Fabrication of PEGylated Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Tenofovir Alafenamide: Synthesis and Characterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
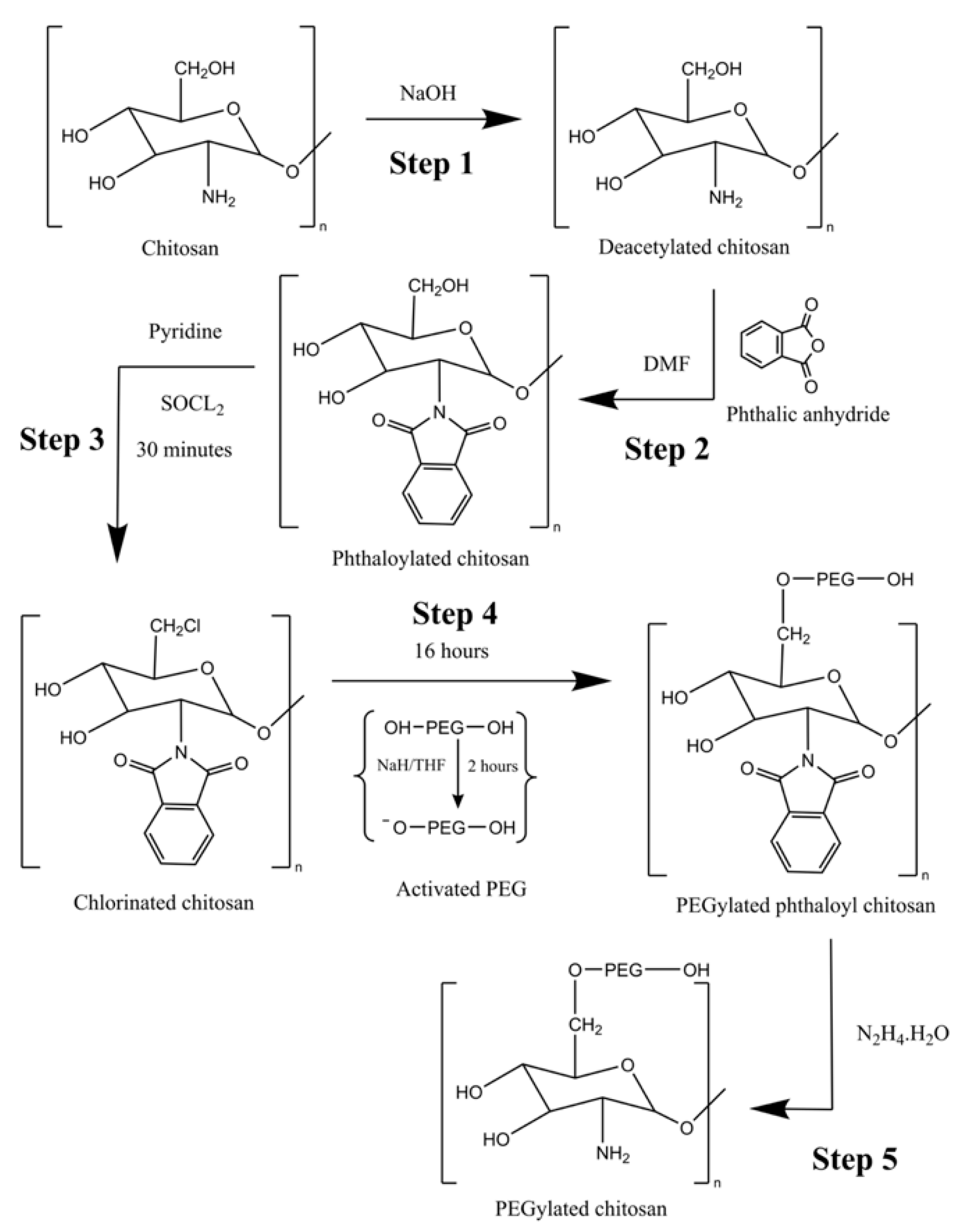
2.2. Method for Synthesis of PEGylated Chitosan
2.3. Method for Preparation of PEGylated Chitosan TAF Nanoparticles
2.4. Characterization
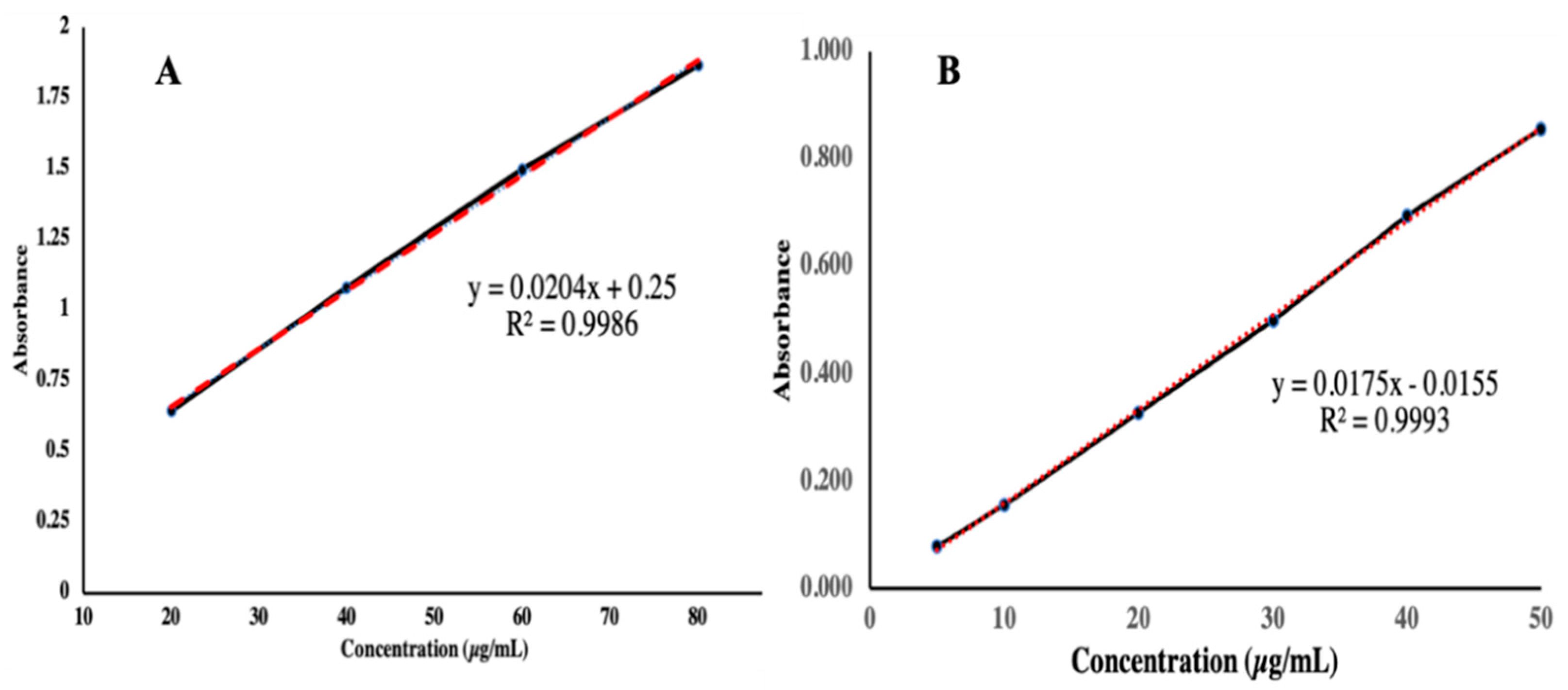
2.4.1. Determination of λmax and Calibration Curve of TAF
2.4.2. Fourier-Transformed Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.4. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.4.5. Particle Size Analysis
2.4.6. Drug-Loading Capacity
2.4.7. Entrapment Efficacy
2.4.8. In Vitro Drug Release
2.4.9. Drug Release Kinetic Modeling
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Determination of Absorption Spectra of TAF
3.2. Determination of Calibration Curve of TAF
3.3. Chemical Compatibility Studies
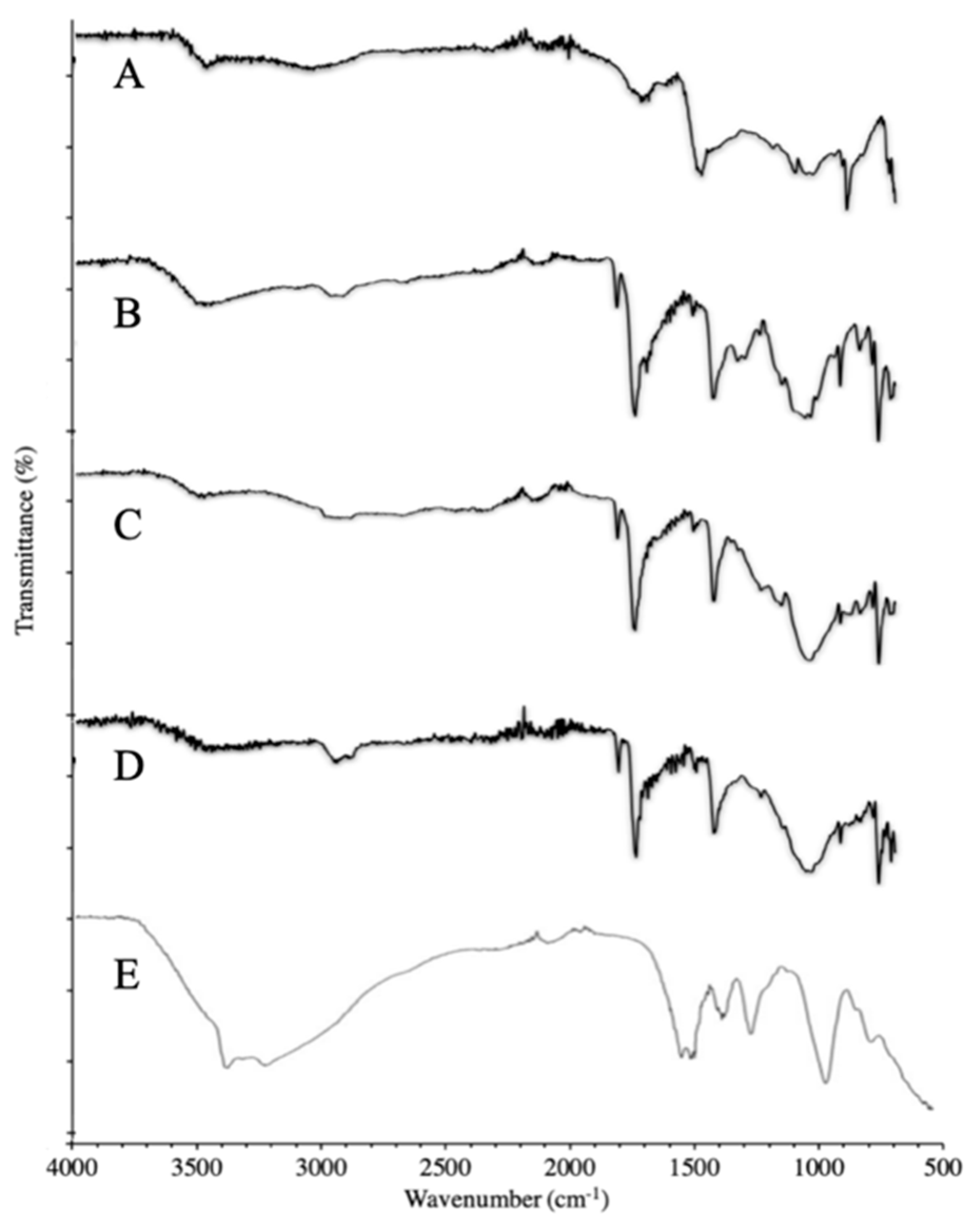
3.3.1. FTIR of Synthesized Polymer
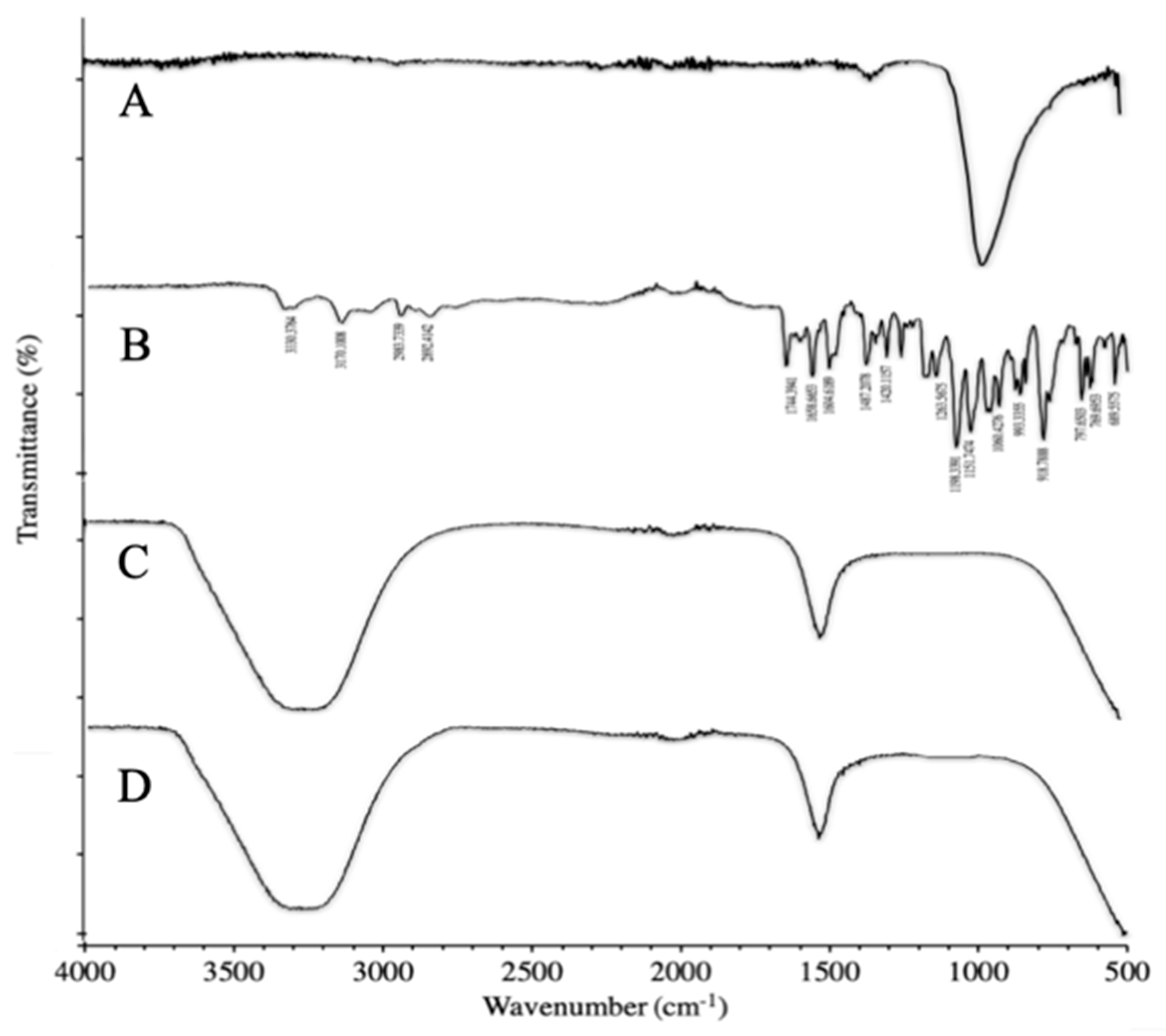
3.3.2. FTIR of Synthesized NPs
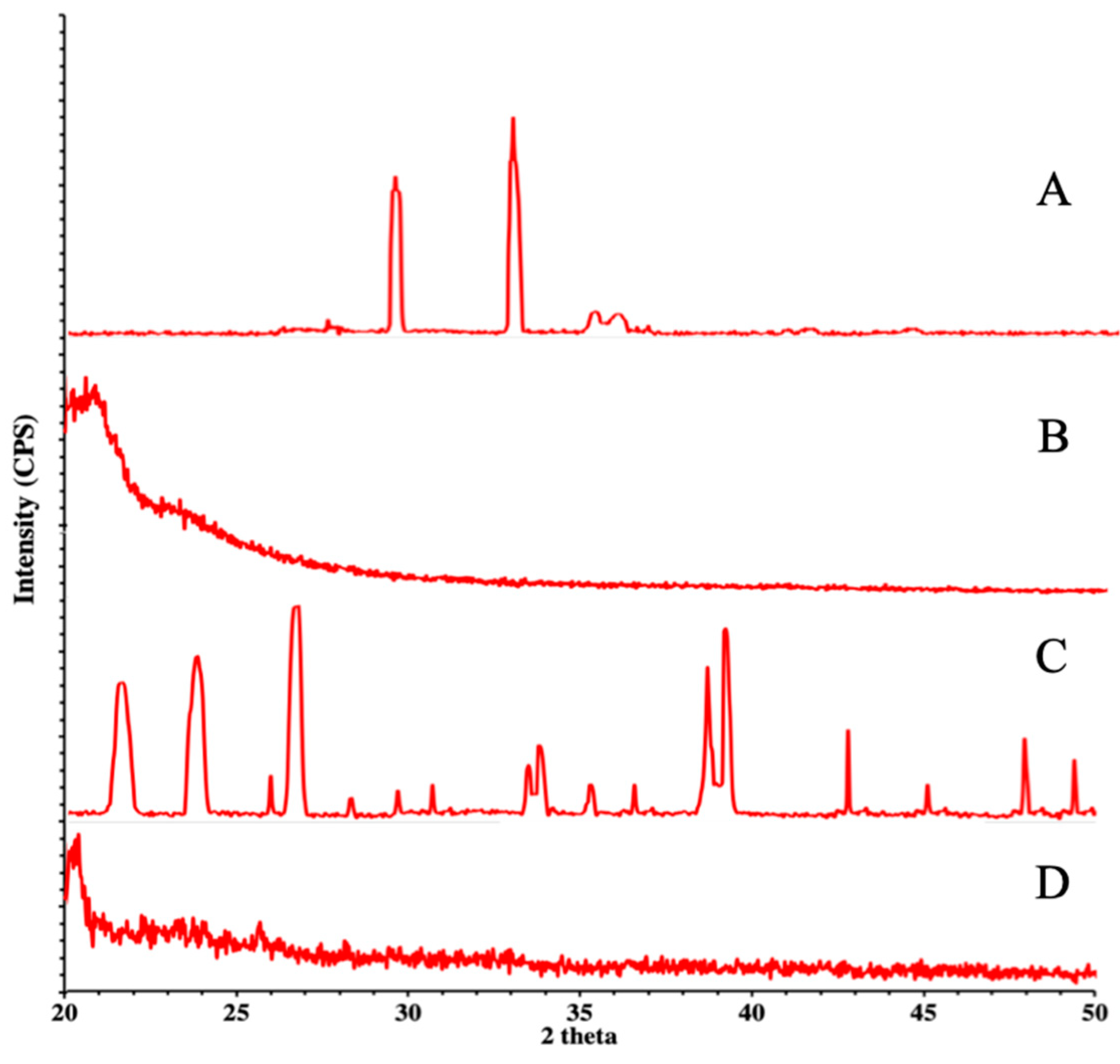
3.4. XRD Studies
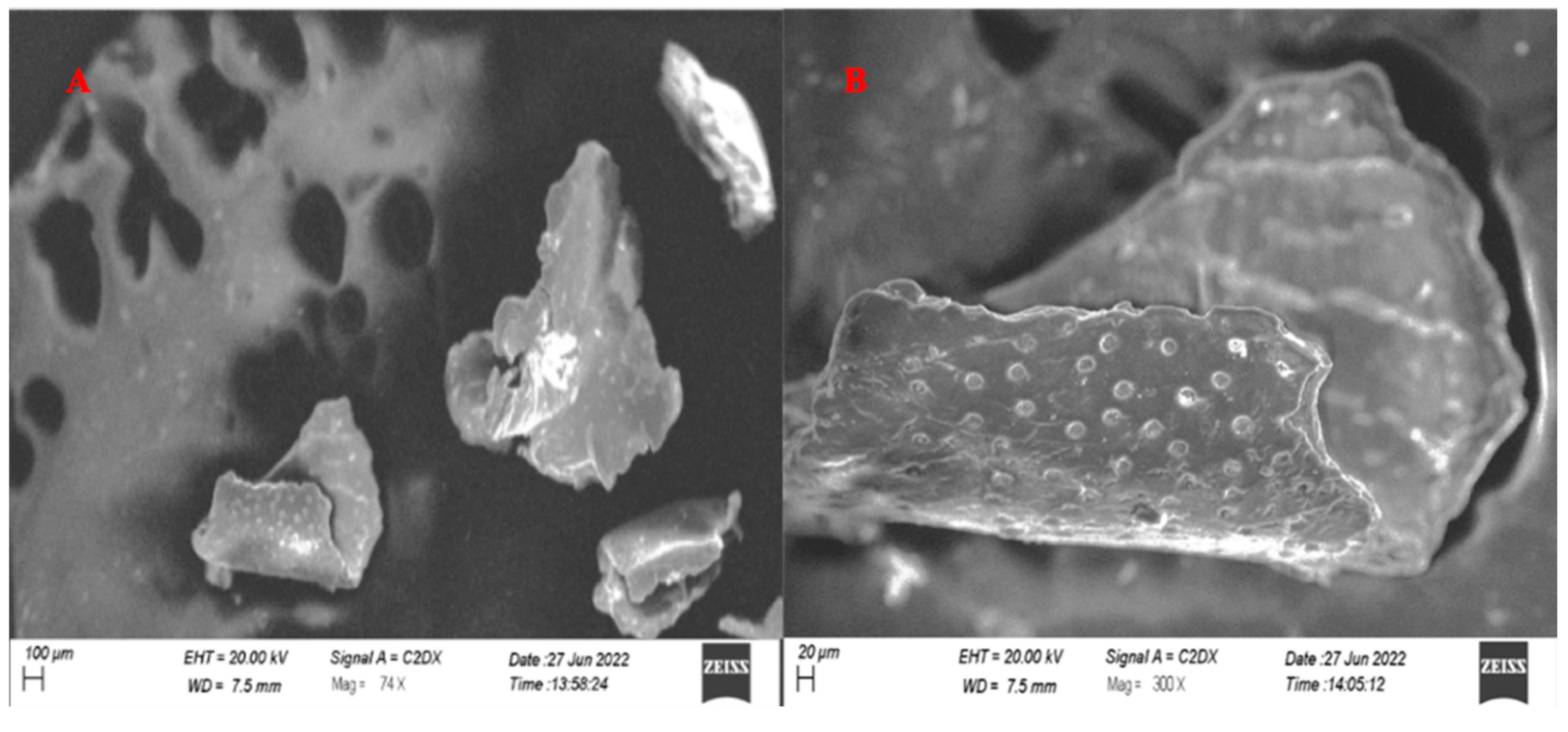
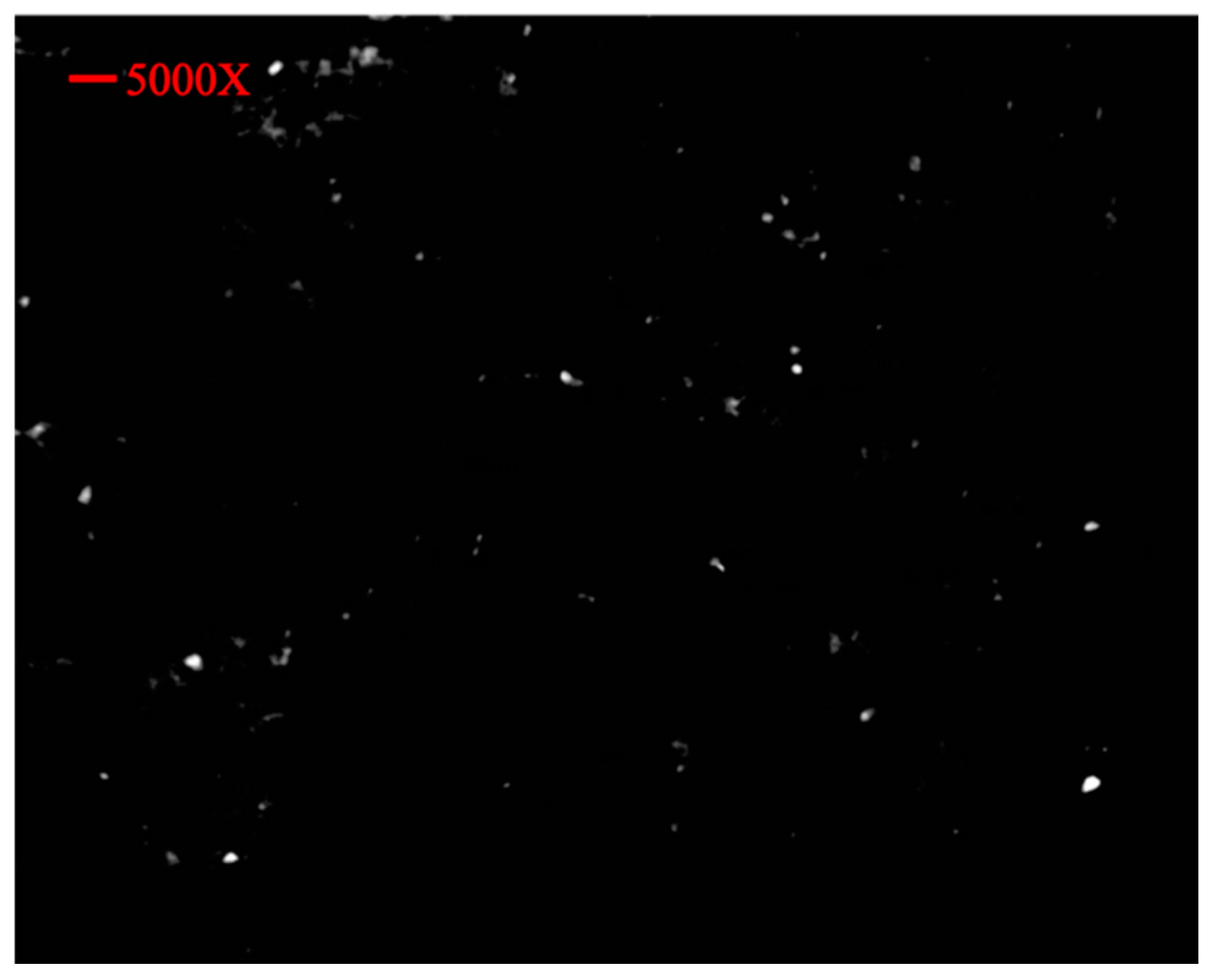
3.5. SEM Analysis
3.6. Drug-Loading Capacity and Entrapment Efficacy of NPs
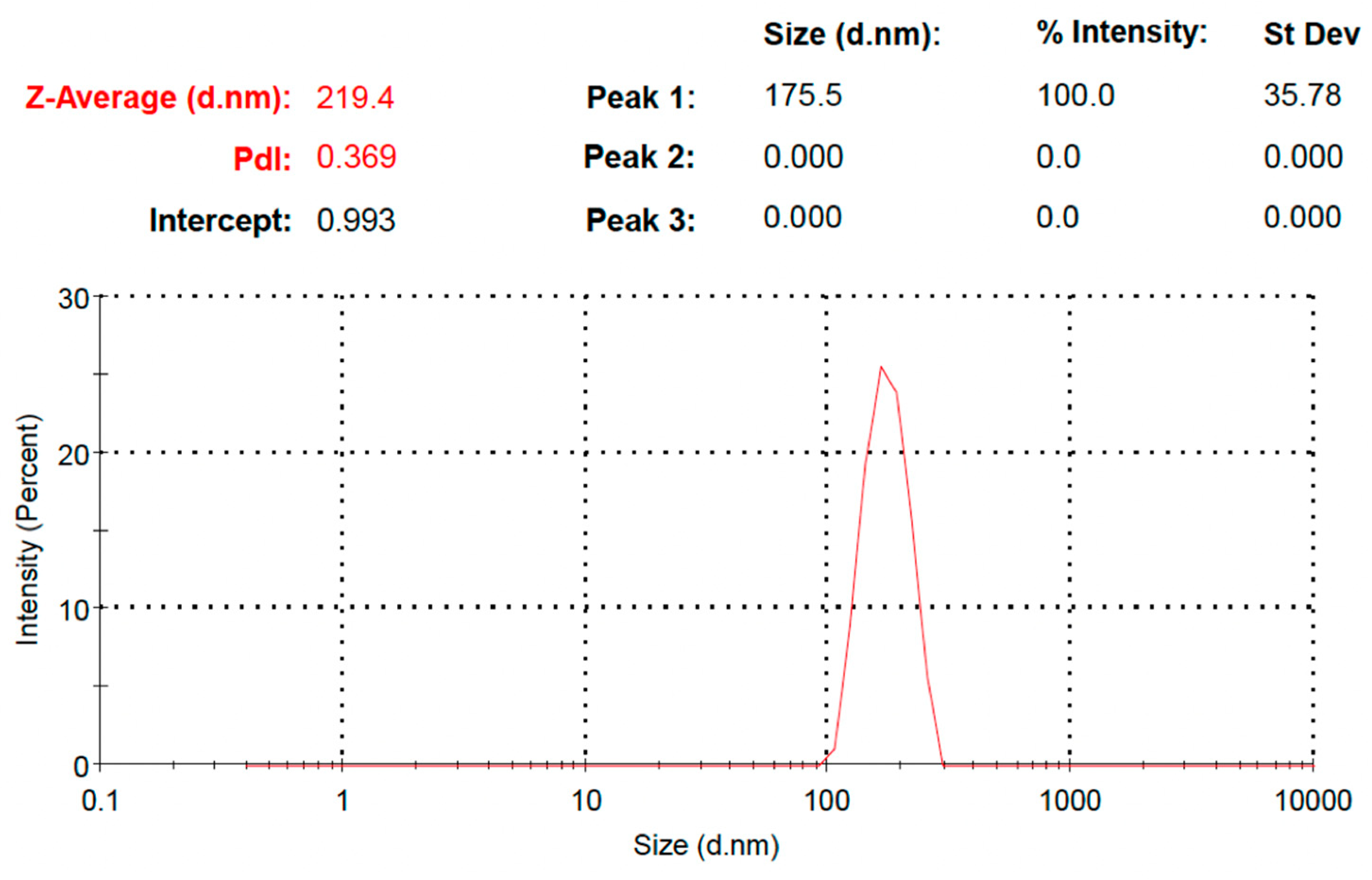
3.7. Particle Size Determination
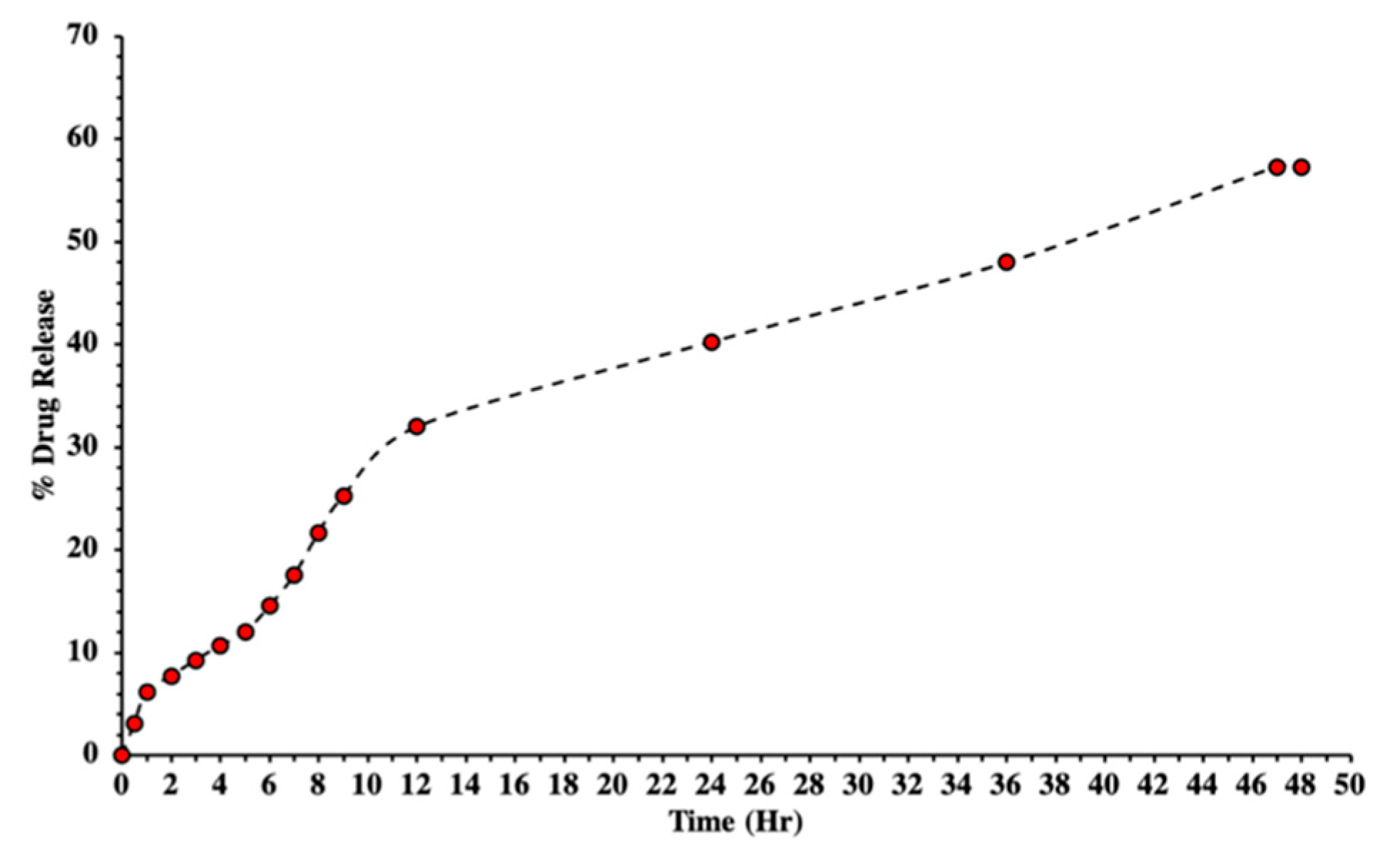
3.8. In Vitro Drug Release
3.9. Kinetic Model Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Saag, M.S.; Benson, C.A.; Gandhi, R.T.; Hoy, J.F.; Landovitz, R.J.; Mugavero, M.J.; Sax, P.E.; Smith, D.M.; Thompson, M.A.; Buchbinder, S.P.; et al. Antiretroviral drugs for treatment and prevention of HIV infection in adults: 2018 recommendations of the International Antiviral Society–USA Panel. JAMA 2018, 320, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, T.; Veikley, W.; Claire, R.L.S., III; Guyer, B.; Kearney, N.C.B.P. Intracellular pharmacokinetics of tenofovir diphosphate, carbovir triphosphate, and lamivudine triphosphate in patients receiving triple-nucleoside regimens. JAIDS J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2005, 39, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, K.; Brunetto, M.; Seto, W.K.; Lim, Y.