Wet End Chemical Properties of a New Kind of Fire-Resistant Paper Pulp Based on Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of Ultralong HAP Nanowires and the Fire-Resistant Paper Pulp
2.2. Laboratory Simulation Studies on Wet End Chemical Properties of the Fire-Resistant Paper Pulp Based on Ultralong HAP Nanowires
2.3. Wet End Chemical Parameters and Their Influencing Factors
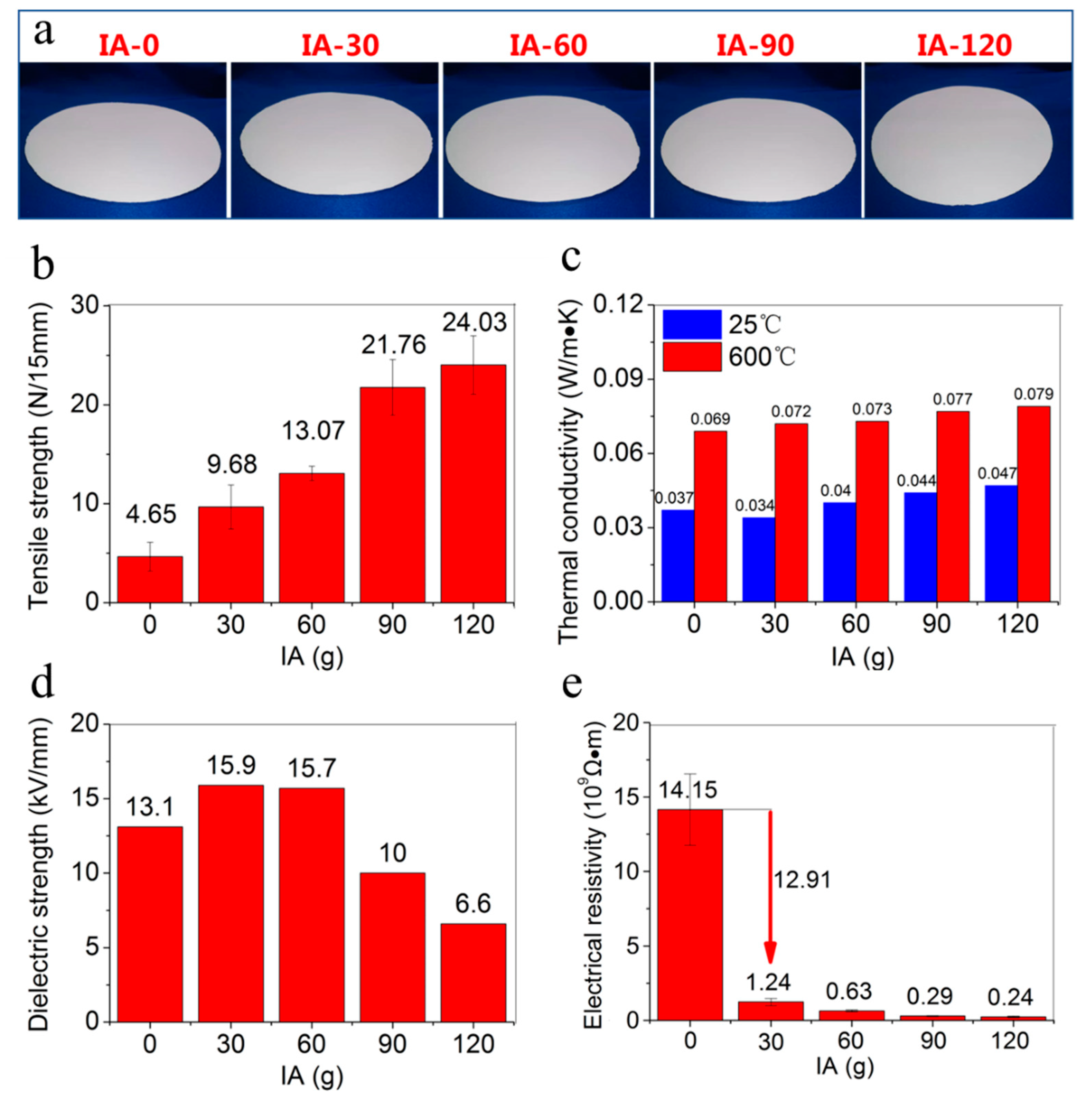
2.4. Effects of Wet End Chemical Properties on Performances of the Fire-Resistant Paper
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of Ultralong HAP Nanowires
3.3. Preparation of the Fire-Resistant Paper Pulp and Fire-Resistant Paper
3.4. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Hubbe, M.A. A Review of Ways to Adjust Papermaking Wet-End Chemistry: Manipulation of Cellulosic Colloidal Behavior. Lignocellulose 2014, 3, 69–107. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, J.C. (Ed.) Paper Chemistry; Blackie & Son: London, UK; Chapman and Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Thorn, I.; Au, C.O. (Eds.) Applications of Wet-End Paper Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Heidelberg, Germany; London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, O.J.; Neuman, R.D. Adsorption of polysaccharide wet-end additives in papermaking systems. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 155, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Li, H.; Liu, W.; Zhan, H. The retention- and drainage-aid behavior of quaternary chitosan in papermaking system. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 297, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, N.A.; Pikulik, I.I.; Gooding, R.; Abdullahi, A.A. Papermaking. Encycl. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2001, 6739–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biedrzycka, A.; Skwarek, E.; Hanna, U.M. Hydroxyapatite with magnetic core: Synthesis methods, properties, adsorption and medical applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 291, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhu, Y.J. Multifunctional calcium phosphate nanostructured materials and biomedical applications. Curr. Nanosci. 2014, 10, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.Q.; Zhu, Y.J. One-dimensional hydroxyapatite materials: Preparation and applications. Can. J. Chem. 2017, 95, 1091–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Lu, B.Q. Deformable biomaterials based on ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 4951–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramhe, S.; Kim, T.N.; Balakrishnan, A.; Chu, M.C. Conversion from biowaste Venerupis clam shells to hydroxyapatite nanowires. Mater. Lett. 2014, 135, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F.; Lu, B.Q.; Qi, C.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J. Hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanorods and nanowires using riboflavin-5′-phosphate monosodium salt as a new phosphorus source and their application in protein adsorption. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 7926–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wang, K.W.; Zhao, K.L. Surfactant-free solvothermal synthesis of hydroxylapatite nanowire/nanotube ordered arrays with biomimic structures. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Tang, Q.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhao, X.Y.; Chen, F. Microwave-assisted hydrothermal rapid synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanowires using adenosine 5′-triphosphate disodium salt as phosphorus source. Mater. Lett. 2012, 85, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Liu, X.; Chang, J.; Zhu, Y.J. Facile synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, nanowires and hollow nano-structured microspheres using similar structured hard-precursors. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3052–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.T.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Li, H.L.; Hu, Z.A. Template synthesis of highly ordered hydroxyapatite nanowire arrays. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.O.; Dixon, S.J.; Rizkalla, A.S. One- and three-dimensional growth of hydroxyapatite nanowires during sol−gel−hydrothermal synthesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Qi, Y.; Hu, C. Preparation of ultrahigh-aspect-ratio hydroxyapatite nanofibers in reverse micelles under hydrothermal conditions. Langmuir 2004, 20, 4784–4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J. Fire-Resistant Paper: Materials, Technologies, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.J. Multifunctional fire-resistant paper based on ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 2296–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.Q.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F. Highly flexible and nonflammable inorganic hydroxyapatite paper. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F.; Wu, J. Solvothermal synthesis of submillimeter ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires using a calcium oleate precursor in a series of monohydroxy alcohols. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 6098–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F.; Wu, J. Ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires synthesized by solvothermal treatment using a series of phosphate sodium salts. Mater. Lett. 2015, 144, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhu, Y.J. Large-scale automated production of highly ordered ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires and construction of various fire-resistant flexible ordered architectures. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 11483–11495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, Y.J.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Yu, Y.D.; Chen, F.; Dong, L.Y.; Wu, J. Hierarchical assembly of monodisperse hydroxyapatite nanowires and construction of high-strength fire-resistant inorganic paper with high-temperature flexibility. ChemNanoMat 2017, 3, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.P.; Zhu, Y.J.; Lu, B.Q. Highly efficient and environmentally friendly microwave-assisted hydrothermal rapid synthesis of ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 12352–12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.F.; Zhu, Y.J.; Xiong, Z.C.; Dong, L.Y.; Chen, F.; Lu, B.Q.; Yang, R.L. Hydroxyapatite nanowire-based all-weather flexible electrically conductive paper with superhydrophobic and flame-retardant properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39534–39548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.F.; Zhu, Y.J.; Xiong, Z.C.; Sun, T.W.; Shen, Y.Q. Highly flexible superhydrophobic and fire-resistant layered inorganic paper. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34715–34724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.Y.; Zhu, Y.J. A new kind of fireproof, flexible, inorganic, nanocomposite paper and its application to the protection layer in flame-retardant fiber-optic cables. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 4597–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Shao, Y.T. Fire-retardant and high-temperature-resistant label paper and its potential applications. ChemNanoMat 2019, 5, 1418–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.Y.; Zhu, Y.J. Fire-resistant inorganic analogous Xuan paper with thousands of years’ super-durability. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 17239–17251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, D.B.; Wu, J.; Dong, L.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Hu, X.L. Flexible, high-wettability and fire-resistant separators based on hydroxyapatite nanowires for advanced lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.C.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F.F.; Zhang, Y.G.; Yang, R.L. Ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires-based paper co-loaded with silver nanoparticles and antibiotic for long-term antibacterial benefit. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 22212–22222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.C.; Yang, R.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F.F.; Dong, L.Y. Flexible hydroxyapatite ultralong nanowire-based paper for highly efficient and multifunctional air filtration. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17482–17491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.C.; Yang, Z.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F.F.; Yang, R.L.; Qin, D.D. Ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowire-based layered catalytic paper for highly efficient continuous flow reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 5762–5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F.F.; Dong, L.Y.; Xiong, Z.C. Luminescent, fire-resistant, and water-proof ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowire-based paper for multimode anticounterfeiting applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 25455–25464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.L.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F.F.; Qin, D.D.; Xiong, Z.C. Superhydrophobic photothermal paper based on ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires for controllable light-driven self-propelled motion. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 13226–13235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhu, Y.J.; Wu, J.; Shao, Y.T.; Cai, A.Y.; Dong, L.Y. Ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowire-based filter paper for high-performance water purification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 4288–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.P.; Zhu, Y.J. Bioinspired flexible, high-strength and versatile hydrogel with the fiberboard-and-mortar hierarchically ordered structure. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 3643–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.T.; Zhu, Y.J.; Dong, L.Y.; Cai, A.Y. A nanocomposite “Xuan paper” made from ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires and cellulose fibers and its anti-mildew properties. J. Inorg. Mater. 2021, 36, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhu, Y.J. Nanowires: Synthesis and energy/environmental applications. Energy Environ. Mater. 2021, 4, 544–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.W.; Zhu, Y.J.; Chen, F. Highly flexible multifunctional biopaper comprising chitosan reinforced by ultralong hydroxyapatite nanowires. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 3850–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| IA (g) | Basis Weight (g m−2) | Thickness (µm) | Tightness (g cm−3) | Bulkness (cm3 g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 92.4 | 128 | 0.72 | 1.39 |
| 30 | 92.7 | 139 | 0.67 | 1.50 |
| 60 | 112.4 | 166 | 0.68 | 1.48 |
| 90 | 124.8 | 181 | 0.69 | 1.45 |
| 120 | 137.6 | 202 | 0.68 | 1.47 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, L.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Wu, J. Wet End Chemical Properties of a New Kind of Fire-Resistant Paper Pulp Based on Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires. Molecules 2022, 27, 6808. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206808
Dong L-Y, Zhu Y-J, Wu J. Wet End Chemical Properties of a New Kind of Fire-Resistant Paper Pulp Based on Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires. Molecules. 2022; 27(20):6808. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206808
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Li-Ying, Ying-Jie Zhu, and Jin Wu. 2022. "Wet End Chemical Properties of a New Kind of Fire-Resistant Paper Pulp Based on Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires" Molecules 27, no. 20: 6808. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206808
APA StyleDong, L.-Y., Zhu, Y.-J., & Wu, J. (2022). Wet End Chemical Properties of a New Kind of Fire-Resistant Paper Pulp Based on Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires. Molecules, 27(20), 6808. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27206808





