Abstract
Nanotechnology has become increasingly important in modern society, and nanoparticles are routinely used in many areas of technology, industry, and commercial products. Many species of nanoparticle (NP) are typically synthesized using toxic or hazardous chemicals, making these methods less environmentally friendly. Consequently, there has been growing interest in green synthesis methods, which avoid unnecessary exposure to toxic chemicals and reduce harmful waste. Synthesis methods which utilize food waste products are particularly attractive because they add value and a secondary use for material which would otherwise be disposed of. Here, we show that spent coffee grounds (SCGs) that have already been used once in coffee brewing can be easily used to synthesize gold and silver NPs. SCGs derived from medium and dark roasts of the same bean source were acquired after brewing coffee by hot brew, cold brew, and espresso techniques. The total antioxidant activity (TAC) and total caffeoylquinic acid (CQA) of the aqueous SCG extracts were investigated, showing that hot brew SCGs had the highest CQA and TAC levels, while espresso SCGs had the lowest. SCG extract proved effective as a reducing agent in synthesizing gold and silver NPs regardless of roast or initial brew method.
1. Introduction
Despite the socio-economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, coffee consumption and popularity continue to rise. Global coffee consumption saw an average compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 1% from the 2017/2018 coffee year to the 2020/2021 coffee year, where a coffee year runs from October to the following September [1]. Regionally, Africa and the Middle East experienced the greatest increase in the consumption of coffee, promoting industry growth in those regions. Within the United States, weekly consumption of coffee increased to 73% of polled individuals in January 2022 from 69% in July of 2021, due to increased specialty coffee consumption [2]. Several popularized brewing methods, such as espresso and cold brew techniques, fall under this increase. Increased coffee consumption correlates to a rise in waste byproducts that have been repurposed in other industries, such as agriculture and biofuel, to follow better green chemistry practices.
Coffee bean extract has been analyzed and researched extensively, with particular emphasis on how consumption impacts health. Caffeine and chlorogenic acid derivatives are the primary biologically active molecules found within coffee, though coffee may be comprised of approximately 1000 other compounds, including phenolic compounds, diterpenes, methylxanthines, and melanoidins [3]. Chlorogenic acid derivatives have demonstrated positive protective activities, including anticarcinogenic, cardioprotective, anti-obesity, and antidiabetic effects [4]. Antioxidant activity contributes to these protective effects by alleviating the free radical imbalance within the body, thus reducing oxidative stress. Oxidative stress has been linked to neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), as well as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and diseases of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and renal systems [5]. Beyond health benefits, coffee bean extract has been utilized in the synthesis of a variety of nanoparticles (NPs), including silver [6,7,8], gold [9], platinum, palladium [8], and copper [10,11]. Additionally, certain byproducts of the coffee extract manufacturing process, such as spent coffee grounds and coffee plant leaves, have been utilized in the synthesis of silver [12] and zinc oxide NPs [13], respectively. Research into NPs is continuously expanding due to their unique properties and wide range of applications.
NPs are known to exhibit interesting properties that can vary with characteristics such as size and morphology. Metal NPs have various applications in catalysis, optics, biotechnology, molecular sensing, targeted drug-delivery, and antimicrobial materials. In particular, silver, gold, and copper are among the most commonly synthesized NPs, due to their stability and variety of uses [14]. NPs can be synthesized into many different shapes and sizes, leading to different functionalities and applications. The surface plasmon resonance (SPR) absorption, which is caused by the resonant oscillation of electrons in the conduction band of these particles [15], also shifts based on the varying structure of metal NPs, allowing researchers to characterize these particles on the nano-scale through optical properties.
Many NPs are typically synthesized using techniques that utilize toxic or hazardous chemicals, which makes these synthesis methods less environmentally friendly. In order to minimize risk from exposure to toxic chemicals and reduce harmful waste, green synthesis methods are becoming more popular in the field of nanotechnology. The increasing demand for nanomaterials in a growing set of applications further requires minimizing the hazardous waste and maximizing the efficacy of green synthesis methods [16]. Green synthesized Au and Ag NPs are known to have many biological and medical applications. Both species of NP can be easily functionalized with antibodies, drugs, polymers, and amino acids [17,18,19,20]. Au NPs have been utilized in cancer diagnosis and therapy, photothermal therapy, biomedical imaging, targeted drug delivery, and enzyme inhibition [21,22,23,24,25,26,27]. Ag NPs have been utilized extensively as antimicrobial agents in surface coatings, wound dressings, catheters, textiles, and consumer products [14,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. Towards achieving greener chemistry methods, synthesis of many different species of NP have been demonstrated using coffee liquid, coffee bean extract, or coffee grounds as a replacement for more caustic, synthesized chemicals such as sodium borohydride. These include silver [6,7,8], gold [9], platinum, palladium [8], copper [10,11], zinc oxide [36], selenium [9], alumina [37], and carbon dots [38]. Most of these syntheses utilize naturally available acids within the coffee product to reduce metal ions in solution and promote aggregation and growth into NPs. Coffee beans, coffee grounds, and coffee liquid are known to contain a host of bioactive compounds, including caffeine, chlorogenic acids, phenolics, and melanoidins. Of these, chlorogenic acid has been singled out and shown to be effective in the synthesis of silver [39], gold [40], platinum [41], and bimetallic NPs [42].
Like many food processing methods, coffee bean extraction processes leave behind a host of active molecules and compounds in the byproducts. The discovery of a diverse array of uses for these coffee byproducts resulted in an expansion of scientific research into coffee chemistry. Primary coffee byproducts include the coffee husk, pulp, silverskin, and spent coffee grounds (SCGs), each with a unique chemical composition [43,44]. SCGs are brewed coffee grounds that contain unextracted material in which active compounds are present. A variety of factors, such as extraction process and roasting temperature, impact the compound extraction yield and the composition of the extract [45,46]. Current research identifies the capacity of SCGs as a potential source of biofuel [47,48,49,50,51], antioxidants [43,44,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59], flavonoids [60,61,62,63], sugars [64,65,66,67,68], and fertilizer [69,70,71,72], to name a few. Due to similarities in composition to unbrewed coffee grounds, SCGs should have related, unrealized applications in NP synthesis in line with coffee liquid, coffee bean extract, and unbrewed coffee grounds [73,74]. Utilization of coffee byproducts offers green chemistry, low-waste processes, and value-added propositions.
Motivated by the expansion of research into coffee byproducts, this study characterized the contents of SCG samples to quantify total caffeoylquinic acid (CQA), total antioxidant capacities (TACs), and efficacy in synthesizing silver and gold NPs. The rich antioxidant content of SCGs is well-documented [43,52,54,56,57,58,75,76,77]. However, the impact of factors such as brewing method [52,58,59] and degree of roast [53,58] on TAC levels in SCGs is not well-understood. This work estimated TAC levels in the aqueous extracts of six SCG samples (Table 1) from various degrees of roast and brewing methods using ABTS+ ((2,2′-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt) decolorization assay, DPPH (2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) decolorization assays, Folin-Ciocalteu assay for total phenolic content (TPC), and ferric ion reducing antioxidant power (FRAP). This work also studied the efficacy of SCG extracts in the synthesis of two types of metal NPs, silver and gold, through a benchtop, green chemistry, single-pot method. Table 1 explains the abbreviations used to differentiate SCG samples among the multiple roast levels and brewing techniques compared in this work. The brewing methods employed were conducted to mimic standard home-brewing conditions with simplicity for industrial scaling.

Table 1.
Sample Code by Variation in Preparation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Standards of 5-Caffeoylquinic acid (5-CQA, CAS: 327-97-9), Caffeine (CAS: 58-08-02), ABTS+• (2,2-Azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt) (CAS: 30931-67-0), Trolox (6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethylchroman-2-carboxylic acid) (CAS: 53188-07-1), Potassium Persulfate (CAS: 7727-21-1), Sodium Acetate Trihydrate (CAS: 6131-90-4), Glacial Acetic Acid (CAS: 64-19-7), Methanol (67-56-1), Iron (II) Sulfate Heptahydrate (7782-63-0), TPTZ (2,4,6-Tris(2-pyridyl)-s-triazine) (CAS: 3682-35-7), Folin-Ciocalteu Reagent (MDL: MFCD00132625), Sodium Carbonate (CAS: 497-19-8), and Standardized 1 M Sodium Hydroxide (CAS: 1310-73-2) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Milwaukee, WI, USA). DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) (CAS: 1898-66-4), Iron (III) Chloride Hexahydrate (CAS: 10025-77-1), and Gallic Acid (3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) (CAS: 149-91-7) were obtained from Alfa Aesar (Ward Hill, MA, USA), while Hydrochloric Acid (CAS: 7647-01-0), Ascorbic Acid (CAS: 50-81-7), Sodium Nitrite (CAS: 7632-00-0), and Aluminium Chloride Hexahydrate (CAS: 7784-13-6) were obtained from Thermo Scientific/Fischer Chemical (Nazareth, PA, USA). HPLC-grade Rutin Hydrate was acquired from Tokyo Chemical Industry (Tokyo, Japan). For NP synthesis, gold chloride hydrate (CAS 27988-77-8) was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Milwaukee, WI, USA), and silver nitrate (CAS 7761-88-8) was obtained from GFS Chemicals (Columbus, OH, USA).
2.2. Coffee Bean Preparation
Unroasted organic Colombian coffee beans were purchased from Golden Valley Coffee Roasters located in West Chester, PA, USA. Samples of 250 g of green coffee beans were roasted in a Hottop coffee roaster (Model No. KN-8828B-2K, HotTop, Hottop Coffee Roaster, Cranston, RI, USA) using the manufacturer’s default temperature-time setting. Beans were ejected from the roaster at two different final temperatures: 194 °C and 209 °C for medium and dark roasts, respectively. One batch was produced for each roast. Roasts were frozen for a minimum of 12 h [78] and ground using a conical burr coffee grinder (Model No. 560.01, Capresso, Montvale, NJ, USA) at the highest medium coarseness setting as designated by the manufacturer. The grinds were then sieved to retain particles in increments of <500 µm, 500–710 µm, and 710–1000 µm. Three sieves were used with mesh openings of 500 µm, 710 µm, and 1000 µm. Sieved grounds were stored at −18 °C before brewing.
2.3. Initial Coffee Brewing
Three brewing methods were prepared for a medium and dark roast Colombian coffee bean: cold brew, hot brew, and espresso. Brewing was completed for each roast level separately.
Cold-brew coffee was prepared in a French press using 10 g of ground coffee with a particle size range of 710–1000 µm in 100 g of room temperature deionized (DI) water. The mixture was steeped at room temperature for 24 h before the plunger was pressed into the grounds and coffee was poured off. SCGs were stored in an air-tight container at −18 °C.
Hot brew coffee was prepared in a French press by pouring 100 g of 100 °C DI water over 10 g of ground coffee of particle size 710–1000 µm. After 6 min, the plunger was pressed into the grounds and the coffee was poured off. SCGs were stored in an air-tight container at −18 °C.
Espresso coffee was prepared using a Breville ESP8SXL espresso machine filled with 75 mL of DI water poured over 10 g of coffee grounds of particle size < 500 µm. Spent espresso grounds were extracted and stored in an air-tight container at −18 °C.
2.4. Spent Coffee Extract Preparation
The previously stored SCGs were dried separately in an oven at 65 °C for 24 h to evaporate excess moisture. For brewing, a ratio of 1 part SCGs by weight to 5 parts boiling DI water by weight was used. The mixture was steeped for 5 min and filtered using the Hario V60 paper filter. Extracts were stored at 4 °C until analysis.
2.5. HPLC Analysis
Standard solutions and coffee extracts were analyzed using a methodology adapted from GL Sciences Technical Note No. 67 [62]. Analyses were performed on an Agilent 1200 Series high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system fitted with a Supelco C-18, 5 µm column (15 cm × 4.6 cm) (Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA), and a C-18 guard column at 25 °C with a mobile phase mixture of 75% mobile phase A and 25% mobile phase B (A: 95% 2.0 mM phosphoric acid and 5% methanol; B: 95% methanol and 5% 2.0 mM phosphoric acid). The mobile phase flow rate was set at 1.0 mL/min with an injection volume of 10.0 µL. CQA isomers were detected using a diode array detector at 325 nm and 280 nm, respectively. Concentrations of 5-CQA were quantified via standard calibration curves. The retention time of 3-CQA and 4-CQA isomers was determined using standard solutions and quantitation of these two isomers was accomplished using the area of the 5-CQA standard combined with the respective molar extinction coefficients of the other two isomers as reported previously [76,79,80,81]. Two batches of coffee were brewed for each brewing style, and each batch of brewed coffee was analyzed in triplicate (n = 6).
2.6. Total Antioxidant Capacity Measurements
TAC of SCG extracts was estimated using four different methods.
2.6.1. ABTS Assay
The ABTS+ radical cation decolorization assay method was previously described by Rao et al. [82]. Equal parts of 7 mM ABTS and 2.45 mM potassium persulfate solutions were combined and incubated for 16 h in a dark room to form a stock solution. A working solution was prepared by diluting the stock ABTS solution with DI water to obtain an absorbance within the range of 0.8 to 0.9 at 734 nm. An amount of 5 µL of sample was added to 3000 µL of the working solution. The resulting solution was mixed for 1 min and incubated for 6 min at room temperature. The absorbance of the solution was then measured at 734 nm using a Thermo Scientific Evolution 201 spectrophotometer. Trolox was used as a standard and results were expressed in mmol of Trolox equivalence (TE) per liter of extract. Each experiment was repeated in duplicate, and each sample was analyzed in triplicate (n = 6).
2.6.2. DPPH Assay
The DPPH radical scavenging activity assay method was adopted from Odžaković et al. [83] and Muzykievicz et al. [84]. In brief, a working solution was prepared by diluting 0.3 mM DPPH methanolic solution with methanol to obtain an absorbance 1.000 ± 0.020 at 517 nm. A 5 µL aliquot of the SCG extract was added to 2850 µL of the DPPH working solution and vortexed for 1 min using a VWR Vortexer 2. The solution was allowed to incubate for 30 min in a dark room at room temperature before its absorbance was taken at 517 nm. Trolox was used as a standard, and results were expressed in mmol of Trolox equivalence (TE) per liter of extract. Each experiment was repeated in duplicate, and each sample was analyzed in triplicate (n = 6).
2.6.3. Folin-Ciocalteu Assay (TPC)
Total phenolic content (TPC) was measured using the Folin-Ciocalteu method adopted from [84]. An amount of 10% v/v Folin-Ciocalteu reagent and 5 mM Na2CO3 aqueous solutions were prepared. Then, 2700 µL of 5 mM Na2CO3, 150 µL of 10% Folin-Ciocalteu, and 30 µL of SCG extract were mixed and incubated for 30 min in a dark room. After 30 min, sample absorbance was measured at 750 nm using UV-VIS spectroscopy. Gallic acid was used as standard and results were expressed in mg gallic acid equivalence (GAE) per liter of extract. Each experiment was repeated in duplicate, and each sample was analyzed in triplicate (n = 6).