-S.; Fung, S.; Marcellin, P.; Ahn, S.H.; Izumi, N.; Chuang, W.; Bae, H.; et al. 96 weeks treatment of tenofovir alafenamide vs. tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassner, C.; Bradleyand, N.; Lee, Y. A review and clinical understanding of tenofovir: Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate versus tenofovir alafenamide. J. Int. Assoc. Provid. AIDS Care (JIAPAC) 2020, 19, 2325958220919231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, K.K. An overview of drug delivery systems. In Drug Delivery Systems; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanraj, V.; Chen, Y. Nanoparticles—A review. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2006, 5, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begines, B.; Ortiz, T.; Pérez-Aranda, M.; Martínez, G.; Merinero, M.; Argüelles-Arias, F.; Alcudia, A. Polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery: Recent developments and future prospects. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, D.; Kondiah, P.P.; Choonaraand, Y.E.; Pillay, V. The design of poly (lactide-co-glycolide) nanocarriers for medical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Dünnhaupt, S. Chitosan-based drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiyaboonchai, W. Chitosan nanoparticles: A promising system for drug delivery. Naresuan Univ. J. Sci. Technol. (NUJST) 2013, 11, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, M.; Huand, Q.; Shen, K. Preparation and structure of chitosan soluble in wide pH range. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Hsieh, Y.-L. PEGylation of chitosan for improved solubility and fiber formation via electrospinning. Cellulose 2007, 14, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, F.M.; Pasut, G. PEGylation, successful approach to drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praseptiangga, D.; Zahara, H.L.; Widjanarko, P.I.; Joniand, I.M.; Panatarani, C. Preparation and FTIR spectroscopic studies of SiO2-ZnO nanoparticles suspension for the development of carrageenan-based bio-nanocomposite film. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Melville, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sagadevan, S.; Koteeswari, P. Analysis of structure, surface morphology, optical and electrical properties of copper nanoparticles. J. Nanomed. Res. 2015, 2, 00040–00048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorontsov, A.V.; Tsybulya, S.V. Influence of nanoparticles size on XRD patterns for small monodisperse nanoparticles of Cu0 and TiO2 anatase. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 2526–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, K.N.; Salameh, J.W.; Wereleyand, S.T.; Kinzer-Ursem, T.L. Physical characterization of nanoparticle size and surface modification using particle scattering diffusometry. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 054107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblatt, K.M.; Bunjes, H. Evaluation of the drug loading capacity of different lipid nanoparticle dispersions by passive drug loading. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 117, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajun, W.; Yan, S.; Liand, G.; Huili, L. Preparation of aspirin and probucol in combination loaded chitosan nanoparticles and in vitro release study. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, S.; Khan, S.; Farooq, U.; Haider, M.S.; Ranjha, N.M.; Rasul, A.; Nawaz, A.; Arshad, N.; Hameed, R. Biocompatible hydrogels for the controlled delivery of anti-hypertensive agent: Development, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Des. Monomers Polym. 2018, 21, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mircioiu, C.; Voicu, V.; Anuta, V.; Tudose, A.; Celia, C.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Sandulovici, R.; Mircioiu, I. Mathematical modeling of release kinetics from supramolecular drug delivery systems. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouchak, M.; Avadi, M.; Abbaspour, M.; Jahangiriand, A.; Boldaji, S.K. Effect of different molecular weights of chitosan on preparation and characterization of insulin loaded nanoparticles by ion gelation method. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 2012, 4, 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- Queiroz, M.F.; Melo, K.R.T.; Sabry, D.A.; Sassakiand, G.L.; Rocha, H.A.O. Does the use of chitosan contribute to oxalate kidney stone formation? Mar. Drugs 2014, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.O.; Ladchumananandasivam, R.; Nascimento, J.H.O.; Silva, K.K.O.S.; Oliveira, F.R.; Souto, A.P.; Felgueiras, H.P.; Zille, A. Multifunctional chitosan/gold nanoparticles coatings for biomedical textiles. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, M.; Lane, C.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Sahaand, S.; Prakash, S. A novel method for synthesizing PEGylated chitosan nanoparticles: Strategy, preparation, and in vitro analysis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 485. [Google Scholar]
- Najafabadi, A.H.; Abdoussand, M.; Faghihi, S. Synthesis and evaluation of PEG-O-chitosan nanoparticles for delivery of poor water soluble drugs: Ibuprofen. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 41, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, M.; Tomaro-Duchesneauand, C.; Prakash, S. Synthesis of TAT peptide-tagged PEGylated chitosan nanoparticles for siRNA delivery targeting neurodegenerative diseases. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1270–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, J.; Iqbal, F.M.; Danish, Z.; Shah, S.N.H.; Umar, H.; Zaman, M.; Alvi, M.N.; Islam, N. Synthesis and characterization of self-assembling chitosan-based nanoparticles. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 35, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ulu, A.; Sezer, S.K.; Yüksel, Ş.; Koçand, A.; Ateş, B. Preparation, Controlled Drug Release, and Cell Viability Evaluation of Tenofovir Alafenamide-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles. Starch-Stärke 2021, 2100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.N.; Pereira, F.M.; Rocha, M.A.; Ribeiro, J.G.; Junges, A.; Monteiro, W.F.; Diz, F.M.; Ligabue, R.A.; Morrone, F.B.; Severino, P.; et al. Chitosan and chitosan/PEG nanoparticles loaded with indole-3-carbinol: Characterization, computational study and potential effect on human bladder cancer cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 124, 112089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Kunduand, P.P.; Chakraborti, A.S. Alginate coated chitosan core-shell