Abstract
Houttuyniae herba, the Saururaceae plant Houttuynia cordata Thunb., has multiple therapeutic effects, including clearing heat, eliminating toxins, reducing swelling, discharging pus, and relieving stagnation. It has a long history as an edible and medicinal plant in China. Phytochemical studies show that the main constituents include volatile oil, flavonoids, and alkaloids. Aristolactam is a major alkaloid with a structure similar to toxic aristolochic acids. However, there has been no systematic study on aristolochic acids and alkaloids in Houttuyniae herba. Therefore, in this study, an LC–MS/MS method was developed to simultaneously detect seven alkaloids and five aristolochic acids in Houttuyniae herba from different origins. Six alkaloids (O-demethyl nornucifrine, N-nornucifrine, aristololactam AII, aristololactam FI, aristololactam BII, cepharadione B) were found and quantitatively determined in 75 batches of samples. Meanwhile, no aristolochic acids or aristololactams were found in Houttuyniae herba at a limit of detection (LOD) of ≤4 ng/mL. The method developed was fully validated in terms of LOD, limit of quantification (LOQ), linearity, precision, accuracy, and stability. These data clarify the content of the above safety-related components in Houttuyniae herba and provide a reference for further research into its safety.
1. Introduction
Houttuynia cordata Thunb. (Saururaceae) is a medicinal and food dual-purpose plant in Asia. Its fresh underground stems have good dietary value and therapeutic benefits. Additionally, its whole fresh plant or the dried aerial part is also used extensively as herbal medicine in treating various diseases [1,2,3]. It possesses the actions of clearing heat, eliminating toxins, reducing swelling, discharging pus, and relieving stagnation. Modern studies revealed that volatile oils, flavonoids, and alkaloids are the main components. These components have several bioactivities, including anti-inflammation, antiviral, antitumor, immune modulation, antioxidation, and antibacterial [4,5,6,7,8,9].
Literature research shows that 11 aristololactams (aristololactam AII, aristololactam FII, aristololactam BII, aristololactam FI, piperolactam B, piperolactam C, piperolactam D, aristololactam FI, 3-hydroxy-1,2-dimethoxy-5-methyl-5H-dibenzoindol-4-one, 3-methoxy-5-methyl-5H-benzodioxolo-benzoindol-4-one, and 3,4-dimethoxy-N-methyl aristolactam) have been isolated from Houttuyniae herba [10,11,12]. Aristolactams are naturally occurring phenanthrene lactam alkaloids, which are the main metabolites of aristolochic acid by nitro-reduction reaction in vivo. It has been proved that some aristolochic acids have renal toxicity, cause carcinogenesis, and may cause gene mutations [13,14,15,16]. The use of aristolochic acid-containing herbal medicines is forbidden in many countries. However, there are insufficient studies on the safety and quantitative analysis of aristololactam components. It is necessary to develop a method for identifying and quantifying of aristolochic acids and alkaloids in Houttuyniae herba.
Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) was used to analyze Houttuyniae herba samples for the natural existence of aristolochic acid I (AA-I) and aristolochic acid II (AA-II) [17]. Studies revealed that neither AA-I nor AA-II exist naturally in Houttuyniae herba or are below the method detection limits (MDLs; <2 ng/g). In this study, LC–MS/MS was used to detect 12 compounds in Houttuyniae herba from different origins, wild and cultivated, to provide a reference for the research into the safety of Houttuyniae herba.
2. Results
An established LC–MS/MS method for seven alkaloids and five aristolochic acids was applied to analyze Houttuyniae herba, and six alkaloids [O-demethyl nornucifrine (C1), N-nornucifrine (C2), aristololactam AII (C5), aristolactam FI (C7), aristolactam BII (C9), and cepharadione B (C11)] were identified. The typical MRM chromatograms for a mixed standard solution and a sample of Houttuyniae herba are shown in Figure 1. These data showed that the method is highly selective.