2.6.4. Ferric Ion Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP)
The reducing capacity of spent coffee brews was determined using the ferric ion reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay adapted from Muzykievicz et al. [84] and Benzie and Strain [85]. A FRAP working solution was prepared by mixing 1 part 10 mM TPTZ in 40 mM HCl, 1 part 20 mM iron (III) chloride hexahydrate, and 10 parts 300 mM acetate buffer of pH 3.6. Acetate buffer was prepared using 3.1 g sodium acetate trihydrate and 16 mL glacial acetic acid into a 1 L volumetric flask and filled with DI water. In a vial, 3 mL of working solution was mixed with a 100 µL sample (10 µL SCG extract + 90 µL DI water). The absorbance was measured at 593 nm after 15 min of incubation. Iron (II) sulfate heptahydrate and ascorbic acid were used as standards with results expressed in mg FeSO4 per liter of extract. Each experiment was repeated in duplicate, and each sample was analyzed in triplicate (n = 6).
2.6.5. Silver and Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis and Preparation
The synthesis of silver and gold NPs followed a typical wet-bench chemical reduction method [86,87,88] with minor modifications detailed herein. To make this synthesis a low-waste process, NPs were synthesized using lab waste-products as reducing, nucleating, or capping agents to investigate their efficacy in replacing the more caustic reagents typically utilized. Specifically, SCG extracts were tested in this work. The NP synthesis was carried out in the presence of ambient white light. In a typical synthesis, a 50 mL Erlenmeyer flask equipped with a thermometer and aluminum foil cap was filled with 30 mL of DI water and placed on a hot plate. The water was then heated to 55 °C while stirring and the metal precursor was added. Depending on the type of SCG extract being used as the reducing agent, SCG liquid was added to the flask in volumes ranging from 0.5 to 2 mL dropwise as the reaction mixture was stirred with a magnetic stir bar. For the synthesis of silver NPs, 30 mg of solid AgNO3 was added to the reaction mixture as the metal precursor. For the synthesis of gold NPs, 0.5 mL of 10mM gold chloride solution was added to the reaction mixture as the metal precursor. Once all reagents were added to the flask, it was constantly stirred for 1 h while maintaining the temperature at 55 °C. The reaction mixture was then cooled naturally to room temperature.
2.6.6. UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopy
A cuvette was filled with the liquid sample collected, ensuring that no particles of solid coffee grounds were transferred to the cuvette. A Thermo Scientific Evolution 201 spectrophotometer was baselined to water prior to any of the spectra being collected. An absorption spectrum was then collected from 250 to 800 nm for each sample using the UV-vis absorption spectrometer.
2.6.7. SEM Imaging
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of samples were taken with a Hitachi FlexSEM 1000. All samples were prepared by centrifuging, washing, and redistributing the silver or gold NPs in deionized water. A droplet from the NP solution was then dried on conducting carbon tape or a carbon-coated, copper mesh transmission electron microscopy (TEM) grid. Analysis of NP size was carried out using the Hitachi FlexSEM software and ImagePro.
2.6.8. Statistical Analysis
Two-way ANOVA analysis with Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference (HSD) test was performed using an R script by Wessa [89]. Differences between means were considered significant at p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
Previous studies have found that, despite having undergone an initial brewing process, SCGs remain rich in total CQA concentrations and TACs [43,52,54,56,57,58,75,76,77]. Only a few studies have reported how different brewing methods [52,58,59] and degree of roast [53,58] affect what compounds are left behind in SCGs. This study analyzed the total CQA concentrations and TACs of extracts from six SCG samples generated from various brewing methods and degrees of roast. The results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 1 and Figure 2.

Table 2.
Total CQA Concentration and TAC Levels of Six (6) SCG Extracts.
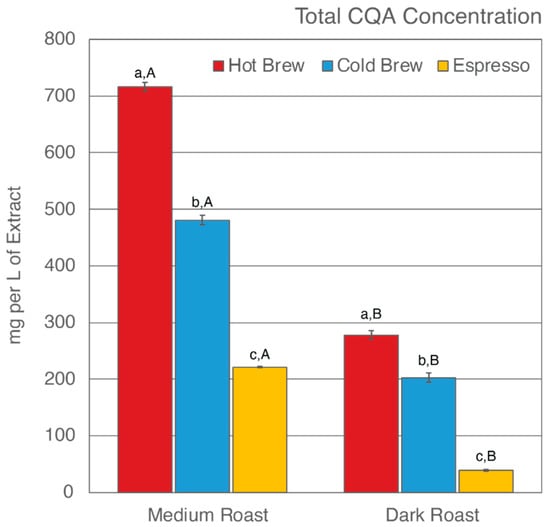
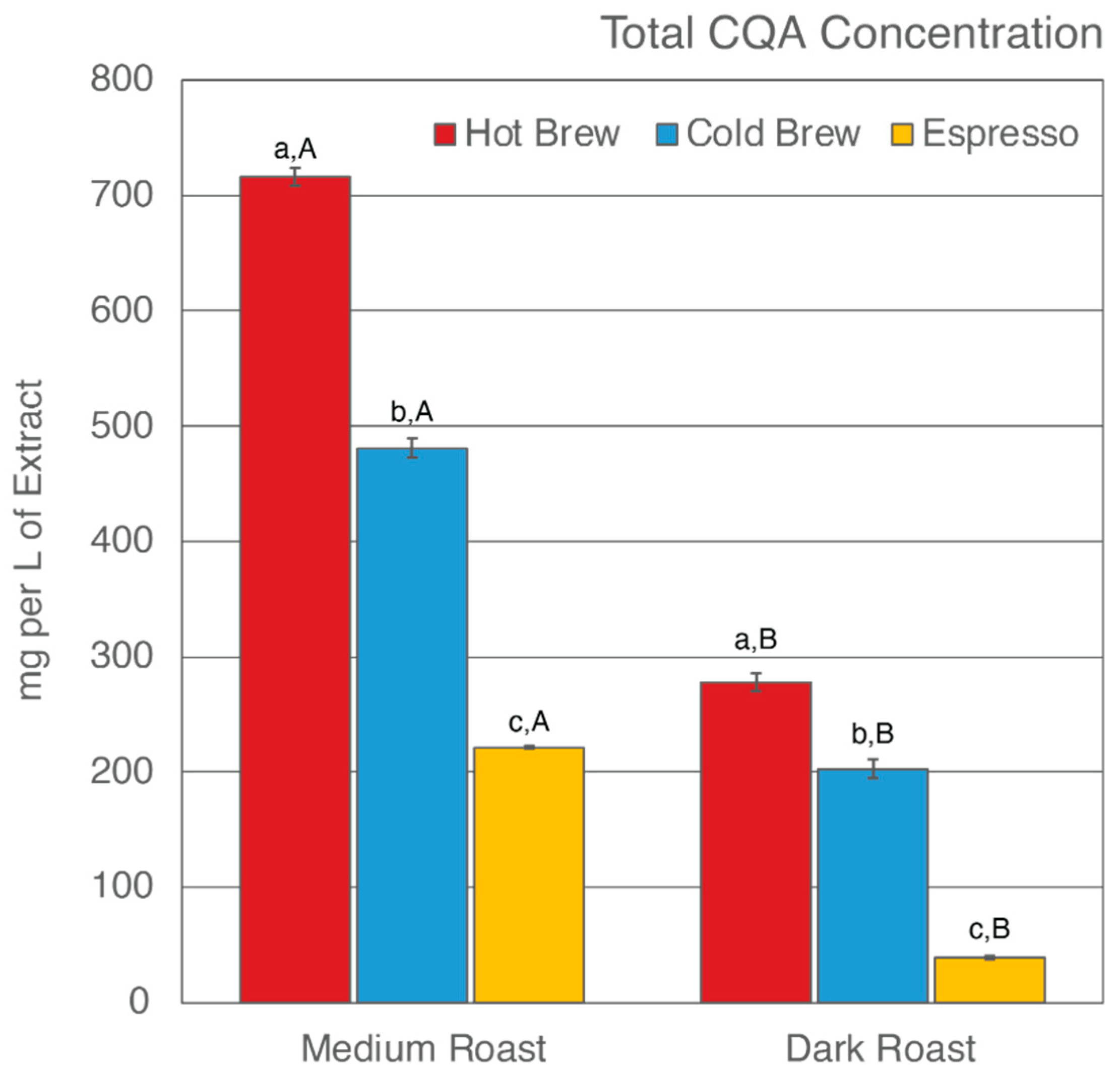
Figure 1.
Total CQA concentration of six SCG extracts. Letters a–c denote significant (p < 0.05) differences among brewing methods at the same degree of roast as determined by the Tukey HDS post-tests. Letters A and B denote significant differences between medium and dark roast within the same brewing method.
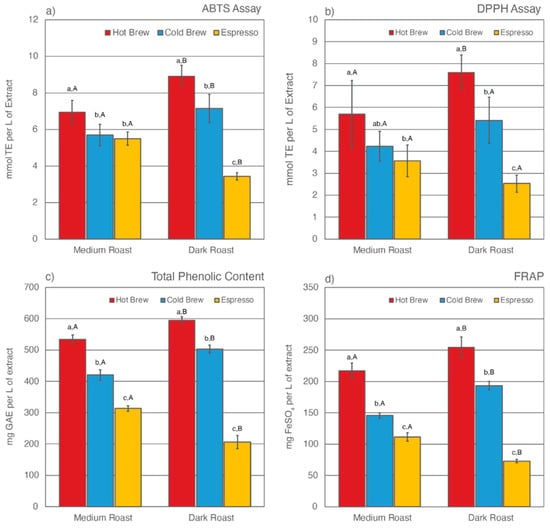
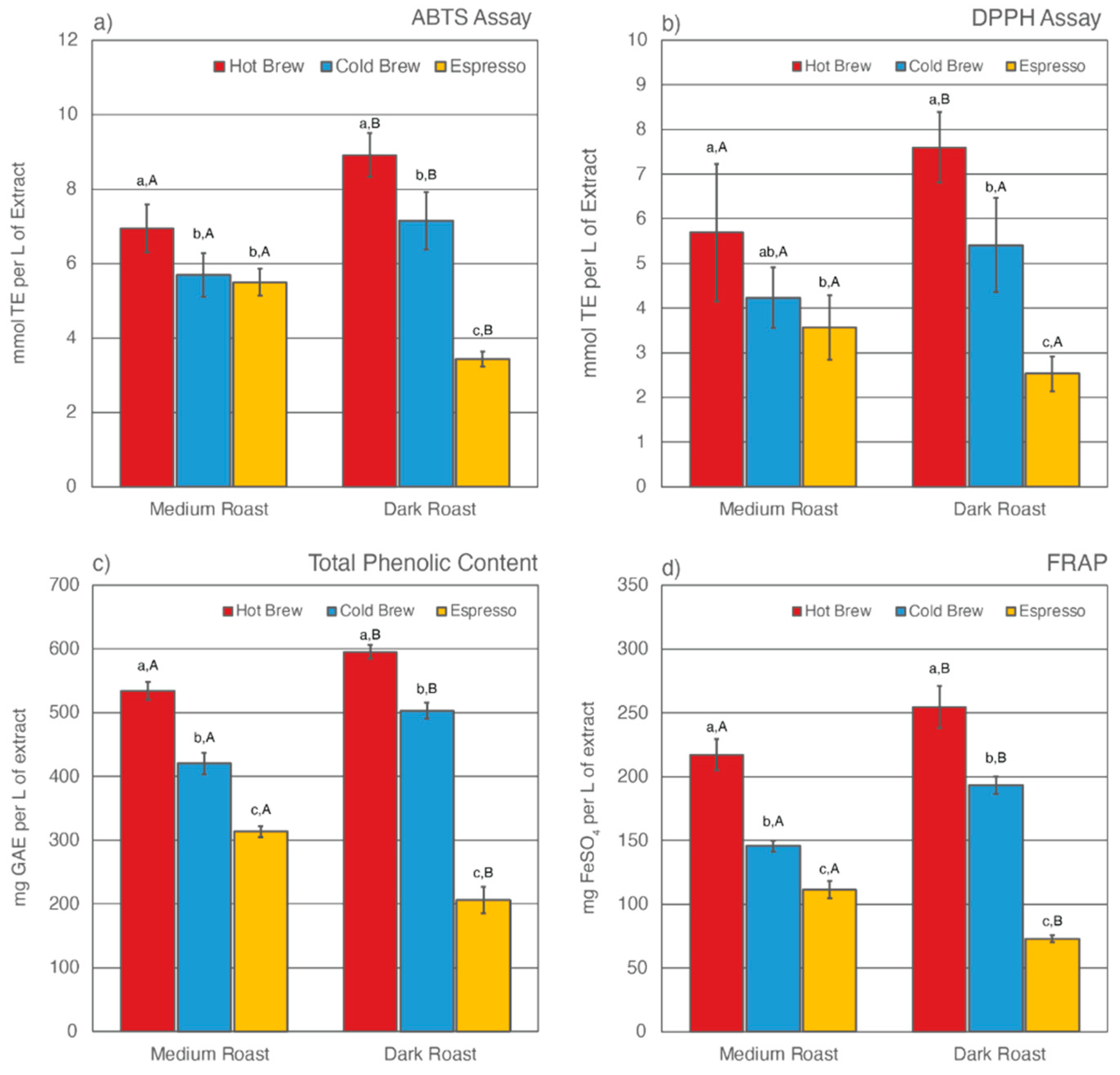
Figure 2.
Total antioxidant capacities (TACs) as estimated by ABTS assay (a), DPPH assay (b), Folin-Ciocalteu assay for total phenolic content (c), and ferric ion reducing antioxidant power (d) for six SCG extracts. Letters a–c denote significant (p < 0.05) differences among brewing methods at the same degree of roast as determined by the Tukey HDS post-tests. Letters A and B denote significant differences between medium and dark roast within the same brewing method.
3.1. Total CQA Concentration
Of the six SCG extracts analyzed, SMH was observed to have the highest total CQA concentration (716.02 mg/L of extract), whereas SDE was observed to have the lowest (38.88 mg/L of extract) (Figure 1). In general, hot brew SCG extracts were observed to have the highest level of CQAs, whereas espresso SCG extracts were observed to have the lowest level of CQAs, regardless of degree of roast. These results suggest that an initial hot brew method did not extract CQAs as efficiently as a cold brew method or espresso brewing, therefore leaving significant CQAs behind in the SCGs. To date, research on the total CQA concentration of SCG extracts from a cold brew method is not available [59]. The cold brew method is known to extract more CQAs due to the prolonged extraction time of the initial brew [46,90,91,92,93]. Indirectly, the observed CQA levels in cold brew SCG extracts were in support of previous findings. The low levels of total CQA concentration in espresso SCG extracts are in agreement with previous studies by Bravo et al. [52]. This finding is corroborated by the high extraction efficiency of the espresso brewing method in comparison to other brewing methods [94,95,96].
