuroprotective versus Neuroinflammatory Roles of Complement, From Development to Disease. Trends Neurosci. 2021, 44, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattanzi, S.; Brigo, F.; Trinka, E.; Zaccara, G.; Cagnetti, C.; Del Giovane, C.; Silvestrini, M. Efficacy and Safety of Cannabidiol in Epilepsy, A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Drugs 2018, 78, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, E.A.; Marsh, E.D.; French, J.A.; Mazurkiewicz-Beldzinska, M.; Benbadis, S.R.; Joshi, C.; Lyons, P.D.; Taylor, A.; Roberts, C.; Sommerville, K. Cannabidiol in patients with seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (GWPCARE4): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Lev Schleider, L.; Abuhasira, R.; Novack, V. Medical cannabis: Aligning use to evidence-based medicine approach. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2458–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raucci, U.; Pietrafusa, N.; Paolino, M.C.; Di Nardo, G.; Villa, M.P.; Pavone, P.; Terrin, G.; Specchio, N.; Striano, P.; Parisi, P. Cannabidiol Treatment for Refractory Epilepsies in Pediatrics. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 586110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huestis, M.A.; Solimini, R.; Pichini, S.; Pacifici, R.; Carlier, J.; Busardò, F.P. Cannabidiol Adverse Effects and Toxicity. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Potential Targeted Disease/Therapeutic Potentials | Subjects | Key Findings on Clinical Biomarkers/Signs | Mechanism of Actions in Relation to Anti-Neuroinflammatory |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epilepsy | Kainic acid-induced mice with seizures [29] | Temporarily attenuated seizure scores | Inhibited inflammatory microglia activation and accumulation, reduced inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression and decreased numbers of ectopic neurons |
| Epilepsy and neuroprotection | Bilateral intra-hippocampal pilocarpine microinjection-induced seizures in C57Bl/6 wild-type (WT) and PI3Kγ-/- mice; Glutamate-induced primary neurons [30] | Increased latency and reduced the severity of behavioral seizures, prevented neurodegeneration, microgliosis and astrocytosis in wild type animals but not in PI3Kγ-/-; PI3Kγ inhibition or deficiency abolished CBD’s neuroprotective effect on glutamate-induced cell death | Involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway |
| MS | Cuprizone-induced MS in male C57BL/6 mice [31] | Ameliorated demyelination | Reduced microglia accumulation and oxidative stress (catalase, superoxide dismutases and glutathione) |
| MS | Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced demyelinating disease (TMEV-IDD)-susceptible female SJL/J mice model [32] | Attenuated motor deficiencies | Reduced proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, inhibited microglial activation and downregulated expressions of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand (CCL)2,CCL5, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interleukin (IL)-1β |
| MS | Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG)-induced EAE in C57BL/6 mice model, MOG induced encephalitogenic T-cell line [26] | Ameliorated clinical signs of EAE, reduced axonal damage and neuroinflammation, inhibited microglial activation | Inhibited T-cell proliferation, downregulatedexpression of ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 (Iba-1) and galectin-3 (Mac-2) in the spinal cord |
| HI | Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)-induced HI in Wistar rats [33] | Improved functional recovery and reduced brain damage | Reduced apoptosis and neuronal loss; inhibited neuroinflammation, reduced microglial and astrogliosis activation and proliferation |
| Schizophrenia | Dizocilpine (MK-801) induced schizophrenia in male C57BL/6 mice [34] | Ameliorated behavioral changes | Modulated expressions of Iba-1 (a microglia marker), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, an astrocyte marker) and neuronal nuclear antigen (a neuronal marker) |
| Neuropathic pain | HI induced-spinal cord injury in female C57Bl/6 mice [35] | Attenuated neuropathic pain and high thermal sensitivity | Reduced proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, including IL-23, CXCL-9, CXCL-11, iNOS and interferon gamma |
| AD | β-amyloid-injected AD C57/BI6 mice; lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced BV-2 and N13 microglia [36] | Improved learning in a spatial navigation task, decreased deposited Aβ peptide | Suppressed neuroinflammation in AD animal model, reduced intracellular calcium (Ca2+), inhibited nitric oxide (NO)-modulated microglial activation, decreased IL-6 gene expression |
| In vitro investigations | LPS-induced BV-2 microglia [37] | Reduced neuroinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6 and interferon-beta (IFN-β) | Downregulated nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) signaling pathway |
| LPS-induced microglia and astrocytes (host not specified) [38] | Ameliorated activation of microglia and astrocytes, inhibited production of IL-6 from microglia and astrocyte cell line | Inhibited phosphorylation of NF-κB and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signalling pathways | |
| LPS-induced microglia in mice [39] | Reduced synthesis of glucose-derived nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen (NADPH) and reduced neuroinflammatory mediators (ROS and TNF-α) | Downregulated NF-kB-dependent signaling pathway |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yousaf, M.; Chang, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, X. Neuroprotection of Cannabidiol, Its Synthetic Derivatives and Combination Preparations against Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Neurological Disorders. Molecules 2022, 27, 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154961
Yousaf M, Chang D, Liu Y, Liu T, Zhou X. Neuroprotection of Cannabidiol, Its Synthetic Derivatives and Combination Preparations against Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Neurological Disorders. Molecules. 2022; 27(15):4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154961
Chicago/Turabian StyleYousaf, Muhammad, Dennis Chang, Yang Liu, Tianqing Liu, and Xian Zhou. 2022. "Neuroprotection of Cannabidiol, Its Synthetic Derivatives and Combination Preparations against Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Neurological Disorders" Molecules 27, no. 15: 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154961
APA StyleYousaf, M., Chang, D., Liu, Y., Liu, T., & Zhou, X. (2022). Neuroprotection of Cannabidiol, Its Synthetic Derivatives and Combination Preparations against Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Neurological Disorders. Molecules, 27(15), 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154961