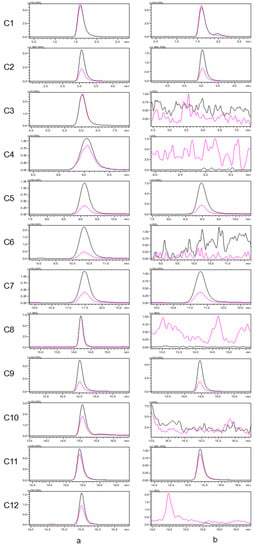
Figure 1.
Typical multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) chromatograms for a mixed standard solution (a) and a sample of Houttuyniae herba (b). [The quantitative ion pairs: C1(m/z 282.0 > 251.1); C2(m/z 282.0 > 265.1); C3(m/z 344.9 > 282.0); C4(m/z 374.9 > 314.1); C5(m/z 266.0 > 251.1); C6(m/z 374.9 > 312.0); C7(m/z 266.0 > 251.1); C8(m/z 329.0 > 268.1); C9(m/z 279.9 > 264.1); C10(m/z 294.0 > 278.9); C11(m/z 322.0 > 306.0); C12(m/z 359.0 > 298.1)].
2.1. Linearity Range, Limits of Detection (LODs), and Limits of Quantification (LOQs)
Working standard solutions containing seven alkaloids and five aristolochic acids were prepared by series dilution of the mixed stock solution with 80% methanol to different concentrations. Then, they were injected and analyzed. The regression equations, linearity, determination coefficient, and limits of detection and quantification of the method are presented in Table 1. All calibration curves showed good linear regression (R2 ≥ 0.9911) within the tested ranges. We precisely diluted the stock mixed solution with methanol quantitatively and stepwise if necessary. The diluted solutions were separately injected and analyzed. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) (Table 1) were defined as the concentrations that could be detected and yield signal-to-noise (S/N) ratios of 3:1 and 10:1, respectively, according to guidelines for validation of analytical methods for pharmaceutical quality standards.

Table 1.
Regression equation, LOD, and LOQ of the six dianthrones of 12 compounds.
2.2. Precision
The precision of the method was evaluated based on intra- and inter-day precision. The intra-day precision was tested with mixed standard solutions over 1 day. The standard solutions were examined in triplicate on three consecutive days for inter-day precision. The corresponding % RSD values were calculated. The RSDs for the intra-day (n = 6) and inter-day (n = 9) assays were less than 3.5% and 4.8%, respectively (see Table 2).

Table 2.
Stability, repeatability, and precision of analysis of 12 compounds.
2.3. Stability and Repeatability
The stability was measured using a sample solution (S14) and performed at 0, 2, 4, 8, 12, and 24 h after preparation and storage at room temperature. Six independent sample solutions were prepared and analyzed to measure the repeatability. The concentration of each solution was determined by calibration curves produced on the same day. The RSDs for stability were less than 5.6% within 24 h. Moreover, the RSDs for repeatability were less than 5.8% (Table 2). The stability and repeatability tests show that all analytes are stable within the whole analysis and that the test method is sufficiently effective for conventional analysis.
2.4. Recovery
The recovery experiment was performed by adding a known amount of individual reference standards into a certain amount of sample (S14). Nine replicates were performed for the test.
The recoveries were calculated using the following equation: recovery (%) = (total amount detected—amount original)/amount spiked × 100%. The results show that the average recoveries ranged from 77% to 120% with RSDs in the range of 1.0–5.8%, indicating that the method was accurate (see Table S1).
2.5. Sample Analysis
Seventy-five batches of samples were prepared and analyzed according to 2.5, 2.6, and 2.7, and the quantification results are summarized. Compounds aristolochicacid IIIa (C3), 7-hydroxy aristolochic acid I (C4), aristolochic acid Iva (C6), aristolochic acid II (C8), aristolactam I (C10), and aristolochic acid I (C12) were not detected in the 75 batches of samples.