Total CQA concentration is also impacted by the degree of roast. It is generally accepted that the roasting process changes the chemical composition of the coffee by producing melanoidin while degrading phenolic compounds [97,98,99]. Numerous studies have reported a decrease in CQA concentration as roasting progresses [82,97,98,100,101]. In this present study, the total CQA concentration was observed to be higher in extracts from medium roast SCG extracts than from dark roast SCG extracts, regardless of which brewing method was used to generate the SCGs (Table 2, Figure 1). The CQA concentration ranged from 221–716 mg/L of extract for medium roast SCGs and 38–277 mg/L of extract for dark roast SCGs. In agreement with previous studies [53,58], the low level of total CQA concentration in dark roast SCG extracts as compared to medium roast SCG extracts supports the understanding that total CQA concentration decreases as degree of roast increases.
3.2. Total Antioxidant Capabilities (TAC)
The TAC levels of SCG extracts were estimated using four different methodologies, including ABTS assay, DPPH assay, Folin-Ciocalteu assay for total phenolic content (TPC), and ferric ion reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) (Figure 2). Of the six SCG extracts analyzed, SDH extract exhibited the highest TAC levels as measured by all four methods, whereas SDE extract was observed to have the lowest TAC levels. Similar to total CQA levels, the prolonged extraction time in the cold brew method was responsible for leaving fewer antioxidants behind in the SCGs. As a result, cold brew SCG extracts for both medium and dark roasts had lower TAC levels than their hot brew counterparts. This result contradicts a recent study by Chongsrimsirisakhol and Pirak, in which cold brew SCG extracts were observed to have higher TAC levels than hot brew SCG extracts [59]. This discrepancy may be attributed to differences in the coffee-to-water ratio, brewing time, water temperature, and bean origin.
The degree of roast also affects TAC levels in SCG extracts. For both hot and cold brewing methods, dark roast SCG extracts were observed to have higher TAC levels than medium roast counterparts. This trend was reversed for espresso brewing methods, in which SME extract was observed to have higher TAC levels than SDE extract. Previous studies have reported that the formation of melanoidins during roasting helps to stabilize TAC levels in coffee [98,99,101]. These complex melanoidin compounds are more soluble in hot water than cold water [82,93,102,103,104]. Although the water temperature in hot brew methods was high enough to extract some of the additional antioxidants formed during roast, the short brewing time significantly lowered the extraction efficiency of the hot brew method, leaving plenty of antioxidants behind in the SCGs. As a result, SDH extract had the highest TAC levels compared to other SCG extracts.
