Rapid SABRE Catalyst Scavenging Using Functionalized Silicas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
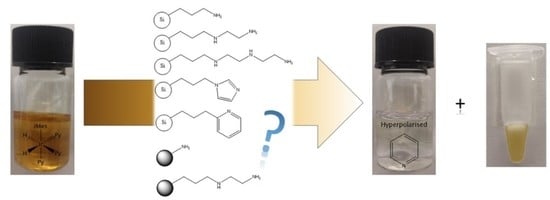
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Apparatus Used for Generation of Parahydrogen
3.3. SABRE Sample Preparation
3.4. Preparation of ICP-OES Samples
3.5. Preparation of ICP-OES Samples with Varying Catalyst Quantities
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Zhang, G.N.; Hilty, C. Applications of dissolution dynamic nuclear polarization in chemistry and biochemistry. Magn. Reason. Chem. 2018, 56, 566–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovtunov, K.V.; Pokochueva, E.V.; Salnikov, O.G.; Cousin, S.F.; Kurzbach, D.; Vuichoud, B.; Jannin, S.; Chekmenev, E.Y.; Goodson, B.M.; Barskiy, D.A.; et al. Hyperpolarized NMR Spectroscopy: D-DNP, PHIP, and SABRE Techniques. Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 1857–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witte, C.; Schroder, L. NMR of hyperpolarised probes. NMR Biomed. 2013, 26, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, B. Quantum-rotor-induced polarization. Magn. Reason. Chem. 2018, 56, 610–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, T.R.; Nacher, P.J.; Saam, B.; Walker, T.G. Optically polarized He-3. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2017, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Pinon, A.C.; Emsley, L.; Rossini, A.J. DNP-enhanced solid-state NMR spectroscopy of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Magn. Reason. Chem. 2018, 56, 583–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Hilty, C. Intermolecular interactions determined by NOE build-up in macromolecules from hyperpolarized small molecules. Methods 2018, 138, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duckett, S.B.; Mewis, R.E. Application of Parahydrogen Induced Polarization Techniques in NMR Spectroscopy and Imaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1247–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovtunov, K.V.; Zhivonitko, V.V.; Skovpin, I.V.; Barskiy, D.A.; Koptyug, I.V. Parahydrogen-Induced Polarization in Heterogeneous Catalytic Processes. In Hyperpolarization Methods in NMR Spectroscopy; Kuhn, L.T., Ed.; Topics in Current Chemistry-Series; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; Volume 338, pp. 123–180. [Google Scholar]
- Viale, A.; Santelia, D.; Napolitano, R.; Gobetto, R.; Dastru, W.; Aime, S. The Detection of PHIP Effects Allows New Insights into the Mechanism of Olefin Isomerisation during Catalytic Hydrogenation. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 4348–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apps, A.; Lau, J.; Peterzan, M.; Neubauer, S.; Tyler, D.; Rider, O. Hyperpolarised magnetic resonance for in vivo real-time metabolic imaging. Heart 2018, 104, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skinner, J.G.; Menichetti, L.; Flori, A.; Dost, A.; Schmidt, A.B.; Plaumann, M.; Gallagher, F.A.; Hovener, J.B. Metabolic and Molecular Imaging with Hyperpolarised Tracers. Mol. Imaging Biol 2018, 20, 902–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallari, E.; Carrera, C.; Aime, S.; Reineri, F. Metabolic Studies of Tumor Cells Using 1-C-13 Pyruvate Hyperpolarized by Means of PHIP-Side Arm Hydrogenation. ChemPhysChem 2019, 20, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, D.P.; Collins, J.H.P.; Lama, B.; Zeng, H.D.; Nguyen, T.; Keller, G.; Febo, M.; Long, J.R. Characterization of Brain Metabolism by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. ChemPhysChem 2019, 20, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, J.