The results showed that the content of compounds in dried Houttuyniae herba (Figure 2) followed the order: O-demethyl nornucifrine (C1) < N-nornucifrine (C2) < aristololactam AII (C5) < aristolactam FI (C7) < cepharadioneB (C11) < aristolactam BII (C9). The total content of the six alkaloids in dried Houttuyniae herba was as follows: aerial part (31–530 μg/g), leaves (12–870 μg/g), and aerial stem (12–380 μg/g). The average content of the total content was: aerial stems (72 μg/g) < leaves (180 μg/g) (see Table S2).
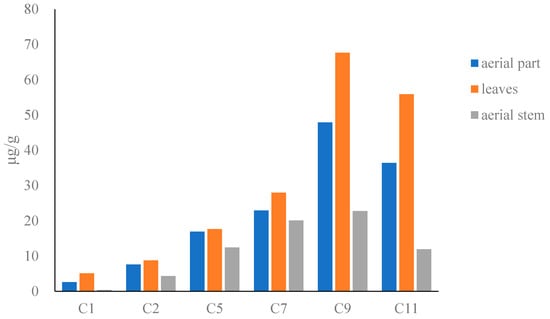
Figure 2.
Bar graph of content of six alkaloids in dried Houttuyniae herba.
The total content of six alkaloids in fresh Houttuyniae herba (Figure 3) (calculated as dry) was as follows: underground stem (6.5–19 μg/g) and whole grass (110–130 μg/g), respectively. The underground stem has a lower potential risk (see Table S3).
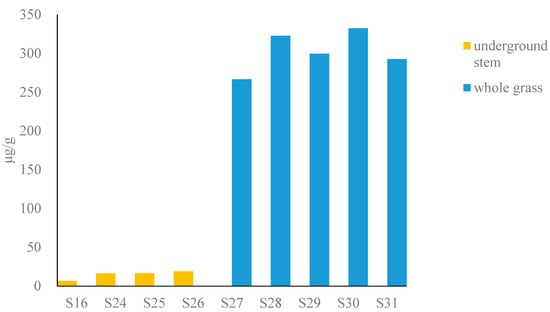
Figure 3.
Bar graph of content of total alkaloids in fresh Houttuyniae herba.
3. Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Extraction Method Optimization of MS Conditions
A sample (S14) was used to optimize the extraction process. Optimization was completed using a three-step approach, which can be described as follows. Step 1. Optimization of the extraction solvent system: the first step in preparing the sample solution was to select a suitable extraction solvent because of its paramount role in achieving good recovery. Six solutions [50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, 90%, and 100% methanol (v/v in water)] were systematically compared considering the peak areas of the six alkaloids in Houttuyniae herba. The result was that 80% methanol exhibited the highest extraction efficiency among the tested solvents (Figure 4a). Hence, 80% methanol was selected as the best extraction solvent for this study. Step 2. Optimization of solvent volume: extractant volume may have been another factor to affect extraction efficiency. This study aimed to obtain the minimum volume of extractant required to achieve the highest extraction efficiency. Five different volumes of methanol (10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 mL) were systematically studied. The peak areas of the six alkaloids increased with an increasing volume of methanol (Figure 4b). However, there was no significant difference among the results of five different volumes of methanol. Therefore, 20 mL was eventually selected as the optimized volume for environmentally friendly reasons. Step 3. Optimization of ultrasonication time: in this study, an ultrasonic process was used to extract the six alkaloids from Houttuyniae herba. There was no significant difference among ultrasonication times of 10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 min (Figure 4c). Accordingly, 30 min was selected as the best extraction time to save energy.
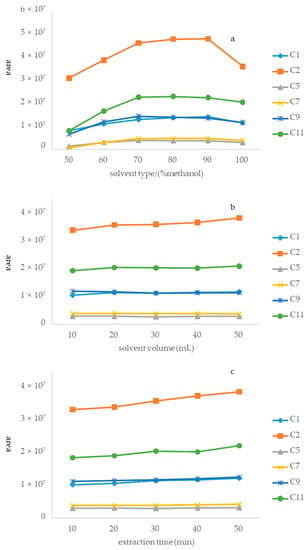
Figure 4.
Optimization of different parameters of the method of sample solution: (a) type of extractant, (b) volume of extractant, and (c) ultrasound time.
