Novel Hydrophobic Polyvinyl-Alcohol Formaldehyde Sponges: Synthesis, Characterization, Fast and Effective Organic Solvent Uptake from Contaminated Soil Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterizations and Properties of Prepared Sponges
2.2. Visual Observations of Oil Uptake by Hydrophobic PVFTX-100 Sponge
2.3. Batch Adsorption Studies
3. Experimental Details
3.1. Materials and Methods
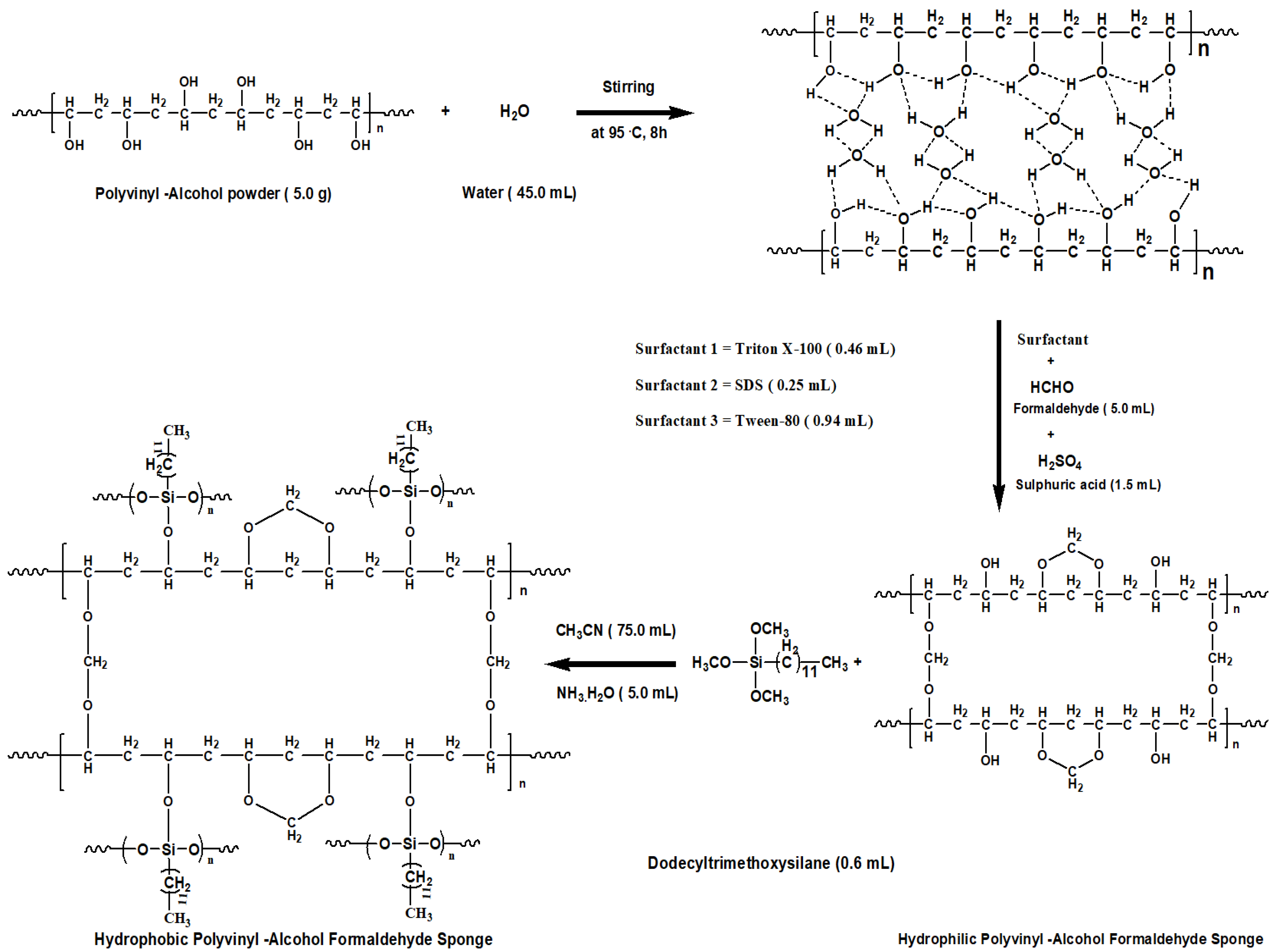
3.2. Synthesis of Polyvinyl-Alcohol Formaldehyde (PVF) Sponges
- (a)
- Synthesis of PVF Sponge Using Triton X-100 Surfactant
- (b)
- Synthesis of PVF Sponges Using Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate Surfactant
- (c)
- Synthesis of PVF Sponges Using Tween 80 Surfactant
3.3. Conversion of Hydrophilic PVF Sponges to Hydrophobic Sponges
3.4. Characterizations of the Prepared Sponges
3.5. Surface Area Determination of the Prepared Sponges
3.6. Determination of Pore (Void) Volume
3.7. Batch Adsorption Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yong, J.; Chen, F.; Li, M.; Yang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Huo, J.; Hou, X. Remarkably simple achievement of super-hydrophobicity, superhydrophilicity, underwater superoleophobicity, underwater superoleophilicity, underwater superaerophobicity, and underwater superaerophilicity on femtosecond laser ablated PDMS surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 25249–25257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Y. 3D-Printed Biomimetic Super Hydrophobic Structure for Microdroplet Manipulation and Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Chauhan, G.; Verma, S.; Singh, U. The emergence of nanotechnology in mitigating petroleum oil spills. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greece Struggles to Clean Up Oil Spill. Available online: https://www.dw.com/en/greece-struggles-to-clean-up-relatively-small-oil-spill-as-black-slick-spreads/a-40511068 (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Huge Oil Spills Spreads in East China Sea, Stirring Environmental Fears. New York Times. 15 January 2018. Available online: https://www.nytimes.com/2018/01/15/world/asia/oil-tanker-spill-sanchi-east-china-sea.html (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Oil Spill Reported in Walsh County. 30 October 2019. Available online: https://www.kxnet.com/news/local-news/oil-spill-reported-in-walsh-county (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Colonial Pipeline Spill Information—Huntersville, N.C.|NC DEQ. Available online: deq.nc.gov (accessed on 25 December 2021).