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Autry, A.; Park, I.; Van Criekinge, M.; Mammoli, D.; Milshteyn, E.; Bok, R.; Xu, D.; Li, Y.; et al. Translation of Carbon-13 EPI for hyperpolarized MR molecular imaging of prostate and brain cancer patients. Magn Reson Med. 2019, 81, 2702–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.W.; Aguilar, J.A.; Atkinson, K.D.; Cowley, M.J.; Elliott, P.I.P.; Duckett, S.B.; Green, G.G.R.; Khazal, I.G.; López-Serrano, J.; Williamson, D.C. Reversible Interactions with para-Hydrogen Enhance NMR Sensitivity by Polarization Transfer. Science 2009, 323, 1708–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, R.W.; Duckett, S.B.; Green, R.A.; Williamson, D.C.; Green, G.G.R. A theoretical basis for spontaneous polarization transfer in non-hydrogenative parahydrogen-induced polarization. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barskiy, D.A.; Knecht, S.; Yurkovskaya, A.V.; Ivanov, K.L. SABRE: Chemical kinetics and spin dynamics of the formation of hyperpolarization. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reason. Spectrosc. 2019, 114-115, 33–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovener, J.B.; Schwaderlapp, N.; Borowiak, R.; Lickert, T.; Duckett, S.B.; Mewis, R.E.; Adams, R.W.; Burns, M.J.; Highton, L.A.R.; Green, G.G.R.; et al. Toward Biocompatible Nuclear Hyperpolarization Using Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange: Quantitative in Situ Spectroscopy and High-Field Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewis, R.E.; Atkinson, K.D.; Cowley, M.J.; Duckett, S.B.; Green, G.G.R.; Green, R.A.; Highton, L.A.R.; Kilgour, D.; Lloyd, L.S.; Lohman, J.A.B.; et al. Probing signal amplification by reversible exchange using an NMR flow system. Magn. Reason. Chem. 2014, 52, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theis, T.; Truong, M.L.; Coffey, A.M.; Shchepin, R.V.; Waddell, K.W.; Shi, F.; Goodson, B.M.; Warren, W.S.; Chekmenev, E.Y. Microtesla SABRE Enables 10% Nitrogen-15 Nuclear Spin Polarization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1404–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, M.L.; Shi, F.; He, P.; Yuan, B.X.; Plunkett, K.N.; Coffey, A.M.; Shchepin, R.V.; Barskiy, D.A.; Kovtunov, K.V.; Koptyug, I.V.; et al. Irreversible Catalyst Activation Enables Hyperpolarization and Water Solubility for NMR Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 13882–13889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olaru, A.M.; Robertson, T.B.R.; Lewis, J.S.; Antony, A.; Iali, W.; Mewis, R.E.; Duckett, S.B. Extending the Scope of (19)F Hyperpolarization through Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange in MRI and NMR Spectroscopy. ChemistryOpen 2018, 7, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacCulloch, K.; Tomhon, P.; Browning, A.; Akeroyd, E.; Lehmkuhl, S.; Chekmenev, E.Y.; Theis, T. Hyperpolarization of common antifungal agents with SABRE. Magn. Reason. Chem. 2021, 59, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.S.; Appleby, K.M.; Fear, E.J.; Duckett, S.B. SABRE-Relay: A Versatile Route to Hyperpolarization. J. Phys. Chem. 2018, 9, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salnikov, O.G.; Chukanov, N.V.; Svyatova, A.; Trofimov, I.A.; Kabir, M.S.H.; Gelovani, J.G.; Kovtunov, K.V.; Koptyug, I.V.; Chekmenev, E.Y. 15N NMR Hyperpolarization of Radiosensitizing Antibiotic Nimorazole by Reversible Parahydrogen Exchange in Microtesla Magnetic Fields. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 2406–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryutin, A.S.; Yurkovskaya, A.V.; Petrov, P.A.; Ivanov, K.L. Simultaneous 15N polarization of several biocompatible substrates in ethanol–water mixtures by signal amplification by reversible exchange (SABRE) method. Magn. Reason. Chem. 2021, 59, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; He, P.; Best, Q.A.; Groome, K.; Truong, M.L.; Coffey, A.M.; Zimay, G.; Shchepin, R.V.; Waddell, K.W.; Chekmenev, E.Y.; et al. Aqueous NMR Signal Enhancement by Reversible Exchange in a Single Step Using Water-Soluble Catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 12149–12156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, M.; Gibard, C.; Dear, G.J.; Green, G.G.R.; Hooper, A.J.J.; Roberts, A.D.; Cisnetti, F.; Duckett, S.B. Utilisation of water soluble iridium catalysts for signal amplification by reversible exchange. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 7870–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spannring, P.; Reile, I.; Emondts, M.; Schleker, P.P.M.; Hermkens, N.K.J.; van der Zwaluw, N.G.J.; van Weerdenburg, B.J.A.; Tinnemans, P.; Tessari, M.; Blumich, B.; et al. A New Ir-NHC Catalyst for Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange in D2O. Chem.-Eur. J. 2016, 22, 9277–9282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, L.S.; Asghar, A.; Burns, M.J.; Charlton, A.; Coombes, S.; Cowley, M.J.; Dear, G.J.; Duckett, S.B.; Genov, G.R.; Green, G.G.R.; et al. Hyperpolarisation through reversible interactions with parahydrogen. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 3544–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, P.J.; Burns, M.J.; Olaru, A.M.; Norcott, P.; Fekete, M.; Green, G.G.R.; Highton, L.A.R.; Mewis, R.E.; Duckett, S.B. Delivering strong H-1 nuclear hyperpolarization levels and long magnetic lifetimes through signal amplification by reversible exchange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3188–E3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manoharan, A.; Rayner, P.J.; Iali, W.; Burns, M.J.; Perry, V.H.; Duckett, S.B. Achieving Biocompatible SABRE: An in vitro Cytotoxicity Study. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manoharan, A.; Rayner, P.J.; Fekete, M.; Iali, W.; Norcott, P.; Hugh Perry, V.; Duckett, S.B. Catalyst-Substrate Effects on Biocompatible SABRE Hyperpolarization. ChemPhysChem 2019, 20, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linakis, J.G.; Cunningham, C.L. Effects of concentration of ethanol injected intraperitoneally on taste aversion, body temperature, and activity. Psychopharmacology 1979, 64, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen-Worthington, K.H.; Brice, A.K.; Marx, J.O.; Hankenson, F.C. Intraperitoneal Injection of Ethanol for the Euthanasia of Laboratory Mice (Mus musculus) and Rats (Rattus norvegicus). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2015, 54, 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lord, R. Use of ethanol for euthanasia of mice. Aust. Vet. J. 1989, 66, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recommendations for euthanasia of experimental animals: Part 1. Lab. Anim. 1996, 30, 293–316. [CrossRef]
- Iavicoli, I.; Cufino, V.; Corbi, M.; Goracci, M.; Caredda, E.; Cittadini, A.; Bergamaschi, A.; Sgambato, A. Rhodium and iridium salts inhibit proliferation and induce DNA damage in rat fibroblasts in vitro. Toxicol. Vitr. 2012, 26, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, Guideline for Elemental Impurities Q3D(R1). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/international-conference-harmonisation-technical-requirements-registration-pharmaceuticals-human-use_en-32.pdf (accessed on 26 November 2021).