In conclusion, the optimal sample preparation method was extracting of a 0.5 g sample with 20 mL of 80% methanol in an ultrasonic water bath for 30 min.
3.2. Optimization of LC–MS/MS Conditions
The chromatographic conditions, especially the mobile phase composition, were optimized to achieve the best possible resolution and symmetric peaks of the six compounds within a suitable run time. Throughout the tests, three mobile phases were examined: acetonitrile–water, acetonitrile–0.1% formic acid, and acetonitrile–0.1% formic acid (containing 5 mM ammonium acetate). The acetonitrile–water containing 0.1% formic acid (v/v) combination had the lowest pressure, best baseline stability, and highest ionization efficiency among those tested and was eventually selected as the mobile phase [18].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
O-Demethyl nornucifrine (C1) (HPLC purity ≥99.74%, Lot no. ZT-24107) and N-Nornucifrine (C2) (HPLC purity ≥99.82%, Lot no. ZC-53802) were from Shanghai Zhenzhun Biochemical Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Aristolochic acid IIIa (C3) (HPLC purity ≥99%, Lot no. C11188894) and 7-hydroxy aristolochic acid I (C4) (HPLC purity ≥98%, Lot No. C12347780) were from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Aristololactam AII (C5) (HPLC purity ≥97%, Lot no. X27S11L125977), aristololactam FI (C7) (HPLC purity ≥98%, Lot no. X09M11L112632), aristolochic acid II (C8) (HPLC purity ≥98%, Lot no. P13J10F90613), aristololactam BII (C9) (HPLC purity ≥97%, Lot no. X09M11L112631), and aristololactam I (C10) (HPLC purity ≥98%, Lot no. P27N10S104067) were from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Aristolochic acid IVa (C6) (HPLC purity ≥98%, Lot no. DST190415-057) was from Chendu DeSiTe Bio-Technology Co., Ltd (Chendu, China). Cepharadione B (C11) (HPLC purity ≥95%) was prepared in the laboratory. Aristolochic acid I (C12) (HPLC purity ≥99.1%, Lot no. 110746–201912) was from National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing, China (Figure 5). Methanol (analytical reagent) was from National Drug Chemical Reagents Co., Ltd (Beijing, China). Acetonitrile (mass spectrometry reagent) and formic acid (mass spectrometry reagent) were from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). Water was of ultrahigh purity.
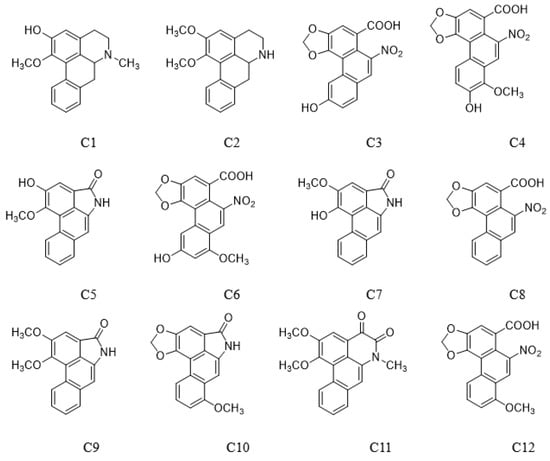
Figure 5.
Chemical structures of 12 compounds.
4.2. Samples
Seventy-five batches of Houttuyniae herba samples were collected from different provinces in China (Table 3). It should be noted that the leaves (S32–50) and aboveground stems (S54–72) come from different parts of aboveground parts (S1–15 and S17–20). The leaves (S51–53) and aboveground stems (S73–75) come from different parts of the aboveground part (S21–23).

Table 3.
Sample collection information for the present study.
The samples were authenticated by Associate Professor Shuai Kang (Institute for Control of Chinese Traditional Medicine and Ethnic Medicine, National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, National Medical Products Administration (Beijing, China)).