The TAC levels of espresso SCG extracts have been reported in multiple previous studies [52,56,58,59,75]. It is generally accepted that espresso SCGs are rich in phenolic compounds. However, there has been no research on how degree of roast affects TAC levels in espresso SCG extracts. The espresso brewing method differs drastically from cold or hot brew methods. In addition to high water temperature, espresso extraction is performed under high pressure using finely ground coffee [105,106,107,108]. Cruz et al. noted a high variability in the chemical composition of espresso SCGs and suggested that “the brewing method itself should be the main contributing factor to the compositional variance” [54].
3.3. Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles
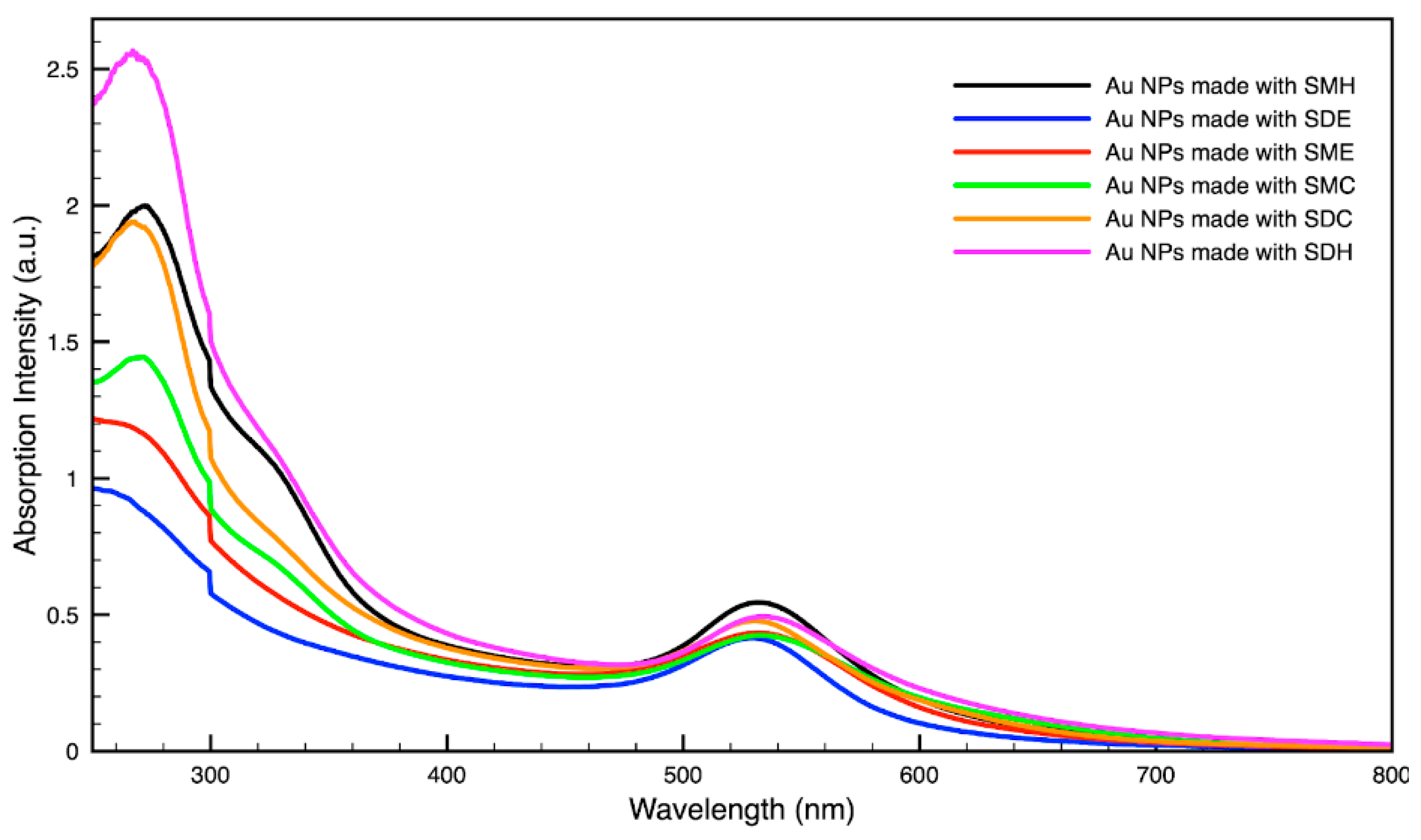
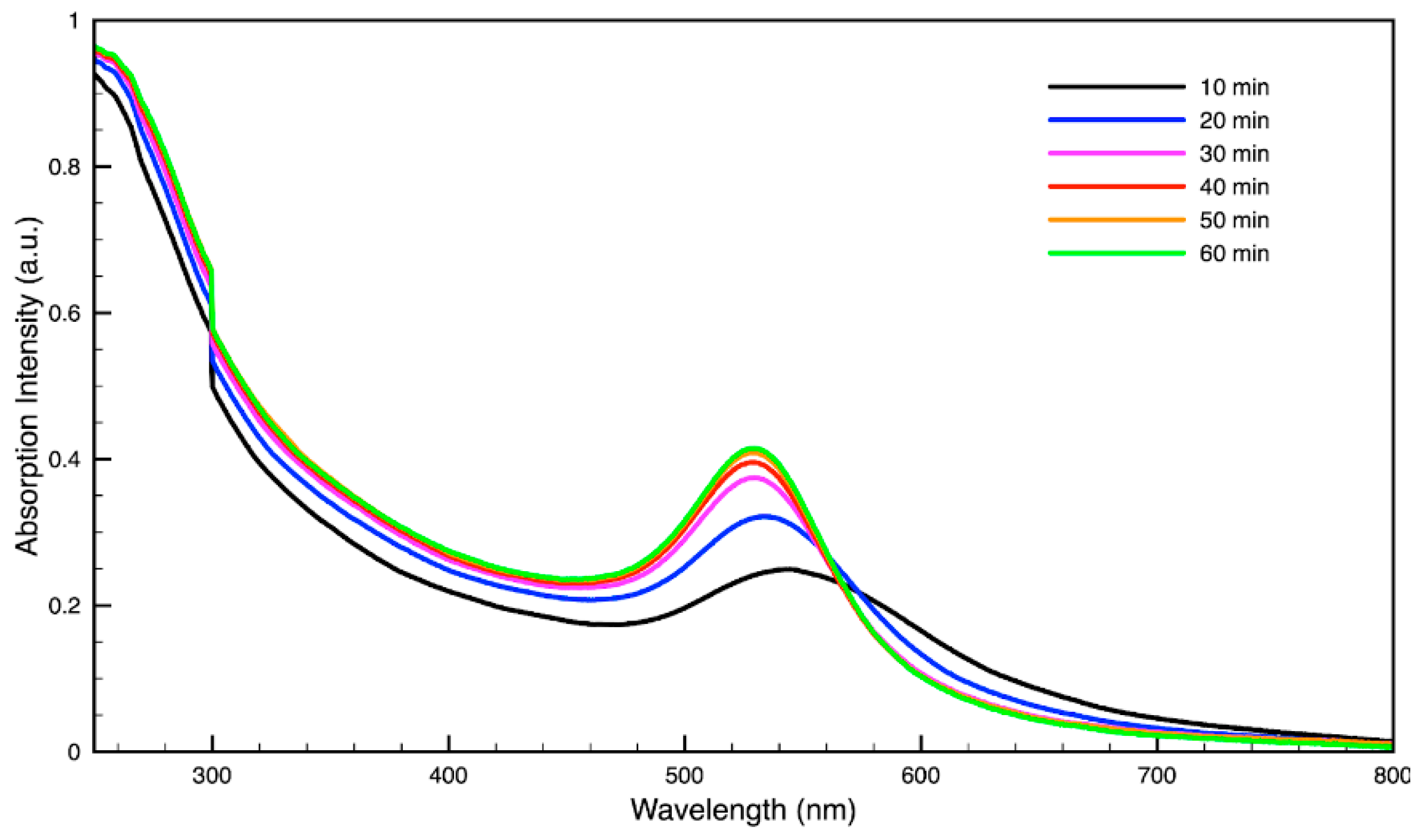
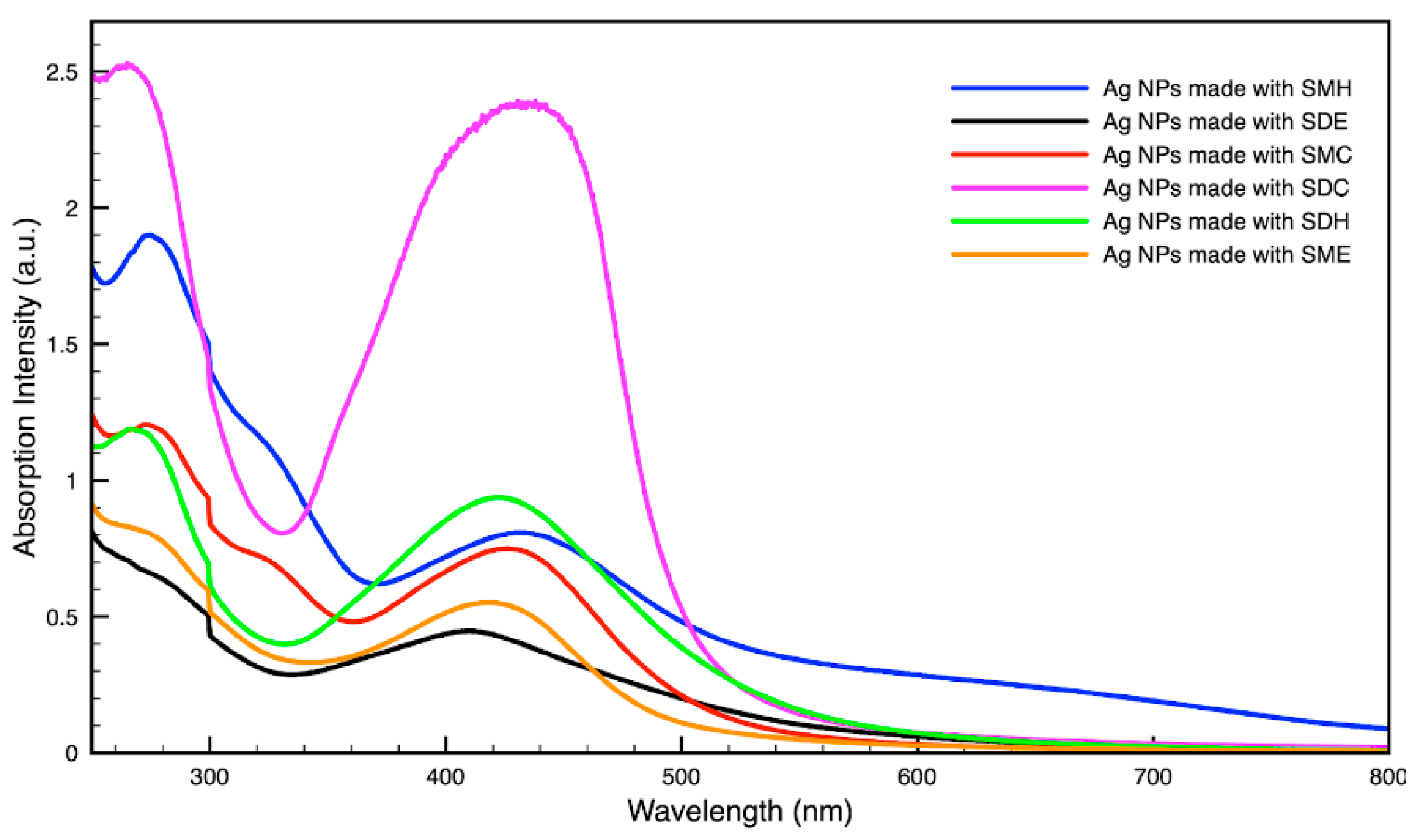
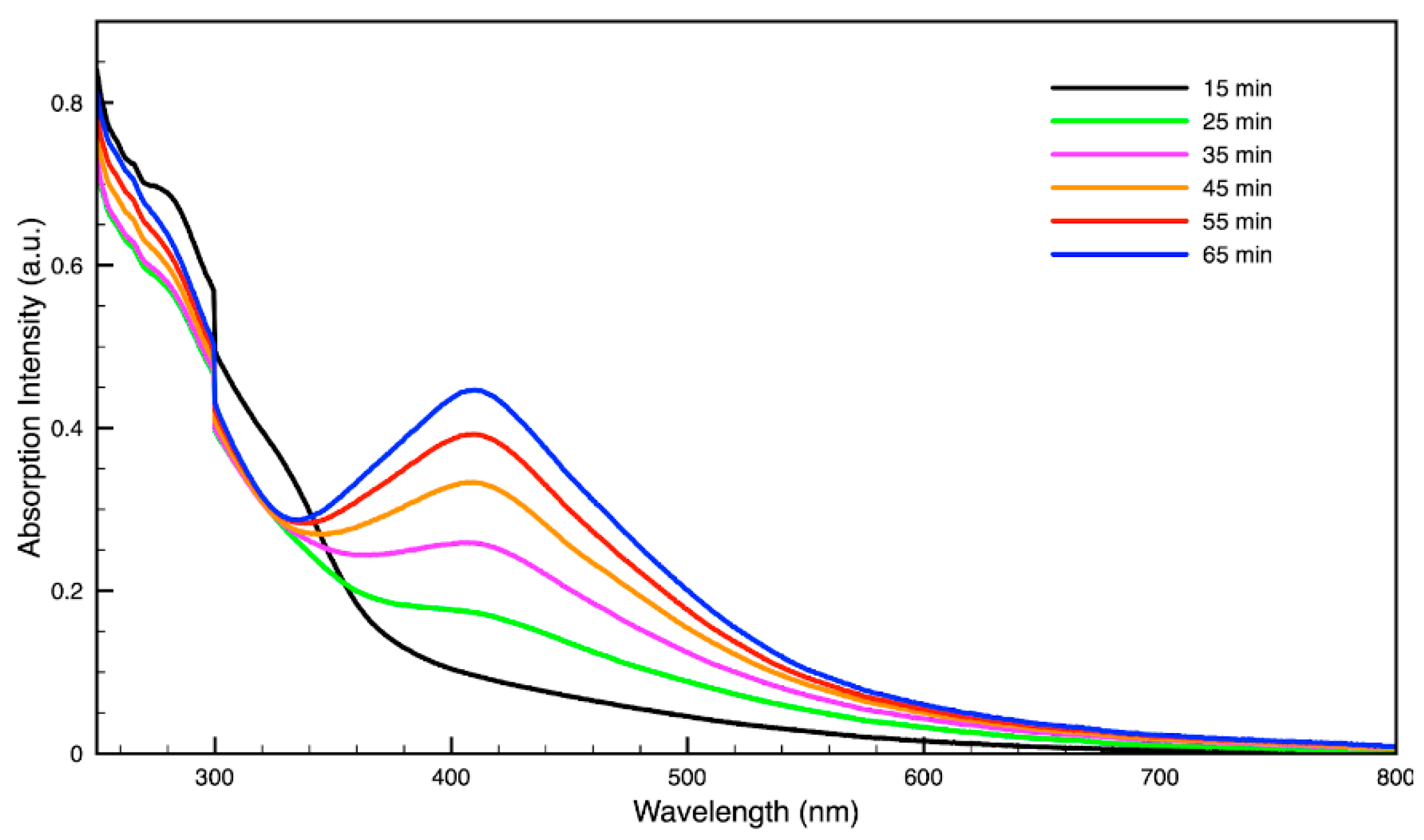
For metal nanoparticles (NPs), it is well known that the absorption of specific wavelengths of light is correlated to the size and shape of the NPs through the effect of the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) [109,110,111]. Therefore, taking an absorption spectrum of the NPs in solution can reveal a great deal of information about the NPs. In the case of gold NPs synthesized using SCGs, a strong absorption peak was observed in the green region of the visible spectrum (about 540 nm) at the start of the synthesis. As the synthesis continued, the peak shifted towards the blue region to end between 525–535 nm (Figure 3 and Figure 4). An absorption peak at these wavelengths indicates an average diameter between 10–80 nm for spherical Au NPs [111,112,113] and an edge length of 15–50 nm for Au nanocubes [114]. As is typical for a single-pot, benchtop NP synthesis, a range of sizes and shapes were found in each sample and confirmed by SEM (Figures 7–12). While different shapes may cause additional absorption peaks further in the red and infrared regions, all Au NPs will exhibit a characteristic SPR band between 500–550 nm [111,112]. Additionally, the relative broadness of the absorption bands indicates a wide distribution of NP sizes present in each sample. In the case of silver NPs, an absorption peak was seen to develop in the 410–455 nm range initially, then became stronger throughout the synthesis without much shift in the peak absorption wavelength (Figure 5 and Figure 6). An absorption peak at these wavelengths for silver NPs indicates a size ranging between 20–100 nm [110,115,116,117,118]. Similar to Au NPs, all Ag NPs will exhibit a characteristic SPR band between 400–450 nm with some nonspherical shapes contributing additional absorption peaks in the red and infrared regions [112,117].
