Effect of Flavonoids in Hawthorn and Vitamin C Prevents Hypertension in Rats Induced by Heat Exposure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antioxidant Compounds in the Extract of Hawthorn
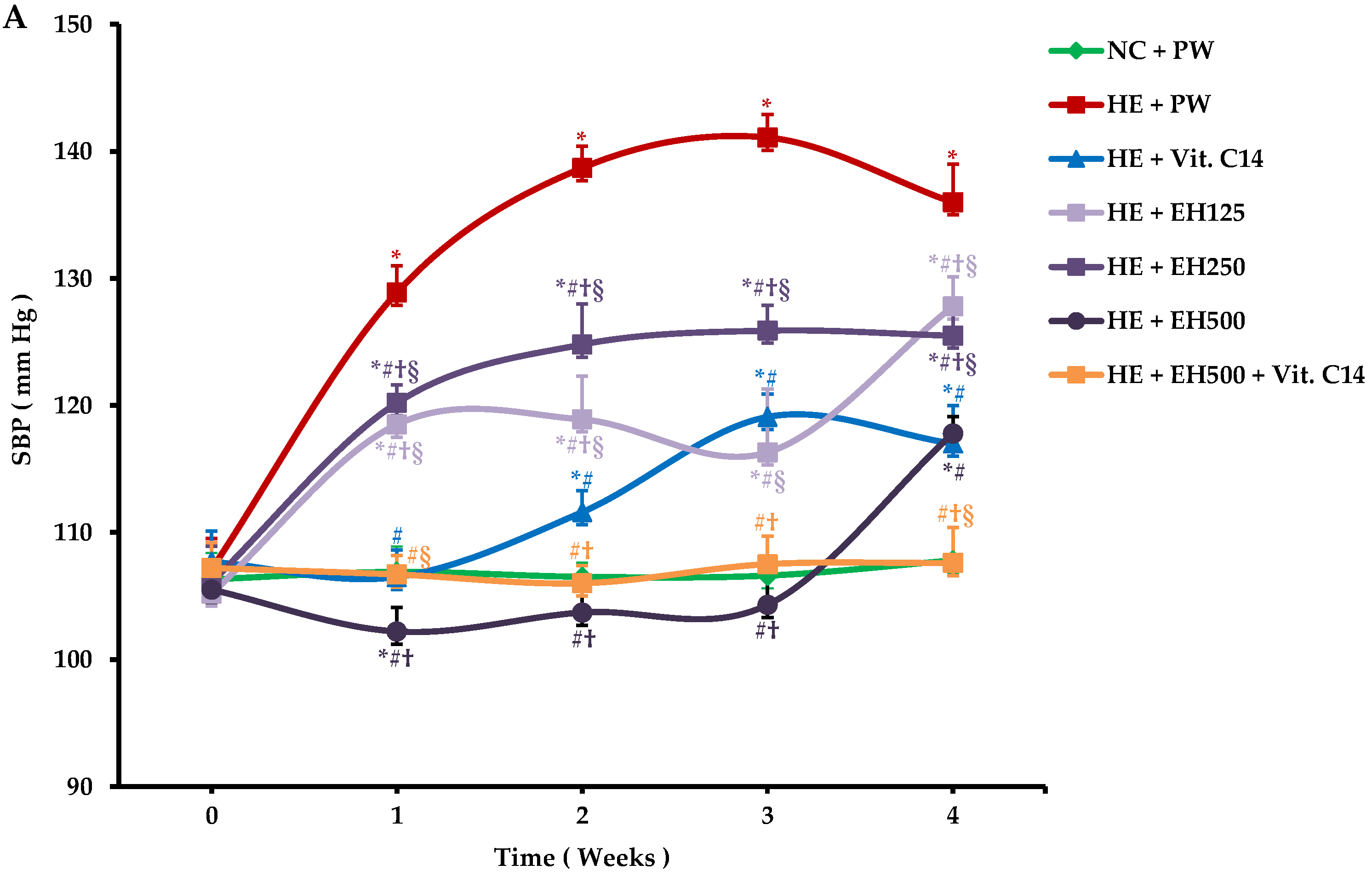
2.2. Effects of Extract of Hawthorn and Vitamin C on Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
2.3. Effects of Extract of Hawthorn and Vitamin C on the Wall Thoracic Artery
2.4. Effects of Extract of Hawthorn and Vitamin C on Markers of Oxidative Stress
2.5. Effects of Extract of Hawthorn and Vitamin C on the Nitric Oxide Generation
2.6. Effects of Extract of Hawthorn and Vitamin C on the Inflammatory and Protective Factors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Ethical Considerations
4.3. Vitamin C and Extract of Hawthorn
4.4. Experimental Conditions
4.5. Experimental Procedures
4.6. Blood Pressure Measurement
4.7. Samples Collection
4.8. Vascular Tissue Preparation
4.9. Biochemical Analyses
4.9.1. Assay of Lipid Oxidation
4.9.2. Assay of Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
4.9.3. Assay of Serum Nitric Oxide
4.9.4. Assay of Serum hs-CRP, IL-2, and TNF-α
4.9.5. Western Blot Analysis of Hsp70
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.J.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. A guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: Executive summary: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension 2018, 71, 1269–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, S.; Thompson, R.; Landeg, O.; Murray, K.A.; Waite, T. Indoor temperature and health:a global systematic review. Public Health 2020, 179, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzik, T.J.; Touyz, R.M. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and vascular aging in hypertension. Hypertension 2017, 70, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangartit, W.; Pakdeechote, P.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Donpunha, W.; Shibahara, S.; Kukongviriyapan, U. Tetrahydrocurcumin in combination with deferiprone attenuates hypertension, vascular dysfunction, baroreflex dysfunction, and oxidative stress in iron-overloaded mice. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 87, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, O.; Benassi, R.; Cesar, T. Orange juice associated with a balanced diet mitigated risk factors of metabolic syndrome: A randomized controlled trial. J. Nutr. Int. Metab. 2019, 17, E100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, A.; Hruskova, J.; Jakubik, J.; Kunzova, S.; Sochor, O.; Barchitta, M.; Agodi, A.; Bauerova, H.; Medina-Inojosa, J.R.; Vinciguerra, M. Dietary antioxidant intake decreases carotid intima media thickness in women but not in men: A cross-sectional assessment in the Kardiovize study. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 131, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Qi, Z.L. Mechanism of Oxidative Stress in Body under Heat Stress. J. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 29, 3051–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périard, J.D.; Travers, G.J.S.; Racinais, S.; Sawka, M.N. Cardiovascular adaptations supporting human exercise-heat acclimation. Auton. Neurosci. 2016, 196, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kagan, V.E.; Freisleben, H.J.; Tsuchiya, M.T.; Packer, F.L. Generation of probucol radicals and their reduction by ascorbate and dihydrolipoic acid in human low density lipoproteins. Free. Radic. Res. Commun. 1991, 15, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, C.G.; González-Alonso, J. Cardiovascular function in the heat-stressed human. Acta Physiol. 2010, 199, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, T.E.; Crandall, C.G. Effect of thermal stress on cardiac function. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2011, 39, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, M.