nanoparticles for efficient oral delivery of naringenin in diabetic animals—An in vitro and in vivo approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 170, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, L.; Ramana, L.N.; Sethuramanand, S.; Krishnan, U.M. Ellagic acid encapsulated chitosan nanoparticles as anti-hemorrhagic agent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahdestani, S.A.; Shahriariand, M.H.; Abdouss, M. Synthesis and characterization of chitosan nanoparticles containing teicoplanin using sol–gel. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, S.N.; Minh, H.D.; Anh, D.N. Study on chitosan nanoparticles on biophysical characteristics and growth of Robusta coffee in green house. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2013, 2, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Shailender, J.; Ravi, P.R.; Sirukuri, M.R.; Dalviand, A.; Priya, O.K. Chitosan nanoparticles for the oral delivery of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: Formulation optimization, characterization and ex vivo and in vivo evaluation for uptake mechanism in rats. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallamuthu, I.; Deviand, A.; Khanum, F. Chlorogenic acid loaded chitosan nanoparticles with sustained release property, retained antioxidant activity and enhanced bioavailability. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Sturgisand, T.F.; Youan, B.-B.C. Engineering tenofovir loaded chitosan nanoparticles to maximize microbicide mucoadhesion. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Jing, Y.; Han, C.; Zhangand, H.; Tian, Y. Encapsulation of curcumin in zein/caseinate/sodium alginate nanoparticles with improved physicochemical and controlled release properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, N.; Erum, A.; Zaman, M.; Iqbal, M.O.; Riaz, R.; Tulain, R.; Hussain, T.; Amjad, M.W.; Raja, M.A.; Farooq, U.; et al. Fabrication of thiolated chitosan based biodegradable nanoparticles of ticagrelor and their pharmacokinetics. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2022, 30, 09673911221108742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Xing, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Sunand, C.; Liang, G. pH-responsive thiolated chitosan nanoparticles for oral low-molecular weight heparin delivery: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, P.; Roy, B.; Mukherjee, N.; Mukherjee, S.; Joardar, N.; Mondal, M.K.; Roy, D.; Babu, S.P.S. Chitosan biopolymer functionalized gold nanoparticles with controlled cytotoxicity and improved antifilarial efficacy. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2018, 1, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yien, L.; Zin, N.M.; Sarwarand, A.; Katas, H. Antifungal activity of chitosan nanoparticles and correlation with their physical properties. Int. J. Biomater. 2012, 2012, 632698. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, A.; Cunha-Reis, C.; Araújo, F.; Nunes, R.; Seabra, V.; Ferreira, D.; das Neves, J.; Sarmento, B. Development and in vivo safety assessment of tenofovir-loaded nanoparticles-in-film as a novel vaginal microbicide delivery system. Acta Biomater. 2016, 44, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shailender, J.; Ravi, P.R.; Saha, P.; Dalviand, A.; Myneni, S. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate loaded PLGA nanoparticles for enhanced oral absorption: Effect of experimental variables and in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 158, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariadoss, A.V.A.; Vinayagam, R.; Senthilkumar, V.; Paulpandi, M.; Murugan, K.; Xu, B.; Gothandam, K.M.; Kotakadi, V.S.; David, E. Phloretin loaded chitosan nanoparticles augments the pH-dependent mitochondrial-mediated intrinsic apoptosis in human oral cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, W.; Yangand, Z.; Feng, Y. α-Santalol functionalized chitosan nanoparticles as efficient inhibitors of polo-like kinase in triple negative breast cancer. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 5487–5501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Agarwal, A.; Majumder, S.; Lariya, N.; Khaya, A.; Agrawal, H.; Majumdar, S.; Agrawal, G.P. Mannosylated solid lipid nanoparticles as vectors for site-specific delivery of an anti-cancer drug. J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Sturgisand, T.F.; Youan, B.