4.3. Instrumentation
A Shimadzu LC–MS/MS 8050 (Shimadzu Co., Kyoto, Japan) equipped with an electrospray ionization device was used for sample analysis. We also used a METTLER XS105 electronic analytical balance (Mettler-Toledo, Zurich, Switzerland), Milli-Q water purification system (Millipore, Burlington, NJ, USA), and KQ-500DE numerical control ultrasound cleaning instrument (Kun Shan Ultrasonic Instruments Co., Ltd., Kunshan, China).
4.4. Preparation of Standard Solutions
Standard stock solutions of O-demethyl nornucifrine (C1), N-nornucifrine (C2), aristolochic acid IIIa (C3), 7-hydroxy aristolochic acid I (C4), aristololactam AII (C5), aristolochic acid Iva (C6), aristolactam FI (C7), aristolochic acid II (C8), aristolactam BII (C9), aristolactam I (C10), cepharadione B (C11), and aristolochic acid I (C12) were prepared by dissolving suitable amounts of reference substance in 80% methanol (v/v in water) to make the concentration of 80 μg/mL. The mixed standard stock solution was freshly prepared by combining an appropriate amount of each standard stock solution and diluting it with a known volume of 80% methanol.
4.5. Sample Preparation
For Houttuyniae herba pulverized to powder, we weighed 0.5 g samples accurately and placed them into a 50 mL plug conical bottle. Twenty milliliters of 80% methanol were added precisely and weighed, respectively. After ultrasonic extraction (power: 500 W; frequency: 40 kHz) for 30 min, the extract was cooled down and then the lost weight was made up by adding 80% methanol. This extract was then filtered through a 0.22 μm microporous filter membrane. For each of the 18 batches of fresh Houttuyniae herba (S16, S21–31, S51–53, S73–75), after drying, we performed the same treatment as described for the already-dried products.
4.6. HPLC Chromatographic Conditions, Instruments, and Analytical Conditions
Using a gradient elution, the chromatographic separation was achieved on an Agilent SB-C18 (2.1 × 50 mm, 1.8 μm) at 30 °C. The mobile phase consisted of solution A (0.1% formic acid in water) and solution B (acetonitrile). The gradient elution profile was as follows: 0–10 min, 25% B; 10–12 min, 25–40% B; 12–17 min, 40% B; 17–17.01 min, 40–80% B; 17.01–20 min, 80% B; 20–20.01 min, 80–25% B; 20.01–25 min, 25% B. The flow rate was 0.3 mL/min, the autosampler temperature was 10 °C, and the sample volume injected was 1 μL. Before sample analysis, the column was equilibrated with the mobile phase at 25% B for 30 min.
4.7. MS Conditions
The triple-quadrupole MS equipped with a positive electrospray ionization source was used in the MRM mode. The electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI–MS) parameters were as follows: interface temperature, 300 °C; desolvation line (DL) temperature, 250 °C; heat block temperature, 400 °C; nebulizer gas flow rate, 3 L/min; heating gas flow rate, 10 L/min; and drying gas flow rate, 9 L/min.
The MRM conditions were individually optimized for each of the 12 compound reference standards because of their different structures. The MS conditions for MRM are summarized in Table 4, and the typical MRM chromatogram is shown in Figure 1.

Table 4.
Mass spectrometry parameters.
5. Conclusions
In this study, an LC–MS/MS method for qualitative and quantitative detection of seven alkaloids (O-demethyl nornucifrine, N-nornucifrine, aristololactam AII, aristololactam FI, aristololactam BII, aristololactam I, and cepharadione B) and five aristolochic acids (aristolochic acid IIIa, 7-hydroxy aristolochic acid I, aristolochic acid IVa, aristolochic acid II, and aristolochic acid I) was established. This method has the outstanding advantages of strong specificity, high sensitivity, high accuracy, good reproducibility, and high throughput automation. The content of the above compounds in dried and fresh samples of Houttuyniae herba was detected for the first time. The safety was not related to aristolochic acid IIIa, 7-hydroxy aristolochic acid I, aristolochic acid IVa, aristolochic acid II, aristolochic acid I, or aristololactam I. Therefore, a follow-up study on the safety of alkaloids in Houttuyniae herba should be a focus. The content of the six alkaloids in aerial stems was less than in leaves. Our findings suggest the edible underground stem has a relatively lower potential risk than aerial plant parts. This study is of great significance for the safety evaluation of Houttuyniae herba. It also provides a scientific basis for follow-up safety risk control measures.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/molecules27248969/s1, Table S1: Results of recovery, Table S2: Contents of six alkaloids in dried Houttuyniae herba (n = 3, μg/g), Table S3: Contents of six alkaloids in fresh Houttuyniae herba (n = 3, μg/g).