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Fan, H.M.; Che, C.L.; Gao, X.J.; Lu, Y.; Cong, Y.L.; Liu, Y.J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, H.; et al. Relationship Between Occupational High temperature exposure years and prevalence of hypertension: Based on restricted cubic spline model. J. Environ. Occup. Med. 2016, 33, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.M.; Wang, D.G.; Li, J.; Li, X.H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, N.; Liu, W.T.; Li, Y.X. Relationships between micronutrient losses in sweat and blood pressure among heat-exposed steelworkers. Indus. Health 2016, 54, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jan-On, G.; Sangartit, W.; Pakdeechote, P.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Sattayasai, J.; Senaphan, K.; Kukongviriyapan, U. Virgin rice bran oil alleviates hypertension through the upregulation of eNOS and reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rats. Nutrition 2019, 69, 110575–110583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türck, P.; Fraga, S.; Salvador, I.; Campos-Carraro, C.; Lacerda, D.; Bahr, A.; Ortiz, V.; Hickmann, A.; Koetz, M.; Belló-Klein, A.; et al. Blueberry extract decreases oxidative stress and improves functional parameters in lungs from rats with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nutrition 2020, 70, 110579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.Y.; Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Liu, Q.; Li, H.B. Effects of vegetables on cardiovascular diseases and related mechanisms. Nutrients 2017, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, T.; Xu, D.P.; Li, H.B. Effects and mechanisms of fruit and vegetable juices on cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Sci. Mol. 2017, 18, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siti, H.N.; Kamisah, Y.; Kamsiah, J. The role of oxidative stress, antioxidants and vascular inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashor, A.W.; Brown, R.; Keenan, P.D.; Willis, N.D.; Siervo, M.; Mathers, J.C. Limited evidence for a beneficial effect of vitamin C supplementation on biomarkers of cardiovascular diseases: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Nutr. Res. 2019, 61, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizer, F.; Whitney, E. Nutrition, 12rd ed.; Wadsworth Cengage Learning: Belmont, CA, USA, 2011; p. 848. ISBN 978-0-538-73494-3. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.S.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.X. Study on Antioxidant Activities of 12 Kinds of Fruit. Food Indus. 2014, 35, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Deng, J.; Wen, L.R.; You, L.J. Bioactive compounds of different hawthorn cultivars and their antioxidant activities. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassell, M.C.; Kingston, R.; Gilroy, D.; Lehane, M.; Furey, A. Hawthorn (Crataegus spp.) in the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koçyildiz, Z.C.; Birman, H.; Olgaç, V.; Akgün-Dar, K.; Melikoğlu, G.; Meriçli, A.H. Crataegus tanacetifolia leaf extract prevents L-NAME-induced hypertension in rats: A morphological study. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, H.N.; Hao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. Synergistic antioxidant effect of green tea extract with vitamin C and lycopene. J. Hyg. Res. 2017, 4, 666–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temitayo, A.; Ademola, O.; Temidayo, O.; Ebunoluwa, A.; Kabirat, A. Quercetin and Vitamin C Mitigate Cobalt Chloride-Induced Hypertension through Reduction in Oxidative Stress and Nuclear Factor Kappa Beta (NF-Kb) Expression in Experimental Rat Model. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 175, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Chen, L.H.; Mo, Y.T. Cooperative antioxidant effects of flavonoids from Hong Guo ginseng and VC. Food Ferment. Ind. 2014, 40, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzi-Petrushev, N.; Jankulovski, N.; Hristov, K.; Mladenov, M. l-2-oxothiazolidine-4-carboxylate influence on age- and heat exposure-dependent redox changes in rat’s blood plasma. J. Physiol. Sci. 2011, 61, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi, C.; Tsioufis, K.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Burnier, M.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Clement, D.; Coca, A.; Desideri, G.; Grassi, G.; Lovic, D.; et al. Nutraceuticals and blood pressure control: A European Society of Hypertension position document. J. Hypertens. 2020, 38, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, B.; Saranya, D.; Prabhu, R. Role of flavonoid troxerutin on blood pressure, oxidative stress and regulation of lipid metabolism. Front. Biosci. 2019, 11, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.L.; Jing, X.Q.; Sheng, Y.C.; Zhang, J.Q.; Hao, Z.X.; Wang, Z.T.; Ji, L.L. Epicatechin attenuates hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome by inhibiting liver oxidative and inflammatory injury. Redox Biol. 2019, 22, 101117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.S.; Guo, Y.; Sun, P.; Lv, X.L.; Zuo, Y.B. Hawthorn fruit increases the antioxidant capacity and reduces lipid peroxidation in senescence-accelerated mice. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2011, 232, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, H.; Soner, B.C.; Baysal, T.; Sahin, A.S. Protective effects of Hawthorn (Crataegus oxyacantha) extract against digoxin-induced arrhythmias in rats. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2015, 15, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.B.; Zheng, R.L. Free Radical Toxicology; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012; pp. 91–108. ISBN 978-7-117-16355-2. [Google Scholar]
- Loperena, R.; Harrison, D.G. Oxidative Stress and Hypertensive Diseases. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 101, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meghwani, H.; Prabhakar, P.; Mohammed, S.A.; Seth, S.; Hote, M.P.; Banerjee, S.K.; Arava, S.; Ray, R.d.; Maulik, S.K. Beneficial effects of aqueous extract of stem bark of Terminalia arjuna (Roxb.), an ayurvedic drug in experimental pulmonary hypertension. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 197, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.H.; Shu, Z.H.; Liao, Y.Q.; Liu, P.Q.; Lu, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, G.X.; Pan, X.D.; Lan, T.; Zang, L.Q.; et al. Effects of short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase on hypertensive vascular remodelling. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 2018, 34, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignarro, L.J. Nitric Oxide: Biology and Pathobiology; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2000; pp. 83–91. ISBN 13 978-0-123-73866-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kukongviriyapan, U.; Kukongviriyapan, V.; Pannangpetch, P.; Donpunha, W.; Sripui, J.; Sae-Eaw, A.; Boonla, O. Mamao pomace extract alleviates hypertension and oxidative stress in nitric oxide deficient rats. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6179–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brito, R.; Castillo, G.; Gonzlez, J.; Valls, N.; Rodrigo, R. Oxidative stress in hypertension: Mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2015, 123, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pueyo, M.E.; Gonzalez, W.; Nicoletti, A.; Savoie, F.; Arnal, J.F.; Michel, J.B. Angiotensin Ⅱ stimulates endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 via nuclear factor-kappaB activation induced by intracellular oxidative stress. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niess, A.M.; Fehrenbach, E.; Lehmann, R.; Opavsky, L.; Jesse, M.; Northoff, H.; Dickhuth, H.H. Impact of elevated ambient temperatures on the acute immune response to intensive endurance exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2003, 89, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mario, N.; Michelle, C.; Tainah, P. Effects of nutrients and exercises to attenuate oxidative stress and prevent cardiovascular disease. Curr. Pharm. Design 2018, 24, 4800–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, Z.; Cseko, C.; Tth, E.; Koller, A. Oxidative stress-induced dysregulation of arteriolar wall shear stress and blood pressure in hyperhomocysteinemia is prevented by chronic vitamin C treatment. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 285, H2277–H2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costello, J.T.; Rendell, R.A.; Furber, M.; Massey, H.C.; Tipton, M.J.; Young, J.S.; Corbett, J. Effects of acute or chronic heat exposure, exercise and dehydration on plasma cortisol, IL-6 and CRP levels in trained males. Cytokine 2018, 110, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flanagan, S.W.; Ryan, A.J.; Gisolfi, C.V.; Moseley, P.L.; Corbett, J. Tissue-specific Hsp70 response in animals undergoing heat stress. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, R.H.; Mohammad, R.P.; Elaheh, M.; Ali, A.N. Antihypertensive effects of hydroalcoholic extract of crataegus azarolus subspecies aronia fruit in rats with renovascular hypertension: An experimental mechanistic study. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 42, 266–274. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.B.; Gao, H.Q.; Yi, Y.L.; Feng, M.L.; Jing, B.Q.; YU, Y. Effect of grape seed proanthocyanidin extract on serum C-reactive protein in rabbits. Chin. J. Arterioscler. 2004, 12, 549–552. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, A.; Welch, A.A.; Spector, T.; Macgregor, A.; Cassidy, A. Intakes of Anthocyanins and Flavones Are Associated with Biomarkers of Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Women. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asgary, S.; Keshvari, M.; Afshani, M.R.; Amiri, M.; Laher, I.; Javanmard, S.H. Effect of fresh orange juice intake on physiological characteristics in healthy volunteers. ISRN Nutr. 2014, 2014, 405867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, W.; Fontaine, V.; Pueyo, M.E.; Laquay, N.; Messika-Zeitoun, D.; Philippe, M.; Arnal, J.F.; Jacob, M.P.; Michel, J.B. Molecular plasticity of vascular wall during NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester-induced hypertension: Modulation of proinflammatory signals. Hypertension 2000, 36, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swei, A.; Lacy, F.; Delano, F.A.; Parks, D.A.; Schmid, S.G.W. A mechanism of oxygen free radical production in the Dahl hypertensive rat. Microcirculation 1999, 6, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.W.; Li, X.X.; Chen, M.; Yang, P.F.; Zhao, X.R.; Zeng, L.; OuYang, Y.A.; Yang, Z.; Tian, Z.M. The protective role of hawthorn fruit extract against high salt- induced hypertension in Dahl salt- sensitive rats: Impact on oxidative stress and metabolic patterns. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasdev, S.C.; Ford, C.A.; Parai, S.K.; Longerich, L.L.; Gadag, V.G. Dietary vitamin C supplementation lowers blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2001, 218, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katusic, Z.S. Vascular endothelial dysfunction: Does tetrahydrobiopterin play a role? Am. J. Physiol. 2001, 281, H981–H986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.; Feng, Y.J.; Li, J.L.; Gu, X.H. Role of MAPKs in Hsp70’s Protection against Heat Stress-Induced Injury in Rat Small Intestine. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1571406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barak, O.F.; Caljkusic, K.; Hoiland, R.L.; Ainslie, P.N.; Thom, S.R.; Yang, M.; Pavle, J.; Zeljko, D. Differential influence of vitamin C on the peripheral and cerebral circulation after diving and exposure to hyperoxia. Am. J. Physiol. 2018, 315, R759–R767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nair, A.B.; Jacob, S. A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2016, 7, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.M.; Feng, F.M.; Wang, H.J.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.Y.; Ning, H.Z.; Zhou, R.H.; Li, H. Dietary Guide for Workers in Hot Environment; Health standard: WS/T 577-2017; National Health Commission of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2017; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Nutrition Society. Chinese Dietary Reference Intakes (2013 Edition); SciPress: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 485–491. ISBN 978-7-03-041401-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bedford, T.G.; Tipton, C.M.; Wilson, N.C.; Oppliger, R.A.; Gisolfi, C.V. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J. Appl. Physiol. Respir. Environ. Exerc. Physiol. 1979, 47, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, H.Y. Establishment of an overtraining rat model on the treadmill. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 2013, 17, 8036–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Zhu, L.Q.; Liu, F.D.; Zhu, X.D.; Niu, J.G.; LI, G.H. Effect of dehydration heat exposure on thoracic aorta reactivity in rats. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 5, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.N.; He, X.C.; Ye, M.; Huang, H.; Chen, H.L.; Peng, W.L.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Yi, T.; Chen, H.B. Cardioprotective effect of total saponins from three medicinal species of Dioscorea against isoprenaline-induced myocardial ischemia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 175, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekhon-Loodu, S.; Catalli, A.; Kulka, M.; Wang, Y.W.; Shahidi, F.; Rupasinghe, H.P.V. Apple flavonols and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid–rich fish oil lowers blood C-reactive protein in rats with hypercholesterolemia and acute inflammation. Nutr. Res. 2014, 34, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Antioxidant Ingredients | Content |
|---|---|
| Total phenolic compounds (mg GAE/g extract) | 264.7 |
| Total flavonoids compounds (mg RE/g extract) | 125.9 |
| Phenolic compounds identification (mg/g extract) | |
| Hyperoside | 3.240 |
| Resveratrol | 0.149 |
| Epicatechin | 0.130 |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.115 |
| Proanthocyanidins B2 | 0.053 |
| Ferulic acid | 0.006 |
| Vitamin C (mg/g extract) | 0.760 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, W.; Fan, H.-M.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Jiang, X.-H.; Li, Y. Effect of Flavonoids in Hawthorn and Vitamin C Prevents Hypertension in Rats Induced by Heat Exposure. Molecules 2022, 27, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030866
Du W, Fan H-M, Zhang Y-X, Jiang X-H, Li Y. Effect of Flavonoids in Hawthorn and Vitamin C Prevents Hypertension in Rats Induced by Heat Exposure. Molecules. 2022; 27(3):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030866
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Wei, Hong-Min Fan, Yu-Xin Zhang, Xiao-Hua Jiang, and Yun Li. 2022. "Effect of Flavonoids in Hawthorn and Vitamin C Prevents Hypertension in Rats Induced by Heat Exposure" Molecules 27, no. 3: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030866
APA StyleDu, W., Fan, H.-M., Zhang, Y.-X., Jiang, X.-H., & Li, Y. (2022). Effect of Flavonoids in Hawthorn and Vitamin C Prevents Hypertension in Rats Induced by Heat Exposure. Molecules, 27(3), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27030866