-B.C. pH-responsive nanoparticles releasing tenofovir intended for the prevention of HIV transmission. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Agrahari, V.; Ezoulin, M.J.; Zhang, C.; Purohit, S.S.; Molteni, A.; Dim, D.; Oyler, N.A.; Youan, B.-B.C. Tenofovir containing thiolated chitosan core/shell nanofibers: In vitro and in vivo evaluations. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 4129–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorochovceva, N.; Makuška, R. Synthesis and study of water-soluble chitosan-O-poly (ethylene glycol) graft copolymers. Eur. Polym. J. 2004, 40, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Leeand, H.; Wang, D. The influence of plasticizers on the release of theophylline from microporous-controlled tablets. J. Control. Release 2004, 99, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Howard, K.A.; Dong, M.Ø.; Andersen, M.; Rahbek, U.L.; Johnsen, M.G.; Hansen, O.C.; Besenbacher, F.; Kjems, J. The influence of polymeric properties on chitosan/siRNA nanoparticle formulation and gene silencing. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1280–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradkhannejhad, L.; Abdouss, M.; Nikfarjam, N.; Shahriariand, M.H.; Heidary, V. The effect of molecular weight and content of PEG on in vitro drug release of electrospun curcumin loaded PLA/PEG nanofibers. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmi, O.; Elshishinyand, F.; Mamdouh, W. Targeted doxorubicin delivery and release within breast cancer environment using PEGylated chitosan nanoparticles labeled with monoclonal antibodies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jusu, S.M.; Obayemi, J.D.; Salifu, A.A.; Nwazojie, C.C.; Uzonwanne, V.; Odusanya, O.S.; Soboyejo, W.O. Drug-encapsulated blend of PLGA-PEG microspheres: In vitro and in vivo study of the effects of localized/targeted drug delivery on the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheeren, L.E.; Nogueira, D.R.; Macedo, L.B.; Vinardell, M.P.; Mitjans, M.; Infante, M.R.; Rolim, C.M. PEGylated and poloxamer-modified chitosan nanoparticles incorporating a lysine-based surfactant for pH-triggered doxorubicin release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 138, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.S.; Hengand, P.W.; Wong, L.F. Relationship between swelling and drug release in a hydrophilic matrix. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1993, 19, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Formulation | Formulation | |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-Order | K0 | 1.329 |
| R2 | 0.8693 | |
| First-Order | K1 | 0.021 |
| R2 | 0.9557 | |
| Higuchi Model | KH | 7.757 |
| R2 | 0.9588 | |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas Model | KKP | 5.066 |
| N | 0.632 | |
| R2 | 0.9885 | |
| Hixson–Crowell Model | KHC | 0.006 |
| R2 | 0.9316 | |
| Diffusion mechanism | Non-Fickian | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaman, M.; Butt, M.H.; Siddique, W.; Iqbal, M.O.; Nisar, N.; Mumtaz, A.; Nazeer, H.Y.; Alshammari, A.; Riaz, M.S. Fabrication of PEGylated Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Tenofovir Alafenamide: Synthesis and Characterization. Molecules 2022, 27, 8401. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238401
Zaman M, Butt MH, Siddique W, Iqbal MO, Nisar N, Mumtaz A, Nazeer HY, Alshammari A, Riaz MS. Fabrication of PEGylated Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Tenofovir Alafenamide: Synthesis and Characterization. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8401. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238401
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaman, Muhammad, Muhammad Hammad Butt, Waqar Siddique, Muhammad Omer Iqbal, Naveed Nisar, Asma Mumtaz, Hafiza Yusra Nazeer, Abdulrahman Alshammari, and Muhammad Shahid Riaz. 2022. "Fabrication of PEGylated Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Tenofovir Alafenamide: Synthesis and Characterization" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8401. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238401
APA StyleZaman, M., Butt, M. H., Siddique, W., Iqbal, M. O., Nisar, N., Mumtaz, A., Nazeer, H. Y., Alshammari, A., & Riaz, M. S. (2022). Fabrication of PEGylated Chitosan Nanoparticles Containing Tenofovir Alafenamide: Synthesis and Characterization. Molecules, 27(23), 8401. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238401