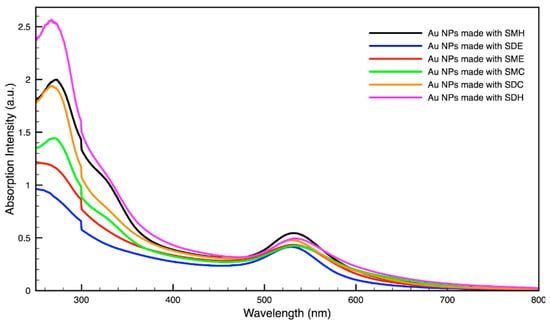
Figure 3.
Absorption spectrum of gold (Au) nanoparticles (NPs) synthesized using various forms of spent coffee ground extract.
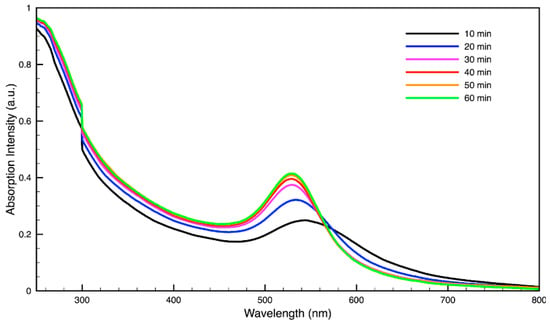
Figure 4.
Time evolution of absorption spectrum of gold (Au) nanoparticles during synthesis using dark roast, spent espresso coffee grounds (SDE).
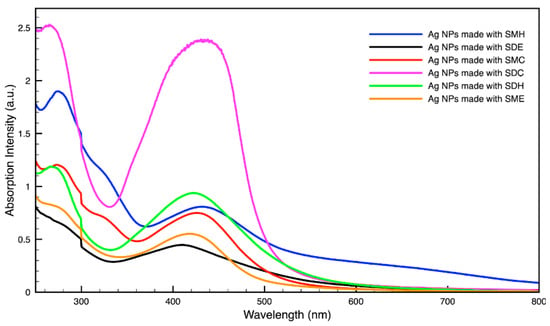
Figure 5.
Absorption spectrum of silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs) synthesized using various forms of spent coffee ground extract.
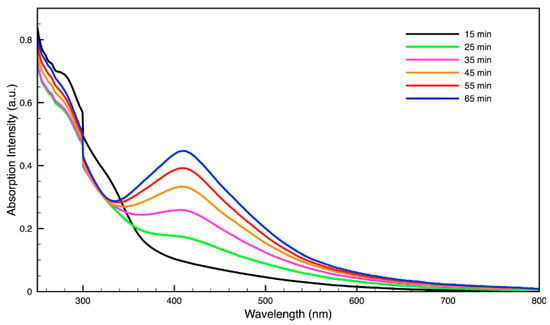
Figure 6.
Time evolution of absorption spectrum of silver (Ag) nanoparticles during synthesis using dark roast, spent espresso coffee grounds (SDE).
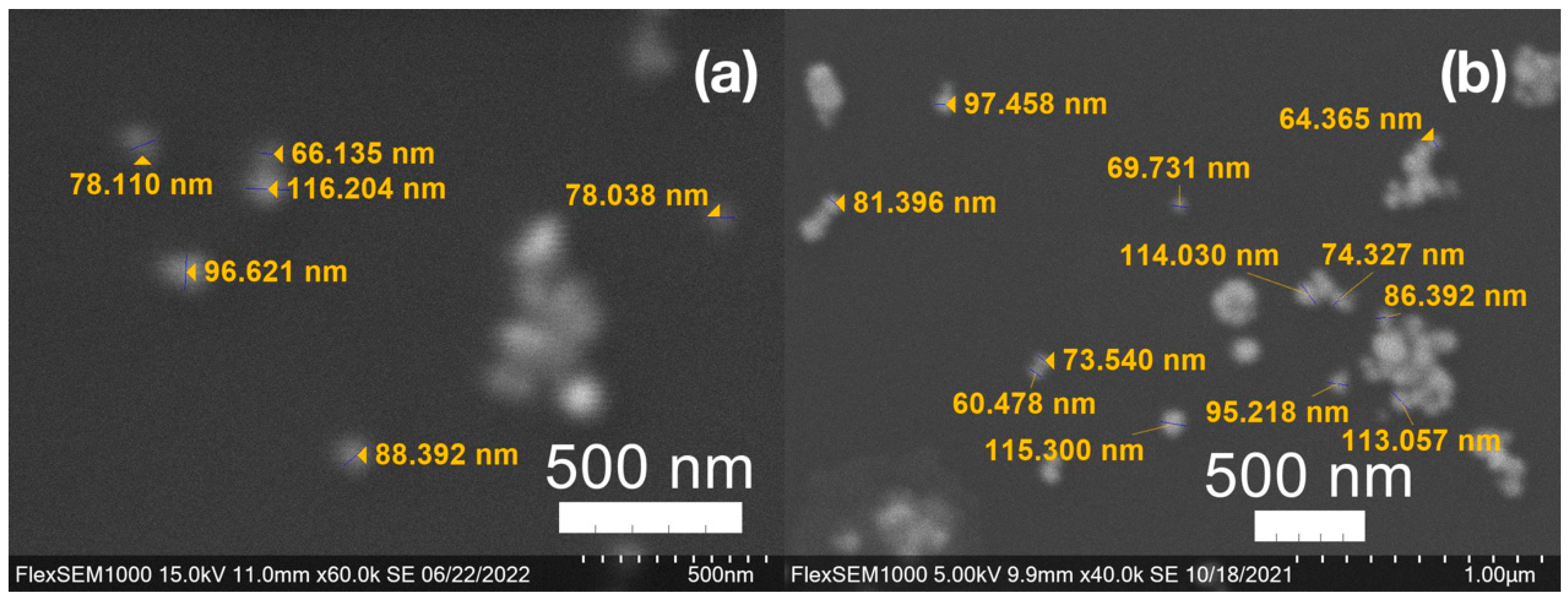
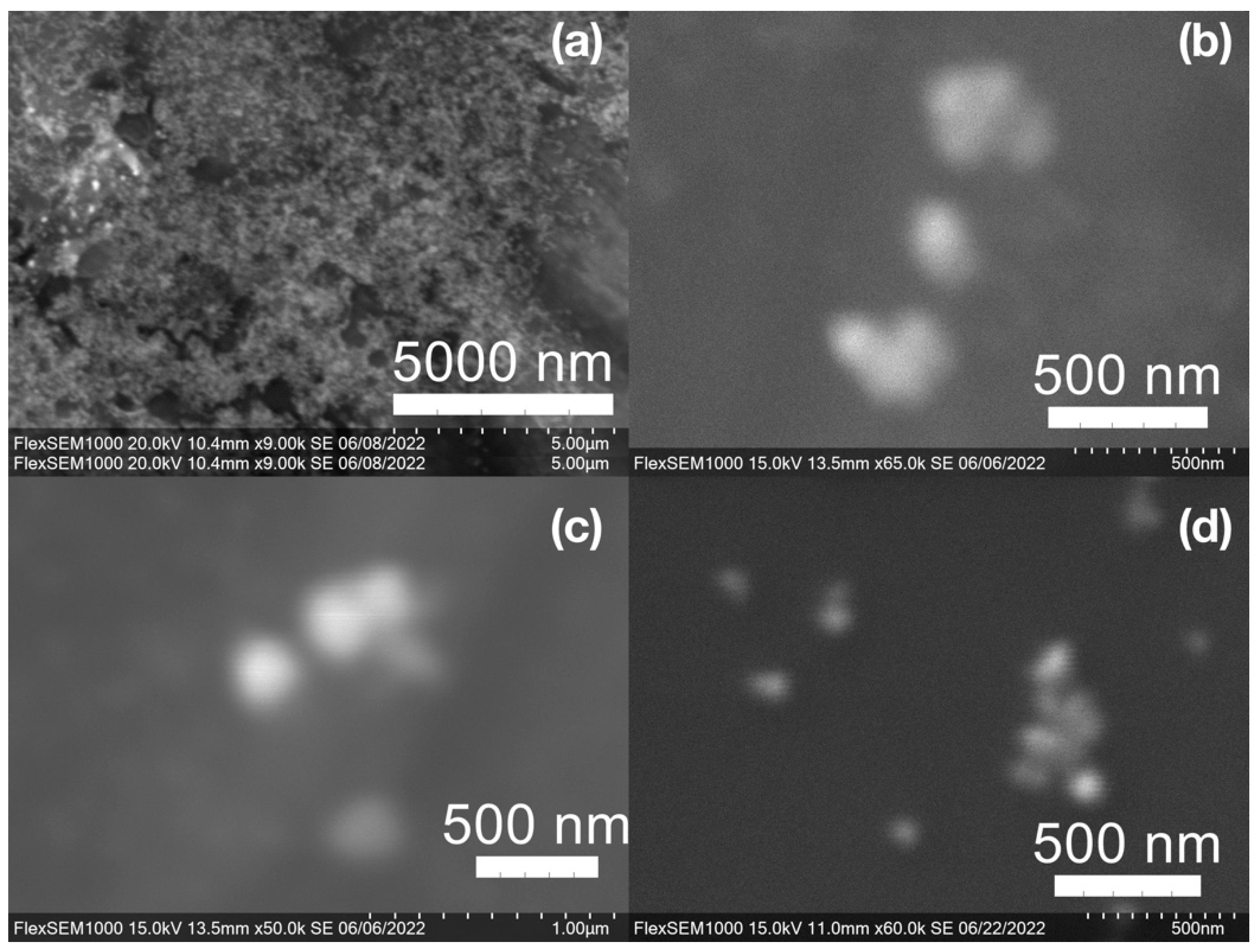
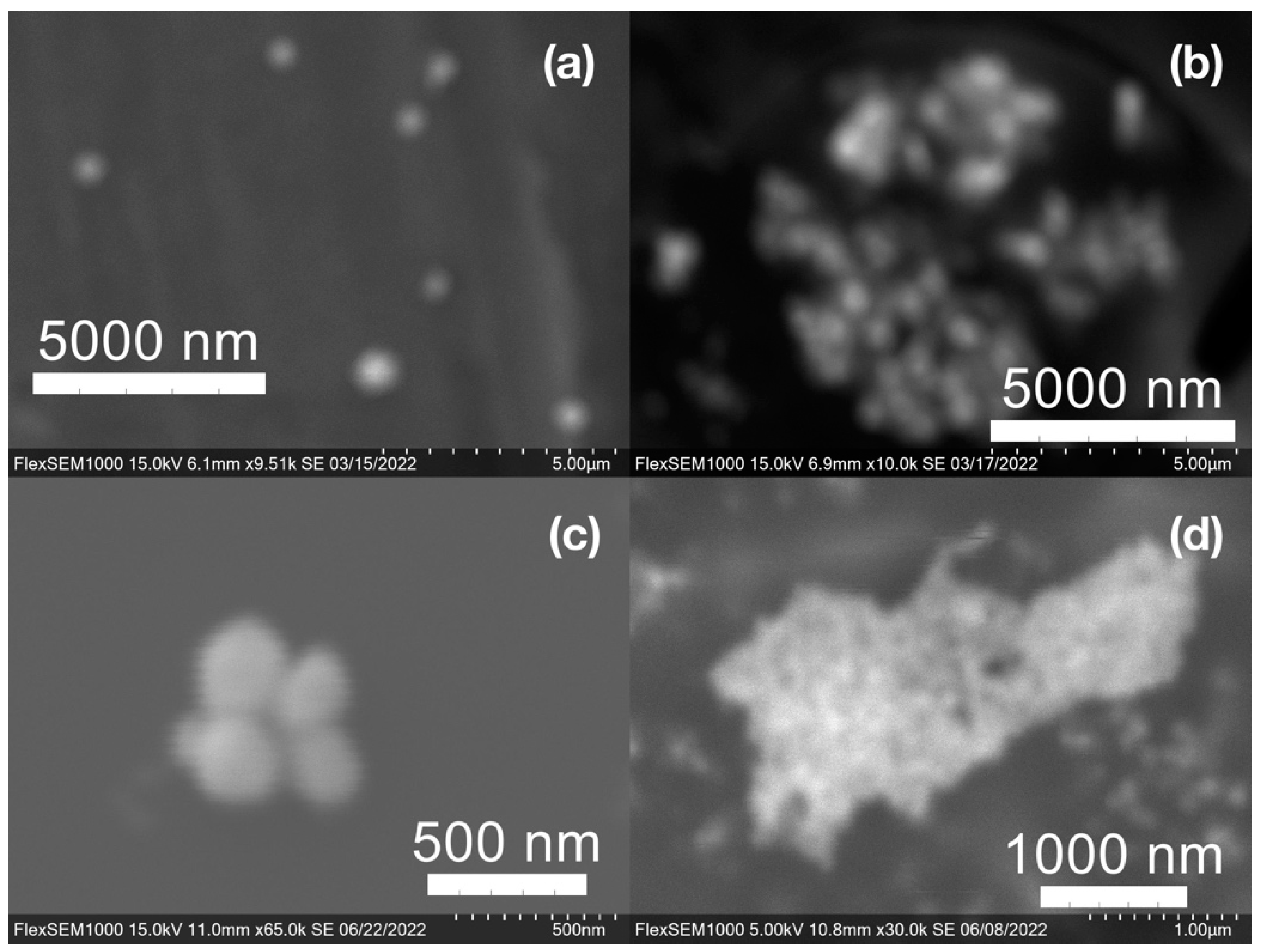
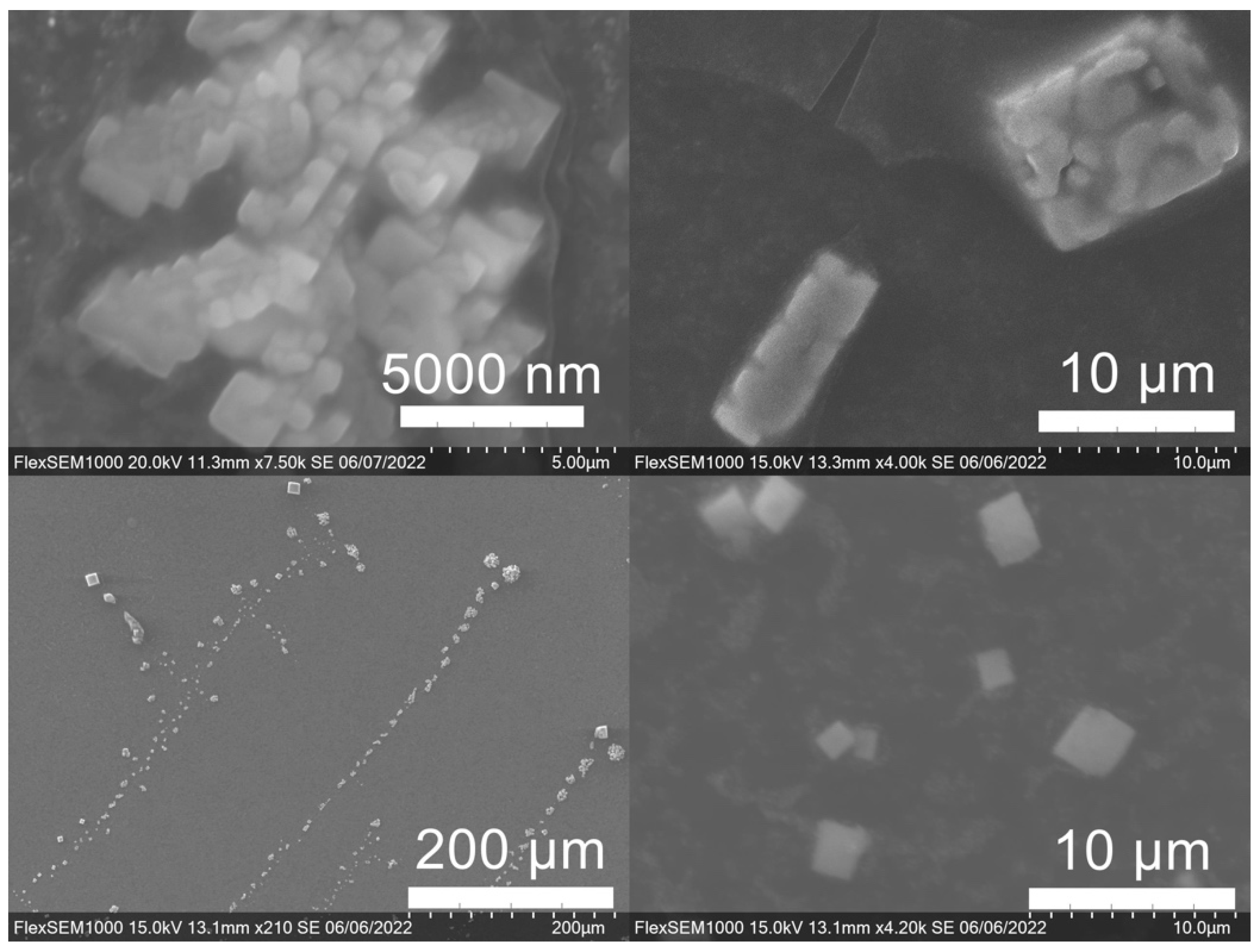
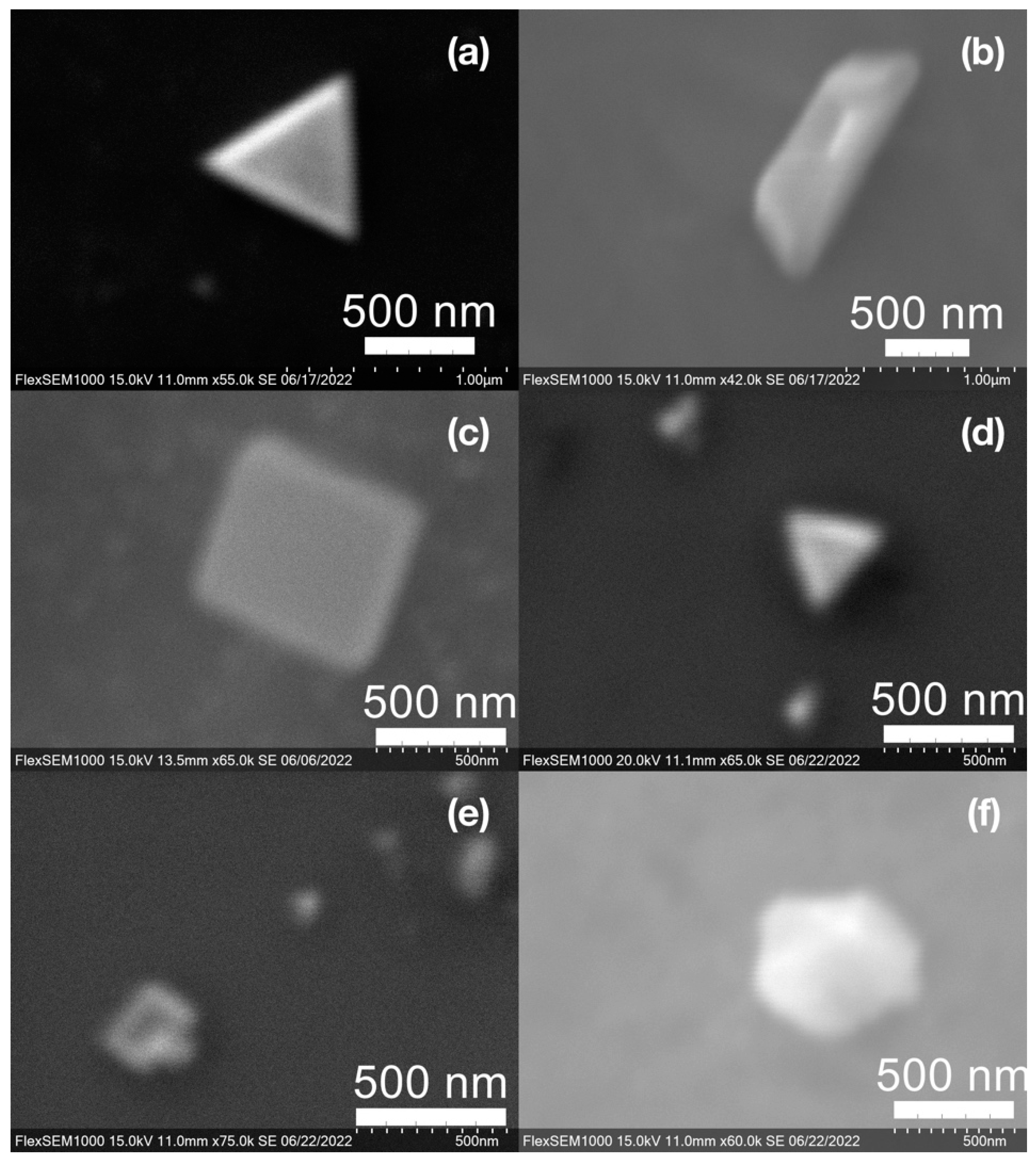
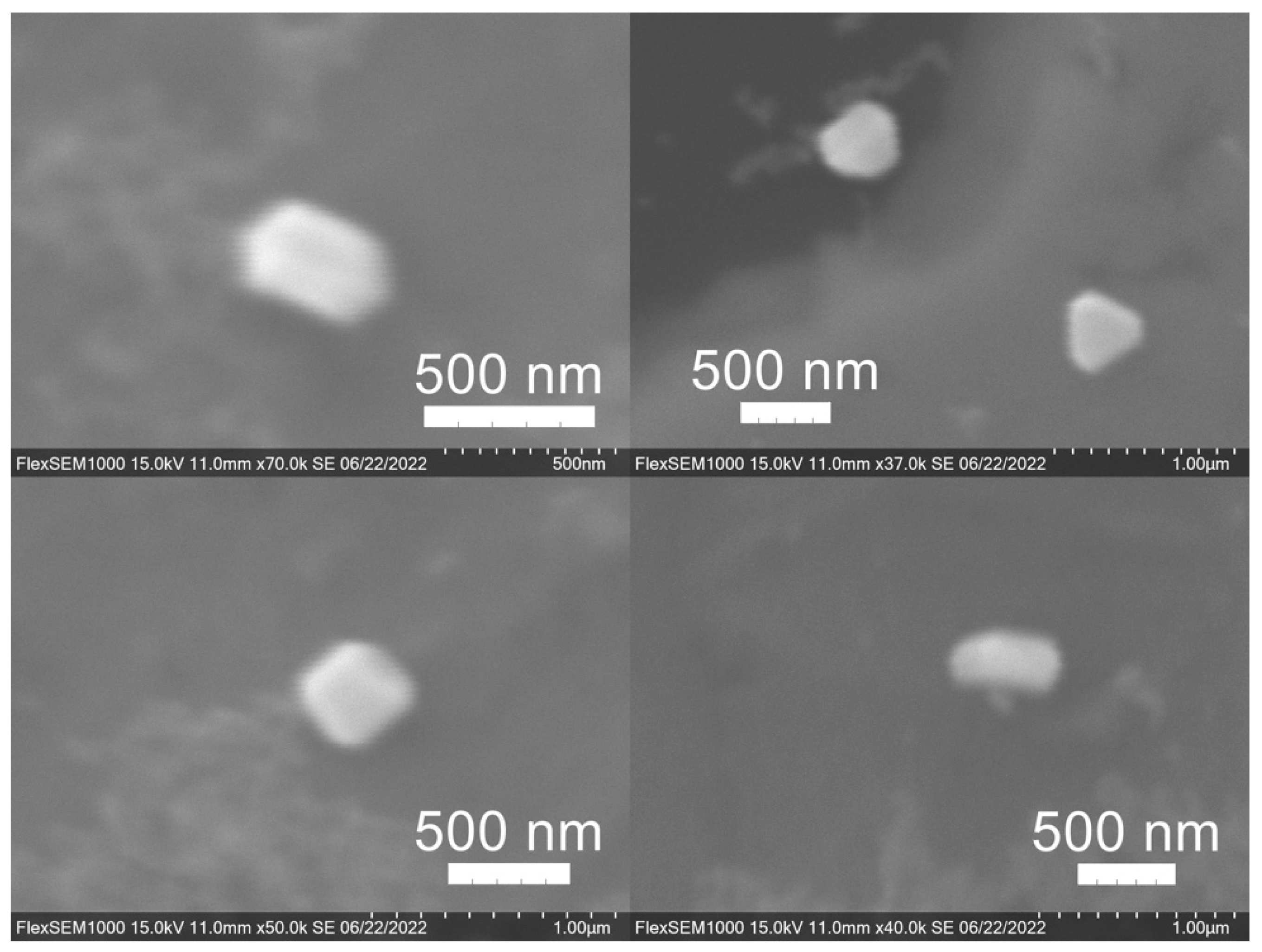
SEM images of the gold NP samples indicate that many of the individual NPs range in diameter from 66–120 nm (Figure 7a), although the exact size is difficult to determine due to the resolution of the imaging system. NPs with dimensions in the 100 s of nanometers were also observed (Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11). Larger clusters of NPs can also be seen (Figure 8 and Figure 10), which is not unusual in aqueous benchtop synthesis methods without the addition of a stabilizing agent to prevent NPs from sticking together. Images of the silver NP samples also indicate a range of individual NP dimensions from 60–120 nm for the smaller ones (Figure 7b) and in the 100s of nanometers (Figure 12) for larger particles. In the gold NP samples, larger cubic superstructures comprised of individual NPs were also observed (Figure 10), which suggests that many of the individual NPs are in fact nanocubes [119,120,121], with the superstructures resembling a Rubix cube. Other shapes were observed in the gold NP samples including pyramids, trapezoids, and spheres (Figure 11) with features ranging in size from 30–500 nm. Silver NP samples also had a variety of shapes (Figure 12) including prisms, hexagons, plates, and cubes with dimensions ranging from 30-400 nm. The presence of a wide range of sizes and shapes is an indication of reduction of metal ions and unchecked growth of NPs throughout the synthesis phase due to the strong antioxidant activity of the SCG extract. Once NPs are formed in an aqueous solution, any remaining reducing agents may cause NPs to continue to grow in size, agglomerate into multiparticle clusters, and fuse into micron-sized structures [111,112,113].