- Bergman, A.; Svedberg, U.; Nilsson, E. Contact urticaria with anaphylactic reactions caused by occupational exposure to iridium salt. Contact Derm. 1995, 32, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Coffey, A.M.; Waddell, K.W.; Chekmenev, E.Y.; Goodson, B.M. Heterogeneous Solution NMR Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7495–7498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Coffey, A.M.; Waddell, K.W.; Chekmenev, E.Y.; Goodson, B.M. Nanoscale Catalysts for NMR Signal Enhancement by Reversible Exchange. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 7525–7533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovtunov, K.V.; Kovtunova, L.M.; Gemeinhardt, M.E.; Bukhtiyarov, A.V.; Gesiorski, J.; Bukhtiyarov, V.I.; Chekmenev, E.Y.; Koptyug, I.V.; Goodson, B.M. Heterogeneous Microtesla SABRE Enhancement of 15N NMR Signals. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 10433–10437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iali, W.; Olaru, A.M.; Green, G.G.R.; Duckett, S.B. Achieving High Levels of NMR-Hyperpolarization in Aqueous Media with Minimal Catalyst Contamination Using SABRE. Chemistry 2017, 23, 10491–10495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barskiy, D.A.; Ke, L.A.; Li, X.; Stevenson, V.; Widarman, N.; Zhang, H.; Truxal, A.; Pines, A. Rapid Catalyst Capture Enables Metal-Free para-Hydrogen-Based Hyperpolarized Contrast Agents. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 2721–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reineri, F.; Viale, A.; Ellena, S.; Boi, T.; Daniele, V.; Gobetto, R.; Aime, S. Use of labile precursors for the generation of hyperpolarized molecules from hydrogenation with parahydrogen and aqueous-phase extraction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7350–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidd, B.E.; Gesiorski, J.L.; Gemeinhardt, M.E.; Shchepin, R.V.; Kovtunov, K.V.; Koptyug, I.V.; Chekmenev, E.Y.; Goodson, B.M. Facile Removal of Homogeneous SABRE Catalysts for Purifying Hyperpolarized Metronidazole, a Potential Hypoxia Sensor. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 16848–16852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iali, W.; Rayner, P.J.; Duckett, S.B. Using para-hydrogen to hyperpolarize amines, amides, carboxylic acids, alcohols, phosphates, and carbonates. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, P.M.; John, R.O.; Parrott, A.J.; Rayner, P.J.; Iali, W.; Nordon, A.; Halse, M.E.; Duckett, S.B. Quantification of hyperpolarisation efficiency in SABRE and SABRE-Relay enhanced NMR spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. 2018, 20, 26362–26371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mewis, R.E.; Fekete, M.; Green, G.G.R.; Whitwood, A.C.; Duckett, S.B. Deactivation of signal amplification by reversible exchange catalysis, progress towards in vivo application. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 9857–9859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norcott, P.; Burns, M.J.; Rayner, P.J.; Mewis, R.E.; Duckett, S.B. Using (2) H labelling to improve the NMR detectability of pyridine and its derivatives by SABRE. Magn. Reson. Chem. MRC 2018, 56, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowley, M.J.; Adams, R.W.; Atkinson, K.D.; Cockett, M.C.R.; Duckett, S.B.; Green, G.G.R.; Lohman, J.A.B.; Kerssebaum, R.; Kilgour, D.; Mewis, R.E. Iridium N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes as Efficient Catalysts for Magnetization Transfer from para-Hydrogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6134–6137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iridium ICP Data. Available online: https://www.inorganicventures.com/element/iridium (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Shchepin, R.V.; Truong, M.L.; Theis, T.; Coffey, A.M.; Shi, F.; Waddell, K.W.; Warren, W.S.; Goodson, B.M.; Chekmenev, E.Y. Hyperpolarization of “Neat” Liquids by NMR Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange. J. Phys. Chem 2015, 6, 1961–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pravdivtsev, A.N. SABRE Hyperpolarization of Bipyridine Stabilized Ir-Complex at High, Low and Ultralow Magnetic Fields. Z. Phys. Chem. 2017, 231, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, P.J.; Gillions, J.P.; Hannibal, V.D.; John, R.O.; Duckett, S.B. Hyperpolarisation of weakly binding N-heterocycles using signal amplification by reversible exchange. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 5910–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shchepin, R.V.; Jaigirdar, L.; Chekmenev, E.Y. Spin-Lattice Relaxation of Hyperpolarized Metronidazole in Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange in Micro-Tesla Fields. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 4984–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iali, W.; Roy, S.S.; Tickner, B.J.; Ahwal, F.; Kennerley, A.J.; Duckett, S.B. Hyperpolarising Pyruvate through Signal Amplification by Reversible Exchange (SABRE). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shchepin, R.V.; Birchall, J.R.; Chukanov, N.V.; Kovtunov, K.V.; Koptyug, I.V.; Theis, T.; Warren, W.S.; Gelovani, J.G.; Goodson, B.M.; Shokouhi, S.; et al. Hyperpolarizing Concentrated Metronidazole 15NO2 Group Over Six Chemical Bonds with More Than 15% Polarization and 20 Minute Lifetime. Chem.-Eur. J. 2019, 25, 8829–8836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, M.; Ahwal, F.; Duckett, S.B. Remarkable Levels of 15N Polarization Delivered through SABRE into Unlabeled Pyridine, Pyrazine, or Metronidazole Enable Single Scan NMR Quantification at the mM Level. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 4573–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiryutin, A.S.; Yurkovskaya, A.V.; Ivanov, K.L. 15N SABRE Hyperpolarization of Metronidazole at Natural Isotope Abundance. ChemPhysChem 2021, 22, 1470–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchall, J.R.; Kabir, M.S.H.; Salnikov, O.G.; Chukanov, N.V.; Svyatova, A.; Kovtunov, K.V.; Koptyug, I.V.; Gelovani, J.G.; Goodson, B.M.; Pham, W.; et al. Quantifying the effects of quadrupolar sinks via15N relaxation dynamics in metronidazoles hyperpolarized via SABRE-SHEATH. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 9098–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Martín, M.; Sola, E. Labile N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes of Iridium. Organometallics 2009, 28, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Weerdenburg, B.J.A.; Gloggler, S.; Eshuis, N.; Engwerda, A.H.J.; Smits, J.M.M.; de Gelder, R.; Appelt, S.; Wymenga, S.S.; Tessari, M.; Feiters, M.C.; et al. Ligand effects of NHC-iridium catalysts for signal amplification by reversible exchange (SABRE). Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7388–7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rayner, P.J.; Norcott, P.; Appleby, K.M.; Iali, W.; John, R.O.; Hart, S.J.; Whitwood, A.C.; Duckett, S.B. Fine-tuning the efficiency of para-hydrogen-induced hyperpolarization by rational N-heterocyclic carbene design. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mewis, R.E.; Green, R.A.; Cockett, M.C.R.; Cowley, M.J.; Duckett, S.B.; Green, G.G.R.; John, R.O.; Rayner, P.J.; Williamson, D.C. Strategies for the Hyperpolarization of Acetonitrile and Related Ligands by SABRE. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 1416–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sample ID | [Ir(IMes)(COD)Cl] Present? | Atmosphere | Additional Ligand Added? | Pyridine Environment | Pyridine 1H Environment T1/s | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ortho | Meta | Para | |||||
| A | No | Vacuum | No | Free | 31.165 | 26.892 | 35.221 |
| B | No | 3 bar H2 | No | Free | 30.384 | 26.232 | 35.166 |
| C | Yes | 3 bar H2 | No | Free | 4.176 | 6.452 | 7.848 |
| D | Yes | 3 bar H2 | No | Equatorially bound | 4.044 | 5.897 | 9.494 |
| E | Yes | 3 bar H2 | No | Axially bound | 1.802 | 3.433 | 5.103 |
| F | Yes | 3 bar H2 | Ethylenediamine (2 eq relative to 1) | Free | 15.094 | 25.316 | 18.871 |
| G | Yes | 3 bar H2 | Diethylenetriamine (2 eq relative to 1) | Free | 30.030 | 25.422 | 33.079 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robertson, T.B.R.; Clarke, L.J.; Mewis, R.E. Rapid SABRE Catalyst Scavenging Using Functionalized Silicas. Molecules 2022, 27, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020332
Robertson TBR, Clarke LJ, Mewis RE. Rapid SABRE Catalyst Scavenging Using Functionalized Silicas. Molecules. 2022; 27(2):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020332
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobertson, Thomas B. R., Leon J. Clarke, and Ryan E. Mewis. 2022. "Rapid SABRE Catalyst Scavenging Using Functionalized Silicas" Molecules 27, no. 2: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020332
APA StyleRobertson, T. B. R., Clarke, L. J., & Mewis, R. E. (2022). Rapid SABRE Catalyst Scavenging Using Functionalized Silicas. Molecules, 27(2), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27020332