- Chen, J.; Yang, W. Analysis of Nano-Silicon Dioxide Modified Waste Building Brick Materials in the Application of Adsorption and Removal of Water Pollutants. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2021, 13, 2393–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, M.; Sun, S.; Wang, X. Synthesis of Coal Gangue-Based Mesoporous X Zeolite with Soft Template and Its Adsorption Methylene Blue. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2021, 13, 2157–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Pan, Q. Three-Dimensionally Macroporous Fe/C Nanocomposites as Highly Selective Oil-Absorption Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2420–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Zeng, Z.; Lin, Z.; Gan, Q.; Xiang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, A.; Tang, Z. Magnetic and Highly Recyclable Macroporous Carbon Nanotubes for Spilled Oil Sorption and Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5845–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X. Synthesis and Characterization of Zeolite X Obtained from Coal Gangue for Adsorption of Cu2+. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2021, 13, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xin, X.; Yu, G.; Gu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, W.; Liu, C. Effect of Asphaltene on Threshold Pressure Gradient of Heavy Oil in Porous Media. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2021, 13, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Wei, X.; Peng, L. Preparation of Carbon Fiber-Polyacrylamide Composite Hydrogel Based on Surface Electric-Initiated Polymerization. J. Nanoelectron. Optoelectron. 2021, 16, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wei, Y.; Wen, Y.; Cai, H.; Xiao, J.; Wu, S.; Jin, S. Adsorption and Migration Characteristics of Fluorine in Ash-Sluicing Water in Soils. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2021, 13, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebajo, M.O.; Frost, R.L.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Carmody, O.; Kokot, S. Porous Materials for Oil Spill Cleanup: A Review of Synthesis and Absorbing Properties. J. Porous Mater. 2003, 10, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulawardana, E.U.; Neckers, D.C. Photoresponsive Oil Sorbers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyurethane Foam Kitchen Sponge. History of Origin—Vortex Power. Available online: www.vortex-power.com (accessed on 14 April 2018).