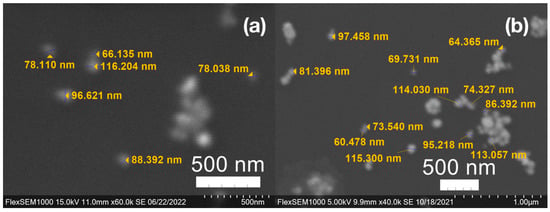
Figure 7.
(a) Gold (Au) and (b) silver (Ag) nanoparticles synthesized with medium roast coffee grounds (SCGs) from French press brew (SMH).
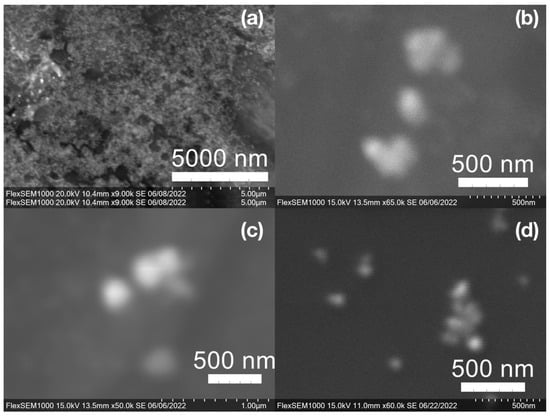
Figure 8.
Gold (Au) nanoparticles synthesized with (a) medium roast coffee grounds (SCGs) from French press brew (SMH); (b,c) dark roast SCGs from espresso brew (SDE); and (d) medium roast SCGs from cold brew (SMC).
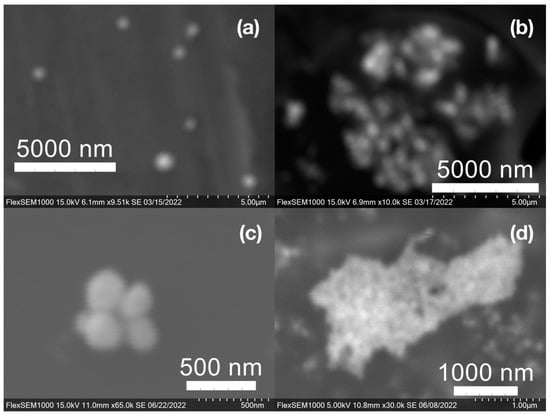
Figure 9.
Silver (Ag) nanoparticles synthesized with (a) medium roast coffee grounds (SCGs) from French press brew (SMH); (b,c) medium roast SCGs from cold brew (SMC); and (d) dark roast SCGs from espresso brew (SDE).
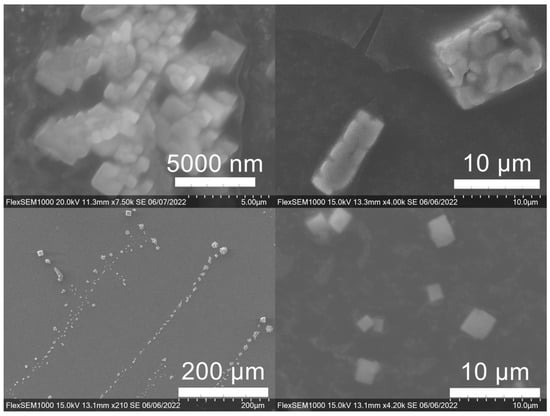
Figure 10.
Gold (Au) nanoparticles synthesized with dark roast coffee grounds from espresso brew (SDE) forming larger superstructure assemblies.
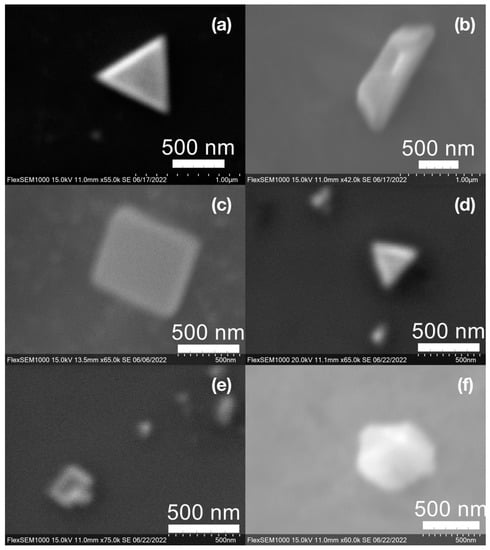
Figure 11.
Various gold (Au) nanoparticle shapes synthesized using spent coffee grounds of (a–c) dark roast used in espresso (SDE), and (d–f) medium roast used in cold brew coffee (SMC).
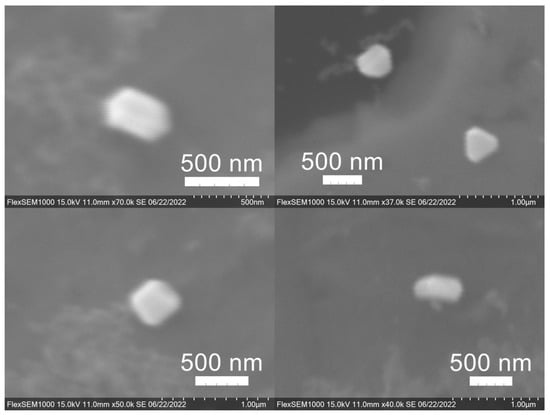
Figure 12.
Silver (Ag) nanoparticles synthesized using spent coffee grounds of medium roast used in cold brew coffee (SME).
Comparing the silver and gold NP samples made with the same amount of metal precursor and extract from SCGs, some variation in peak absorption wavelength can be observed (Table 3), which indicates differentiation in sizes and shapes of NPs present. These differences may be due to more complex interactions between the various active compounds, as well as the physical chemistry involved in growing and shaping the NPs in these particular environments. SDE and SME, which had the lowest TAC levels, produced silver NPs with the lowest SPR absorption wavelength, indicating that the average NP size was smaller when using espresso SCG extract as a reducing agent. However, this was the only discernible correlation between the peak absorption wavelength and TAC or CQA levels present in the SCG extract.

Table 3.
Peak absorption wavelength of nanoparticles (NPs) prepared with 0.5 mL of spent coffee ground (SCG)-derived extract per 30 mL sample.
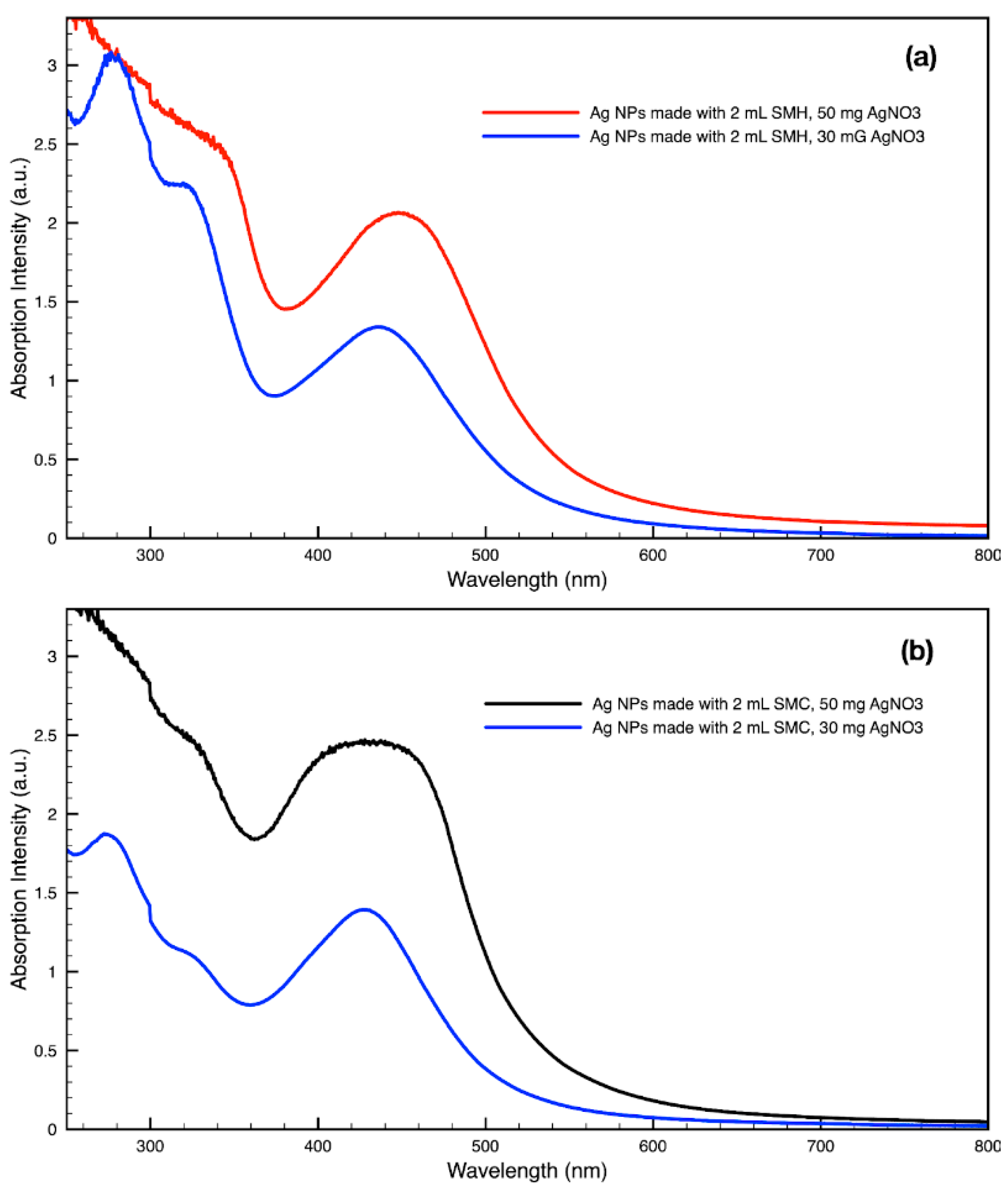
By varying the ratio of SCG extract to the total liquid volume while synthesizing NPs, it was seen that more SCG extract resulted in a more intense absorption peak without changing the peak wavelength (Figure 13). This suggests that within the range explored in this work, 0.5–2 mL, the addition of more SCG extract will yield more NPs without altering their relative sizes and shapes. By contrast, varying the ratio of metal precursor to total liquid volume corresponded to a shift in the peak absorbance wavelength (Figure 14). Samples synthesized using extract from SMH with more metal precursor yielded NPs with a peak wavelength of 449 nm, while the batch with less metal precursor had a peak wavelength of 437 nm. Samples synthesized using extract from SMC with more metal precursor yielded NPs with a peak wavelength of 434 nm, while the batch with less metal precursor had a peak wavelength of 428 nm. Since longer absorption wavelengths are correlated to larger size in metal NPs [112], these results indicate that higher metal precursor concentrations yield larger NPs overall rather than more NPs of the same size. More research is needed to investigate a wider range of metal precursor concentrations. Future studies should also clarify the exact roles the chemical components in SCG extracts play in reducing metal ions, promoting NP aggregation and growth, preferentially growing specific NP shapes, and capping or surface coating these NP species. Various metal, oxide, and other species of NPs which are synthesized by similar reduction methods can likely use this SCG extract technique.