Author Contributions
Resources, S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.W. and J.L.; visualization, S.M.; project administration, Z.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Drug Standard Formulation and Revision Research Project, grant number 2021Z15.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data included in this study are available upon request by contact with the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds C1–12 are available from the authors.
References
- He, J.; Peng, L.; Li, W.; Luo, J.; Li, Q.; Zeng, H.; Ali, M.; Long, C. Traditional knowledge of edible plants used as flavoring for fish-grilling in Southeast Guizhou, China. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2022, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; He, M.; Yan, H. Complete plastome of Houttuynia cordata (Saururaceae), a medicinal and edible plant. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 3208–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Feng, Q.; Yu, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, J.; Hu, X.; Cai, M. Chloroplast genome features of an important medicinal and edible plant: Houttuynia cordata (Saururaceae). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Tan, R.X.; Li, E. Houttuynia cordata blocks HSV infection through inhibition of NF-κB activation. Antivir. Res. 2011, 92, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Ahn, J.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, H.P. Flavonoids from the aerial parts of Houttuynia cordata attenuate lung inflammation in mice. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Hwang, I.H.; Jang, I.S.; Kim, M.; Bang, I.S.; Park, S.J.; Chung, Y.J.; Joo, J.C.; Lee, M.G. Houttuynia cordata Thunb promotes activation of HIF-1A–FOXO3 and MEF2A pathways to induce apoptosis in human HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 360–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ling, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, D. Beneficial effects of Houttuynia cordata polysaccharides on “two-hit” acute lung injury and endotoxic fever in rats associated with anti-complementary activities. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanarojana, M.; Nararatwanchai, T.; Thairat, S.; Tancharoen, S. Antiproliferative activity and induction of apoptosis in human melanoma cells by Houttuynia cordata Thunb Extract. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6619–6628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ding, Q.; Liu, J.; Dai, Z.; Ma, S. Research progress on chemical components, pharmacology and quality control of Houttuyniae Herba. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 42, 108–120. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, S.C.; Su, C.R.; Ku, Y.C.; Wu, T.S. The Constituents and their bioactivities of Houttuynia cordata. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Wei, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Sang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, H. Bioactive alkaloids from the aerial parts of Houttuynia cordata. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 195, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.U.; Fei-Hua, W.U.; Juan, L.I.; Liang, J.Y. Alkaloids from Houttuynia cordata and their antiplatelet aggregation activities. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2011, 9, 425–428. [Google Scholar]
- Michl, J.; Ingrouille, M.J.; Simmonds, M.S.; Heinrich, M. Naturally occurring aristolochic acid analogues and their toxicities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 31, 676–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.L.; Guo, X.Q.; Wang, H.R.; Chen, T.; Mei, N. Aristolochic acid-induced genotoxicity and toxicogenomic changes in rodents. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2020, 6, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, A.W.; Poon, S.L.; Huang, M.N.; Lim, J.Q.; Boot, A.; Yu, W.; Suzuki, Y.; Thangaraju, S.; Ng, C.C.; Tan, P.; et al. Aristolochic acids and their derivatives are widely implicated in liver cancers in Taiwan and throughout Asia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Guo, R.; Dai, Z.; Ma, S. Research progress on aristolochic acids. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Mater. Med-World Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.K.; Pan, G.; Chan, W. Analysis of aristolochic acids in Houttuynia cordata by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 56, e4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dai, Z.; Ma, S. Rapid analysis of aristolochic acid analogues in traditional chinese patent medicine by LC-MS/MS. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2020, 2020, 8823596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).