- Jung, Y.C.; Bhushan, B. Wetting Behavior of Water and Oil Droplets in Three-Phase Interfaces for Hydrophobicity/philicity and Oleophobicity/philicity. Langmuir 2009, 25, 14165–14173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Pan, Q.; Liu, F. Facile Removal and Collection of Oils from Water Surfaces through Superhydrophobic and Superoleophilic Sponges. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 17464–17470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Qiu, S.; Jiang, W.; Wu, D.; Zhang, C. Evaluation of Electrospun Polyvinyl chloride/Polystyrene Fibers as Sorbent Materials for Oil Spill Cleanup. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4527–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Lackey, M.A.; Cui, J.; Tew, G.N. Gels based on cyclic polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 4140–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.Q.; Huang, J.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, W.L.; Wei, F. Improvement of oil adsorption performance by a sponge-like natural vermiculite-carbon nanotube hybrid. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Tai, N.-H.; Lee, S.-B.; Kuo, W.-S. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic properties of graphene-based sponges fabricated using a facile dip coating method. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7908–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Seiffert, S.; Thiele, J.; Abate, A.R.; Weitz, D.A.; Richteringa, W. Non-coalescence of oppositely charged droplets in pH-sensitive emulsions. Appl. Phys. Sci. 2012, 109, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, N.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Pan, Q. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, W.; Peng, C.; Shi, K.; Luo, Y.; Ji, X. Novel hydrophobic polyvinyl alcohol–formaldehyde foams for organic solvents absorption and effective separation. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Meng, G.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Magnetic Cellulose Sponge for Removing Oil from Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Sha, D.; Shi, K.; Xu, J.; Ji, X. Silane Functionalized Polyvinyl-Alcohol Formaldehyde Sponges on Fast Oil Absorption. Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 5309–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Gómez, E.; Tapia, J.I.; Encinas, A. A sustainable hydrophobic luffa sponge for efficient removal of oils water. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2021, 28, e00273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.; Alhazzaa, M.I.; Asif, M. Treatment of Oily Water using Hydrophobic Nano-silica. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 167, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Kaipa, U.; Mather, Q.Z.; Wang, X.; Nesterov, V.; Venero, A.F.; Omary, M.A. Fluorous Metal−organic Frameworks with Superior Adsorption and Hydrophobic Properties toward Oil Spill Cleanup and Hydrocarbon Storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18094–18097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, S.; Sakthivel, T.; Reid, D.; Goldstein, I.; Hench, L. Hydrophobic High Surface Area Zeolites Derived from Fly Ash for Oil Spill Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5843–5850. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N.; El-Harbawi, M.; Jabal, A.A.; Yin, C.-Y. Characteristics and Oil Sorption Effectiveness of Kapok Fibre, Sugarcane Bagasse and Rice Husks: Oil Removal Suitability Matrix. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husseien, M.; Amer, A.; El-Maghraby, A.; Hamedallah, N. A Comprehensive Characterization of Corn Stalk and Study of Carbonized Corn Stalk in Dye and Gas Oil Sorption. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 86, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chung, T.C.M. Novel Solution to Oil Spill Recovery: Using Thermo degradable Polyolefin Oil Superabsorbent Polymer (Oil−SAP). Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 4896–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharan, Y.; Singh, J.; Goyat, R.; Umar, A.; Akbar, S.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Baskoutas, S. Novel Supramolecular Organo-Oil Gelators for Fast and Effective Oil Trapping: Mechanism and Applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 442, 129977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, W.C.; Peng, C.; Shi, K.; Ji, X.L. Highly Efficient Macroporous Adsorbents for Toxic Metal Ions in Water Systems Based on Polyvinyl Alcohol−Formaldehyde Sponges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 2537–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Ali, A.; Kumar, R. Removal of Ni2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ using different agricultural residues: Kinetic, isotherm modeling and mechanism via chemical blocking. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 6377–6386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.X.; Li, B.R.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Z.Y.; Yang, X.; Shi, K.; Li, W.; Peng, C.; Wang, W.C.; Ji, X.L. Superfast and Reversible Thermoresponsive of Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) Hydrogels Grafted on Macroporous Poly(vinyl alcohol) Formaldehyde Sponges. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 32747–32759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sears, G. Determination of specific surface area of colloidal silica by titration with sodium hydroxide. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 1981–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Saharan, Y.; Goyat, R.; Vikash, K.; Algadi, H.; Akbar, S.; Baskoutas, S.; Umar, A. Modified low-temperature synthesis of graphene oxide nanosheets: Enhanced adsorption, antibacterial and antioxidant properties. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114245. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, B.; Gao, H.; He, M.; Zhang, L. Hydrophobic Modification on Surface of Chitin Sponges for Highly Effective Separation of Oil. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 19933–19942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzari, K.; Zampieri, K.; Zanini, M.; Zattera, A.; Baldasso, C. Sorption capacity of hydrophobic cellulose aerogels silanized by two different methods. Cellulose 2017, 24, 3421–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Akram, M.Y.; Ali, S.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. Decomposable PVA-based super-hydrophobic 3D porous material for effective water/oil separation. Langmuir 2018, 34, 15700–15707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Xue, Y.; Wu, X.; Donga, Y.; Meng, X. Self-assembly modification of polyurethane sponge for application in oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 40378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K.; Gibril, M.; Kong, F.; Wang, F. Lignin-based superhydrophobic melamine resin sponges and their application in oil/water separation Author links open overlay panel. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.M.; Learmonth, D.A.; Gomes, D.B. Mussel-Inspired Catechol Functionalisation as a Strategy to Enhance Biomaterial Adhesion: A Systematic Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Saharan, Y.; Goyat, R.; Kumar, R.; Algadi, H.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Baskoutas, S.; Umar, A. Nanoporous and hydrophobic new Chitosan-Silica blend aerogels for enhanced oil adsorption capacity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 351, 131247. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Saharan, Y.; Kumar, R.; Alothman, A.A.; Ifseisi, A.A.; Aljado, A.K.; Umar, A. Trapping of oil molecules in clathrates: Oil trapping mechanism, soil composition, and thermal studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114169. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Ali, A.; Prakash, V. Removal of lead (II) from synthetic and batteries wastewater using agricultural residues in batch/column mode. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sponge Samples | Surface Area ± 5 m2/g | Pore Volume ± 0.2 cm3/g |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrophobic PVFTX-100 | 83.8 | 1.21 |
| Hydrophobic PVFSDS | 77.4 | 1.09 |
| Hydrophobic PVFT-80 | 74.2 | 1.05 |
| Sponge Samples | Number of Cycles | Removal Efficiency ± 1 (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorobenzene | Toluene | Diesel | Petrol | Hexane | ||
| PVFTX-100 | 2 | 27.0 | 24.4 | 24.0 | 22.7 | 21.0 |
| 4 | 53.0 | 48.2 | 47.6 | 44.0 | 41.4 | |
| 6 | 76.0 | 71.8 | 70.5 | 64.5 | 60.7 | |
| 8 | 96.0 | 91.0 | 89.9 | 85.6 | 80.0 | |
| PVFSDS | 2 | 23.6 | 22.5 | 22.0 | 21.4 | 19.0 |
| 4 | 45.2 | 43.3 | 43.4 | 41.6 | 36.4 | |
| 6 | 67.0 | 64.2 | 64.0 | 60.6 | 54.7 | |
| 8 | 85.0 | 82.8 | 81.6 | 77.5 | 71.8 | |
| PVFT-80 | 2 | 22.4 | 22.0 | 21.8 | 21.0 | 18.4 |
| 4 | 41.8 | 40.6 | 40.2 | 39.0 | 36.0 | |
| 6 | 63.6 | 61.3 | 61.0 | 59.6 | 53.3 | |
| 8 | 83.7 | 80.0 | 78.6 | 77.0 | 69.7 | |
| Raw Materials | Amount of Sponge Taken (g) | Organic Solvent Uptake Capacity (g/g) | Number of Cycles | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly (5-hydroxy-1-cyclooctene) | 1.0 | 199 | Dna | [22] |
| Ferric nitrate and Ammonium molybdate | 1.0 | 80–180 | 20 | [23] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | 1.0 | 89.3 | 35 | [27] |
| Chitin | 1.0 | 29–58 | 10 | [43] |
| Cellulose | 1.0 | 65 | Dna | [44] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | 1.0 | 1.8–7.0 | 10 | [45] |
| Polyurethane | 1.0 | 25 | Dna | [46] |
| Melamine | 1.0 | 61.0 | 30 | [47] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | 1.0 | 4.0 | 10 | [29] |
| Catechol | 1.0 | 99% | 50 | [48] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | 1.0 | 100% | 10 | Present work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saharan, Y.; Singh, J.; Goyat, R.; Umar, A.; Akbar, S. Novel Hydrophobic Polyvinyl-Alcohol Formaldehyde Sponges: Synthesis, Characterization, Fast and Effective Organic Solvent Uptake from Contaminated Soil Samples. Molecules 2022, 27, 8429. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238429
Saharan Y, Singh J, Goyat R, Umar A, Akbar S. Novel Hydrophobic Polyvinyl-Alcohol Formaldehyde Sponges: Synthesis, Characterization, Fast and Effective Organic Solvent Uptake from Contaminated Soil Samples. Molecules. 2022; 27(23):8429. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238429
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaharan, Yajvinder, Joginder Singh, Rohit Goyat, Ahmad Umar, and Sheikh Akbar. 2022. "Novel Hydrophobic Polyvinyl-Alcohol Formaldehyde Sponges: Synthesis, Characterization, Fast and Effective Organic Solvent Uptake from Contaminated Soil Samples" Molecules 27, no. 23: 8429. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238429
APA StyleSaharan, Y., Singh, J., Goyat, R., Umar, A., & Akbar, S. (2022). Novel Hydrophobic Polyvinyl-Alcohol Formaldehyde Sponges: Synthesis, Characterization, Fast and Effective Organic Solvent Uptake from Contaminated Soil Samples. Molecules, 27(23), 8429. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27238429