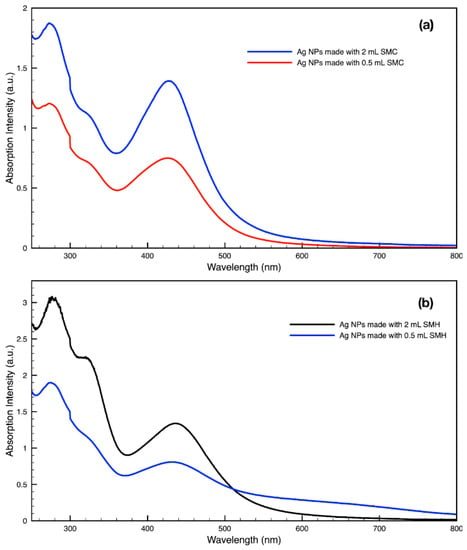
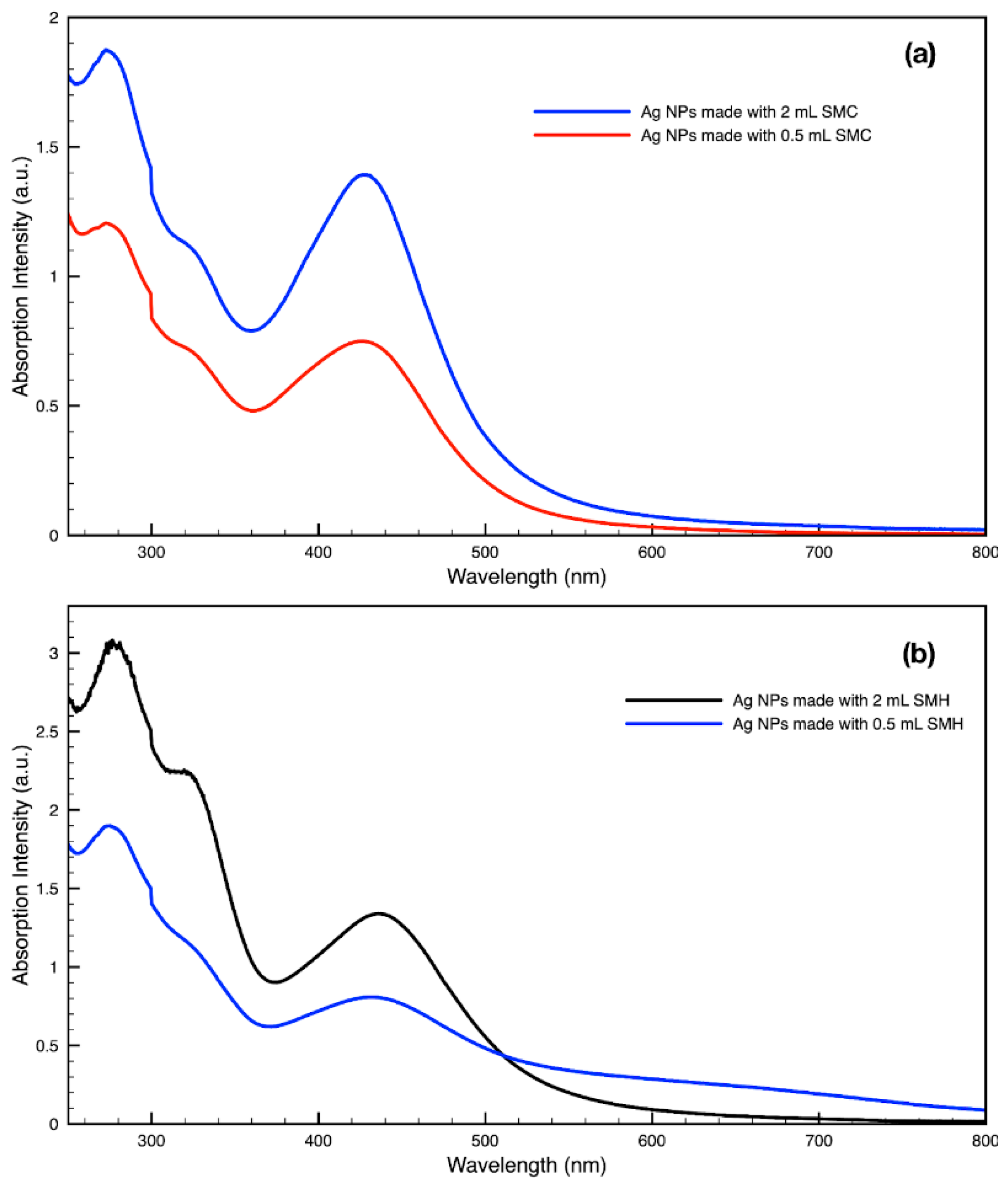
Figure 13.
Absorption spectra of silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs) synthesized with either 2 mL or 0.5 mL of (a) SMC extract or (b) SMH extract per 30 mL sample.
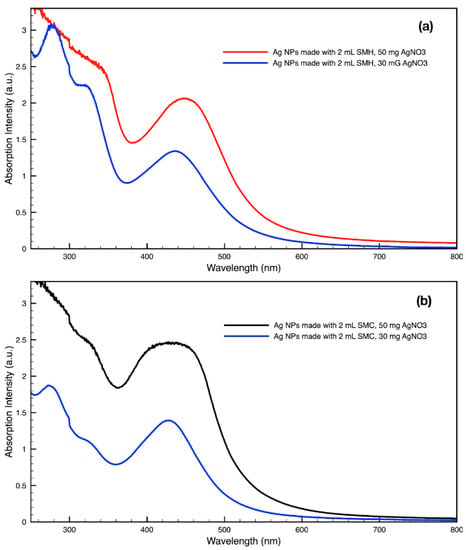
Figure 14.
Absorption spectra of silver (Ag) nanoparticles (NPs) synthesized with either 30 mg or 50 mg of metal precursor, AgNO3, per 30 mL sample by (a) SMH and (b) SMC.
4. Conclusions
The chemical components present in spent coffee grounds (SCG) available for ex-traction through a simple secondary brew process were characterized and quantified including total caffeoylquinic acid (CQA), total antioxidant capacities (TACs), as well as efficacy in synthesizing gold and silver nanoparticles (NPs). SCGs of both medium and dark roasts, which were initially brewed using hot brew, cold brew, and espresso methods, were investigated. It was found that SCGs from an initial hot brew exhibited the highest CQA and TAC levels, followed by SCGs from an initial cold brew, with SCGs from an initial espresso brew exhibiting the lowest CQA and TAC levels regardless of degree of roast. Compared to dark roast SCGs, medium roast SCGs yielded higher CQA levels but lower TAC levels whether processed via hot or cold brewing methods. This trend was reversed for espresso-derived SCGs, which showed higher CQA levels and lower TAC levels for the dark roast. This work also demonstrated a green chemistry, single-pot, aqueous workflow for synthesizing both gold and silver NPs with only two reagents, SCG extract and a metal precursor. It is shown that silver and gold NPs of various shapes and sizes ranging from 10 s of nm to 500 nm may be easily synthesized using SCGs regardless of the initial brewing method or degree of roast. Therefore, SCGs are shown to be as effective as coffee bean extract, coffee liquid, and fresh coffee grounds in synthesizing metal NPs through green chemistry methods. This confirms the utility of food-waste materials such as SCGs in synthesizing nanomaterials, whose wide-ranging applications provide a value-added opportunity to sectors of the economy that produce or handle SCGs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.Z.R., B.G.Y. and M.H.P.; Data curation, E.T.S.; Formal analysis, N.Z.R., E.T.S. and B.G.Y.; Investigation, N.Z.R., B.G.Y., E.T.S. and M.H.P.; Methodology, N.Z.R., B.G.Y., E.T.S. and M.H.P.; Project administration, N.Z.R.; Validation, N.Z.R. and B.G.Y.; Writing—original draft, N.Z.R., B.G.Y., E.T.S. and M.H.P.; Writing—review and editing, N.Z.R., B.G.Y., E.T.S. and M.H.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Thomas Jefferson University and in part by the Improving Food Quality 2019-67018-29187/1018488 from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture. Publication made possible in part by support from the Thomas Jefferson University Open Access Fund.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank our friends at Golden Valley Coffee Roasters in West Chester, Pennsylvania for their constant support. Publication made possible in part by support from the Thomas Jefferson University Open Access Fund.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- International Coffee Organization. Trade Statistics Tables. 2021. Available online: https://www.ico.org/trade_statistics.asp?section=Statistics (accessed on 24 June 2022).
- National Coffee Association. NCA-SCA 2022 Consumption Report; National Coffee Association: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bhandarkar, N.S.; Brown, L.; Panchal, S.K. Chlorogenic acid attenuates high-carbohydrate, high-fat diet–induced cardiovascular, liver, and metabolic changes in rats. Nutr. Res. 2019, 62, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, A.; de Paula Lima, J. Consumption of Chlorogenic Acids through Coffee and Health Implications. Beverages 2019, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghaienezhad, M.; Boroghani, M.; Anabestani, R. Silver nanoparticles Synthesis by coffee residues extract and their antibacterial activity. Nanomed. Res. J. 2020, 5, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Dhand, V.; Soumya, L.; Bharadwaj, S.; Chakra, S.; Bhatt, D.; Sreedhar, B. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Coffea arabica seed extract and its antibacterial activity, Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 58, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadagouda, M.N.; Varma, R.S. Green synthesis of silver and palladium nanoparticles at room temperature using coffee and tea extract. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, R.; Jafarizadeh-Malmiri, H. Green approach in gold, silver and selenium nanoparticles using coffee bean extract. Open Agric. 2020, 5, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, K.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Mei, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, P. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles using green coffee bean and their applications for efficient reduction of organic dyes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardood, S.T.; Ramazani, A. Green synthesis and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles using coffee powder extract. J. Nanostruct. 2016, 6, 167–171. Available online: http://jns.kashanu.ac.ir/article_15495.html (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- El-Desouky, N.; Shoueir, K.; El-Mehasseb, I.; El-Kemary, M. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using bio valorization coffee waste extract: Photocatalytic flow-rate performance, antibacterial activity, and electrochemical investigation. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Tesfaye, J.L.; Shanmugam, R.; Dwarampudi, L.P.; Lamessa, G.; Nagaprasad, N.; Krishnaraj, R. Green Synthesis and Characterizations of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Leaf Extracts of Coffee (Coffea arabica) and Its Application in Environmental Toxicity Reduction. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 3413350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.J.; Lee, J.; Wark, A.W.; Lee, H.J. Nanoparticle-enhanced surface plasmon resonance detection of proteins at attomolar concentrations: Comparing different nanoparticle shapes and sizes. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 1702–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, M.R.; Umadevi, M. Antibacterial and catalytic activities of green synthesized silver nanoparticles, Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 135, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, J.R.; García-Hernández, L.; Ortega, P.A.R.; Islas, D.A. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) by Cupressus Goveniana Extract. ECS Trans. 2018, 84, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herizchi, R.; Abbasi, E.; Milani, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Current methods for synthesis of gold nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresma, P.; Soares, L.; Contar, L.; Miranda, A.; Osório, I.; Carvalho, P.A.; Franco, R.; Pereira, E. Green photocatalytic synthesis of stable Au and Ag nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1889–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Yin, J.; Bai, M.; Wang, F. Green Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles Using Carrageenan Oligosaccharide and Their In Vitro Antitumor Activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Han, Y.; Gao, S.; Yan, H.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; Liang, X.-J.; Zhang, J. Ultrasmall gold nanoparticles in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 4944–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeshkumar, S. Anticancer activity of eco-friendly gold nanoparticles against lung and liver cancer cells. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2016, 14, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, M.; Whiley, H.; Köper, I. Antibiotic delivery using gold nanoparticles. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Alkilany, A.M.; Huang, X.; Murphy, C.J.; El-Sayed, M.A. The golden age: Gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2740–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, H.; Khan, I.; Alghamdi, S.; Almehmadi, M.; Ali, M.; Ullah, A.; Hussain, H.; Khan, N.M.; Ali, F.; et al. Green synthesis of gold nanaoparticles using Delphinium Chitralense tuber extracts, their characterization and enzyme inhibitory potential. Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 82, e257622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, K.; Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, H.; Ullah, F.; Sadiq, A.; Uddin, A.; Khan, I.; Ahmad, M. Green synthesis, characterization and cholinesterase inhibitory potential of gold nanoparticles. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2021, 65, 416–423. [Google Scholar]
- Simončič, B.; Klemenčič, D. Preparation and performance of silver as an antimicrobial agent for textiles: A review. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebeish, A.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Fouda, M.M.G.; Ramadan, M.A.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Rafie, M.H. Highly effective antibacterial textiles containing green synthesized silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 936–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, S.; Mohan, Y.M.; Reddy, N.N.; Raju, K.M. Fabrication of antibacterial cotton fibres loaded with silver nanoparticles via “Green Approach,” Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 367, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Chitosan Combined with ZnO, TiO2 and Ag Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Wound Healing Applications: A Mini Review of the Research Trends. Polymers 2017, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.D.; Rajendran, N.K.; Houreld, N.N.; Abrahamse, H. Recent advances on silver nanoparticle and biopolymer-based biomaterials for wound healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 115, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.-Y.; Jin, H.; Park, Y. Assessing the antioxidant, cytotoxic, apoptotic and wound healing properties of silver nanoparticles green-synthesized by plant extracts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmaaty, T.A.; El-Nagare, K.; Raouf, S.; Abdelfattah, K.; El-Kadi, S.; Abdelaziz, E. One-step green approach for functional printing and finishing of textiles using silver and gold NPs. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 25546–25557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, S.; Salem, S.S.; L-Belely, E.F.E.; Niedbała, G.; Alnoman, M.M.; Hassan, S.E.-D.; Eid, A.M.; Shaheen, T.I.; Elkelish, A.; Fouda, A. Bactericidal and In-Vitro Cytotoxic Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) Fabricated by Endophytic Actinomycetes and Their Use as Coating for the Textile Fabrics. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouri, Z.K.; Al-Meer, S.; Barakat, N.A.M.; Kim, H.Y. ZnO@C (core@shell) microspheres derived from spent coffee grounds as applicable non-precious electrode material for DMFCs. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutradhar, P.; Debnath, N.; Saha, M. Microwave-assisted rapid synthesis of alumina nanoparticles using tea, coffee and triphala extracts. Adv. Manuf. 2013, 1, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crista, D.M.A.; el Mragui, A.; Algarra, M.; da Silva, J.C.G.E.; Luque, R.; da Silva, L.P. Turning Spent Coffee Grounds into Sustainable Precursors for the Fabrication of Carbon Dots. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.J.; Kim, H.-S.; Jun, S.H.; Kang, Y.-H.; Cho, S.; Park, Y. Biogenic silver nanoparticles with chlorogenic acid as a bioreducing agent. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 5787–5793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Bai, X. Synthesis of antibacterial gold nanoparticles with different particle sizes using chlorogenic acid. R Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 191141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wu, S.; Meng, C. Size-tunable green synthesis of platinum nanoparticles using chlorogenic acid. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2021, 47, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yi, G.; Wu, S.; Meng, C. Controlled green synthesis of Au–Pt bimetallic nanoparticles using chlorogenic acid. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2021, 47, 4051–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Vega, R.; Loarca-Piña, G.; Vergara-Castañeda, H.A.; Oomah, B.D. Spent coffee grounds: A review on current research and future prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, G.D.; Bhosale, R.; Shobana, S.; Banu, J.R.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Mahmoud, E.; Sirohi, R.; Bhatia, S.K.; At-abani, A.E.; Mulone, V.; et al. A review on valorization of spent coffee grounds (SCG) towards biopolymers and biocatalysts production. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janda, K.; Jakubczyk, K.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Kapczuk, P.; Kochman, J.; Rębacz-Maron, E.; Gutowska, I. Mineral Composition and Antioxidant Potential of Coffee Beverages Depending on the Brewing Method. Foods 2020, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, M.; Rao, N.Z. The Effect of Time, Roasting Temperature, and Grind Size on Caffeine and Chlorogenic Acid Concentrations in Cold Brew Coffee. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, X.J.; Ong, H.C.; Gao, W.; Ok, Y.S.; Chen, W.-H.; Goh, B.H.H.; Chong, C.T. Solid biofuel production from spent coffee ground wastes: Process optimisation, characterisation and kinetic studies. Fuel 2021, 292, 120309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabani, A.E.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Kumar, G.; Saratale, G.D.; Aslam, M.; Khan, H.A.; Said, Z.; Mahmoud, E. Valorization of spent coffee grounds into biofuels and value-added products: Pathway towards integrated bio-refinery. Fuel. 2019, 254, 115640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmee, S.K. A spent coffee grounds based biorefinery for the production of biofuels, biopolymers, antioxidants and biocomposites. Waste Manag. 2018, 72, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battista, F.; Barampouti, E.M.; Mai, S.; Bolzonella, D.; Malamis, D.; Moustakas, K.; Loizidou, M. Added-value molecules recovery and biofuels production from spent coffee grounds. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 110007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabani, A.E.; Ali, I.; Naqvi, S.R.; Badruddin, I.A.; Aslam, M.; Mahmoud, E.; Almomani, F.; Juchelková, D.; Atelge, M.R.; Khan, T.M.Y. A state-of-the-art review on spent coffee ground (SCG) pyrolysis for future biorefinery. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, J.; Juániz, I.; Monente, C.; Caemmerer, B.; Kroh, L.W.; de Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Evaluation of spent coffee obtained from the most common coffeemakers as a source of hydrophilic bioactive compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 12565–12573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Barrera, D.M.; Vázquez-Sánchez, K.; Loarca-Piña, M.G.F.; Campos-Vega, R. Spent coffee grounds, an innovative source of colonic fermentable compounds, inhibit inflammatory mediators in vitro. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, R.; Cardoso, M.M.; Fernandes, L.; Oliveira, M.; Mendes, E.; Baptista, P.; Morais, S.; Casal, S. Espresso coffee residues: A valuable source of unextracted compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7777–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuorro, A.; Lavecchia, R. Spent coffee grounds as a valuable source of phenolic compounds and bioenergy. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 34, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengin, G.; Sinan, K.I.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Angeloni, S.; Mustafa, A.M.; Vittori, S.; Maggi, F.; Caprioli, G. Chemical Composition, Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Properties of Different Extracts Obtained from Spent Coffee Ground and Coffee Silverskin. Foods 2020, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, D.; Liu, C.; Gominho, J.; Olivella, M.À.; Fiol, N.; Villaescusa, I.; Pereira, H. The chemical composition of exhausted coffee waste. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Głowacka, R.; Górska, A.; Wirkowska-Wojdyła, M.; Wołosiak, R.; Majewska, E.; Derewiaka, D. The influence of brewing method on bioactive compounds residues in spent coffee grounds of different roasting degree and geographical origin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 3008–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongsrimsirisakhol, O.; Pirak, T. Total polyphenol content and antioxidant properties of cold brew coffee extracts as affected by ultrasound treatment and their application in low fat pork sausage. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Ballesteros, L.F.; Martins, S.; Teixeira, J.A. Extraction of antioxidant phenolic compounds from spent coffee grounds. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 83, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozuna, C.; Mulík, S.; Valdez-Rodríguez, B.; Abraham-Juárez, M.d.; Fernández-López, C.L. The effect of organic farming on total phenols, total flavonoids, brown compounds and antioxidant activity of spent coffee grounds from Mexico. Biol. Agric. Hortic. 2020, 36, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.E.; Jeong, K.M.; Han, S.Y.; Kim, E.M.; Jin, Y.; Lee, J. Deep eutectic solvent-based valorization of spent coffee grounds. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Páscoa, R.N.M.J.; Magalhães, L.M.; Lopes, J.A. FT-NIR spectroscopy as a tool for valorization of spent coffee grounds: Application to assessment of antioxidant properties. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, G.F.Y.; Pabiloña, K.B.C.; Manlangit, K.B.L.; Go, A.W. Direct dilute acid hydrolysis of spent coffee grounds: A new approach in sugar and lipid recovery. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.E.; Yi, H.; Jeon, Y.J. Sequential co-production of biodiesel and bioethanol with spent coffee grounds. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Qin, L.; Li, O.L. Reducing sugar production from spent coffee grounds using microbubble-assisted synthesis of silica acid catalyst. Catal. Today 2022, 388–389, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.W.; Conag, A.T.; Cuizon, D.E.S. Recovery of sugars and lipids from spent coffee grounds: A new approach. Waste Biomass Valorization 2016, 7, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I.; Carneiro, L.M.; Silva, J.P.A.; Roberto, I.C.; Teixeira, J.A. A study on chemical constituents and sugars extraction from spent coffee grounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.P.; Vicente, E.D.; Gomes, A.P.; Nunes, M.I.; Alves, C.; Tarelho, L.A.C. Effect of industrial and domestic ash from biomass combustion, and spent coffee grounds, on soil fertility and plant growth: Experiments at field conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 15270–15277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Price, G.W. Evaluation of three composting systems for the management of spent coffee grounds. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7966–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragauskaitė, D.; Šlinkšienė, R. Influence of Urea on Organic Bulk Fertilizer of Spent Coffee Grounds and Green Algae Chlorella sp. Biomass. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielczuk, T.; Rosik-Dulewska, C.; Poluszyńska, J.; Miłek, D.; Szewczyk, A.; Sławińska, I. Acute Toxicity of Experimental Fertilizers Made of Spent Coffee Grounds. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangindaan, D.; Lin, G.-Y.; Kuo, C.-J.; Chien, H.-W. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles as catalyst by spent coffee ground/recycled poly(ethylene terephthalate) composites. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 121, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzella, L.; Cerruti, P.; Aprea, P.; Paolillo, R.; Pellegrino, G.; Moccia, F.; Condorelli, G.G.; Vollaro, A.; Ambrogi, V.; Catania, M.R.; et al. Silver nanoparticles on hydrolyzed spent coffee grounds (HSCG) for green antibacterial devices. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzano, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Tundis, R.; Lucci, P.; Nunez, O.; Fiorini, D.; Giardinieri, A.; Frega, N.G.; Pacetti, D. Spent espresso coffee grounds as a source of anti-proliferative and antioxidant compounds. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 59, 102254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monente, C.; Ludwig, I.A.; Irigoyen, A.; de Peña, M.-P.; Cid, C. Assessment of total (free and bound) phenolic compounds in spent coffee extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 4327–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.; Monente, C.; Juániz, I.; de Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Influence of extraction process on antioxidant capacity of spent coffee. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uman, E.; Colonna-Dashwood, M.; Colonna-Dashwood, L.; Perger, M.; Klatt, C.; Leighton, S.; Miller, B.; Butler, K.T.; Melot, B.C.; Speirs, R.W.; et al. The effect of bean origin and temperature on grinding roasted coffee. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Analysis of chlorogenic acid in coffee by HPLC, GL Science Inc. (n.d.). Available online: https://www.glsciences.com/technique/app/detail.php?data_number=LT067 (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Farah, A.; de Paulis, T.; Trugo, L.C.; Martin, P.R. Effect of roasting on the formation of chlorogenic acid lactones in coffee. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trugo, L.C.; Macrae, R. Chlorogenic acid composition of instant coffees. Analyst 1984, 109, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, N.Z.; Fuller, M.; Grim, M.D. Physiochemical Characteristics of Hot and Cold Brew Coffee Chemistry: The Effects of Roast Level and Brewing Temperature on Compound Extraction. Foods 2020, 9, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odžaković, B.; Džinić, N.; Kukrić, Z.; Grujić, S. Effect of roasting degree on the antioxidant activity of different Arabica coffee quality classes. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2016, 15, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzykiewicz, A.; Zielonka-Brzezicka, J.; Klimowicz, A. The antioxidant potential of flesh, albedo and flavedo extracts from different varieties of grapefruits. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2019, 18, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The Ferric Reducing Ability of Plasma (FRAP) as a Measure of “Antioxidant Power”: The FRAP Assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulfinger, L.; Solomon, S.D.; Bahadory, M.; Jeyarajasingam, A.V.; Rutkowsky, S.A.; Boritz, C. Synthesis and Study of Silver Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Educ. 2007, 84, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.C.; Lee, S.M.; Park, T.S.; Lee, B.S. Preparation of colloidal silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction method. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 26, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merga, G.; Wilson, R.; Lynn, G.; Milosavljevic, B.H.; Meisel, D. Redox Catalysis on “Naked” Silver Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12220–12226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessa, P. Free Statistics Software, version 1.2.1; Office for Research Development and Education. 2020. Available online: https://www.wessa.net (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Cordoba, N.; Pataquiva, L.; Osorio, C.; Moreno, F.L.M.; Ruiz, R.Y. Effect of grinding, extraction time and type of coffee on the physicochemical and flavour characteristics of cold brew coffee. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.-E.; Lee, H.-U.; Davaatseren, M.; Chung, M.-S. Comparison of acrylamide and furan concentrations, antioxidant activities, and volatile profiles in cold or hot brew coffees. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimowski, D.; Pachura, N.; Oziembłowski, M.; Nawirska-Olszańska, A.; Szumny, A. Coffee Roasting and Extraction as a Factor in Cold Brew Coffee Quality. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, N.; Moreno, F.L.; Osorio, C.; Velásquez, S.; Ruiz, Y. Chemical and sensory evaluation of cold brew coffees using different roasting profiles and brewing methods. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeloni, G.; Guerrini, L.; Masella, P.; Bellumori, M.; Daluiso, S.; Parenti, A.; Innocenti, M. What kind of coffee do you drink? An investigation on effects of eight different extraction methods. Food Res. Int. 2018, 116, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, I.A.; Sanchez, L.; Caemmerer, B.; Kroh, L.W.; de Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Extraction of coffee antioxidants: Impact of brewing time and method. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šeremet, D.; Fabečić, P.; Cebin, A.V.; Jarić, A.M.; Pudić, R.; Komes, D. Antioxidant and Sensory Assessment of Innovative Coffee Blends of Reduced Caffeine Content. Molecules 2022, 27, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoli, M.C.; Anese, M.; Manzocco, L.; Lerici, C.R. Antioxidant Properties of Coffee Brews in Relation to the Roasting Degree. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 30, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, S.E.W.; Smrke, S.; Goodman, B.A.; Keller, M.; Schenker, S.; Yeretzian, C. Antioxidant Generation during Coffee Roasting: A Comparison and Interpretation from Three Complementary Assays. Foods 2014, 3, 586–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilipczuk, T.; Kusznierewicz, B.; Zielińska, D.; Bartoszek, A. The influence of roasting and additional processing on the content of bioactive components in special purpose coffees. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 5736–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-K.; Shibamoto, T. Role of roasting conditions in the profile of volatile flavor chemicals formed from coffee beans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5823–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, J.A.; Viegas, M.C.; Bassoli, D.G.; Benassi, M.d.T. Roasting process affects differently the bioactive compounds and the antioxidant activity of arabica and robusta coffees. Food Res. Int. 2014, 61, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzykiewicz-Szymańska, A.; Nowak, A.; Wira, D.; Klimowicz, A. The Effect of Brewing Process Parameters on Antioxidant Activity and Caffeine Content in Infusions of Roasted and Unroasted Arabica Coffee Beans Originated from Different Countries. Molecules 2021, 26, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, G. Investigating the effects of geographical origin, roasting degree, particle size and brewing method on the physicochemical and spectral properties of Arabica coffee by PCA analysis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 3345–3354. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13197-020-04367-9?noAccess=true (accessed on 5 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Rao, N.Z.; Fuller, M. Acidity and Antioxidant Activity of Cold Brew Coffee. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andueza, S.; Maeztu, L.; Pascual, L.; Ibáñez, C.; de Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Influence of extraction temperature on the final quality of espresso coffee. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 240–248. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.co (accessed on 5 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Andueza, S.; de Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Chemical and sensorial characteristics of espresso coffee as affected by grinding and torrefacto roast. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7034–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andueza, S.; Maeztu, L.; Dean, B.; de Peña, M.P.; Bello, J.; Cid, C. Influence of water pressure on the final quality of arabica espresso coffee. Application of multivariate analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7426–7431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andueza, S.; Vila, M.A.; de Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Influence of coffee/water ratio on the final quality of espresso coffee. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2007, 87, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Review of some interesting surface plasmon resonance-enhanced properties of noble metal nanoparticles and their applications to Biosystems. Plasmonics 2007, 2, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramelle, D.; Sadovoy, A.; Gorelik, S.; Free, P.; Hobley, J.; Fernig, D.G. A rapid method to estimate the concentration of citrate capped silver nanoparticles from UV-visible light spectra. Analyst 2014, 139, 4855–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amendola, V.; Pilot, R.; Frasconi, M.; Maragò, O.M.; Iatì, M.A. Surface plasmon resonance in gold nanoparticles: A review. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 203002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burda, C.; Chen, X.; Narayanan, R.; El-Sayed, M.A. Chemistry and properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 1025–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Casas, J.; Venkataramasubramani, M.; Tang, L. Synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles with plasmon absorbance wavelength tunable from visible to near infrared region. Int. Bus. Rev. 2012, 2012, 659043. Available online: https://downloads.hindawi.com/archive/2012/659043.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Lee, Y.; Nam, J.-M. Correction to Precisely Shaped, Uniformly Formed Gold Nanocubes with Ultrahigh Reproducibility in Single-Particle Scattering and Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim-Al-Razy, M.; Bayazid, G.M.A.; Rahman, R.U.; Bosu, R.; Shamma, S.S. Silver nanoparticle synthesis, UV-Vis spectroscopy to find particle size and measure resistance of colloidal solution. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1706, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamplecoskie, K.G.; Scaiano, J.C.; Tiwari, V.S.; Anis, H. Optimal Size of Silver Nanoparticles for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.L.; Coronado, E.; Zhao, L.L.; Schatz, G.C. The Optical Properties of Metal Nanoparticles: The Influence of Size, Shape, and Dielectric Environment. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, S.; Mukherji, S.; Mukherji, S. Size-controlled silver nanoparticles synthesized over the range 5–100 nm using the same protocol and their antibacterial efficacy. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göppert, A.-K.; González-Rubio, G.; Cölfen, H. Microscopic Analysis of Heterogeneous Nucleation of Nanoparticle Superstructures. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 124, 5657–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Gonzalez-Rubio, G.; Cölfen, H. Self-Assembly of Colloidal Nanocrystals into 3D Binary Mesocrystals. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.H.; Thoka, S. Formation of supercrystals through self-assembly of polyhedral nanocrystals. Nano Today 2015, 10, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).